Exploring the Expression of CD73 in Lung Adenocarcinoma with EGFR Genomic Alterations
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Samples
2.2. Immunohistochemistry
2.3. EGFR In Situ Fluorescent Hybridisation
2.4. EGFR Mutation Analysis
2.5. Statistical Design and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients and Characteristics of Samples
3.2. Analysis of Expression of CD73 and Correlation with Clinicopathological Features
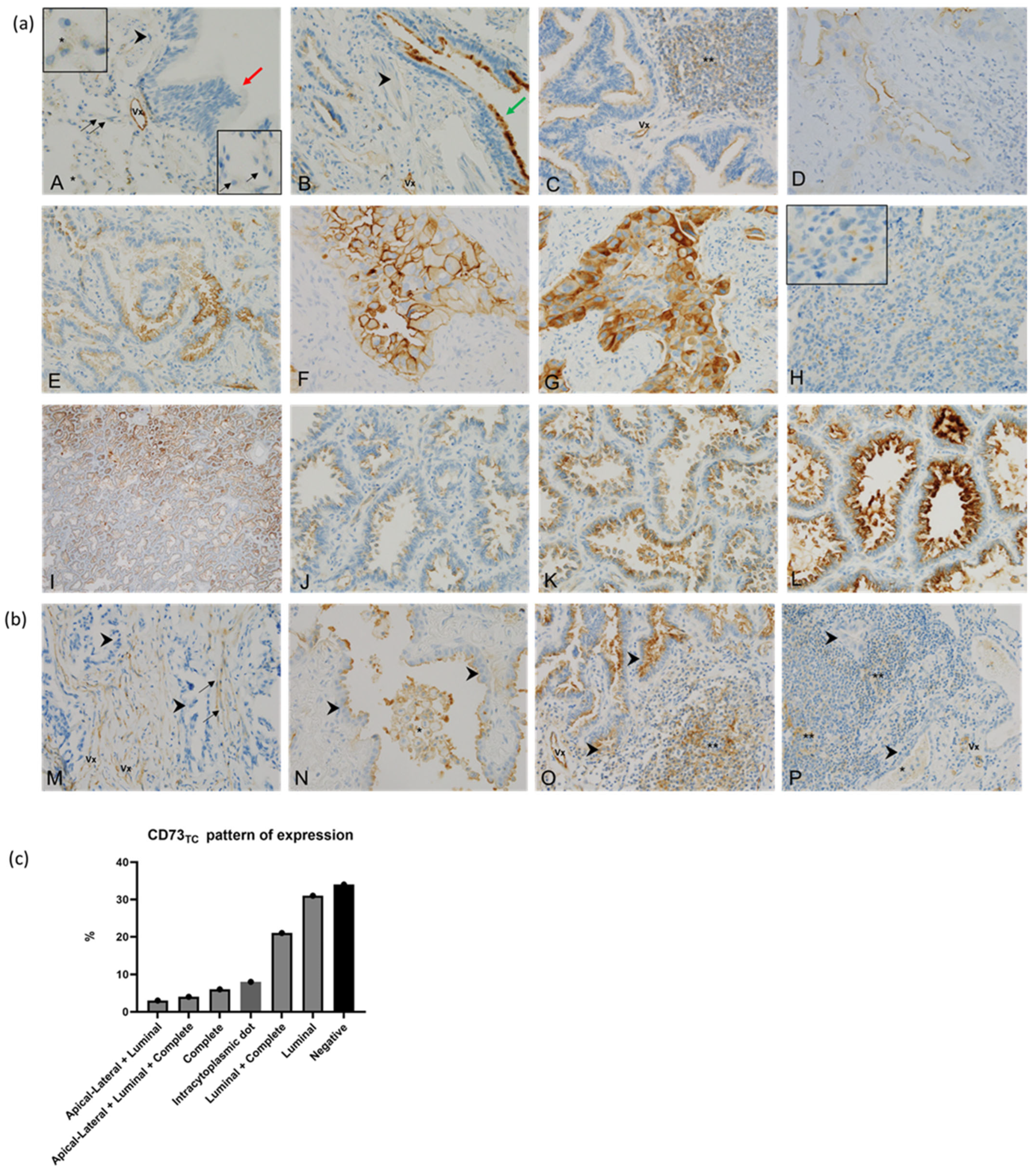
3.2.1. CD73 in Adjacent Non-Tumour Lung Tissue
3.2.2. CD73 in Tumour Cells (CD73TC)
| Variable (n = 76, Unless Stated Otherwise) | Type | HIGH CD73TC (TPS > 50%) | LOW CD73TC (TPS ≤ 5 0%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical and follow-up data | ||||
| Age at diagnosis | Mean (sd) | 66 (7) | 66.48 (11.07) | 0.9525 |
| Median [IQR] | 67 [60–71] | 67 [63–74] | ||
| Sexe | Female | 9 (75) | 43 (67.19) | 0.8447 |
| Male | 3 (25) | 21 (32.81) | ||
| Smoking (n = 72) | Smoker | 5 (41.67) | 24 (40) | 1 |
| Non-smoker | 7 (58.33) | 36 (60) | ||
| Stage category | Advanced | 5 (42) | 37 (58) | 0.4740 |
| Early | 7 (58) | 27 (42) | ||
| Brain_metastasis (n = 53) | No | 6 (75) | 32 (71) | 1.0000 |
| Yes | 2 (25) | 13 (29) | ||
| OS_Month | ||||
| Mean (sd) | 75 (50) | 41 (36) | 0.0868 | |
| Median [IQR] | 65 [29–79] | 28 [14–60] | ||
| Pathological data | ||||
| Origin of samples | Metastasis | 3 (25) | 20 (31) | 0.9282 |
| Primary | 9 (75) | 44 (695) | ||
| Histology subtype (n = 39) | Acinar | 2 (22) | 13 (43) | 0.35 |
| Cribriform | 1 (11) | 0 (0) | ||
| Lepidic | 0 (0) | 1 (3) | ||
| Papillary | 5 (56) | 12 (40) | ||
| Solid | 0 (0) | 2 (7) | ||
| Micropapillary | 1 (11) | 2 (7) | ||
| High-grade component (n = 71) | No | 6 (50) | 36 (61) | 0.6998 |
| Yes | 6 (50) | 23 (39) | ||
| Emboli (n = 46) | No | 3 (27) | 14 (29) | 1.0000 |
| Yes | 8 (73) | 34 (71) | ||
| Immunohistochemistry data | ||||
| PD-L1 expression category (n = 73) | High | 0 (0) | 10 (17) | 0.2467 |
| Moderate | 2 (17) | 5 (8) | ||
| Negative | 10 (83) | 46 (75) | ||
| PDL1 % TC | Mean (sd) | 1 (3) | 13 (30) | 0.44 |
| Median [IQR] | 0 [0–0] | 0 [0–0] | ||
| CD73TC pattern (n = 50) | Apical lateral | 1 (8) | 0 (0) | 0.0152 |
| Complete | 9 (75) | 16 (42) | ||
| Luminal | 2 (17) | 22 (58) | ||
| CD73TC dot staining (n = 50) | Yes | 3 (25) | 5 (8) | 0.11 |
| No | 9 (75) | 59 (92) | ||
| CD73SC in lymphocyte | Negative | 12 (100) | 57 (89) | 0.5103 |
| Positive | 0 (0) | 7 (11) | ||
| CD73SC in macrophage | Negative | 11 (92) | 60 (94) | 1.0000 |
| Positive | 1 (8) | 4 (6) | ||
| Molecular data | ||||
| EGFR amplification status (n = 71) | Yes | 9 (75) | 38 (64) | 0.7096 |
| No | 3 (25) | 21 (36) | ||
| EGFR mutation at baseline | Ex18_G719 | 1 (8) | 2 (3) | 0.7366 |
| Ex20_S768I | 0 (0) | 2 (3) | ||
| L858R | 5 (42) | 23 (36) | ||
| del19 | 6 (50) | 37 (58) | ||
| EGFR mutation at baseline classification (Common vs. Uncommon) | Common | 11 (92) | 60 (94) | 1.0000 |
| Uncommon | 1 (8) | 4 (6) | ||
| T790M during follow-up (n = 21) | No | 2 (100) | 9 (47) | 0.5007 |
| Yes | 0 (0) | 10 (53) | ||
3.2.3. CD73 in Stromal Cells (CD73 SC)
3.3. EGFR Amplification and Correlation with Clinicopathological Features and Expression of CD73
3.4. Event-Free Survival and Follow-Up
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EFS | Event-Free Survival |
| EGFR | Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor |
| EGFR-amp | EGFR-amp |
| EGFRm | EGFR-Mutated |
| EMT | Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition |
| FFPE | Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded |
| FISH | In Situ Fluorescent Hybridisation |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| LUAD | Lung Adenocarcinoma |
| MDSCs | Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells |
| NSCLC | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer |
| SC | Stromal Cells |
| TC | Tumour Cells |
| TKIs | Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors |
| TME | Tumour Microenvironment |
| TPS | Tumour Proportion Score |
| HIF1α | Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1-alpha |
| LDH5 | Lactate Dehydrogenase 5 |
References
- Remon, J.; Soria, J.-C.; Peters, S. Early and Locally Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: An Update of the ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines Focusing on Diagnosis, Staging, Systemic and Local Therapy. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1637–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, J.-C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettinger, D.S.; Wood, D.E.; Aisner, D.L.; Akerley, W.; Bauman, J.R.; Bharat, A.; Bruno, D.S.; Chang, J.Y.; Chirieac, L.R.; D’Amico, T.A.; et al. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 3.2022, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2022, 20, 497–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Yu, D.; Tian, W.; Wu, F. Resistance Mechanisms to Osimertinib and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies in Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2022, 34, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Shin, J.-Y.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Park, C.; Kim, J.-Y.; Koh, Y.; Keam, B.; Min, H.S.; Kim, T.M.; et al. Primary Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs) in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Harboring TKI-Sensitive EGFR Mutations: An Exploratory Study. