SOD: A Corpus for Saudi Offensive Language Detection Classification
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The development of a comprehensive offensive language corpus comprising over 24,000 tweets, representing Saudi dialects from all regions.
- The implementation of a hierarchical annotation system for offensive language detection, enabling both broad classification and deeper, more nuanced categorization.
- An extensive analysis of the linguistic aspects of the Saudi dialect, enhancing understanding of its unique features.
- The evaluation of various NLP tools, including machine learning, traditional deep learning, and transformer-based models, for detecting offensive language.
- The implementation of data augmentation techniques to address the issue of dataset imbalance.
2. Literature Review
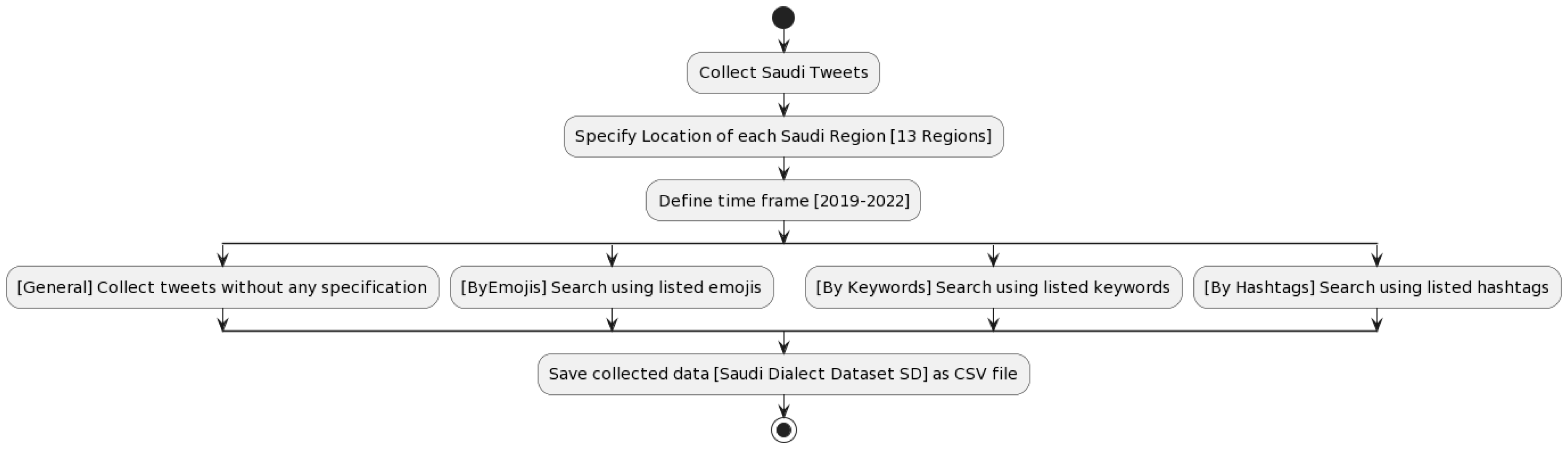
3. Corpus Generation
- Regions and Locations: Data was collected from all 13 regions of Saudi Arabia, with search radii adjusted between 50 km and 300 km around major cities to capture relevant locations, while excluding extraneous areas.
- Specific Timeframes: Data was gathered over the past four years (2019–2022) to ensure comprehensive coverage and avoid biases toward specific periods or topics, such as COVID-19 or the World Cup 2022.
- Query-Driven Approach: In addition to predetermined geographical boundaries and timeframes, we followed a four-step approach:
- -
- General Collection: The initial phase involved scraping data without specific filters or predefined seeds.
- -
- By Emoji: Data was collected based on specific emojis that could indicate potentially offensive language.
- -
- By Keyword: Tweets containing keywords indicative of the Saudi dialect and potential offensive language were targeted.
- -
- By Hashtag: We selected specific hashtags popular within the Saudi Twitter community, indicative of broader conversations, for data extraction.
- Emojis: These visual symbols are among the most common in offensive Arabic tweets. The list provided in the table is sourced from existing literature [31]. Notably, while these emojis are representative of broader Arabic culture, they may not specifically reflect the nuances of the Saudi dialect. For example, the emoji “
”, ranked as the most used emoji for offensive language, is generally understood as raindrops in Saudi culture and is often paired with prayers and supplications.
- Keywords: These words and phrases encompass a wide range of topics, many of which relate to fine-grained hate classes identified in prior research [32]. Their selection includes general offensive remarks, racial or nationality-based slurs, sports-related ideologies, social class descriptors, and gender-based terms. For instance, terms like “يلعن” (Yilan, “Curse”) and “كلب” (Kalb, “Dog”) are categorized as general offenses, while “يمني” (Yamani, “Yemeni”) and “مصري” (Masri, “Egyptian”) relate to race or nationality.
- Hashtags: The hashtags in our collection touch upon themes similar to those in the keywords, including general offenses, race or nationality, sports ideologies, social classes, and gender topics.
3.1. Data Annotation
- Level 1 [Offensive vs. Non-offensive]: At this foundational level, each tweet was assessed for its overall tone to determine whether it was offensive or not.
- Level 2 [Offensive Tweets]: Focus was placed only on tweets identified as offensive in Level 1, which were then annotated into:
- -
- General Insult: Speech that is simply offensive but poses no risk to others, generally NOT considered a human rights violation [33].
- -
- Sarcasm: The use of remarks that clearly mean the opposite of what they say, made to hurt someone’s feelings or to criticize something in a humorous way [4].
- -
- Hate Speech: Becomes a human rights violation if it incites discrimination, hostility, or violence towards a person or a group defined by their race, religion, ethnicity, or other factors [33].
- Level 3 [Hate Speech Tweets]: Focus was only on tweets identified as hate speech in Level 2. It was then classified into more specific types of hate speech: racial, gender-based, sports-related, political/religious, vulgar, violence-related, and others.
3.1.1. Annotation Tools
3.1.2. Annotators Guideline
3.2. Post-Annotation Data Refinement
3.3. Annotation Category Examples
4. Descriptive Analysis
4.1. Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
4.2. Token Analysis
- Unigrams: Unigrams are the simplest form of n-gram analysis, where ‘n’ denotes the number of contiguous items in a sequence. For unigrams, the sequence consists of individual tokens or words. Analyzing unigrams allows us to assess the frequency and distribution of standalone words within the text corpus [34].
- Bigrams: Bigrams build on unigrams by analyzing pairs of contiguous tokens. This approach provides insights into common two-word phrases or collocations within the dataset, offering a deeper understanding of language structure and contextual usage [34].
- Trigrams: Trigrams involve the analysis of triples of contiguous tokens, further enriching the context captured by the analysis. Trigrams help identify common phrases or expressions, offering a more nuanced view of language patterns compared to unigrams and bigrams [34].
