1. Introduction
The prevention of communicable and non-communicable diseases can be achieved by promoting a healthy lifestyle, diet, and physical activity. Heart attacks and kidney failure are more likely to occur when we have high blood pressure, diabetes, or hypertension [
1]. It has been shown that moderate exercise reduces morbidity and mortality after viral infection [
2,
3]. Exercises and meditation are detrimental to the treatment of respiratory viral infections in preclinical studies [
4].
A traditional Indian health practice promotes strength and immunity through exercise, meditation, and yoga poses. Stress and depression can be reduced through these exercises as well as improving sleep patterns and boosting immunity [
5,
6]. Focusing on a particular thought or object combats stress, and exercise-induced adaptations enhance the immune system and mental health [
7,
8]. The immune system is influenced by physical activity. Increasing fitness can reduce cancer risk, cardiovascular disease risk, type 2 diabetes risk, and obesity risk [
9]. Physical activity is recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) for battling viral infections [
10].
Communication technology has made it possible for people to share and motivate physical activity through recommendation systems. A healthy lifestyle and balance can be found on health websites [
11,
12]. Online communities provide quality healthcare, but their inconsistent advice may negatively impact health, leading to untrustworthiness and the need for filtered accurate information [
13,
14,
15]. In addition, the disclaimer on healthcare solutions does not apply to health recommendations [
16,
17,
18].
The recommendation system based on physical activity promotes individual health and prevents communicable and non-communicable diseases. The effects of high-volume exercise and calorie reduction are attributed to preserving metabolic, cardiovascular, neuromuscular, fiber degeneration, and insulin resistance [
19]. The authors of [
20], mention that exercise and antipathogenic activity improve the immune system. As a result of user behavior, health recommendation systems provide actionable knowledge [
21,
22,
23,
24]. Technology-assisted personalized recommendations enable people to monitor their health and improve it. When exposed to viral infections, regular exercisers will respond better to vaccines and their physical and mental health will be enhanced [
25].
In the healthcare sector, intelligent health systems have become a critical component of decision-making. Systems like these ensure access to critical information at the right time, as well as the quality, trustworthiness, authentication, and privacy of the information. Deep learning has also helped healthcare organizations provide personalized care for their patients by analyzing medical histories, symptoms, and tests of patients. Physicians use these health recommendation systems for diagnostic assistance and to provide advice to users of personal health tools [
26]. The results of some deep learning-based studies suggest recommendation systems for lesion classification, smart diabetes management, and posture detection.
Physical exercise recommendation systems are arguably under-researched. Consequently, healthcare costs are rising as a result of sedentary lifestyles. Several recent studies [
27,
28] advocate walking, stair climbing, running, and jumping to prevent chronic viral infections and maintain health after the pandemic. During this study, we developed a recommendation system that included yoga, meditation, and exercises geared toward boosting people’s immune systems, as well as preventing viral infections and respiratory diseases. Using a convolutional neural network, a recommendation system is developed based on the user’s physical activity levels and immune system. Furthermore, it generates automatic recommendations for patients and healthy individuals to boost their immunity.
4. Discussions
Muscles are used to consume energy during physical activity. Through the spread of communicable and non-communicable diseases, physical inactivity increases risk factors, including mortality. Smartphones and wearable devices track step counts, but there is a subtle difference between them. There was a discrepancy of 20% between the monitored step count and the wearable devices.
The performance of various leisure activities during leisure time is improved by recommendation systems for outdoor activities [
30]. As a result of individual healthcare awareness, various functionalities have been integrated into the healthcare system [
31,
32]. Analyzes fitness data and workouts to determine their effectiveness. A mobile application generates recommendations for physical activity but lacks an indication of personal details, location, and intensity [
33].
Using accelerometer data, Profit’s framework recommends physical activity based on users’ past activities, preferences, and health status [
34]. The program analyzes the user’s daily routine and heart rate to determine the amount of physical activity he or she should perform [
35]. It lacks full personalization and is more engaging than My Behaviors, a mobile app that tracks user activity and suggests food and physical activity [
36].
When recommending activity and exercise models, the recommendation system considers the activity profile, demographics, and contextual data [
37]. Using sociodemographic data and a person’s behavior, the framework generated recommendations [
38]. Daily routines are To determine the optimal marathon finishing time at various distances, the K nearest neighbor extreme gradient boosting method is used [
39].
Exercise is the same for people of all ages, regardless of their health conditions. There are several confounding variables considered in the proposed recommendation system, including age and health conditions. The proposed system allows fitness assistants to provide continuous recommendations, and daily fitness program recommendations can be made at any time. The proposed model is more accurate due to the use of more comprehensive personal data, comorbidities, individual habits, and location.
It is critical to consider an individual’s age, gender, height, and weight when making a recommendation for physical activity. The participants in the conversation will need to manually label vigorous exercises in the future. Regarding calorie burning, which varies from person to person, we will consider confounding variables that negatively affect reliability.
