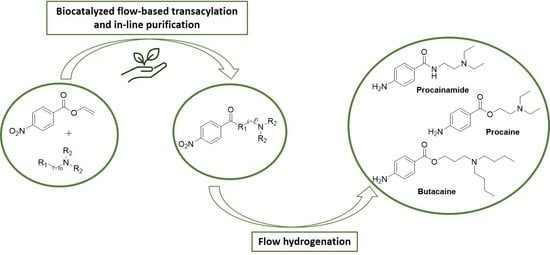
Efficient Chemo-Enzymatic Flow Synthesis of High Value Amides and Esters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Analytical Method
3.2. Synthesis of Vinyl 4-nitrobenzoate (4)
3.3. Biocatalysed Flow Synthesis of N-(2-(diethylamino)ethyl)-4-nitrobenzamide (8)
3.4. Biocatalysed Flow Synthesis of 2-(diethylamino)ethyl 4-nitrobenzoate (9) and 3-(dibutylamino)propyl 4-nitrobenzoate (10)
3.5. Synthesis of Procainamide (1), Procaine (2) and Butacaine (3)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gutmann, B.; Cantillo, D.; Kappe, C.O. Continuous-flow technology-a tool for the safe manufacturing of active pharmaceutical ingredients. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 6688–6728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, M.; Baxendale, I.R. The synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) using continuous flow chemistry. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2015, 11, 1194–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baumann, M.; Moody, T.S.; Smyth, M.; Wharry, S. A perspective on continuous flow chemistry in the pharmaceutical industry. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A.; Pereira, P.C. Biocatalysis engineering: The big picture. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 2678–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A.; Woodley, J.M. Role of Biocatalysis in Sustainable Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 801–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A.; Brady, D. Broadening the Scope of Biocatalysis in Sustainable Organic Synthesis. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 2859–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, P.N.; Howard, R.M.; Kumar, R.; Thompson, M.P.; Truppo, M.D.; Turner, N.J. Extending the application of biocatalysis to meet the challenges of drug development. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2018, 2, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.; Contente, M.L.; Tamborini, L. Advances on whole-cell biocatalysis in flow. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2020, 25, 100343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamborini, L.; Fernandes, P.; Paradisi, F.; Molinari, F. Flow bioreactors as complementary tools for biocatalytic process intensification. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britton, J.; Majumdar, S.; Weiss, G.A. Continuous flow biocatalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 5891–5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, M.P.; Peñafiel, I.; Cosgrove, S.C.; Turner, N.J. Biocatalysis using immobilized enzymes in continuous flow for the synthesis of fine chemicals. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2019, 23, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vitis, V.; Dall’Oglio, F.; Pinto, A.; De Micheli, C.; Molinari, F.; Conti, P.; Romano, D.; Tamborini, L. Chemoenzymatic synthesis in flow reactors: A rapid and convenient preparation of captopril. Chem. Open 2017, 6, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žnidaršič-Plazl, P. Biotransformations in Microflow Systems: Bridging the Gap between Academia and Industry. J. Flow Chem. 2017, 7, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Oglio, F.; Contente, M.L.; Conti, P.; Molinari, F.; Monfredi, D.; Pinto, A.; Romano, D.; Ubiali, D.; Tamborini, L.; Serra, I. Flow-based stereoselective reduction of ketones using an immobilized ketoreductase/glucose dehydrogenase mixed bed system. Catal. Commun. 2017, 93, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vitis, V.; Dall’Oglio, F.; Tentori, F.; Contente, M.L.; Romano, D.; Brenna, E.; Tamborini, L.; Molinari, F. Bioprocess Intensification Using Flow Reactors: Stereoselective Oxidation of Achiral 1,3-diols with Immobilized Acetobacter Aceti. Catalysts 2019, 9, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Contente, M.L.; Tamborini, L.; Molinari, F.; Paradisi, F. Aromas flow: Eco-friendly, continuous, and scalable preparation of flavour esters. J. Flow Chem. 2020, 10, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contente, M.L.; Farris, S.; Tamborini, L.; Molinari, F.; Paradisi, F. Flow-based enzymatic synthesis of melatonin and other high value tryptamine derivatives: A five-minute intensified process. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 3263–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalu, F.; Scorciapino, M.A.; Cara, C.; Luridiana, A.; Musinu, A.; Casu, M.; Secci, F.; Cannas, C. A catalyst-free, waste-less ethanol-based solvothermal synthesis of amides. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, S.; Nageswar Rao, D.; Siva Reddy, A.; Shankarb, R.; Das, P. Sulphuric acid immobilized on silica gel (H2SO4–SiO2) as an eco-friendly catalyst for transamidation. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 10567–10574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, S.M.; Lipshutz, B.H. Chemoselective reductions of nitroaromatics in water at room temperature. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vardanyan, R.S.; Hruby, V.J. Local Anesthetics in Synthesis of Essential Drugs; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullaev, M.G. Development of the method of novocain production. Pharm. Chem. J. 2001, 35, 556–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoica Dinu, C.; Zhu, G.; Sundhar Bale, S.; Anand, G.; Reeder, P.J.; Sanford, K.; Whited, G.; Kane, R.S.; Dordick, J.S. Enzyme-based nanoscale composites for use as active decontamination surfaces. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, K.; Odrozek, K.; Zniszczoł, A.; Torrelo, G.; Resch, V.; Hanefeld, U.; Jarzębski, A.B. MsAcT in siliceous monolithic microreactors enables quantitative ester synthesis in water. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 4882–4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kadidae, L.O.; Usami, A.; Honda, M. Palladium(II) acetate as catalyst in transvinylation reactions of hydroxycinnamic acid and its derivatives. Asian J. Chem. 2018, 30, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonsi, K.; Collberg, J.; Dunn, P.J.; Fevig, T.; Jennings, S.; Johnson, T.A.; Kleine, H.P.; Knight, C.; Nagy, M.A.; Perry, D.A.; et al. Green chemistry tools to influence a medicinal chemistry and research chemistry based organization. Green Chem. 2008, 10, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, I.; Soltis, M.; Saldajeno, M.; Ganshaw, G.; Sala, R.; Weyler, W.; Cervin, M.A.; Whited, G.; Bott, R. Structure of a novel enzyme that catalyzes acyl transfer to alcohols in aqueous conditions. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 8969–8979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambelli, P.; Tamborini, L.; Cazzamalli, S.; Pinto, A.; Arioli, S.; Balzaretti, S.; Plou, F.J.; Fernandez-Arrojo, L.; Molinari, F.; Conti, P.; et al. An efficient continuous flow process for the synthesis of a non-conventional mixture of fructooligosaccharides. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamborini, L.; Previtali, C.; Annunziata, F.; Bavaro, T.; Terreni, M.; Calleri, E.; Rinaldi, F.; Pinto, A.; Speranza, G.; Ubiali, D.; et al. An enzymatic flow-based preparative route to vidarabine. Molecules 2020, 25, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Contente, M.L.; Pinto, A.; Molinari, F.; Paradisi, F. Biocatalytic N-acylation of amines in water using an acyltransferase from Mycobacterium smegmatis. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2018, 360, 4814–4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guisàn, J.M. Aldehyde-agarose gels as activated supports for immobilization-stabilization of enzymes. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 1988, 10, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Entry | Residence Time (min) | Conversion b (%) | r (µmol min−1 mgenzyme−1) c |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | 44 | 18 |
| 2 | 7 | 100 | 28 |
| 3 | 15 | 100 | 13 |
| Entry | Nucleophile | Nucleophile Concentration (M) | Residence Time (min) | Conversion b (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | 0.5 | 7 | 25 |
| 2 | 7 | 0.5 | 7 | 15 |
| 3 | 6 | 1 | 7 | 32 |
| 4 | 6 | 1 | 15 | 72 |
| 5 | 6 | 1 | 30 | 74 |
| 6 | 7 | 1 | 15 | 36 |
| 7 | 7 | 1 | 30 | 37 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Annunziata, F.; Letizia Contente, M.; Betti, D.; Pinna, C.; Molinari, F.; Tamborini, L.; Pinto, A. Efficient Chemo-Enzymatic Flow Synthesis of High Value Amides and Esters. Catalysts 2020, 10, 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080939
Annunziata F, Letizia Contente M, Betti D, Pinna C, Molinari F, Tamborini L, Pinto A. Efficient Chemo-Enzymatic Flow Synthesis of High Value Amides and Esters. Catalysts. 2020; 10(8):939. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080939
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnnunziata, Francesca, Martina Letizia Contente, Daniele Betti, Cecilia Pinna, Francesco Molinari, Lucia Tamborini, and Andrea Pinto. 2020. "Efficient Chemo-Enzymatic Flow Synthesis of High Value Amides and Esters" Catalysts 10, no. 8: 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080939
APA StyleAnnunziata, F., Letizia Contente, M., Betti, D., Pinna, C., Molinari, F., Tamborini, L., & Pinto, A. (2020). Efficient Chemo-Enzymatic Flow Synthesis of High Value Amides and Esters. Catalysts, 10(8), 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080939