The Landscape of Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL): Clinicopathologic and Genomic Characteristics and Therapeutic Perspectives
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pathogenesis and Genetic Alterations
2.1. Genetic Mutations and Signaling Pathway Modulation
2.2. Epigenetic Modifications
2.3. Recurrent Amplifications and Deletions
2.4. Microenvironments
3. Diagnosis
3.1. Epidemiology and Clinical Presentation
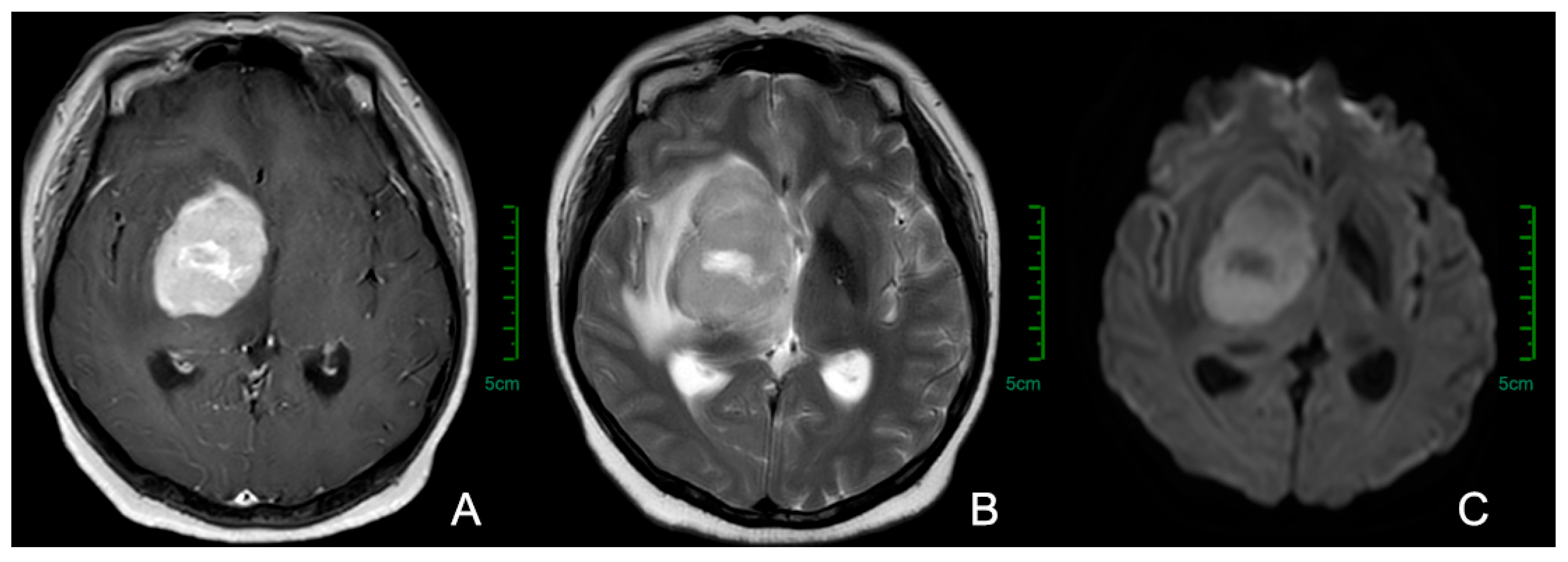
3.2. Imaging Examinations
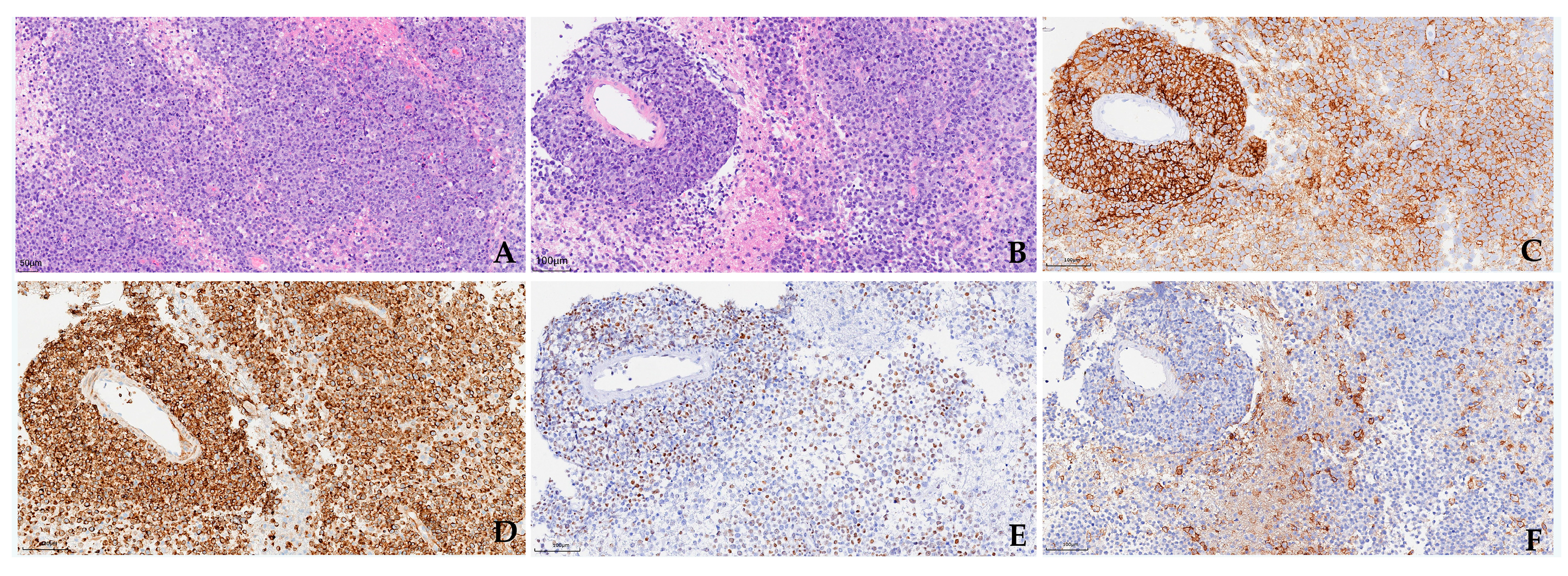
3.3. Pathology and Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Examinations
4. Prognosis
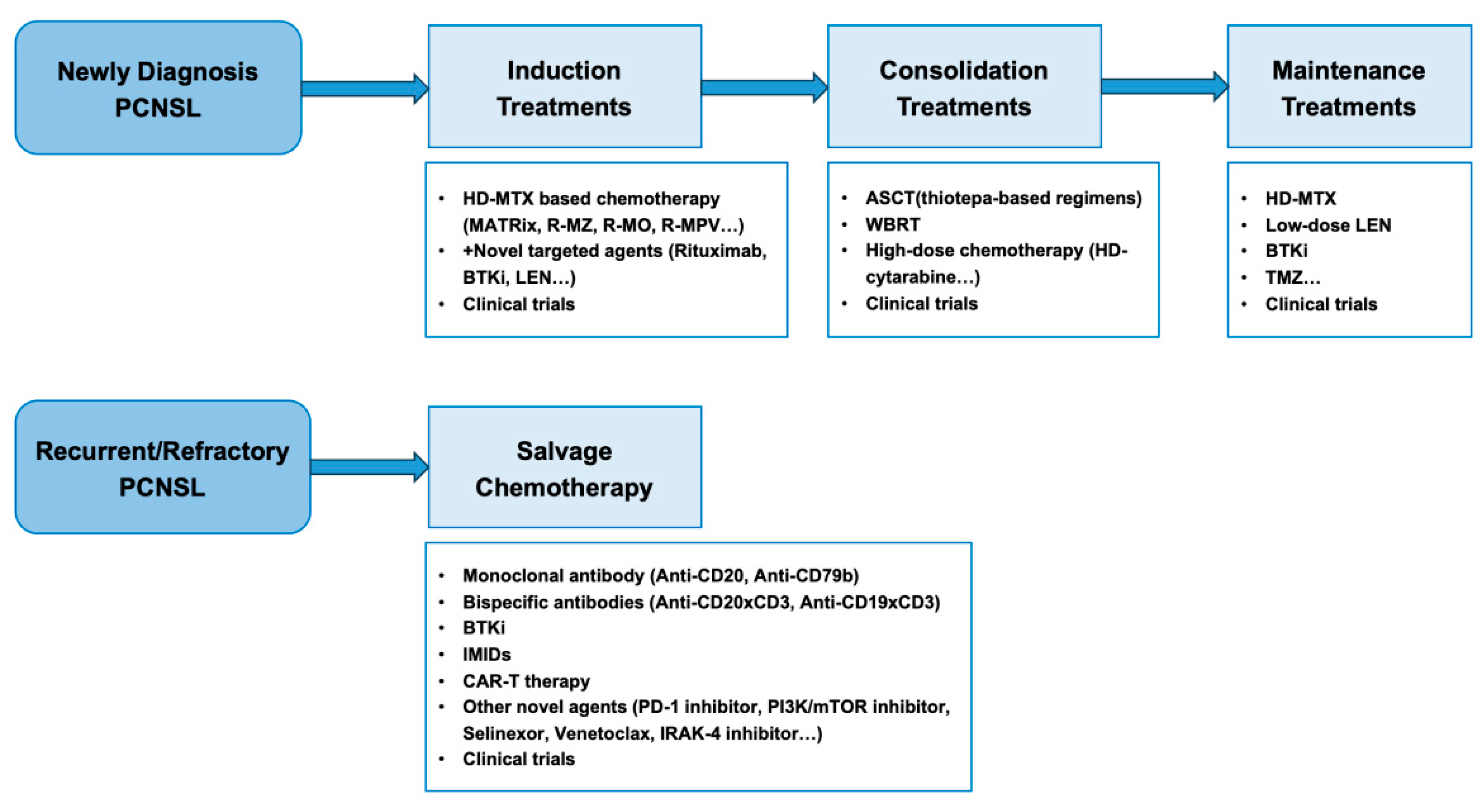
5. Treatments
5.1. Induction Treatments
5.2. Consolidation and Maintenance Treatments
5.3. Treatment of Recurrent/Refractory (R/R) PCNSL
5.3.1. Immunotherapy and Novel Targeted Treatments
- Novel monoclonal antibodies and bispecific antibodies
- BTK inhibitors
- IMIDs
- Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy
5.3.2. Other Novel Targeted Treatments
6. Conclusion and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCNSL | Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| GCB | Germinal Center B-cell-like |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| EBV | Epstein–Barr Virus |
| BBB | Blood–brain Barrier |
| ABC | Activated B-Cell-like |
| CNVs | Copy Number Alterations |
| TME | Tumor Microenvironment |
| CS | Significant Cluster |
| IME | Invasive Margin Excluded |
| IMS | Invasive Margin immunosuppressed |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| FDG | Fluorodeoxyglucose |
| PET | Positron Emission Tomography |
| IPCG | International Primary CNS Lymphoma Collaborative Group |
| SCNSL | Secondary Central Nervous System Lymphoma |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal Fluid |
| PD-L1 | Programmed Death Ligand 1 |
| FCM | Flow Cytometry |
| ctDNA | circulating tumor DNA |
| miRNA | microRNAs |
| IL-10 | Interleukin-10 |
| OS | Overall Survival |
| HD-MTX | High-dose Methotrexate |
| ASCT | Autologous Stem Cell Transplant |
| WBRT | Whole Brain Radiotherapy |
| EANO | European Association of Neuro-Oncology |
| TMZ | Temozolomide |
| ORR | Overall Response Rate |
| CR | Complete Remission |
| RCT | Randomized Controlled Trials |
| PR | Partial Response |
| NRM | Non-Relapse Mortality |
| LEN | low-dose lenalidomide |
| BTK | Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase |
| IMIDs | Immunomodulatory Drugs |
| BsAb | Bispecific Antibodies |
| PVRL | Primary Vitreoretinal Lymphoma |
| POR | Pomalidomide/Orelabrutinib/Rituximab |
| CAR-T | Chimeric Antigen Receptor T cell |
| LBCL | Large B-Cell Lymphoma |
| RFS | Relapse-free Survival |
| IRAK-4 | Interleukin-1 Receptor-associated Kinase-4 |
| WGS | Whole-genome Sequencing |
References
- Kluin, P.M.D.M.; Ferry, J.A. Primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the CNS. In WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues; Swerdlow, S.H., Campo, E., Harris, N.L., Jaffe, E.S., Pileri, S.A., Stein, H., Thiele, J., Arber, D.A., Hasserjian, R.P., Beau, M.M.L., Orazi, A., Siebert, R., Eds.; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2017; pp. 300–302. [Google Scholar]
- Radke, J.; Ishaque, N.; Koll, R.; Gu, Z.; Schumann, E.; Sieverling, L.; Uhrig, S.; Hübschmann, D.; Toprak, U.H.; López, C.; et al. The genomic and transcriptional landscape of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaggio, R.; Amador, C.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Attygalle, A.D.; Araujo, I.B.O.; Berti, E.; Bhagat, G.; Borges, A.M.; Boyer, D.; Calaminici, M.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1720–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, M.K.; Hoang, T.; Law, S.C.; Brosda, S.; O’Rourke, K.; Tobin, J.W.D.; Vari, F.; Murigneux, V.; Fink, L.; Gunawardana, J.; et al. EBV-associated primary CNS lymphoma occurring after immunosuppression is a distinct immunobiological entity. Blood 2021, 137, 1468–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, B.P.; Decker, P.A.; Tieu, C.; Cerhan, J.R. The changing incidence of primary central nervous system lymphoma is driven primarily by the changing incidence in young and middle-aged men and differs from time trends in systemic diffuse large B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Am. J. Hematol. 2013, 88, 997–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pindzola, G.M.; Razzaghi, R.; Tavory, R.N.; Nguyen, H.T.; Morris, V.M.; Li, M.; Agarwal, S.; Huang, B.; Okada, T.; Reinhardt, H.C.; et al. Aberrant expansion of spontaneous splenic germinal centers induced by hallmark genetic lesions of aggressive lymphoma. Blood 2022, 140, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phelan, J.D.; Young, R.M.; Webster, D.E.; Roulland, S.; Wright, G.W.; Kasbekar, M.; Shaffer, A.L., III; Ceribelli, M.; Wang, J.Q.; Schmitz, R.; et al. A multiprotein supercomplex controlling oncogenic signalling in lymphoma. Nature 2018, 560, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahnke, K.; Thiel, E.; Martus, P.; Herrlinger, U.; Weller, M.; Fischer, L.; Korfel, A.; Group GPCNSLS. Relapse of primary central nervous system lymphoma: Clinical features, outcome and prognostic factors. J. Neurooncol. 2006, 80, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubenstein, J.L.; Gupta, N.K.; Mannis, G.N.; Lamarre, A.K.; Treseler, P. How I treat CNS lymphomas. Blood 2013, 122, 2318–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuitunen, H.K.; Rönkä, A.L.K.; Sonkajärvi, E.M.; Isokangas, J.M.; Pyörälä, M.; Palosaari, K.A.A.; Jokimäki, A.S.; Partanen, A.E.; Littow, H.J.; Vakkala, M.A.; et al. Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption (BBBD)-Based Immunochemotherapy for Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL), Early Results of a Phase II Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deckert, M.; Engert, A.; Brück, W.; Ferreri, A.J.; Finke, J.; Illerhaus, G.; Klapper, W.; Korfel, A.; Küppers, R.; Maarouf, M.; et al. Modern concepts in the biology, diagnosis, differential diagnosis and treatment of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Leukemia 2011, 25, 1797–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Phelan, J.D.; Coulibaly, Z.A.; Roulland, S.; Young, R.M.; Wang, J.Q.; Schmitz, R.; Morin, R.D.; Tang, J.; et al. A Probabilistic Classification Tool for Genetic Subtypes of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma with Therapeutic Implications. Cancer Cell. 2020, 37, 551–568.