5. Conclusions
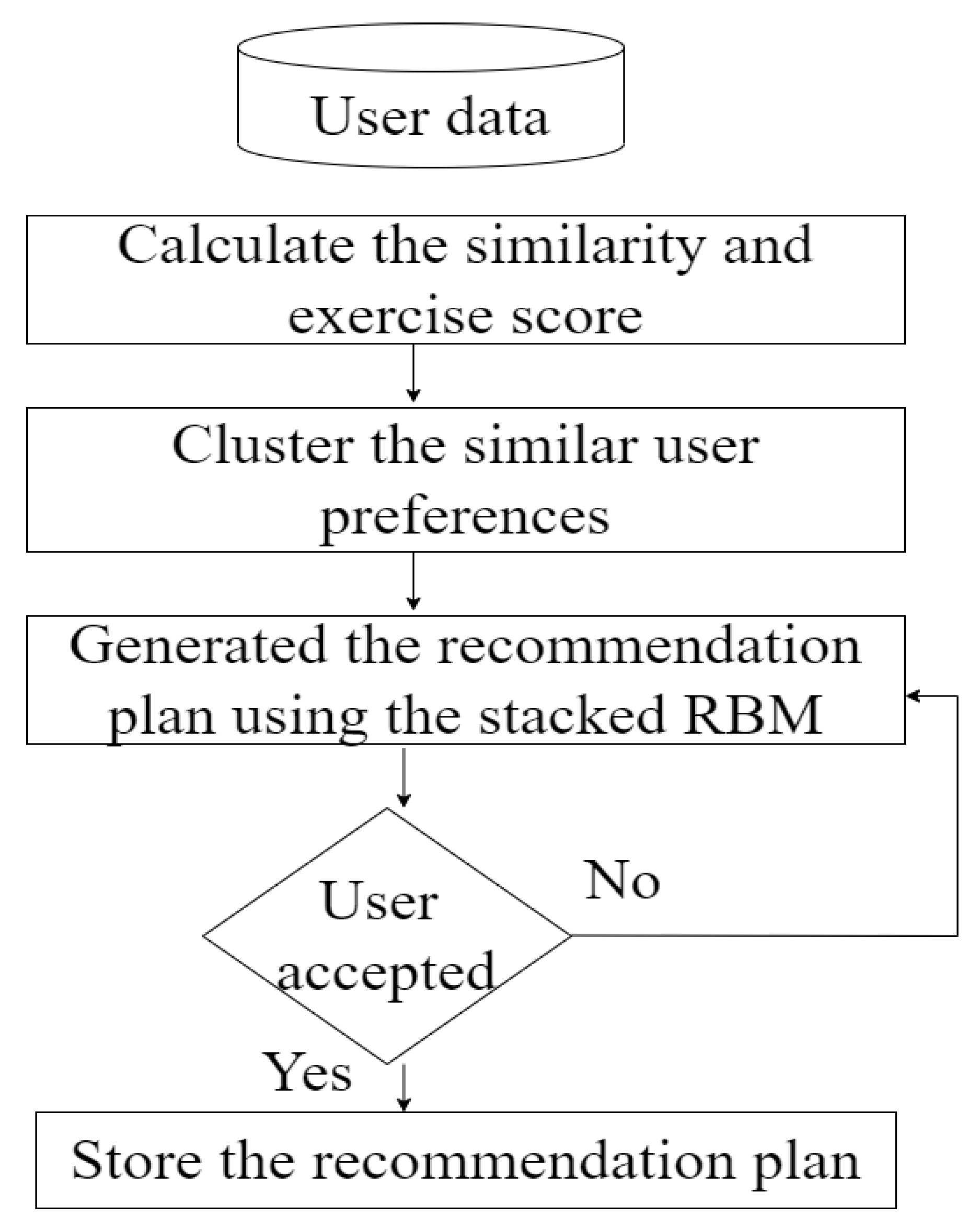
In this paper, we discuss physical activity frameworks that prevent and avoid respiratory viral infections. Three algorithms were presented for recommending physical activity. By analyzing the features collected during data collection, the yoga feature extraction algorithm extracts features. In the proposed yoga clustering algorithm, individuals are grouped according to their health status and preferences. Physical activity frameworks can benefit both healthy individuals and those who have recovered from respiratory viral infections. We compare the proposed results with those of random forests, K-nearest neighbors, support vector machines, and decision trees. Based on the results, the proposed model outperformed all existing machine learning algorithms.
The main highlights of this study are:
- ✓
All the data were extracted including gender, age, height, weight, comorbidities, respiratory infections, exercise habits, nationality, food, and habits;
- ✓
A similarity and exercise score were calculated for each dataset;
- ✓
Integrated similarity scores and exercise scores to cluster similar users;
- ✓
The proposed recommendation model should be developed based on the following factors: gender, age, height, weight, comorbidities, respiratory infections, exercise habits, nationality, food, and habits;
- ✓
If the user accepts the recommendation plan, store the list. Otherwise, provide an alternate recommendation plan.