Simple Summary
Breast cancer accounts for 1 in 6 cancer deaths worldwide. It is also the most commonly diagnosed cancer among women worldwide. Metastasis is the main cause of death in breast cancer; the 5-year survival rate of patients with metastatic breast cancer (MBC) is still less than 30%. The aim of our study was to present current clinical trials in treatment of metastatic and advanced breast cancer. To identify those studies, a search was performed in the clinicaltrials.gov database. Further studies, particularly interventional and randomized trials, are needed to determine the effectiveness and safety of innovative therapies patients with advanced and metastatic breast cancer.
Abstract
Globally, breast cancer is both the most common cancer and the most common cause of death related to cancer among women. It is estimated that over 2 million women were diagnosed with breast cancer in 2022 worldwide, while almost 400,000 were diagnosed in the EU. Breast cancer has different histopathological subtypes that require different therapeutic approaches. Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is a type that is considered more aggressive; it occurs in about 10 to 20% of all breast cancer cases. Approximately 40% of women initially diagnosed with TNBC will develop metastases. The objective of this study is to present current clinical trials focused on new treatment of advanced and metastatic TNBC. The study was conducted by searching the clinicaltrials.gov database. Due to the scope of this paper, primary endpoints in the included studies were objective response rate, treatment-emergent adverse events or serious adverse events, progression-free survival, and probability of pathologic complete response. Some of the selected studies were phase I or II RCTs; therefore, we should carefully examine their future results and implications for clinical guidelines.
1. Introduction
Globally, breast cancer is both the most common cancer and the most common cause of death related to cancer among women. According to the WHO data, more than 2 million women have been diagnosed with breast cancer (BC) and almost 700,000 deaths have been reported in 2022 [1]. The incidence rate in Europe in the same year was 34.8 per 100,000 women. The highest mortality rates were recorded in Cyprus (45.1 per 100,000 women), followed by Slovakia (44.9 per 100,000 women). In turn, the lowest mortality rate was recorded in Spain (23.3 per 100,000 women) [2]. In Poland, according to data from the National Cancer Registry, the crude death rate for women was 32.64 in 2021 [3]. Although breast cancer mainly affects women, it can also occur in men [4,5].
There are several subtypes of breast cancer: luminal A, luminal B, HER2-positive, and triple-negative (TNBC) [6,7]. Differences underlying gene expression patterns between cancer subtypes reflect fundamental differences between cancers at the molecular level [7,8]. Research suggests that breast cancers with different biological characteristics have different activities that result in different responses to treatment. Considering therapeutic decision-making, it is important to appropriately group breast cancer into clinically relevant subtypes. Luminal tumors show expression of hormone receptors [9]. Luminal A breast cancer is diagnosed in 50–60% of all breast cancer cases. Compared to the other subtypes, it is less aggressive and more susceptible to treatment. Luminal B subtype is much less common and is estimated to account for approximately 10% of breast cancer cases [10]. This subtype rarely shows expression of the HER2 protein, which can accelerate the growth of cancer cells [11]. As a result, luminal B cancer is usually more aggressive and has a higher stage of advancement and worse prognosis than luminal A cancer [12,13,14].
Tumors with overexpression of human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2) constitute approximately 20% of all breast cancer cases [15]. They are identified by immunostaining or fluorescence in-situ hybridization (FISH). Tumors with HER2 overexpression are most often grade III, but the prognosis in this subtype has improved after the introduction of anti-HER2 therapy because these tumors are sensitive to neoadjuvant chemotherapy based on anthracyclines and taxanes.
In triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), there is no expression of estrogen (ER), progesterone (PR), and HER2 receptors. TNBC is considered an aggressive subtype; it is estimated that 5-year survival varies from 4% to 20% [16]. There is currently no standard targeted therapy for this subtype. Standard treatments include surgery and prior neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy [16].
Factors such as younger age at first pregnancy and having several children have a protective effect in the luminal A subtype, while in the case of triple-negative cancer they increase the risk of the disease [17]. This subtype is associated with lower survival and an increased risk of relapse, and is additionally characterized by faster growth and metastases, most often to the brain, lungs, and liver [18]. Patients with TNBC have a significantly shorter survival period, having experienced distant metastases, and the disease is most often detected at an advanced stage. TNBC, more often than other subtypes, is associated with hereditary factors [19]. It is estimated that 35% of TNBC patients are carriers of BRCA1 gene mutations and 8% of patients are carriers of BRCA2 mutations [19].