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapuy, B.; Stewart, C.; Dunford, A.J.; Kim, J.; Kamburov, A.; Redd, R.A.; Lawrence, M.S.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Li, A.J.; Ziepert, M.; et al. Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma are associated with distinct pathogenic mechanisms and outcomes. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Sun, T.; Li, G.; Li, M.; Wang, D.; Su, X.; Ye, J.; Ji, C. Spatial single cell analysis of tumor microenvironment remodeling pattern in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Leukemia 2023, 37, 1499–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Jiang, C.; Yao, X.; Fang, M.; Qiao, X.; Zhu, L.; Yang, Z.; Gao, X.; Ji, Y.; Niu, C.; et al. Single-cell landscape of primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cell. Discov. 2023, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severson, E.A.; Haberberger, J.; Hemmerich, A.; Huang, R.S.P.; Edgerly, C.; Schiavone, K.; Najafian, A.; Hiemenz, M.; Lechpammer, M.; Vergilio, J.A.; et al. Genomic Profiling Reveals Differences in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma and Large B-Cell Lymphoma, With Subtyping Suggesting Sensitivity to BTK Inhibition. Oncologist 2023, 28, e26–e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreri, A.J.M.; Calimeri, T.; Cwynarski, K.; Dietrich, J.; Grommes, C.; Hoang-Xuan, K.; Hu, L.S.; Illerhaus, G.; Nayak, L.; Ponzoni, M.; et al. Primary central nervous system lymphoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2023, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Jiang, H.; Han, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chai, Y.; Zeng, P.; Yue, L.; Wu, C. Frequent Gene Mutations and Their Possible Roles in the Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prognosis of Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. World Neurosurg. 2023, 170, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, W.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, H.; Xiao, D.; Su, W.; Zeng, R.; Feng, Y.; Duan, Y.; Zhou, J.; et al. Analysis of Genomic Alteration in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma and the Expression of Some Related Genes. Neoplasia 2018, 20, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrun, L.; Allard-Demoustiez, S.; Salmon, I. Pathology and new insights in central nervous system lymphomas. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2023, 35, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, A.; Iwadate, Y.; Komohara, Y.; Sano, M.; Kajiwara, K.; Yajima, N.; Tsuchiya, N.; Homma, J.; Aoki, H.; Kobayashi, T.; et al. Gene expression signature-based prognostic risk score in patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 5672–5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Wan, H.; Own, S.A.; Berglund, M.; Wang, X.; Yang, M.; Li, X.; Liu, D.; Ye, X.; Sonnevi, K.; et al. Genetic and transcriptomic analyses of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients with poor outcomes within two years of diagnosis. Leukemia 2024, 38, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumura, K.; Kawazu, M.; Kojima, S.; Ueno, T.; Sai, E.; Soda, M.; Ueda, H.; Yasuda, T.; Yamaguchi, H.; Lee, J.; et al. Genomic characterization of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, D.; Tan, K.L.; Steidl, C.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Al Moosawi, M.; Shenkier, T.N.; Connors, J.M.; Sehn, L.H.; Savage, K.J.; Scott, D.W.; et al. Molecular features of a large cohort of primary central nervous system lymphoma using tissue microarray. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 3953–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayyar, N.; White, M.D.; Gill, C.M.; Lastrapes, M.; Bertalan, M.; Kaplan, A.; D’Andrea, M.R.; Bihun, I.; Kaneb, A.; Dietrich, J.; et al. MYD88 L265P mutation and CDKN2A loss are early mutational events in primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos-Rongen, M.; Brunn, A.; Sanchez-Ruiz, M.; Kuppers, R.; Siebert, R.; Deckert, M. Impact of a Faulty Germinal Center Reaction on the Pathogenesis of Primary Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma of the Central Nervous System. Cancers 2021, 13, 6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos-Rongen, M.; Kuppers, R.; Schluter, D.; Spieker, T.; Van Roost, D.; Schaller, C.; Reifenberger, G.; Wiestler, O.D.; Deckert-Schluter, M. Primary central nervous system lymphomas are derived from germinal-center B cells and show a preferential usage of the V4-34 gene segment. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 155, 2077–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompsett, A.R.; Ellison, D.W.; Stevenson, F.K.; Zhu, D. V(H) gene sequences from primary central nervous system lymphomas indicate derivation from highly mutated germinal center B cells with ongoing mutational activity. Blood 1999, 94, 1738–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos-Rongen, M.; Schmitz, R.; Brunn, A.; Gesk, S.; Richter, J.; Hong, K.; Wiestler, O.D.; Siebert, R.; Küppers, R.; Deckert, M. Mutations of CARD11 but not TNFAIP3 may activate the NF-kappaB pathway in primary CNS lymphoma. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 120, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualucci, L.; Compagno, M.; Houldsworth, J.; Monti, S.; Grunn, A.; Nandula, S.V.; Aster, J.C.; Murty, V.V.; Shipp, M.A.; Dalla-Favera, R. Inactivation of the PRDM1/BLIMP1 gene in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, C.A.; Mack, D.H., Jr.; Davis, M.M. Blimp-1, a novel zinc finger-containing protein that can drive the maturation of B lymphocytes into immunoglobulin-secreting cells. Cell 1994, 77, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Aguilar, A.; Idbaih, A.; Boisselier, B.; Habbita, N.; Rossetto, M.; Laurenge, A.; Bruno, A.; Jouvet, A.; Polivka, M.; Adam, C.; et al. Recurrent mutations of MYD88 and TBL1XR1 in primary central nervous system lymphomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 5203–5211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunn, A.; Nagel, I.; Montesinos-Rongen, M.; Klapper, W.; Vater, I.; Paulus, W.; Hans, V.; Blümcke, I.; Weis, J.; Siebert, R.; et al. Frequent triple-hit expression of MYC, BCL2, and BCL6 in primary lymphoma of the central nervous system and absence of a favorable MYC(low)BCL2 (low) subgroup may underlie the inferior prognosis as compared to systemic diffuse large B cell lymphomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 126, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Xia, X.; Wu, M.; Yang, H.; Zhu, X.; Sun, W.; Ge, M. The impact of BCL-2/MYC protein expression and gene abnormality on primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 12, 2215–2223. [Google Scholar]
