Clinical Practice-Based Failure Modes and Root Cause Analysis of Cone Beam CT-Guided Online Adaptive Radiotherapy of the Pelvis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
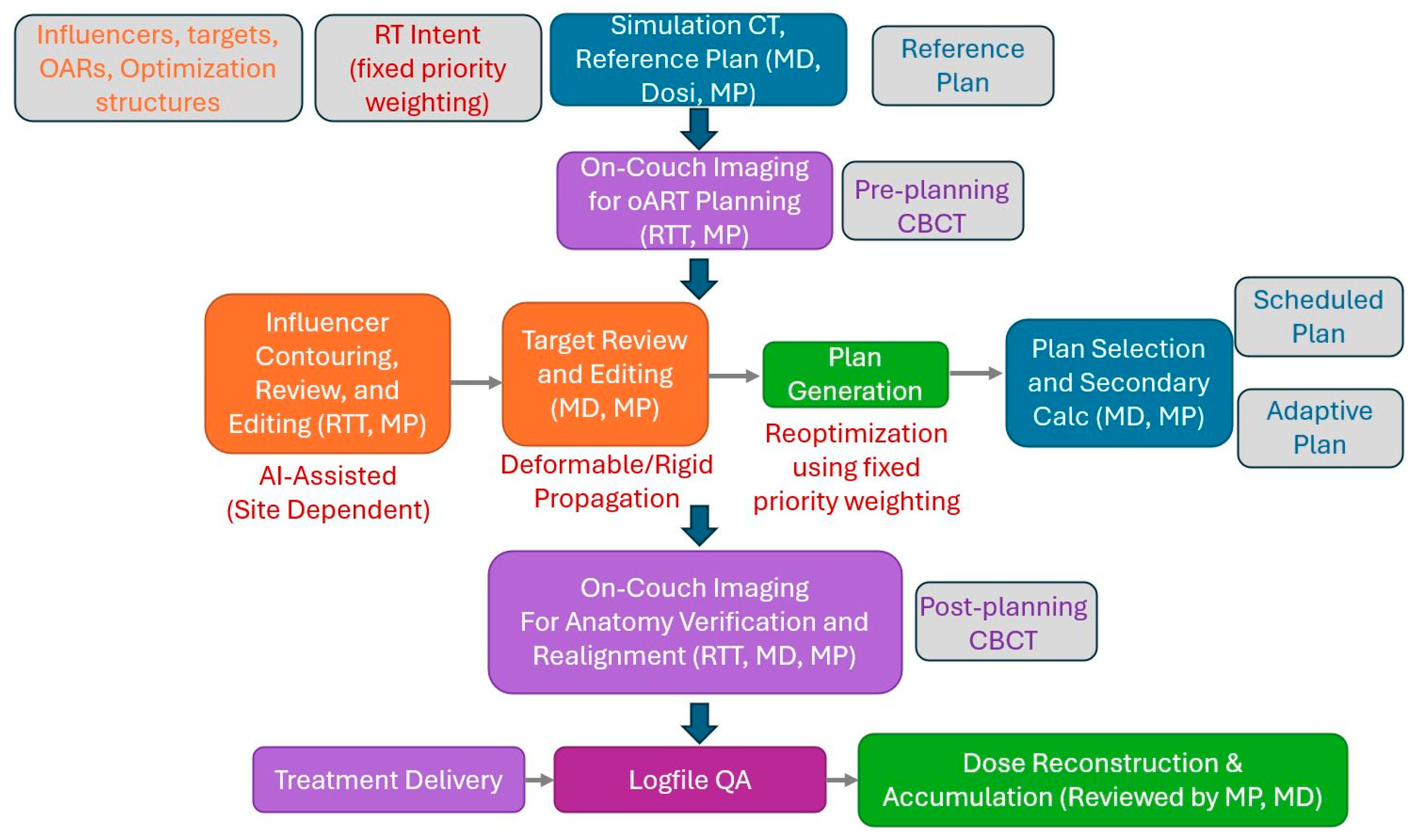
2.1. Overview of the Reviewed Pelvic oART Cases and Our Adaptive Workflow
2.2. Multidisciplinary Approach and Retrospective Review Methodology
3. Results
3.1. Aborted Sessions
3.2. Other FMs and Irregularities
3.2.1. System-Driven Issues
3.2.2. Patient-Driven Challenges
3.2.3. Treatment Planning and Execution Failures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dona Lemus, O.M.; Cao, M.; Cai, B.; Cummings, M.; Zheng, D. Adaptive Radiotherapy: Next-Generation Radiotherapy. Cancers 2024, 16, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J. IMRT, IGRT, SBRT: Advances in the Treatment Planning and Delivery of Radiotherapy; Karger Medical and Scientific Publishers: Basel, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Castadot, P.; Lee, J.A.; Geets, X.; Grégoire, V. (Eds.) Adaptive radiotherapy of head and neck cancer. In Seminars in Radiation oncology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sonke, J.J.; Aznar, M.; Rasch, C. Adaptive Radiotherapy for Anatomical Changes. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 29, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.; Stewart, J.; Kelly, V.; Xie, J.; Brock, K.K.; Moseley, J.; Cho, Y.