The most dangerous feature of cancer is the spread of cancer to distant organs (metastases). Metastatic breast cancer (MBC) begins in the breast and spreads to nearby lymph nodes as well as other more distant sites in the body [20]. Of all breast cancer patients, up to 15% develop aggressive disease, leading to the spread of the cancer to other organs within 3 years of the development of the primary tumor. The mechanism of metastatic formation is complicated. It involves numerous cellular processes, such as tumor division, invasion, avoidance of immune surveillance, and regulation of the tissue environment [21]. It was found that after metastasis, breast cancer cells are less sensitive to chemotherapy, and in patients with stage IV breast cancer, the 5-year survival rate ranges from several to several dozen percent [22,23]. Depending on the subtype of breast cancer, the prognosis, occurrence and types of metastases, and overall survival vary [24].
Metastases may be a target for treatment or an indicator of disease progression. Targeted therapies include drugs for which the mechanism of action is based on, among other things, interfering with the proliferation and survival of cancer cells [25]. Targeted treatment for MBC is selected based on several factors i.e., presence hormone receptors, HER-2, cancer recurrence, and the presence and location of metastasis [26]. Current treatment strategies for metastatic breast cancer include systemic therapy (i.e., hormone therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy) and local therapy. The choice of first-line treatment for metastatic cancer is based on tumor-related factors (e.g., tumor subtype) and a number of disease-related factors (e.g., disease-free period, location of recurrence, prior treatment), as well as patient-related factors (e.g., overall physical condition or comorbidities) [26]. According to ESMO recommendations, therapeutic decisions should not be made based on the patient’s age; a multidisciplinary approach is recommended, considering comorbidities and patient’s preferences [26]. MBC is an incurable disease, but implementing appropriate therapeutic strategies can prolong survival. In most cases of TNBC, chemotherapy is recommended as standard treatment. From the perspective of treatment effectiveness, it is important to determine the PD-L1 (Programmed Death Ligand 1) status and mutations within BCRA1/2 [26].