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2080–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackman, D.M.; Yeap, B.Y.; Sequist, L.V.; Lindeman, N.; Holmes, A.J.; Joshi, V.A.; Bell, D.W.; Huberman, M.S.; Halmos, B.; Rabin, M.S.; et al. Exon 19 Deletion Mutations of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Are Associated with Prolonged Survival in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Gefitinib or Erlotinib. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 3908–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riely, G.J.; Pao, W.; Pham, D.; Li, A.R.; Rizvi, N.; Venkatraman, E.S.; Zakowski, M.F.; Kris, M.G.; Ladanyi, M.; Miller, V.A. Clinical Course of Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Exon 19 and Exon 21 Mutations Treated with Gefitinib or Erlotinib. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhang, X.-C.; Chen, Z.-H.; Yin, X.-L.; Yang, J.-J.; Xu, C.-R.; Yan, H.-H.; Chen, H.-J.; Su, J.; Zhong, W.-Z.; et al. Relative Abundance of EGFR Mutations Predicts Benefit from Gefitinib Treatment for Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3316–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, M.; Okamoto, I.; Fujita, Y.; Arao, T.; Ito, H.; Fukuoka, M.; Nishio, K.; Nakagawa, K. De Novo Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in EGFR Mutation-Positive Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 399–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhao, J.; He, Q.; Chen, M.; Yan, J.; Ou, Q.; Wu, X.; Shao, Y.W.; Yu, X. Mechanisms of Primary Resistance to EGFR Targeted Therapy in Advanced Lung Adenocarcinomas. Lung Cancer 2018, 124, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.M.; Kim, H.R.; Cho, E.K.; Min, Y.J.; Ahn, J.S.; Ahn, M.-J.; Park, K.; Cho, B.C.; Lee, J.-H.; Jeong, H.C.; et al. Targeted Sequencing Identifies Genetic Alterations That Confer Primary Resistance to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor (Korean Lung Cancer Consortium). Oncotarget 2016, 7, 36311–36320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Chu, H.; Yao, Y. Intrinsic Resistance to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Activating EGFR Mutations. Onco Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 3711–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, K.-H.; Huang, Y.-H.; Tseng, J.-S.; Chen, K.-C.; Ku, W.-H.; Su, K.-Y.; Chen, J.J.W.; Chen, H.-W.; Yu, S.-L.; Yang, T.-Y.; et al. High PD-L1 Expression Correlates with Primary Resistance to EGFR-TKIs in Treatment Naïve Advanced EGFR-Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients. Lung Cancer 2019, 127, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passaro, A.; Jänne, P.A.; Mok, T.; Peters, S. Overcoming Therapy Resistance in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.A.; Arcila, M.E.; Rekhtman, N.; Sima, C.S.; Zakowski, M.F.; Pao, W.; Kris, M.G.; Miller, V.A.; Ladanyi, M.; Riely, G.J. Analysis of Tumor Specimens at the Time of Acquired Resistance to EGFR-TKI Therapy in 155 Patients with EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2240–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielecki, J.; Gray, J.E.; Cheng, Y.; Ohe, Y.; Imamura, F.; Cho, B.C.; Lin, M.-C.; Majem, M.; Shah, R.; Rukazenkov, Y.; et al. Candidate Mechanisms of Acquired Resistance to First-Line Osimertinib in EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamiya, A.; Osuga, M.; Harada, D.; Isa, S.; Taniguchi, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Mizumori, Y.; Shinohara, T.; Yanai, H.; Nakatomi, K.; et al. Mechanisms of Resistance and Correlation between Pre-Treatment Co-Alterations and p-Prognosis to Osimertinib in Chemo-Naïve Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2024, 195, 107917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, T.; Kondo, M.; Goto, Y.; Fukui, T.; Yoshioka, H.; Yokoi, K.; Osada, H.; Imaizumi, K.; Hasegawa, Y.; Shimokata, K.; et al. EGFR Point Mutation in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Is Occasionally Accompanied by a Second Mutation or Amplification. Cancer Sci. 2006, 97, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, X.; Gao, J.; Wu, S.; Liu, T. Relationship between EGFR Expression, Copy Number and Mutation in Lung Adenocarcinomas. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grob, T.J.; Hoenig, T.; Clauditz, T.S.; Atanackovic, D.; Koenig, A.M.; Vashist, Y.K.; Klose, H.; Simon, R.; Pantel, K.; Izbicki, J.R.; et al. Frequent Intratumoral Heterogeneity of EGFR Gene Copy Gain in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2013, 79, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, M.D.; Marin-Acevedo, J.A.; Pellini, B. Immunotherapy for Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Decade of Progress. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2021, 41, e105–e127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.K.; Man, J.; Lord, S.; Links, M.; Gebski, V.; Mok, T.; Yang, J.C.