Alterations of MicroRNAs in Solid Cancers and Their Prognostic Value
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Evolution, Biogenesis, Function and Nomenclature
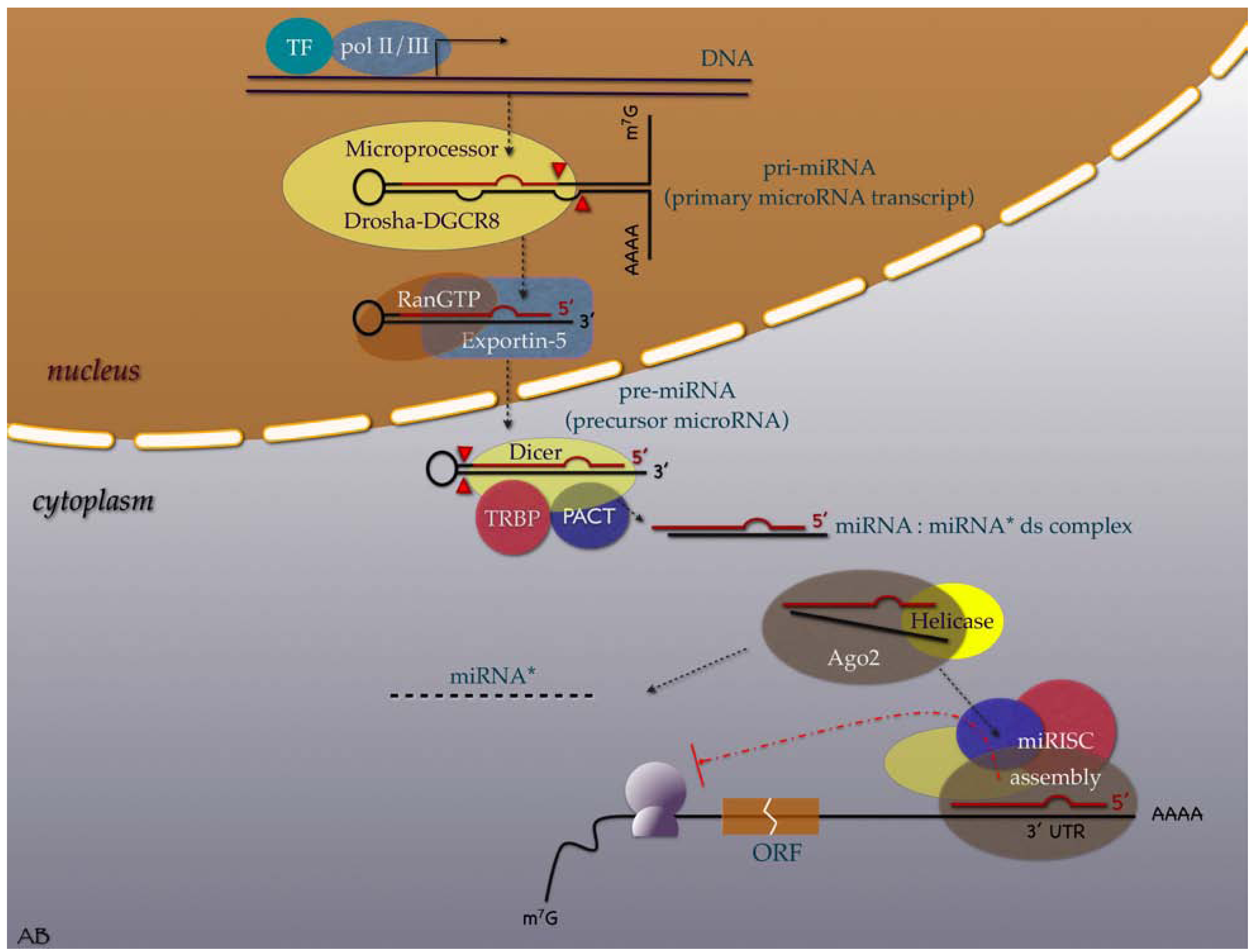
3. MiRNAs in the Cancer Research Scene
4. Deregulated miRNA Expression in Human Cancers
4.1. Cancers of the Respiratory System
Lung Cancer
4.2. Breast Cancer
4.3. Cancers of the Genital System
4.3.1. Ovarian Cancer
4.3.2. Germ Cell Cancer
4.3.3. Prostate Cancer
4.4. Cancers of the Endocrine System
4.4.1. Pituitary Cancer
4.4.2. Thyroid Cancer
4.5. Cancers of the Digestive System
4.5.1. Hepatocellular Cancer
4.5.2. Colorectal Cancer
4.5.3. Gastric Cancer
4.5.4. Pancreatic Cancer
4.6. Cancers of Central Nervous System
4.7. Head and Neck Cancers
4.8. Urinary System Cancers
4.8.1. Kidney Cancer
4.8.2. Bladder Cancer
4.9. Sarcomas
4.9.1. Soft Tissue Sarcomas
4.9.2. Bone Sarcomas
4.10. Skin Cancers
5. Identified Prognostic miRNA

5.1. Suppressed/Missing miRNAs as Biomarkers of Poor Cancer Prognosis
5.2. Overexpressed miRNAs as Biomarkers of Poor Cancer Prognosis
6. Cancer Predisposition miRNA Polymorphisms
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgment
References
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambros, V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Hannon, G.J. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandiera, S.; Hatem, E.; Lyonnet, S.; Henrion-Caude, A. microRNAs in diseases: from candidate to modifier genes. Clin. Genet. 2010, 77, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, M.; Condorelli, G.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNAs in diseases and drug response. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2008, 8, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, N.; Aharonov, R.; Meiri, E.; Rosenwald, S.; Spector, Y.; Zepeniuk, M.; Benjamin, H.; Shabes, N.; Tabak, S.; Levy, A.; Lebanony, D.; Goren, Y.; Silberschein, E.; Targan, N.; Ben-Ari, A.; Gilad, S.; Sion-Vardy, N.; Tobar, A.; Feinmesser, M.; Kharenko, O.; Nativ, O.; Nass, D.; Perelman, M.; Yosepovich, A.; Shalmon, B.; Polak-Charcon, S.; Fridman, E.; Avniel, A.; Bentwich, I.; Bentwich, Z.; Cohen, D.; Chajut, A.; Barshack, I. MicroRNAs accurately identify cancer tissue origin. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Hao, Y.; Juan, L.; Teng, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y. miR2Disease: a manually curated database for microRNA deregulation in human disease. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calin, G.A.; Sevignani, C.; Dumitru, C.D.; Hyslop, T.; Noch, E.; Yendamuri, S.; Shimizu, M.; Rattan, S.; Bullrich, F.; Negrini, M.; Croce, C.M. Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2999–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimson, A.; Srivastava, M.; Fahey, B.; Woodcroft, B.J.; Chiang, H.R.; King, N.; Degnan, B.M.; Rokhsar, D.S.; Bartel, D.P. Early origins and evolution of microRNAs and Piwi-interacting RNAs in animals. Nature 2008, 455, 1193–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, F.; Raible, F.; Tomer, R.; Simakov, O.; Trachana, K.; Klaus, S.; Snyman, H.; Hannon, G.J.; Bork, P.; Arendt, D. Ancient animal microRNAs and the evolution of tissue identity. Nature 2010, 463, 1084–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Jeon, K.; Lee, J.T.; Kim, S.; Kim, V.N. MicroRNA maturation: stepwise processing and subcellular localization. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 4663–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, M.; Han, J.; Yeom, K.H.; Lee, S.; Baek, S.H.; Kim, V.N. MicroRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 4051–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchert, G.M.; Lanier, W.; Davidson, B.L. RNA polymerase III transcribes human microRNAs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2006, 13, 1097–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Ahn, C.; Han, J.; Choi, H.; Kim, J.; Yim, J.; Lee, J.; Provost, P.; Radmark, O.; Kim, S.; Kim, V.N. The nuclear RNase III Drosha initiates microRNA processing. Nature 2003, 425, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, E.; Guttinger, S.; Calado, A.; Dahlberg, J.E.; Kutay, U. Nuclear export of microRNA precursors. Science 2004, 303, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, R.I.; Chendrimada, T.P.; Cooch, N.; Shiekhattar, R. Human RISC couples microRNA biogenesis and posttranscriptional gene silencing. Cell 2005, 123, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matranga, C.; Tomari, Y.; Shin, C.; Bartel, D.P.; Zamore, P.D. Passenger-strand cleavage facilitates assembly of siRNA into Ago2-containing RNAi enzyme complexes. Cell 2005, 123, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, S.; Qi, H.H.; Chowdhury, D.; Shi, Y.; Novina, C.D. Distinct passenger strand and mRNA cleavage activities of human Argonaute proteins. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourelatos, Z. Small RNAs: The seeds of silence. Nature 2008, 455, 44–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, B.P.; Shih, I.H.; Jones-Rhoades, M.W.; Bartel, D.P.; Burge, C.B. Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell 2003, 115, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutvagner, G.; Zamore, P.D. A microRNA in a multiple-turnover RNAi enzyme complex. Science 2002, 297, 2056–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths-Jones, S.; Grocock, R.J.; van Dongen, S.; Bateman, A.; Enright, A.J. miRBase: microRNA sequences, targets and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Dutta, A. MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2009, 4, 199–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karube, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Osada, H.; Tomida, S.; Tatematsu, Y.; Yanagisawa, K.; Yatabe, Y.; Takamizawa, J.; Miyoshi, S.; Mitsudomi, T.; Takahashi, T. Reduced expression of Dicer associated with poor prognosis in lung cancer patients. Cancer Sci. 2005, 96, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugito, N.; Ishiguro, H.; Kuwabara, Y.; Kimura, M.; Mitsui, A.; Kurehara, H.; Ando, T.; Mori, R.; Takashima, N.; Ogawa, R.; Fujii, Y. RNASEN regulates cell proliferation and affects survival in esophageal cancer patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 7322–7328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lujambio, A.; Ropero, S.; Ballestar, E.; Fraga, M.F.; Cerrato, C.; Setien, F.; Casado, S.; Suarez-Gauthier, A.; Sanchez-Cespedes, M.; Git, A.; Spiteri, I.; Das, P.P.; Caldas, C.; Miska, E.; Esteller, M. Genetic unmasking of an epigenetically silenced microRNA in human cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 1424–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Liang, G.; Egger, G.; Friedman, J.M.; Chuang, J.C.; Coetzee, G.A.; Jones, P.A. Specific activation of microRNA-127 with downregulation of the proto-oncogene BCL6 by chromatin-modifying drugs in human cancer cells. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.C.; Yu, D.; Lee, Y.S.; Wentzel, E.A.; Arking, D.E.; West, K.M.; Dang, C.V.; Thomas-Tikhonenko, A.; Mendell, J.T. Widespread microRNA repression by Myc contributes to tumorigenesis. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Donnell, K.A.; Wentzel, E.A.; Zeller, K.I.; Dang, C.V.; Mendell, J.T. c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1 expression. Nature 2005, 435, 839–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, N.; Naraba, H. Polymorphisms in human pre-miRNAs. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 331, 1439–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, C.; Hemann, M.T.; Bartel, D.P. Disrupting the pairing between let-7 and Hmga2 enhances oncogenic transformation. Science 2007, 315, 1576–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Pan, X.; Cobb, G.P.; Anderson, T.A. microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev. Biol. 2007, 302, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volinia, S.; Calin, G.A.; Liu, C.G.; Ambs, S.; Cimmino, A.; Petrocca, F.; Visone, R.; Iorio, M.; Roldo, C.; Ferracin, M.; Prueitt, R.L.; Yanaihara, N.; Lanza, G.; Scarpa, A.; Vecchione, A.; Negrini, M.; Harris, C.C.; Croce, C.M. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2257–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorio, M.V.; Visone, R.; Di Leva, G.; Donati, V.; Petrocca, F.; Casalini, P.; Taccioli, C.; Volinia, S.; Liu, C.G.; Alder, H.; Calin, G.A.; Menard, S.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA signatures in human ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 8699–8707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Henson, R.; Lang, M.; Wehbe, H.; Maheshwari, S.; Mendell, J.T.; Jiang, J.; Schmittgen, T.D.; Patel, T. Involvement of human micro-RNA in growth and response to chemotherapy in human cholangiocarcinoma cell lines. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 2113–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.A.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Kosik, K.S. MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 6029–6033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamichi, N.; Shimomura, R.; Inada, K.; Sakurai, K.; Haraguchi, T.; Ozaki, Y.; Fujita, S.; Mizutani, T.; Furukawa, C.; Fujishiro, M.; Ichinose, M.; Shiogama, K.; Tsutsumi, Y.; Omata, M.; Iba, H. Locked nucleic acid in situ hybridization analysis of miR-21 expression during colorectal cancer development. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 4009–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Henson, R.; Wehbe-Janek, H.; Ghoshal, K.; Jacob, S.T.; Patel, T. MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimmino, A.; Calin, G.A.; Fabbri, M.; Iorio, M.V.; Ferracin, M.; Shimizu, M.; Wojcik, S.E.; Aqeilan, R.I.; Zupo, S.; Dono, M.; Rassenti, L.; Alder, H.; Volinia, S.; Liu, C.G.; Kipps, T.J.; Negrini, M.; Croce, C.M. miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13944–13949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturini, L.; Battmer, K.; Castoldi, M.; Schultheis, B.; Hochhaus, A.; Muckenthaler, M.U.; Ganser, A.; Eder, M.; Scherr, M. Expression of the miR-17-92 polycistron in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) CD34+ cells. Blood 2007, 109, 4399–4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazawa, H.; Tsuchiya, N.; Izumiya, M.; Nakagama, H. Tumor-suppressive miR-34a induces senescence-like growth arrest through modulation of the E2F pathway in human colon cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15472–15477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, C.; Chen, Y.; Stallings, R.L. MicroRNA-34a functions as a potential tumor suppressor by inducing apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells. Oncogene 2007, 26, 5017–5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodygin, D.; Tarasov, V.; Epanchintsev, A.; Berking, C.; Knyazeva, T.; Korner, H.; Knyazev, P.; Diebold, J.; Hermeking, H. Inactivation of miR-34a by aberrant CpG methylation in multiple types of cancer. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 2591–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrini, M.; Calin, G.A. Breast cancer metastasis: a microRNA story. Breast Cancer Res. 2008, 10, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Weinberg, R.A. Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast cancer. Nature 2007, 449, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leva, G.; Gasparini, P.; Piovan, C.; Ngankeu, A.; Garofalo, M.; Taccioli, C.; Iorio, M.V.; Li, M.; Volinia, S.; Alder, H.; Nakamura, T.; Nuovo, G.; Liu, Y.; Nephew, K.P.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA cluster 221–222 and estrogen receptor alpha interactions in breast cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2010, 102, 706–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krutzfeldt, J.; Rajewsky, N.; Braich, R.; Rajeev, K.G.; Tuschl, T.; Manoharan, M.; Stoffel, M. Silencing of microRNAs in vivo with 'antagomirs'. Nature 2005, 438, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, L.; Fiori, M.E.; Albini, S.; Cifaldi, L.; Giovinazzi, S.; Forloni, M.; Boldrini, R.; Donfrancesco, A.; Federici, V.; Giacomini, P.; Peschle, C.; Fruci, D. Antagomir-17-5p abolishes the growth of therapy-resistant neuroblastoma through p21 and BIM. PLoS One 2008, 3, e2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Reinhardt, F.; Pan, E.; Soutschek, J.; Bhat, B.; Marcusson, E.G.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Bell, G.W.; Weinberg, R.A. Therapeutic silencing of miR-10b inhibits metastasis in a mouse mammary tumor model. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 341–347. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, W.; Zhao, J.J.; He, L.; Cheng, J.Q. Strategies for profiling microRNA expression. J. Cell Physiol. 2009, 218, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.G.; Calin, G.A.; Volinia, S.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA expression profiling using microarrays. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 563–578. [Google Scholar]
- Benes, V.; Castoldi, M. Expression profiling of microRNA using real-time quantitative PCR, how to use it and what is available. Methods 2010, 50, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gelfond, J.A.; McManus, L.M.; Shireman, P.K. Reproducibility of quantitative RT-PCR array in miRNA expression profiling and comparison with microarray analysis. BMC Genomics 2009, 10, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.X.; Wilfred, B.R.; Baldwin, D.A.; Isett, R.B.; Ren, N.; Stromberg, A.; Nelson, P.T. Focus on RNA isolation: obtaining RNA for microRNA (miRNA) expression profiling analyses of neural tissue. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1779, 749–757. [Google Scholar]
- Lerman, M.I.; Minna, J.D. The 630-kb lung cancer homozygous deletion region on human chromosome 3p21.3: identification and evaluation of the resident candidate tumor suppressor genes. The International Lung Cancer Chromosome 3p21.3 Tumor Suppressor Gene Consortium. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 6116–6133. [Google Scholar]
- Landi, M.T.; Zhao, Y.; Rotunno, M.; Koshiol, J.; Liu, H.; Bergen, A.W.; Rubagotti, M.; Goldstein, A.M.; Linnoila, I.; Marincola, F.M.; Tucker, M.A.; Bertazzi, P.A.; Pesatori, A.C.; Caporaso, N.E.; McShane, L.M.; Wang, E. MicroRNA expression differentiates histology and predicts survival of lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamizawa, J.; Konishi, H.; Yanagisawa, K.; Tomida, S.; Osada, H.; Endoh, H.; Harano, T.; Yatabe, Y.; Nagino, M.; Nimura, Y.; Mitsudomi, T.; Takahashi, T. Reduced expression of the let-7 microRNAs in human lung cancers in association with shortened postoperative survival. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 3753–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.M.; Grosshans, H.; Shingara, J.; Byrom, M.; Jarvis, R.; Cheng, A.; Labourier, E.; Reinert, K.L.; Brown, D.; Slack, F.J. RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell 2005, 120, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.S.; Erkeland, S.J.; Pester, R.E.; Chen, C.Y.; Ebert, M.S.; Sharp, P.A.; Jacks, T. Suppression of non-small cell lung tumor development by the let-7 microRNA family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3903–3908. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, G.J.; Bemis, L.T.; Nakajima, E.; Sugita, M.; Birks, D.K.; Robinson, W.A.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Bunn, P.A., Jr.; Haney, J.; Helfrich, B.A.; Kato, H.; Hirsch, F.R.; Franklin, W.A. EGFR regulation by microRNA in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response and survival to gefitinib and EGFR expression in cell lines. Ann. Oncol. 2008, 19, 1053–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, M.; Garzon, R.; Cimmino, A.; Liu, Z.; Zanesi, N.; Callegari, E.; Liu, S.; Alder, H.; Costinean, S.; Fernandez-Cymering, C.; Volinia, S.; Guler, G.; Morrison, C.D.; Chan, K.K.; Marcucci, G.; Calin, G.A.; Huebner, K.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA-29 family reverts aberrant methylation in lung cancer by targeting DNA methyltransferases 3A and 3B. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15805–15810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.L.; Chen, H.Y.; Chang, G.