-B.; Fyles, A.; Lundin, A.; Rehbinder, H. Dosimetrically triggered adaptive intensity modulated radiation therapy for cervical cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 90, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Vicini, F.; Wong, J.; Martinez, A. Adaptive radiation therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 1997, 42, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archambault, Y.; Boylan, C.; Bullock, D.; Morgas, T.; Peltola, J.; Ruokokoski, E.; Genghi, A.; Haas, B.; Suhonen, P.; Thompson, S. Making on-line adaptive radiotherapy possible using artificial intelligence and machine learning for efficient daily re-planning. Med. Phys. Int. J. 2020, 8, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, A.; Hansen, V.; Oelfke, U.; Nill, S.; Hafeez, S. Adaptive radiotherapy enabled by MRI guidance. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 30, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkel, D.; Bol, G.H.; Kroon, P.S.; van Asselen, B.; Hackett, S.S.; Werensteijn-Honingh, A.M.; Intven, M.P.; Eppinga, W.S.; Tijssen, R.H.; Kerkmeijer, L.G. Adaptive radiotherapy: The Elekta Unity MR-linac concept. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 18, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, M.; Archibald-Heeren, B.; Hu, Y.; Teh, A.; Beserminji, R.; Cai, E.; Liu, G.; Yates, A.; Rijken, J.; Collett, N.; et al. Varian ethos online adaptive radiotherapy for prostate cancer: Early results of contouring accuracy, treatment plan quality, and treatment time. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2022, 23, e13479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Pasetsky, J.; Lavrova, E.; Wang, Y.-F.; Sedor, G.; Li, F.L.; Gallitto, M.; Garrett, M.; Elliston, C.; Price, M. CT-guided online adaptive stereotactic body radiotherapy for pancreas ductal adenocarcinoma: Dosimetric and initial clinical experience. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 48, 100813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Riess, J.; Kim, J.; Vance, S.; Chetty, I.J.; Movsas, B.; Kretzler, A. Evaluation of Auto-Contouring and Dose Distributions for Online Adaptive Radiation Therapy of Patients With Locally Advanced Lung Cancers. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 12, e329–e338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazzezi, M.; Rose, B.; Kisling, K.; Moore, K.L.; Ray, X. Prospects for daily online adaptive radiotherapy via ethos for prostate cancer patients without nodal involvement using unedited CBCT auto-segmentation. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2021, 22, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiff, J.P.; Price, A.T.; Stowe, H.B.; Laugeman, E.; Chin, R.-I.; Hatscher, C.; Pryser, E.; Cai, B.; Hugo, G.D.; Kim, H. Simulated computed tomography-guided stereotactic adaptive radiotherapy (CT-STAR) for the treatment of locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2022, 175, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibolt, P.; Andersson, L.M.; Calmels, L.; Sjostrom, D.; Bjelkengren, U.; Geertsen, P.; Behrens, C.F. Clinical implementation of artificial intelligence-driven cone-beam computed tomography-guided online adaptive radiotherapy in the pelvic region. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 17, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwart, L.G.; Ong, F.; Ten Asbroek, L.A.; van Dieren, E.B.; Koch, S.A.; Bhawanie, A.; de Wit, E.; Dasselaar, J.J. Cone-beam computed tomography-guided online adaptive radiotherapy is feasible for prostate cancer patients. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 22, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, D.; Mayadev, J.; Moore, K.; Ray, X. Dosimetric and feasibility evaluation of a CBCT-based daily adaptive radiotherapy protocol for locally advanced cervical cancer. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2023, 24, e13783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelley, C.E.; Bolt, M.A.; Hollingdale, R.; Chadwick, S.J.; Barnard, A.P.; Rashid, M.; Reinlo, S.C.; Fazel, N.; Thorpe, C.R.; Stewart, A.J. Implementing cone-beam computed tomography-guided online adaptive radiotherapy in cervical cancer. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 40, 100596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, D.N.; Harms, J.; Pogue, J.A.; Belliveau, J.G.; Marcrom, S.R.; McDonald, A.M.; Dobelbower, M.C.; Boggs, D.H.; Soike, M.H.; Fiveash, J.A. A roadmap for implementation of kV-CBCT online adaptive radiation therapy and initial first year experiences. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2023, 24, e13961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huq, M.S.; Fraass, B.A.; Dunscombe, P.B.; Gibbons Jr, J.P.; Ibbott, G.S.; Mundt, A.J.; Mutic, S.; Palta, J.R.; Rath, F.; Thomadsen, B.R. The report of Task Group 100 of the AAPM: Application of risk analysis methods to radiation therapy quality management. Med. Phys. 2016, 43, 4209–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Iqbal, Z.; Parsons, D.; Salazar, D.; Visak, J.; Zhong, X.; Wang, S.; Stanley, D.; Godley, A.; Cai, B. Mitigating Risks in Cone Beam Computed Tomography Guided Online Adaptive Radiation Therapy: A Preventative Reference Planning Review Approach. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 9, 101614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-F.; Price, M.J.; Elliston, C.D.; Munbodh, R.; Spina, C.S.; Horowitz, D.P.; Kachnic, L.A. Enhancing Safety in AI-Driven Cone Beam CT-based Online Adaptive Radiation Therapy: Development and Implementation of an Interdisciplinary Workflow. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 9, 101399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegener, S.; Exner, F.; Weick, S.; Stark, S.; Hutzel, H.; Lutyj, P.; Tamihardja, J.; Razinskas, G. Prospective risk analysis of the online-adaptive artificial intelligence-driven workflow using the Ethos treatment system. Z. Med. Phys. 2024, 34, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegener, S.; Käthner, P.; Weick, S.; Schindhelm, R.; Breuer, K.; Stark, S.; Hutzel, H.; Lutyj, P.; Zimmermann, M.; Tamihardja, J. Re-evaluation of the prospective risk analysis for artificial-intelligence driven cone beam computed tomography-based online adaptive radiotherapy after one year of clinical experience. Z. Med. Phys. 2024, 34, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.M.; Byrne, M.; van Dieren, E.; Zwart, L.; Ray, X.; Harms, J.; Aland, T.; Stanley, D.; Pawlicki, T. Safety and Efficiency Analysis of Operational Decision-Making During Cone Beam Computed Tomography-Based Online Adaptive Radiation Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2024, 119, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemus, O.M.D.; Tanny, S.; Cummings, M.; Webster, M.; Wancura, J.; Jung, H.; Zhou, Y.; Yoon, J.; Pacella, M.; Zheng, D. Influence of air mapping errors on the dosimetric accuracy of prostate CBCT-guided online adaptive radiation therapy. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2023, 24, e14057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanny, S.; Dona Lemus, O.M.; Wancura, J.; Sperling, N.; Webster, M.; Jung, H.; Zhou, Y.; Li, F.; Yoon, J.; Podgorsak, A. MU variability in CBCT-guided online adaptive radiation therapy. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2024, 25, e14440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

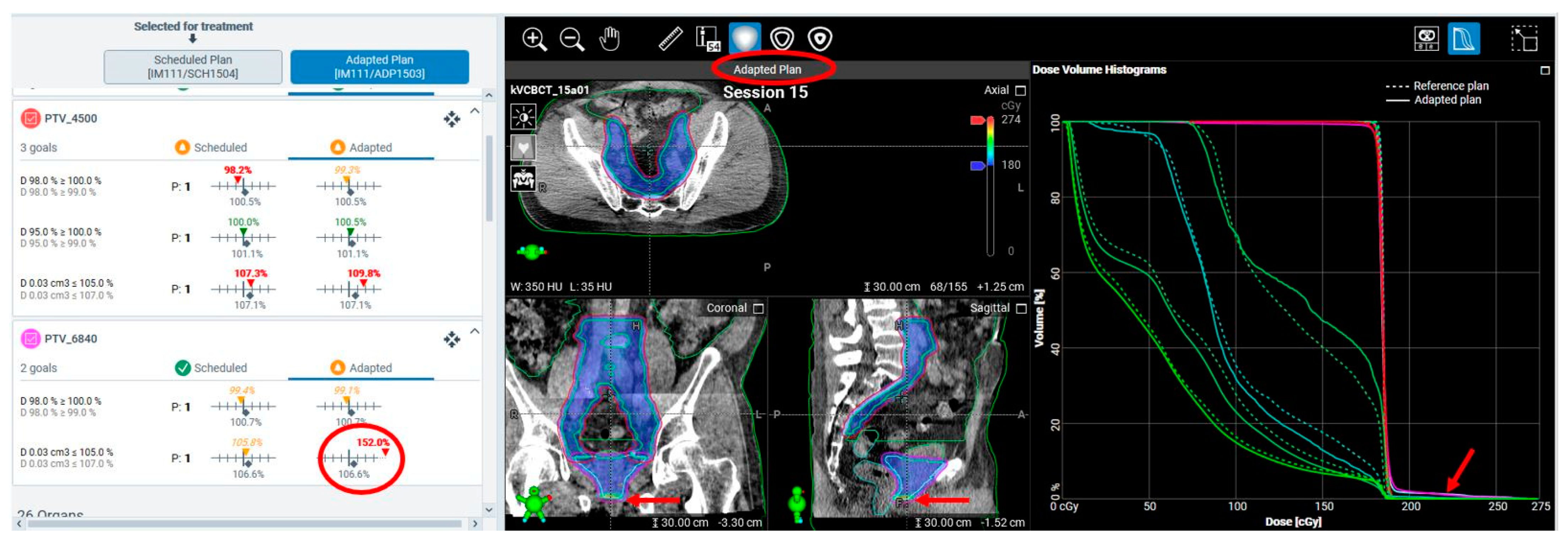
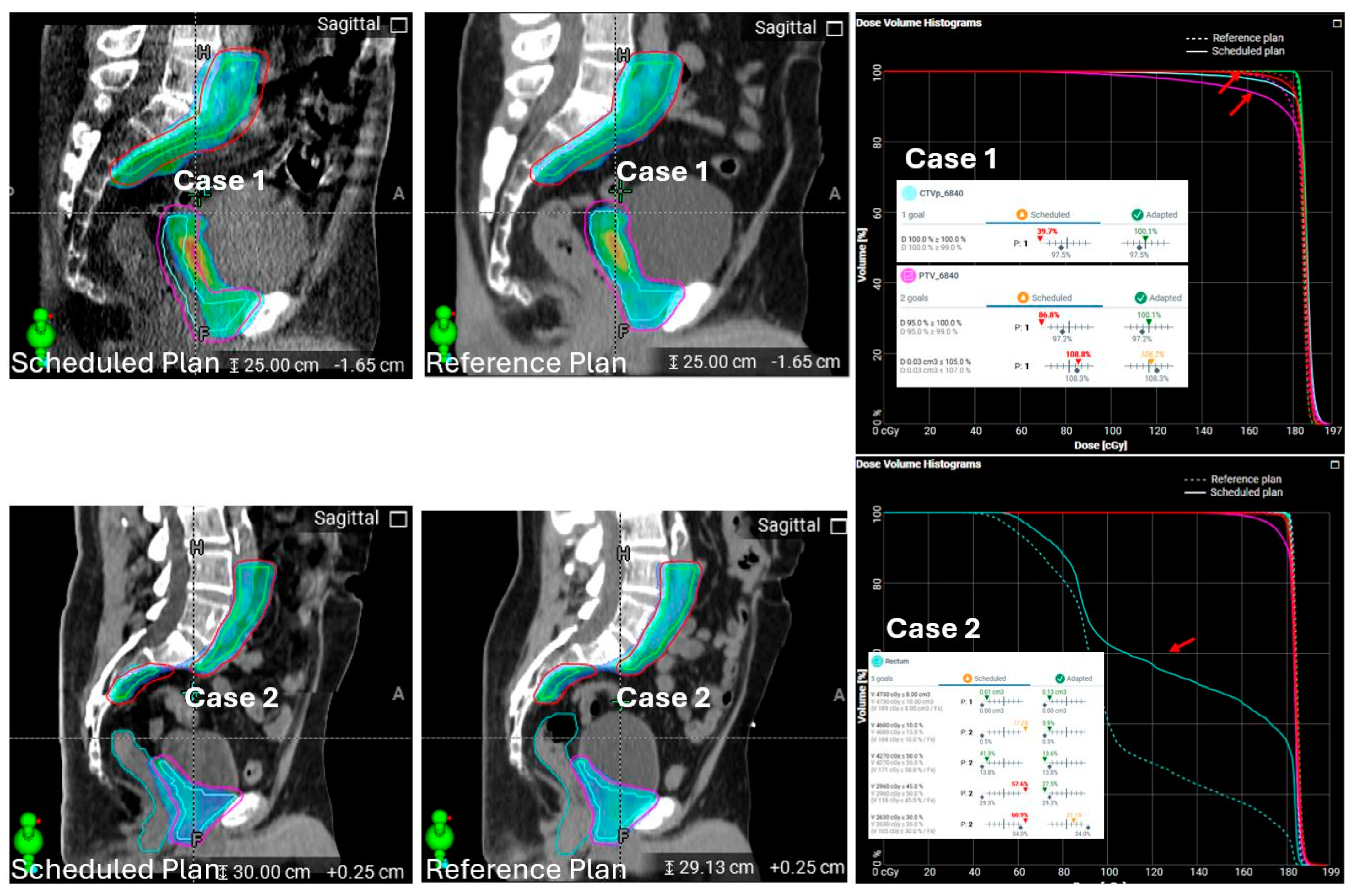
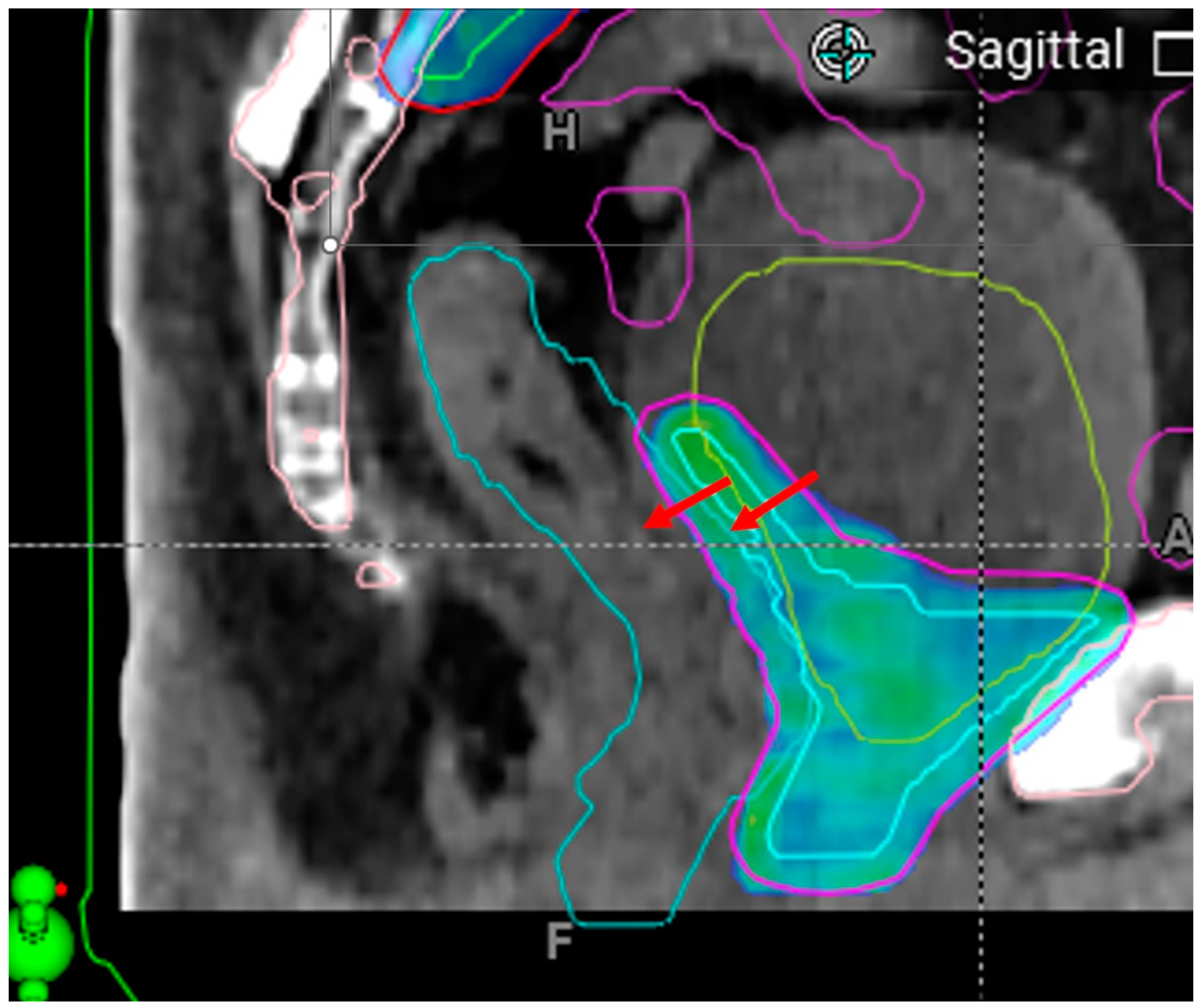

| Type | Dose and Fractionation | Number of Cases (% of Total Cases) |
|---|---|---|
| Prostate bed, conventional | 1.8 Gy * 38 fx (25 fx, phase 1 to prostate bed + LN% & 13 fx, phase 2 to prostate bed) | 30 (60%) |
| Pelvic SBRT (LN, intact prostate, prostate bed) | 5, 7, or 7.25 Gy * 5 fx | 9 (18%) |
| Intact prostate, conventional # | 1.8 or 2 Gy * 20, 28, or 39 fx | 5 (10%) |
| Other pelvis (bladder, rectum, etc.) | 1.8, 2, or 2.75 Gy * 20, 27, or 30 fx | 6 (12%) |
| FM | Frequency Before Intervention/Prevention | Frequency After Intervention/Prevention |
|---|---|---|
| Severe intrafractional rectal gas change | 1% (5 instances) | 0.6% (2 instances) |
| Patient unable to hold the bladder | 0.3% (2 instances) | 0% (0 instance) |
| Process termination from contour extending beyond the body | 1% (2 instances) | 0% (0 instance) |
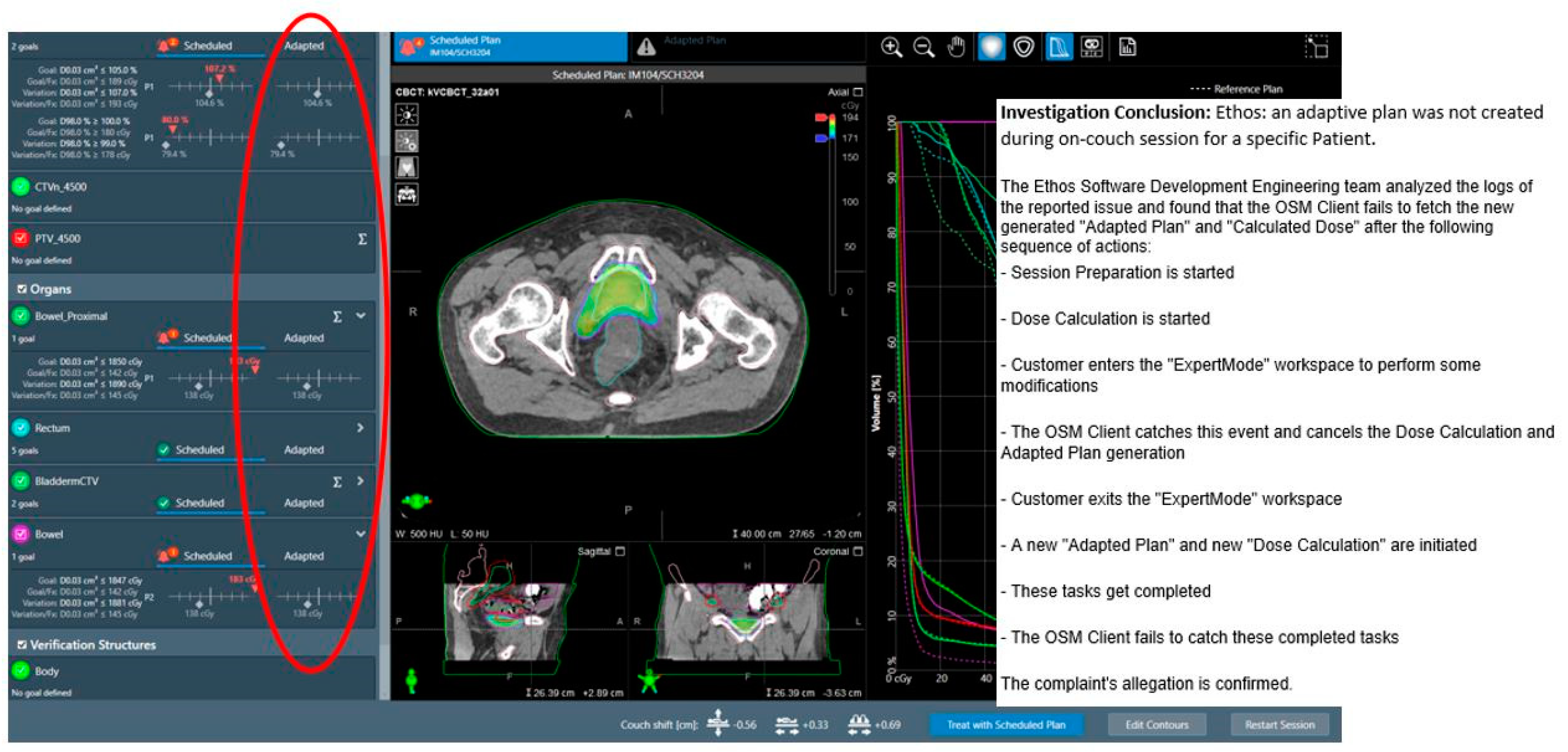
| Adaptive plan unavailability due to internal software communication issues | 0.1% (1 instance) | N/A |