- Emojis: The analysis also extends to emojis, ideograms, and smileys used in electronic messages and web pages. Emojis have become integral to online communication, often conveying emotions and replacing traditional text. Their analysis provides unique insights into the emotional undertones and sentiments within the dataset [35].
4.2.1. All Tweets: Offensive or Not Offensive
 (angry face) and
(angry face) and  (thumbs down) further confirm the negative sentiment and confrontational tone in these texts.
(thumbs down) further confirm the negative sentiment and confrontational tone in these texts. (blue heart) and
(blue heart) and  (sweat droplets) suggest a softer, potentially more positive or neutral emotional tone.
(sweat droplets) suggest a softer, potentially more positive or neutral emotional tone.4.2.2. Offensive Tweets: General Insult, Hate Speech, and Sarcasm
 and other negative symbols frequently accompany hate speech, emphasizing the aggressive tone and amplifying expressions of disdain and contempt. The Sarcasm category is notable for its higher use of laughing emojis
and other negative symbols frequently accompany hate speech, emphasizing the aggressive tone and amplifying expressions of disdain and contempt. The Sarcasm category is notable for its higher use of laughing emojis  , suggesting ridicule or irony. This aligns with sarcasm’s subtler and often humorous form of offense.
, suggesting ridicule or irony. This aligns with sarcasm’s subtler and often humorous form of offense.4.2.3. Hate Speech Tweets: Sport, Religious–Political–Racial, and Insult–Violence
 (angry face) and
(angry face) and  (thumbs down) in all categories. These emojis underscore the strong emotions and confrontational nature of communication.
(thumbs down) in all categories. These emojis underscore the strong emotions and confrontational nature of communication.5. Data Experiment
5.1. Experimental Setting
- Machine Learning (ML): We employed various classifiers, including support vector machine (SVM), Gaussian naive Bayes, multinomial naive Bayes, random forest, logistic regression, and K-nearest neighbors. Text data was vectorized using term frequency-inverse document frequency (TF-IDF) with n-grams ranging from unigrams to trigrams. The scikit-learn library was utilized for model training, with default hyperparameters unless otherwise specified.
- Traditional Deep Learning (DL): Three models—feedforward neural network (FFNN), convolutional neural network (CNN), and gated recurrent unit (GRU)—were implemented using TensorFlow and Keras. The text data was tokenized and padded to a maximum sequence length of 128 tokens, with an embedding layer of 100 dimensions applied across all models. The FFNN included a dense layer with 128 units, the CNN used 128 convolutional filters with a kernel size of 5, and the GRU incorporated a single GRU layer with 128 units. All models were trained for 3 epochs using the Adam optimizer and a binary cross-entropy loss function.
- Transformer-Based DL Model (AraBERT): The aubmindlab/bert-base-arabertv02-twitter model was fine-tuned on the SOD dataset. Tokenization was conducted using HuggingFace’s AutoTokenizer, with a maximum sequence length of 128 tokens. The model was trained using the Adam optimizer with a learning rate of 2 × 10−5 and epsilon set to 1 × 10−8 over 2 epochs. To enhance model robustness, 5-fold cross-validation was employed, and metrics were computed using the HuggingFace Trainer API.
5.2. Experimental Results
5.3. Comparative Analysis
6. Data Augmentation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nobata, C.; Tetreault, J.; Thomas, A.; Mehdad, Y.; Chang, Y. Abusive Language Detection in Online User Content. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on World Wide Web, Montréal, QC, Canada, 11–15 April 2016; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, G.; Fan, B.; Wang, L.; Hong, J.; Rose, C. Detecting offensive tweets via topical feature discovery over a large scale twitter corpus. In Proceedings of the 21st ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management–CIKM’12, Maui, Hawaii, USA, 29 October–2 November 2012; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; p. 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abozinadah, E.A.; Mbaziira, A.V.; Jones, J.H.J. Detection of Abusive Accounts with Arabic Tweets. Int. J. Knowl. Eng. 2015, 1, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouheb, D.; Ismail, R.; Al Qaraghuli, S.; Al Aghbari, Z.; Kamel, I. Detection of Offensive Messages in Arabic Social Media Communications. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Innovations in Information Technology (IIT), Al Ain, United Arab Emirates, 18–19 November 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.G.; Didolkar, A.; Sawhney, R.; Shah, R.R. ARHNet-Leveraging Community Interaction for Detection of Religious Hate Speech in Arabic. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Student Research Workshop, Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019; Association for Computational Linguistics: Pennsylvania, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdy, W.; Darwish, K.; Weber, I. #FailedRevolutions: Using Twitter to study the antecedents of ISIS support. First Monday 2016, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidar, B.; Chamoun, M.; Serhrouchni, A. A Multilingual System for Cyberbullying Detection: Arabic Content Detection using Machine Learning. Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 2017, 2, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshaalan, R.; Al-Khalifa, H. Hate Speech Detection in Saudi Twittersphere: A Deep Learning Approach. In Proceedings of the Fifth Arabic Natural Language Processing Workshop, Barcelona, Spain, 12 December 2020; Zitouni, I., Abdul-Mageed, M., Bouamor, H., Bougares, F., El-Haj, M., Tomeh, N., Zaghouani, W., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Pennsylvania, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 12–23. Available online: https://aclanthology.org/2020.wanlp-1.2 (accessed on 19 November 2023).
- Alshalan, R.; Al-Khalifa, H. A Deep Learning Approach for Automatic Hate Speech Detection in the Saudi Twittersphere. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohaouchane, H.; Mourhir, A.; Nikolov, N.S. Detecting Offensive Language on Arabic Social Media Using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 Sixth International Conference on Social Networks Analysis, Management and Security (SNAMS), Granada, Spain, 22–25 October 2019; pp. 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hassan, A.; Al-Dossari, H. Detection of Hate Speech in Social Networks: A Survey on Multilingual Corpus. In Proceedings of the 2019 Sixth International Conference on Social Networks Analysis, Management and Security (SNAMS), Granada, Spain, 22–25 October 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habash, N.Y. Introduction to Arabic Natural Language Processing. Synth. Lect. Hum. Lang. Technol. 2010, 3, 1–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abozinadah, E.A.; Jones, J.J.H. Improved Micro-Blog Classification for Detecting Abusive Arabic Twitter Accounts. Int. J. Data Min. Knowl. Manag. Process. 2016, 6, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, K.; Magdy, W. Arabic Information Retrieval. Found. Trends® Inf. Retr. 2014, 7, 239–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Countries with Most X/Twitter Users 2023|Statista. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/242606/number-of-active-twitter-users-in-selected-countries/ (accessed on 22 January 2024).
- Habash, N.; Eskander, R.; Hawwari, A. A Morphological Analyzer for Egyptian Arabic. In Proceedings of the Twelfth Meeting of the Special Interest Group on Computational Morphology and Phonology, Montréal, QC, Canada, 7 June 2012; Cahill, L., Albright, A., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Pennsylvania, PA, USA, 2012; pp. 1–9. Available online: https://aclanthology.org/W12-2301 (accessed on 14 February 2024).