-H. Checkpoint Inhibitors in Metastatic EGFR-Mutated Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer—A Meta-Analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gainor, J.F.; Shaw, A.T.; Sequist, L.V.; Fu, X.; Azzoli, C.G.; Piotrowska, Z.; Huynh, T.G.; Zhao, L.; Fulton, L.; Schultz, K.R.; et al. EGFR Mutations and ALK Rearrangements Are Associated with Low Response Rates to PD-1 Pathway Blockade in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Analysis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4585–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garon, E.B.; Rizvi, N.A.; Hui, R.; Leighl, N.; Balmanoukian, A.S.; Eder, J.P.; Patnaik, A.; Aggarwal, C.; Gubens, M.; Horn, L.; et al. Pembrolizumab for the Treatment of Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2018–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisberg, A.; Cummings, A.; Goldman, J.W.; Bornazyan, K.; Reese, N.; Wang, T.; Coluzzi, P.; Ledezma, B.; Mendenhall, M.; Hunt, J.; et al. A Phase II Study of Pembrolizumab in EGFR-Mutant, PD-L1+, Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Naïve Patients with Advanced NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1138–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.C.-H.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Sequist, L.V.; Wu, C.-L.; Papadimitrakopoulou, V.A.; Su, W.-C.; Fiore, J.; Saraf, S.; Raftopoulos, H.; Patnaik, A. Pembrolizumab in Combination with Erlotinib or Gefitinib as First-Line Therapy for Advanced NSCLC with Sensitizing EGFR Mutation. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creelan, B.C.; Yeh, T.C.; Kim, S.-W.; Nogami, N.; Kim, D.-W.; Chow, L.Q.M.; Kanda, S.; Taylor, R.; Tang, W.; Tang, M.; et al. A Phase 1 Study of Gefitinib Combined with Durvalumab in EGFR TKI-Naive Patients with EGFR Mutation-Positive Locally Advanced/Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, R.; Gandhi, L.; Carcereny Costa, E.; Felip, E.; Ahn, M.-J.; Eder, J.P.; Balmanoukian, A.S.; Leighl, N.B.; Aggarwal, C.; Horn, L.; et al. Long-Term OS for Patients with Advanced NSCLC Enrolled in the KEYNOTE-001 Study of Pembrolizumab (Pembro). J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 9026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garassino, M.C.; Cho, B.-C.; Kim, J.-H.; Mazières, J.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Lena, H.; Jaime, J.C.; Gray, J.E.; Powderly, J.; Chouaid, C.; et al. Final Overall Survival and Safety Update for Durvalumab in Third- or Later-Line Advanced NSCLC: The Phase II ATLANTIC Study. Lung Cancer 2020, 147, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Cheng, G.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, G.; Xu, Y.; Yu, X.; Huang, Z.; Fan, Y. PD-L1 Expression and T Cells Infiltration in Patients with Uncommon EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and the Response to Immunotherapy. Lung Cancer 2020, 142, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneshima, Y.; Ijichi, K.; Anai, S.; Ota, K.; Otsubo, K.; Iwama, E.; Tanaka, K.; Oda, Y.; Nakanishi, Y.; Okamoto, I. PD-L1 Expression in Lung Adenocarcinoma Harboring EGFR Mutations or ALK Rearrangements. Lung Cancer 2018, 118, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gettinger, S.; Hellmann, M.D.; Chow, L.Q.M.; Borghaei, H.; Antonia, S.; Brahmer, J.R.; Goldman, J.W.; Gerber, D.E.; Juergens, R.A.; Shepherd, F.A.; et al. Nivolumab Plus Erlotinib in Patients with EGFR-Mutant Advanced NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1363–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Li, X.; Jiang, T.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Shi, J.; Qiao, M.; Luo, J.; et al. EGFR-Targeted Therapy Alters the Tumor Microenvironment in EGFR-Driven Lung Tumors: Implications for Combination Therapies. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 1432–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S.; Majem, M.; Barlesi, F.; Carcereny, E.; Chu, Q.; Monnet, I.; Sanchez-Hernandez, A.; Dakhil, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Winzer, L.; et al. COAST: An Open-Label, Phase II, Multidrug Platform Study of Durvalumab Alone or in Combination with Oleclumab or Monalizumab in Patients with Unresectable, Stage III Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3383–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, D.; O’Leary, C.L.; Reilly, A.; Teo, M.Y.; O’Kane, G.; Hendriks, L.; Bennett, K.; Naidoo, J. Toxicity of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Combinations in Solid Tumours: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1380453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiest, N.; Majeed, U.; Seegobin, K.; Zhao, Y.; Lou, Y.; Manochakian, R. Role of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy in Advanced EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 751209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, X.; Negrao, M.V.; Reuben, A.; Federico, L.; Diao, L.; McGrail, D.; Nilsson, M.; Robichaux, J.; Munoz, I.G.; Patel, S.; et al. Characterization of the Immune Landscape of EGFR-Mutant NSCLC Identifies CD73/Adenosine Pathway as a Potential Therapeutic Target. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 583–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.-Y.; Zhang, J.-T.; Liu, S.-Y.; Su, J.; Zhang, C.; Xie, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Tu, H.-Y.; Xu, C.-R.; Yan, L.-X.; et al. EGFR Mutation Correlates with Uninflamed Phenotype and Weak Immunogenicity, Causing Impaired Response to PD-1 Blockade in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1356145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Su, C.; Li, X.; Zhou, C. Association of CD8 T Cell Apoptosis and EGFR Mutation in Non-Small Lung Cancer Patients. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 2130–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yegutkin, G.G. Nucleotide- and Nucleoside-Converting Ectoenzymes: Important Modulators of Purinergic Signalling Cascade. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1783, 673–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, A.; Gorelik, E.; Prasad, S.J.; Ronchese, F.; Lukashev, D.; Wong, M.K.K.; Huang, X.; Caldwell, S.; Liu, K.; Smith, P.; et al. A2A Adenosine Receptor Protects Tumors from Antitumor T Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13132–13137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stagg, J.; Divisekera, U.; McLaughlin, N.; Sharkey, J.; Pommey, S.; Denoyer, D.; Dwyer, K.M.; Smyth, M.J. Anti-CD73 Antibody Therapy Inhibits Breast Tumor Growth and Metastasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1547–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.-W.; Liu, C.; Yang, L.; Chen, H.-C.; Yang, L.-F.; Zhang, H.-Z.; Dong, K. CD73 Severed as a Potential Prognostic Marker and Promote Lung Cancer Cells Migration via Enhancing EMT Progression. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 728200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, M.-W.; Kim, C.-W.; Choi, K.-C. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition-Inducing Factors Involved in the Progression of Lung Cancers. Biomol. Ther. 2022, 30, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarek, P.E.; Huang, C.-T.; Lutz, E.R.; Kowalski, J.; Horton, M.R.; Linden, J.; Drake, C.G.; Powell, J.D. A2A Receptor Signaling Promotes Peripheral Tolerance by Inducing T-Cell Anergy and the Generation of Adaptive Regulatory T Cells. Blood 2008, 111, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Chen, Y.; Li, F.; Li, W.; Zhou, H.; Yang, Y.; Pei, Z. Effects of CD73 on Human Colorectal Cancer Cell Growth in Vivo and in Vitro. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 1750–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Jia, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Wu, Z.; Yu, W.; Zhang, M.; Ding, G.; Cao, L. The Distinct Role of CD73 in the Progression of Pancreatic Cancer. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 97, 803–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Huang, C.; Zhao, T.; Wang, X.; Gao, S.; Ma, Y.; et al. CD73 Induces Gemcitabine Resistance in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: A Promising Target with Non-Canonical Mechanisms. Cancer Lett. 2021, 519, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, N.T.; Altshuler, P.J.; Wan, S.; Welling, T.H.; Cavalcoli, J.; Omary, M.B. Alternative Splicing of Human NT5E in Cirrhosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Produces a Negative Regulator of Ecto-5′-Nucleotidase (CD73). Mol. Biol. Cell 2014, 25, 4024–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, B.; Allard, D.; Buisseret, L.; Stagg, J. The Adenosine Pathway in Immuno-Oncology. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, C.M.; Sult, E.; Huang, Q.; Mulgrew, K.; Fuhrmann, S.R.; McGlinchey, K.A.; Hammond, S.A.; Rothstein, R.; Rios-Doria, J.; Poon, E.; et al. Targeting CD73 in the Tumor Microenvironment with MEDI9447. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1208875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isomoto, K.; Haratani, K.; Hayashi, H.; Shimizu, S.; Tomida, S.; Niwa, T.; Yokoyama, T.; Fukuda, Y.; Chiba, Y.; Kato, R.; et al. Impact of EGFR-TKI Treatment on the Tumor Immune Microenvironment in EGFR Mutation–Positive Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2037–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, H.; Azuma, K.; Kawahara, A.; Kinoshita, T.; Matsuo, N.; Naito, Y.; Tokito, T.; Yamada, K.; Akiba, J.; Hoshino, T. Predictive Value of CD73 Expression for the Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in NSCLC. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 950–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, E.; McGlinchey, K.; Wang, J.; Martin, P.; Ching, S.L.K.; Floc’h, N.; Kurasawa, J.; Starrett, J.H.; Lazdun, Y.; Wetzel, L.; et al. Anti–PD-L1 and Anti-CD73 Combination Therapy Promotes T Cell Response to EGFR-Mutated NSCLC. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e142843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Yoshimura, K.; Kurabe, N.; Kahyo, T.; Kawase, A.; Tanahashi, M.; Ogawa, H.; Inui, N.; Funai, K.; Shinmura, K.; et al. Prognostic Impact of CD73 and A2A Adenosine Receptor Expression in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 8738–8751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, S.; Yim, J.; Keam, B.; Kim, T.M.; Jeon, Y.K.; Kim, D.-W.; Heo, D.S. Targeting CD73 to Overcomes Resistance to First-Generation EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 55, 1134–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, P.; Salazar, R.; Zhang, J.; Ledesma, D.; Solorzano, J.L.; Mino, B.; Villalobos, P.; Dejima, H.; Douse, D.Y.; Diao, L.; et al. CD73 Expression Defines Immune, Molecular, and Clinicopathological Subgroups of Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2021, 70, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giatromanolaki, A.; Kouroupi, M.; Pouliliou, S.; Mitrakas, A.; Hasan, F.; Pappa, A.; Koukourakis, M.I. Ectonucleotidase CD73 and CD39 Expression in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Relates to Hypoxia and Immunosuppressive Pathways. Life Sci. 2020, 259, 118389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramdani, H.O.; Falk, M.; Heukamp, L.C.; Schatz, S.; Tiemann, M.; Wesseler, C.; Diehl, L.; Schuuring, E.; Groen, H.J.M.; Griesinger, F. Immune Related Endonucleases and GTPases Are Not Associated with Tumor Response in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Checkpoint Inhibitors. Pathol.