- Los-de Vries, G.T.; Stathi, P.; Rutkens, R.; Hijmering, N.J.; Luijks, J.A.C.W.; Groenen, P.J.T.A.; de Jong, D.; Ylstra, B.; Roemer, M.G.M. Large B-cell Lymphomas of Immune-Privileged Sites Relapse via Parallel Clonal Evolution from a Common Progenitor B Cell. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 1917–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Yang, A.; Yang, J.; Zhang, S.; Xing, Z.; Wang, X.; Mei, W.; Jiang, C.; Lin, J.; Wu, X.; et al. Sintilimab (anti-PD-1 antibody) combined with high-dose methotrexate, temozolomide, and rituximab (anti-CD20 antibody) in primary central nervous system lymphoma: A phase 2 study. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.; Wei, L.; Kaminska, B. Emerging insights into origin and pathobiology of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Cancer Lett. 2021, 509, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, T.; Weber, R.G.; Kaulich, K.; Actor, B.; Meyer-Puttlitz, B.; Lampel, S.; Büschges, R.; Weigel, R.; Deckert-Schlüter, M.; Schmiedek, P.; et al. Characteristic chromosomal imbalances in primary central nervous system lymphomas of the diffuse large B-cell type. Brain Pathol. 2000, 10, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwindt, H.; Vater, I.; Kreuz, M.; Montesinos-Rongen, M.; Brunn, A.; Richter, J.; Gesk, S.; Ammerpohl, O.; Wiestler, O.D.; Hasenclever, D.; et al. Chromosomal imbalances and partial uniparental disomies in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Leukemia 2009, 23, 1875–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yuan, X.; Yu, T.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, H.; Hao, Y.; Lei, W.; Liang, Y.; Li, B.; Qian, W. Analysis of the genomic landscape of primary central nervous system lymphoma using whole-genome sequencing in Chinese patients. Front. Med. 2023, 17, 889–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, C.O.; Kim, S.C.; Karnan, S.; Karube, K.; Shin, H.J.; Nam, D.H.; Suh, Y.L.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, S.J.; et al. Genomic profiling combined with gene expression profiling in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Blood 2011, 117, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braggio, E.; McPhail, E.R.; Macon, W.; Lopes, M.B.; Schiff, D.; Law, M.; Fink, S.; Sprau, D.; Giannini, C.; Dogan, A.; et al. Primary central nervous system lymphomas: A validation study of array-based comparative genomic hybridization in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tumor specimens. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 4245–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapuy, B.; Roemer, M.G.; Stewart, C.; Tan, Y.; Abo, R.P.; Zhang, L.; Dunford, A.J.; Meredith, D.M.; Thorner, A.R.; Jordanova, E.S.; et al. Targetable genetic features of primary testicular and primary central nervous system lymphomas. Blood 2016, 127, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, K.; Chen, L.; Berglund, M.; Ren, W.; de Miranda, N.F.; Lisboa, S.; Fangazio, M.; Zhu, S.; Hou, Y.; Wu, K.; et al. Genetic basis of PD-L1 overexpression in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood 2016, 127, 3026–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertus, J.L.; Harms, G.; Blokzijl, T.; Booman, M.; de Jong, D.; van Imhoff, G.; Rosati, S.; Schuuring, E.; Kluin, P.; van den Berg, A. Specific expression of miR-17-5p and miR-127 in testicular and central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Mod. Pathol. 2009, 22, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraniskin, A.; Kuhnhenn, J.; Schlegel, U.; Chan, A.; Deckert, M.; Gold, R.; Maghnouj, A.; Zöllner, H.; Reinacher-Schick, A.; Schmiegel, W.; et al. Identification of microRNAs in the cerebrospinal fluid as marker for primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the central nervous system. Blood 2011, 117, 3140–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraniskin, A.; Kuhnhenn, J.; Schlegel, U.; Schmiegel, W.; Hahn, S.; Schroers, R. MicroRNAs in cerebrospinal fluid as biomarker for disease course monitoring in primary central nervous system lymphoma. J. Neurooncol. 2012, 109, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzoni, M.; Berger, F.; Chassagne-Clement, C.; Tinguely, M.; Jouvet, A.; Ferreri, A.J.; Dell’Oro, S.; Terreni, M.R.; Doglioni, C.; Weis, J.; et al. Reactive perivascular T-cell infiltrate predicts survival in primary central nervous system B-cell lymphomas. Br. J. Haematol. 2007, 138, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roemer, M.G.M.; van de Brug, T.; Bosch, E.; Berry, D.; Hijmering, N.; Stathi, P.; Weijers, K.; Doorduijn, J.; Bromberg, J.; van de Wiel, M.; et al. Multi-scale spatial modeling of immune cell distributions enables survival prediction in primary central nervous system lymphoma. iScience 2023, 26, 107331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelis, L.; Antoranz, A.; Delsupehe, A.M.; Biesemans, P.; Ferreiro, J.F.; Debackere, K.; Vandenberghe, P.; Verhoef, G.; Gheysens, O.; Cattoretti, G.; et al. In-depth characterization of the tumor microenvironment in central nervous system lymphoma reveals implications for immune-checkpoint therapy. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2020, 69, 1751–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challa-Malladi, M.; Lieu, Y.K.; Califano, O.; Holmes, A.B.; Bhagat, G.; Murty, V.V.; Dominguez-Sola, D.; Pasqualucci, L.; Dalla-Favera, R. Combined genetic inactivation of beta2-Microglobulin and CD58 reveals frequent escape from immune recognition in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Cancer Cell. 2011, 20, 728–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fangazio, M.; Ladewig, E.; Gomez, K.; Garcia-Ibanez, L.; Kumar, R.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Rossi, D.; Filip, I.; Pan-Hammarström, Q.; Inghirami, G.; et al. Genetic mechanisms of HLA-I loss and immune escape in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2104504118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booman, M.; Szuhai, K.; Rosenwald, A.; Hartmann, E.; Kluin-Nelemans, H.; de Jong, D.; Schuuring, E.; Kluin, P. Genomic alterations and gene expression in primary diffuse large B-cell lymphomas of immune-privileged sites: The importance of apoptosis and immunomodulatory pathways. J. Pathol. 2008, 216, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Verdin, I.; Kirasic, E.; Wienand, K.; Mokhtari, K.; Eimer, S.; Loiseau, H.; Rousseau, A.; Paillassa, J.; Ahle, G.; Lerintiu, F.; et al. Molecular and clinical diversity in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, J.H.; Gunn, M.D.; Fecci, P.E.; Ashley, D.M. Brain immunology and immunotherapy in brain tumours. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Verdin, I.; Morales-Martínez, A.; Hoang-Xuan, K.; Alentorn, A. Primary central nervous system lymphoma: Advances in its pathogenesis, molecular markers and targeted therapies. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2022, 35, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, D.; Cho, H.; Yoon, D.H.; Go, H. Clinicopathological Significance of Tumor-Infiltrating T Lymphocytes and Macrophages in Primary Large B-Cell Lymphoma of Immune-Privileged Sites. Cancer Res. Treat. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villano, J.L.; Koshy, M.; Shaikh, H.; Dolecek, T.A.; McCarthy, B.J. Age, gender, and racial differences in incidence and survival in primary CNS lymphoma. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 1414–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touitou, V.; LeHoang, P.; Bodaghi, B. Primary CNS lymphoma. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2015, 26, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataille, B.; Delwail, V.; Menet, E.; Vandermarcq, P.; Ingrand, P.; Wager, M.; Guy, G.; Lapierre, F. Primary intracerebral malignant lymphoma: Report of 248 cases. J. Neurosurg. 2000, 92, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaff, L.R.; Grommes, C. Primary central nervous system lymphoma. Blood 2022, 140, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Koning, M.E.; Hof, J.J.; Jansen, C.; Doorduijn, J.K.; Bromberg, J.E.C.; van der Meulen, M. Primary central nervous system lymphoma. J. Neurol. 2024, 271, 2906–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Küker, W.; Nägele, T.; Korfel, A.; Heckl, S.; Thiel, E.; Bamberg, M.; Weller, M.; Herrlinger, U. Primary central nervous system lymphomas (PCNSL): MRI features at presentation in 100 patients. J. Neurooncol. 2005, 72, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabouret, E.; Houillier, C.; Martin-Duverneuil, N.; Blonski, M.; Soussain, C.; Ghesquières, H.; Houot, R.; Larrieu, D.; Soubeyran, P.; Gressin, R.; et al. Patterns of response and relapse in primary CNS lymphomas after first-line chemotherapy: Imaging analysis of the ANOCEF-GOELAMS prospective randomized trial. Neuro. Oncol. 2017, 19, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, S.; Barasch, J.G.; Young, R.J.; Grommes, C.; Schöder, H. Positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in primary central nervous system lymphoma-a narrative review. Ann. Lymphoma 2021, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barajas, R.F.; Politi, L.S.; Anzalone, N.; Schöder, H.; Fox, C.P.; Boxerman, J.L.; Kaufmann, T.J.; Quarles, C.C.; Ellingson, B.M.; Auer, D.; et al. Consensus recommendations for MRI and PET imaging of primary central nervous system lymphoma: Guideline statement from the International Primary CNS Lymphoma Collaborative Group (IPCG). Neuro. Oncol. 2021, 23, 1056–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenblum, L.; Houillier, C.; Soussain, C.; Bertaux, M.; Choquet, S.; Galanaud, D.; Hoang-Xuan, K.; Kas, A. Role of Positron Emission Tomography in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malani, R.; Bhatia, A.; Wolfe, J.; Grommes, C. Staging identifies non-CNS malignancies in a large cohort with newly diagnosed lymphomatous brain lesions. Leuk. Lymphoma 2019, 60, 2278–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herhaus, P.; Lipkova, J.; Lammer, F.; Yakushev, I.; Vag, T.; Slotta-Huspenina, J.; Habringer, S.; Lapa, C.; Pukrop, T.; Hellwig, D.; et al. CXCR4-Targeted PET Imaging of Central Nervous System B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 1765–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postnov, A.; Toutain, J.; Pronin, I.; Valable, S.; Gourand, F.; Kalaeva, D.; Vikhrova, N.; Pyzhik, E.; Guillouet, S.; Kobyakov, G.; et al. First-in-Man Noninvasive Initial Diagnostic Approach of Primary CNS Lymphoma Versus Glioblastoma Using PET With 18 F-Fludarabine and l -[methyl- 11 C]Methionine. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2022, 47, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaji, F.A.; Martinez-Calle, N.; Sovani, V.; Fox, C.P. Rare central nervous system lymphomas. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 197, 662–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubenstein, J.L.; Fridlyand, J.; Shen, A.; Aldape, K.; Ginzinger, D.; Batchelor, T.; Treseler, P.; Berger, M.; McDermott, M.; Prados, M.; et al. Gene expression and angiotropism in primary CNS lymphoma. Blood 2006, 107, 3716–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos-Rongen, M.; Brunn, A.; Bentink, S.; Basso, K.; Lim, W.K.; Klapper, W.; Schaller, C.; Reifenberger, G.; Rubenstein, J.; Wiestler, O.D.; et al. Gene expression profiling suggests primary central nervous system lymphomas to be derived from a late germinal center B cell. Leukemia 2008, 22, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, R.; Chen, H.; Zheng, X.; Liu, L.; Lan, L.; Li, P.; Wu, S.; Cao, Q.; et al. A multicenter proof-of-concept study on deep learning-based intraoperative discrimination of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, C.P.; Phillips, E.H.; Smith, J.; Linton, K.; Gallop-Evans, E.; Hemmaway, C.; Auer, D.P.; Fuller, C.; Davies, A.J.; McKay, P.; et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 184, 348–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraniskin, A.; Schroers, R. Liquid Biopsy and Other Non-Invasive Diagnostic Measures in PCNSL. Cancers 2021, 13, 2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saggese, C.E.; Cecotti, L.; Lazzarino de Lorenzo, L.G. Neuroborreliosis and CNS lymphoma: What is the nexus? Neurol. Sci. 2013, 34, 2253–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreri, A.J.M.; Calimeri, T.; Lopedote, P.; Francaviglia, I.; Daverio, R.; Iacona, C.; Belloni, C.; Steffanoni, S.; Gulino, A.; Anghileri, E.; et al. MYD88 L265P mutation and interleukin-10 detection in cerebrospinal fluid are highly specific discriminating markers in patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma: Results from a prospective study. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 193, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordone, I.; Masi, S.; Carosi, M.; Vidiri, A.; Marchesi, F.; Marino, M.; Telera, S.; Pasquale, A.; Mengarelli, A.; Conti, L.; et al. Brain stereotactic biopsy flow cytometry for central nervous system lymphoma characterization: Advantages and pitfalls. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, J.; Chen, K.; Li, Q.; Ma, J.; Ma, Y.; Lin, Z.; Kang, H.; Chen, B. High Level of IL-10 in Cerebrospinal Fluid is Specific for Diagnosis of Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 6261–6268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiemcke-Jiwa, L.S.; Leguit, R.J.; Snijders, T.J.; Bromberg, J.E.C.; Nierkens, S.; Jiwa, N.M.; Minnema, M.C.; Huibers, M.M.H. MYD88 p.(L265P) detection on cell-free DNA in liquid biopsies of patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 185, 974–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calimeri, T.; Anzalone, N.; Cangi, M.G.; Fiore, P.; Gagliardi, F.; Miserocchi, E.; Ponzoni, M.; Ferreri, A.J.M. Molecular diagnosis of primary CNS lymphoma in 2024 using MYD88. Lancet Haematol. 2024, 11, e540–e549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutter, J.A.; Alig, S.K.; Esfahani, M.S.; Lauer, E.M.; Mitschke, J.; Kurtz, D.M.; Kuhn, J.; Bleul, S.; Olsen, M.; Liu, C.L.; et al. Circulating Tumor DNA Profiling for Detection, Risk Stratification, and Classification of Brain Lymphomas. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 1684–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.E.; Kim, Y.J.; Shim, J.H.; Park, D.; Cho, J.; Ko, Y.H.; Park, W.Y.; Mun, Y.C.; Lee, K.E.; Cho, D.; et al. Plasma Circulating Tumor DNA in Patients with Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 54, 597–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevel, K.S.; Wilcox, J.A.; Robell, L.J.; Umemura, Y. The Utility of Liquid Biopsy in Central Nervous System Malignancies. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 20, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sromek, M.; Rymkiewicz, G.; Paziewska, A.; Szafron, L.M.; Kulecka, M.; Zajdel, M.; Kulinczak, M.; Dabrowska, M.; Balabas, A.; Bystydzienski, Z.; et al. A Set of 17 microRNAs Common for Brain and Cerebrospinal Fluid Differentiates Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma from Non-Malignant Brain Tumors. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Xu, P.P.; Feng, R.; Cui, G.H.; Wang, L.; Cheng, S.; Mu, R.J.; Zhang, H.L.; Wei, X.L.; Song, Y.P.; et al. Extranodal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Clinical and molecular insights with survival outcomes from the multicenter EXPECT study. Cancer Commun. 2025, 45, 919–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, L.D.; Munker, R.; Li, N.; Yan, D.; Pryor, P.; Nozad, S.; Keller, P.; Monohan, G.P.; Iragavarapu, C.; Krem, M.M. Performance status, comorbidities, and cycles of methotrexate exert the greatest influence on outcomes of primary and secondary CNS lymphomas: The Lexington experience. Ann. Hematol. 2023, 102, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houillier, C.; Soussain, C.; Ghesquieres, H.; Soubeyran, P.; Chinot, O.; Taillandier, L.; Lamy, T.; Choquet, S.; Ahle, G.; Damaj, G.; et al. Management and outcome of primary CNS lymphoma in the modern era: An LOC network study. Neurology 2020, 94, e1027–e1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwueke, U.; Grommes, C.; Nayak, L. Primary Central Nervous System Lymphomas. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 36, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Carnevale, J.; Rubenstein, J.L. Progress in central nervous system lymphomas. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 166, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zuo, M.; Li, L.; Li, F.; Ke, P.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, Y.; Gao, X.; Guan, Y.; Xia, X.; et al. PIM1 and CD79B Mutation Status Impacts the Outcome of Primary Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma of the CNS. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 824632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, K.A.; Sundaram, S.; Kim, S.H.; Vaca, R.; Lin, Y.; Singer, S.; Malecek, M.K.; Carter, J.; Zayac, A.; Kim, M.S.; et al. Older patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma: Survival and prognostication across 20 U.S. cancer centers. Am. J. Hematol. 2023, 98, 900–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang-Xuan, K.; Deckert, M.; Ferreri, A.J.M.; Furtner, J.; Gallego Perez-Larraya, J.; Henriksson, R.; Hottinger, A.F.; Kasenda, B.; Lefranc, F.; Lossos, A.; et al. European Association of Neuro-Oncology (EANO) guidelines for treatment of primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL). Neuro. Oncol. 