Low WT1 Expression Identifies a Subset of Acute Myeloid Leukemia with a Distinct Genotype
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Population
2.2. WT1 Expression
2.3. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
2.4. CHIP and MR Mutation Detection
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Dealing with Missing Data
2.7. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Low-Level WT1 Is Associated with CHIP and MR Mutations
3.2. The Incidence of MR Mutations Is Higher than Expected in a Standard Population of AML
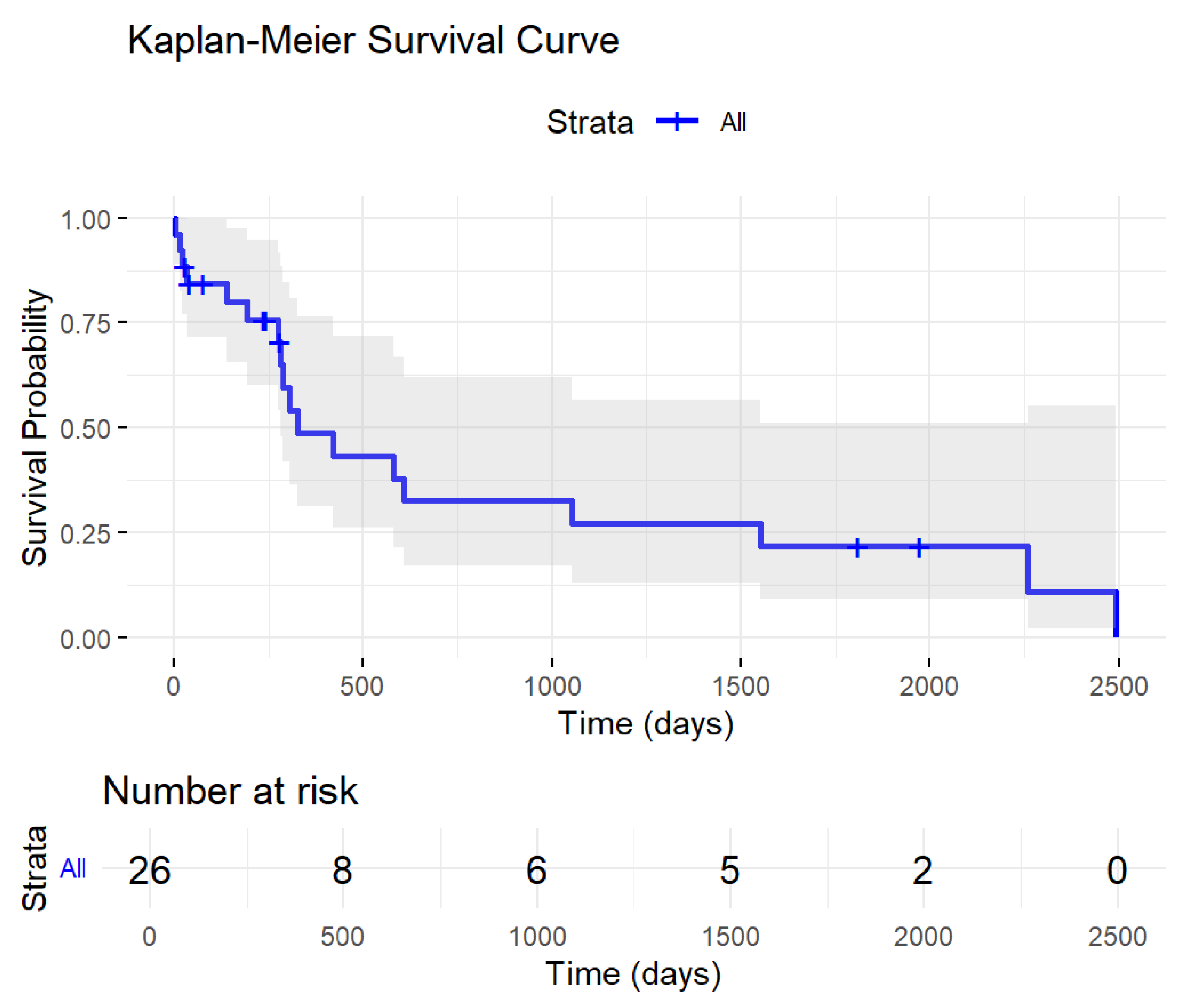
3.3. Low-Level WT1 Impacted Patients’ Prognosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DiNardo, C.D.; Erba, H.P.; Freeman, S.D.; Wei, A.H. Acute myeloid leukaemia. Lancet 2023, 401, 2073–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barragán, E.; Cervera, J.; Bolufer, P.; Ballester, S.; Martín, G.; Fernández, P.; Collado, R.; Sayas, M.J.; Sanz, M.A. Prognostic implications of Wilms’ tumor gene (WT1) expression in patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2004, 89, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lapillonne, H.; Renneville, A.; Auvrignon, A.; Flamant, C.; Blaise, A.; Perot, C.; Lai, J.L.; Ballerini, P.; Mazingue, F.; Fasola, S.; et al. High WT1 expression after induction therapy predicts high risk of relapse and death in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 1507–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hämäläinen, M.M.; Kairisto, V.; Juvonen, V.; Johansson, J.; Aurén, J.; Kohonen, K.; Remes, K.; Salmi, T.T.; Helenius, H.; Pelliniemi, T.T. Wilms tumour gene 1 overexpression in bone marrow as a marker for minimal residual disease in acute myeloid leukaemia. Eur. J. Haematol. 2008, 80, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzarotto, D.; Candoni, A. The Role of Wilms’ Tumor Gene (WT1) Expression as a Marker of Minimal Residual Disease in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilloni, D.; Messa, F.; Arruga, F.; Defilippi, I.; Gottardi, E.; Fava, M.; Carturan, S.; Catalano, R.; Bracco, E.; Messa, E.; et al. Early prediction of treatment outcome in acute myeloid leukemia by measurement of WT1 transcript levels in peripheral blood samples collected after chemotherapy. Haematologica 2008, 93, 921–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candoni, A.; Tiribelli, M.; Toffoletti, E.; Cilloni, D.; Chiarvesio, A.; Michelutti, A.; Simeone, E.; Pipan, C.; Saglio, G.; Fanin, R.; et al. Quantitative assessment of WT1 gene expression after allogeneic stem cell transplantation is a useful tool for monitoring minimal residual disease in acute myeloid leukemia. Eur. J. Haematol. 