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Chen, H.W.; Singh, S.; Cheng, C.L.; Yu, C.J.; Lee, Y.C.; Chen, H.S.; Su, T.J.; Chiang, C.C.; Li, H.N.; Hong, Q.S.; Su, H.Y.; Chen, C.C.; Chen, W.J.; Liu, C.C.; Chan, W.K.; Chen, W.J.; Li, K.C.; Chen, J.J.; Yang, P.C. MicroRNA signature predicts survival and relapse in lung cancer. Cancer Cell 2008, 13, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashita, Y.; Osada, H.; Tatematsu, Y.; Yamada, H.; Yanagisawa, K.; Tomida, S.; Yatabe, Y.; Kawahara, K.; Sekido, Y.; Takahashi, T. A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17-92, is overexpressed in human lung cancers and enhances cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 9628–9632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, B.D.; Furneaux, H.; White, B.A. The micro-ribonucleic acid (miRNA) miR-206 targets the human estrogen receptor-alpha (ERalpha) and represses ERalpha messenger RNA and protein expression in breast cancer cell lines. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007, 21, 1132–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, N.; Toyama, T.; Sugiura, H.; Fujii, Y.; Yamashita, H. miR-206 Expression is down-regulated in estrogen receptor alpha-positive human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 5004–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorio, M.V.; Ferracin, M.; Liu, C.G.; Veronese, A.; Spizzo, R.; Sabbioni, S.; Magri, E.; Pedriali, M.; Fabbri, M.; Campiglio, M.; Menard, S.; Palazzo, J.P.; Rosenberg, A.; Musiani, P.; Volinia, S.; Nenci, I.; Calin, G.A.; Querzoli, P.; Negrini, M.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 7065–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Gumireddy, K.; Schrier, M.; le Sage, C.; Nagel, R.; Nair, S.; Egan, D.A.; Li, A.; Huang, G.; Klein-Szanto, A.J.; Gimotty, P.A.; Katsaros, D.; Coukos, G.; Zhang, L.; Pure, E.; Agami, R. The microRNAs miR-373 and miR-520c promote tumour invasion and metastasis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, L.B.; Christoffersen, N.R.; Jacobsen, A.; Lindow, M.; Krogh, A.; Lund, A.H. Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is an important functional target of the microRNA miR-21 in breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Si, M.L.; Wu, H.; Mo, Y.Y. MicroRNA-21 targets the tumor suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1). J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 14328–14336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, M.L.; Zhu, S.; Wu, H.; Lu, Z.; Wu, F.; Mo, Y.Y. miR-21-mediated tumor growth. Oncogene 2007, 26, 2799–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, Y.; Nakajima, M.; Takagi, S.; Taniya, T.; Yokoi, T. MicroRNA regulates the expression of human cytochrome P450 1B1. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 9090–9098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.; Kuo, M.T.; Saunders, G.F. Mir-17-5p regulates breast cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting translation of AIB1 mRNA. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 26, 8191–8201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louie, M.C.; Zou, J.X.; Rabinovich, A.; Chen, H.W. ACTR/AIB1 functions as an E2F1 coactivator to promote breast cancer cell proliferation and antiestrogen resistance. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 24, 5157–5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzick, S.L.; Kononen, J.; Walker, R.L.; Azorsa, D.O.; Tanner, M.M.; Guan, X.Y.; Sauter, G.; Kallioniemi, O.P.; Trent, J.M.; Meltzer, P.S. AIB1, a steroid receptor coactivator amplified in breast and ovarian cancer. Science 1997, 277, 965–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioachim, E.; Charchanti, A.; Briasoulis, E.; Karavasilis, V.; Tsanou, H.; Arvanitis, D.L.; Agnantis, N.J.; Pavlidis, N. Immunohistochemical expression of extracellular matrix components tenascin, fibronectin, collagen type IV and laminin in breast cancer: their prognostic value and role in tumour invasion and progression. Eur. J. Cancer 2002, 38, 2362–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavazoie, S.F.; Alarcon, C.; Oskarsson, T.; Padua, D.; Wang, Q.; Bos, P.D.; Gerald, W.L.; Massague, J. Endogenous human microRNAs that suppress breast cancer metastasis. Nature 2008, 451, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, R.D.; Murray, M.J.; Saini, H.K.; van Dongen, S.; Abreu-Goodger, C.; Muralidhar, B.; Pett, M.R.; Thornton, C.M.; Nicholson, J.C.; Enright, A.J.; Coleman, N. Malignant germ cell tumors display common microRNA profiles resulting in global changes in expression of messenger RNA targets. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 2911–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorhoeve, P.M.; le Sage, C.; Schrier, M.; Gillis, A.J.; Stoop, H.; Nagel, R.; Liu, Y.P.; van Duijse, J.; Drost, J.; Griekspoor, A.; Zlotorynski, E.; Yabuta, N.; De Vita, G.; Nojima, H.; Looijenga, L.H.; Agami, R. A genetic screen implicates miRNA-372 and miRNA-373 as oncogenes in testicular germ cell tumors. Cell 2006, 124, 1169–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Looijenga, L.H.; Gillis, A.J.; Stoop, H.; Hersmus, R.; Oosterhuis, J.W. Relevance of microRNAs in normal and malignant development, including human testicular germ cell tumours. Int. J. Androl. 2007, 30, 304–314; discussion 314–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozen, M.; Creighton, C.J.; Ozdemir, M.; Ittmann, M. Widespread deregulation of microRNA expression in human prostate cancer. Oncogene 2008, 27, 1788–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porkka, K.P.; Pfeiffer, M.J.; Waltering, K.K.; Vessella, R.L.; Tammela, T.L.; Visakorpi, T. MicroRNA expression profiling in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6130–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottoni, A.; Piccin, D.; Tagliati, F.; Luchin, A.; Zatelli, M.C.; degli Uberti, E.C. miR-15a and miR-16-1 down-regulation in pituitary adenomas. J. Cell Physiol. 