Applicability of Nickel-Based Catalytic Systems for Hydrodehalogenation of Recalcitrant Halogenated Aromatic Compounds
Abstract
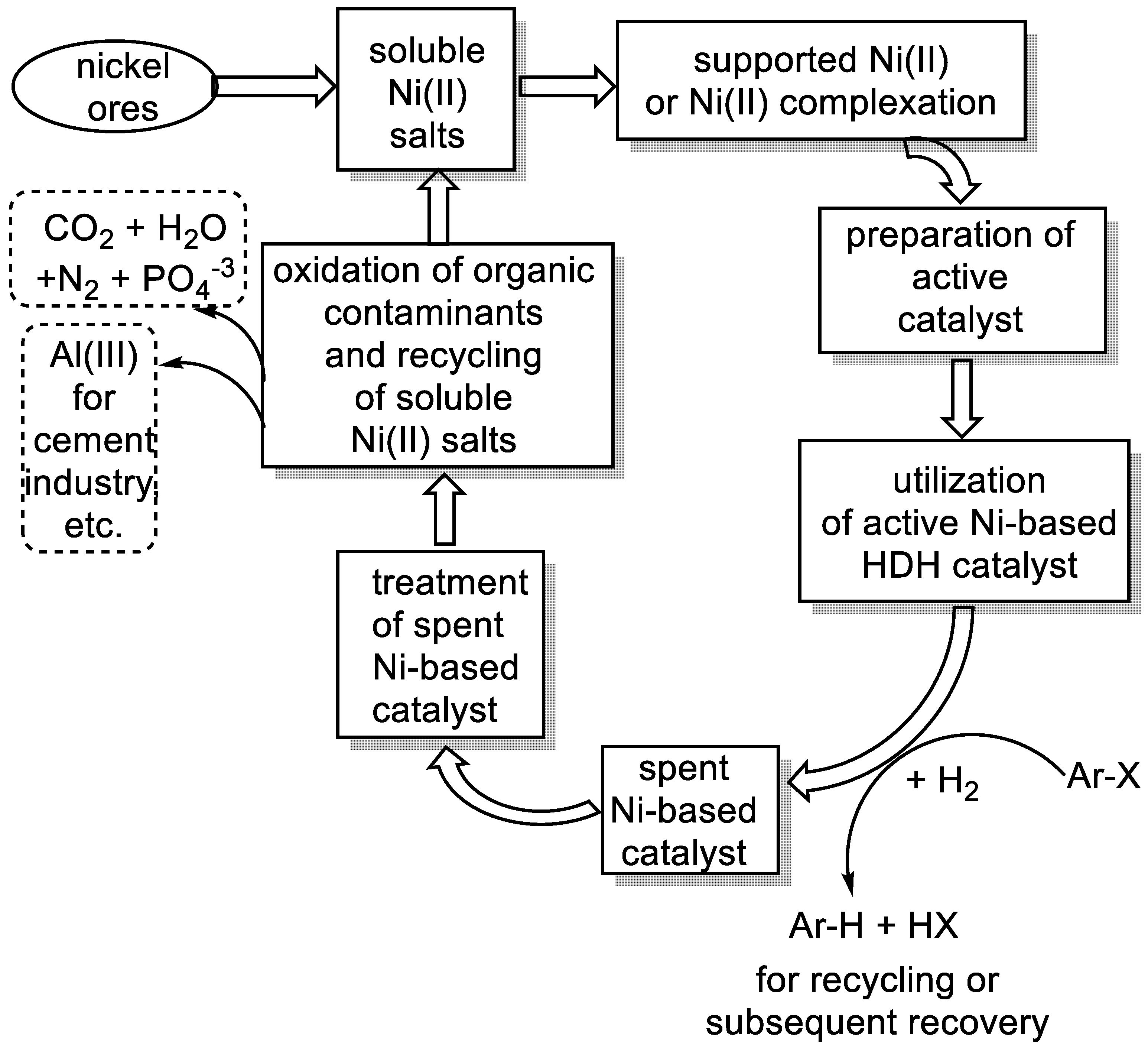
:1. Introduction
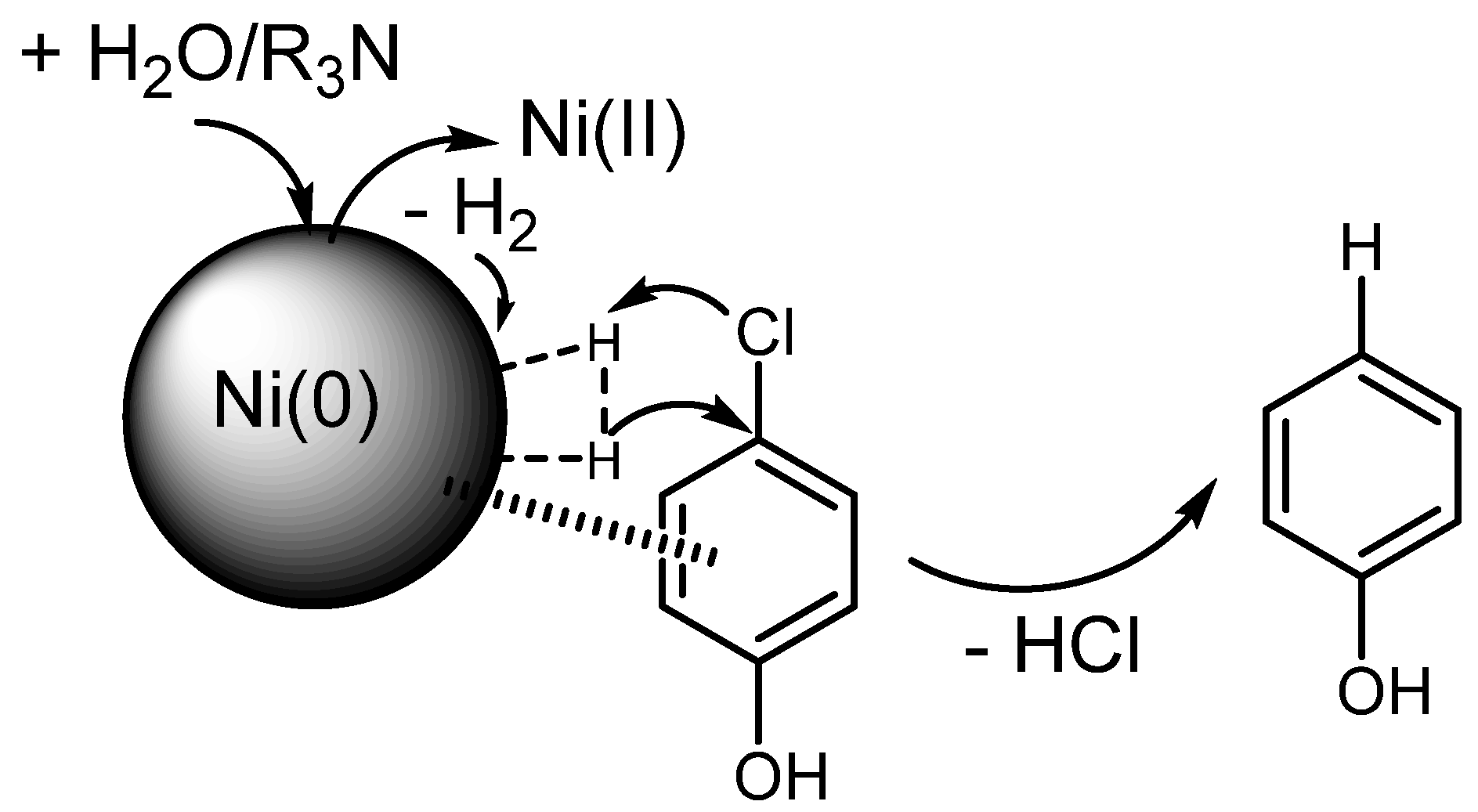
2. Ni-Catalyzed HDH Using Gaseous H2
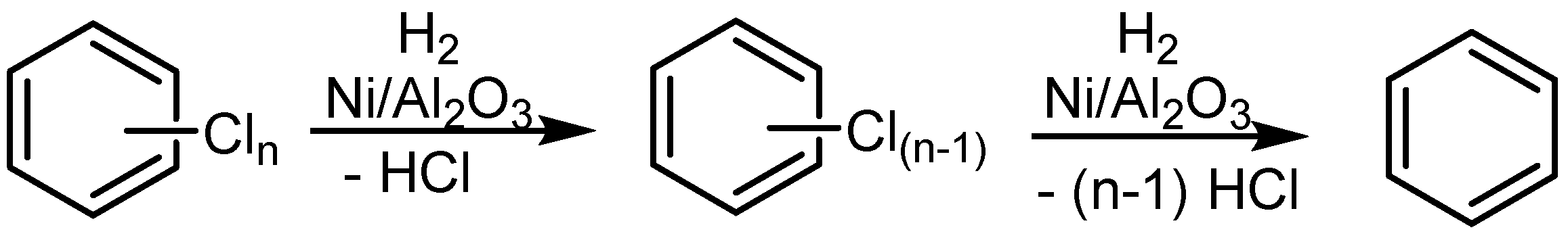
2.1. Gas Phase HDH Catalyzed by Nickel on Alumina
2.2. HDH Catalyzed by Nickel on Silica
2.3. HDH Using Ni on Active Carbon
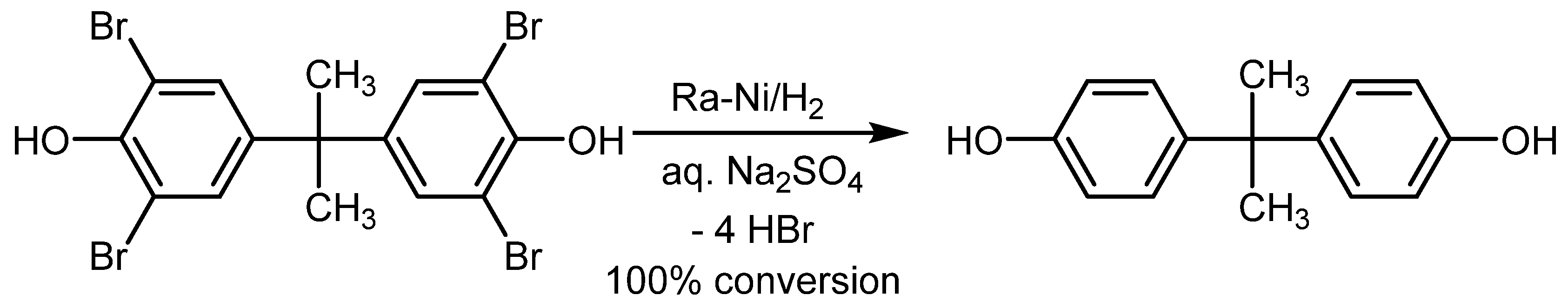
2.4. Raney Nickel Based HDH
3. Hydrogentransfer in Ni-Catalyzed Hydrodehalogenation Reactions
4. Decontamination Methods Based on Transfer HDH for Treatment of Contaminated Aqueous Solutions
4.1. Raney Nickel Applications in Transfer HDH
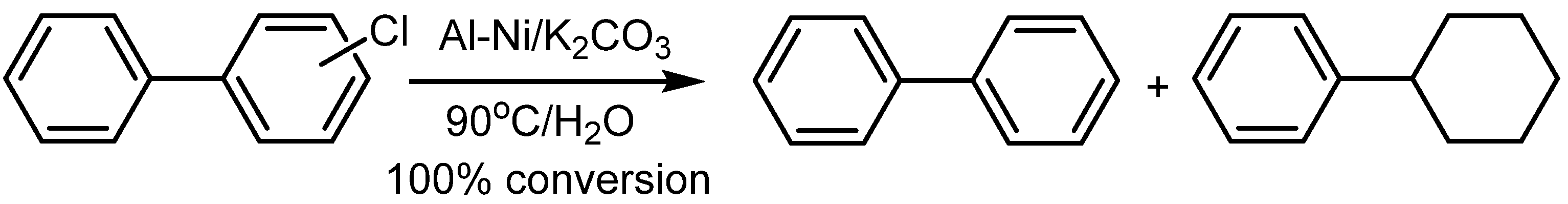
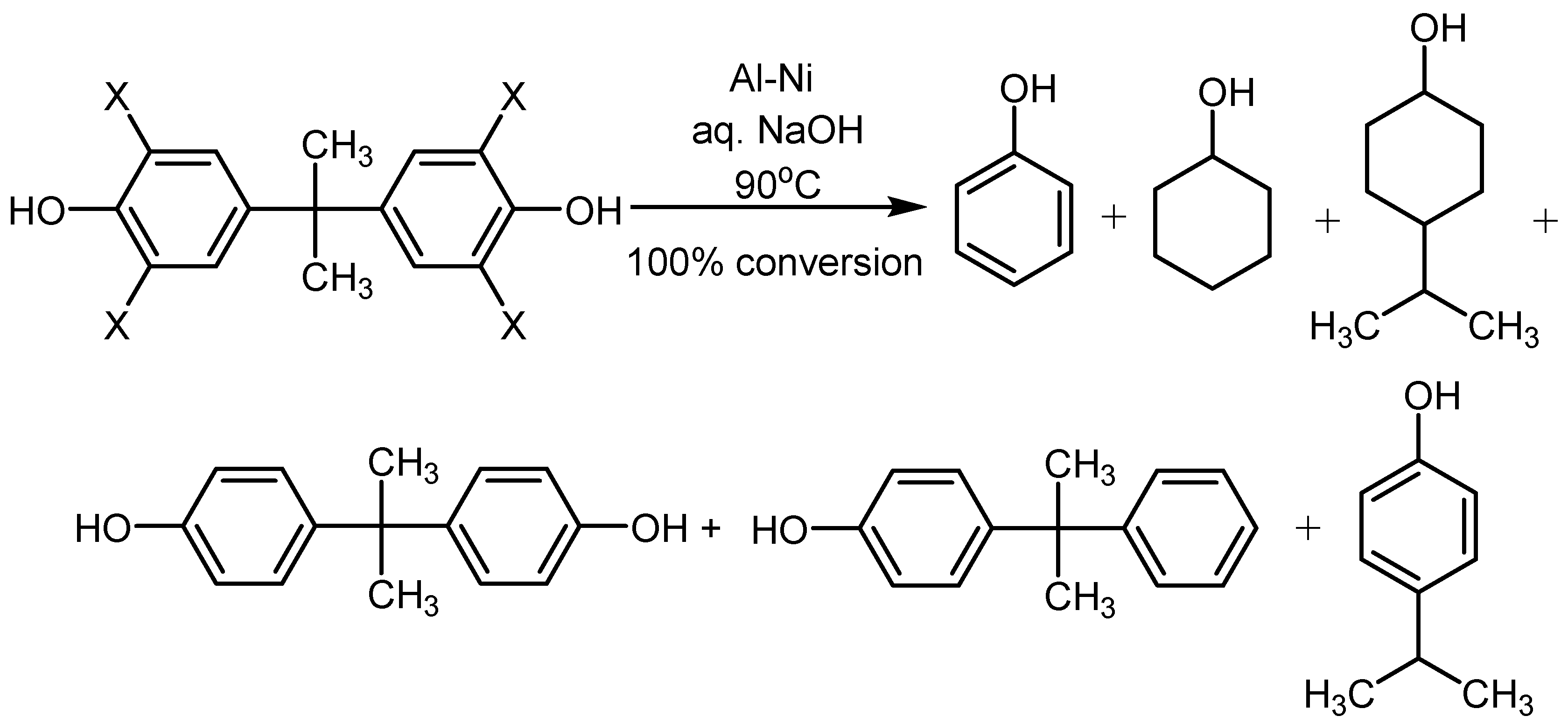
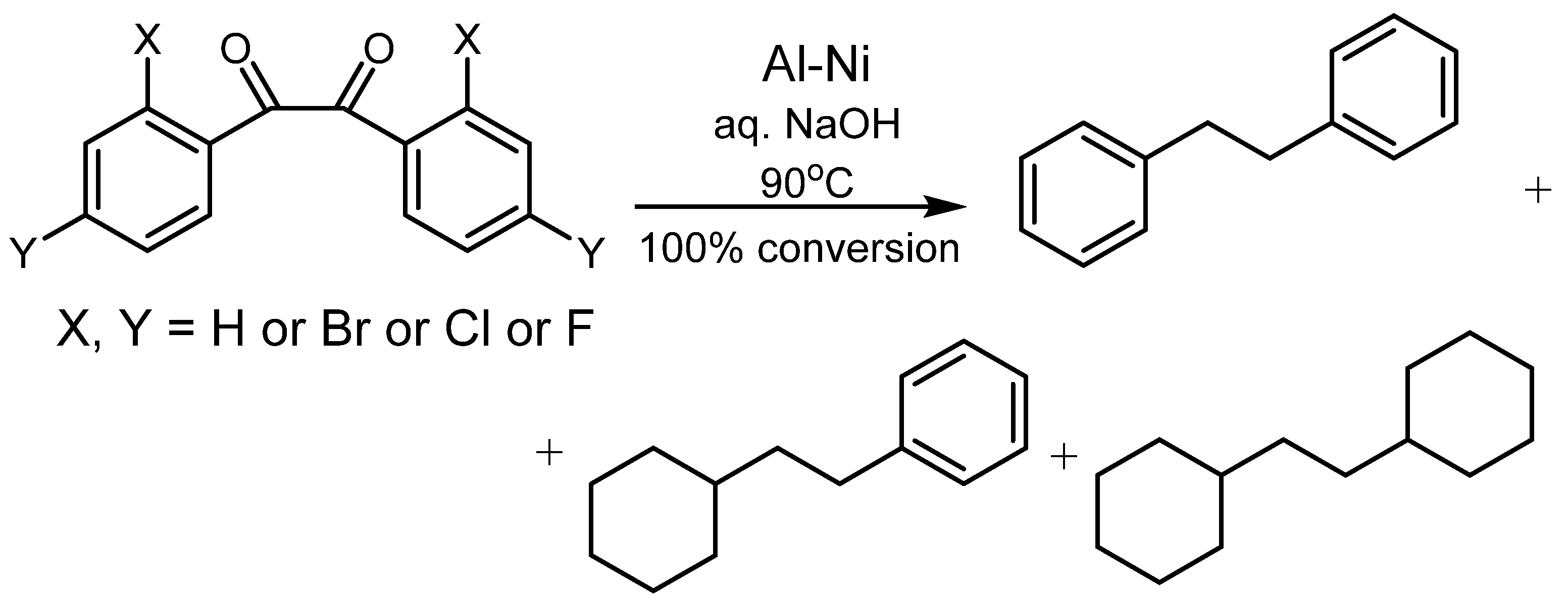
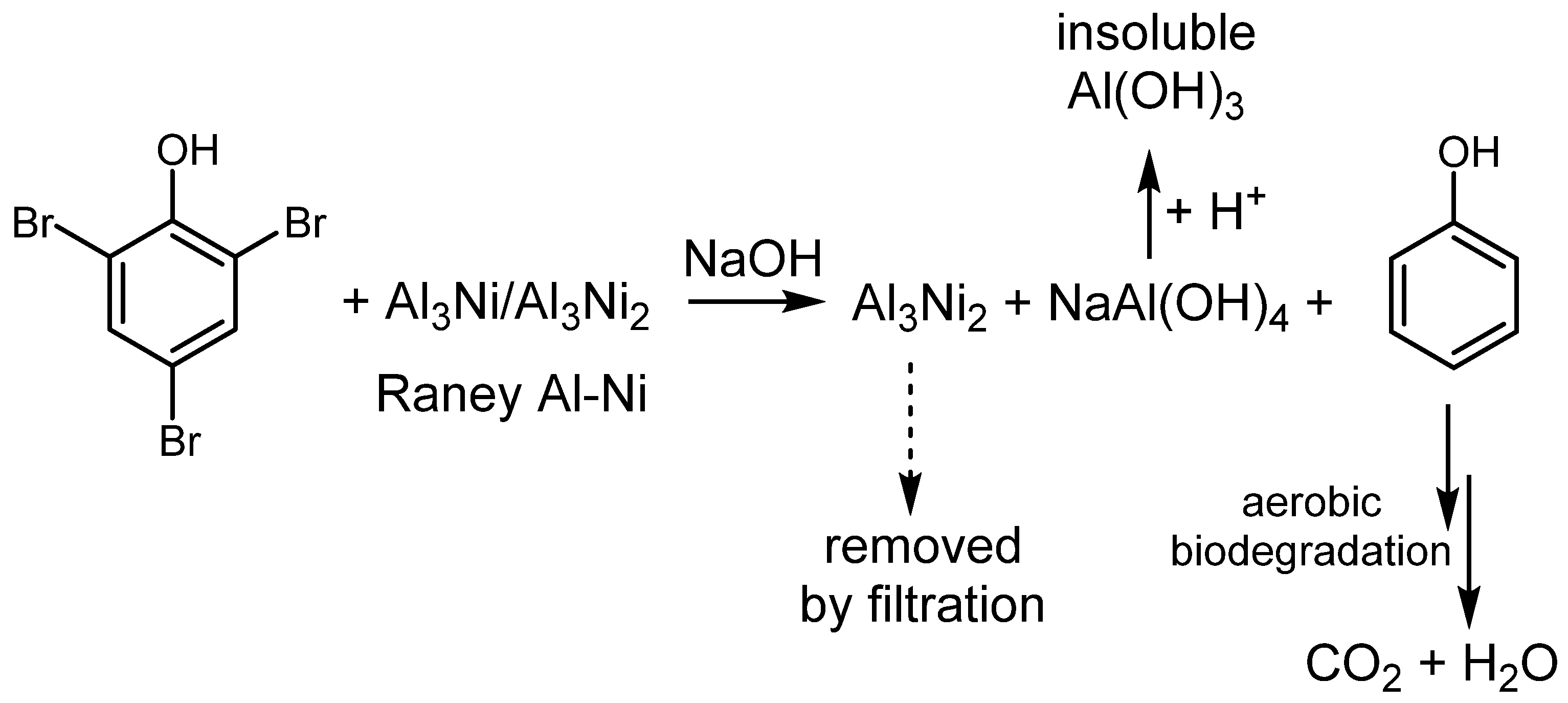
4.2. Utilization of Raney Al–Ni Alloy in HDH Processes
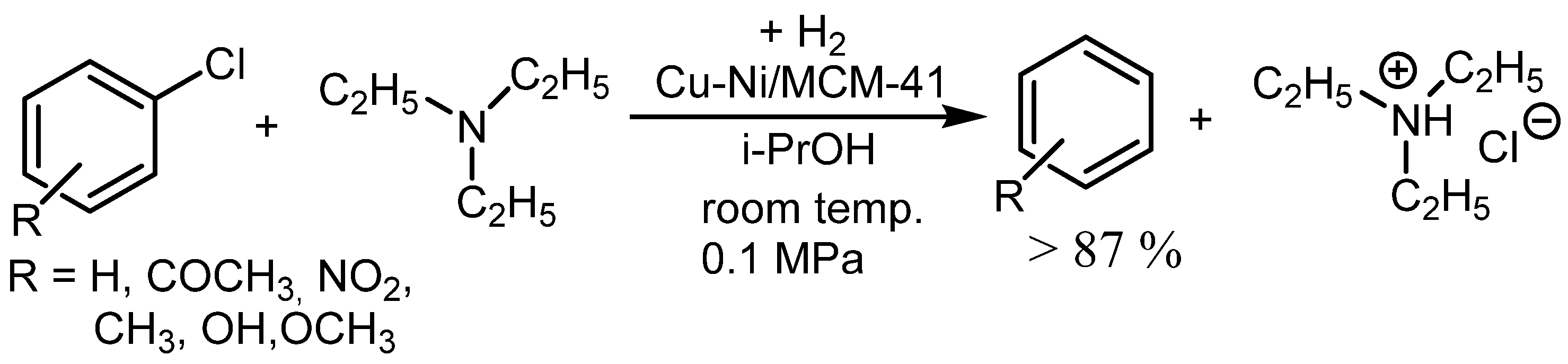
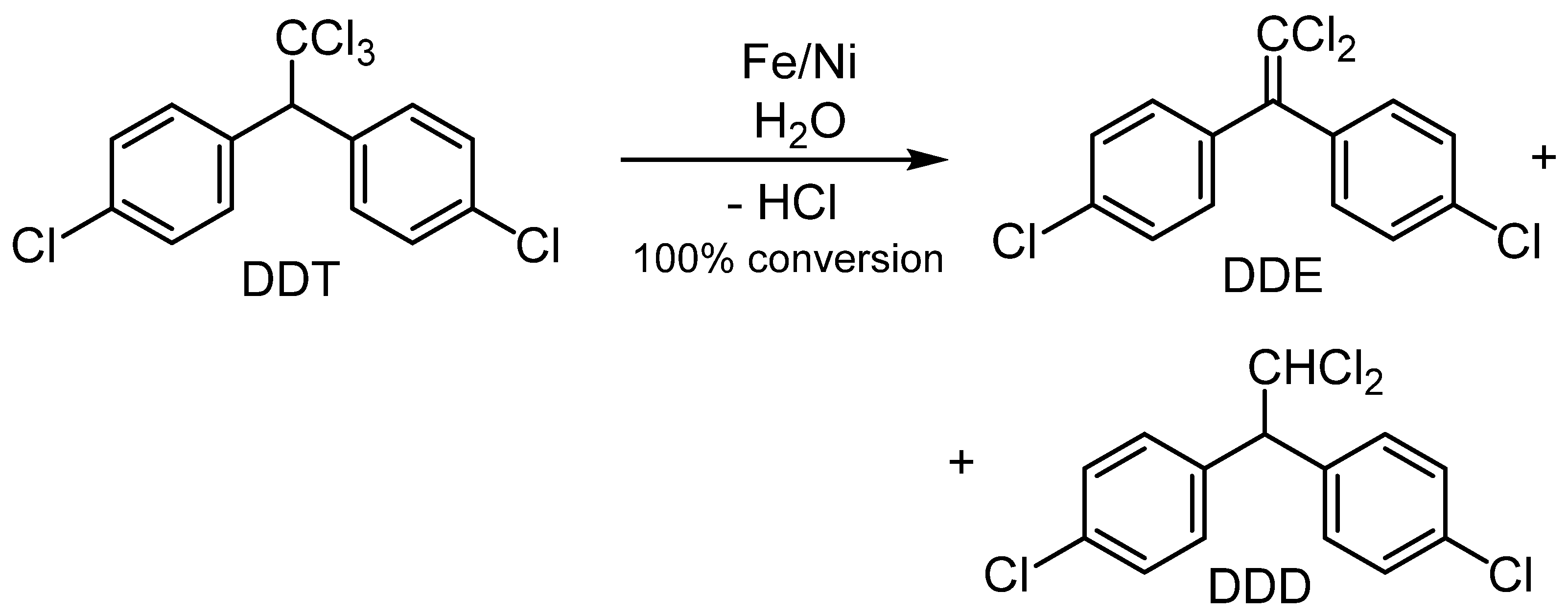
4.3. Ni-Based Bimetals Applied in Transfer HDH
5. The Role of HDH for Application of Halide as Protecting and Directing Group
6. Available Methods for Recycling of Spent Ni Catalysts
7. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keane, M.A. Supported Transition Metal Catalysts for Hydrodechlorination Reactions. ChemCatChem 2011, 3, 800–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Converti, A.; Zilli, M.; De Favari, D.M.; Ferraiola, G. Hydrogenolysis of Organochlorinated Pollutants: Kinetics and thermodynamics. J. Hazard. Mater. 1991, 27, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.P.; Harris, G.D., Jr.; Carroll, J.N.; Boehm, T.L.; McReynolds, M.D.; Struble, J.R.; van Herpt, J.; van Zwieten, D.; Koeller, K.J.; Bore, M. A new process to prepare 3,6-dichloro-2-hydroxybenzoic acid, the penultimate intermediate in the synthesis of herbicide dicamba. Tetrahedron Lett. 2019, 60, 1032–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, F.; Beletskaya, I.P.; Yus, M. Metal-Mediated Reductive Hydrodehalogenation of Organic Halides. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 4009–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buono, F.; Nguyen, T.; Qu, B.; Wu, H.; Haddad, N. Recent Advances in Nonprecious Metal Catalysis. Org. Proc. Res. Dev. 2021, 25, 1471–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, S.; Wolff, C.; Sures, B. Toxicity of platinum, palladium and rhodium to Daphnia magna in single and binary metal exposure experiments. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 224, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlak, J.; Lodyga-Chruścińska, E.; Chrustowicz, J. Fate of platinum metals in the environment. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2014, 28, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harasim, P.; Filipek, T. Nickel in the environment. J. Elem. 2015, 20, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahzad, B.; Tanveer, M.; Rehman, A.; Cheema, S.A.; Fahad, S.; Rehman, S.; Sharma, A. Nickel; whether toxic or essential for plants and environment-A review. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 132, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denkhaus, E.; Salnikow, K. Nickel essentiality, toxicity, and carcinogenicity. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hemat. 2002, 42, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zamble, D.B. Nickel Homeostasis and Nickel Regulation: An Overview. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 4617–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konkol, M.; Wróbel, W.; Bicki, R.; Golebiowski, A. The Influence of the Hydrogen Pressure on Kinetics of the Canola Oil Hydrogenation on Industrial Nickel Catalyst. Catalysts 2016, 6, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, V.; Louw, R. Performance of supported nickel and other metal catalysts in the hydrodechlorination of chlorobenzene and 1-chlorohexane. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2004, 271, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, C.; Keane, M.A. Catalytic hydrodechlorination of chloroaromatic gas streams promoted by Pd and Ni: The role of hydrogen spillover. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 211–212, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesteros, Y.; Salagre, P.; Medina, F.; Sueiras, J.E. Synthesis and characterization of several Ni/NiAl2O4 catalysts active for the 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene hydrodechlorination. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2000, 25, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesteros, Y.; Salagre, P.; Medina, F.; Sueiras, J.E. TPD study about the surface modification of some Ni/spinel catalysts in the hydrodechlorination of 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene. Influence on hydrogenation ability. Catal. Lett. 2000, 67, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzdorf, A.R.; Morozov, S.V.; Anshits, N.N.; Tsiganova, S.I. Gas-phase hydrodechlorination of chlorinated aromatic-compounds on nickel-catalysts. Catal. Lett. 1994, 29, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keane, M.A.; Gomez-Quero, S.; Cardenas-Lizana, F.; Shen, W. Alumina-Supported Ni–Au: Surface Synergistic Effects in Catalytic Hydrodechlorination. ChemCatChem 2009, 1, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, M.; Zdrazil, M. Effects of sulfidation and synergism in hydrodechlorination of o-dichlorobenzene over alumina catalyst. Bull. Soc. Chim. Belg. 1993, 102, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murena, F. Catalytic hydroprocessing of chlorobenzene: The effect of thiophene. J. Hazard. Mater. 2000, 75, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schioppa, E.; Murena, F.; Gioia, F. Mass-transfer resistances in the catalytic hydrodechlorination of polychlorobiphenyls. Experimental results of 2-chlorobiphenyl hydrodechlorination in a slurry reactor and in a rotating basket reactor. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 2011–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryglewicz, S.; Piechocki, W. Hydrodechlorination of dichlorobenzenes and their derivatives over Ni–Mo/C catalyst: Kinetic analysis and effect of molecular structure of reactant. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesteros, Y.; Salagre, P.; Medina, F.; Sueiras, J.E.; Tichit, D.; Coq, B. Hydrodechlorination of 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene on nickel-based catalysts prepared from several Ni/Mg/Al hydrotalcite-like precursors. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2001, 32, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menini, C.; Park, C.; Shin, E.J.; Tavoularis, G.; Keane, M.A. Catalytic hydrodehalogenation as a detoxification methodology. Catal. Today 2000, 62, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Menini, C.; Valverde, J.L.; Keane, M.A. Carbon–Chlorine and Carbon–Bromine Bond Cleavage in the Catalytic Hydrodehalogenation of Halogenated Aromatics. J. Catal. 2002, 211, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keane, M.A.; Pina, G.; Tavoularis, G. The catalytic hydrodechlorination of mono-, di- and trichlorobenzenes over supported nickel. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2004, 48, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keane, M.A. Hydrodehalogenation of haloarenes over Silica supported Pd and Ni. A consideration of catalytic activity/selectivity and haloarene reactivity. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2004, 271, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, K.V.; Patterson, P.M.; Jacobs, G.; Davis, B.H.; Keane, M.A. An exploration of activity loss during hydrodechlorination and hydrodebromination over Ni/SiO2. J. Catal. 2004, 223, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, K.V.; Patterson, P.M.; Keane, M.A. C–X bond reactivity in the catalytic hydrodehalogenation of haloarenes over unsupported and silica supported Ni. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2005, 225, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.; Kim, Y.; Kang, T.; Song, I.K.; Yi, J. Preparation of nickel-mesoporous materials and their application to the hydrodechlorination of chlorinated organic compounds. Catal. Surv. Asia 2007, 11, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.; Joo, J.B.; Kim, H.; Kim, W.; Kim, Y.; Song, I.K.; Yi, J. Preparation of mesoporous Ni-alumina catalyst by one-step sol-gel method: Control of textural properties and catalytic application to the hydrodechlorination of o-dichlorobenzene. Catal. Lett. 2005, 104, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Kang, T.; Kim, P.; Yi, J. Encapsulation method for the dispersion of NiO onto ordered mesoporous silica, SBA-15, using polyethylene oxide (PEO). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 295, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, D.; Parida, K.M. Copper and Nickel Modified MCM-41 an Efficient Catalyst for Hydrodehalogenation of Chlorobenzene at Room Temperature. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 2839–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Xu, J.; Ohnishi, R. Complete hydrodechlorination of chlorobenzene and its derivatives over supported nickel catalysts under liquid phase conditions. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2005, 60, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, K.; Huang, D.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, W.; Niu, J. Ultrasonication-Enhanced Reduction of Tetrabromobisphenol A by Activating Nascent H2 on Raney Ni Catalyst: Kinetics, Mechanisms, and Hydrogenation Pathways. ACS EST Eng. 2021, 1, 884–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Gu, G.; Xia, C. Promoted liquid-phase hydrodechlorination of chlorophenol over Raney Ni via controlling base: Performance, mechanism, and application. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, C.A.; Selva, M.; Tundo, P. Hydrodehalogenation of polyhalogenated aromatics under multiphase conditions with H-2 and metal catalyst: Kinetics and selectivity. Gazz. Chim. Ital. 1996, 126, 317–327. [Google Scholar]
- Cardenas-Lizana, F.; Gomez-Quero, S.; Keane, M.A. Clean production of chloroanilines by selective gas phase hydrogenation over supported Ni catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2008, 334, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, C.; Wang, X.; Keane, M.A. Application of Hydrodechlorination in Environmental Pollution Control: Comparison of the Performance of Supported and Unsupported Pd and Ni Catalysts. Chin. J. Catal. 2011, 32, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birke, P.; Wilfried, R.; Heubner, U.; Koppe, J.; Neumann, U.; Shoedel, R. DE Patent 4320462, 1995. Chem. Abstr. 1995, 123, 231952. [Google Scholar]
- Keane, M.A.; Larsson, R. Isokinetic behaviour in gas phase catalytic hydrodechlorination of chlorobenzene over supported nickel. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2007, 268, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keane, M.A.; Park, C.; Menini, C. Structure sensitivity in the hydrodechlorination of chlorobenzene over supported nickel. Catal. Lett. 2003, 88, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, E.-J.; Keane, M.A. Structure sensitivity in the hydrodechlorination of chlorophenols. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 2000, 69, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prati, L.; Rossi, M. Reductive catalytic dehalogenation of light chlorocarbons. Appl. Catal. B 1999, 23, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keane, M.A. A review of catalytic approaches to waste minimization: Case study-liquid-phase catalytic treatment of chlorophenols. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2005, 80, 1211–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramendia, M.A.; Borau, V.; Garcia, I.M.; Jimenez, C.; Lafont, F.; Marinas, A.; Marinas, J.M.; Urbano, F.J. Influence of the Reaction Conditions and Catalytic Properties on the Liquid-Phase Hydrodechlorination of Chlorobenzene over Palladium-Supported Catalysts: Activity and Deactivation. J. Catal. 1999, 187, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fan, G.; Li, F. Carbon-supported Ni catalysts with enhanced metal dispersion and catalytic performance for hydrodechorination of chlorobenzene. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 9976–9985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Yang, C.; Liu, S.; Guo, S.; Liu, Q.; Yu, J.; Chen, J. The influence of ion effects on the Pd-catalyzed hydrodechlorination of 4-chlorophenol in aqueous solutions. Catal. Commun. 2009, 10, 1443–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, J.A.; Calvo, L.; Gilarranz, M.A.; Rodriguez, J.J. Effect of size and oxidation state of size-controlled rhodium nanoparticles on the aqueous-phase hydrodechlorination of 4-chlorophenol. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 240, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Astruc, D. The Golden Age of Transfer Hydrogenation. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 6621–6686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiles, M. Nickel Complexes as Soluble Catalysts for Reductive Dehalogenation of Aromatic Halides. J. Org. Chem. 1994, 59, 5381–5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, H.; Lee, H.; Kang, J.; Cho, J. A high-spin nickel(II) borohydride complex in dehalogenation. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2016, 3, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vcelak, J.; Hetflejs, J. Dehalogenation of chloroarenes with sodium dihydrobis(2-methoxyethoxo)aluminate in the presence of transition metal compounds. Collect. Czech. Chem. Commun. 1994, 59, 1645–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, C.M.; King, R.B.; Bhattacharyya, N.K.; Newton, M.G. Organonickel chemistry in the catalytic hydrodechlorination of polychlorobiphenyls (PCBs): Ligand steric effects and molecular structure of reaction intermediates. J. Organomet. Chem. 2000, 600, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, F.; Riente, P.; Sirvent, J.A.; Yus, M. Nickel nanoparticles in hydrogen-transfer reductions: Characterisation and nature of the catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2010, 378, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alonso, F.; Foubelo, F.; González-Gómez, J.C.; Martínez, R.; Ramón, D.J.; Riente, P.; Yus, M. Efficiency in chemistry: From hydrogen autotransfer to multicomponent catalysis. Mol. Divers. 2010, 14, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, F.; Riente, P.; Yus, M. Nickel Nanoparticles in Hydrogen Transfer Reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabaei, S.-M.H.; Pittman, C.U., Jr.; Mead, K.T. Dehalogenation of Organic Compounds. 3. Dechlorination of Polychlorinated Biphenyls, 4-Chlorobiphenyl, and Chloro-p-xylene with Alkoxyborohydrides. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 6669–6671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabaei, S.-M.H.; Pittman, C.U., Jr. Dehalogenation of Organic Compounds. 4. Dechlorination of Pentachlorophenol and 1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene with Transition Metal-Promoted Alkoxyborohydrides. Tetrahedron Lett. 1993, 34, 3263–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrivanti, A.; Vicentini, B.; Beghetto, V.; Chessa, G.; Matteoli, U. Hydrodehalogenation of aromatic chlorides with NaBH4, in the presence of Ni(0) catalysts. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 1998, 1, 246–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Gardinier, J.R. The Electronic Properties of Ni(PNN) Pincer Complexes Modulate Activity in Catalytic Hydrodehalogenation Reactions. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 2020, 4425–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipshutz, B.H.; Tomioka, T.; Pfeiffer, S.S. Mild and selective reductions of aryl halides catalyzed by low-valent nickel complexes. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 7737–7740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, M.; Lee, M.-S.; Yamaguchi, K.; Kawai, Y. Metallic Nickel-Catalyzed Reduction of Aryl Halides with Zinc Powder and Ethanol. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1992, 65, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prikhodko, S.A.; Popov, A.G.; Adonin, N.Y. Effects arising from the replacement of aprotic dipolar solvents with ionic liquids in the nickel-catalyzed reduction of aryl chlorides. Mol. Catal. 2018, 461, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prikhodko, S.A.; Adonin, N.Y.; Parmon, V.N. Reaction of pentafluoroacetanilide with zinc catalyzed by nickel complexes. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2009, 58, 2304–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shteingarts, V.D. Recent advances in practice and theory of polyfluoroarene hydrodehalogenation. J. Fluorine Chem. 2007, 128, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Hayashida, N.; Maruyama, T. Ni-catalyzed dehalogenation polycondensation of dihaloaromatic compounds with NaH. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1997, 198, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Gong, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Duan, R.; Chen, C.; Song, W.; Zhao, J. Ligand directed debromination of tetrabromodiphenyl ether mediated by nickel under visible irradiation. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 1585–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gantzer, C.J.; Wackett, L.P. Reductive Dechlorination Catalyzed by Bacterial Transition-Metal Coenzymes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1991, 25, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraishi, K.; Yamamoto, T. New pi-conjugated polymers constituted of dialkoxybenzodithiophene units: Synthesis and electronic properties. Synth. Met. 2002, 130, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, P.K.; Ramnath, N.; Richardson, A.D. The Photochemistry of Polyhalogarenes. 10. The Photochemistry of Pentachlorobenzene. J. Org. Chem. 1991, 56, 3643–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidauer, M.; Irran, E.; Someya, C.I.; Haberberger, M.; Enthaler, S. Nickel-catalyzed hydrodehalogenation of aryl halides. J. Organomet. Chem. 2013, 729, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiak, C.; Deblon, S.; Uehlin, L. Synthesis of 6,6′-diamino-2,2′-biquinoline and 2,2′-bi-1,6-naphthyridine. Synth.-Stuttg. 1999, 1999, 959–964. [Google Scholar]
- Fort, Y. Lithium Hydride Containing Complex Reducing Agent–A New And Simple Activation of Commercial Lithium Hydride. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 6051–6054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caubere, P. Complex Reducing Agents–their Applications and their Outcome in the Field of Carbonylations. Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 1875–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, J.M.; Fort, Y.; Tillement, O. FR Patent 2768638. Chem. Abstr. 1999, 130, 254063. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Liao, S.; Xu, Y. Catalytic Hydrogenolysis of Aromatic Halides with Sodium Hydride of Nanometric Size. Chem. Lett. 1996, 25, 1059–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liao, S.; Yu, D.; Qiao, Z. An effective method for the hydrodehalogenation of organic halides. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1997, 42, 966–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massicot, F.; Schneider, R.; Fort, Y.; Illy, S.; Tillement, O. Synergistic Effect in Bimetallic Ni±Al Clusters. Application to Efficient Catalytic Reductive Dehalogenation of Polychlorinated Arenes. Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 4765–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazellot, P.; Leclercq, C.; Fort, Y.; Caubere, P. Subnanometer Nickel Clusters in Complex Reducing Agents. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 1994, 93, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illy, S.; Tillement, O.; Dubois, J.M.; Massicot, F.; Fort, Y.; Ghanbaja, J. First direct evidence of size-dependent structural transition in nanosized nickel particles. Philos. Mag. A 1999, 79, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastanek, F.; Maleterova, Y.; Kastanek, P.; Rott, J.; Jiricny, V.; Jiratova, K. Complex treatment of wastewater and groundwater contaminated by halogenated organic compounds. Desalination 2007, 211, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keane, M.A. Advances in greener separation processes - case study: Recovery of chlorinated aromatic compounds. Green Chem. 2003, 5, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, J.; Gu, G.; Xia, C. Water: The most effective solvent for liquid-phase hydrodechlorination of chlorophenols over Raney Ni catalyst. Appl. Catal. B 2015, 165, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, Y.; Wang, K.; Pei, Y.; Niu, J. Ultrasonic-enhanced nascent H-2 activation on Raney Ni for the degradation of triclosan. Chin. Sci. Bull. Chin. 2021, 66, 1923–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, S.S.; Shetty, R.; Raju, N.M.; Kamble, S.P.; Kulkarni, P.S. Screening of zero valent mono/bimetallic catalysts and recommendation of Raney Ni (without reducing agent) for dechlorination of 4-chlorophenol. Chemosphere 2020, 250, 126298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Gu, G.; Xia, C. Comparative study on catalytic hydrodehalogenation of halogenated aromatic compounds over Pd(5 wt%)/C and Raney Ni catalysts. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidlich, T.; Kamenicka, B.; Melanova, K.; Cicmancova, V.; Komersova, A.; Cermak, J. Hydrodechlorination of Different Chloroaromatic Compounds at Room Temperature and Ambient Pressure—Differences in Reactivity of Cu- and Ni-Based Al Alloys in an Alkaline Aqueous Solution. Catalysts 2020, 10, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.B.; Zhao, H.Y.; Dai, L.; Thiemann, T. A convenient method for the reductive degradation of mono-, di-, and tribromodiphenyl ethers, tetrabromo- and tetrachlorobisphenol A with Raney Ni-Al alloy. Ark. J. Chem. Res. 2009, 13, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, G.B.; Zhao, H.Y.; Zhang, J.; Thiemann, T. Raney Ni-Al alloy mediated hydrodehalogenation and aromatic ring hydrogenation of halogenated phenols in aqueous medium. J. Chem. Res. 2009, 6, 342–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidlich, T.; Prokes, L. Facile dehalogenation of halogenated anilines and their derivatives using Al–Ni alloy in alkaline aqueous solution. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2011, 9, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidlich, T.; Prokes, L.; Pospisilova, D. Debromination of 2,4,6-tribromophenol coupled with biodegradation. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2013, 11, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidlich, T.; Oprsal, J.; Krejcova, A.; Jasurek, B. Effect of glucose on lowering Al–Ni alloy consumption in dehalogenation of halogenoanilines. Monatsh. Chem. 2015, 146, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perko, J.; Kamenicka, B.; Weidlich, T. Degradation of the antibacterial agents triclosan and chlorophene using hydrodechlorination by Al-based alloys. Monatsh. Chem. 2018, 149, 1777–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.-B.; Tsukinoki, T.; Kanda, T.; Mitoma, Y.; Tashiro, M. Organic Reaction in Water. Part 2. A New Method for Dechlorination of Chlorobiphenyls Using a Raney Ni-Al Alloy in Dilute Aqueous Alkaline Solution. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 5991–5994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.B.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Zhu, J.-D.; He, H.-J.; Yang, H.-J.; Thiemann, T.; Tashiro, H.; Tashiro, M. New Method for the Reduction of Benzophenones with Raney Ni-Al Alloy in Water. Synth. Commun. 2008, 38, 1651–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.B.; Tashiro, M.; Thiemann, T. A facile method for the dechlorination of mono- and dichlorobiphenyls using Raney Ni–Al alloy in dilute aqueous solutions of alkali hydroxides or alkali metal carbonates. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 2497–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegedus, M.; Gaborova, K.; Weidlich, T.; Kalivoda, P.; Briancin, J.; Tothova, E. Rapid hydrodehalogenation of chlorinated benzoic acids using mechano-thermally prepared Raney alloy with enhanced kinetics. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.B.; Dai, L.; Gao, X.; Li, M.K.; Thiemann, T. Reductive degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) in aqueous medium. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 781–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zhang, F.; Deng, S.; Yu, G.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, J.; Shi, L.; Shen, J. A facile method for the highly efficient hydrodechlorination of 2-chlorophenol using Al–Ni alloy in the presence of fluorine ion. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 209, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, S.; Yu, G.; Wu, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J. Promoting effect of EDTA on catalytic activity of highly stable Al–Ni bimetal alloy for dechlorination of 2-chlorophenol. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 250, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keefer, L.K.; Lunn, G. Nickel-Aluminum Alloy as a Reducing Agent. Chem. Rev. 1989, 89, 459–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegedus, M.; Lacina, P.; Ploteny, M.; Lev, J.; Kamenicka, B.; Weidlich, T. Fast and efficient hydrodehalogenation of chlorinated benzenes in real wastewaters using Raney alloy. J. Water Proc. Eng. 2020, 38, 101645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.-B.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Dai, L.; Thiemann, T.; Tashiro, H.; Tashiro, M. Raney Ni–Al alloy-mediated reduction of benzils in water. J. Chem. Res. 2009, 9, 579–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidheesh, P.V.; Khatri, J.; Anatha Singh, T.S.; Gandhimathi, R.; Ramesh, S.T. Review of zero-valent aluminium based water and wastewater treatment methods. Chemosphere 2018, 200, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.