Tandem Synthesis of High Yield MoS2 Nanosheets and Enzyme Peroxidase Mimicking Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of MoS2 NSs
2.2. Optical Properties of MoS2 NSs
2.3. XRD and Raman Spectra Analysis of MoS2 NSs
2.4. Peroxidase Mimetic Properties of MoS2 NSs
2.5. Peroxidase Activity Mechanism
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Material
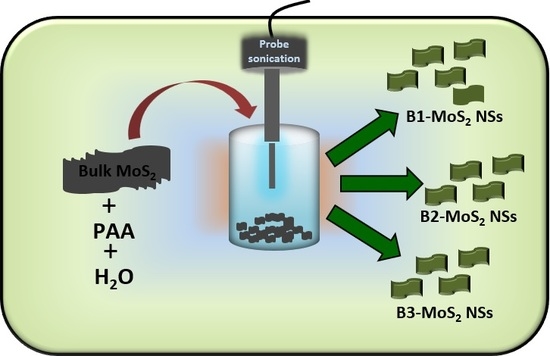
3.2. Synthesis of MoS2 NSs
3.3. Characterization
3.4. Enzyme Peroxidase Activity Measurement
3.5. Identification of Hydroxyl Radicals (•OH)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Das, S.; Robinson, J.A.; Dubey, M.; Terrones, H.; Terrones, M. Beyond Graphene: Progress in Novel Two-Dimensional Materials and van der Waals Solids. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2015, 45, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna Matte, H.S.S.; Gomathi, A.; Manna, A.K.; Late, D.J.; Datta, R.; Pati, S.K.; Rao, C.N.R. MoS2 and WS2 Analogues of Graphene. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 4059–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, L.; Zhang, Q. Recent progress in crystalline metal chalcogenides as efficient photocatalysts for organic pollutant degradation. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2017, 4, 1953–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radisavljevic, B.; Radenovic, A.; Brivio, J.; Giacometti, V.; Kis, A. Single-layer MoS2 transistors. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, V.; Roy, S.; Singh, P.; Khan, Z.; Jaiswal, A. 2D MoS2-Based Nanomaterials for Therapeutic, Bioimaging, and Biosensing Applications. Small 2019, 15, 1803706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Theerthagiri, J.; Senthil, R.A.; Senthilkumar, B.; Reddy Polu, A.; Madhavan, J.; Ashokkumar, M. Recent advances in MoS2 nanostructured materials for energy and environmental applications—A review. J. Solid State Chem. 2017, 252, 43–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganatra, R.; Zhang, Q. Few-Layer MoS2: A Promising Layered Semiconductor. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 4074–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Splendiani, A.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Kim, J.; Chim, C.-Y.; Galli, G.; Wang, F. Emerging Photoluminescence in Monolayer MoS2. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 1271–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, J.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, H. Preparation and Applications of Mechanically Exfoliated Single-Layer and Multilayer MoS2 and WSe2 Nanosheets. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgin, I.; Liu, F.; Vargas, A.; Winchester, A.; Man, M.K.L.; Upmanyu, M.; Dani, K.M.; Gupta, G.; Talapatra, S.; Mohite, A.D.; et al. Chemical Vapor Deposition Synthesized Atomically Thin Molybdenum Disulfide with Optoelectronic-Grade Crystalline Quality. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 8822–8832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jawaid, A.; Nepal, D.; Park, K.; Jespersen, M.; Qualley, A.; Mirau, P.; Drummy, L.F.; Vaia, R.A. Mechanism for Liquid Phase Exfoliation of MoS2. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Xu, P.; Zhou, D.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.C.; Nguyen, M.A.T.; Terrones, M.; Mallouk, T.E. Fast and Efficient Preparation of Exfoliated 2H MoS2 Nanosheets by Sonication-Assisted Lithium Intercalation and Infrared Laser-Induced 1T to 2H Phase Reversion. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 5956–5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Jiang, D.; Schedin, F.; Booth, T.J.; Khotkevich, V.V.; Morozov, S.V.; Geim, A.K. Two-dimensional atomic crystals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 10451–10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.-H.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Zhang, W.; Chang, M.-T.; Lin, C.-T.; Chang, K.-D.; Yu, Y.-C.; Wang, J.T.-W.; Chang, C.-S.; Li, L.-J.; et al. Synthesis of Large-Area MoS2 Atomic Layers with Chemical Vapor Deposition. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2320–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, S.; Zou, X.; Du, H.; Gan, L.; Xu, C.; Lv, W.; He, Y.-B.; Yang, Q.-H.; Kang, F.; Li, J. Theoretical Investigation of the Intercalation Chemistry of Lithium/Sodium Ions in Transition Metal Dichalcogenides. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 13599–13605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, P.; Chen, S.; Liu, X.; Mi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, W.; Chang, J. High-Yield Production of MoS2 and WS2 Quantum Sheets from Their Bulk Materials. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 7767–7772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, S.; Tiwari, U.K.; Choubey, R.K.; Singh, K.; Sinha, R.K. Study of Sonication Assisted Synthesis of Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS2) Nanosheets. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 21, 1969–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, A.; Khan, U.; Coleman, J.N. Preparation of High Concentration Dispersions of Exfoliated MoS2 with Increased Flake Size. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 2414–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Coleman, J.N.; Zhang, H.; Shin, H.; Chhowalla, M.; Zheng, Z. Production of Two-Dimensional Nanomaterials via Liquid-Based Direct Exfoliation. Small 2016, 12, 272–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Lakshmi, K.V.; Huang, L. Eco-friendly synthesis of metal dichalcogenides nanosheets and their environmental remediation potential driven by visible light. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, K.-G.; Mao, N.-N.; Wang, H.-X.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, H.-L. A Mixed-Solvent Strategy for Efficient Exfoliation of Inorganic Graphene Analogues. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 10839–10842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esfandiari, M.; Mohajerzadeh, S. Formation of large area WS2 nanosheets using an oxygen-plasma assisted exfoliation suitable for optical devices. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 425204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Ma, J.; Li, H.; Zeng, R.; Guo, Z.; Liu, H. Synthesis of molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) for lithium ion battery applications. Mater. Res. Bull. 2009, 44, 1811–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Kim, H.-Y.; Lotya, M.; Coleman, J.N.; Kim, G.-T.; Duesberg, G.S. Electrical Characteristics of Molybdenum Disulfide Flakes Produced by Liquid Exfoliation. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4178–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.; Chaudhary, P.; Uttam, K.N.; Varma, A.; Vashistha, M.; Yadav, B.C. Facile synthesis of molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) quantum dots and its application in humidity sensing. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 295501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.-R.; Chan, M.K.Y.; Sun, Y. Edge-terminated molybdenum disulfide with a 9.4-Å interlayer spacing for electrochemical hydrogen production. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benson, J.; Li, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, P.; Papakonstantinou, P. Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Reaction on Edges of a Few Layer Molybdenum Disulfide Nanodots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 14113–14122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, W.J. Single-Layered MoS2–PEI–PEG Nanocomposite-Mediated Gene Delivery Controlled by Photo and Redox Stimuli. Small 2016, 12, 1184–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Xia, B.; Ge, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.-Y.; Wang, X. Ultrathin MoS2 Nanoplates with Rich Active Sites as Highly Efficient Catalyst for Hydrogen Evolution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 12794–12798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, K.F.; Lee, C.; Hone, J.; Shan, J.; Heinz, T.F. Atomically MoS2: A New Direct-Gap Semiconductor. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 136805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Štengl, V.; Henych, J. Strongly luminescent monolayered MoS2 prepared by effective ultrasound exfoliation. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 3387–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Jiang, L.; Li, X.; Ran, P.; Zuo, P.; Wang, A.; Qu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Lu, Y. Preparation of Monolayer MoS2 Quantum Dots using Temporally Shaped Femtosecond Laser Ablation of Bulk MoS2 Targets in Water. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Yan, H.; Brus, L.E.; Heinz, T.F.; Hone, J.; Ryu, S. Anomalous Lattice Vibrations of Single- and Few-Layer MoS2. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 2695–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thangudu, S. Next Generation Nanomaterials: Smart Nanomaterials, Significance, and Biomedical Applications. In Applications of Nanomaterials in Human Health; Khan, F.A., Ed.; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2020; pp. 287–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangudu, S.; Kulkarni, S.S.; Vankayala, R.; Chiang, C.-S.; Hwang, K.C. Photosensitized reactive chlorine species-mediated therapeutic destruction of drug-resistant bacteria using plasmonic core–shell Ag@AgCl nanocubes as an external nanomedicine. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 12970–12984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangudu, S.; Kalluru, P.; Vankayala, R. Preparation, Cytotoxicity, and In Vitro Bioimaging of Water Soluble and Highly Fluorescent Palladium Nanoclusters. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maji, S.K.; Mandal, A.K.; Nguyen, K.T.; Borah, P.; Zhao, Y. Cancer Cell Detection and Therapeutics Using Peroxidase-Active Nanohybrid of Gold Nanoparticle-Loaded Mesoporous Silica-Coated Graphene. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 9807–9816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Yu, J.; Lv, F.; Yan, L.; Zheng, L.R.; Gu, Z.; Zhao, Y. Functionalized Nano-MoS2 with Peroxidase Catalytic and Near-Infrared Photothermal Activities for Safe and Synergetic Wound Antibacterial Applications. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 11000–11011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Duan, D.; Gao, L.; Zhou, M.; Fan, K.; Tang, Y.; Xi, J.; Bi, Y.; Tong, Z.; Gao, G.F.; et al. Standardized assays for determining the catalytic activity and kinetics of peroxidase-like nanozymes. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 1506–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qi, K.; Yu, S.; Jia, G.; Cheng, Z.; Zheng, L.; Wu, Q.; Bao, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, J.; et al. Revealing the Intrinsic Peroxidase-Like Catalytic Mechanism of Heterogeneous Single-Atom Co–MoS2. Nano-Micro Lett. 2019, 11, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Method | Reagents | Remarks | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrothermal | (NH4)6Mo7O24·4H2O, Sulfocarbamide, oxalic acid | Low yield Micro particles Time consuming | [23] |
| Liquid exfoliation | MoS2 powders, N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone | Toxic solvents Micro sheets | [24,25] |
| Microwave synthesis | (NH4)2MoS4, DMF | Toxic solvents | [26] |
| Mechanical exfoliation | High temperature, transfer process | High temperature, transfer process | [9] |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | MoO2, SiO2, Sulfur | [10] | |
| Ionic liquid assisted grinding exfoliation | MoS2 powder, BMIMPF6, DMF | Toxic solvents | [27] |
| Ball milling and chemical intercalation | MoS2 powders, DMF, NMP | Toxic solvents, Disordered NSs, lower yields | [16] |
| Morrison method | MoS2 Bulk, Hexane, n-buthyllithium, N2 atmosphere | Toxic solvents, inert condition | [28] |
| Ultra-sonication followed by hydrothermal | ((NH4)2MoS4, DMF and water | Toxic solvents | [29] |
| Probe sonication (tandem process) | MoS2 powder, PAA and water | High yield, water soluble NSs, batch manner | Present work |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thangudu, S.; Lee, M.T.; Rtimi, S. Tandem Synthesis of High Yield MoS2 Nanosheets and Enzyme Peroxidase Mimicking Properties. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10091009
Thangudu S, Lee MT, Rtimi S. Tandem Synthesis of High Yield MoS2 Nanosheets and Enzyme Peroxidase Mimicking Properties. Catalysts. 2020; 10(9):1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10091009
Chicago/Turabian StyleThangudu, Suresh, Mu Tzu Lee, and Sami Rtimi. 2020. "Tandem Synthesis of High Yield MoS2 Nanosheets and Enzyme Peroxidase Mimicking Properties" Catalysts 10, no. 9: 1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10091009
APA StyleThangudu, S., Lee, M. T., & Rtimi, S. (2020). Tandem Synthesis of High Yield MoS2 Nanosheets and Enzyme Peroxidase Mimicking Properties. Catalysts, 10(9), 1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10091009