2005, 204, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, M.P.; Khan, A. Micro-RNAs in thyroid neoplasms: molecular, diagnostic and therapeutic implications. J. Clin. Pathol. 2009, 62, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, S.Y.; Grabellus, F.; Schwertheim, S.; Worm, K.; Broecker-Preuss, M.; Schmid, K.W. Differential miRNA expression profiles in variants of papillary thyroid carcinoma and encapsulated follicular thyroid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Jazdzewski, K.; Li, W.; Liyanarachchi, S.; Nagy, R.; Volinia, S.; Calin, G.A.; Liu, C.G.; Franssila, K.; Suster, S.; Kloos, R.T.; Croce, C.M.; de la Chapelle, A. The role of microRNA genes in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 19075–19080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Yasuda, T.; Saigo, K.; Urashima, T.; Toyoda, H.; Okanoue, T.; Shimotohno, K. Comprehensive analysis of microRNA expression patterns in hepatocellular carcinoma and non-tumorous tissues. Oncogene 2006, 25, 2537–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladeiro, Y.; Couchy, G.; Balabaud, C.; Bioulac-Sage, P.; Pelletier, L.; Rebouissou, S.; Zucman-Rossi, J. MicroRNA profiling in hepatocellular tumors is associated with clinical features and oncogene/tumor suppressor gene mutations. Hepatology 2008, 47, 1955–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Xie, L.; He, X.; Li, J.; Tu, K.; Wei, L.; Wu, J.; Guo, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhang, P.; Pan, Z.; Hu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, H.; Jiang, G.; Chen, T.; Wang, J.; Zheng, S.; Cheng, J.; Wan, D.; Yang, S.; Li, Y.; Gu, J. Diagnostic and prognostic implications of microRNAs in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 1616–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Gusev, Y.; Aderca, I.; Mettler, T.A.; Nagorney, D.M.; Brackett, D.J.; Roberts, L.R.; Schmittgen, T.D. Association of MicroRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinomas with hepatitis infection, cirrhosis, and patient survival. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Yang, J.R.; Xu, T.; Huang, J.; Xu, L.; Yuan, Y.; Zhuang, S.M. MicroRNA-101, down-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma, promotes apoptosis and suppresses tumorigenicity. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornari, F.; Gramantieri, L.; Ferracin, M.; Veronese, A.; Sabbioni, S.; Calin, G.A.; Grazi, G.L.; Giovannini, C.; Croce, C.M.; Bolondi, L.; Negrini, M. MiR-221 controls CDKN1C/p57 and CDKN1B/p27 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5651–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akao, Y.; Nakagawa, Y.; Naoe, T. let-7 microRNA functions as a potential growth suppressor in human colon cancer cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 903–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, M.Z.; SM, O.C.; van Holst Pellekaan, N.G.; Young, G.P.; James, R.J. Reduced accumulation of specific microRNAs in colorectal neoplasia. Mol. Cancer Res. 2003, 1, 882–891. [Google Scholar]
- Schetter, A.J.; Leung, S.Y.; Sohn, J.J.; Zanetti, K.A.; Bowman, E.D.; Yanaihara, N.; Yuen, S.T.; Chan, T.L.; Kwong, D.L.; Au, G.K.; Liu, C.G.; Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M.; Harris, C.C. MicroRNA expression profiles associated with prognosis and therapeutic outcome in colon adenocarcinoma. JAMA 2008, 299, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, R.; le Sage, C.; Diosdado, B.; van der Waal, M.; Oude Vrielink, J.A.; Bolijn, A.; Meijer, G.A.; Agami, R. Regulation of the adenomatous polyposis coli gene by the miR-135 family in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 5795–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.H.; Wu, C.W.; Li, A.F.; Chi, C.W.; Lin, W.C. miR-21 microRNA expression in human gastric carcinomas and its clinical association. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 907–911. [Google Scholar]
- Motoyama, K.; Inoue, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Uetake, H.; Sugihara, K.; Mori, M. Clinical significance of high mobility group A2 in human gastric cancer and its relationship to let-7 microRNA family. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 2334–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, T.; Volinia, S.; Okumura, H.; Shimizu, M.; Taccioli, C.; Rossi, S.; Alder, H.; Liu, C.G.; Oue, N.; Yasui, W.; Yoshida, K.; Sasaki, H.; Nomura, S.; Seto, Y.; Kaminishi, M.; Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. Relation between microRNA expression and progression and prognosis of gastric cancer: a microRNA expression analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujiura, M.; Ichikawa, D.; Komatsu, S.; Shiozaki, A.; Takeshita, H.; Kosuga, T.; Konishi, H.; Morimura, R.; Deguchi, K.; Fujiwara, H.; Okamoto, K.; Otsuji, E. Circulating microRNAs in plasma of patients with gastric cancers. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 1174–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomston, M.; Frankel, W.L.; Petrocca, F.; Volinia, S.; Alder, H.; Hagan, J.P.; Liu, C.G.; Bhatt, D.; Taccioli, C.