| FM Category | FM | Frequency Before Intervention/Prevention | Frequency After Intervention/Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| System-driven | Failure of automated Boolean structure propagation in oART planning | 10% (3 plans) | 0% |
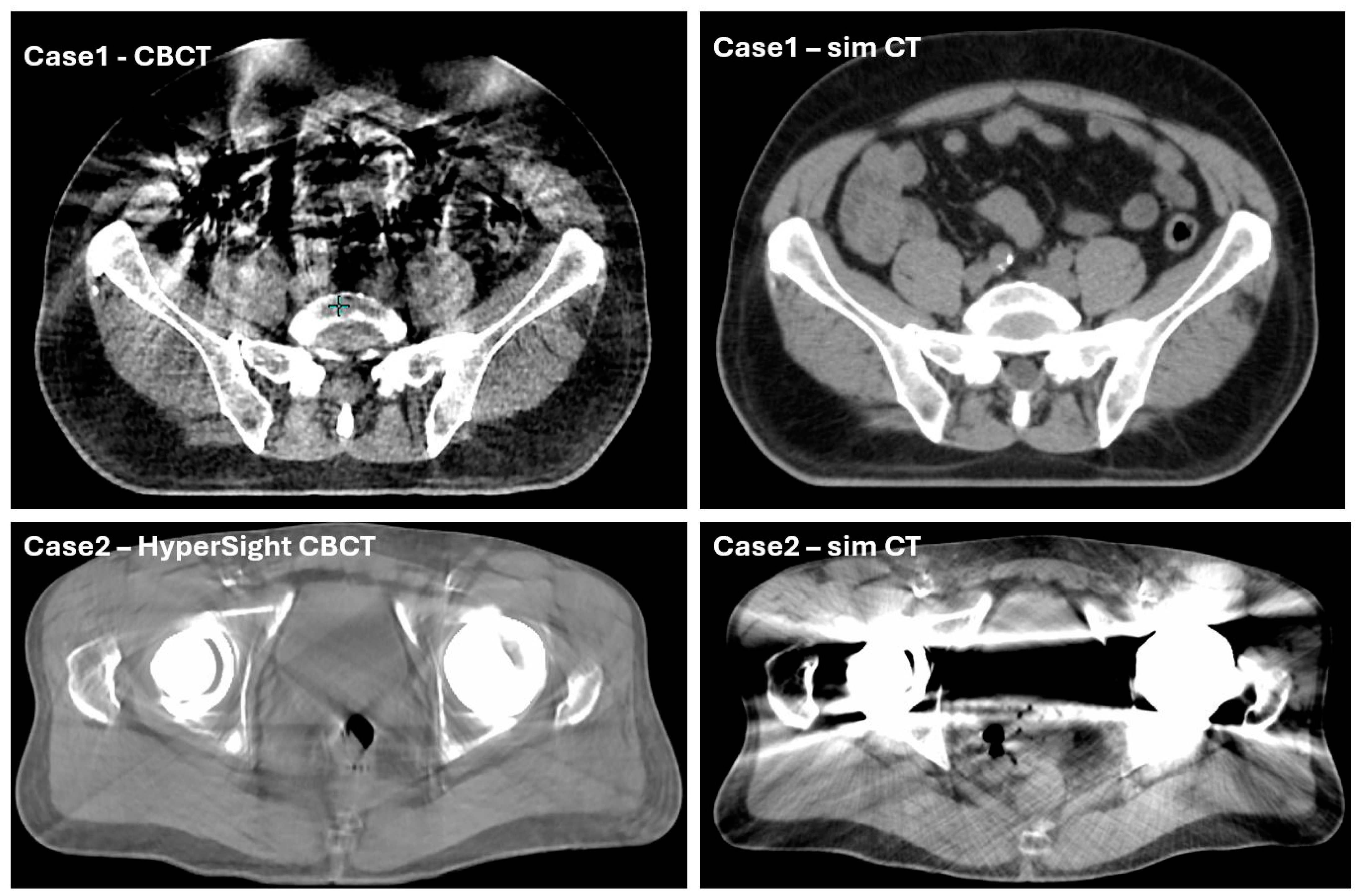
| Reduced auto-contouring accuracy due to imaging artifacts | 20% estimated with varying severity, not quantified | <5% estimated, not quantified | |
| Inaccurate air mapping from CBCT to sCT | 20% estimated with varying severity, not quantified | 10% estimated, not quantified | |
| Extreme adaptive plan hotspots due to limited maximum MLC field size | Two instances * | Never occurred after intervention | |
| Streamlined alignment process causing large dose-coverage or dose-sparing discrepancies on the scheduled plan | 4% | NA | |
| Patient-driven | Inadequate on-couch anatomy imaged, leading to workflow interruption | 0.2% | 0% |
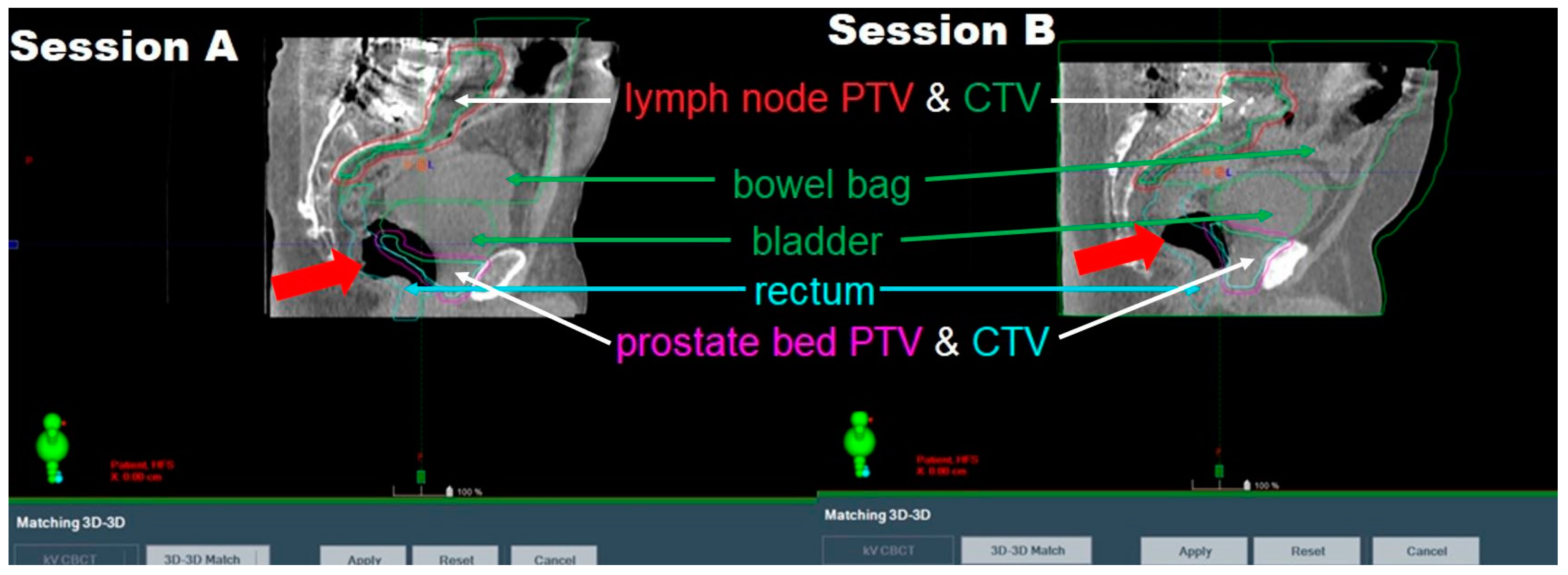
| Intrafractional anatomy changes affecting treatment dose | 40% estimated with varying severity, not quantified | 30% estimated, not quantified | |
| Treatment planning and execution failures | Manual contour selection mismatch | 1 instance caught at checking | 0 |
| On-couch optimization structure generation | 3% | 1% | |
| Monitor unit (MU) deviations in adaptive plan compared to reference plans | 16% with >10% MU deviation in v1.0 and 1.1 | Stopped using it as a metric for ART plan assessment | |
| Unacceptable hotspots in adaptive plans due to planning system variability | 10% estimated, not quantified | 5% estimated, not quantified | |