- Farghaly, A.; Shaalan, K. Arabic Natural Language Processing. ACM Trans. Asian Lang. Inf. Process. 2009, 8, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almuqren, L.; Cristea, A. AraCust: A Saudi Telecom Tweets corpus for sentiment analysis. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azmi, A.M.; Alzanin, S.M. Aara’–A system for mining the polarity of Saudi public opinion through e-newspaper comments. J. Inf. Sci. 2014, 40, 398–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harbi, W.; Emam, A. Emam Effect of Saudi Dialect Preprocessing on Arabic Sentiment Analysis. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Technol. (IJACT) 2015, 4, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Twairesh, N.; Al-Khalifa, H.; Al-Salman, A.; Al-Ohali, Y. AraSenTi-Tweet: A Corpus for Arabic Sentiment Analysis of Saudi Tweets. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 117, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Thubaity, A.; Alharbi, M.; Alqahtani, S.; Aljandal, A. A Saudi Dialect Twitter Corpus for Sentiment and Emotion Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2018 21st Saudi Computer Society National Computer Conference (NCC), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 25–26 April 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqarafi, A.; Adeel, A.; Hawalah, A.; Swingler, K.; Hussain, A. A Semi-supervised Corpus Annotation for Saudi Sentiment Analysis Using Twitter. In Proceedings of the BICS 2018: 9th International Conference on Brain Inspired Cognitive Systems, Xi’an, China, 7–8 July 2018; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alruily, M. Issues of Dialectal Saudi Twitter Corpus. Int. Arab. J. Inf. Technol. 2019, 17, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayazed, A.; Torabah, O.; AlSulami, R.; Alahmadi, D.; Babour, A.; Saeedi, K. SDCT: Multi-Dialects Corpus Classification for Saudi Tweets. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2020, 11, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abozinadah, E.A.; Jones, J.H., Jr. A Statistical Learning Approach to Detect Abusive Twitter Accounts. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Compute and Data Analysis, in ICCD’17, Lakeland, FL, USA, 19–23 May 2017; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, H.; Darwish, K.; Magdy, W. Abusive Language Detection on Arabic Social Media. In Proceedings of the First Workshop on Abusive Language Online, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 4 August 2017; Association for Computational Linguistics: Pennsylvania, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Abdelfatah, K.; Terejanu, G.; A Alhelbawy, A. Unsupervised Detection of Violent Content in Arabic Social Media. Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol. (CS IT) 2017, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alakrot, A.; Murray, L.; Nikolov, N.S. Towards Accurate Detection of Offensive Language in Online Communication in Arabic. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 142, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albadi, N.; Kurdi, M.; Mishra, S. Are they Our Brothers? Analysis and Detection of Religious Hate Speech in the Arabic Twittersphere. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining (ASONAM), Barcelona, Spain, 28–31 August 2018; pp. 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, H.; Hassan, S.; Chowdhury, S.A. Emojis as anchors to detect Arabic offensive language and hate speech. Nat. Lang. Eng. 2023, 29, 1436–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, H.; Al-Khalifa, H.; Al-Thubaity, A. Overview of OSACT5 Shared Task on Arabic Offensive Language and Hate Speech Detection. In Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Open-Source Arabic Corpora and Processing Tools with Shared Tasks on Qur’an QA and Fine-Grained Hate Speech Detection, Marseille, France, 25 June 2022; pp. 162–166. Available online: https://aclanthology.org/2022.osact-1.20 (accessed on 6 December 2022).
- What Is Hate Speech? Rights for Peace. Available online: https://www.rightsforpeace.org/hate-speech (accessed on 26 December 2022).
