Towards Achieving the Full Clinical Potential of Proton Therapy by Inclusion of LET and RBE Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- accuracy and reproducibility of BP position.
- inadequate knowledge of the relative biological effect (RBE) in different tissues and at different doses.

1.1. Proton Range Uncertainties
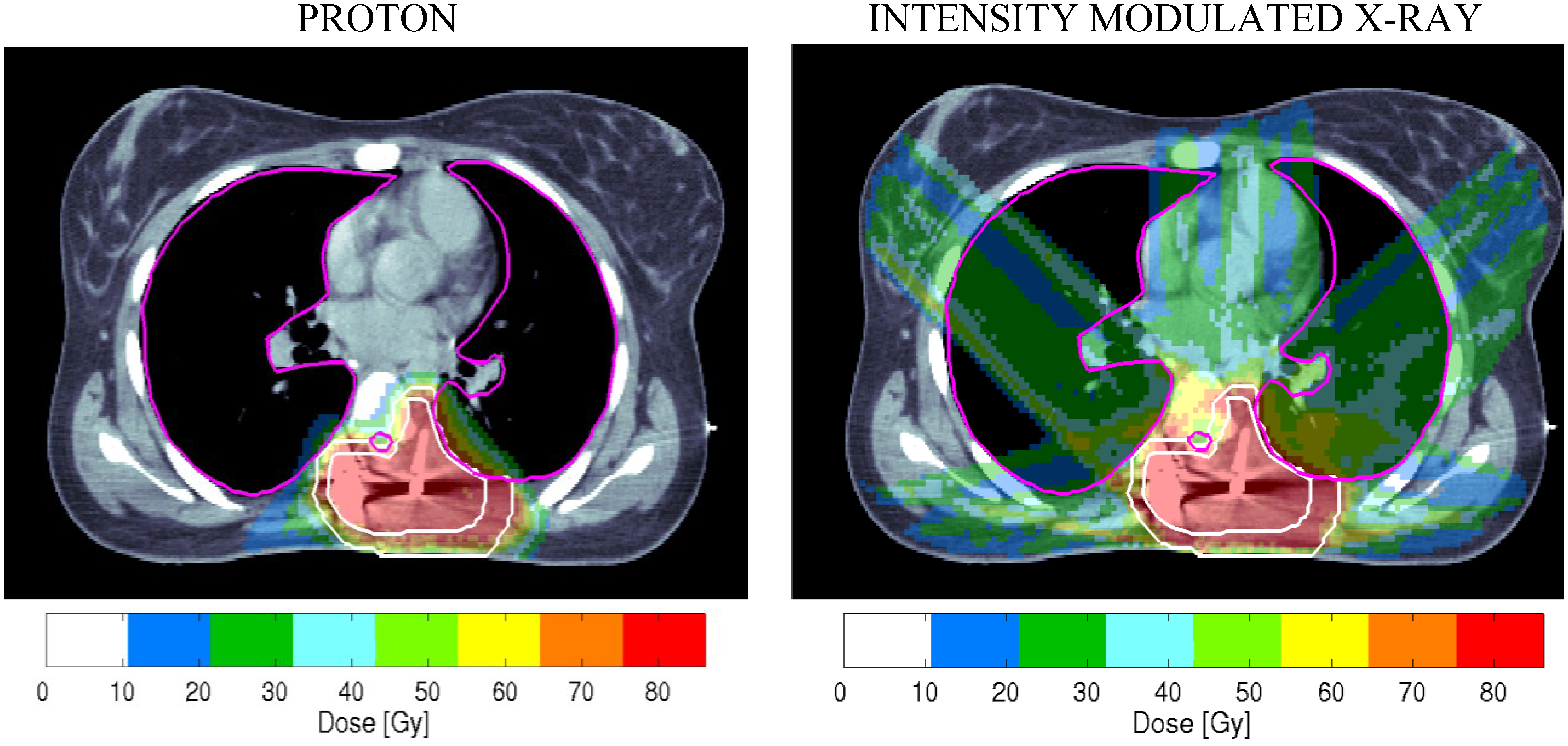
1.2. RBE Uncertainties
2. Methods
2.1. Description of Quantitative Model

2.2. The Qualitative ICRU Approach
3. Results
3.1. Quantitative Model Approach



3.2. An “ICRU” Qualitative Matrix for Particle Beams
| Dose Status | Tumour Control in GTV and {CTV+PTV} | {CTV+PTV} Side Effects | OTV Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| GTV↑, {CTV+PTV}↑, OTV↓ | Much better *** | Worse * | Better |
| GTV↑, {CTV+PTV}=, OTV↓ | Better *** | Equal ** | Better |
| GTV=, {CTV+PTV}=, OTV↓ | Equal ** | Equal ** | Better |
| GTV=, {CTV+PTV}↓, OTV↓ | Worse **** | Better | Better or worse |
3.3. Two Clinical Examples Where PBT can be Suboptimal
3.3.1. Prostate Cancer
- (a)
- Use of one field per day treatments to save gantry sweep time, and only two field plans, which inevitably increase the dose per fraction outside the high dose treatment volume.