2023, 25, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdhoff, M.; Mrugala, M.M.; Grommes, C.; Kaley, T.J.; Swinnen, L.J.; Perez-Heydrich, C.; Nayak, L. Challenges in the Treatment of Newly Diagnosed and Recurrent Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 2020, 18, 1571–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreri, A.J.; Cwynarski, K.; Pulczynski, E.; Ponzoni, M.; Deckert, M.; Politi, L.S.; Torri, V.; Fox, C.P.; Rosée, P.L.; Schorb, E.; et al. Chemoimmunotherapy with methotrexate, cytarabine, thiotepa, and rituximab (MATRix regimen) in patients with primary CNS lymphoma: Results of the first randomisation of the International Extranodal Lymphoma Study Group-32 (IELSG32) phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2016, 3, e217–e227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreri, A.J.M.; Cwynarski, K.; Pulczynski, E.; Fox, C.P.; Schorb, E.; Celico, C.; Falautano, M.; Nonis, A.; La Rosée, P.; Binder, M.; et al. Long-term efficacy, safety and neurotolerability of MATRix regimen followed by autologous transplant in primary CNS lymphoma: 7-year results of the IELSG32 randomized trial. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1870–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Four, M.; Cacheux, V.; Tempier, A.; Platero, D.; Fabbro, M.; Marin, G.; Leventoux, N.; Rigau, V.; Costes-Martineau, V.; Szablewski, V. PD1 and PDL1 expression in primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphoma are frequent and expression of PD1 predicts poor survival. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 35, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Ding, K.; Ma, J.; Peng, H.; Zhao, X.; Sun, M.; Shi, W.; Zhang, F.; et al. Prospective phase II trial of first-line rituximab, methotrexate, and orelabrutinib (R-MO) in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Blood Cancer J. 2025, 15, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcantara, M.; Chevrier, M.; Jardin, F.; Schmitt, A.; Houillier, C.; Oberic, L.; Chinot, O.; Morschhauser, F.; Peyrade, F.; Houot, R.; et al. Phase IB part of LOC-R01, a LOC network non-comparative randomized phase IB/II study testing R-MPV in combination with escalating doses of lenalidomide or ibrutinib for newly diagnosed primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) patients. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 17, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houillier, C.; Taillandier, L.; Dureau, S.; Lamy, T.; Laadhari, M.; Chinot, O.; Moluçon-Chabrot, C.; Soubeyran, P.; Gressin, R.; Choquet, S.; et al. Radiotherapy or Autologous Stem-Cell Transplantation for Primary CNS Lymphoma in Patients 60 Years of Age and Younger: Results of the Intergroup ANOCEF-GOELAMS Randomized Phase II PRECIS Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritsch, D.; Mrugala, M.M.; Marks, L.A.; Mangipudi, K.; Neal, M.; Wingerchuk, D.M.; O’Carroll, C.B. Is Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation a Safe and Effective Alternative to Whole Brain Radiation as Consolidation Therapy in Patients With Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma?: A Critically Appraised Topic. Neurologist 2021, 26, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorb, E.; Isbell, L.K.; Kerkhoff, A.; Mathas, S.; Braulke, F.; Egerer, G.; Röth, A.; Schliffke, S.; Borchmann, P.; Brunnberg, U.; et al. High-dose chemotherapy and autologous haematopoietic stem-cell transplantation in older, fit patients with primary diffuse large B-cell CNS lymphoma (MARTA): A single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2024, 11, e196–e205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scordo, M.; Wang, T.P.; Ahn, K.W.; Chen, Y.; Ahmed, S.; Awan, F.T.; Beitinjaneh, A.; Chen, A.; Chow, V.A.; Dholaria, B.; et al. Outcomes Associated With Thiotepa-Based Conditioning in Patients With Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma After Autologous Hematopoietic Cell Transplant. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, O.S.; Arshad, S.; Lian, Q.; Ahn, K.W.; D’Souza, A.; Dhakal, B.; Mohan, M.; Pasquini, M.; Longo, W.; Shah, N.N.; et al. Comparison of Thiotepa-based Conditioning Regimens for Older Adults with Primary Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma of the Central Nervous System Undergoing Autologous Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2024, 30, 1191.e1–1191.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, F.A.; Dekker, T.J.A.; Doorduijn, J.K.; Böhringer, S.; Brink, M.; de Groen, R.A.L.; de Haan, L.M.; Woei-A-Jin, F.J.S.H.; Noordenbos, T.; Sijs-Szabo, A.; et al. Clinical characteristics and survival outcomes of patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma treated with high-dose methotrexate-based polychemotherapy and consolidation therapies. Eur. J. Cancer 2024, 213, 115068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, T.T.; Giri, S.; Ruppert, A.S.; Geyer, S.M.; Smith, S.E.; Mohile, N.; Swinnen, L.J.; Friedberg, J.W.; Kahl, B.S.; Bartlett, N.L.; et al. Myeloablative vs nonmyeloablative consolidation for primary central nervous system lymphoma: Results of Alliance 51101. Blood Adv. 2024, 8, 3189–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, K.; Mannis, G.; Hwang, J.; Geng, H.; Rubenstein, J.L. Low-dose lenalidomide maintenance after induction therapy in older patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 186, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhao, D.; Chong, W.; Chen, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, D. The role of upfront lenalidomide maintenance for primary central nervous system lymphoma following first-line methotrexate treatment: A retrospective study. Cancer Med. 2024, 13, e7193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.R.; Godby, R.C.; Negaard, B.J.; Mwangi, R.; Nedved, A.N.; Barreto, J.N.; Micallef, I.N.; Ansell, S.M.; Porrata, L.; Durani, U.; et al. Comparison of outcomes in postinduction strategies for primary central nervous system lymphoma: A Mayo Clinic experience. Blood Adv. 2025, 9, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, K.; Mizobuchi, Y.; Fujihara, T.; Azumi, M.; Takagi, Y. Continued-Maintenance Therapy with High-dose Methotrexate Improves Overall Survival of Patients with Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. J. Med. Investig. 