In operable TNBC tumors, the first line of treatment includes surgery followed by adjuvant chemotherapy
The objective of this study is to present currently ongoing clinical trials on possible methods of treating advanced and metastatic triple negative breast cancer.
2. Materials and Methods
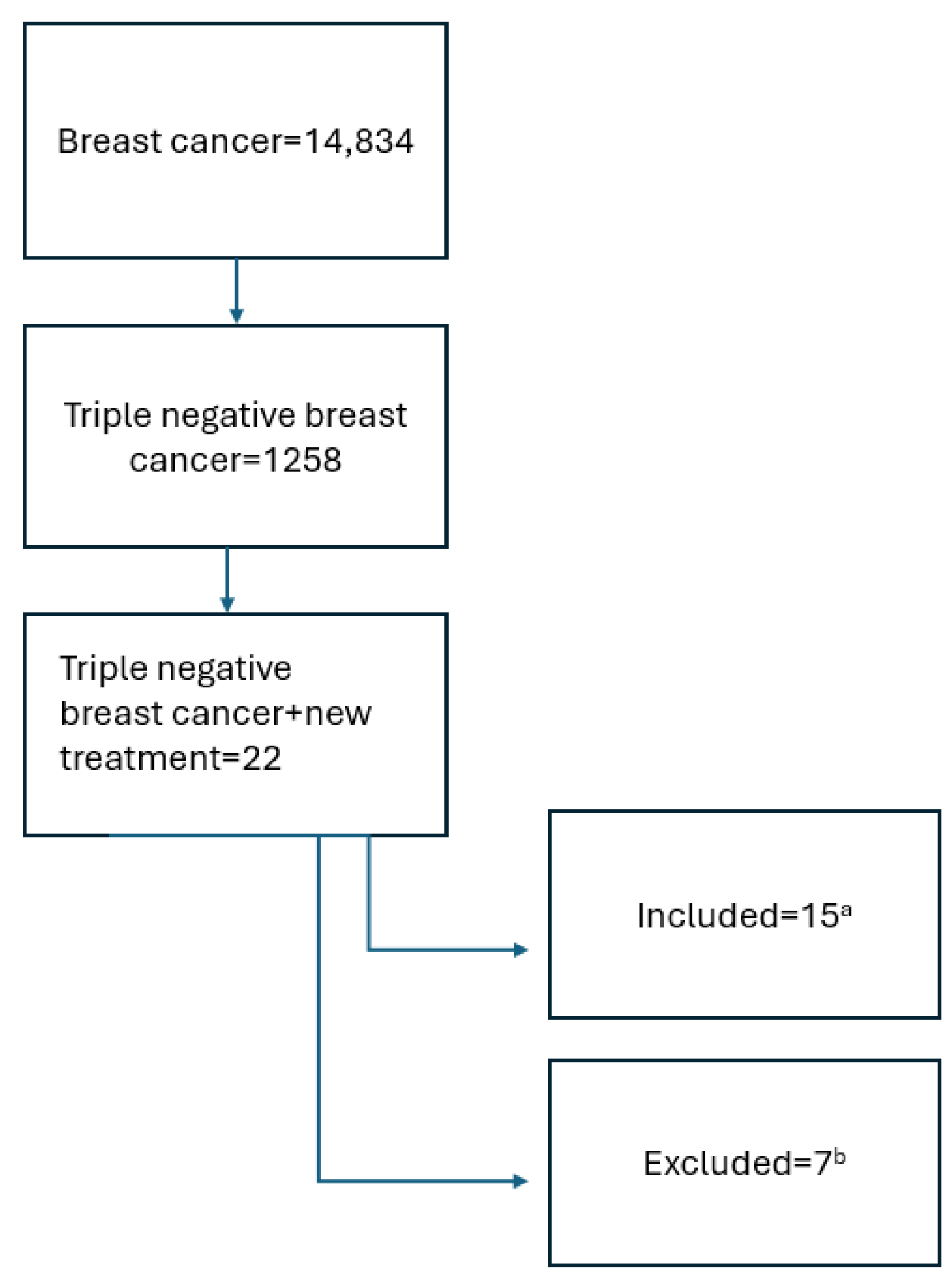
This publication was based on a search in the: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/search?cond=Triple%20Negative%20Breast%20Cancer&intr=new%20treatment&page=1&limit=50 (accessed on 30 January 2025). The keywords “breast cancer”, “triple negative breast cancer”, “treatment”, and “new treatment” were used. Inclusion criteria included active studies recruiting, active, not recruiting, or completed according to the protocol. Studies that were terminated were excluded. Interventional and observational studies that started in the period from 1 January 2019 to 1 January 2025 were included. The process of qualifying studies for analysis is presented in Figure 1 below.
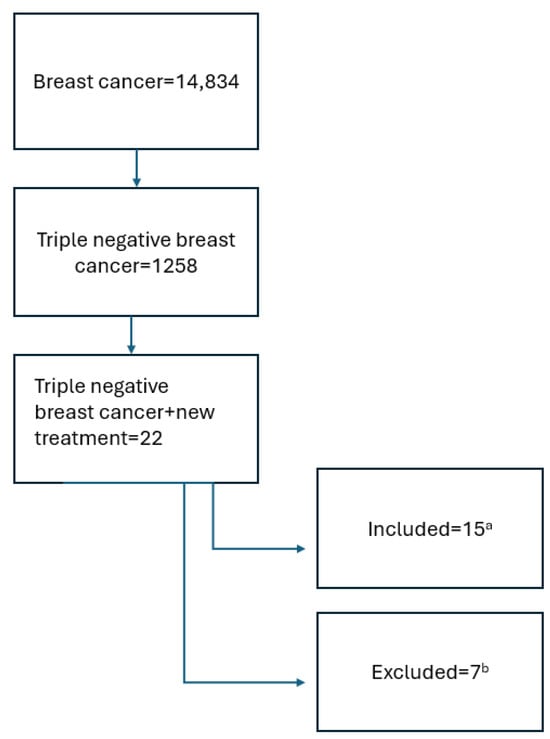
Figure 1.
Search scheme. a the review included studies actively ongoing, recruiting, or completed according to the protocol, with available results. b terminated studies, observational, and interventional studies where inclusion criteria did not directly concern patients with advanced and metastatic TNBC or intervention did not include new therapies were excluded.
3. Results
Detailed search results are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Current studies for TNBC started from 1 January 2019 to 1 January 2025.
In total, fifteen studies were included in the analysis; fourteen were interventional studies and one was observational. The size of the study population varied and ranged from 9 to 5000 participants. The main endpoints included in our review were objective response rate, treatment-emergent adverse events or serious adverse events, progression-free survival, and probability of pathologic complete response. In the research of new treatment of advanced and metastatic TNBC, parameters such as objective response rate and progression-free survival are important.
