Simulation-Omitting and Using Library Patients for Pre-Planning Online Adaptive Radiotherapy (SUPPORT): A Feasibility Study for Spine Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (SAbR) Patients
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Proposed Workflow
2.2. Spine SAbR Patient Planning
2.3. Library Cases and ART Strategy Development
2.4. Validation of Simulation-Omitted Spine SAbR
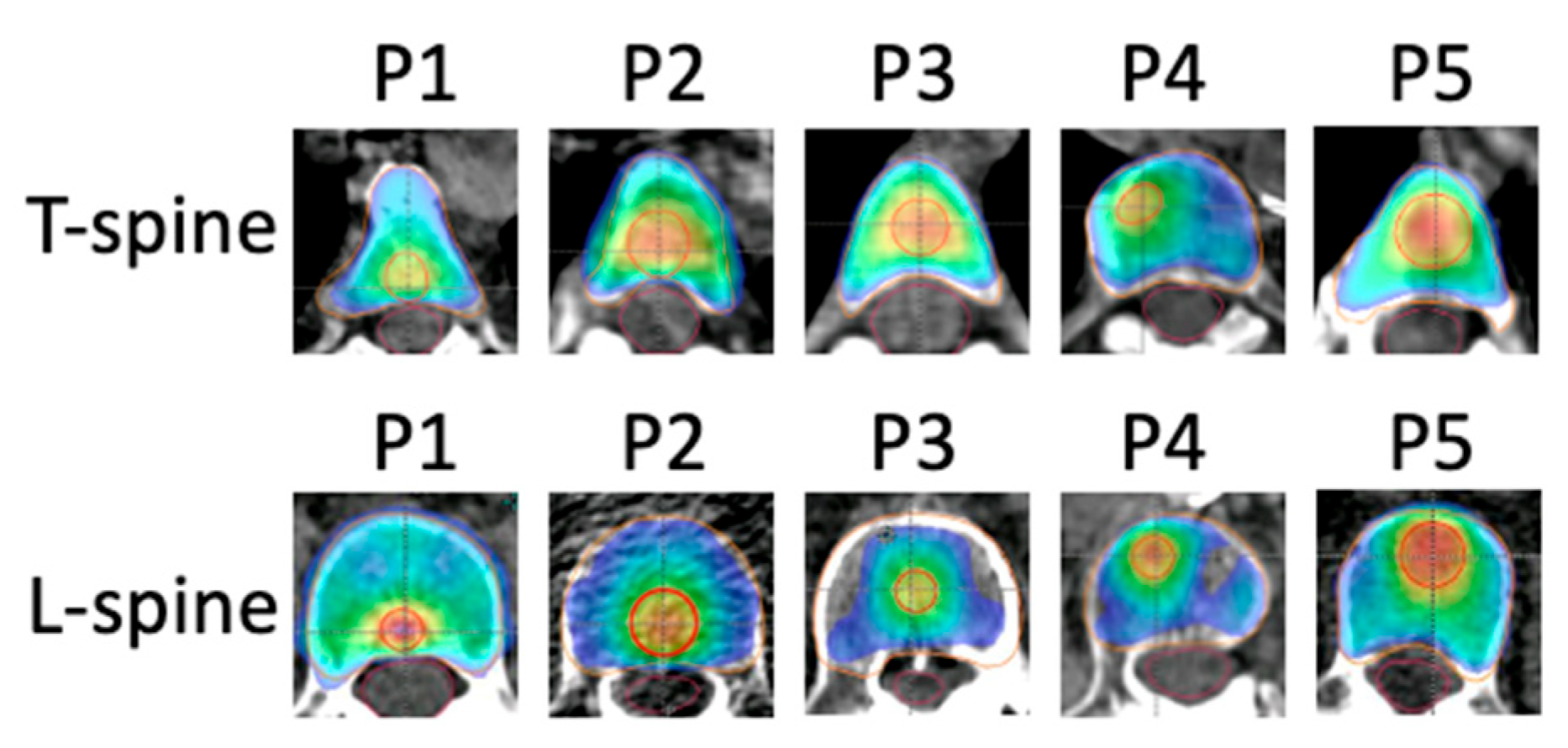
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dona Lemus, O.M.; Cao, M.; Cai, B.; Cummings, M.; Zheng, D. Adaptive Radiotherapy: Next-Generation Radiotherapy. Cancers 2024, 16, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrova, E.; Garrett, M.D.; Wang, Y.F.; Chin, C.; Elliston, C.; Savacool, M.; Price, M.; Kachnic, L.A.; Horowitz, D.P. Adaptive Radiation Therapy: A Review of CT-based Techniques. Radiol. Imaging Cancer 2023, 5, e230011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teh, B.S.; Woo, S.Y.; Butler, E.B. Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT): A New Promising Technology in Radiation Oncology. Oncologist 1999, 4, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, K. Volumetric modulated arc therapy: IMRT in a single gantry arc. Med. Phys. 2007, 35, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elith, C.; Dempsey, S.E.; Findlay, N.; Warren-Forward, H.M. An Introduction to the Intensity-modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Techniques, Tomotherapy, and VMAT. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Sci. 2011, 42, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palta, J.R.; Liu, C.; Li, J.G. Quality Assurance of Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2008, 71, S108–S112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benk, V.; Przybysz, R.; McGowan, T.; Paszat, L. Waiting times for radiation therapy in Ontario. Can. J. Surg. 2006, 49, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Agazaryan, N.; Chow, P.; Lamb, J.; Cao, M.; Raldow, A.; Beron, P.; Hegde, J.; Steinberg, M. The Timeliness Initiative: Continuous Process Improvement for Prompt Initiation of Radiation Therapy Treatment. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 5, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarnold, J. 8 Gy single fraction radiotherapy for the treatment of metastatic skeletal pain: Randomised comparison with a multifraction schedule over 12 months of patient follow-upOn behalf of the Bone Pain Trial Working Party. Radiother. Oncol. 1999, 52, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harstell, W.F.; Scott, C.B.; Bruner, D.W.; Scarantino, C.W.; Ivker, R.A.; Roach, M.; Suh, J.H.; Demas, W.F.; Movsas, B.; Petersen, I.A.; et al. Randomized trial of short- versus long-course radiotherapy for palliation of painful bone metastases. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2005, 97, 798–804. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, S.; Deshmukh, S.; Timmerman, R.D.; Movsas, B.; Gerszten, P.; Yin, F.F.; Dicker, A.; Abraham, C.D.; Zhong, J.; Shiao, S.L.; et al. Stereotactic Radiosurgery vs Conventional Radiotherapy for Localized Vertebral Metastases of the Spine. JAMA Oncol. 