- Daniel, J.; Martin, J.H.; Peter, N.; Stuart, R. Speech and Language Processing, 3rd ed.; Pearson: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Novak, P.K.; Smailović, J.; Sluban, B.; Mozetič, I. Sentiment of Emojis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Torki, M.; El-Makky, N. Imbalanced Toxic Comments Classification Using Data Augmentation and Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 17th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Orlando, FL, USA, 17–20 December 2018; pp. 875–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, H.; Rashed, A.; Darwish, K.; Samih, Y.; Abdelali, A. Arabic Offensive Language on Twitter: Analysis and Experiments. In Proceedings of the Sixth Arabic Natural Language Processing Workshop, Kyiv, Ukraine (Virtual), 19 April 2021; pp. 126–135. [Google Scholar]
- Alkadri, A.M.; Elkorany, A.; Ahmed, C. Enhancing Detection of Arabic Social Spam Using Data Augmentation and Machine Learning. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Ref. | Author/Year | Dataset Size | Main Task/Purpose | Label |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [19] | Azmi and Alzanin (2014) | 815 comments from two Saudi newspapers | Sentiment classification | Strongly positive, positive, negative, or strongly negative |
| [20] | Al-Harbi and Emam (2015) | 5500 tweets | Sentiment classification | Positive, negative, or neutral |
| [21] | Al-Twairesh et al. (2017) | 17,000+ tweets | Sentiment classification | Positive, Negative, Neutral |
| [22] | Al-Thubaity et al. (2018) | 5400 tweets | Sentiment classification; | Positive, negative, neutral, objective, spam, or not sure; |
| Emotion classification | anger, fear, disgust, sadness, happiness, surprise, no emotion, and not sure | |||
| [23] | Alqarafi et al. (2018) | 4000 tweets | Sentiment classification | Positive or negative |
| [24] | Alruily (2020) | 207,452 tweets | Linguistic analysis | Various linguistic features |
| [8] | Alshalan and Al-Khalifa (2020) | 9316 tweets | Hate speech detection | Normal, abusive, hateful |
| [25] | Bayazed et al. (2020) | 4180 tweets | Dialect classification; Sentiment classification | Hijazi, Najdi, and eastern; positive, negative, or neutral |
| [18] | Almuqren and Cristea (2021) | 20,000 tweets, telecom-related tweets | Sentiment classification | Negative, positive |
| Query-Driven | List | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Emojis |  , ,  , ,  , ,  , ,  , ,  , ,  , ,  , ,  , ,  , ,  , ,  , ,  , ,  , ,  , ,  , ,  , ,  | Curse, Rudeness, Dirty, Rude, Dog, Donkey, Pig, Trash, Spit on you, Despicable, Lowly, You animal, Filthy, You Yemeni, You Egyptian, You Indian, You Bengali, Cap, [Direct names for Football Clubs and Regional Terms] |
| Keywords | يلعن, قلة أدب, وسخ, وقح, كلب, حمار, خنزير, زبالة, تفو عليك, خسيس, نذل, ياحيوان, نجس, يايمني, يايماني, يامصري, ياهندي, يابنقالي, طاقية, دوري يلو, أهلي, هلال, اتحاد, نصراوي, طحالب, تماسيح, سحالي, نصر, اتحادي, هلالي, هلال, أهلاوي, شبابي, يابدوي, ياحضري, يابدو, ياحضر, ياقروي, ياخضيري, طرش بحر, بقايا حجاج, أعرابي, حجازي, نجدي, قصيمي, حساوي, زيدي, زيود, يابيض, ذباب الكتروني, ياشيعي, ياسني, ياداعشي, ياأخواني, ياوطنجي, ياإرهابي, داعشي, إرهابي, سني, شيعي, إيراني, أخواني, ليبرالي, حرمة, ياحريم, يابنت, البنات, الرجال, رجل, الرياجيل, بنات اليوم, أولاد اليوم, الأولاد | #AlShabab, #AlNassr, #AlHilal, #AlAhli, #AlIttihad, #SaudiLeague, #Crocodiles, #Algae, #Tigers, #Urban, #Bedouin, #Feminism, #Feminist, #Masculinity, #Masculine, #Independent, #Free |
| Hashtags | #الشباب, #النصر, #الهلال, #الأهلي, #الاتحاد, #الدوري_السعودي, #التماسيح, #الطحالب, #النمور, #حضر, #بدو, #نسوية, #نسوي, #ذكورية, #ذكوري, #مستقلة, #حرة | Curse, Rudeness, Dirty, Rude, Dog, Donkey, Pig, Trash, Spit on you, Despicable, Lowly, You animal, Filthy, You Yemeni, You Egyptian, You Indian, You Bengali, Cap, [Direct names for Football Clubs & Regional Terms] |
| Tweet | Location | Search by |
|---|---|---|
| @User والله من ضعافة النفس وقلة المروءه (Translation: Truly, this is due to a weak spirit and lack of chivalry.) | Dammam | General |
@User مغربية خاشعة كالندى تُرطب الروح تبارك الله  ، ، (Translation: A sunset, humble like the dew, refreshing the soul. God bless  ,) ,) | Jeddah | General |
اقسم بالله لو يخلو الحمير يسوقو حيسوقو احسن من البهايم الي هنا (Translation: I swear if they let donkeys drive, they would drive better than the idiots here.  ) ) | Medina | Emojis |
