Synthesis Chemistry and Properties of Ni Catalysts Fabricated on SiC@Al2O3 Core-Shell Microstructure for Methane Steam Reforming
Abstract
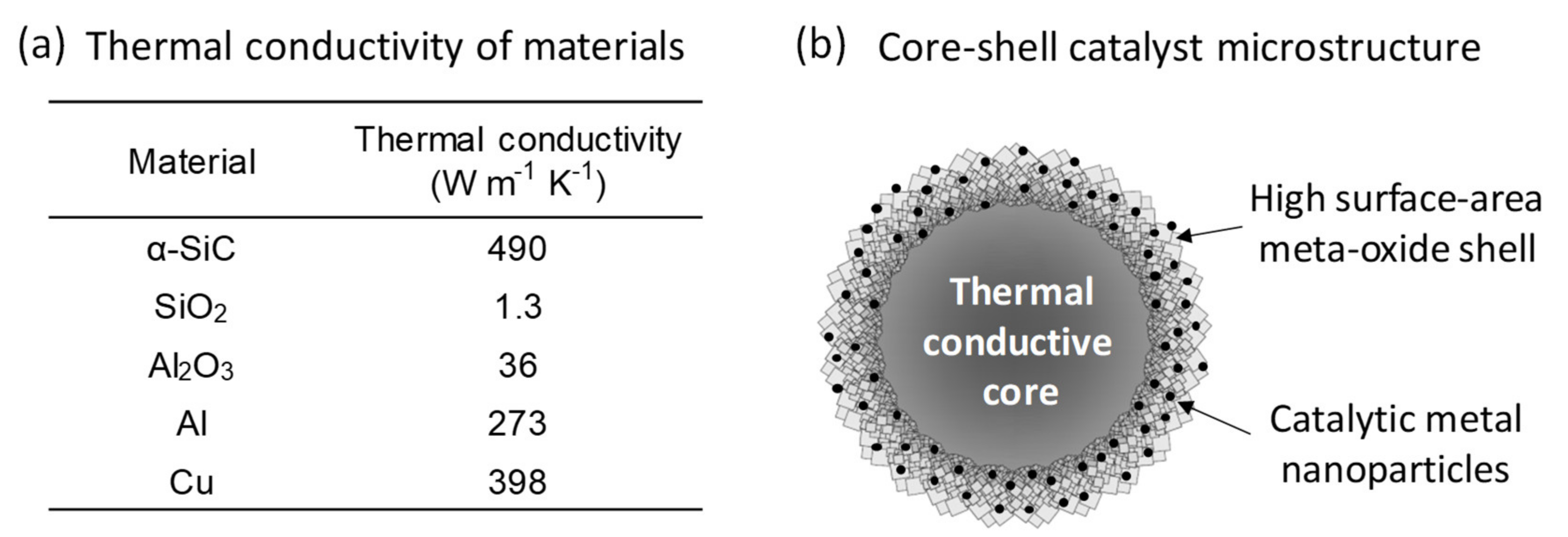
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
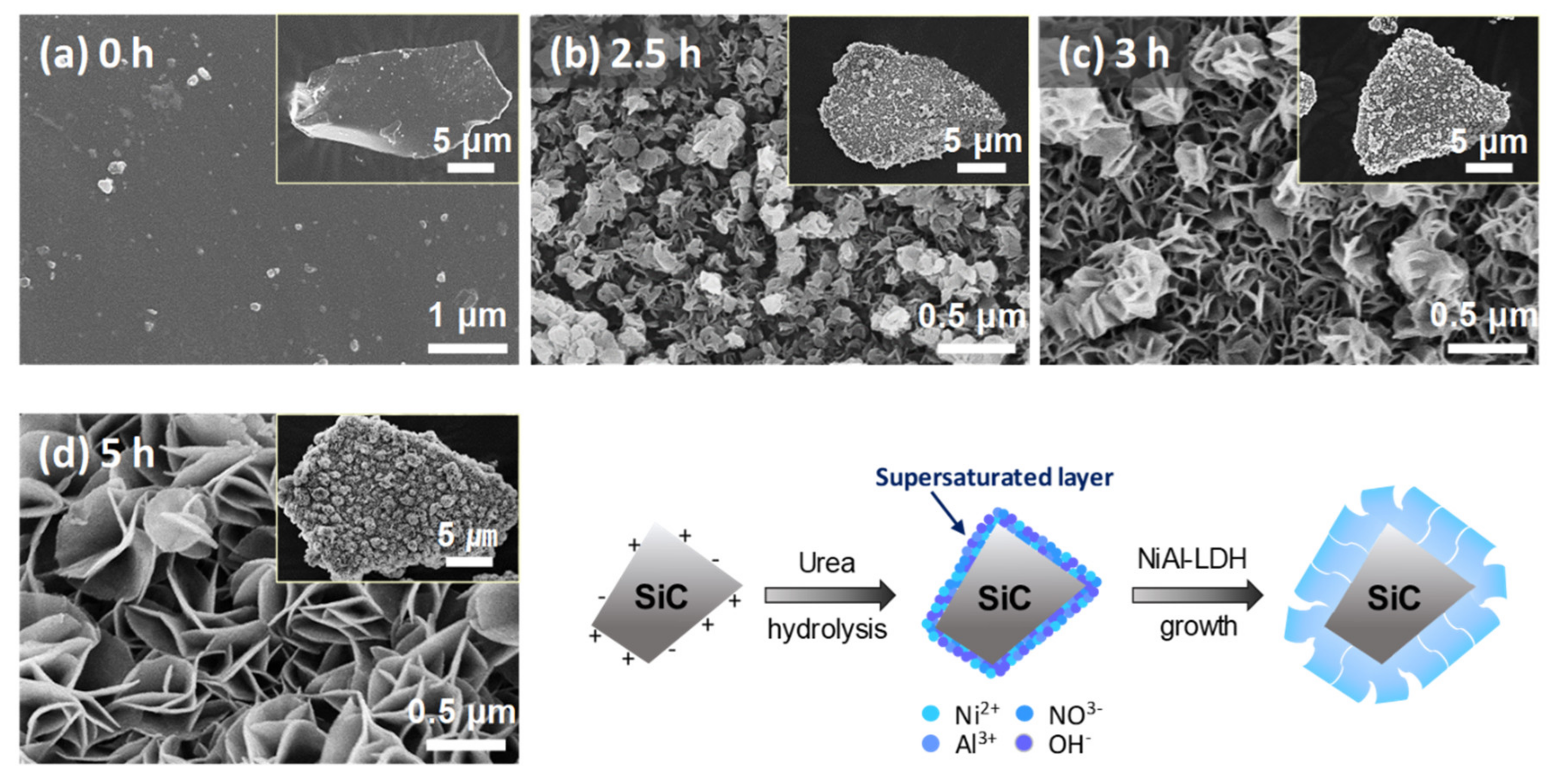
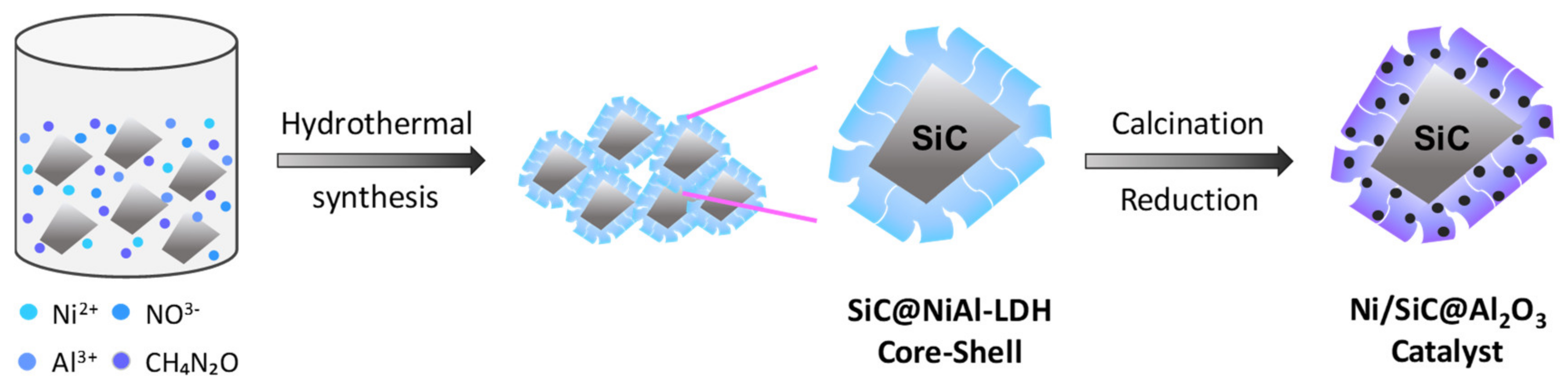
2.1. Synthesis Chemistry and Mechanism of Ni/SiC@Al2O3 Core-Shell Microstructures
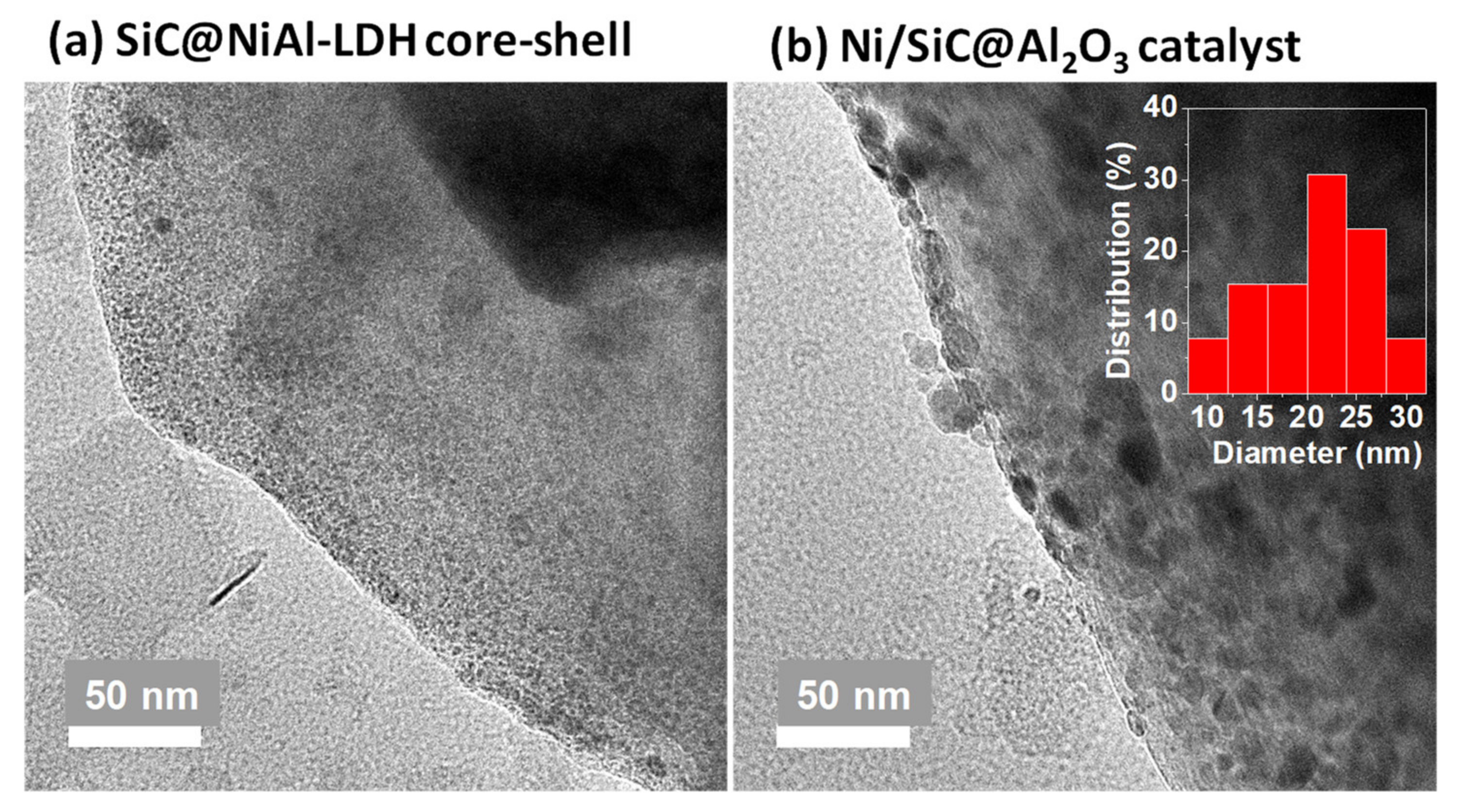
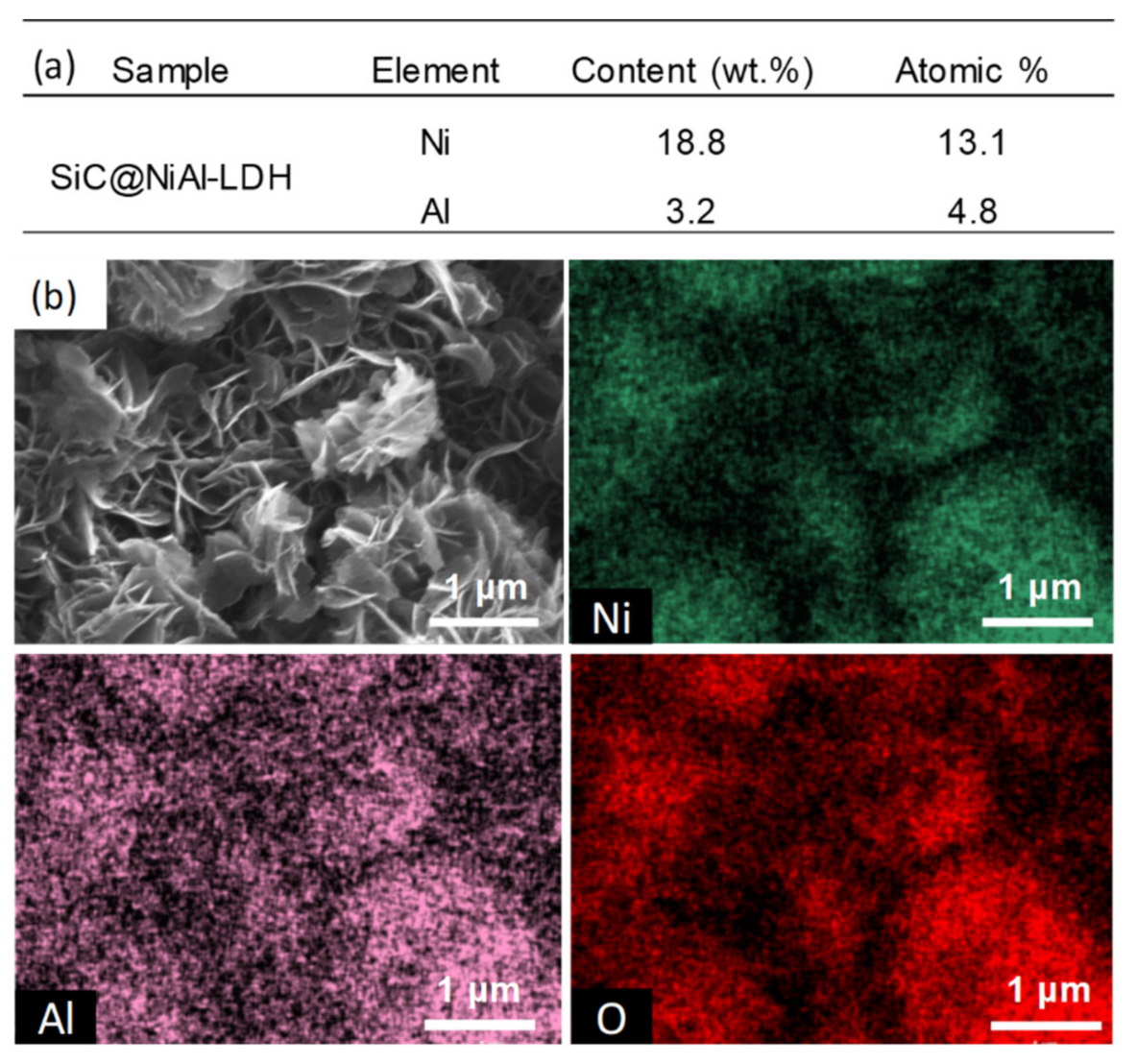
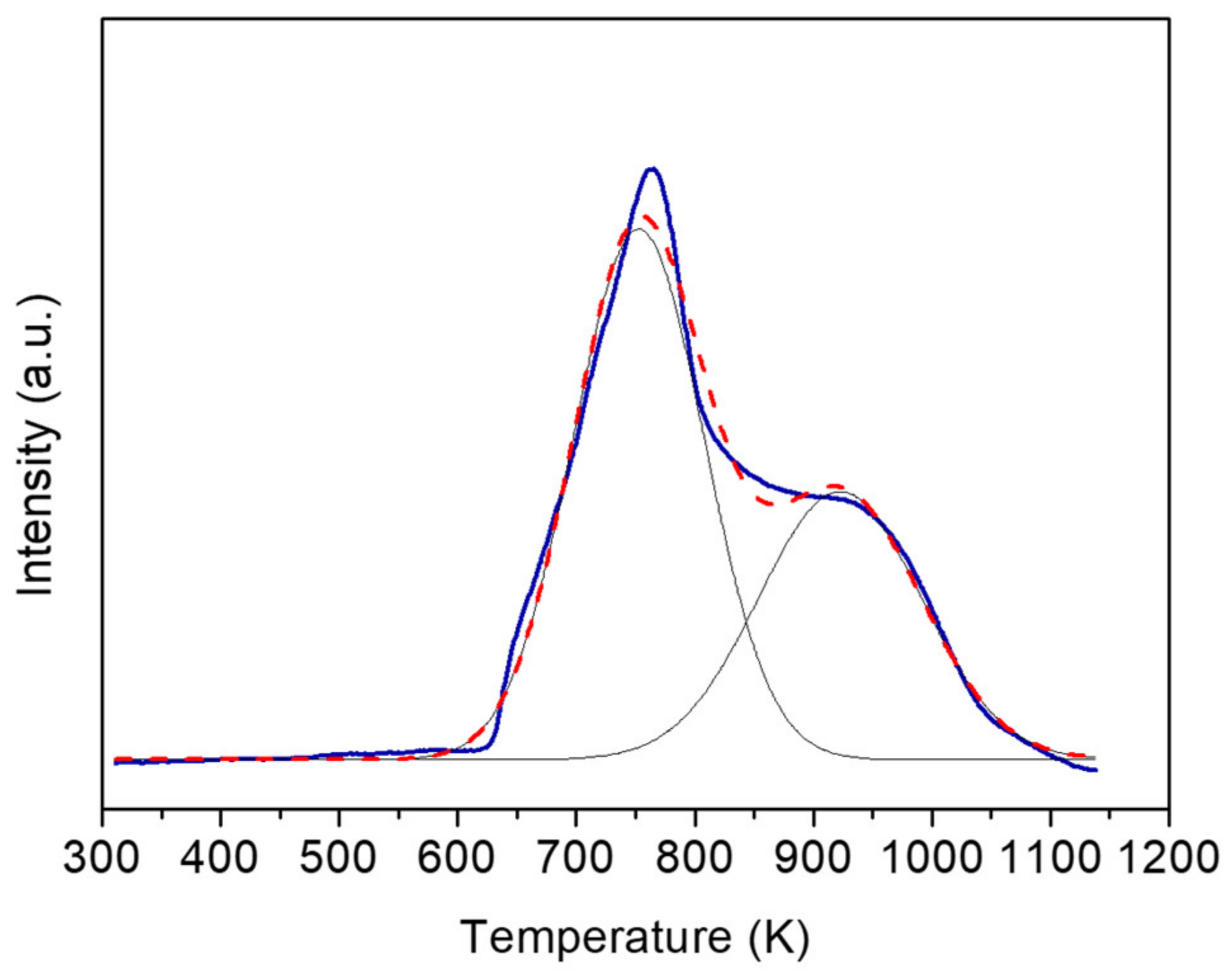
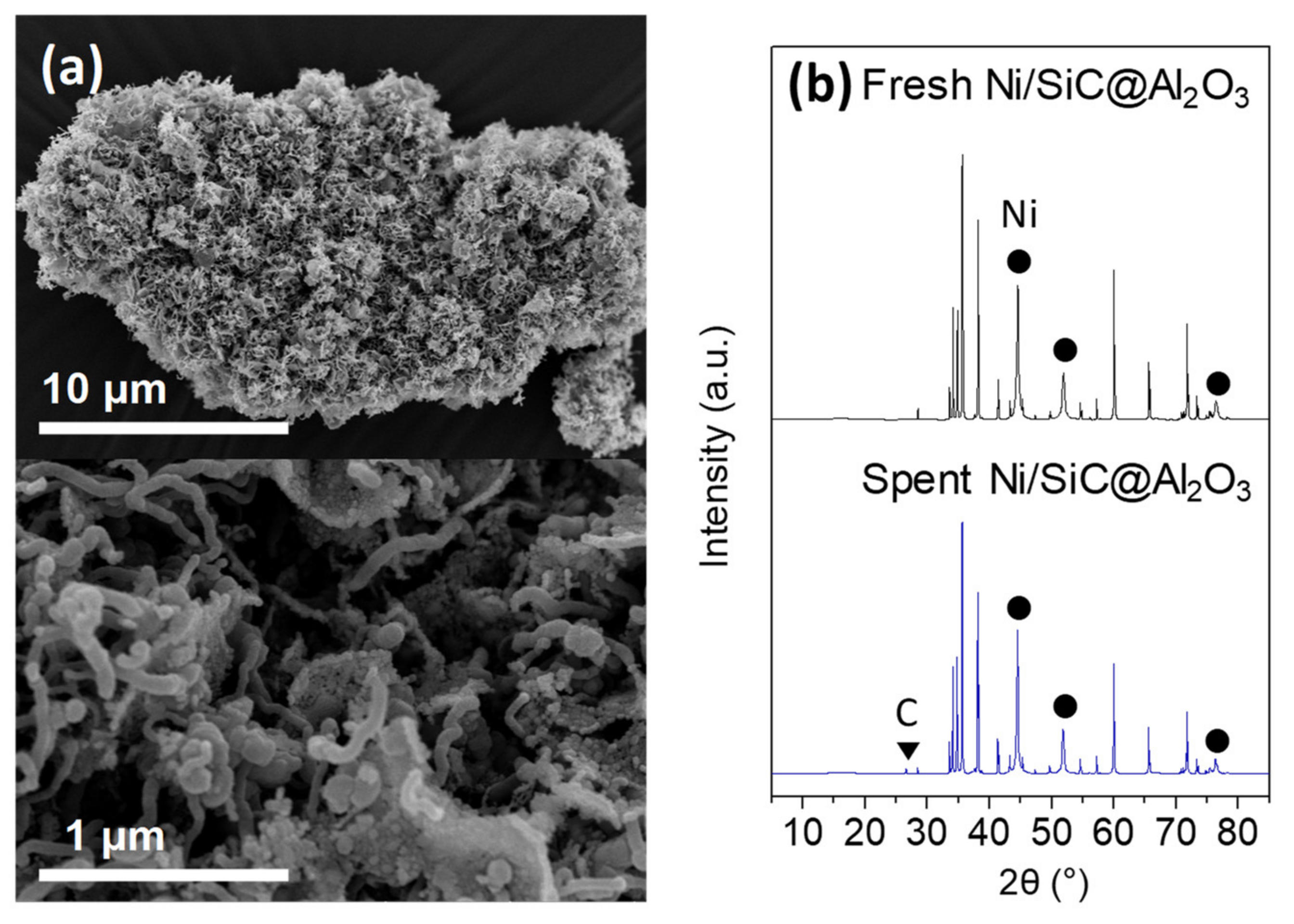
2.2. Properties of Ni/SiC@Al2O3 Core-Shell Catalysts
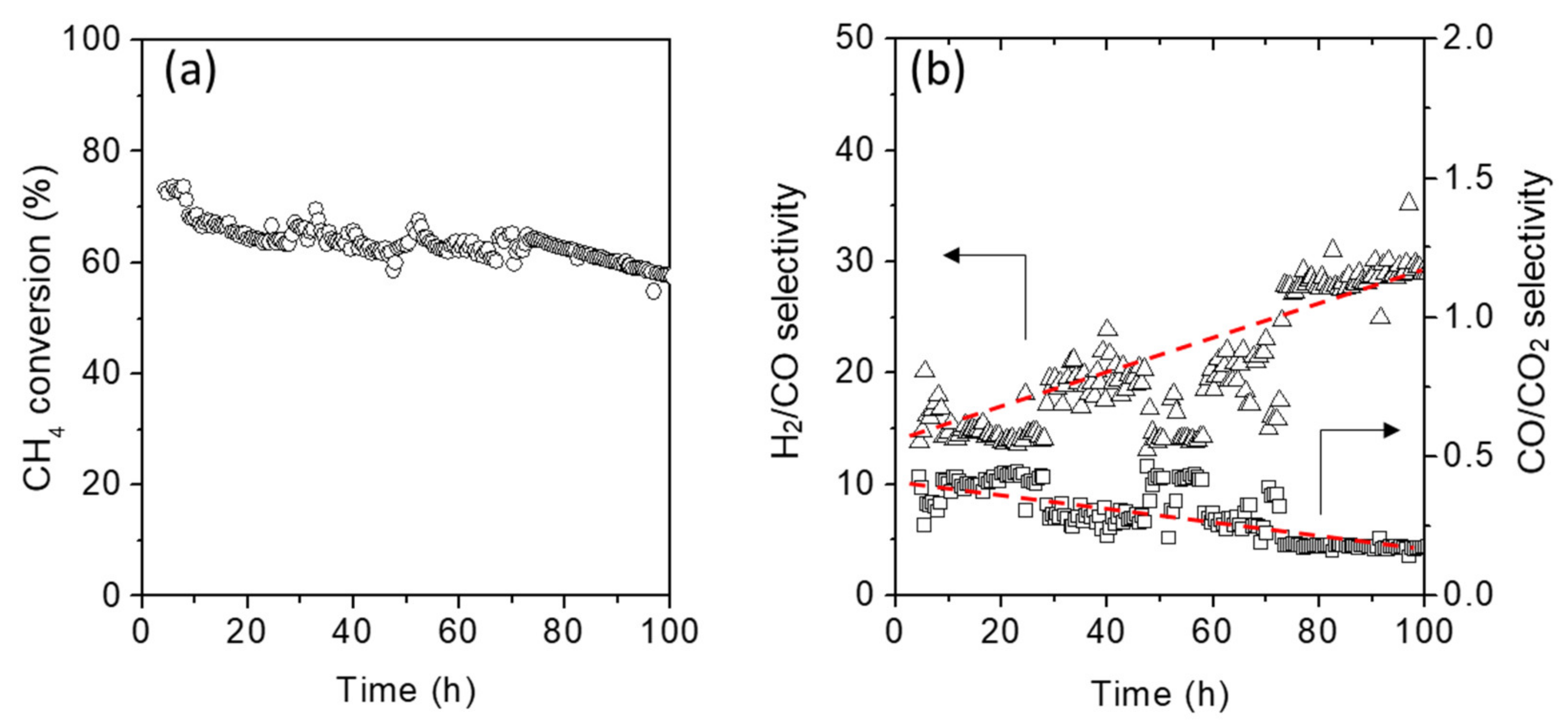
2.3. Methane Steam Reforming on Ni/SiC@Al2O3 Catalyst
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Catalyst Preparation
3.2. Characterization
3.3. Methane Steam Reforming
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ertl, G.; Knözinger, H.; Schüth, F.; Weitkamp, J. (Eds.) Handbook of Heterogeneous Catalysis, 2nd