–Res. Pract. 2021, 227, 153651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haratani, K.; Nakamura, A.; Mamesaya, N.; Mitsuoka, S.; Yoneshima, Y.; Saito, R.; Tanizaki, J.; Fujisaka, Y.; Hata, A.; Tsuruno, K.; et al. Tumor Microenvironment Landscape of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Reveals Resistance Mechanisms for PD-L1 Blockade Following Chemoradiotherapy: A Multi-Center Prospective Biomarker Study (WJOG11518L/SUBMARINE). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 8, 1334–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowash, R.R.; Akbay, E.A. Tumor Intrinsic and Extrinsic Functions of CD73 and the Adenosine Pathway in Lung Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1130358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janho Dit Hreich, S.; Benzaquen, J.; Hofman, P.; Vouret-Craviari, V. The Purinergic Landscape of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Classification of Tumours Online. Available online: https://tumourclassification.iarc.who.int/welcome/ (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- Goldstraw, P.; Chansky, K.; Crowley, J.; Rami-Porta, R.; Asamura, H.; Eberhardt, W.E.E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Groome, P.; Mitchell, A.; Bolejack, V.; et al. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for Revision of the TNM Stage Groupings in the Forthcoming (Eighth) Edition of the TNM Classification for Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilie, M.; Hofman, V.; Dietel, M.; Soria, J.; Hofman, P. Assessment of the PD-L1 Status by Immunohistochemistry: Challenges and Perspectives for Therapeutic Strategies in Lung Cancer Patients. Virchows Arch. 2016, 468, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, A.; Yazbeck, N.; Guibert, N.; Chamorey, E.; Paquet, A.; Ribeyre, L.; Bence, C.; Zahaf, K.; Leroy, S.; Marquette, C.; et al. Effect of Mutant Variants of the KRAS Gene on PD-L1 Expression and on the Immune Microenvironment and Association with Clinical Outcome in Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients. Lung Cancer 2018, 121, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantuejoul, S.; Damotte, D.; Hofman, V.; Adam, J. Programmed Death Ligand 1 Immunohistochemistry in Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, S89–S101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappuzzo, F.; Hirsch, F.R.; Rossi, E.; Bartolini, S.; Ceresoli, G.L.; Bemis, L.; Haney, J.; Witta, S.; Danenberg, K.; Domenichini, I.; et al. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Gene and Protein and Gefitinib Sensitivity in Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2005, 97, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varella-Garcia, M.; Diebold, J.; Eberhard, D.A.; Geenen, K.; Hirschmann, A.; Kockx, M.; Nagelmeier, I.; Ruschoff, J.; Schmitt, M.; Arbogast, S.; et al. EGFR Fluorescence in Situ Hybridisation Assay: Guidelines for Application to Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Pathol. 2009, 62, 970–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilie, M.; Butori, C.; Lassalle, S.; Heeke, S.; Piton, N.; Sabourin, J.; Tanga, V.; Washetine, K.; Long-Mira, E.; Maitre, P.; et al. Optimization of EGFR Mutation Detection by the Fully-Automated QPCR-Based Idylla System on Tumor Tissue from Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 103055–103062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassalle, S.; Hofman, V.; Heeke, S.; Benzaquen, J.; Long, E.; Poudenx, M.; Lantéri, E.; Boutros, J.; Tanga, V.; Zahaf, K.; et al. Targeted Assessment of the EGFR Status as Reflex Testing in Treatment-Naive Non-Squamous Cell Lung Carcinoma Patients: A Single Laboratory Experience (LPCE, Nice, France). Cancers 2020, 12, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeke, S.; Benzaquen, J.; Long-Mira, E.; Audelan, B.; Lespinet, V.; Bordone, O.; Lalvée, S.; Zahaf, K.; Poudenx, M.; Humbert, O.; et al. In-House Implementation of Tumor Mutational Burden Testing to Predict Durable Clinical Benefit in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Melanoma Patients. Cancers 2019, 11, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcazer, V. StatAid: An R Package with a Graphical User Interface for Data Analysis. J. Open Source Softw. 2020, 5, 2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendell, J.; LoRusso, P.; Overman, M.; Noonan, A.M.; Kim, D.-W.; Strickler, J.H.; Kim, S.-W.; Clarke, S.; George, T.J.; Grimison, P.S.; et al. First-in-Human Study of Oleclumab, a Potent, Selective Anti-CD73 Monoclonal Antibody, Alone or in Combination with Durvalumab in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2023, 72, 2443–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horinouchi, H. Another Pirate in the Red Ocean? CD73-Targeted Therapy in EGFR-Mutated NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 18, 552–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spira, A.I.; Conkling, P.R.; Johnson, M.L.; Gardner, O.; Gilbert, H.N.; Scharville, M.; Yin, F.; Krishnan, K.; Paoloni, M.C.; Chaudhry, A. ARC-4 Study: Efficacy and Safety of AB928 plus Carboplatin, Pemetrexed and a PD-1 Antibody in Participants with Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (MNSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, e21659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.