يارب يخلص هالشهر بسرعه و اروح اشوف لوسي   (Translation: Oh God, I hope this month ends quickly so I can go see Lucy   .) .) | Riyadh | Emojis |
| اخي بدر هؤلاء ليسوا هلاليين. هذول. مندسين مافيه عاشق هلالي الا قال معوضين خير ومبروك للوحده جماهير الزعيم الصادقه حملت الاعبين المسؤليه الامور الاداريه والفنيه في منتهى الروعه لاتلتفتوا لم يريد الايقاع وشق الصف اتركوهم ولاتصغون لثرثرتهم (Translation: Brother Badr, these are not Hilal supporters. These are infiltrators. No true Hilal fan would say anything but ‘we will be compensated for the best’ and ‘congratulations to Al-Wehda’. The true fans of the leader held the players responsible. Administrative and technical matters are superb. Do not pay attention to those who want to cause division and break ranks. Leave them and do not listen to their chatter.) | Najran | Keywords |
@User @Userاكرم الحمار منه ع الاقل الحمار يستفاد منه هذا خنزير الله يكرمك احد يعرف رقم حسابه البنكي    (Translation: It’s better to honor the donkey than him, at least the donkey is beneficial. This one’s a pig, God bless you. Does anyone know his bank account number?    ) ) | Tabuk | Keywords |
| @User لاعبي #الهلال مدللين يلتحقون على كيفهم!! #المنتخب_السعودي #التصر #الأهلي #الاتحاد #التعاون #الشباب (Translation: The #Alhilal players are pampered and join as they please!! #Saudi_national_team #Alahli #Alittihad #Altaawon #Alshabab) | Buraidah | Hashtag |
لا زلت أقول ، الحمد لله على نعمة #الهلال  (Translation: I still say, thank God for the blessing of #Alhilal  .) .) | Albaha | Hashtag |
| Label | Meaning | Description & Examples (If Applicable) |
|---|---|---|
| Tweet Type | Offensive | Contains any offensive terms, either general or specific to an individual or group. General Example (Arabic): ‘حظي مع الأفلام زبااالة’. Translation: ‘My luck with movies is trash’. Specific Example (Arabic): ‘الله ياخذك يا متخلف يا طرش بحر’. Translation: (Derogatory terms directed at a specific person) |
| Non-Offensive | Neutral words that aren’t meant to offend. Example (Arabic): ‘صباح الخير، أحوال الطقس اليوم كأننا في لندن’. Translation: ‘Good morning, today’s weather feels like we’re in London’. | |
| Type of Offense | Hate Speech | Any term that shows hatred towards individuals or groups based on their race, gender, orientation, etc. |
| Sarcasm | Words that appear complimentary but are meant sarcastically. Example (Arabic): ‘خف علينا يا أجمل واحد في العالم.. سوبهان الله’. Translation: ‘Ease up on us, the most beautiful person in the world… Praise be to God’. (Meant sarcastically) | |
| General Insult | The tweet contains abrasive language not directed at anyone specific. Example (Arabic): ‘حظي مع الأفلام زبااالة’. Translation: ‘My luck with movies is trash’. | |
| Type of Hate Speech | Racial | Hatred is directed towards a specific race. Example (Arabic): ‘ياعبد ياأسود، يايماني، ياحضري، يابدوي’. Translation:
|
| Gender | Insults are based on the opposing gender. Example (Arabic): ‘أنتم يا الرجال، الحريم دائما’. Translation: ‘You men, women always… | |
| Sport | Any insult due to sports affiliations, either towards teams or individuals in the sports field. | |
| Political/Religious | Insults stemming from religious or political differences. | |
| Vulgar | Any sexually explicit content. | |
| Insult–Violence | Direct insult towards someone without relating to the above reasons. Example (Arabic): ‘ياحمار ما تفهم!’. Translation: ‘You donkey, you don’t understand!’ | |
| Other | Undefined category; ideally chosen very rarely. | |
| Any Note | In this column, the reasons for deletion are recorded, whether it’s due to a lack of understanding requiring further review or if something in the tweet was noticed. |
| Label | Category | Example 1 | Example 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Offensive | Non-Offensive | أسأل الله أن يرزقني ويرزقكم فوق مآ تتمنون NLسـعآدة تسع الكون بأكمله”.NLNL سنة سعيدة عليكم متابعيني سنة سعيدة عليكم متابعيني  NLNL#السنه_الجديده_2022 NLNL#السنه_الجديده_2022(Translation: I ask God to bless me and you beyond our wishes. Happiness that fills the entire universe.) | تغيب عن عيني ولا تغيب روحك عن روحي (Translation: You disappear from my eyes, but your soul never leaves mine.) |