The methods of treatment used in the studies presented in Table 1 can be divided into following groups: antibody-drug conjugate, PARP inhibitors, immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) in monotherapy and in combination with AKT inhibitors and chemotherapy, AKT inhibitors, PD-1 inhibitors, and oncolytic virus treatment. Standard treatment for TNBC includes neoadjuvant chemotherapy and surgery followed by adjuvant treatment based on the characteristics of tumor and patients’ status. Detailed treatment options and guidelines are also mentioned in Section 4.
4. Discussion
TNBC is the most difficult type of breast cancer to treat, therefore further research is required to develop new therapeutic solutions that will significantly improve the prognosis in this group of patients. The IMpassion130 study evaluated atezolizumab (an anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody) in combination with nab-paclitaxel, while the IMpassion131 study evaluated atezolizumab in combination with paclitaxel [42]. In the IM-passion130 study, defined primary endpoints included progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) [43]. In the intention-to-treat (ITT) patient group, atezolizumab provided a median PFS benefit of 7.2 months compared to 5.5 months in the placebo plus nab-paclitaxel group (HR = 0.8, 0.95% CI 0.69–0.92; p = 0.002). In the PD-L1 positive group, the median PFS was 7.5 months with atezolizumab compared to 5 months in the placebo plus nab-paclitaxel group (HR = 0.62, 95% CI 0.49–0.78; p < 0.001). Atezolizumab was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic PD-L1-positive TNBC. Meanwhile, in the IMpassion131 study, in the primary PFS analysis, the addition of atezolizumab to paclitaxel did not show improvement in PFS in the PD-L1-positive population (HR = 0.82, 95%, CI 0.60–1.12; p = 0.20; median PFS was 6 months in the atezolizumab-paclitaxel group compared with 5.7 months in the placebo-paclitaxel group). Despite the unsatisfactory results of the IMpassion131 study, some patients benefited from atezolizumab/paclitaxel combination therapy [43]. It should be mentioned that the manufacturer of atezolizumab has withdrawn the indication for the use of atezolizumab plus chemotherapy in the treatment of adult patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic TNBC in the USA following an extended analysis carried out by the FDA [44].
In the KEYNOTE-355 trial, the addition of pembrolizumab to platinum-based chemotherapy in patients with advanced TNBC who had PD-L1 expression and combined positive score (CPS) was assessed. Patients were divided into groups based on their CPS score [45]. In patients with CPS of 10 or more the median OS was 23 months in the pembrolizumab–chemotherapy group and 16.1 months in the placebo–chemotherapy group (HR for death, 0.73; 95% CI 0.55 to 0.95; two-sided p = 0.0185). In the group of patients with CPS of 1 or more, the median OS was 17.6 and 16.0 months in the two groups, respectively (HR 0.86; 95% CI, 0.72 to 1.04; two-sided p = 0.1125). In 2020, the FDA granted accelerated approval to pembrolizumab combined with chemotherapy for the treatment of patients with metastatic or locally unresectable TNBC whose tumor has PD-L1 expression [46].
Durvalumab, a PD-L1 inhibitor, has shown promising results in the treatment of bladder and lung cancers [47,48]. BEGONIA phase I/II trial showed promising results in treatment with datopotamab deruxtecan plus durvalumab in patients with unresectable or metastatic TNBC. Preliminary results showed a manageable safety profile and lasting response rates [49].
The CREATE-X study presented the effectiveness of adjuvant capecitabine in patients with residual disease after standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy. The ipatasertib study showed promising results. It was noticed that continuous administration of ipatasertib in combination with chemotherapy had a good safety profile and good tolerance [50].
The randomized phase III EMBRACA study compared the safety and effectiveness of talazoparib with chemotherapy in patients with locally advanced and/or metastatic breast cancer, HER-2 negative, with BRCA1/2 mutations. The study showed that talazoparib had better results in terms of PFS compared to standard chemotherapy. Based on those results, talazoparib was approved by the FDA [51].
Based on data from the Cancer Genome Atlas, it was shown that the most frequently altered genomic factors in TNBC include the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-AKT-mTOR signaling pathway [52]. Ipatasertib is a selective, small molecule, ATP-competitive AKT inhibitor that preferentially targets active phosphorylated Akt (pAkt) and is potent in cell lines that have demonstrated Akt activation. In the LOTUS study, the combination of paclitaxel and ipatasertib showed a moderate improvement in PFS in patients with TNBC [53].