ed.; Wiely-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jarenwattananon, N.N.; Glöggler, S.; Otto, T.; Melkonian, A.; Morris, W.; Burt, S.R.; Yaghi, O.M.; Bouchard, L.S. Thermal maps of gases in heterogeneous reactions. Nature 2013, 502, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mei, D.; Lin, G. Effects of heat and mass transfer on the kinetics of CO oxidation over RuO2(110) catalyst. Catal. Today 2011, 165, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarulina, I.; Kapteijn, F.; Gascon, J. The importance of heat effects in the methanol to hydrocarbons reaction over ZSM-5: On the role of mesoporosity on catalyst performance. J. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 5320–5325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, M.; Yang, H.; Cahela, D.R.; Tatarchuk, B.J. Novel catalyst structures with enhanced heat transfer characteristics. J. Catal. 2011, 281, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.H.; Lee, K.Y.; La, H.; Kim, H.J.; Yang, J.I.; Jung, H. Ni catalyst wash-coated on metal monolith with enhanced heat-transfer capability for steam reforming. J. Power Sources 2007, 171, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Lee, D. Core—Shell metal—Ceramic microstructures: Mechanism of hydrothermal formation and properties as catalyst materials. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 2786–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, D. Synthesis and properties of Al2O3@Al metal-ceramic core-shell microstructures for catalyst applications. Top. Catal. 2015, 58, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, D. Synthesis and properties of core-shell metal-ceramic microstructures and their application as heterogeneous catalysts. ChemCatChem 2014, 6, 2642–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.C.; Potapova, Y.; Lee, D. A core-shell structured, metal-ceramic composite-supported Ru catalyst for methane stream reforming. J. Power Sources 2012, 216, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, D. Glycerol steam reforming on Ru catalysts supported on core-shell metal-ceramic microcomposites developed by microwave-induced hydrothermal method. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2015, 499, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rah, I.J.; Kim, T.W.; Kim, J.; Lee, D.; Park, E.D. Selective CO oxidation in the hydrogen stream over Ru/Al@Al2O3 catalysts. Catal. Today 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.W.; Perry, R.H. Perry’s Chemical Engineers’ Handbook, 8th ed.; The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, Y.; Levinshtein, M.E.; Rumyantsev, S.L. Properties of Advanced Semiconductor Materials: GaN, AlN, SiC, BN, SiC, SiGe; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 93–148. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Wang, Q.; O’Hare, D.; Sun, L. Preparation of two dimensional layered double hydroxide nanosheets and their applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 5950–5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Wei, M. Layered double hydroxide—Based catalysts: Recent advances in preparation, structure, and applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1802943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Xiang, X.; Li, F.; Duan, X. Layered double hydroxides as catalytic materials: Recent development. Catal. Surv. Asia 2008, 12, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, F. Transformation mechanism of magnesium and aluminum precursor solution into crystallites of layered double hydroxide. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, F.; Evans, D.G.; Duan, X. Layered double hydroxide films: Synthesis, properties and applications. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 5197–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhtiyarova, M.V. A review on effect of synthesis conditions on the formation of layered double hydroxides. J. Solid State Chem. 2019, 269, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashiba, M.; Okamoto, H.; Nurishi, Y.; Hiraastsu, K. The