| Offensive | الفار حرمني من الفرحه حسبي الله بس يا عيني يا ماني  (Translation: The VAR deprived me of joy, I rely on God, oh my eyes, oh my fate  ) ) | اذا عفوه من منصبه جابو العنّ منه  #اقيلوا_معين_قبل_نفاذ_صبرنا #اقيلوا_معين_قبل_نفاذ_صبرنا(Translation: If they pardoned him from his position, they brought disaster from him  #Remove_Mu’een_Before_Our_Patience_Runs_Out) #Remove_Mu’een_Before_Our_Patience_Runs_Out) | |
| Hate Speech | General Insult | شششنوووو القرف الي انا شفته الييوم؟؟؟ (Translation: What the hell did I see today?) | الحين ليش المباره بجدة؟ انا ملعب الجوهره يسبب لي تشاؤم والعياذ بالله (Translation: Why is the match in Jeddah now? The Jewel Stadium brings me pessimism, I seek refuge in God) |
| Sarcasm | #الارجنتين_كرواتياNLالاسم : دي بول NLالوظيفه: الحارس الشخصي لميسي (Translation: #Argentina_Croatia Name: De Paul, Occupation: Messi’s personal guard) | سؤال للبنات الشخص اللي قالكNLهيحارب الدنيا عشانك   NLلسى يحارب والا مات NLلسى يحارب والا مات   (Translation: A question for the girls, the person who told you “He would fight the world for you”   , is he still fighting or did he die? , is he still fighting or did he die?    ) ) | |
| Hate Speech | قسم بالله حكم ضايعع (Translation: I swear to God, the referee is lost) | USER تاريخه الفني زفت في زفتNLدور مقزز ومقرف (Translation: USER, his artistic history is crap upon crap, a disgusting and repulsive role) | |
| Hate Speech Types | Religious/Politics/Racial | USER جرب تزور الشعب السعودي علشان يقومون بواجبك سوف يستقبلونك    افهم وخل الحمير لي وراك تفهم الشعب السعودي محمد بن سلمان وأنتم مو أهل رد معروف انتم ناكرين للمعروف منافقين خونه افهم وخل الحمير لي وراك تفهم الشعب السعودي محمد بن سلمان وأنتم مو أهل رد معروف انتم ناكرين للمعروف منافقين خونه(Translation: USER, try visiting the Saudi people to fulfill your duty, they will receive you with shoes     . Understand and leave the donkeys behind you. The Saudi people understand Mohammed bin Salman, and you are not people of gratitude, you are ungrateful, hypocrites, traitors) . Understand and leave the donkeys behind you. The Saudi people understand Mohammed bin Salman, and you are not people of gratitude, you are ungrateful, hypocrites, traitors) | USER USER USER حتى فيه من يدعي أنه سني يبوس جزمة الخميني ويقدم أخته وأمه متعه لي الفرس خذ حزب الإخوان الخونه خذ حماس هذول يدعون أنهم سنه ولكنهم جنود لي الفرس يحاربون الإسلام والعرب ومعهم حزب الإصلاح اليمني كلهم يبوسون جزمة الخميني (Translation: USER USER USER, there are even those who claim to be Sunni, they kiss Khomeini’s shoes, and offer their sisters and mothers for pleasure to the Persians. Take the traitor Muslim Brotherhood, take Hamas. These claim to be Sunnis, but they are soldiers for the Persians, fighting Islam and the Arabs, and with them is the Yemeni Reform Party, all of them kissing Khomeini’s shoe) |
| Sports | الفار حرمني من الفرحه حسبي الله بس يا عيني يا ماني  (Translation: The VAR deprived me of joy, I rely on God, oh my eyes, oh my fate  ) ) | اقذر مهاجم كوستا (Translation: The dirtiest attacker, Costa) | |
| Violence/Insult | USER لعنة الله وسخط عليه ابن ال (Translation: May God’s curse and wrath be upon him, son of the  ) ) | عندنا إذا واحد يبي يسب واحد آخر لأنه ما يفهم أو ما يستوعب الكلام يقول لهNLياثور أو يابقره أو يابقره  وغاب عنه هذا الذي يسب أنه هو لم ينتج ولا شيء مما أنتجه الثور أو أنتجته البقره!!NLشاهد وتأمل وغاب عنه هذا الذي يسب أنه هو لم ينتج ولا شيء مما أنتجه الثور أو أنتجته البقره!!NLشاهد وتأمل URL URL(Translation: In our culture, if someone wants to insult another because they don’t understand or grasp something, they call them “bull” or “cow”.) | |
| Gender: Male–Female | وبعدين يجي يقول البنات مايعرفو يسوقو  (Translation: And then he comes saying girls don’t know how to drive  ) ) | USERاغلب بنات اليوم كذا اجل تبيها تصحى الصباح تسوي لك الفطور والظهر تسوي لك الغدا حلم ابليس في الجنه (Translation: Most of the girls these days are like this, do you expect her to wake up in the morning, prepare breakfast for you and then lunch? It’s like Iblis’s dream in paradise) |
| All Tweets | Offensive Tweets | Hate Speech Tweets | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tweet | Offensive | Non-Offensive | General Insult | Hate Speech | Sarcasm | Sport | Religious–Political–Racial | Insult–Violence |
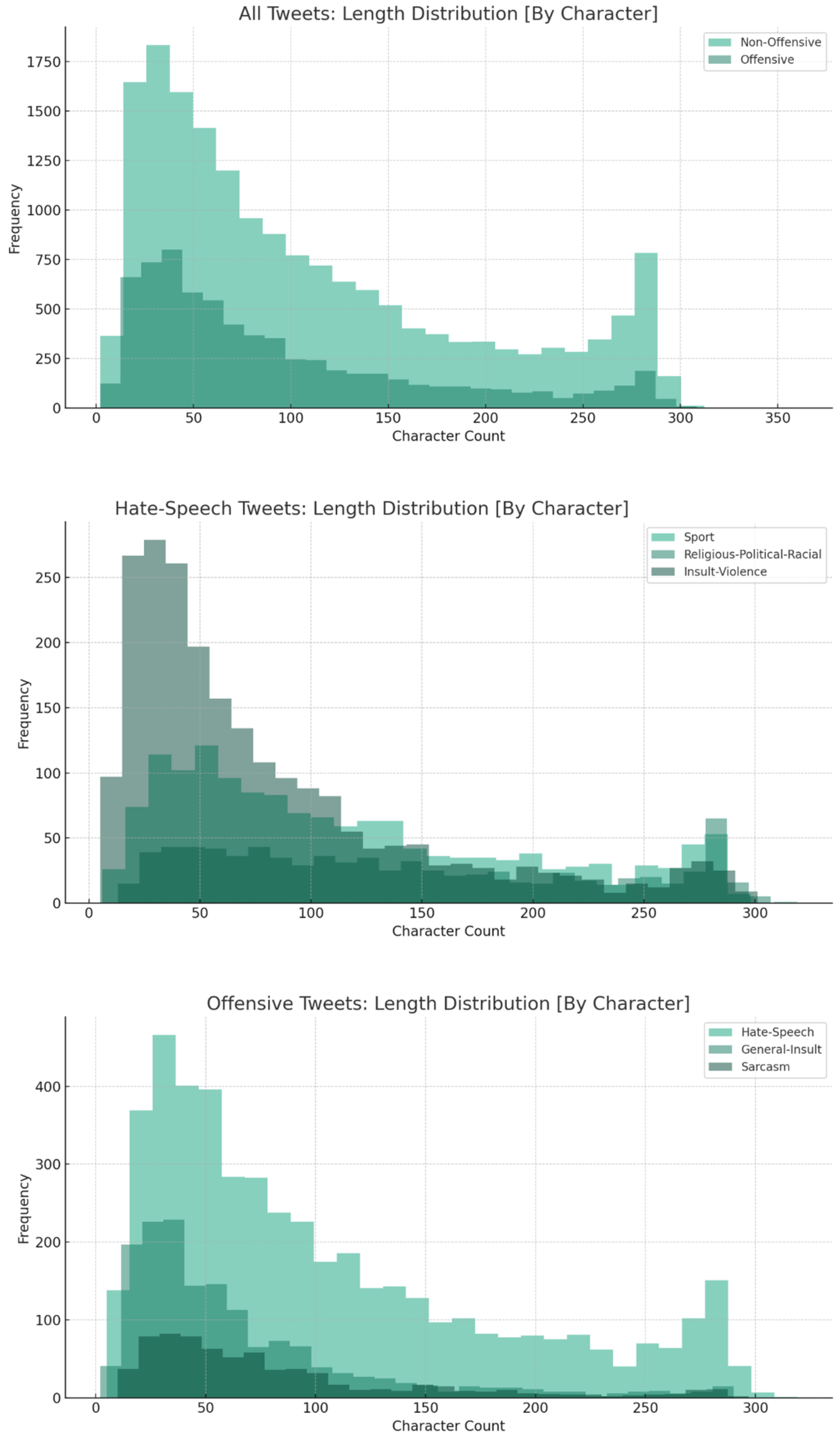
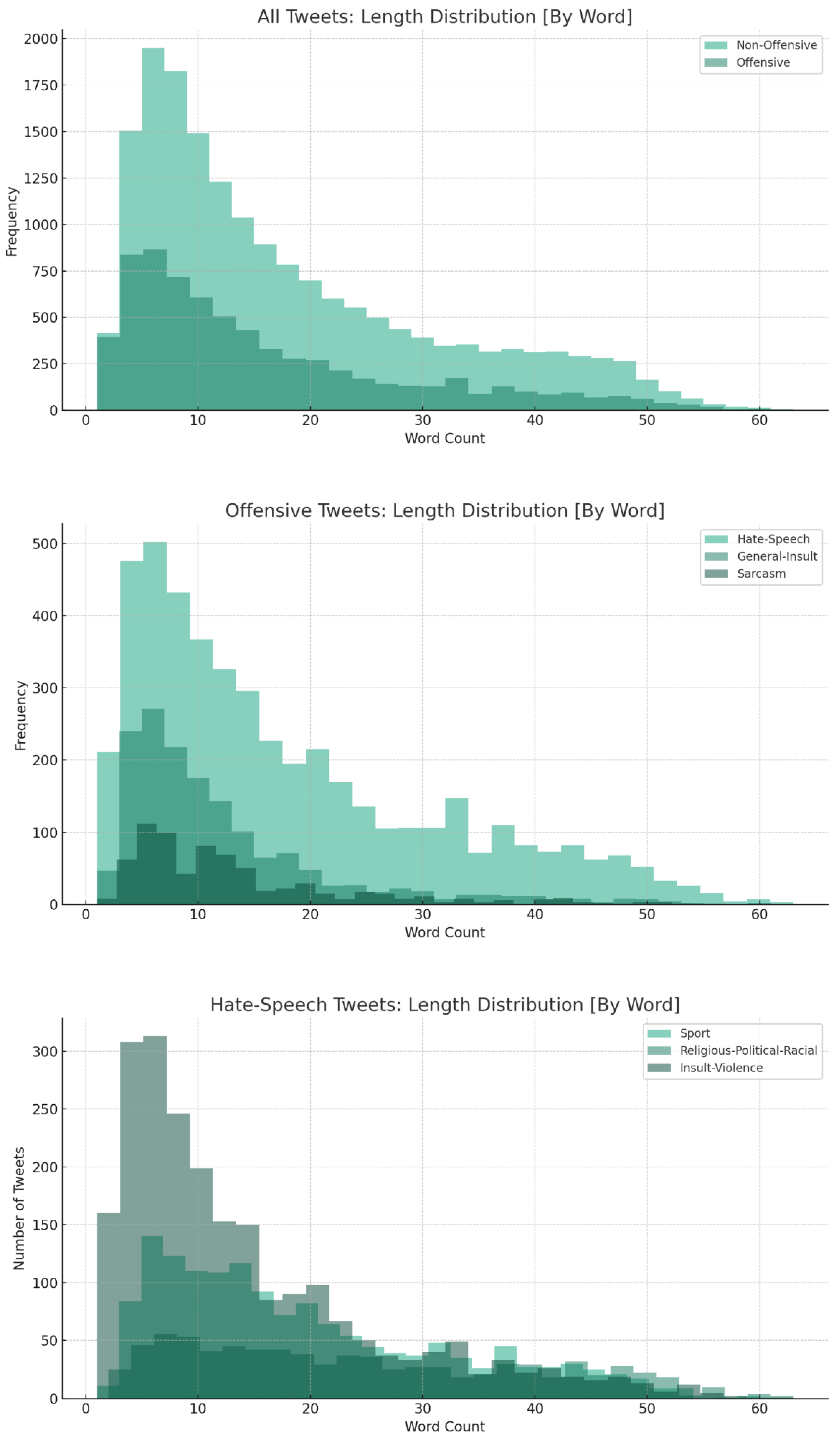
| Count | 7008 | 17,509 | 1588 | 4707 | 717 | 1500 | 825 | 2274 |
| Word | ||||||||
| Avg. length | 16.08 | 17.48 | 11.77 | 17.96 | 13.30 | 19.33 | 24.67 | 14.57 |