2023, 9, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; King, W.; Pearcey, R.; Kerba, M.; Mackillop, W.J. The relationship between waiting time for radiotherapy and clinical outcomes: A systematic review of the literature. Radiother. Oncol. 2008, 87, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackillop, W.J. Killing time: The consequences of delays in radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2007, 84, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattaneo, R.; Hanna, R.K.; Jacobsen, G.; Elshaikh, M.A. Interval Between Hysterectomy and Start of Radiation Treatment Is Predictive of Recurrence in Patients with Endometrial Carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 88, 866–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; King, W.; Korzeniowski, M.; Wallace, D.; Mackillop, W. The Effect of Waiting Times for Postoperative Radiotherapy on Outcomes for Women Receiving Partial Mastectomy for Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 28, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, K.; Trotti, A.; Brown, B.W.; Garden, A.S.; Foote, R.L.; Morrison, W.H.; Geara, F.B.; Klotch, D.W.; Goepfert, H.; Peters, L.J. Randomized trial addressing risk features and time factors of surgery plus radiotherapy in advanced head-and-neck cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2001, 51, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, D.; James, M.; Lah, M.; Pope, K.; Shorthouse, A.; Govindaraj, R.; Holt, T. Rapid Access Palliative Radiation Therapy Clinics: The Evidence Is There, but Where Are the Clinics? An Australian and New Zealand Perspective. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 111, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, D.; Job, M.; Holt, T. Establishing a palliative Advanced Practice Radiation Therapist role: A viable alternative to a Rapid Access Palliative Radiation Therapy clinic in Australia. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 66, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiff, J.P.; Zhao, T.; Huang, Y.; Sun, B.; Hugo, G.D.; Spraker, M.B.; Abraham, C.D. Simulation-Free Radiation Therapy: An Emerging Form of Treatment Planning to Expedite Plan Generation for Patients Receiving Palliative Radiation Therapy. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 8, 101091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, T.; Back, M.; Hruby, G.; Carroll, S.; Jayamanne, D.; Kneebone, A.; Stevens, M.; Lamoury, G.; Morgia, M.; Wong, S.; et al. Introducing Computed Tomography Simulation–Free and Electronic Patient-Reported Outcomes–Monitored Palliative Radiation Therapy into Routine Care: Clinical Outcomes and Implementation Experience. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 6, 100632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, T.; Parsons, D.; Desai, N.; Gibbard, G.; Keilty, D.; Lin, M.H.; Cai, B.; Nguyen, D.; Chiu, T.; Godley, A.; et al. Simulation and pre-planning omitted radiotherapy (SPORT): A feasibility study for prostate cancer. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2024, 10, 025019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.; Roderick, S.; Kejda, A.; Atyeo, J.; Grimberg, K.; Porter, B.; Booth, J.; Hruby, G.; Eade, T. Diagnostic Computed Tomography Enabled Planning for Palliative Radiation Therapy: Removing the Need for a Planning Computed Tomography Scan. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 11, e146–e153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neil, M.; Laba, J.M.; Nguyen, T.K.; Lock, M.; Goodman, C.D.; Huynh, E.; Snir, J.; Munro, V.; Alce, J.; Schrijver, L.; et al. Diagnostic CT-Enabled Planning (DART): Results of a Randomized Trial in Palliative Radiation Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 120, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DART: Diagnostic-CT-Enabled Planning: A Randomized Trial in Palliative Radiation Therapy (DART). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05233904 (accessed on 26 January 2025).
- Yan, D. Adaptive Radiotherapy: Merging Principle into Clinical Practice. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2010, 20, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Schoot, A.J.; Hoffmans, D.; van Ingen, K.M.; Simons, M.J.; Wiersma, J. Characterization of Ethos therapy systems for adaptive radiation therapy: A multi-machine comparison. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2023, 24, e13905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, D.N.; Harms, J.; Pogue, J.A.; Belliveau, J.; Marcrom, S.R.; McDonald, A.M.; Dobelbower, M.C.; Boggs, D.H.; Soike, M.H.; Fiveash, J.A.; et al. A roadmap for implementation of kV-CBCT online adaptive radiation therapy and initial first year experiences. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2023, 24, e13961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, M.; Archibald-Heeren, B.; Hu, Y.; Teh, A.; Beserminji, R.; Cai, E.; Liu, G.; Yates, A.; Rijken, J.; Collett, N.; et al. Varian ethos online adaptive radiotherapy for prostate cancer: Early results of contouring accuracy, treatment plan quality, and treatment time. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2021, 23, e13479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Placidi, L.; Romano, A.; Chiloiro, G.; Cusumano, D.; Boldrini, L.; Cellini, F.; Mattiucci, G.C.; Valentini, V. On-line adaptive MR guided radiotherapy for locally advanced pancreatic cancer: Clinical and dosimetric considerations. Tech. Innov. Patient Support Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.H.; Price, A.T.; Reynoso, F.J.; Laugeman, E.; Morris, E.D.; Samson, P.P.; Huang, J.; Badiyan, S.N.; Kim, H.; Brenneman, R.J.; et al. A Pilot Study of Simulation-Free Hippocampal-Avoidance Whole Brain Radiation Therapy Using Diagnostic MRI-Based and Online Adaptive Planning. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 119, 1422–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazzezi, M.; Rose, B.; Kisling, K.; Moore, K.L.; Ray, X. Prospects for daily online adaptive radiotherapy via ethos for prostate cancer patients without nodal involvement using unedited CBCT auto-segmentation. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2021, 22, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, A.T.; Schiff, J.P.; Silberstein, A.; Beckert, R.; Zhao, T.; Hugo, G.D.; Samson, P.P.; Laugeman, E.; Henke, L.E. Feasibility of simulation free abdominal stereotactic adaptive radiotherapy using an expedited pre-plan workflow. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 31, 100611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios, M.A.; Verheijen, S.; Schneiders, F.L.; Bohoudi, O.; Slotman, B.J.; Lagerwaard, F.J.; Senan, S. Same-day consultation, simulation and lung Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy delivery on a Magnetic Resonance-linac. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 24, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, R.L.; Fallone, C.; Chytyk-Praznik, K.; Robar, J.; Cherpak, A. The feasibility of CT simulation-free adaptive radiation therapy. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2024, 25, e14438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelissen, K.J.; Versteijne, E.; Senan, S.; Hoffmans, D.; Slotman, B.J.; Verbakel, W.F. Evaluation of a workflow for cone-beam CT-guided online adaptive palliative radiotherapy planned using diagnostic CT scans. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2022, 24, e13841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visak, J.; Inam, E.; Meng, B.; Wang, S.; Parsons, D.; Nyugen, D.; Zhang, T.; Moon, D.; Avkshtol, V.; Jiang, S.; et al. Evaluating machine learning enhanced intelligent-optimization-engine (IOE) performance for ethos head-and-neck (HN) plan generation. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2023, 24, e13950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Kim, H.; Zhuang, T.; Visak, J.D.; Lin, M.H.; Cai, B.; Parsons, D.D.; Godley, A.R.; Jiang, S. Simulation-Omitted and Using Library Patients for Pre-Planning Online Adaptive Radiotherapy (SUPPORT): A Feasibility Study for Spine Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (SAbR) Patients. In AAPM 66th Annual Meeting & Exhibition; AAPM: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Kim, H.; Zhuang, T.; Visak, J.; Lin, M.; Cai, B.; Parsons, D.; Godley, A.; Jiang, S. Unlocking the Simulation-Omitted Spine SAbR with Advanced CBCT and Online Adaptive Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 120, S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glide-Hurst, C.K.; Lee, P.; Yock, A.D.; Olsen, J.R.; Cao, M.; Siddiqui, F.; Parker, W.; Doemer, A.; Rong, Y.; Kishan, A.U.; et al. Adaptive Radiation Therapy (ART) Strategies and Technical Considerations: A State of the ART Review From NRG Oncology. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 109, 1054–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunnen, B.; van de Schoot, A.J.; Fremeijer, K.P.; Nicolai-Koornneef, E.M.; Offereins-van Harten, K.; Sluijter, J.H.; Sijtsema, N.D.; Oomen-de Hoop, E.; El Yaakoubi, A.; Froklage, F.E.; et al. The added value of a new high-performance ring-gantry CBCT imaging system for prostate cancer patients. Radiother. Oncol. 2024, 200, 110458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robar, J.L.; Cherpak, A.; MacDonald, R.L.; Yashayaeva, A.; McAloney, D.; McMaster, N.; Zhan, K.; Cwajna, S.; Patil, N.; Dahn, H. Novel Technology Allowing Cone Beam Computed Tomography in 6 Seconds: A Patient Study of Comparative Image Quality. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 14, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustermans, D.; Fonseca, G.P.; Taasti, V.T.; van de Schoot, A.; Petit, S.; van Elmpt, W.; Verhaegen, F. Image quality evaluation of a new high-performance ring-gantry cone-beam computed tomography imager. Phys. Med. Biol. 2024, 69, 105018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluijter, J.H.; van de Schoot, A.J.; El Yaakoubi, A.; de Jong, M.; van der Knaap-van, M.S.; Kunnen, B.; Sijtsema, N.D.; Penninkhof, J.J.; de Vries, K.C.; Petit, S.F.; et al. Evaluation of artificial intelligence-based autosegmentation for a high-performance cone-beam computed tomography imaging system in the pelvic region. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 33, 100687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archambault, Y.; Boylan, C.; Bullock, D.; Morgas, T.; Peltola, J.; Ruokokoski, E.; Genghi, A.; Haas, B.; Suhonen, P.; Thompson, S. Making on-line adaptive radiotherapy possible using artificial intelligence and machine learning for efficient daily re-planning. Med. Phys. Int. J. 2020, 8, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Pokharel, S.; Pacheco, A.; Tanner, S. Assessment of efficacy in automated plan generation for Varian Ethos intelligent optimization engine. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2022, 23, e13539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.; Hsu, C.C.; Chen, W.M.; Chen, B.P.; Han, C.; Story, M.; Aguilera, T.; Pop, L.M.; Hannan, R.; Fu, Y.X.; et al. Personalized Ultrafractionated Stereotactic Adaptive Radiotherapy (PULSAR) in Preclinical Models Enhances Single-Agent Immune Checkpoint Blockade. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 110, 1306–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohopolski, M.; Schmitt, L.G.; Anand, S.; Zhang, H.; Stojadinovic, S.; Youssef, M.; Shaikh, N.; Patel, T.; Patel, A.; Barnett, S.; et al. Exploratory Evaluation of Personalized Ultrafractionated Stereotactic Adaptive Radiation Therapy (PULSAR) With Central Nervous System-Active Drugs in Brain Metastases Treatment. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2024. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haertter, A.; Salerno, M.; Koger, B.; Kennedy, C.; Alonso-Basanta, M.; Dong, L.; Teo, B.K.; Li, T. ACR bench-mark testing of a novel high-speed ring-gantry linac kV-CBCT system. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2024, 25, e14299. [Google Scholar]


| Ranking a | Structure | Primary Goal | Alternative Goal |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 Most Important | Spinal Cord | V10Gy ≤ 0.35cc | |
| P1 | Spinal Cord | D0.03cc ≤ 14Gy | |
| P2 Very Important | * PTV20Gy-Cord3mm b | D10% ≥ 110% | |
| P2 | * PTV14Gy-Cord2mm b | V100% ≥ 96% | |
| P2 | * PTV20Gy-Cord3mm b | V100% ≥ 95.1% | |
| P2 | PTV20Gy | V100% ≥ 95.1% | ≥90% |
| P2 | PTV14Gy | V100% ≥ 95.1% | ≥90% |
| P2 | * Ring14Gy3mm c | Dmax ≤ 12Gy | |
| P2 | * Ring20Gy3mm c | Dmax ≤ 15Gy | ≤20Gy |
| P2 | Heart | V16Gy ≤ 15cc | |
| P2 | Heart | D0.03cc ≤ 22Gy | |
| P2 | Small Bowel | D0.03cc ≤ 20Gy | |
| P2 | Esophagus | V20Gy ≥ 5cc | |
| P2 | Esophagus | D0.03cc ≤ 24Gy | |