2021, 68, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairey, O.; Taliansky, A.; Glik, A.; Amiel, A.; Yust-Katz, S.; Gurion, R.; Zektser, M.; Porges, T.; Sarid, N.; Horowitz, N.A.; et al. A phase 2 study of ibrutinib maintenance following first-line high-dose methotrexate-based chemotherapy for elderly patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma. Cancer 2023, 129, 3905–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulczynski, E.J.; Simonsen, M.R.; Kuittinen, O.; Fagerli, U.M.; Erlanson, M.; Fluge, Ø.; Leppä, S.; Østenstad, B.; Fosså, A.; Eriksson, M.; et al. Elderly long-term survivors in the Nordic phase II study with first-line maintenance temozolomide for primary central nervous system lymphoma: A 10-year follow-up. Haematologica 2024, 109, 2359–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, K.; Nishikawa, R.; Narita, Y.; Mizusawa, J.; Sumi, M.; Koga, T.; Sasaki, N.; Kinoshita, M.; Nagane, M.; Arakawa, Y.; et al. Randomized phase III study of high-dose methotrexate and whole-brain radiotherapy with/without temozolomide for newly diagnosed primary CNS lymphoma: JCOG1114C. Neuro. Oncol. 2023, 25, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, J.S.; Grommes, C. Treatment of Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma: From Chemotherapy to Small Molecules. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2018, 38, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelikson, V.; Gurumurthi, A.; Sawalha, Y.; Annunzio, K.; Saha, A.; Dong, N.; Qualls, D.; Amoozgar, B.; Kahl, B.; Baird, J.; et al. Loncastuximab in high-risk and heavily pretreated relapsed / refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A real-world analysis from 21 US centers. Haematologica 2024, 110, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falchi, L.; Vardhana, S.A.; Salles, G.A. Bispecific antibodies for the treatment of B-cell lymphoma: Promises, unknowns, and opportunities. Blood 2023, 141, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, J.K.; Gao, L.; Shouse, G.; Song, J.Y.; Pak, S.; Lee, B.; Chen, B.T.; Kallam, A.; Baird, J.H.; Marcucci, G.; et al. Glofitamab stimulates immune cell infiltration of CNS tumors and induces clinical responses in secondary CNS lymphoma. Blood 2024, 144, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budde, L.E.; Olszewski, A.J.; Assouline, S.; Lossos, I.S.; Diefenbach, C.; Kamdar, M.; Ghosh, N.; Modi, D.; Sabry, W.; Naik, S.; et al. Mosunetuzumab with polatuzumab vedotin in relapsed or refractory aggressive large B cell lymphoma: A phase 1b/2 trial. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, W.H.; Young, R.M.; Schmitz, R.; Yang, Y.; Pittaluga, S.; Wright, G.; Lih, C.J.; Williams, P.M.; Shaffer, A.L.; Gerecitano, J.; et al. Targeting B cell receptor signaling with ibrutinib in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 922–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grommes, C.; Tang, S.S.; Wolfe, J.; Kaley, T.J.; Daras, M.; Pentsova, E.I.; Piotrowski, A.F.; Stone, J.; Lin, A.; Nolan, C.P.; et al. Phase 1b trial of an ibrutinib-based combination therapy in recurrent/refractory CNS lymphoma. Blood 2019, 133, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soussain, C.; Choquet, S.; Blonski, M.; Leclercq, D.; Houillier, C.; Rezai, K.; Bijou, F.; Houot, R.; Boyle, E.; Gressin, R.; et al. Ibrutinib monotherapy for relapse or refractory primary CNS lymphoma and primary vitreoretinal lymphoma: Final analysis of the phase II ’proof-of-concept’ iLOC study by the Lymphoma study association (LYSA) and the French oculo-cerebral lymphoma (LOC) network. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 117, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narita, Y.; Nagane, M.; Mishima, K.; Terui, Y.; Arakawa, Y.; Yonezawa, H.; Asai, K.; Fukuhara, N.; Sugiyama, K.; Shinojima, N.; et al. Phase I/II study of tirabrutinib, a second-generation Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in relapsed/refractory primary central nervous system lymphoma. Neuro. Oncol. 2021, 23, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaff, L.; Nayak, L.; Grommes, C. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors for the treatment of primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL): Current progress and latest advances. Leuk. Lymphoma 2024, 65, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghesquieres, H.; Chevrier, M.; Laadhari, M.; Chinot, O.; Choquet, S.; Moluçon-Chabrot, C.; Beauchesne, P.; Gressin, R.; Morschhauser, F.; Schmitt, A.; et al. Lenalidomide in combination with intravenous rituximab (REVRI) in relapsed/refractory primary CNS lymphoma or primary intraocular lymphoma: A multicenter prospective ’proof of concept’ phase II study of the French Oculo-Cerebral lymphoma (LOC) Network and the Lymphoma Study Association (LYSA). Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tun, H.W.; Johnston, P.B.; DeAngelis, L.M.; Atherton, P.J.; Pederson, L.D.; Koenig, P.A.; Reeder, C.B.; Omuro, A.M.P.; Schiff, D.; O’Neill, B.; et al. Phase 1 study of pomalidomide and dexamethasone for relapsed/refractory primary CNS or vitreoretinal lymphoma. Blood 2018, 132, 2240–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyao, K.; Yokota, H.; Sakemura, R.L. Is CD19-directed chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy a smart strategy to combat central nervous system lymphoma? Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1082235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigault, M.J.; Dietrich, J.; Gallagher, K.; Roschewski, M.; Jordan, J.T.; Forst, D.; Plotkin, S.R.; Cook, D.; Casey, K.S.; Lindell, K.A.; et al. Safety and efficacy of tisagenlecleucel in primary CNS lymphoma: A phase 1/2 clinical trial. Blood 2022, 139, 2306–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, M.R.; Dorris, C.S.; Makambi, K.H.; Luo, Y.; Munshi, P.N.; Donato, M.; Rowley, S.; Saad, A.; Goy, A.; Dunleavy, K.; et al. Toxicity and efficacy of CAR T-cell therapy in primary and secondary CNS lymphoma: A meta-analysis of 128 patients. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choquet, S.; Soussain, C.; Azar, N.; Morel, V.; Metz, C.; Ursu, R.; Waultier-Rascalou, A.; di Blasi, R.; Houot, R.; Souchet, L.; et al. CAR T-cell therapy induces a high rate of prolonged remission in relapsed primary CNS lymphoma: Real-life results of the LOC network. Am. J. Hematol. 