Currently, according to the guidelines for patients with TNBC, chemotherapy is recommended as standard treatment [26]. In the case of positive PD-L1, therapy with pembrolizumab in combination with chemotherapy is recommended. In the event of a BRCA1/2 mutation, platinum-based chemotherapy (if it has not been used before) or targeted therapy based on PARP inhibitors is recommended [54].
In the study by Li et al., the analysis was carried out on the data of nearly 160,000 patients who were diagnosed with breast cancer between 2010 and 2012 [55]. The study focused on comparison of OS and cause-specific survival for patients with TNBC and non-TNBC cancer. Patients with TNBC had worse overall survival and cause-specific survival at each stage and substage in univariate and multivariate analyses adjusting for age, race, tumor stage, and surgical and radiotherapy treatment in comparison with non-TNBC patients. A study by Lindman et al. investigated long-term treatment patterns as well as OS in a cohort of patients with MBC stratified by subtype in standard clinical practice and the correlation with current treatment guidelines [56]. Patients with TNBC had the lowest 5-year survival rate of 7% compared to the HER2+/luminal subtype, which was 46% and 29% in the luminal B subtype, respectively. This indicates the need to search for new therapies that will improve prognosis and OS in the group of patients with TNBC.
The ability of cancer cells to evade the immune system has been a significant difficulty in cancer treatment. Oncolytic viruses show promising results in that area; however, according to preliminary reports, viral therapy should be combined with other treatment methods such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapies. The study No. 9 presented in Table 1 will determine safety, dosage, and objective response rate for a novel chimeric orthopoxvirus in monotherapy or in combination with pembrolizumab in patients with metastatic or advanced solid tumors [35,57].
5. Conclusions
Currently, there is ongoing research to develop therapies that might have a positive impact on OS and PFS in patients with advanced TNBC. Patients with this subtype have a much shorter OS, have experienced distant metastases, the disease is most often diagnosed at an advanced stage, and remains incurable. Some novel therapies show promising results, such as durvalumab or oncolytic virus treatment. Oncolytic virus therapies might become an effective therapy in this type of cancer. Since some of the selected studies were phase I or II RCTs, we should carefully examine their future results and implications for clinical guidelines in TNBC.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, M.P., O.P., A.C. and A.D.; methodology, A.C. and A.D.; validation, K.M. and K.S.; formal analysis, E.B.; investigation, A.S. and S.P.; data curation, U.G.-B., and W.C.; writing—original draft preparation, M.P., O.P., S.G., T.B., A.M.C., I.G. and N.C.; writing—review and editing, A.D., E.G., D.S.-M. and J.D.; visualisation, J.F.-P. and P.P.; supervision, A.D., M.M. and R.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created during preparation of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Piotr Pobrotyn was employed by the company Pulsantis Specialist and Rehabilitation Clinic Ltd. Author Joanna Furtak-Pobrotyn was employed by the company Limited Partnership. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/breast-cancer (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1452371/breast-cancer-mortality-rate-for-women-in-europe-by-country/ (accessed on 2 June 2024).
- Available online: https://onkologia.org.pl/pl/raporty/ (accessed on 2 June 2024).