-W.; Li, Y.-C.; Ma, S.-R.; Mao, L.; Yu, G.-T.; Bu, L.-L.; Kulkarni, A.B.; Zhang, W.-F.; Sun, Z.-J. Specific Blockade CD73 Alters the “Exhausted” Phenotype of T Cells in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 1494–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, B.; Turcotte, M.; Stagg, J. CD73-Generated Adenosine: Orchestrating the Tumor-Stroma Interplay to Promote Cancer Growth. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 485156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamonte, M.L.; Torrejón-Escribano, B.; Rodríguez-Martínez, A.; Trapero, C.; Vidal, A.; Gómez de Aranda, I.; Sévigny, J.; Matías-Guiu, X.; Martín-Satué, M. Characterization of Ecto-Nucleotidases in Human Oviducts with an Improved Approach Simultaneously Identifying Protein Expression and in Situ Enzyme Activity. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 149, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcedo, K.P.; Guerrero, A.; Basrur, V.; Fu, D.; Richardson, M.L.; McLane, J.S.; Tsou, C.; Nesvizhskii, A.I.; Welling, T.H.; Lebrilla, C.B.; et al. Tumor-Selective Altered Glycosylation and Functional Attenuation of CD73 in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatol. Commun. 2019, 3, 1400–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, X.; Chen, S.; Zhou, P.; Shao, Z.; Wang, L.; Ou, Z.; Yin, L. RNA Interference of Ecto-5′-Nucleotidase (CD73) Inhibits Human Breast Cancer Cell Growth and Invasion. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2007, 24, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yu, J.; Jian, R.; Tang, S.; Yin, L.; Zhou, P. RNAi-Mediated CD73 Suppression Induces Apoptosis and Cell-Cycle Arrest in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 2561–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terp, M.G.; Olesen, K.A.; Arnspang, E.C.; Lund, R.R.; Lagerholm, B.C.; Ditzel, H.J.; Leth-Larsen, R. Anti-Human CD73 Monoclonal Antibody Inhibits Metastasis Formation in Human Breast Cancer by Inducing Clustering and Internalization of CD73 Expressed on the Surface of Cancer Cells. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 4165–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koszałka, P.; Gołuńska, M.; Stanisławowski, M.; Urban, A.; Stasiłojć, G.; Majewski, M.; Wierzbicki, P.; Składanowski, A.C.; Bigda, J. CD73 on B16F10 Melanoma Cells in CD73-Deficient Mice Promotes Tumor Growth, Angiogenesis, Neovascularization, Macrophage Infiltration and Metastasis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2015, 69, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Yang, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wei, F.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X.; Ren, X. Significantly Different Immunological Score in Lung Adenocarcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma and a Proposal for a New Immune Staging System. Oncoimmunology 2020, 9, 1828538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclerc, B.G.; Charlebois, R.; Chouinard, G.; Allard, B.; Pommey, S.; Saad, F.; Stagg, J. CD73 Expression Is an Independent Prognostic Factor in Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Patiño, A.; Castro, C.D.; Ricaurte, L.M.; Cardona, A.F.; Rojas, L.; Zatarain-Barrón, Z.L.; Wills, B.; Reguart, N.; Carranza, H.; Vargas, C.; et al. EGFR Amplification and Sensitizing Mutations Correlate with Survival in Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients Treated with Erlotinib (MutP-CLICaP). Target. Oncol. 2018, 13, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, H.; He, J. EGFR Gene Copy Number as a Predictive/Biomarker for Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Receiving Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Investig. Med. 2017, 65, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casorzo, L.; Corigliano, M.; Ferrero, P.; Venesio, T.; Risio, M. Evaluation of 7q31 Region Improves the Accuracy of EGFR FISH Assay in Non Small Cell Lung Cancer. Diagn. Pathol. 2009, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacic, S.; Flanagan, M.; Cieply, K.; Ramalingam, S.; Luketich, J.; Belani, C.; Yousem, S.A. Significance of EGFR Protein Expression and Gene Amplification in Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2006, 125, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.F.; Li, J.; Zhao, H.B.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.J. Correlation of EGFR Gene Amplification with Invasion and Metastasis of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 11006–11012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wei, X.-W.; Zheng, M.-Y.; Chen, Z.-H.; Zhang, X.-C.; Zhong, W.-Z.; Yang, J.-J.; Wu, Y.-L.; Zhou, Q. Impact of EGFR Amplification on Survival of Patients with EGFR Exon 20 Insertion-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 5822–5832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, L.; Wang, Z.; Guo, L.; Sun, H.; Qiu, T.; Ling, Y.; Li, W.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Zheng, B.; et al. Concurrence of EGFR Amplification and Sensitizing Mutations Indicate a Better Survival Benefit from EGFR-TKI Therapy in Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients. Lung Cancer 2015, 89, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuoka, M.; Wu, Y.-L.; Thongprasert, S.; Sunpaweravong, P.; Leong, S.-S.; Sriuranpong, V.; Chao, T.-Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Chu, D.