2009, 82, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilloni, D.; Renneville, A.; Hermitte, F.; Hills, R.K.; Daly, S.; Jovanovic, J.V.; Gottardi, E.; Fava, M.; Schnittger, S.; Weiss, T.; et al. Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction detection of minimal residual disease by standardized WT1 assay to enhance risk stratification in acute myeloid leukemia: A European LeukemiaNet Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5195–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilloni, D. Is WT1 helping the molecular monitoring of minimal residual disease to get easier in acute myeloid leukaemia? Leuk. Res. 2009, 33, 603–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, L.; Yan, H.; Ren, X.; Zhou, M.; Xiong, S.; Wang, H.; Tao, Q.; Zhai, Z.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Prognostic value of the WT-1 gene combined with recurrent cytogenetic genes in acute myeloid leukemia. Immunogenetics 2023, 75, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barajas, J.M.; Umeda, M.; Contreras, L.; Khanlari, M.; Westover, T.; Walsh, M.P.; Xiong, E.; Yang, C.; Otero, B.; Arribas-Layton, M.; et al. UBTF tandem duplications in pediatric myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia: Implications for clinical screening and diagnosis. Haematologica 2024, 109, 2459. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Jia, Y.; Huai, L.; He, K.; Yu, P.; Wang, M.; Xing, H.; Rao, Q.; et al. Role of the Wilms’ tumor 1 gene in the aberrant biological behavior of leukemic cells and the related mechanisms. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 2680–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampal, R.; Figueroa, M.E. Wilms tumor 1 mutations in the pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2016, 101, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murata, Y.; Kudoh, T.; Sugiyama, H.; Toyoshima, K.; Akiyama, T. The Wilms tumor suppressor gene WT1 induces G1 arrest and apoptosis in myeloblastic leukemia M1 cells. FEBS Lett. 1997, 409, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Maurer, U.; Brieger, J.; Weidmann, E.; Mitrou, P.S.; Hoelzer, D.; Bergmann, L. The Wilms’ tumor gene is expressed in a subset of CD34+ progenitors and downregulated early in the course of differentiation in vitro. Exp. Hematol. 1997, 25, 945–950. [Google Scholar]
- Karakas, T.; Miething, C.C.; Maurer, U.; Weidmann, E.; Ackermann, H.; Hoelzer, D.; Bergmann, L. The coexpression of the apoptosis-related genes bcl-2 and wt1 in predicting survival in adult acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2002, 16, 846–854. [Google Scholar]