2024, 99, 1240–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yu, Q.; Dai, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Y. CD19/CD22 CAR-T-cell cocktail therapy following autologous transplantation is an optimizing strategy for treating relapsed/refractory central nervous system lymphoma. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 13, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Huang, L.; Mei, H.; Li, Y.; Niu, T.; Zou, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, P.; Wu, J.; et al. Real-world experience of commercial relmacabtagene autoleucel (relma-cel) for relapsed/refractory central nervous system lymphoma: A multicenter retrospective analysis of patients in China. J. Immunother. Cancer 2024, 12, e008553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederquist, G.Y.; Schefflein, J.; Devlin, S.M.; Shah, G.L.; Shouval, R.; Hubbeling, H.; Tringale, K.; Alarcon Tomas, A.; Fregonese, B.; Hajj, C.; et al. CNS bridging radiotherapy achieves rapid cytoreduction before CAR T-cell therapy for aggressive B-cell lymphomas. Blood Adv. 2024, 8, 5192–5199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Zheng, P.; Fu, Z.; Cao, M.; Yang, F.; Guo, Y.; Liu, R.; Ma, L.; Feng, S.; Tao, X.; et al. Whole brain radiotherapy combined with CART-cell therapy for relapsed/refractory central nervous system B-cell lymphoma. Ann. Hematol. 2025, 104, 2495–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, L.; Iwamoto, F.M.; LaCasce, A.; Mukundan, S.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Chapuy, B.; Armand, P.; Rodig, S.J.; Shipp, M.A. PD-1 blockade with nivolumab in relapsed/refractory primary central nervous system and testicular lymphoma. Blood 2017, 129, 3071–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uawithya, E.; Kulchutisin, K.; Jitprapaikulsan, J.; Leelakanok, N.; Owattanapanich, W. Safety and efficacy of programmed cell death-1 inhibitors in relapsed immune-privileged site lymphoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0319714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashima, Y.; Hayano, A.; Yamanaka, R. Metabolome Analysis Reveals Excessive Glycolysis via PI3K/AKT/mTOR and RAS/MAPK Signaling in Methotrexate-Resistant Primary CNS Lymphoma-Derived Cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2754–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korfel, A.; Schlegel, U.; Herrlinger, U.; Dreyling, M.; Schmidt, C.; von Baumgarten, L.; Pezzutto, A.; Grobosch, T.; Kebir, S.; Thiel, E.; et al. Phase II Trial of Temsirolimus for Relapsed/Refractory Primary CNS Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 1757–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grommes, C.; Pentsova, E.; Schaff, L.R.; Nolan, C.P.; Kaley, T.; Reiner, A.S.; Panageas, K.S.; Mellinghoff, I.K. Preclinical and clinical evaluation of Buparlisib (BKM120) in recurrent/refractory Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2023, 64, 1545–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Roemeling, C.A.; Doonan, B.P.; Klippel, K.; Schultz, D.; Hoang-Minh, L.; Trivedi, V.; Li, C.; Russell, R.A.; Kanumuri, R.S.; Sharma, A.; et al. Oral IRAK-4 Inhibitor CA-4948 Is Blood-Brain Barrier Penetrant and Has Single-Agent Activity against CNS Lymphoma and Melanoma Brain Metastases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 1751–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, R.; Zhou, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, P.; Xia, F.; Kang, L.; Yu, L.; Wu, D.; Jin, Z.; Qu, C. Long-term Complete Remission of Decitabine-Primed Tandem CD19/CD22 CAR-T Therapy with PD-1 and BTK Inhibitors Maintenance in a Refractory Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma Patient. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 55, 1363–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, I.; Carabia, J.; Bobillo, S.; Palacio, C.; Abrisqueta, P.; Pagès, C.; Nieto, J.C.; Castellví, J.; Martínez-Ricarte, F.; Escoda, L.; et al. Repolarization of tumor infiltrating macrophages and increased survival in mouse primary CNS lymphomas after XPO1 and BTK inhibition. J. Neurooncol. 2020, 149, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, F.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Dong, G.; Yang, S.; Kang, X.; Kang, Z.; Han, C.; et al. Zanubrutinib delays selinexor resistance evolution in biopsy sample-derived primary central nervous system lymphoma models. iScience 2024, 27, 109799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez Solsona, B.; Horn, H.; Schmitt, A.; Xu, W.; Bucher, P.; Heinrich, A.; Kalmbach, S.; Kreienkamp, N.; Franke, M.; Wimmers, F.; et al. Inhibition of glutaminase-1 in DLBCL potentiates venetoclax-induced antitumor activity by promoting oxidative stress. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 7433–7444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Mo, Z.; Pan, L.; Zhou, M.; Ye, X.; Liu, X.; Cai, X.; Qian, C.; Chen, F.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Dual PI3K/HDAC Inhibitor BEBT-908 Exhibits Potent Efficacy as Monotherapy for Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Target Oncol. 2023, 18, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, H.; Nong, L. The Landscape of Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL): Clinicopathologic and Genomic Characteristics and Therapeutic Perspectives. Cancers 2025, 17, 2909. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17172909
Jiang H, Nong L. The Landscape of Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL): Clinicopathologic and Genomic Characteristics and Therapeutic Perspectives. Cancers. 2025; 17(17):2909. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17172909
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Huijuan, and Lin Nong. 2025. "The Landscape of Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL): Clinicopathologic and Genomic Characteristics and Therapeutic Perspectives" Cancers 17, no. 17: 2909. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17172909
APA StyleJiang, H., & Nong, L. (2025). The Landscape of Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL): Clinicopathologic and Genomic Characteristics and Therapeutic Perspectives. Cancers, 17(17), 2909. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17172909