-T.; Saijo, N.; et al. Biomarker Analyses and Final Overall Survival Results from a Phase III, Randomized, Open-Label, First-Line Study of Gefitinib versus Carboplatin/Paclitaxel in Clinically Selected Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in Asia (IPASS). J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 2866–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiala, O.; Pesek, M.; Finek, J.; Minarik, M.; Benesova, L.; Sorejs, O.; Svaton, M.; Bortlicek, Z.; Kucera, R.; Topolcan, O. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Gene Amplification in Patients with Advanced-Stage NSCLC. Anticancer. Res. 2016, 36, 455–460. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, K.; Altorki, N.K.; Eberhardt, W.E.E.; O’Brien, M.E.R.; Spigel, D.R.; Crinò, L.; Tsai, C.-M.; Kim, J.-H.; Cho, E.K.; Hoffman, P.C.; et al. Adjuvant Erlotinib Versus Placebo in Patients with Stage IB-IIIA Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (RADIANT): A Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 4007–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The Biology, Function, and Biomedical Applications of Exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrugo-Ramírez, J.; Mir, M.; Samitier, J. Blood-Based Cancer Biomarkers in Liquid Biopsy: A Promising Non-Invasive Alternative to Tissue Biopsy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turiello, R.; Capone, M.; Morretta, E.; Monti, M.C.; Madonna, G.; Azzaro, R.; Gaudio, P.D.; Simeone, E.; Sorrentino, A.; Ascierto, P.A.; et al. Exosomal CD73 from Serum of Patients with Melanoma Suppresses Lymphocyte Functions and Is Associated with Therapy Resistance to Anti-PD-1 Agents. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e004043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardani, C.F.F.; Cappellari, A.R.; de Souza, J.B.; da Silva, B.T.; Engroff, P.; Moritz, C.E.J.; Scholl, J.N.; Battastini, A.M.O.; Figueiró, F.; Morrone, F.B. Hydrolysis of ATP, ADP, and AMP Is Increased in Blood Plasma of Prostate Cancer Patients. Purinergic Signal. 2019, 15, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| CD73TC Expression and Correlation with | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| References | Type of Study | No. of Cases | Sample | Stage | Histological Subtype | No. of EGFR Mutant | Treatment History | IHC (Clone and Dilution) | Interpretation | Cut-Off | Histological Pattern | Patients Characteristics | EGFRm | TMB | PDL1 | Survival | Response to ICI |
| Inoue, 2017 [55] | retrospective | 642 | FFPE (TMA) | I-III | SCC; LUAD; others | 119 (protein expression) | before or after chemo | D7F9A 1:200 | H-score | low < 162 < high | Yes (LUAD; TTF-1; ALK) | Yes (female; never smoked) | Yes (based on EGFR protein expression) | _ | _ | Yes (whole cohort; shorter OS and RFS) | _ |
| Isomoto, 2020 [52] | retrospective | 70 | FFPE | Advanced | LUAD | 70 | before and after TKI | D7F9A | H-score TILs | _ | _ | _ | _ | Yes (High PD-L1, after TKI) | _ | _ | |
| Giatromanolaki, 2020 [58] | retrospective | 98 | FFPE | I-III | SCC; LUAD; others | _ | treatment-naive | EPR6114 1:200 | TPS CAF (% stained stroma area) | 5% < low < 40% 50% < medium < 70% 80% < high < 100% | Yes Inverse correlation between CD73TC and CAF Less CD73SC expression in stage I | No | _ | _ | No | No | _ |
| Ishii, 2020 [53] | retrospective | 91 | FFPE | Advanced | NSCLC | 25 | after TKI | D7F9A | TPS | ≥50% | _ | No | No | _ | Yes (high PD-L1) | Yes (longer PFS, OS) | Yes (better ORR in EGFRm) |
| Ramdani, 2021 [59] | retrospective | 48 | FFPE | Advanced | SCC; LUAD; others | 3 | treatment-naive | 1D7 | no or heavy staining for TC and IC | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | No | No |
| Rocha, 2021 [57] | retrospective | 106 | FFPE (TMA) | I–III | LUAD | 15 | treatment-naive | D7F9A 1:200 | TPS luminal; basolateral and total stain | T negative ≤ 1%; 1% > T low < 55%; T high ≥ 55% | Yes (solid) | Yes (smoking; sex) | No | Yes | Yes (high PD-L1) | No | _ |
| Tu, 2022 [54] | retrospective | 231 | FFPE | _ | NSCLC | 99 | _ | EPR6115 | TPS luminal or complete stain | _ | _ | _ | Yes | _ | _ | _ | _ |
| Herbst, 2022 [34] | prospective | 107 | FFPE | III | NSCLC | _ | treatment-naive | D7F9A 1:200 | TPS | low < 10 ≤ high | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | No | No |
| Bendell, 2023 [63] | retrospective | 126 | FFPE | Advanced | LUAD; PDAC, CRC | 42 | after treatment | EPR6115 | TPS | >10% | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ |
| Kim, 2023 [56] | retrospective | 26 paired tumour | FFPE | _ | LUAD | 26 | before and after TKI 1st generation | D7F9A 1:100 | H-score | low < 60 ≤ high | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | Yes (shorter PFS with 1st generation TKI) | _ |
| Haratani, 2023 [60] | prospective | 135 | FFPE | III | NSCLC | 13 | treatment naive | D7F9A 1:200 | H-score IC | low < 70 < high | Yes (NS-NSCLC) | _ | No | _ | _ | shorter PFS (with ICI) | _ |
| Variable (n = 76 Unless Stated Otherwise) | Type | Whole Cohort, n (%) Unless Stated Otherwise |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical and follow-up data | ||
| Age at diagnosis | Median [IQR] | 67 [62–73] |
| Sex | Female | 52 (68) |
| Male | 24 (32) | |
| Follow-up | Median [IQR] | 29 [14–63] |
| Smoking status | Former smoker | 10 (13) |
| Smoker | 19 (25) | |
| Non-smoker | 43 (65) | |
| Stage category | Advanced | 42 (55) |
| Early | 34 (45) | |