| Median | 12 | 13 | 9 | 14 | 10 | 16 | 22 | 11 |
| Minimum | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Max | 63 | 61 | 61 | 63 | 54 | 60 | 63 | 63 |
| Character | ||||||||
| Avg. length | 92.93 | 108.32 | 65.56 | 103.89 | 81.74 | 117.40 | 141.96 | 80.89 |
| Median | 67 | 82 | 47 | 79 | 62 | 97 | 127 | 57 |
| Minimum | 2 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 10 | 6 | 13 | 5 |
| Max | 319 | 360 | 290 | 319 | 297 | 319 | 307 | 301 |
| All Tweets | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Offensive | Non-Offensive | ||||||
| Unigram | Bigram | Trigram | Emoji | Unigram | Bigram | Trigram | Emoji |
| USER | USER USER | USER USER USER |  | USER | USER USER | USER USER USER |  |
| من | الله يلعن | الله ونعم الوكيل |  | من | USER الله | ان شا الله |  |
| في | USER الله | كذابين كذابين كذابين |  | في | شا الله | USER USER الله |  |
| URL | USER والله | USER USER والله |  | URL | في كل | صلى الله عليه |  |
| على | قلة ادب | حسبي الله ونعم |  | الله | كل شي | الله عليه وسلم |  |
| الله | USER هذا | USER USER لا |  | على | الف مبروك | عام وانتم بخير |  |
| و | حسبي الله | USER USER هذا |  | و | USER URL | عام ونتم بخير |  |
| يا | USER لا | USER USER الله |   | لا | USER لا | USER USER لا |  |
| ما | تفو عليك | USER USER يا |  | ما | كل عام | ما شا الله |  |
| لا | اقسم بالله | USER حسبي الله |   | كل | نادي #الشباب | NLUSER NLUSER NLUSER |  |
| Offensive Tweets | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General Insult | Hate Speech | Sarcasm | |||||||||
| Unigram | Bigram | Trigram | Emoji | Unigram | Bigram | Trigram | Emoji | Unigram | Bigram | Trigram | Emoji |
| user | user user | user user user |  | user | user user | user user user |  | user | user user | user user user |  |
| من | قلة ادب | كذابين كذابين كذابين |  | من | user هذا | الله ونعم الوكيل |  | url | دوري يلو | في دوري يلو |   |
| url | الله يلعن | الله ونعم الوكيل |  | في | user الله | user user والله |  | من | الدوري السعودي | user user طحالب |    |
| في | كذابين كذابين | user قلة ادب |  | الله | user والله | user user لا |  | nl | user طحالب | user user يا |  |
| الله | يلعن ام | حسبي الله ونعم |  | على | الله يلعن | حسبي الله ونعم |  | في | nl الهلال | nl الهلال nl |     |
| على | user الله | user قله ادب |  | url | حسبي الله | user user هذا |  | الهلال | user والله | nl الاهلي url |  |
| ما | user قلة | user user الله |    | يا | اقسم بالله | user user الله |  | النصر | user يا | ترجيع ترجيع ترجيع |  |
| يلعن | تفو عليك | user user من |  | ما | user لا | لعنة الله على |  | على | يا طاقية | في كرة القدم |  |
| لا | حسبي الله | user user وش |   | nl | تفو عليك | محمد بن سلمان |   | يا | يا طاقيه | على أدلة دارون |  |
| ادب | قله ادب | حول ولا قوة |   | هذا | nl النصر | user user يا |   | nlnl | nl nl | حافظ مش فاهم |  |
| Hate Speech Tweets | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sport | Religious–Political–Racial | Insult–Violence | |||||||||
| Unigram | Bigram | Trigram | Emoji | Unigram | Bigram | Trigram | Emoji | Unigram | Bigram | Trigram | Emoji |
| user | user user | user user user |  | user | user user | user user user |  | user | user user | user user user |  |
| من | nl النصر | الله ونعم الوكيل |  | من | user هذا | لعنة الله على |  | من | user الله | user user لا |  |
| النصر | اقسم بالله | الدوري مع وليد |  | في | user انت | user لعنة الله |  | الله | user هذا | user user الله |  |
| في | حسبي الله | حسبي الله ونعم |   | الله | لعنة الله | user user هذا |  | يا | user والله | user user والله |  |
| الهلال | الله يلعن | النصر ضمك الدوري |  | على | طرش بحر | الله ونعم الوكيل |  | في | user لا | الله ونعم الوكيل |  |
| على | user والله | محمد بن سلمان |   | url | الله على | حسن نصر الله |  | url | تفو عليك | حسبي الله ونعم |  |
| nl | nl الاهلي | user user والله |    | هذا | user والله | في العراق وسوريا |  | على | الله يلعن | user user يا |  |
| الاتحاد | nl الهلال | النصر الاتفاق دوري |   | يا | user الله | الله عليه وسلم |  | ما | حسبي الله | user user هذا |   |
| الله | الله ونعم | حسبي الله عليك |  | ما | نصر الله | لعنة الله عليهم |  | اللي | user يا | الله عليك يا |  |
| url | مع وليد | user user لا |  | لا | اكثر من | صلى الله عليه |  | حمار | يا حمار | user user حمار |  |
| Classification Task | Model | Classifier | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | F1-Macro |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