- Spanaki, A.; Linardakis, E.; Perdikogianni, C.; Stiakaki, E.; Morotti, A.; Cilloni, D.; Kalmanti, M. Quantitative assessment of WT1 expression in diagnosis of childhood acute leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2007, 31, 570–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuser, M.; Freeman, S.; Ossenkoppele, G.; Buccisano, F.; Hourigan, C.; Ngai, L.; Tettero, J.; Bachas, C.; Baer, C.; Béné, M.C.; et al. 2021 Update on MRD in acute myeloid leukemia: A consensus document from the European LeukemiaNet MRD Working Party. Blood 2021, 138, 2753–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronier, E.; Bowman, R.L.; Ahn, J.; Glass, J.; Kandoth, C.; Merlinsky, T.R.; Whitfield, J.T.; Durham, B.H.; Gruet, A.; Hanasoge Somasundara, A.V.; et al. Genetic and epigenetic evolution as a contributor to WT1-mutant leukemogenesis. Blood 2018, 132, 1265–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauth, M.T.; Alpermann, T.; Bacher, U.; Eder, C.; Dicker, F.; Ulke, M.; Kuznia, S.; Nadarajah, N.; Kern, W.; Haferlach, C.; et al. WT1 mutations are secondary events in AML, show varying frequencies and impact on prognosis between genetic subgroups. Leukemia 2015, 29, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconi, G.; Rondoni, M.; Zannetti, B.A.; Zacheo, I.; Nappi, D.; Mattei, A.; Rocchi, S.; Lanza, F. Novel insights and therapeutic approaches in secondary AML. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1400461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arber, D.A.; Orazi, A.; Hasserjian, R.; Thiele, J.; Borowitz, M.J.; Le Beau, M.M.; Bloomfield, C.D.; Cazzola, M.; Vardiman, J.W. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood 2016, 127, 2391–2405. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gabert, J.; Beillard, E.; van der Velden, V.H.; Bi, W.; Grimwade, D.; Pallisgaard, N.; Barbany, G.; Cazzaniga, G.; Cayuela, J.M.; Cavé, H.; et al. Standardization and quality control studies of ‘real-time’ quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction of fusion gene transcripts for residual disease detection in leukemia—A Europe Against Cancer Program. Leukemia 2003, 17, 2318–2357. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arber, D.A.; Orazi, A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Borowitz, M.J.; Calvo, K.R.; Kvasnicka, H.M.; Wang, S.A.; Bagg, A.; Barbui, T.; Branford, S.; et al. International Consensus Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms and Acute Leukemia: Integrating Morphological, Clinical, and Genomic Data. Blood 2022, 140, 1200–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaemmanuil, E.; Gerstung, M.; Bullinger, L.; Gaidzik, V.I.; Paschka, P.; Roberts, N.D.; Potter, N.E.; Heuser, M.; Thol, F.; Bolli, N.; et al. Genomic Classification and Prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2209–2221. [Google Scholar]
- R Foundation for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2021.