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA expression patterns to differentiate pancreatic adenocarcinoma from normal pancreas and chronic pancreatitis. JAMA 2007, 297, 1901–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szafranska, A.E.; Davison, T.S.; John, J.; Cannon, T.; Sipos, B.; Maghnouj, A.; Labourier, E.; Hahn, S.A. MicroRNA expression alterations are linked to tumorigenesis and non-neoplastic processes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 2007, 26, 4442–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szafranska, A.E.; Doleshal, M.; Edmunds, H.S.; Gordon, S.; Luttges, J.; Munding, J.B.; Barth, R.J., Jr.; Gutmann, E.J.; Suriawinata, A.A.; Marc Pipas, J.; Tannapfel, A.; Korc, M.; Hahn, S.A.; Labourier, E.; Tsongalis, G.J. Analysis of microRNAs in pancreatic fine-needle aspirates can classify benign and malignant tissues. Clin. Chem. 2008, 54, 1716–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.C.; Kwok, W.K.; Chen, Z.; Ng, H.K. Oncogenic role of microRNAs in brain tumors. Acta Neuropathol. 2009, 117, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, P.T.; Baldwin, D.A.; Kloosterman, W.P.; Kauppinen, S.; Plasterk, R.H.; Mourelatos, Z. RAKE and LNA-ISH reveal microRNA expression and localization in archival human brain. RNA 2006, 12, 187–191. [Google Scholar]
- Childs, G.; Fazzari, M.; Kung, G.; Kawachi, N.; Brandwein-Gensler, M.; McLemore, M.; Chen, Q.; Burk, R.D.; Smith, R.V.; Prystowsky, M.B.; Belbin, T.J.; Schlecht, N.F. Low-level expression of microRNAs let-7d and miR-205 are prognostic markers of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.; McLean, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, C.J.; Thomson, J.M.; O'Brien, C.; Rose, B. MicroRNA expression profiles in head and neck cancer cell lines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 358, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, C.; Norris, K.; Scheper, M.A.; Nikitakis, N.; Sauk, J.J. High mobility group A2 is a target for miRNA-98 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2007, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Getz, G.; Miska, E.A.; Alvarez-Saavedra, E.; Lamb, J.; Peck, D.; Sweet-Cordero, A.; Ebert, B.L.; Mak, R.H.; Ferrando, A.A.; Downing, J.R.; Jacks, T.; Horvitz, H.R.; Golub, T.R. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 2005, 435, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottardo, F.; Liu, C.G.; Ferracin, M.; Calin, G.A.; Fassan, M.; Bassi, P.; Sevignani, C.; Byrne, D.; Negrini, M.; Pagano, F.; Gomella, L.G.; Croce, C.M.; Baffa, R. Micro-RNA profiling in kidney and bladder cancers. Urol. Oncol. 2007, 25, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kort, E.J.; Farber, L.; Tretiakova, M.; Petillo, D.; Furge, K.A.; Yang, X.J.; Cornelius, A.; Teh, B.T. The E2F3-Oncomir-1 axis is activated in Wilms' tumor. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4034–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, H.; He, H.; Tong, W.; Wang, B.; Liao, G.; Chen, Z.; Du, C. Up-regulation of microRNA in bladder tumor tissue is not common. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2010, 42, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarver, A.L.; Phalak, R.; Thayanithy, V.; Subramanian, S. S-MED: sarcoma microRNA expression database. Lab Invest. 2010, 90, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Hara, A.J.; Chugh, P.; Wang, L.; Netto, E.M.; Luz, E.; Harrington, W.J.; Dezube, B.J.; Damania, B.; Dittmer, D.P. Pre-micro RNA signatures delineate stages of endothelial cell transformation in Kaposi sarcoma. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taulli, R.; Bersani, F.; Foglizzo, V.; Linari, A.; Vigna, E.; Ladanyi, M.; Tuschl, T.; Ponzetto, C. The muscle-specific microRNA miR-206 blocks human rhabdomyosarcoma growth in xenotransplanted mice by promoting myogenic differentiation. J. Clin. Invest. 2009, 119, 2366–2378. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, D.; Dong Xda, E.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Lu, C.; Wang, J.; Qu, J.; Tu, L. MicroRNA-1/206 targets c-Met and inhibits rhabdomyosarcoma development. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 29596–29604. [Google Scholar]
- Ciarapica, R.; Russo, G.; Verginelli, F.; Raimondi, L.; Donfrancesco, A.; Rota, R.; Giordano, A. Deregulated expression of miR-26a and Ezh2 in rhabdomyosarcoma. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Garzon, R.; Sun, H.; Ladner, K.J.; Singh, R.; Dahlman, J.; Cheng, A.; Hall, B.M.; Qualman, S.J.; Chandler, D.S.; Croce, C.M.; Guttridge, D.C. NF-kappaB-YY1-miR-29 regulatory circuitry in skeletal myogenesis and rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Cell 2008, 14, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, S.; Lui, W.O.; Lee, C.H.; Espinosa, I.; Nielsen, T.O.; Heinrich, M.C.; Corless, C.L.; Fire, A.Z.; van de Rijn, M. MicroRNA expression signature of human sarcomas. Oncogene 2008, 27, 2015–2026. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.; Xiong, J.; Xu, X.; Lu, W.; Liu, L.; Xiao, D.; Wang, D. Functional elucidation of MiR-34 in osteosarcoma cells and primary tumor samples. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 388, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, D.P. How the NOTCH Pathway Contributes to the Ability of Osteosarcoma Cells to Metastasize. Cancer Treat Res. 2010, 152, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Choy, E.; Nielsen, G.P.; Rosenberg, A.; Iafrate, J.; Yang, C.; Schwab, J.; Mankin, H.; Xavier, R.; Hornicek, F.J. Differential expression of microRNA (miRNA) in chordoma reveals a role for miRNA-1 in Met expression. J. Orthop. Res. 2010, 28, 746–752. [Google Scholar]