- (b)
- Reduced beam shaping and conformity indices, especially with passive scattering, when compared to best photon techniques; this may be improved by scanned beams.
- (c)
- Late complication RBE values are likely to exceed 1.1, so the biological doses to relevant volumes of small bowel and parts of rectum adjacent to the prostate can be higher than for photons.
3.3.2. Paediatric Cancers and Other Radiosensitive Tumours such as Lymphomas

4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Appendix



Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ellis, F.; British Institute of Radiology, London, UK. Personal Communication, 2005.
- Darby, S.C.; Ewertz, M.; McGale, P.; Bennet, A.M.; Blom-Goldman, U.; Brønnum, D.; Correa, C.; Cutter, D.; Gagliardi, G.; Gigante, B.; et al. Risk of ischemic heart disease in women after radiotherapy for breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, E.J.; Giaccia, A.J. Radioprotection in Radiobiology for the Radiologist, 7th ed.; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012; pp. 253–270. [Google Scholar]
- De Ruysscher, D.; Mark Lodge, M.; Jones, B.; Brada, M.; Munro, A.; Jefferson, T.; Pijls-Johannesma, M. Charged particles in radiotherapy: A 5-year update of a systematic review. Radiother. Oncol. 2012, 103, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitin, T.; Zietman, A.L. Promise and pitfalls of heavy-particle therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 2855–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combs, S.E.; Debus, J. Treatment with heavy charged particles: Systematic review of clinical data and current clinical (comparative) trials. Acta Oncol. 2013, 52, 1272–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.H.; Wang, Z.; Wong, W.W.; Murad, M.H.; Buckey, C.R.; Mohammed, K.; Alahdab, F.; Altayar, O.; Nabhan, M.; Schild, S.E.; et al. Charged particle therapy versus photon therapy for paranasal sinus and nasal cavity malignant diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, D.R.; Bruland, O.S.; Frykholm, G.; Norderhaug, I.N. Proton therapy—A systematic review of clinical effectiveness. Radiother. Oncol. 2007, 83, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.M.; Stevens, D.L.; Sumption, N.D.; Townsend, K.M.; Goodhead, D.T.; Hill, M.A. Effect of linear energy transfer (LET) on the complexity of alpha-particle-induced chromosome aberrations in human CD34+ cells. Radiat. Res. 2007, 167, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, R.G.; Jones, B.; Carabe-Fernandez, A. Why more needs to be known about RBE effects in modern radiotherapy. J. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2009, 67, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belli, M.; Bettega, D.; Calzolari, P.; Cera, F.; Cherubini, R.; Dalla Vecchia, M.; Durante, M.; Favaretto, S.; Gialanella, G.; Grossi, G.; et al. Inactivation of human normal and tumour cells irradiated with low energy protons. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2000, 76, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britten, R.A.; Nazaryan, V.; Davis, L.K.; Klein, S.B.; Nichiporov, D.; Mendonca, M.S.; Wolanski, M.; Nie, X.; George, J.; Keppel, C. Variations in the RBE for cell killing along the depth-dose profile of a modulated proton therapy beam. Radiat. Res. 2013, 179, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki-Nakano, M.; Furusawa, Y.; Uzawa, A.; Matsumoto, Y.; Hirayama, R.; Tsuruoka, C.; Ogino, T.; Nishio, T.; Kagawa, K.; Murakami, M.; et al. Relative biological effectiveness of therapeutic proton beams for HSG cells at Japanese proton therapy facilities. J. Radiat. Res. 2014, 55, 812–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barendsen, G.W. Responses of cultured cells, tumours and normal tissues to radiations of different linear energy transfer. Curr. Top. Radiat. Res. Q 1968, 4, 293–356. [Google Scholar]
- Furusawa, Y.; Fukutsu, K.; Aoki, M.; Itsukaichi, H.; Eguchi-Kasai, K.; Ohara, H.; Yatagai, F.; Kanai, T.; Ando, K. Inactivation of aerobic and hypoxic cells from three different cell lines by accelerated (3)He-, (12)C- and (20)Ne-ion beams. Radiat. Res. 2000, 154, 485–496, Erratum in: Radiat. Res. 2012, 177, 129–131. [Google Scholar]