- Abelson, S.; Collord, G.; Ng, S.W.K.; Weissbrod, O.; Mendelson Cohen, N.; Niemeyer, E.; Barda, N.; Zuzarte, P.C.; Heisler, L.; Sundaravadanam, Y.; et al. Prediction of acute myeloid leukaemia risk in healthy individuals. Nature 2018, 559, 400. [Google Scholar]
- Shlush, L.I.; Zandi, S.; Mitchell, A.; Chen, W.C.; Brandwein, J.M.; Gupta, V.; Kennedy, J.A.; Schimmer, A.D.; Schuh, A.C.; Yee, K.W.; et al. Identification of pre-leukaemic haematopoietic stem cells in acute leukaemia. Nature 2014, 506, 328–333. [Google Scholar]
- Corces-Zimmerman, M.R.; Hong, W.J.; Weissman, I.L.; Medeiros, B.C.; Majeti, R. Preleukemic mutations in human acute myeloid leukemia affect epigenetic regulators and persist in remission. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2548–2553. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Jia, M.; Mao, Y.; Cai, H.; Jiang, X.; Cao, X.; Zhou, D.; Li, J. Distinct Mutation Landscapes Between Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Myelodysplasia-Related Changes and De Novo Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2022, 157, 691–700. [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg, O.K.; Seetharam, M.; Ren, L.; Seo, K.; Ma, L.; Merker, J.D.; Gotlib, J.; Zehnder, J.L.; Arber, D.A. Clinical characterization of acute myeloid leukemia with myelodysplasia-related changes as defined by the 2008 WHO classification system. Blood 2009, 113, 1906–1908. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen-Bjergaard, J.; Andersen, M.K.; Andersen, M.T.; Christiansen, D.H. Genetics of therapy-related myelodysplasia and acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2008, 22, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazi, Y.; Arango-Ossa, J.E.; Zhou, Y.; Bernard, E.; Thomas, I.; Gilkes, A.; Freeman, S.; Pradat, Y.; Johnson, S.J.; Hills, R.; et al. Unified classification and risk-stratification in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
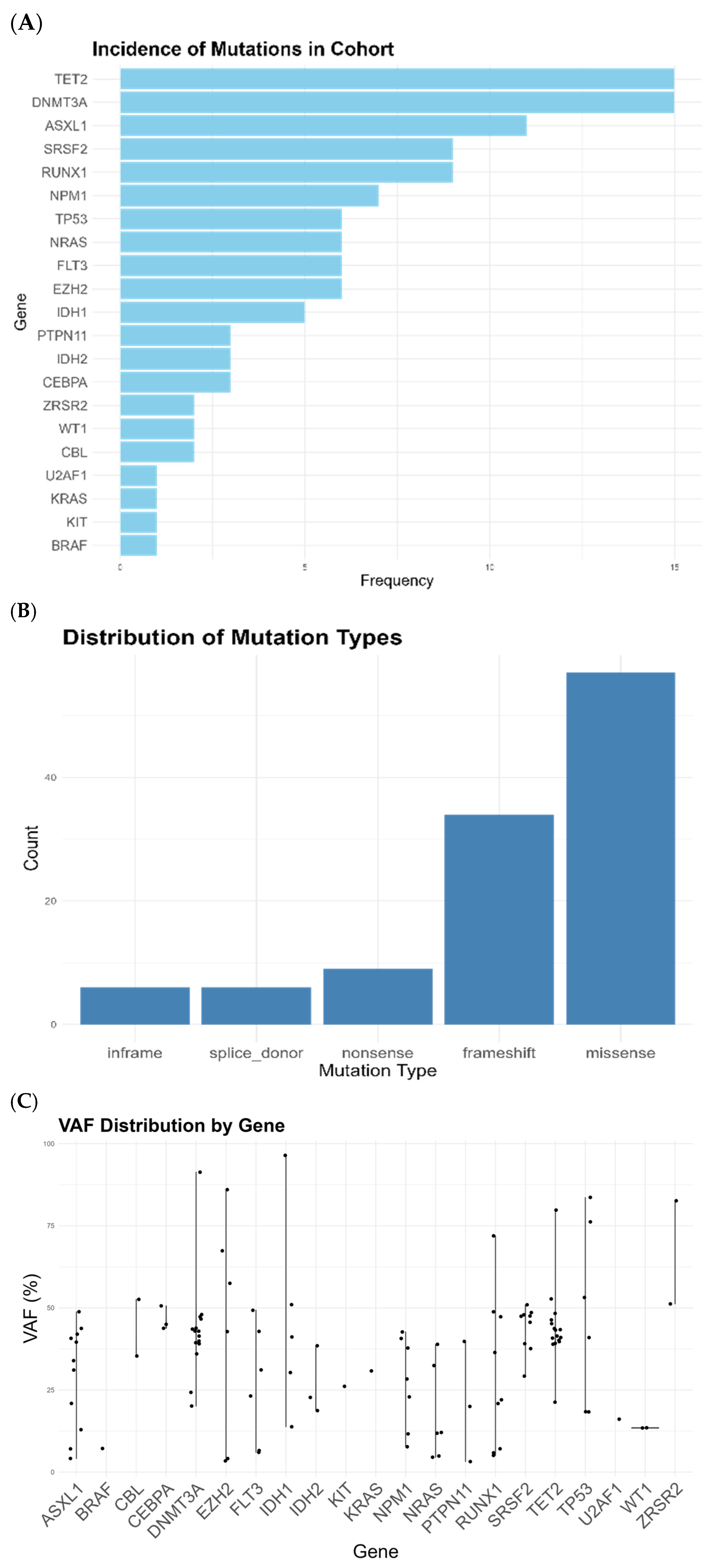
| Gene | Low-Level WT1 Cohort | Papaemanuouil et al. [25] | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| DNMT3A | 13 (14%) | 382 (15.9%) | 0.222 |
| TET2 | 11 (11.8%) | 205 (8.5%) | 0.017 |
| ASXL1 | 10 (10.8%) | 71 (3.0%) | 0.001 |
| RUNX1 | 9 (9.7%) | 151 (6.3%) | 0.013 |