| Limitations of QA software logfile analysis in handling treatment delivery interruptions | 0.2% | NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, D.; Cummings, M.; Zhang, H.; Podgorsak, A.; Li, F.; Dona Lemus, O.; Webster, M.; Joyce, N.; Hagenbach, E.; Bylund, K.; et al. Clinical Practice-Based Failure Modes and Root Cause Analysis of Cone Beam CT-Guided Online Adaptive Radiotherapy of the Pelvis. Cancers 2025, 17, 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091462
Zheng D, Cummings M, Zhang H, Podgorsak A, Li F, Dona Lemus O, Webster M, Joyce N, Hagenbach E, Bylund K, et al. Clinical Practice-Based Failure Modes and Root Cause Analysis of Cone Beam CT-Guided Online Adaptive Radiotherapy of the Pelvis. Cancers. 2025; 17(9):1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091462
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Dandan, Michael Cummings, Hong Zhang, Alexander Podgorsak, Fiona Li, Olga Dona Lemus, Matthew Webster, Neil Joyce, Erika Hagenbach, Kevin Bylund, and et al. 2025. "Clinical Practice-Based Failure Modes and Root Cause Analysis of Cone Beam CT-Guided Online Adaptive Radiotherapy of the Pelvis" Cancers 17, no. 9: 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091462
APA StyleZheng, D., Cummings, M., Zhang, H., Podgorsak, A., Li, F., Dona Lemus, O., Webster, M., Joyce, N., Hagenbach, E., Bylund, K., Qiu, H., Pacella, M., Chen, Y., & Tanny, S. (2025). Clinical Practice-Based Failure Modes and Root Cause Analysis of Cone Beam CT-Guided Online Adaptive Radiotherapy of the Pelvis. Cancers, 17(9), 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091462