- Weyrather, W.K.; Ritter, S.; Scholz, M.; Kraft, G. RBE for carbon track-segment irradiation in cell lines of differing repair capacity. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 1999, 75, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paganetti, H. Range uncertainties in proton therapy and the role of Monte Carlo simulations. Phys. Med. Biol. 2012, 57, R99–R117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuemann, J.; Dowdell, S.; Grassberger, C.; Min, C.H.; Paganetti, H. Site-specific range uncertainties caused by dose calculation algorithms for proton therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2014, 59, 4007–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmbrecht, S.; Kuess, P.; Birkfellner, W.; Enghardt, W.; Stützer, K.; Georg, D.; Fiedler, F. Systematic analysis on the achievable accuracy of PT-PET through automated evaluation techniques. Z. Med. Phys. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poludniowski, G.; Allinson, N.M.; Anaxagoras, T.; Esposito, M.; Green, S.; Manolopoulos, S.; Nieto-Camero, J.; Parker, D.J.; Price, T.; Evans, P.M. Proton-counting radiography for proton therapy: A proof of principle using CMOS APS technology. Phys. Med. Biol. 2014, 59, 2569–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, K.; Bauer, J.; Unholtz, D.; Kurz, C.; Krämer, M.; Bortfeld, T.; Parodi, K. TPS(PET)-A TPS-based approach for in vivo dose verification with PET in proton therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2014, 59, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testa, M.; Min, C.H.; Verburg, J.M.; Schümann, J.; Lu, H.M.; Paganetti, H. Range verification of passively scattered proton beams based on prompt gamma time patterns. Phys. Med. Biol. 2014, 59, 4181–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelsman, M.; DeLaney, T.F.; Hong, T.S. Proton radiotherapy: The biological effect of treating alternating subsets of fields for different treatment fractions. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 79, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassberger, C.; Trofimov, A.; Lomax, A.; Paganetti, H. Variations in linear energy transfer within clinical proton therapy fields and the potential for biological treatment planning. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 80, 1559–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carabe, A.; Moteabbed, M.; Depauw, N.; Schuemann, J.; Paganetti, H. Range uncertainty in proton therapy due to variable biological effectiveness. Phys. Med. Biol. 2012, 57, 1159–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calugaru, V.; Nauraye, C.; Noël, G.; Giocanti, N.; Favaudon, V.; Mégnin-Chanet, F. Radiobiological characterization of two therapeutic proton beams with different initial energy spectra used at the Institut Curie Proton Therapy Center in Orsay. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 81, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, B.; Underwood, T.C.; Carabe-Fernandez, A.; Dale, R.G. Further analysis of fast neutron relative biological effects and implications for charged particle therapy. Br. J. Radiol. 2011, 84, S11–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paganetti, H. Significance and implementation of RBE variations in proton beam therapy. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2003, 2, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blomquist, E.; Russell, K.R.; Stenerlöw, B.; Montelius, A.; Grusell, E.; Carlsson, J. Relative biological effectiveness of intermediate energy protons. Comparisons with 60Co gamma-radiation using two cell lines. Radiother. Oncol. 1993, 28, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paganetti, H. Relative biological effectiveness (RBE) values for proton beam therapy. Variations as a function of biological endpoint, dose, and linear energy transfer. Phys. Med. Biol. 2014, 59, R419–R472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkens, J.J.; Oelfke, U. A phenomenological model for the relative biological effectiveness in therapeutic proton beams. Phys. Med. Biol. 2004, 49, 2811–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, B.S.; Overgaard, J.; Bassler, N. In vitro RBE-LET dependence for multiple particle types. Acta Oncol. 2011, 50, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, B. The apparent increase in the β-parameter of the linear quadratic model with increased linear energy transfer during particle irradiation. Br. J. Radiol. 2010, 83, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Commission on Radiation Units & Measurements. Prescribing, Recording, and Reporting Proton-Beam Therapy (ICRU Report 78); National Institute of Health: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, P.J.; Paly, J.J.; Yeap, B.Y.; Sanda, M.G.; Sandler, H.M.; Michalski, J.M.; Talcott, J.A.; Coen, J.J.; Hamstra, D.A.; Shipley, W.U.; et al. Patient-reported outcomes after 3-dimensional conformal, intensity-modulated, or proton beam radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer. Cancer 2013, 119, 1729–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, T.J.; Munsell, M.F.; Choi, S.; Nguyen, Q.N.; Mathai, B.; Zhu, X.R.; Sahoo, N.; Gillin, M.; Johnson, J.L.; Amos, R.A.; et al. Quality of life and toxicity from passively scattered and spot-scanning proton beam therapy for localized prostate cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 87, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, B.; Wilson, P.; Nagano, A.; Fenwick, J.; McKenna, G. Dilemmas concerning dose distribution and the influence of relative biological effect (RBE) in proton beam therapy of Medulloblastoma. Br. J. Radiol. 