| TP53 | 6 (6.5%) | 110 (4.6%) | 0.057 |
| SRSF2 | 7 (6.5%) | 93 (3.9%) | 0.030 |
| FLT3 | 8 (6.5%) | 572 (23.8%) | 0.017 |
| EZH2 | 9 (6.5%) | 48 (2.0%) | 0.001 |
| NPM1 | 5 (5.4%) | 438 (18.2%) | 0.068 |
| NRAS | 3 (3.2%) | 292 (12.1%) | 0.160 |
| IDH2 | 3 (3.2%) | 152 (6.3%) | 1.000 |
| CEBPA | 3 (3.2%) | 216 (9.0%) | 0.490 |
| ZRSR2 | 2 (2.2%) | 13 (0.5%) | 0.048 |
| PTPN11 | 2 (2.2%) | 131 (5.5%) | 0.770 |
| IDH1 | 2 (2.2%) | 105 (4.4%) | 1.000 |
| U2AF1 | 1 (1.1%) | 38 (1.6%) | 0.612 |
| KRAS | 1 (1.1%) | 80 (3.3%) | 1.000 |
| KIT | 1 (1.1%) | 71 (3.0%) | 1.000 |
| CBL | 1 (1.1%) | 42 (1.7%) | 1.000 |
| Characteristic | Patients (n = 26) |
| Age, n (IQR) | 70 (64.9–75.8) |
| Sex (M/F) | 15/11 |
| Karyotype | |
| 3/26 2/26 3/26 1/26 3/26 3/26 11/26 |
| Secondary to myelodysplasia, n(%) | 11/15 (75%) [11 not known] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rondoni, M.; Marconi, G.; Nicoletti, A.; Giannini, B.; Zuffa, E.; Giannini, M.B.; Mianulli, A.; Norata, M.; Monaco, F.; Zaccheo, I.; et al. Low WT1 Expression Identifies a Subset of Acute Myeloid Leukemia with a Distinct Genotype. Cancers 2025, 17, 1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071213
Rondoni M, Marconi G, Nicoletti A, Giannini B, Zuffa E, Giannini MB, Mianulli A, Norata M, Monaco F, Zaccheo I, et al. Low WT1 Expression Identifies a Subset of Acute Myeloid Leukemia with a Distinct Genotype. Cancers. 2025; 17(7):1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071213
Chicago/Turabian StyleRondoni, Michela, Giovanni Marconi, Annalisa Nicoletti, Barbara Giannini, Elisa Zuffa, Maria Benedetta Giannini, Annamaria Mianulli, Marianna Norata, Federica Monaco, Irene Zaccheo, and et al. 2025. "Low WT1 Expression Identifies a Subset of Acute Myeloid Leukemia with a Distinct Genotype" Cancers 17, no. 7: 1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071213
APA StyleRondoni, M., Marconi, G., Nicoletti, A., Giannini, B., Zuffa, E., Giannini, M. B., Mianulli, A., Norata, M., Monaco, F., Zaccheo, I., Rocchi, S., Zannetti, B. A., Santoni, A., Graziano, C., Bocchia, M., & Lanza, F. (2025). Low WT1 Expression Identifies a Subset of Acute Myeloid Leukemia with a Distinct Genotype. Cancers, 17(7), 1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071213