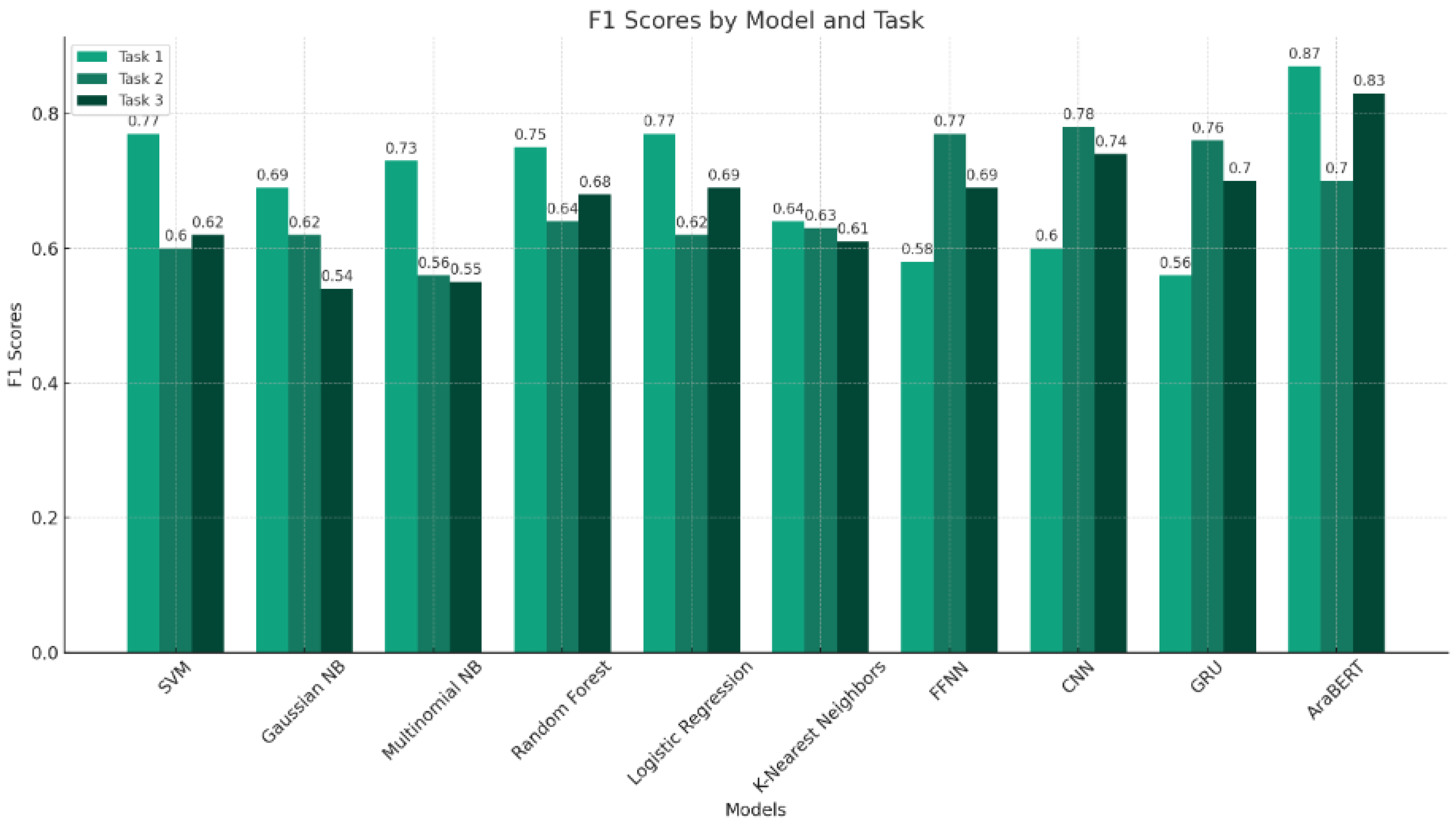
| All Tweets: Offensive or Non-Offensive | ML | SVM | 0.80 | 0.81 | 0.80 | 0.77 | 0.69 |
| Gaussian naive Bayes | 0.67 | 0.71 | 0.67 | 0.69 | 0.63 | ||
| Multinomial naive Bayes | 0.78 | 0.81 | 0.78 | 0.73 | 0.62 | ||
| Random forest | 0.78 | 0.79 | 0.78 | 0.75 | 0.65 | ||
| Logistic regression | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.77 | 0.69 | ||
| K-nearest neighbors | 0.71 | 0.65 | 0.71 | 0.64 | 0.49 | ||
| DL | FFNN | 0.78 | 0.65 | 0.53 | 0.58 | 0.72 | |
| CNN | 0.79 | 0.65 | 0.55 | 0.60 | 0.73 | ||
| GRU | 0.77 | 0.61 | 0.52 | 0.56 | 0.70 | ||
| Transformer | AraBERT | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.84 | |
| Offensive Tweets: General Insult, Hate Speech, or Sarcasm | ML | SVM | 0.70 | 0.69 | 0.70 | 0.60 | 0.34 |
| Gaussian naive Bayes | 0.64 | 0.61 | 0.64 | 0.62 | 0.43 | ||
| Multinomial naive Bayes | 0.69 | 0.66 | 0.69 | 0.56 | 0.28 | ||
| Random forest | 0.70 | 0.66 | 0.70 | 0.64 | 0.43 | ||
| Logistic regression | 0.71 | 0.69 | 0.71 | 0.62 | 0.38 | ||
| K-nearest neighbors | 0.66 | 0.63 | 0.66 | 0.63 | 0.45 | ||
| DL | FFNN | 0.70 | 0.79 | 0.75 | 0.77 | 0.66 | |
| CNN | 0.70 | 0.79 | 0.77 | 0.78 | 0.67 | ||
| GRU | 0.69 | 0.79 | 0.74 | 0.76 | 0.65 | ||
| Transformer | AraBERT | 0.74 | 0.75 | 0.74 | 0.70 | 0.48 | |
| Hate Speech Tweets: Sport, Religious–Political–Racial, or Insult–Violence | ML | SVM | 0.68 | 0.77 | 0.68 | 0.62 | 0.50 |
| Gaussian naive Bayes | 0.54 | 0.57 | 0.54 | 0.54 | 0.52 | ||
| Multinomial naive Bayes | 0.62 | 0.76 | 0.62 | 0.55 | 0.43 | ||
| Random rorest | 0.71 | 0.77 | 0.71 | 0.68 | 0.59 | ||
| Logistic regression | 0.72 | 0.74 | 0.72 | 0.69 | 0.61 | ||
| K-nearest neighbors | 0.64 | 0.63 | 0.64 | 0.61 | 0.54 | ||
| DL | FFNN | 0.69 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.69 | 0.66 | |
| CNN | 0.74 | 0.75 | 0.74 | 0.74 | 0.73 | ||
| GRU | 0.69 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.66 | ||
| Transformer | AraBERT | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.81 |
| Reference | Model | Preprocessing Methods | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Our Study (SOD) | AraBERT: Transformer model pre-trained on Arabic, fine-tuned on Saudi dialect dataset. | Replaced user mentions with “USER”, URLs with “URL”, and newline indicators with “NL”. | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 |
| Best of OSACT5 Shared Task [37] | Ensemble: Combines MARBERT (without emojis), AraBERT-Large-Twitter, QARiB, and others. | Removed non-Arabic letters, punctuation marks, digits, Arabic diacritics, repeated characters, and replaced URL, @USER, and e-mail. | 0.87 | 0.86 | 0.85 | 0.85 |
| Mubarak et al. [38] | AraBERT (TF-IDF + FastText): Combines TF-IDF and FastText embeddings with AraBERT. | Performed text tokenization, removed URLs, numbers, tweet-specific tokens (mentions, retweets, and hashtags); normalized Arabic letters. | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.83 |
| Augmentation Techniques | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | F1-Macro |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline (No Augmentation) | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.84 |
| Random Deletion | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.85 |
| Random Swap | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.89 |
| Random Punctuation Insertion | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asiri, A.; Saleh, M. SOD: A Corpus for Saudi Offensive Language Detection Classification. Computers 2024, 13, 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers13080211
Asiri A, Saleh M. SOD: A Corpus for Saudi Offensive Language Detection Classification. Computers. 2024; 13(8):211. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers13080211
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsiri, Afefa, and Mostafa Saleh. 2024. "SOD: A Corpus for Saudi Offensive Language Detection Classification" Computers 13, no. 8: 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers13080211
APA StyleAsiri, A., & Saleh, M. (2024). SOD: A Corpus for Saudi Offensive Language Detection Classification. Computers, 13(8), 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers13080211