| P2 | Kidney left | D33.4% ≤ 9.5Gy | |
| P2 | Kidney left | V14Gy ≤ 15cc | |
| P2 | Kidney right | D33.4% ≤ 9.5Gy | |
| P2 | Kidney right | V14Gy ≤ 15cc | |
| P2 | Both Kidneys | D33.4% ≤ 9.5Gy | |
| P2 | Small Bowel | V7.6Gy ≤ 30cc | |
| P2 | Skin | D0.03cc ≤ 27.5Gy | |
| P2 | Skin | V25.5Gy ≤ 10cc | |
| P2 | Both Lungs | D33.3% ≤ 7.2Gy | |
| P3 Important | Both Lungs | D950cc ≤ 7.2Gy | |
| P3 | Both Lungs | D1500cc ≤ 7.2Gy | |
| P3 | Both Lungs | V8Gy ≤ 37% |
| P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Library Pre-Plan | Test ART | Library Pre-Plan | Test ART | Library Pre-Plan | Test ART | Library Pre-Plan | Test ART | Library Pre-Plan | Test ART | |
| PTV20GY(%) | 89.5 | 90.2 | 89.1 | 92.2 | 95.5 | 95.1 | 95.0 | 95.2 | 95.0 | 95.1 |
| PTV14GY(%) | 96.7 | 92.9 | 95.2 | 95.4 | 92.8 | 92.0 | 93.9 | 92.0 | 93.2 | 93.0 |
| CORD MAX (GY) | 12.2 | 12.0 | 11.7 | 12.3 | 10.5 | 11.2 | 10.8 | 10.7 | 10.5 | 11.1 |
| CORD V10GY (CC) | 0.20 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09 |
| P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Library Pre-Plan | Test ART | Library Pre-Plan | Test ART | Library Pre-Plan | Test ART | Library Pre-Plan | Test ART | Library Pre-Plan | Test ART | |
| PTV20GY(%) | 87.9 | 91.3 | 92.6 | 94.9 | 95.0 | 95.1 | 95.0 | 95.1 | 95.3 | 95.1 |
| PTV14GY(%) | 97.3 | 98.1 | 97.2 | 90.4 | 92.8 | 91.3 | 91.9 | 92.6 | 94.3 | 95.2 |
| CORD MAX (GY) | 13.7 | 13.3 | 13.5 | 11.0 | 10.4 | 9.4 | 10.2 | 10.6 | 10.4 | 10.2 |
| CORD V10GY (CC) | 0.21 | 0.24 | 0.77 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, D.; Kim, H.; Zhuang, T.; Visak, J.D.; Cai, B.; Parsons, D.D.M.; Jiang, S.; Godley, A.R.; Lin, M.-H. Simulation-Omitting and Using Library Patients for Pre-Planning Online Adaptive Radiotherapy (SUPPORT): A Feasibility Study for Spine Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (SAbR) Patients. Cancers 2025, 17, 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071216
Wang D, Kim H, Zhuang T, Visak JD, Cai B, Parsons DDM, Jiang S, Godley AR, Lin M-H. Simulation-Omitting and Using Library Patients for Pre-Planning Online Adaptive Radiotherapy (SUPPORT): A Feasibility Study for Spine Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (SAbR) Patients. Cancers. 2025; 17(7):1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071216
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Da, Heejung Kim, Tingliang Zhuang, Justin D. Visak, Bin Cai, David D. M. Parsons, Steve Jiang, Andrew R. Godley, and Mu-Han Lin. 2025. "Simulation-Omitting and Using Library Patients for Pre-Planning Online Adaptive Radiotherapy (SUPPORT): A Feasibility Study for Spine Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (SAbR) Patients" Cancers 17, no. 7: 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071216
APA StyleWang, D., Kim, H., Zhuang, T., Visak, J. D., Cai, B., Parsons, D. D. M., Jiang, S., Godley, A. R., & Lin, M.-H. (2025). Simulation-Omitting and Using Library Patients for Pre-Planning Online Adaptive Radiotherapy (SUPPORT): A Feasibility Study for Spine Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (SAbR) Patients. Cancers, 17(7), 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071216