| Brain metastasis (n = 53) | Yes | 15 (28) |
| No | 38 (72) | |
| Treatment type (n = 59) | Including TKI | 44 (75) |
| Including immunotherapy | 4 (7) | |
| Chemotherapy alone | 11 (19) | |
| Radiotherapy alone | 3 (5) | |
| Number of treatments (n = 76) | Mean (sd) | 1 (1) |
| Median [IQR] | 1 [0–2] | |
| Status at end of follow-up (n = 49) | Dead | 23 (47) |
| Alive | 26 (53) | |
| Pathological data | ||
| Type of sample | Biopsy | 36 (47) |
| Cytology | 1 (2) | |
| Surgical specimen | 39 (51) | |
| Origin of samples | Metastasis | 23 (30) |
| Primitive | 53 (70) | |
| High-grade component (n = 71) | No | 42 (60) |
| Yes | 29 (41) | |
| Type of high-grade component (n = 23) | Cribriform | 7 (31) |
| Micropapillary | 4 (17) | |
| Solid | 12 (52) | |
| Necrosis (n = 47) | No | 32 (68) |
| Yes | 15 (32) | |
| Emboli (n = 59) | No | 17 (29) |
| Yes | 42 (71) | |
| Mitosis (n = 45) | No | 5 (11) |
| Yes | 40 (89) | |
| Immunohistochemistry data | ||
| TTF1 expression on tumour cells | Negative | 1 (1) |
| Positive | 75 (99) | |
| Percentage of PD-L1 expression on tumour cells (n = 73) | Mean (sd) | 11 (28) |
| Median [IQR] | 0 [0–5] | |
| PD-L1 expression category (n = 73) | Negative (<1%) | 56 (77) |
| Moderate (1–49%) | 7 (9) | |
| High (≥50%) | 10 (14) | |
| CD73 tumour expression (n = 76) | Negative | 26 (34) |
| Positive | 50 (66) | |
| Type of CD73 staining (n = 50) | Apical–lateral | 5 (7) |
| (co-existing within same tumour) | Complete | 24 (48) |
| Luminal | 44 (88) | |
| Dot intracytoplasmic | 8 (16) | |
| Percentage of CD73 tumour staining (n = 76) | Mean (sd) | 27 (31) |
| Median [IQR] | 10 [0-51] | |
| Percentage of CD73 tumour expression 1+ (n = 76) | Mean (sd) | 5 (10) |
| Median [IQR] | 0 [0–5] | |
| Percentage of CD73 tumour expression 2+ (n = 76) | Mean (sd) | 22 (28) |
| Median [IQR] | 10 [0–40] | |
| Percentage of CD73 tumour expression 3+ (n = 76) | Mean (sd) | 33 (59) |
| Median [IQR] | 0 [0–53] | |
| CD73 H-score (n = 76) | High | 11 (14) |
| Low | 65 (86) | |
| CD73 TPS (n = 76) | High | 12 (16) |
| Low | 64 (84) | |
| CD73 expression on lymphocytes (n = 76) | Negative | 69 (91) |
| Positive | 7 (9) | |
| CD73 expression on macrophages (n = 76) | Negative | 71 (93) |
| Positive | 5 (7) | |
| CD73 expression on CAFs (n = 73) | Negative | 71 (97) |
| Positive | 2 (3) | |
| Molecular data | ||
| EGFR mutation at baseline | Ex18_G719 | 3 (4) |
| Ex20_S768I | 2 (3) | |
| L858R | 28 (37) | |
| del19 | 43 (56) | |
| T790M during follow-up (n = 21) | No | 11 (52) |
| Yes | 10 (48) |
| Variable (n = 76, Unless Stated Otherwise) | Type | CD73SC Negative, n (%) | CD73SC Positive, n (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| STAGE | Advanced | 38 (61) | 4 (29) | 0.0372 |
| Early | 24 (39) | 10 (71) | ||
| EGFR mutation at baseline | Ex18_G719 | 2 (3) | 1 (7) | 0.0670 |
| Ex20_S768I | 2 (3) | 0 (0) | ||
| L858R | 19 (31) | 9 (64) | ||
| Del19 | 39 (63) | 4 (29) | ||
| PD-L1 expression (n = 73) | Moderate/high | 17 (29) | 0 (0) | 0.0303 |
| Negative | 42 (71) | 14 (100) | ||
| PDL1 category | High | 10 (16.95) | 0 (0) | 0.0710 |
| Moderate | 7 (11.86) | 0 (0) | ||
| Negative | 42 (71.19) | 14 (100) | ||
| EGFR amplification (n = 71) | Amplified | 44 (75) | 3 (25) | 0.0018 |
| Not amplified | 15 (25) | 9 (75) |
| Variable | No. of Patients with Data | Median Survival, Month | HR (95%CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 2.5 (1.4–4.4) | 0.019 | ||
| Male | 51 | 12 | ||
| Female | 22 | 30 | ||
| Stage | 5.4 (3.0–9.9) | <0.001 | ||
| Advanced | 36 | 14 | ||
| Early | 33 | 76 | ||
| High-grade component | 2.6 (1.5–4.7) | 0.016 | ||
| Yes | 29 | 18 | ||
| No | 38 | 47 | ||
| PD-L1 expression | 2.5 (1.2–4.9) | 0.025 | ||
| High | 10 | 11 | ||
| Negative/moderate | 58 | 27 | ||
| CD73 TPS | 2.2 (1.0–4.9) | 0.045 | ||
| Low | 52 | 24 | ||
| High | 8 | Not Reached | ||
| CD73 H-score | 2.0 (0.9–4.7) | 0.092 | ||
| Low | 53 | 24 | ||
| High | 7 | Not Reached | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Long-Mira, E.; Bontoux, C.; Rignol, G.; Hofman, V.; Lassalle, S.; Benzaquen, J.; Boutros, J.; Lalvée-Moret, S.; Zahaf, K.; Lespinet-Fabre, V.; et al. Exploring the Expression of CD73 in Lung Adenocarcinoma with EGFR Genomic Alterations. Cancers 2025, 17, 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17061034
Long-Mira E, Bontoux C, Rignol G, Hofman V, Lassalle S, Benzaquen J, Boutros J, Lalvée-Moret S, Zahaf K, Lespinet-Fabre V, et al. Exploring the Expression of CD73 in Lung Adenocarcinoma with EGFR Genomic Alterations. Cancers. 2025; 17(6):1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17061034
Chicago/Turabian StyleLong-Mira, Elodie, Christophe Bontoux, Guylène Rignol, Véronique Hofman, Sandra Lassalle, Jonathan Benzaquen, Jacques Boutros, Salomé Lalvée-Moret, Katia Zahaf, Virginie Lespinet-Fabre, and et al. 2025. "Exploring the Expression of CD73 in Lung Adenocarcinoma with EGFR Genomic Alterations" Cancers 17, no. 6: 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17061034
APA StyleLong-Mira, E., Bontoux, C., Rignol, G., Hofman, V., Lassalle, S., Benzaquen, J., Boutros, J., Lalvée-Moret, S., Zahaf, K., Lespinet-Fabre, V., Bordone, O., Maistre, S., Bonnetaud, C., Cohen, C., Berthet, J.-P., Marquette, C.-H., Vouret-Craviari, V., Ilié, M., & Hofman, P. (2025). Exploring the Expression of CD73 in Lung Adenocarcinoma with EGFR Genomic Alterations. Cancers, 17(6), 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17061034