- Bemis, L.T.; Chen, R.; Amato, C.M.; Classen, E.H.; Robinson, S.E.; Coffey, D.G.; Erickson, P.F.; Shellman, Y.G.; Robinson, W.A. MicroRNA-137 targets microphthalmia-associated transcription factor in melanoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, M.F.; Hanniford, D.; Menendez, S.; Reavie, L.; Zou, X.; Alvarez-Diaz, S.; Zakrzewski, J.; Blochin, E.; Rose, A.; Bogunovic, D.; Polsky, D.; Wei, J.; Lee, P.; Belitskaya-Levy, I.; Bhardwaj, N.; Osman, I.; Hernando, E. Aberrant miR-182 expression promotes melanoma metastasis by repressing FOXO3 and microphthalmia-associated transcription factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1814–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliore, C.; Petrelli, A.; Ghiso, E.; Corso, S.; Capparuccia, L.; Eramo, A.; Comoglio, P.M.; Giordano, S. MicroRNAs impair MET-mediated invasive growth. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 10128–10136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Zhou, X.; Chen, X.; Hu, D.N.; Dong, X.D.; Wang, J.; Lu, F.; Tu, L.; Qu, J. MicroRNA-34a inhibits uveal melanoma cell proliferation and migration through downregulation of c-Met. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 1559–1565. [Google Scholar]
- Schultz, J.; Lorenz, P.; Gross, G.; Ibrahim, S.; Kunz, M. MicroRNA let-7b targets important cell cycle molecules in malignant melanoma cells and interferes with anchorage-independent growth. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, D.W.; Bosserhoff, A.K. Integrin beta 3 expression is regulated by let-7a miRNA in malignant melanoma. Oncogene 2008, 27, 6698–6706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Feilotter, H.E.; Pare, G.C.; Zhang, X.; Pemberton, J.G.; Garady, C.; Lai, D.; Yang, X.; Tron, V.A. MicroRNA-193b represses cell proliferation and regulates cyclin D1 in melanoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 2520–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, P.S.; Parkin, R.K.; Kroh, E.M.; Fritz, B.R.; Wyman, S.K.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Peterson, A.; Noteboom, J.; O'Briant, K.C.; Allen, A.; Lin, D.W.; Urban, N.; Drescher, C.W.; Knudsen, B.S.; Stirewalt, D.L.; Gentleman, R.; Vessella, R.L.; Nelson, P.S.; Martin, D.B.; Tewari, M. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10513–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calin, G.A.; Ferracin, M.; Cimmino, A.; Di Leva, G.; Shimizu, M.; Wojcik, S.E.; Iorio, M.V.; Visone, R.; Sever, N.I.; Fabbri, M.; Iuliano, R.; Palumbo, T.; Pichiorri, F.; Roldo, C.; Garzon, R.; Sevignani, C.; Rassenti, L.; Alder, H.; Volinia, S.; Liu, C.G.; Kipps, T.J.; Negrini, M.; Croce, C.M. A MicroRNA signature associated with prognosis and progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcucci, G.; Radmacher, M.D.; Maharry, K.; Mrozek, K.; Ruppert, A.S.; Paschka, P.; Vukosavljevic, T.; Whitman, S.P.; Baldus, C.D.; Langer, C.; Liu, C.G.; Carroll, A.J.; Powell, B.L.; Garzon, R.; Croce, C.M.; Kolitz, J.E.; Caligiuri, M.A.; Larson, R.A.; Bloomfield, C.D. MicroRNA expression in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1919–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.S.; Johansson, P.; Chen, Q.R.; Song, Y.K.; Durinck, S.; Wen, X.; Cheuk, A.T.; Smith, M.A.; Houghton, P.; Morton, C.; Khan, J. microRNA profiling identifies cancer-specific and prognostic signatures in pediatric malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5560–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Schwarz, J.K.; Lewis, J.S., Jr.; Huettner, P.C.; Rader, J.S.; Deasy, J.O.; Grigsby, P.W.; Wang, X. A microRNA expression signature for cervical cancer prognosis. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roukos, D.H.; Murray, S.; Briasoulis, E. Molecular genetic tools shape a roadmap towards a more accurate prognostic prediction and personalized management of cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2007, 6, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slack, F.J.; Weidhaas, J.B. MicroRNA in cancer prognosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2720–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanaihara, N.; Caplen, N.; Bowman, E.; Seike, M.; Kumamoto, K.; Yi, M.; Stephens, R.M.; Okamoto, A.; Yokota, J.; Tanaka, T.; Calin, G.A.; Liu, C.G.; Croce, C.M.; Harris, C.C. Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spahn, M.; Kneitz, S.; Scholz, C.J.; Stenger, N.; Rudiger, T.; Strobel, P.; Riedmiller, H.; Kneitz, B. Expression of microRNA-221 is progressively reduced in aggressive prostate cancer and metastasis and predicts clinical recurrence. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 394–403. [Google Scholar]