2012, 85, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B. Editorial: Patterns of failure after proton therapy in Medulloblastoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 90, 25–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, J.; Loeffler, J.S.; Niemierko, A.; Chiocca, E.A.; Batchelor, T.; Chakravarti, A. Long-term outcomes of patients with spinal cord gliomas treated by modern conformal radiation techniques. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 81, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, V.S.; Giansoudi, D.; Raiford, M.; Mahli, I.; Niemerko, A.; Rapalino, O.; Caruso, P.; Yock, T.I.; Tarbell, N.J.; Paganetti, H.; et al. Patterns of Failure after proton therapy in medulloblastoma: Linear energy transfer distributions and relative biological effectiveness. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 88, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, S.M.; Sethi, R.; Lavally, B.; Yeap, B.Y.; Marcus, K.J.; Caruso, P.; Pulsifer, M.; Huang, M.; Ebb, D.; Tarbell, N.J.; et al. Proton radiotherapy for pediatric central nervous system ependymoma: Clinical outcomes for 70 patients. Neurooncology 2013, 15, 1552–1559. [Google Scholar]
- Pehlivan, B.; Ares, C.; Lomax, A.J.; Stadelmann, O.; Goitein, G.; Timmermann, B.; Schneider, R.A.; Hug, E.B. Temporal lobe toxicity analysis after proton radiation therapy for skull base tumors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 83, 1432–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frese, M.C.; Wilkens, J.J.; Huber, P.E.; Jensen, A.D.; Oelfke, U.; Taheri-Kadkhoda, Z. Application of constant vs. variable relative biological effectiveness in treatment planning of intensity-modulated proton therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 79, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedenberg, M.; Lind, B.K.; Hårdemark, B. A model for the relative biological effectiveness of protons: The tissue specific parameter α/β of photons is a predictor for the sensitivity to LET changes. Acta Oncol. 2013, 52, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamada, T. Overview of the Heavy-Ion Medical Accelerator in Chiba (HIMAC). In Carbon-Ion Radiotherapy; Tsujiim, H., Kamada, T., Shirai, T., Noda, K., Tsuji, H., Karasawa, K., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2014; pp. 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Dasu, A.; Toma-Dasu, I. Impact of variable RBE on proton fractionation. Med. Phys. 2013, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cometto, A.; Russo, G.; Bourhaleb, F.; Milian, F.M.; Giordanengo, S.; Marchetto, F.; Cirio, R.; Attili, A. Direct evaluation of radiobiological parameters from clinical data in the case of ion beam therapy: An alternative approach to the relative biological effectiveness. Phys. Med. Biol. 2014, 59, 7393–7417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuskin, A.C.; Michiels, C.; Lucas, S. Toward computer simulation of high-LET in vitro survival curves. Phys. Med. Biol. 2013, 58, 6495–6510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzscheiter, M.H.; Bassler, N.; Dosanjh, M.; Sørensen, B.S.; Overgaard, J. A community call for a dedicated radiobiological research facility to support particle beam cancer therapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2012, 105, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dosanjh, M.; Jones, B.; Myers, S. A possible biomedical facility at CERN. Br. J. Radiol. 2013, 86, 1025–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, J.D.; Blakely, E.A.; Smith, K.C.; Urtasun, R.C. Radiobiological characterization of the inactivating events produced in mammalian cells by helium and heavy ions. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1977, 3, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carabe-Fernandez, A.; Dale, R.G.; Jones, B. The incorporation of the concept of minimum RBE (RBEmin) into the linear-quadratic model and the potential for improved radiobiological analysis of high-LET treatments. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2007, 83, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jones, B. Towards Achieving the Full Clinical Potential of Proton Therapy by Inclusion of LET and RBE Models. Cancers 2015, 7, 460-480. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers7010460
Jones B. Towards Achieving the Full Clinical Potential of Proton Therapy by Inclusion of LET and RBE Models. Cancers. 2015; 7(1):460-480. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers7010460
Chicago/Turabian StyleJones, Bleddyn. 2015. "Towards Achieving the Full Clinical Potential of Proton Therapy by Inclusion of LET and RBE Models" Cancers 7, no. 1: 460-480. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers7010460
APA StyleJones, B. (2015). Towards Achieving the Full Clinical Potential of Proton Therapy by Inclusion of LET and RBE Models. Cancers, 7(1), 460-480. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers7010460