- Winters, S.; Martin, C.; Murphy, D.; Shokar, N.K. Chapter One—Breast Cancer Epidemiology, Prevention, and Screening. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2017, 151, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, H.; Verkooijen, H.M.; Chia, K.S. Incidence and outcome of male breast cancer: An international population-based study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 4381–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makki, J. Diversity of Breast Carcinoma: Histological Subtypes and Clinical Relevance. Clin. Med. Insights Pathol. 2015, 8, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blows, F.M.; Driver, K.E.; Schmidt, M.K.; Broeks, A.; van Leeuwen, F.E.; Wesseling, J.; Cheang, M.C.; Gelmon, K.; Nielsen, T.O.; Blomqvist, C.; et al. Subtyping of breast cancer by immunohistochemistry to investigate a relationship between subtype and short and long term survival: A collaborative analysis of data for 10,159 cases from 12 studies. PLoS Med. 2010, 7, e1000279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, G.K.; Zhao, X.; Band, H.; Band, V. Histological, molecular and functional subtypes of breast cancers. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2010, 10, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.J.; Swain, S.M. Luminal A Breast Cancer and Molecular Assays: A Review. Oncologist 2018, 23, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikarmane, S.; Tirumani, S.; Howard, S.; Jagannathan, J.; DiPiro, P. Metastatic patterns of breast cancer subtypes: What radiologists should know in the era of personalized cancer medicine. Clin. Radiol. 2015, 70, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loibl, S.; Gianni, L. HER2-positive breast cancer. Lancet 2017, 389, 2415–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höller, A.; Nguyen-Sträuli, B.D.; Frauchiger-Heuer, H.; Ring, A. Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers of Luminal Breast Cancer: Where are We Now? Breast Cancer Targets Ther. 2023, 15, 525–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirman, Y.; Lubovsky, S.; Shai, A. HER2-Low Breast Cancer: Current Landscape and Future Prospects. Breast Cancer Targets Ther. 2023, 15, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obidiro, O.; Battogtokh, G.; Akala, E.O. Triple Negative Breast Cancer Treatment Options and Limitations: Future Outlook. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehanna, J.; Haddad, F.G.; Eid, R.; Lambertini, M.; Kourie, H.R. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Current Perspective on the Evolving Therapeutic Landscape. Int. J. Womens Health 2019, 11, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łukasiewicz, S.; Czeczelewski, M.; Forma, A.; Baj, J.; Sitarz, R.; Stanisławek, A. Breast Cancer-Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Classification, Prognostic Markers, and Current Treatment Strategies—An Updated Review. Cancers 2021, 13, 4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, M.E.; Boeke, C.E.; Tamimi, R.M. Established breast cancer risk factors and risk of intrinsic tumor subtypes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1856, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, F.M.; Olopade, O.I. Epidemiology of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Review. Cancer J. 2021, 27, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, H.L.; Ellsworth, D.L.; Shriver, C.D.; Ellsworth, R.E. Breast cancer metastasis to the axillary lymph nodes: Are changes to the lymph node “soil” localized or systemic? Breast Cancer 2017, 11, 1178223417691246. [Google Scholar]
- Park, M.; Kim, D.; Ko, S.; Kim, A.; Mo, K.; Yoon, H. Breast Cancer Metastasis: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valachis, A.; Carlqvist, P.; Ma, Y.; Szilcz, M.; Freilich, J.; Vertuani, S.; Holm, B.; Lindman, H. Overall survival of patients with metastatic breast cancer in Sweden: A nationwide study. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 127, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, C.; Shao, W.; Liu, X.; Sun, L.; Yu, Z. Survival analysis and prognosis of patients with breast cancer with pleural metastasis. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1104246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- InformedHealth. Metastatic Breast Cancer: Learn More—Treatment Options and Supportive Care. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK361017/ (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Cheng, Y.C.; Ueno, N.T. Improvement of survival and prospect of cure in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer 2012, 19, 191–199. [Google Scholar]
- Bonotto, M.; Gerratana, L.; Poletto, E.; Driol, P.; Giangreco, M.; Russo, S.; Minisini, A.M.; Andreetta, C.; Mansutti, M.; Pisa, F.E.; et al. Measures of outcome in metastatic breast cancer: Insights from a real-world scenario. Oncologist 2014, 19, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gennari, A.; André, F.; Barrios, C.; Cortés, J.; de Azambuja, E.; DeMichele, A.; Dent, R.; Fenlon, D.; Gligorov, J.; Hurvitz, S.; et al. ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for the diagnosis, staging and treatment of patients with metastatic breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1475–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06508216 (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06404736?titles=QUEEN-Dream&rank=1 (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06371274?titles=A%20Study%20on%20the%20Efficacy%20and%20Safety%20of%20Oral%20All-trans%20Retinoic%20Acid%20Combined%20With%20Toripalimab%20in%20TNBC&rank=1 (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06249048 (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06240195?titles=(BIO-PROSA)&rank=1 (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06134375?titles=A%20Study%20of%20Tetrathiomolybdate%20(TM)%20Plus%20Capecitabine&rank=1 (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05810870?titles=SABINA&rank=2 (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05485766?titles=novel%20Adjuvant%20Strategy%20for%20Germline%20BRCA%201%2F2%20Mutated%20Triple%20Negative%20Breast%20Cancer&rank=1 (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05346484 (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04683679 (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03891953 (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03742102?titles=BEGONIA&rank=1 (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03251378 (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03170960 (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01042379 (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Schmid, P.; Adams, S.; Rugo, H.S.; Schneeweiss, A.; Barrios, C.H.; Iwata, H.; Diéras, V.; Hegg, R.; Im, S.-A.; Shaw Wright, G.; et al. Atezolizumab and nab-paclitaxel in advanced triple-negative breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2108–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miles, D.; Gligorov, J.; André, F.; Cameron, D.; Schneeweiss, A.; Barrios, C.; Xu, B.; Wardley, A.; Kaen, D.; Andrade, L.; et al. Primary results from IMpassion131, a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised phase III trial of first-line paclitaxel with or without atezolizumab for unresectable locally advanced/metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.onclive.com/view/roche-withdraws-atezolizumab-pd-l1-positive-metastatic-tnbc-indication-in-the-united-states (accessed on 9 January 2025).