- Dyrskjot, L.; Ostenfeld, M.S.; Bramsen, J.B.; Silahtaroglu, A.N.; Lamy, P.; Ramanathan, R.; Fristrup, N.; Jensen, J.L.; Andersen, C.L.; Zieger, K.; Kauppinen, S.; Ulhoi, B.P.; Kjems, J.; Borre, M.; Orntoft, T.F. Genomic profiling of microRNAs in bladder cancer: miR-129 is associated with poor outcome and promotes cell death in vitro. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 4851–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, P.S.; Tacon, L.J.; Gill, A.J.; Bambach, C.P.; Sywak, M.S.; Campbell, P.R.; Yeh, M.W.; Wong, S.G.; Clifton-Bligh, R.J.; Robinson, B.G.; Sidhu, S.B. miR-195 and miR-483-5p Identified as Predictors of Poor Prognosis in Adrenocortical Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 7684–7692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulouarn, C.; Factor, V.M.; Andersen, J.B.; Durkin, M.E.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. Loss of miR-122 expression in liver cancer correlates with suppression of the hepatic phenotype and gain of metastatic properties. Oncogene 2009, 28, 3526–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandres, E.; Bitarte, N.; Arias, F.; Agorreta, J.; Fortes, P.; Agirre, X.; Zarate, R.; Diaz-Gonzalez, J.A.; Ramirez, N.; Sola, J.J.; Jimenez, P.; Rodriguez, J.; Garcia-Foncillas, J. microRNA-451 regulates macrophage migration inhibitory factor production and proliferation of gastrointestinal cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 2281–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, H.; Sun, L.; Yang, M.; Pan, C.; Chen, W.; Wu, D.; Lin, Z.; Zeng, C.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, P.; Song, E. MiR-21 indicates poor prognosis in tongue squamous cell carcinomas as an apoptosis inhibitor. Clin Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3998–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markou, A.; Tsaroucha, E.G.; Kaklamanis, L.; Fotinou, M.; Georgoulias, V.; Lianidou, E.S. Prognostic value of mature microRNA-21 and microRNA-205 overexpression in non-small cell lung cancer by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Clin. Chem. 2008, 54, 1696–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.X.; Huang, X.F.; Shao, Q.; Huang, M.Y.; Deng, L.; Wu, Q.L.; Zeng, Y.X.; Shao, J.Y. MicroRNA miR-21 overexpression in human breast cancer is associated with advanced clinical stage, lymph node metastasis and patient poor prognosis. RNA 2008, 14, 2348–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raponi, M.; Dossey, L.; Jatkoe, T.; Wu, X.; Chen, G.; Fan, H.; Beer, D.G. MicroRNA classifiers for predicting prognosis of squamous cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 5776–5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camps, C.; Buffa, F.M.; Colella, S.; Moore, J.; Sotiriou, C.; Sheldon, H.; Harris, A.L.; Gleadle, J.M.; Ragoussis, J. hsa-miR-210 Is induced by hypoxia and is an independent prognostic factor in breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 1340–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satzger, I.; Mattern, A.; Kuettler, U.; Weinspach, D.; Voelker, B.; Kapp, A.; Gutzmer, R. MicroRNA-15b represents an independent prognostic parameter and is correlated with tumor cell proliferation and apoptosis in malignant melanoma. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 126, 2553–2562. [Google Scholar]
- Segura, M.F.; Belitskaya-Levy, I.; Rose, A.E.; Zakrzewski, J.; Gaziel, A.; Hanniford, D.; Darvishian, F.; Berman, R.S.; Shapiro, R.L.; Pavlick, A.C.; Osman, I.; Hernando, E. Melanoma MicroRNA signature predicts post-recurrence survival. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 1577–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greither, T.; Grochola, L.F.; Udelnow, A.; Lautenschlager, C.; Wurl, P.; Taubert, H. Elevated expression of microRNAs 155, 203, 210 and 222 in pancreatic tumors is associated with poorer survival. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, B.M.; Robles, A.I.; Harris, C.C. Genetic variation in microRNA networks: the implications for cancer research. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Liang, J.; Wang, Z.; Tian, T.; Zhou, X.; Chen, J.; Miao, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Shen, H. Common genetic variants in pre-microRNAs were associated with increased risk of breast cancer in Chinese women. Hum. Mutat. 2009, 30, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Ambrosone, C.B.; DiCioccio, R.A.; Odunsi, K.; Lele, S.B.; Zhao, H. A functional polymorphism in the miR-146a gene and age of familial breast/ovarian cancer diagnosis. Carcinogenesis 2008, 29, 1963–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazdzewski, K.; Murray, E.L.; Franssila, K.; Jarzab, B.; Schoenberg, D.R.; de la Chapelle, A. Common SNP in pre-miR-146a decreases mature miR expression and predisposes to papillary thyroid carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7269–7274. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, W.C. MicroRNAs: Potential biomarkers for cancer diagnosis, prognosis and targets for therapy. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, S.S. Cancer biomarker profiling with microRNAs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 400–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chira, P.; Vareli, K.; Sainis, I.; Papandreou, C.; Briasoulis, E. Alterations of MicroRNAs in Solid Cancers and Their Prognostic Value. Cancers 2010, 2, 1328-1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers2021328
Chira P, Vareli K, Sainis I, Papandreou C, Briasoulis E. Alterations of MicroRNAs in Solid Cancers and Their Prognostic Value. Cancers. 2010; 2(2):1328-1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers2021328
Chicago/Turabian StyleChira, Panagiota, Katerina Vareli, Ioannis Sainis, Christos Papandreou, and Evangelos Briasoulis. 2010. "Alterations of MicroRNAs in Solid Cancers and Their Prognostic Value" Cancers 2, no. 2: 1328-1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers2021328
APA StyleChira, P., Vareli, K., Sainis, I., Papandreou, C., & Briasoulis, E. (2010). Alterations of MicroRNAs in Solid Cancers and Their Prognostic Value. Cancers, 2(2), 1328-1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers2021328