-H.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Su, Y.-F. Reduction of hexachlorobenzene by nanoscale zero-valent iron: Kinetics, pH effect, and degradation mechanism. Sep. Pur. Technol. 2011, 76, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, H.M.; Wai, C.M.; Yuan, T.; Kim, J.-K.; Marshall, W.D. Catalytic hydrodechlorination of chlorophenols in aqueous solution under mild conditions. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2004, 271, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Kim, Y.H. Reduction of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol with zero-valent zinc and catalyzed zinc. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.H.; Chen, M.Y.; Su, Y.F. Pentachlorophenol reduction by Pd/Fe bimetallic nanoparticles: Effect of copper, nickel, and ferric cations. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 105, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Al-Abed, S.R.; Dionysiou, D.D. Enhanced corrosion based Pd/Mg bimetallic systems for dichlorination of PCBs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 3722–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Ahn, S.; Seyfferth, A.I.; Masue-Slowey, Y.; Fendorf, S.; Luthy, R.G. Dehalogenation of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers and Polychlorinated Biphenyl by Bimetallic, Impregnated, and Nanoscale Zerovalent Iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4896–4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, B.; Deng, S.; Yu, G.; Zhang, H.; Wu, J.; Zhuo, Q. Bimetallic Pd/Al particles for highly efficient hydrodechlorination of 2-chlorobiphenyl in acidic aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 189, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cissoko, N.; Wo, J.; Xu, X. Factors influencing the dechlorination of 2,4-dichlorophenol by Ni-Fe nanoparticles in the presence of humic acid. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Li, J.; Mu, Z.; Li, L.; Hao, Z. Effect of pH on DDT degradation in aqueous solution using bimetallic Ni/Fe nanoparticles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 66, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Zhou, W.; Wang, J.-L.; Qi, D.; Guo, L.; Zhang, W.-X.; Qian, Y. Dechlorination of pentachlorophenol using nanoscale Fe/Ni particles: Role of nano-Ni and its size effect. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 180, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghauch, A.; Assi, H.A.; Bdeir, S. Aqueous removal of diclofenac by plated elemental iron: Bimetallic systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hu, S.; Ali, S.; Tang, J.; Xu, X. Catalytic dechlorination of Aroclor 1242 by Ni/Fe bimetallic nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 385, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Shih, Y.; MacFarlane, J. Amphiphilic compounds enhance the dechlorination of pentachlorophenol with Ni/Fe bimetallic nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gu, C.; Ye, M.; Bian, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, F.; Yang, X.; Song, Y.; Jiang, X. Debromination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers by attapulgite-supported Fe/Ni bimetallic nanoparticles: Influencing factors, kinetics and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 298, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Qian, W.; Yu, C.; Wang, T.; Zeng, G.; Lei, C. Effective catalytic hydrodechlorination of o-, p- and m-chloronitrobenzene over Ni/Fe nanoparticles: Effects of experimental parameter and molecule structure on the reduction kinetics and mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 306, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Han, D.; Huang, W.; Yang, C. New insights into the role of Ni loading on the surface structure and the reactivity of nZVI toward tetrabromo- and tetrachlorobisphenol A. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 311, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.F.; Wu, S.C. Feasibility of using metals to remediate water containing TCE. Chemosphere 2001, 43, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashiro, M.; Fukata, G. Selective Electrophilic Aromatic Substitutions via Positional Protective Groups. A Review. Org. Prep. Proc. Int. 1976, 8, 51–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, A.; Jimenez, L.S. Reductive Dehalogenation of Aryl Bromides and Chlorides and Their Use as Aryl Blocking Groups. Synthesis 2010, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.Y.; Chi, Y. A Facile Debromination Reaction: Can Bromide Now Be Used as a Protective Group in Aromatic Systems? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 9202–9203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Effenberger, F. How Attractive is Bromine as a Protecting Group in Aromatic Chemistry? Angew. Chem. 2002, 41, 1699–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Cano, J.; González-Zamarripa, G.; Carrillo-Pedroza, R.; de Jesús Soria-Aguilar, M.; Hurtado-Macías, A.; Cano-Vielma, A. Kinetics and statistical analysis of nickel leaching from spent catalyst in nitric acid solution. Int. J. Min. Proc. 2016, 148, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez Stagnaro, S.Y.; Mesquida, C.D.; Stábile, F.M.; Zysler, R.; Ramos, S.B.; Giaveno, A. Recovery and characterization of nickel particles by chemical reduction method from wastes generated in electroless industry. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 376, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coman, V.; Robotin, B.; Ilea, P. Nickel recovery/removal from industrial wastes: A review. Res. Conserv. Rec. 2013, 73, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidlich, T.; Kamenicka, B. Recycling of Spent Hydrodehalogenation Catalysts–Problems Dealing with Separation of Aluminium. Inz. Min. J. Pol. Min. Eng. Soc. 2019, 1, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendova, H.; Weidlich, T. Application of diffusion dialysis in hydrometallurgical separation of nickel from spent Raney Ni catalyst. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 1218–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A. Atom efficiency and catalysis in organic synthesis. Pure Appl. Chem. 2000, 72, 1233–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, H.-Y.; Cunningham, J. Remediation of contaminated soil by solvent extraction and catalytic hydrodehalogenation: Semicontinuous process with solvent recycle. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2011, 30, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altarawneh, M.; Ahmed, O.H.; Al-Harahsheh, M.; Jiang, Z.-T.; Huang, N.M.; Lim, H.N.; Dlugogorski, B.Z. Co-pyrolysis of polyethylene with products from thermaldecomposition of brominatedflame retardants. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 1267662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecilia, J.A.; Infantes-Molina, A.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E. Hydrodechlorination of polychlorinated molecules using transition metal phosphide catalysts. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 296, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balda, M.; Kopinke, F.-D. The role of nickel traces in fine chemicals for hydrodechlorination reactions with zero-valent iron. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 388, 124185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


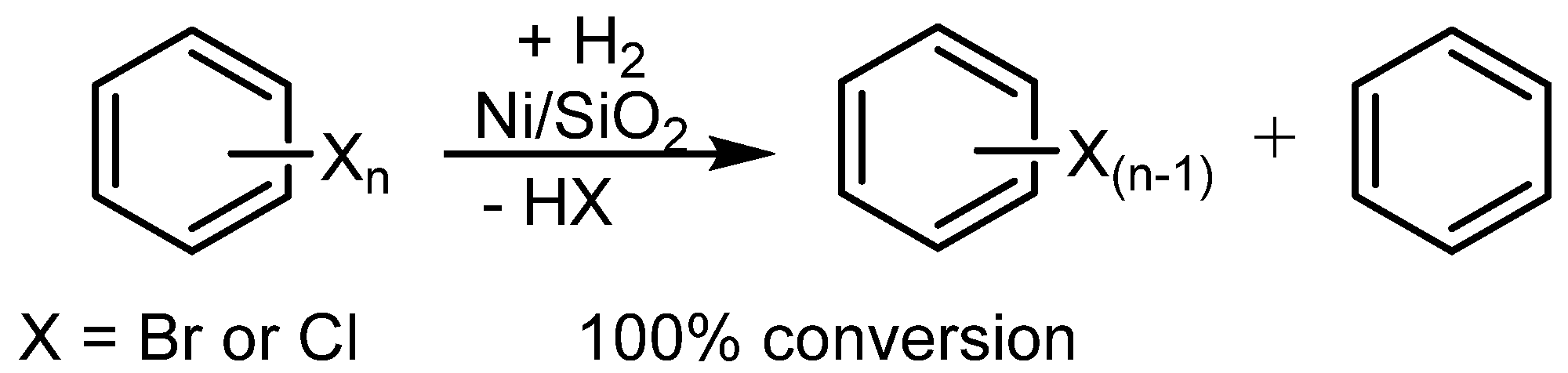
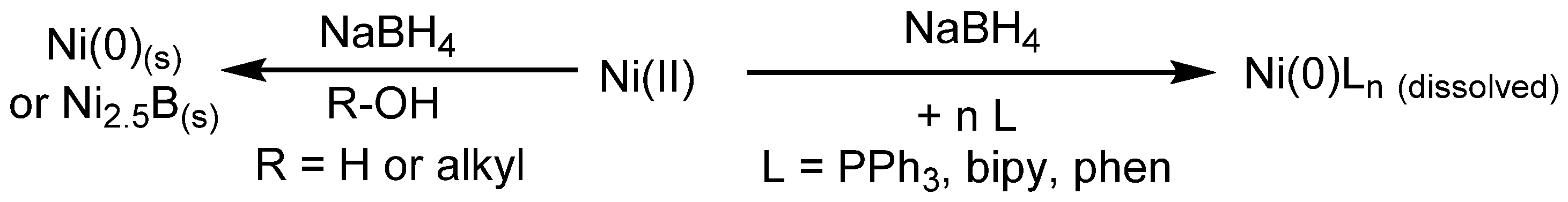




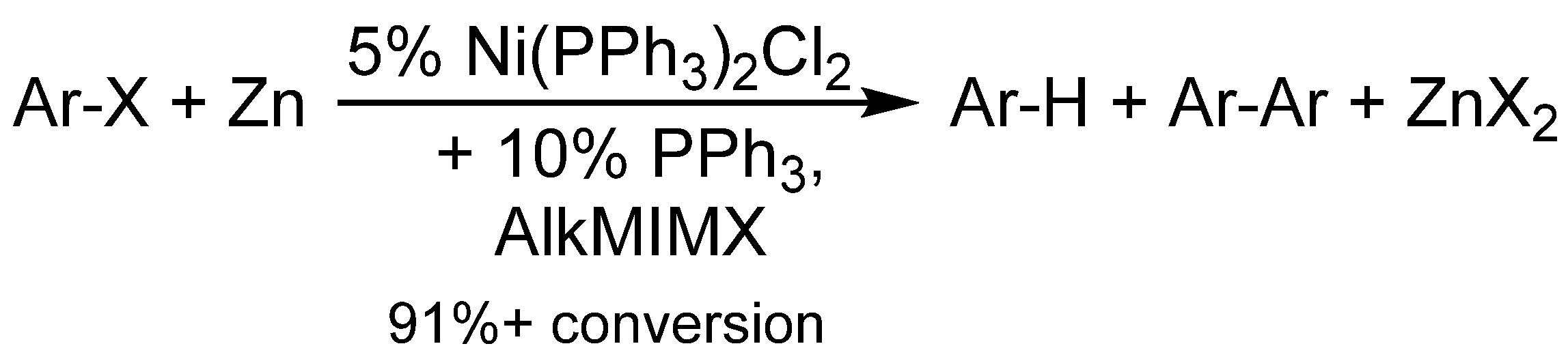








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weidlich, T. Applicability of Nickel-Based Catalytic Systems for Hydrodehalogenation of Recalcitrant Halogenated Aromatic Compounds. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11121465
Weidlich T. Applicability of Nickel-Based Catalytic Systems for Hydrodehalogenation of Recalcitrant Halogenated Aromatic Compounds. Catalysts. 2021; 11(12):1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11121465
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeidlich, Tomáš. 2021. "Applicability of Nickel-Based Catalytic Systems for Hydrodehalogenation of Recalcitrant Halogenated Aromatic Compounds" Catalysts 11, no. 12: 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11121465
APA StyleWeidlich, T. (2021). Applicability of Nickel-Based Catalytic Systems for Hydrodehalogenation of Recalcitrant Halogenated Aromatic Compounds. Catalysts, 11(12), 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11121465





