Decomposition of Ruthenium Olefin Metathesis Catalyst
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Non-Specific Decomposition Routes
2.1. Olefin-Driven Self-Degradations
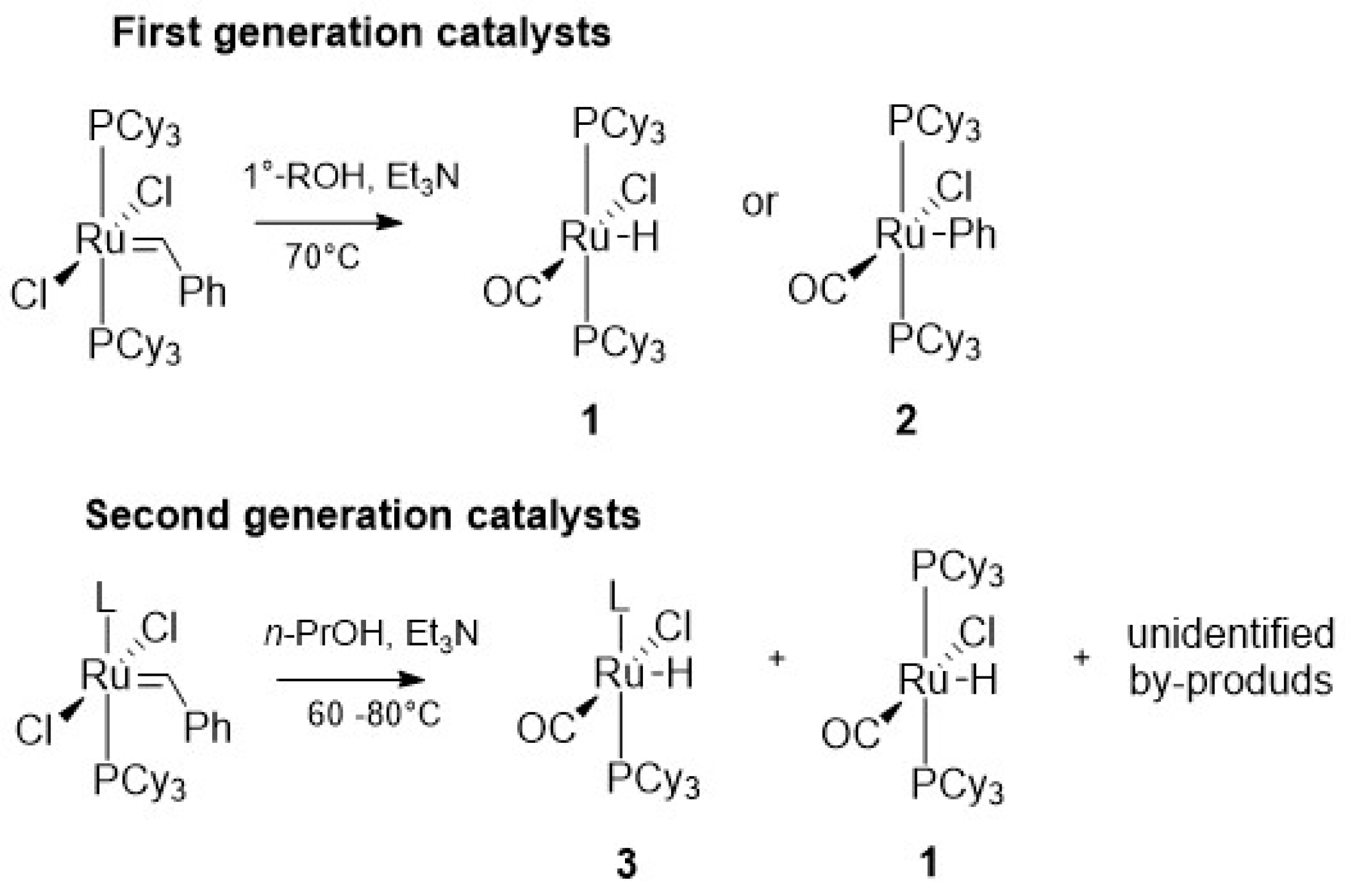
2.2. Alcohol and Alkoxy-Driven Decomposition
2.3. Phenols
2.4. Water-Mediated Degradation
2.5. Phosphines and General Routes to Metallacyclobutane Deprotonation
2.6. Amines
2.7. N-Heterocyclic Carbenes
2.8. Acrylonitrile
2.9. CO and O2
2.10. CO
3. Decomposition Routes Depending on the Ligands of Catalysts
3.1. Phosphine-Driven Decomposition
3.2. C-H Activation
3.3. Buchner-Type Expansion fo NHCs
4. Conclusions and Future Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rinehart, R.E.; Smith, H.P. The emulsion polymerization of the norbornene ring system catalyzed by noble metal compounds. J. Polym. Sci. B 1965, 3, 1049–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelotti, F.W.; Keaveney, W.P. Coordinated polymerization of the bicyclo-[2.2.1]-heptene-2 ring system (norbornene) in polar media. J. Polym. Sci. A 1965, 3, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, S.T.; Johnson, L.K.; Grubbs, R.H.; Ziller, J.W. Ring-opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP) of norbornene by a Group VIII carbene complex in protic media. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 3974–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwab, P.; France, M.B.; Ziller, J.W.; Grubbs, R.H. A Series of Well-Defined Metathesis Catalysts–Synthesis of [RuCl2(=CHR′)(PR3)2] and Its Reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1995, 34, 2039–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Stevens, E.D.; Nolan, S.P.; Petersen, J.L. Olefin Metathesis-Active Ruthenium Complexes Bearing a Nucleophilic Carbene Ligand. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 2674–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholl, M.; Trnka, T.M.; Morgan, J.P.; Grubbs, R.H. Increased ring closing metathesis activity of ruthenium-based olefin metathesis catalysts coordinated with imidazolin-2-ylidene ligands. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 2247–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, L.; Fürstner, A.; Weskamp, T.; Kohl, F.J.; Herrmann, W.A. Ruthenium carbene complexes with imidazolin-2-ylidene ligands allow the formation of tetrasubstituted cycloalkenes by RCM. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 4787–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, J.A.; Morgan, J.P.; Trnka, T.M.; Grubbs, R.H. A Practical and Highly Active Ruthenium-Based Catalyst that Effects the Cross Metathesis of Acrylonitrile. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 4035–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, S.B.; Kingsbury, J.S.; Gray, B.L.; Hoveyda, A.H. Efficient and Recyclable Monomeric and Dendritic Ru-Based Metathesis Catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 8168–8179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vougioukalakis, G.C.; Grubbs, R.H. Ruthenium-Based Heterocyclic Carbene-Coordinated Olefin Metathesis Catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 1746–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samojłowicz, C.; Bieniek, M.; Grela, K. Ruthenium-Based Olefin Metathesis Catalysts Bearing N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ligands. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 3708–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano-Vila, A.M.; Monsaert, S.; Bajek, A.; Verpoort, F. Ruthenium-Based Olefin Metathesis Catalysts Derived from Alkynes. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 4865–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamad, F.B.; Sun, T.; Xiao, S.; Verpoort, F. Olefin metathesis ruthenium catalysts bearing unsymmetrical heterocylic carbenes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2013, 257, 2274–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, S.P.; Clavier, H. Chemoselective olefin metathesis transformations mediated by ruthenium complexes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higman, C.S.; Lummiss, J.A.M.; Fogg, D.E. Olefin Metathesis at the Dawn of Implementation in Pharmaceutical and Specialty-Chemicals Manufacturing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3552–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, D.; Wheeler, P.; Ene, D. Olefin Metathesis in Drug Discovery and Development—Examples from Recent Patent Literature. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2017, 21, 1938–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Lou, S.; Gonzalez-Bobes, F. Ring-Closing Metathesis in Pharmaceutical Development: Fundamentals, Applications, and Future Directions. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2018, 22, 918–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turczel, G.; Kovács, E.; Merza, G.; Coish, P.; Anastas, P.T.; Tuba, R. Synthesis of Semiochemicals via Olefin Metathesis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flick, A.C.; Leverett, C.A.; Ding, H.X.; McInturff, E.; Fink, S.J.; Helal, C.J.; O’Donnell, C.J. Synthetic Approaches to the New Drugs Approved During 2017. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 7340–7382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sytniczuk, A.; Milewski, M.; Kajetanowicz, A.; Grela, K. Preparation of macrocyclic musks via olefin metathesis: Comparison with classical syntheses and recent advances. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2020, 89, 469–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, T.P.; Johns, A.M.; Grubbs, R.H. Recent Advancements in Stereoselective Olefin Metathesis Using Ruthenium Catalysts. Catalysts 2017, 7, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chikkali, S.; Mecking, S. Refining of Plant Oils to Chemicals by Olefin Metathesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5802–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winkler, M.; Meier, M.A.R. Olefin cross-metathesis as a valuable tool for the preparation of renewable polyesters and polyamides from unsaturated fatty acid esters and carbamates. Green Chem 2014, 16, 3335–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vignon, P.; Vancompernolle, T.; Couturier, J.-L.; Dubois, J.-L.; Mortreux, A.; Gauvin, R.M. Cross-Metathesis of Biosourced Fatty Acid Derivatives: A Step Further Toward Improved Reactivity. ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 1143–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean-Louis Hérisson, P.; Chauvin, Y. Catalyse de transformation des olefines par les complexes du tungstene II. Telomerisation des oleffines cycliques en presence d’olefines acycliques. Makromol. Chem. 1971, 141, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.J.; Manzini, S.; Urbina-Blanco, C.A.; Nolan, S.P. Key processes in ruthenium-catalysed olefin metathesis. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 10355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janse van Rensburg, W.; Steynberg, P.J.; Meyer, W.H.; Kirk, M.M.; Forman, G.S. DFT Prediction and Experimental Observation of Substrate-Induced Catalyst Decomposition in Ruthenium-Catalyzed Olefin Metathesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 14332–14333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeois, D.; Pancrazi, A.; Nolan, S.P.; Prunet, J. The Cl2(PCy3)(IMes)Ru(=CHPh) catalyst: Olefin metathesis versus olefin isomerization. J. Organomet. Chem. 2002, 643–644, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rensburg, W.J.; Steynberg, P.J.; Kirk, M.M.; Meyer, W.H.; Forman, G.S. Mechanistic comparison of ruthenium olefin metathesis catalysts: DFT insight into relative reactivity and decomposition behavior. J. Organomet. Chem. 2006, 691, 5312–5325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lysenko, Z.; Maughon, B.R.; Mokhtar-Zadeh, T.; Tulchinsky, M.L. Stability of the first-generation Grubbs metathesis catalyst in a continuous flow reactor. J. Organomet. Chem. 2006, 691, 5197–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bespalova, N.B.; Nizovtsev, A.V.; Afanasiev, V.V.; Shutko, E.V. Metathesis Catalysts Stability and Decomposition Pathway. In Metathesis Chemistry; Imamoglu, Y., Dragutan, V., Karabulut, S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 125–135. [Google Scholar]
- Ashworth, I.W.; Hillier, I.H.; Nelson, D.J.; Percy, J.M.; Vincent, M.A. Searching for the Hidden Hydrides: The Competition between Alkene Isomerization and Metathesis with Grubbs Catalysts. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 2012, 5673–5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawiczuk, M.; Młodzikowska-Pieńko, K.; Trzaskowski, B. Impact of the olefin structure on the catalytic cycle and decomposition rates of Hoveyda–Grubbs metathesis catalysts. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 13062–13069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jawiczuk, M.; Marczyk, A.; Młodzikowska-Pieńko, K.; Trzaskowski, B. Impact of the Carbene Derivative Charge on the Decomposition Rates of Hoveyda–Grubbs-like Metathesis Catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. A 2020, acs.jpca.0c03096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, J.; Smit, W.; Foscato, M.; Occhipinti, G.; Törnroos, K.W.; Jensen, V.R. Loss and Reformation of Ruthenium Alkylidene: Connecting Olefin Metathesis, Catalyst Deactivation, Regeneration, and Isomerization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 16609–16619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, G.A.; Foscato, M.; Higman, C.S.; Day, C.S.; Jensen, V.R.; Fogg, D.E. Bimolecular Coupling as a Vector for Decomposition of Fast-Initiating Olefin Metathesis Catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 6931–6944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, D.L.; Fogg, D.E. Origin of the Breakthrough Productivity of Ruthenium–Cyclic Alkyl Amino Carbene Catalysts in Olefin Metathesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 19236–19240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinger, M.B.; Mol, J.C. Degradation of the First-Generation Grubbs Metathesis Catalyst with Primary Alcohols, Water, and Oxygen. Formation and Catalytic Activity of Ruthenium(II) Monocarbonyl Species. Organometallics 2003, 22, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinger, M.B.; Mol, J.C. Degradation of the Second-Generation Grubbs Metathesis Catalyst with Primary Alcohols and Oxygen—Isomerization and Hydrogenation Activities of Monocarbonyl Complexes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 2827–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banti, D.; Mol, J.C. Degradation of the ruthenium-based metathesis catalyst [RuCl2(CHPh)(H2IPr)(PCy3)] with primary alcohols. J. Organomet. Chem. 2004, 689, 3113–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, H.; Grünwald, C.; Stüer, W.; Wolf, J. Deactivation of the Grubbs Carbene Complex [RuCl2(CHPh)(PCy3)2] by Allylic Alcohols. Organometallics 2003, 22, 1558–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, N.J.; Camm, K.D.; Fogg, D.E. Hydrogenolysis versus Methanolysis of First- and Second-Generation Grubbs Catalysts: Rates, Speciation, and Implications for Tandem Catalysis. Organometallics 2010, 29, 5450–5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, N.J.; Lummiss, J.A.M.; Bates, J.M.; Fogg, D.E. Reactions