- Cortes, J.; Rugo, H.S.; Cescon, D.W.; Im, S.-A.; Yusof, M.M.; Gallardo, C.; Lipatov, O.; Barrios, C.H.; Perez-Garcia, J.; Iwata, H.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus Chemotherapy in Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-grants-accelerated-approval-pembrolizumab-locally-recurrent-unresectable-or-metastatic-triple (accessed on 17 March 2025).
- Powles, T.; O’Donnell, P.H.; Massard, C.; Arkenau, H.-T.; Friedlander, T.W.; Hoimes, C.J.; Lee, J.L.; Ong, M.; Sridhar, S.S.; Vogelzang, N.J.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Durvalumab in Locally Advanced or Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma: Updated Results from a Phase 1/2 Open-label Study. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, e172411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonia, S.J.; Villegas, A.; Daniel, D.; Vicente, D.; Murakami, S.; Hui, R.; Yokoi, T.; Chiappori, A.; Lee, K.H.; De Wit, M.; et al. Durvalumab after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, P.; Wysocki, P.; Ma, C.; Park, Y.; Fernandes, R.; Lord, S.; Baird, R.; Prady, C.; Jung, K.; Asselah, J.; et al. 379MO Datopotamab deruxtecan (Dato-DXd) + durvalumab (D) as first-line (1L) treatment for unresectable locally advanced/metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (a/mTNBC): Updated results from BEGONIA, a phase Ib/II study. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, N.; Lee, S.-J.; Ohtani, S.; Im, Y.-H.; Lee, E.-S.; Yokota, I.; Kuroi, K.; Im, S.-A.; Park, B.-W.; Kim, S.-B.; et al. Adjuvant capecitabine for breast cancer after preoperative chemotherapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2147–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litton, J.; Hurvitz, S.; Mina, L.; Rugo, H.; Lee, K.-H.; Gonçalves, A.; Diab, S.; Woodward, N.; Goodwin, A.; Yerushalmi, R.; et al. Talazoparib versus chemotherapy in patients with germline BRCA1/2-mutated HER2-negative advanced breast cancer: Final overall survival results from the EMBRACA trial. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1526–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, J.; Turner, N.C. Targeting the PI3-kinase pathway in triple-negative breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-B.; Dent, R.; Im, S.-A.; Espié, M.; Blau, S.; Tan, A.R.; Isakoff, S.J.; Oliveira, M.; Saura, C.; Wongchenko, M.J.; et al. LOTUS investigators. Ipatasertib plus paclitaxel versus placebo plus paclitaxel as first-line therapy for metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (LOTUS): A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1360–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortesi, L.; Rugo, H.S.; Jackisch, C. An Overview of PARP Inhibitors for the Treatment of Breast Cancer. Target Oncol. 2021, 16, 255–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, J.; Peng, L.; Sahin, A.A.; Huo, L.; Ward, K.C.; O’Regan, R.; Torres, M.A.; Meisel, J.L. Triple-negative breast cancer has worse overall survival and cause-specific survival than non-triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 161, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindman, H.; Wiklund, F.; Andersen, K.K. Long-term treatment patterns and survival in metastatic breast cancer by intrinsic subtypes—An observational cohort study in Sweden. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Luo, S.; Wen, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Du, L.; Zhang, P.; Tang, J.; Yang, D.; et al. Low-dose paclitaxel improves the therapeutic efficacy of recombinant adenovirus encoding CCL21 chemokine against murine cancer. Cancer Sci. 2014, 105, 1393–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).