The Hedgehog Inhibitor Cyclopamine Reduces β-Catenin-Tcf Transcriptional Activity, Induces E-Cadherin Expression, and Reduces Invasion in Colorectal Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Cyclopamine Treatment Reduces β-Catenin-Related Transcription in the Colorectal Cancer Cell Line SW480 in a Dose-Dependent Manner


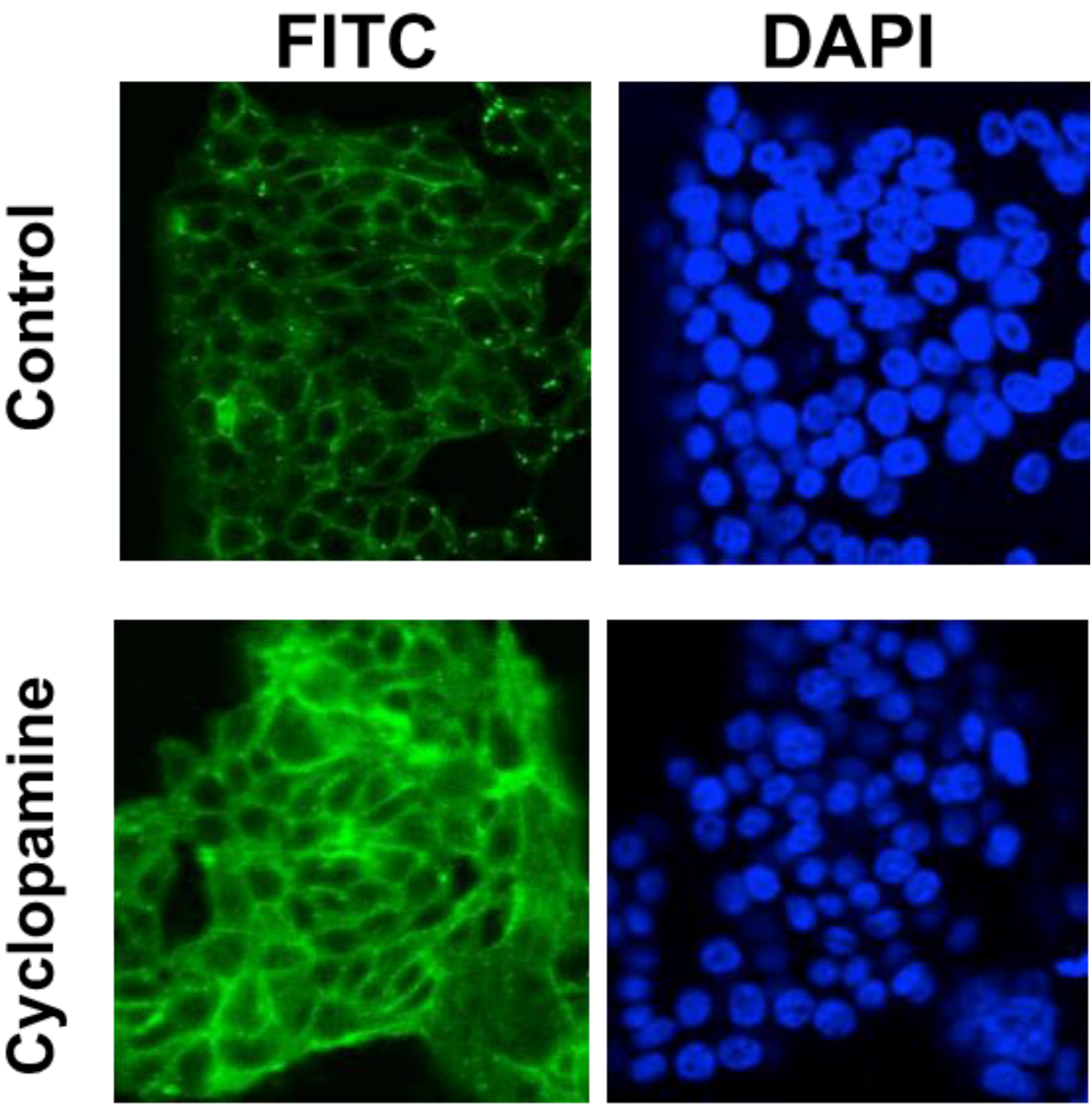
2.2. Cyclopamine Treatment Induces the Expression of E-Cadherin in Both Benign and Malignant Colorectal Tumour-Derived Cell Lines and Reduces Invasion in SW480 Cells



3. Experimental Section
3.1. Cell Culture and Cyclopamine Treatment
3.2. Promoter-Reporter Assays
3.3. Production of Recombinant SHH-N Protein
3.4. Western Blot Analysis
3.5. Immunocytochemistry
3.6. In Vitro Invasion Assay
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cancer Research UK. Worldwide Cancer Mortality Statistics. Available online: http://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/worldwide-cancer/mortality-heading-One (accessed on 1 June 2015).