of Grubbs Catalysts with Excess Methoxide: Formation of Novel Methoxyhydride Complexes. Organometallics 2012, 31, 2349–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coalter, J.N.; Bollinger, J.C.; Eisenstein, O.; Caulton, K.G. R-Group reversal of isomer stability for RuH(X)L2(CCHR) vs. Ru(X)L2(CCH2R): Access to four-coordinate ruthenium carbenes and carbynes. New J. Chem. 2000, 24, 925–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanford, M.S.; Henling, L.M.; Day, M.W.; Grubbs, R.H. Ruthenium-Based Four-Coordinate Olefin Metathesis Catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 3451–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, J.C.; Amoroso, D.; Czechura, P.; Yap, G.P.A.; Fogg, D.E. The First Highly Active, Halide-Free Ruthenium Catalyst for Olefin Metathesis. Organometallics 2003, 22, 3634–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caskey, S.R.; Stewart, M.H.; Ahn, Y.J.; Johnson, M.J.A.; Kampf, J.W. Dehydrohalogenation by a Germylene: Conversion of Carbene Ligands into Carbynes at Ruthenium. Organometallics 2005, 24, 6074–6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudreault, A.Y.; Walden, D.M.; Nascimento, D.L.; Botti, A.G.; Steinmann, S.N.; Michel, C.; Fogg, D.E. Hydroxide-Induced Degradation of Olefin Metathesis Catalysts: A Challenge for Metathesis in Alkaline Media. ACS Catal. 2020, 3838–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.; Vincent, M.A.; Hillier, I.H.; Percy, J.M.; Tuttle, T. Forming a ruthenium isomerisation catalyst from Grubbs II: A DFT study. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 8493–8498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzini, S.; Urbina-Blanco, C.A.; Poater, A.; Slawin, A.M.Z.; Cavallo, L.; Nolan, S.P. From Olefin Metathesis Catalyst to Alcohol Racemization Catalyst in One Step. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 1042–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzini, S.; Nelson, D.J.; Lebl, T.; Poater, A.; Cavallo, L.; Slawin, A.M.Z.; Nolan, S.P. From ruthenium olefin metathesis catalyst to (η5-3-phenylindenyl)hydrido complex via alcoholysis. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 2205–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzini, S.; Poater, A.; Nelson, D.J.; Cavallo, L.; Slawin, A.M.Z.; Nolan, S.P. Insights into the Decomposition of Olefin Metathesis Precatalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 8995–8999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, N.J.; Blacquiere, J.M.; Drouin, S.D.; Fogg, D.E. Carbonyl-Amplified Catalyst Performance: Balancing Stability against Activity for Five-Coordinate Ruthenium Hydride and Hydridocarbonyl Catalysts. Organometallics 2009, 28, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouen, M.; Queval, P.; Borré, E.; Falivene, L.; Poater, A.; Berthod, M.; Hugues, F.; Cavallo, L.; Baslé, O.; Olivier-Bourbigou, H.; et al. Selective Metathesis of α-Olefins from Bio-Sourced Fischer–Tropsch Feeds. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 7970–7976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, G.S.; McConnell, A.E.; Tooze, R.P.; Janse van Rensburg, W.; Meyer, W.H.; Kirk, M.M.; Dwyer, C.L.; Serfontein, D.W. A Convenient System for Improving the Efficiency of First-Generation Ruthenium Olefin Metathesis Catalysts. Organometallics 2005, 24, 4528–4542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, D.M.; Mohr, B.; Grubbs, R.H.; Henling, L.M.; Day, M.W. Water-Soluble Ruthenium Alkylidenes: Synthesis, Characterization, and Application to Olefin Metathesis in Protic Solvents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 6601–6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dowden, J.; Savović, J. Olefin metathesis in non-degassed solvent using a recyclable, polymer supported alkylideneruthenium. Chem. Commun. 2001, 37–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Veldhuizen, J.J.; Garber, S.B.; Kingsbury, J.S.; Hoveyda, A.H. A Recyclable Chiral Ru Catalyst for Enantioselective Olefin Metathesis. Efficient Catalytic Asymmetric Ring-Opening/Cross Metathesis in Air. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 4954–4955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connon, S.J.; Rivard, M.; Zaja, M.; Blechert, S. Practical Olefin Metathesis in Protic Media under an Air Atmosphere. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2003, 345, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, J.B.; Guzei, I.A.; Raines, R.T. Salicylaldimine Ruthenium Alkylidene Complexes: Metathesis Catalysts Tuned for Protic Solvents. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2007, 349, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vila, A.M.L.; Monsaert, S.; Drozdzak, R.; Wolowiec, S.; Verpoort, F. New Indenylidene-Schiff Base-Ruthenium Complexes for Cross-Metathesis and Ring-Closing Metathesis. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2009, 351, 2689–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtscher, D.; Grela, K. Aqueous Olefin Metathesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kniese, M.; Meier, M.A.R. A simple approach to reduce the environmental impact of olefin metathesis reactions: A green and renewable solvent compared to solvent-free reactions. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowerski, K.; Szczepaniak, G.; Wierzbicka, C.; Gułajski, Ł.; Bieniek, M.; Grela, K. Highly active catalysts for olefin metathesis in water. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 2424–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowerski, K.; Kasprzycki, P.; Bieniek, M.; Olszewski, T.K. Efficient, durable and reusable olefin metathesis catalysts with high affinity to silica gel. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 7408–7415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Occhipinti, G.; Hansen, F.R.; Törnroos, K.W.; Jensen, V.R. Simple and Highly Z-Selective Ruthenium-Based Olefin Metathesis Catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 3331–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasek, J.; Schatz, J. Olefin metathesis in aqueous media. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 2317–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skowerski, K.; Białecki, J.; Tracz, A.; Olszewski, T.K. An attempt to provide an environmentally friendly solvent selection guide for olefin metathesis. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 1125–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablialimov, O.; Kędziorek, M.; Malińska, M.; Woźniak, K.; Grela, K. Synthesis, Structure, and Catalytic Activity of New Ruthenium(II) Indenylidene Complexes Bearing Unsymmetrical N-Heterocyclic Carbenes. Organometallics 2014, 33, 2160–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, J.B.; Blank, J.J.; Raines, R.T. Olefin Metathesis in Homogeneous Aqueous Media Catalyzed by Conventional Ruthenium Catalysts. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 4885–4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuo, T.; Yoshida, T.; Fujii, A.; Kawahara, K.; Hirota, S. Effect of Added Salt on Ring-Closing Metathesis Catalyzed by a Water-Soluble Hoveyda–Grubbs Type Complex to Form N-Containing Heterocycles in Aqueous Media. Organometallics 2013, 32, 5313–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Böhm, V.P.W.; Chadwick, D.; Roeper, M.; Braddock, D.C. Anionic Ligand Exchange in Hoveyda−Grubbs Ruthenium(II) Benzylidenes. Organometallics 2006, 25, 5696–5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirngast, M.; Pump, E.; Leitgeb, A.; Albering, J.H.; Slugovc, C. Pyridine as trigger for chloride isomerisation in chelated ruthenium benzylidene complexes: Implications for olefin metathesis. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2261–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keitz, B.K.; Endo, K.; Patel, P.R.; Herbert, M.B.; Grubbs, R.H. Improved Ruthenium Catalysts for Z-Selective Olefin Metathesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Falivene, L.; Poater, A.; Cazin, C.S.J.; Slugovc, C.; Cavallo, L. Energetics of the ruthenium—Halide bond in olefin metathesis (pre)catalysts. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 7312–7317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wappel, J.; Urbina-Blanco, C.A.; Abbas, M.; Albering, J.H.; Saf, R.; Nolan, S.P.; Slugovc, C. Halide exchanged Hoveyda-type complexes in olefin metathesis. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2010, 6, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, J.O.; Nuyken, O.; Wurst, K.; Buchmeiser, M.R. Synthesis and Reactivity of Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Ruthenium-Based Metathesis Catalysts Containing Electron-Withdrawing Ligands. Chem. Eur. J. 2004, 10, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pump, E.; Fischer, R.C.; Slugovc, C. Halide Exchange in Second-Generation cis-Dihalo Ruthenium Benzylidene Complexes. Organometallics 2012, 31, 6972–6979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, G.A.; Fogg, D.E. Acrylate Metathesis via the Second-Generation Grubbs Catalyst: Unexpected Pathways Enabled by a PCy3-Generated Enolate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 7318–7321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, J.M.; Lummiss, J.A.M.; Bailey, G.A.; Fogg, D.E. Operation of the Boomerang Mechanism in Olefin Metathesis Reactions Promoted by the Second-Generation Hoveyda Catalyst. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 2387–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, G.A.; Lummiss, J.A.M.; Foscato, M.; Occhipinti, G.; McDonald, R.; Jensen, V.R.; Fogg, D.E. Decomposition of Olefin Metathesis Catalysts by Brønsted Base: Metallacyclobutane Deprotonation as a Primary Deactivating Event. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 16446–16449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.G.; Bailey, G.A.; Dos Santos, E.N.; Fogg, D.E. Overcoming Catalyst Decomposition in Acrylate Metathesis: Polyphenol Resins as Enabling Agents for PCy3-Stabilized Metathesis Catalysts. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 3181–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compain, P. Olefin Metathesis of Amine-Containing Systems: Beyond the Current Consensus. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2007, 349, 1829–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, H.H.; Wenzel, A.G.; Salguero, T.T.; Day, M.W.; Grubbs, R.H. Decomposition of ruthenium olefin metathesis catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7961–7968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, G.O.; Porter, K.A.; Weissman, H.; White, S.R.; Sottos, N.R.; Moore, J.S. Stability of Second Generation Grubbs’ Alkylidenes to Primary Amines: Formation of Novel Ruthenium-Amine Complexes. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2009, 351, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, G.O.; Caruso, M.M.; Reimer, N.T.; White, S.R.; Sottos, N.R.; Moore, J.S. Evaluation of Ruthenium Catalysts for Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization-Based Self-Healing Applications. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 3288–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lummiss, J.A.M.; Ireland, B.J.; Sommers, J.M.; Fogg, D.E. Amine-mediated degradation in olefin metathesis reactions that employ the second-generation Grubbs catalyst. ChemCatChem 2014, 6, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lummiss, J.A.M.; Botti, A.G.G.; Fogg, D.E. Isotopic probes for ruthenium-catalyzed olefin metathesis. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 4210–4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanford, M.S.; Love, J.A.; Grubbs, R.H. A Versatile Precursor for the Synthesis of New Ruthenium Olefin Metathesis Catalysts. Organometallics 2001, 20, 5314–5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Getty, K.; Delgado-Jaime, M.U.; Kennepohl, P. Assignment of pre-edge features in the Ru K-edge X-ray absorption spectra of organometallic ruthenium complexes. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2008, 361, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ireland, B.J.; Dobigny, B.T.; Fogg, D.E. Decomposition of a Phosphine-Free Metathesis Catalyst by Amines and Other Bronsted Bases: Metallacyclobutane Deprotonation as a Major Deactivation Pathway. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 4690–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClennan, W.L.; Rufh, S.A.; Lummiss, J.A.M.; Fogg, D.E. A General Decomposition Pathway for Phosphine-Stabilized Metathesis Catalysts: Lewis Donors Accelerate Methylidene Abstraction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 14668–14677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lummiss, J.A.M.; Higman, C.S.; Fyson, D.L.; McDonald, R.; Fogg, D.E. The divergent effects of strong NHC donation in catalysis. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 6739–6746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rufh, S.A.; Goudreault, A.Y.; Foscato, M.; Jensen, V.R.; Fogg, D.E. Rapid decomposition of olefin metathesis catalysts by a truncated N-heterocyclic carbene: Efficient catalyst quenching and n-heterocyclic carbene vinylation. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 11822–11826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-X.; Wang, H.-Y.; Guo, Y.-L. Studies on CH3CN-assisted decomposition of 1st Grubbs catalyst by electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 25, 3401–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.H.; Day, M.W.; Grubbs, R.H. Decomposition of a Key Intermediate in Ruthenium-Catalyzed Olefin Metathesis Reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 7414–7415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulman, M.; Grubbs, R.H. Ruthenium Carbene-Based Olefin Metathesis Initiators: Catalyst Decomposition and Longevity. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 7202–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, H.; He, J.; Li, N. In situ analysis and real-time monitoring of the decomposition of the 2nd Grubbs catalyst in CH3CN by droplet spray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 4201–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawiczuk, M.; Młodzikowska-Pieńko, K.; Osella, S.; Trzaskowski, B. Molecular Modeling of Mechanisms of Decomposition of Ruthenium Metathesis Catalysts by Acrylonitrile. Organometallics 2020, 39, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trnka, T.M.; Morgan, J.P.; Sanford, M.S.; Wilhelm, T.E.; Scholl, M.; Choi, T.L.; Ding, S.; Day, M.W.; Grubbs, R.H. Synthesis and activity of ruthenium alkylidene complexes coordinated with phosphine and N-heterocyclic carbene ligands. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 2546–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guidone, S.; Songis, O.; Nahra, F.; Cazin, C.S.J. Conducting Olefin Metathesis Reactions in Air: Breaking the Paradigm. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 2697–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ton, S.J.; Fogg, D.E. The Impact of Oxygen on Leading and Emerging Ru-Carbene Catalysts for Olefin Metathesis: An Unanticipated Correlation Between Robustness and Metathesis Activity. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 11329–11334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feast, W.J.; Gibson, V.C.; Khosravi, E.; Marshall, E.L.; Mitchell, J.P. Bimolecular termination in living ring opening metathesis polymerization. Polymer 1992, 33, 872–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, G.S.; McConnell, A.E.; Hanton, M.J.; Slawin, A.M.Z.; Tooze, R.P.; van Rensburg, W.J.; Meyer, W.H.; Dwyer, C.; Kirk, M.M.; Serfontein, D.W. A Stable Ruthenium Catalyst for Productive Olefin Metathesis. Organometallics 2004, 23, 4824–4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Schanz, H.-J.; Stevens, E.D.; Nolan, S.P. Influence of Sterically Demanding Carbene Ligation on Catalytic Behavior and Thermal Stability of Ruthenium Olefin Metathesis Catalysts. Organometallics 1999, 18, 5375–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Nguyen, S.T.; Grubbs, R.H.; Ziller, J.W. Reactions of Ruthenium Carbenes of the Type (PPh3)2(X)2Ru:CH-CH:CPh2 (X = Cl and CF3COO) with Strained Acyclic Olefins and Functionalized Olefins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 5503–5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louie, J.; Grubbs, R.H. Metathesis of Electron-Rich Olefins: Structure and Reactivity of Electron-Rich Carbene Complexes. Organometallics 2002, 21, 2153–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansen, S.M.; Rominger, F.; Metz, M.; Hofmann, P. The first grubbs-type metathesis catalyst with cis stereochemistry: Synthesis of [(n2-dtbpm)Cl2Ru=CH-CH=CMe2] from a novel, coordinatively unsaturated dinuclear ruthenium dihydride. Chem. Eur. J. 1999, 5, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lummiss, J.A.M.; McClennan, W.L.; McDonald, R.; Fogg, D.E. Donor-induced decomposition of the Grubbs catalysts: An intercepted intermediate. Organometallics 2014, 33, 6738–6741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Metzger, J.O. ESI-MS Study on First-Generation Ruthenium Olefin Metathesis Catalysts in Solution: Direct Detection of the Catalytically Active 14-Electron Ruthenium Intermediate. Organometallics 2008, 27, 2761–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labinger, J.A.; Bercaw, J.E. Understanding and exploiting C–H bond activation. Nature 2002, 417, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, R.G. C–H activation. The stability of the chemical bonds in saturated hydrocarbons makes them generally unreactive. But the invention of processes in which carbon–hydrogen (C–H) bonds in hydrocarbons can be activated is allowing chemists to exploit organic compounds in previously unimaginable ways. Nature 2007, 446, 391–393. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Forsman, Å.; Grimvall, A. Reduced models for efficient simulation of spatially integrated outputs of one-dimensional substance transport models. Environ. Model. Softw. 2003, 18, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyker, G. Transition Metal Catalyzed Coupling Reactions under C-H Activation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 1698–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guari, Y.; Sabo-Etienne, S.; Chaudret, B. Catalytic Formation of Carbon-Carbon Bonds by Activation of Carbon-Hydrogen Bonds. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 1999, 1999, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazzar, R.F.R.; Macgregor, S.A.; Mahon, M.F.; Richards, S.P.; Whittlesey, M.K. C-C and C-H bond activation reactions in N-heterocyclic carbene complexes of ruthenium. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 4944–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilvers, M.J.; Jazzar, R.F.R.; Mahon, M.F.; Whittlesey, M.K. Reversible C-H Bond Activation Reactions of theN-Heterocyclic Carbene Ligands in Ru(Ph2PCH2CH2CH2PPh2)(IMes)(CO)H2 and Ru(Ph2AsCH2CH2PPh2)(IMes)(CO)H2 (IMes=1,3-Dimesityl-1,3-dihydro-2H-imidazol-2-ylidene). Adv. Synth. Catal. 2003, 345, 1111–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diggle, R.A.; Macgregor, S.A.; Whittlesey, M.K. Computational study of C-C activation of 1,3-dimesitylimidazol-2-ylidene (IMes) at ruthenium: The role of Ligand bulk in accessing reactive intermediates. Organometallics 2008, 27, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M.G.; Jazzar, R.F.R.; Paine, B.M.; Shermer, D.J.; Whittlesey, M.K.; Williams, J.M.J.; Edney, D.D. Borrowing hydrogen: A catalytic route to C–C bond formation from alcohols. Chem. Commun. 2004, 4, 90–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burling, S.; Whittlesey, M.K.; Williams, J.M.J. Direct and transfer hydrogenation of ketones and imines with a ruthenium N-heterocyclic carbene complex. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2005, 347, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burling, S.; Paine, B.M.; Nama, D.; Brown, V.S.; Mahon, M.F.; Prior, T.J.; Pregosin, P.S.; Whittlesey, M.K.; Williams, J.M.J. C-H activation reactions of ruthenium N-heterocyclic carbene complexes: Application in a catalytic tandem reaction involving C-C bond formation from alcohols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 1987–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenz, K.M.; Liu, P.; Houk, K.N. Intramolecular C-H Activation Reactions of Ru(NHC) Complexes Combined with H2 Transfer to Alkenes: A Theoretical Elucidation of Mechanisms and Effects of Ligands on Reactivities. Organometallics 2017, 36, 3613–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Młodzikowska-Pieńko, K.; Trzaskowski, B. Rate-limiting Steps in the Intramolecular C-H Activation of Ruthenium N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes. J. Phys. Chem. A 2020, 124, 3609–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdur-Rashid, K.; Fedorkiw, T.; Lough, A.J.; Morris, R.H. Coordinatively unsaturated hydridoruthenium(II) complexes of N-heterocyclic carbenes. Organometallics 2004, 23, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burling, S.; Mahon, M.F.; Paine, B.M.; Whittlesey, M.K.; Williams, J.M.J. Reversible intramolecular Alkyl C-H bond activation, alcohol dehydrogenation, and trans-Cis dihydride isomerization in ruthenium N-heterocyclic carbene complexes. Organometallics 2004, 23, 4537–4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.H.; Chlenov, A.; Day, M.W.; Grubbs, R.H. Double C-H activation of an N-heterocyclic carbene ligand in a ruthenium olefin metathesis catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 5148–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandford, M.S.; Love, J.A.; Grubbs, R.H. Mechanism and activity of ruthenium olefin metathesis catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 6543–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mathew, J.; Koga, N.; Suresh, C.H. C-H bond activation through σ-bond metathesis and agostic interactions: Deactivation pathway of a Grubbs second-generation catalyst. Organometallics 2008, 27, 4666–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poater, A.; Cavallo, L. Mechanistic insights into the double C-H (de)activation route of a Ru-based olefin metathesis catalyst. J. Mol. Catal. Chem. 2010, 324, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vehlow, K.; Gessler, S.; Blechert, S. Deactivation of ruthenium olefin metathesis catalysts through intramolecular carbene-arene bond formation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 8082–8085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galan, B.R.; Kalbarczyk, K.P.; Szczepankiewicz, S.; Keister, J.B.; Diver, S.T. A rapid and simple cleanup procedure for metathesis reactions. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 1203–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitao, E.M.; Dubberley, S.R.; Piers, W.E.; Wu, Q.; McDonald, R. Thermal decomposition modes for four-coordinate ruthenium phosphonium alkylidene olefin metathesis catalysts. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 11565–11572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Eide, E.F.; Romero, P.E.; Piers, W.E. Generation and spectroscopic characterization of ruthenacyclobutane and ruthenium olefin carbene intermediates relevant to ring closing metathesis catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 4485–4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solari, E.; Gauthier, S.; Scopelliti, R.; Severin, K. Multifaceted chemistry of [(Cymene)RuCl2]2 and PCy3. Organometallics 2009, 28, 4519–4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, M.B.; Lan, Y.; Keitz, B.K.; Liu, P.; Endo, K.; Day, M.W.; Houk, K.N.; Grubbs, R.H. Decomposition pathways of Z-selective ruthenium metathesis catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 7861–7866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Endo, K.; Grubbs, R.H. Chelated ruthenium catalysts for Z-selective olefin metathesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 8525–8527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weng, W.; Parkin, S.; Ozerov, O.V. Double C-H activation results in ruthenium complexes of a neutral PCP ligand with a central carbene moiety. Organometallics 2006, 25, 5345–5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliván, M.; Caulton, K.G. C-(halide) oxidative addition routes to ruthenium carbenes. Inorg. Chem. 1999, 38, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prechtl, M.H.G.; Ben-David, Y.; Giunta, D.; Busch, S.; Taniguchi, Y.; Wisniewski, W.; Görls, H.; Mynott, R.J.; Theyssen, N.; Milstein, D.; et al. Synthesis and characterisation of nonclassical ruthenium hydride complexes containing chelating bidentate and tridentate phosphine ligands. Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 1539–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poater, A.; Bahri-Laleh, N.; Cavallo, L. Rationalizing current strategies to protect N-heterocyclic carbene-based ruthenium catalysts active in olefin metathesis from C-H (de)activation. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 6674–6676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, I.; Lugan, N.; Lavigne, G. Effects of attractive through space π-π* Interactions on the structure, reactivity, and activity of Grubbs II complexes. Organometallics 2012, 31, 1155–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comas-Vives, A.; Harvey, J.N. How important is backbonding in metal complexes containing N-heterocyclic carbenes? Structural and NBO analysis. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 5025–5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vummaleti, S.V.C.; Nelson, D.J.; Poater, A.; Gómez-Suárez, A.; Cordes, D.B.; Slawin, A.M.Z.; Nolan, S.P.; Cavallo, L. What can NMR spectroscopy of selenoureas and phosphinidenes teach us about the π-accepting abilities of N-heterocyclic carbenes? Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 1895–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Credendino, R.; Falivene, L.; Cavallo, L. π-face donation from the aromatic N-substituent of N-heterocyclic carbene ligands to metal and its role in catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 8127–8135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, M.M.; Rooney, A.D.; Rooney, J.J. Variable temperature 1H NMR studies on Grubbs catalysts. J. Organomet. Chem. 2008, 693, 1252–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotyk, M.W.; Gorelsky, S.I.; Conrad, J.C.; Carra, C.; Fogg, D.E. Geometric and electronic structure of a C1-symmetric ruthenium-Aryloxide metathesis catalyst: An experimental and computational study. Organometallics 2009, 28, 5424–5431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Xu, B. Metal-catalyzed C-H functionalization involving isocyanides. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 1103–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyarskiy, V.P.; Bokach, N.A.; Luzyanin, K.V.; Kukushkin, V.Y. Metal-mediated and metal-catalyzed reactions of isocyanides. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 2698–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, S.; Choudhary, S.; Doshi, A.; Liu, F.Q.; Mohan, R.; Ravindra, M.P.; Shah, D.; Yang, X.; Fleming, F.F. Catalytic isonitrile insertions and condensations initiated by RNC-X complexation. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2014, 356, 2135–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vlaar, T.; Ruijter, E.; Maes, B.U.W.; Orru, R.V.A. Palladium-catalyzed migratory insertion of isocyanides: An emerging platform in cross-coupling chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 7084–7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galan, B.R.; Gembicky, M.; Dominiak, P.M.; Keister, J.B.; Diver, S.T. Carbon monoxide-promoted carbene insertion into the aryl substituent of an N-heterocyclic carbene ligand: Buchner reaction in a ruthenium carbene complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 15702–15703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchner, E.; Curtius, T. Ueber die Einwirkung von Diazoessigäther auf aromatische Kohlenwasserstoffe. Berichte Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1885, 18, 2377–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galan, B.R.; Pitak, M.; Keister, J.B.; Diver, S.T. Isocyanide-promoted ylidene transfer to phosphorus: Rearrangement in the first-generation grubbs complex. Organometallics 2008, 27, 3630–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.K.; Frey, M.; Ulibarri, T.A.; Virgil, S.C.; Grubbs, R.H.; Ziller, J.W. Alkylidene Transfer from Phosphoranes to Tungsten(IV) Imido Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 8167–8177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poater, A.; Ragone, F.; Correa, A.; Cavallo, L. Exploring the reactivity of ru-based metathesis catalysts with a π-acid ligand trans to the Ru-ylidene bond. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 9000–9006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galan, B.R.; Pitak, M.; Gembicky, M.; Keister, J.B.; Diver, S.T. Ligand-promoted carbene insertion into the aryl substituent of an n-heterocyclic carbene ligand in ruthenium-based metathesis catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6822–6832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monnier, F.; Castillo, D.; Dérien, S.; Toupet, L.; Dixneuf, P.H. Addition of Diazoalkanes to Enynes Promoted by a Ruthenium Catalyst: Simple Synthesis of Alkenyl Bicyclo[3.1.0]hexane Derivatives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 5474–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppers, B.P.; Diver, S.T. Tandem cyclopropanation/ring-closing metathesis of dienynes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9524–9525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, T.; Sato, Y.; Mori, M. Unexpected results of enyne metathesis using a ruthenium complex containing an N-heterocyclic carbene ligand. Chem. Commun. 2001, 1258–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, H.; Itoh, Y.; Matsumoto, H.; Park, S.B.; Itoh, K. New Chiral Ruthenium Bis(oxazolinyl)pyridine Catalyst. Efficient Asymmetric Cyclopropanation of Olefins with Diazoacetates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 2223–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anciaux, A.J.; Demonceau, A.; Noels, A.F.; Hubert, A.J.; Warin, R.; Teyssié, P. Transition-Metal-Catalyzed Reactions of Diazo Compounds. 2.1 Addition to Aromatic Molecules: Catalysis of Buchner’s Synthesis of Cycloheptatrienes. J. Org. Chem. 1981, 46, 873–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basato, M.; Tubaro, C.; Biffis, A.; Bonato, M.; Buscemi, G.; Lighezzolo, F.; Lunardi, P.; Yianini, C.; Benetollo, F.; Del Zotto, A. Reactions of diazo compounds with alkenes catalysed by [RuCl(cod)(Cp)]: Effect of the substituents in the formation of cyclopropanation or metathesis products. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 1516–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczepaniak, G.; Urbaniak, K.; Wierzbicka, C.; Kosiński, K.; Skowerski, K.; Grela, K. High-Performance Isocyanide Scavengers for Use in Low-Waste Purification of Olefin Metathesis Products. ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 4139–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szczepaniak, G.; Nogaś, W.; Piatkowski, J.; Ruszczyńska, A.; Bulska, E.; Grela, K. Semiheterogeneous Purification Protocol for the Removal of Ruthenium Impurities from Olefin Metathesis Reaction Products Using an Isocyanide Scavenger. Org. Process. Res. Dev. 2019, 23, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepaniak, G.; Ruszczyńska, A.; Kosiński, K.; Bulska, E.; Grela, K. Highly efficient and time economical purification of olefin metathesis products from metal residues using an isocyanide scavenger. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 1280–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blacquiere, J.M.; Jurca, T.; Weiss, J.; Fogg, D.E. Time as a dimension in high-throughput homogeneous catalysis. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2008, 350, 2849–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, J.R.; Hofman, E.J.; Keister, J.B.; Diver, S.T. Kinetics and Mechanism of Isocyanide-Promoted Carbene Insertion into the Aryl Substituent of an N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ligand in Ruthenium-Based Metathesis Catalysts. Organometallics 2017, 36, 3043–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klose, A.; Solari, E.; Hesschenbrouck, J.; Floriani, C.; Re, N.; Geremia, S.; Randaccio, L. Ruthenium-carbene functionality bonded to dibenzotetramethyltetraaza[14]annulene: Metal-to-macrocycle ligand-induced carbene migration. Organometallics 1999, 18, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małecki, P.; Gajda, K.; Gajda, R.; Woźniak, K.; Trzaskowski, B.; Kajetanowicz, A.; Grela, K. Specialized ruthenium olefin metathesis catalysts bearing bulky unsymmetrical NHC Ligands: Computations, synthesis, and application. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
































































© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jawiczuk, M.; Marczyk, A.; Trzaskowski, B. Decomposition of Ruthenium Olefin Metathesis Catalyst. Catalysts 2020, 10, 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080887
Jawiczuk M, Marczyk A, Trzaskowski B. Decomposition of Ruthenium Olefin Metathesis Catalyst. Catalysts. 2020; 10(8):887. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080887
Chicago/Turabian StyleJawiczuk, Magdalena, Anna Marczyk, and Bartosz Trzaskowski. 2020. "Decomposition of Ruthenium Olefin Metathesis Catalyst" Catalysts 10, no. 8: 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080887
APA StyleJawiczuk, M., Marczyk, A., & Trzaskowski, B. (2020). Decomposition of Ruthenium Olefin Metathesis Catalyst. Catalysts, 10(8), 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080887