zeta-potential measurement for concentrated aqueous suspension by improved electrophoretic mass transport apparatus—Application to Al2O3, ZrO3 and SiC suspensions. J. Mater. Sci. 1988, 23, 2893–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drift, A.V.D. Evolutionary Selection, a principle governing growth orientation in vapour-deposited layers. Philips Res. Repts. 1967, 22, 267–288. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, K.; Deo, G. A potential descriptor for the CO2 hydrogenation to CH4 over Al2O3 supported Ni and Ni-based alloy catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 218, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, S.; Ray, K.; Deo, D. Effects of modifying Ni/Al2O3 catalyst with cobalt on the reforming of CH4 with CO2 and cracking of CH4 reactions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 11462–11472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Tan, B.; Ozkan, U.S. Effect of preparation method on structural characteristics and propane steam reforming performance of Ni–Al2O3 catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2009, 297, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavani, F.; Trifirò, F.; Vaccari, A. Hydrotalcite-type anionic clays: Preparation, properties and applications. Catal. Today 1991, 11, 173–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, C.; Kranenborg, J.; Monai, M.; Wechhuysen, B.M. Structure sensitivity in steam and dry methane reforming over nickel: Activity and carbon formation. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 1428–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






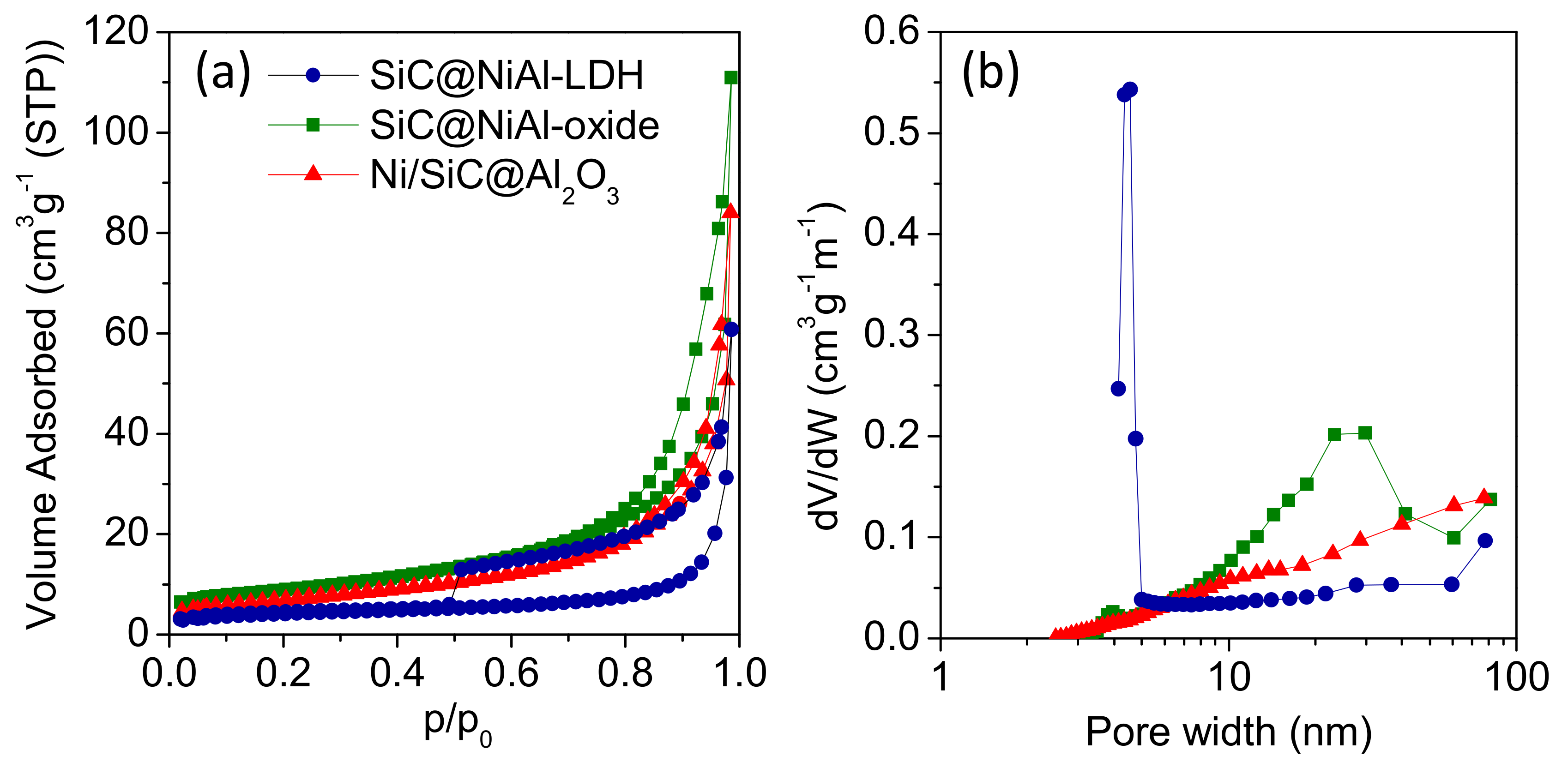
| Catalyst | BET Surface Area (m2g−1) | Average Pore Size (nm) | Total Pore Volume (cm3 g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiC@NiAl-LDH | 15 | 11 | 0.11 |
| SiC@NiAl-oxide | 31 | 21 | 0.18 |
| Ni/SiC@Al2O3 | 25 | 21 | 0.13 |
| NiAl-oxide [a] | 105 | 7 | 0.22 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.; Lee, D. Synthesis Chemistry and Properties of Ni Catalysts Fabricated on SiC@Al2O3 Core-Shell Microstructure for Methane Steam Reforming. Catalysts 2020, 10, 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040391
Lee H, Lee D. Synthesis Chemistry and Properties of Ni Catalysts Fabricated on SiC@Al2O3 Core-Shell Microstructure for Methane Steam Reforming. Catalysts. 2020; 10(4):391. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040391
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hyunju, and Doohwan Lee. 2020. "Synthesis Chemistry and Properties of Ni Catalysts Fabricated on SiC@Al2O3 Core-Shell Microstructure for Methane Steam Reforming" Catalysts 10, no. 4: 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040391
APA StyleLee, H., & Lee, D. (2020). Synthesis Chemistry and Properties of Ni Catalysts Fabricated on SiC@Al2O3 Core-Shell Microstructure for Methane Steam Reforming. Catalysts, 10(4), 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040391