- Bienz, M.; Clevers, H. Linking colorectal cancer to wnt signaling. Cell 2000, 103, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabletz, T.; Jung, A.; Spaderna, S.; Hlubek, F.; Kirchner, T. Opinion: Migrating cancer stem cells—An integrated concept of malignant tumour progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Brink, G.R. Hedgehog signaling in development and homeostasis of the gastrointestinal tract. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 1343–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qualtrough, D.; Buda, A.; Gaffield, W.; Williams, A.C.; Paraskeva, C. Hedgehog signalling in colorectal tumour cells: Induction of apoptosis with cyclopamine treatment. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 110, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oniscu, A.; James, R.M.; Morris, R.G.; Bader, S.; Malcomson, R.D.; Harrison, D.J. Expression of sonic hedgehog pathway genes is altered in colonic neoplasia. J. Pathol. 2004, 203, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douard, R.; Moutereau, S.; Pernet, P.; Chimingqi, M.; Allory, Y.; Manivet, P.; Conti, M.; Vaubourdolle, M.; Cugnenc, P.H.; Loric, S. Sonic hedgehog-dependent proliferation in a series of patients with colorectal cancer. Surgery 2006, 139, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arimura, S.; Matsunaga, A.; Kitamura, T.; Aoki, K.; Aoki, M.; Taketo, M.M. Reduced level of smoothened suppresses intestinal tumorigenesis by down-regulation of wnt signaling. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varnat, F.; Duquet, A.; Malerba, M.; Zbinden, M.; Mas, C.; Gervaz, P.; Ruiz i Altaba, A. Human colon cancer epithelial cells harbour active HEDGEHOG-Gli signalling that is essential for tumour growth, recurrence, metastasis and stem cell survival and expansion. EMBO Mol. Med. 2009, 1, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazumdar, T.; deVecchio, J.; Shi, T.; Jones, J.; Agyeman, A.; Houghton, J.A. Hedgehog signaling drives cellular survival in human colon carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1092–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, A.N.; Bernardazzi, C.; Carneiro, A.J.; Elia, C.C.; Martinusso, C.A.; Ventura, G.M.; Castelo-Branco, M.T.; de Souza, H.S. Hedgehog pathway signaling regulates human colon carcinoma HT-29 epithelial cell line apoptosis and cytokine secretion. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Brink, G.R.; Bleuming, S.A.; Hardwick, J.C.; Schepman, B.L.; Offerhaus, G.J.; Keller, J.J.; Nielsen, C.; Gaffield, W.; van Deventer, S.J.; Roberts, D.J.; et al. Indian hedgehog is an antagonist of Wnt signaling in colonic epithelial cell differentiation. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Sheng, T.; Stelter, A.A.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Sinha, M.; Luxon, B.A.; Xie, J. Suppressing Wnt signaling by the hedgehog pathway through sFRP-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 35598–35602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, O.; Kondo, M.; Fujita, T.; Usami, N.; Fukui, T.; Shimokata, K.; Ando, T.; Goto, H.; Sekido, Y. Enhancement of GLI1-transcriptional activity by β-catenin in human cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2006, 16, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korinek, V.; Barker, N.; Morin, P.J.; van Wichen, D.; de Weger, R.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B.; Clevers, H. Constitutive transcriptional activation by a β-catenin-TCF complex in APC−/− colon carcinoma. Science 1997, 275, 1784–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roelink, H.; Porter, J.A.; Chiang, C.; Tanabe, Y.; Chang, D.T.; Beachy, P.A.; Jessell, T.M. Floor plate and motor neuron induction by different concentrations of the amino-terminal cleavage product of sonic hedgehog autoproteolysis. Cell 1995, 81, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Shi, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Peng, Y.; Chen, X.; Tang, C.; Li, X.; Zhou, X. Expression of indian hedgehog is negatively correlated with APC gene mutation in colorectal tumors. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 2150–2155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buller, N.V.; Rosekrans, S.L.; Metcalfe, C.; Heijmans, J.; van Dop, W.A.; Fessler, E.; Jansen, M.; Ahn, C.; Vermeulen, J.L.; Westendorp, B.F.; et al. Stromal indian hedgehog signaling is required for intestinal adenoma formation in mice. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 170–180.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyak, K.; Weinberg, R.A. Transitions between epithelial and mesenchymal states: Acquisition of malignant and stem cell traits. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, D.M.; Medici, D. Signaling mechanisms of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Sci. Signal. 2014, 7, re8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conacci-Sorrell, M.; Simcha, I.; Ben-Yedidia, T.; Blechman, J.; Savagner, P.; Ben-Ze’ev, A. Autoregulation of E-cadherin expression by cadherin-cadherin interactions: The roles of beta-catenin signaling, Slug, and MAPK. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 163, 847–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Gan, H.Z.; Peng, Q. Resveratrol inhibits the hedgehog signaling pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition and suppresses gastric cancer invasion and metastasis. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 9, 2381–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, Z.; Caiping, S.; Qing, Z.; Xiaojing, W. Sonic hedgehog-Gli1 signals promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition in ovarian cancer by mediating PI3K/AKT pathway. Med. Oncol. 2015, 32, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, X.; Li, S.; Shi, T.; Suo, A.; Ruan, Z.; Yao, Y. Tripartite motif 16 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis by down-regulating sonic hedgehog pathway in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 460, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varnat, F.; Siegl-Cachedenier, I.; Malerba, M.; Gervaz, P.; Ruiz i Altaba, A. Loss of WNT-TCF addiction and enhancement of HH-Gli1 signalling define the metastatic transition of human colon carcinomas. EMBO Mol. Med. 2010, 2, 440–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paraskeva, C.; Buckle, B.G.; Sheer, D.; Wigley, C.B. The isolation and characterization of colorectal epithelial cell lines at different stages in malignant transformation from familial polyposis coli patients. Int. J. Cancer 1984, 34, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.C.; Harper, S.J.; Paraskeva, C. Neoplastic transformation of a human colonic epithelial cell line: In vitro evidence for the adenoma to carcinoma sequence. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 4724–4730. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paraskeva, C.; Finerty, S.; Mountford, R.A.; Powell, S.C. Specific cytogenetic abnormalities in two new human colorectal adenoma-derived epithelial cell lines. Cancer Res. 1989, 49, 1282–1286. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaidi, A.; Williams, A.C.; Paraskeva, C. Interaction between beta-catenin and HIF-1 promotes cellular adaptation to hypoxia. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qualtrough, D.; Kaidi, A.; Chell, S.; Jabbour, H.N.; Williams, A.C.; Paraskeva, C. Prostaglandin F2α stimulates motility and invasion in colorectal tumor cells. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, A.; Rea, D. ABC of colorectal cancer: Treatment of advanced disease. Br. Med. J. 2000, 321, 1278–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporn, M.B. The war on cancer. Lancet 1996, 347, 1377–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batsaikhan, B.E.; Yoshikawa, K.; Kurita, N.; Iwata, T.; Takasu, C.; Kashihara, H.; Shimada, M. Cyclopamine decreased the expression of sonic hedgehog and its downstream genes in colon cancer stem cells. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 6339–6344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Li, Z.Y.; Liu, W.P.; Zhao, M.R. Crosstalk between Wnt/β-catenin and Hedgehog/Gli signaling pathways in colon cancer and implications for therapy. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Brink, G.R.; Hardwick, J.C. Hedgehog wnteraction in colorectal cancer. Gut 2006, 55, 912–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varnat, F.; Zacchetti, G.; Ruiz i Altaba, A. Hedgehog pathway activity is required for the lethality and intestinal phenotypes of mice with hyperactive wnt signaling. Mech. Dev. 2010, 127, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Mei, L.; Pan, L.; Xiong, W.; Zhu, H.; Ruan, H.; Zou, C.; Tang, L.; Iguchi, T.; Wu, X. Hedgehog signaling through Gli1 and Gli2 is required for epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human trophoblasts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1850, 1438–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qualtrough, D.; Rees, P.; Speight, B.; Williams, A.C.; Paraskeva, C. The Hedgehog Inhibitor Cyclopamine Reduces β-Catenin-Tcf Transcriptional Activity, Induces E-Cadherin Expression, and Reduces Invasion in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancers 2015, 7, 1885-1899. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers7030867
Qualtrough D, Rees P, Speight B, Williams AC, Paraskeva C. The Hedgehog Inhibitor Cyclopamine Reduces β-Catenin-Tcf Transcriptional Activity, Induces E-Cadherin Expression, and Reduces Invasion in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancers. 2015; 7(3):1885-1899. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers7030867
Chicago/Turabian StyleQualtrough, David, Phil Rees, Beverley Speight, Ann C. Williams, and Christos Paraskeva. 2015. "The Hedgehog Inhibitor Cyclopamine Reduces β-Catenin-Tcf Transcriptional Activity, Induces E-Cadherin Expression, and Reduces Invasion in Colorectal Cancer Cells" Cancers 7, no. 3: 1885-1899. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers7030867
APA StyleQualtrough, D., Rees, P., Speight, B., Williams, A. C., & Paraskeva, C. (2015). The Hedgehog Inhibitor Cyclopamine Reduces β-Catenin-Tcf Transcriptional Activity, Induces E-Cadherin Expression, and Reduces Invasion in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancers, 7(3), 1885-1899. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers7030867




