Na3[Ru2(µ-CO3)4] as a Homogeneous Catalyst for Water Oxidation; HCO3− as a Co-Catalyst
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Catalytic Water Oxidation in Neutral Medium
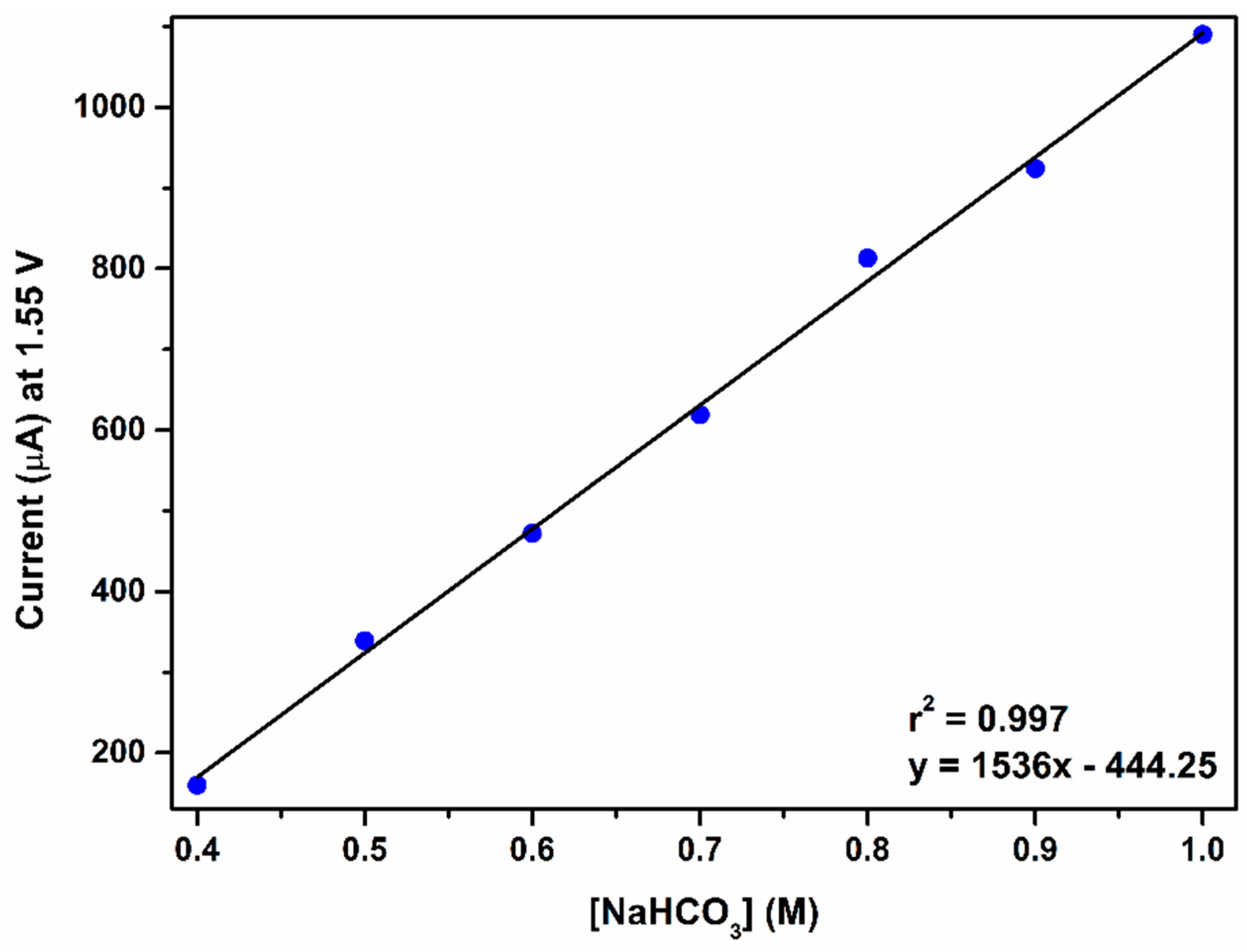
2.2. Catalytic Water Oxidation in Bicarbonate/Carbonate Medium
2.2.1. The First Wave, RuIIIRuIII/RuIIIRuII Redox Couple
2.2.2. The Second Wave, RuIVRuIII/RuIIIRuIII Redox Couple
2.2.3. The Third Wave, RuIVRuIV/RuIVRuIII Redox Couple
2.2.4. The Fourth Wave, Catalytic Oxidation
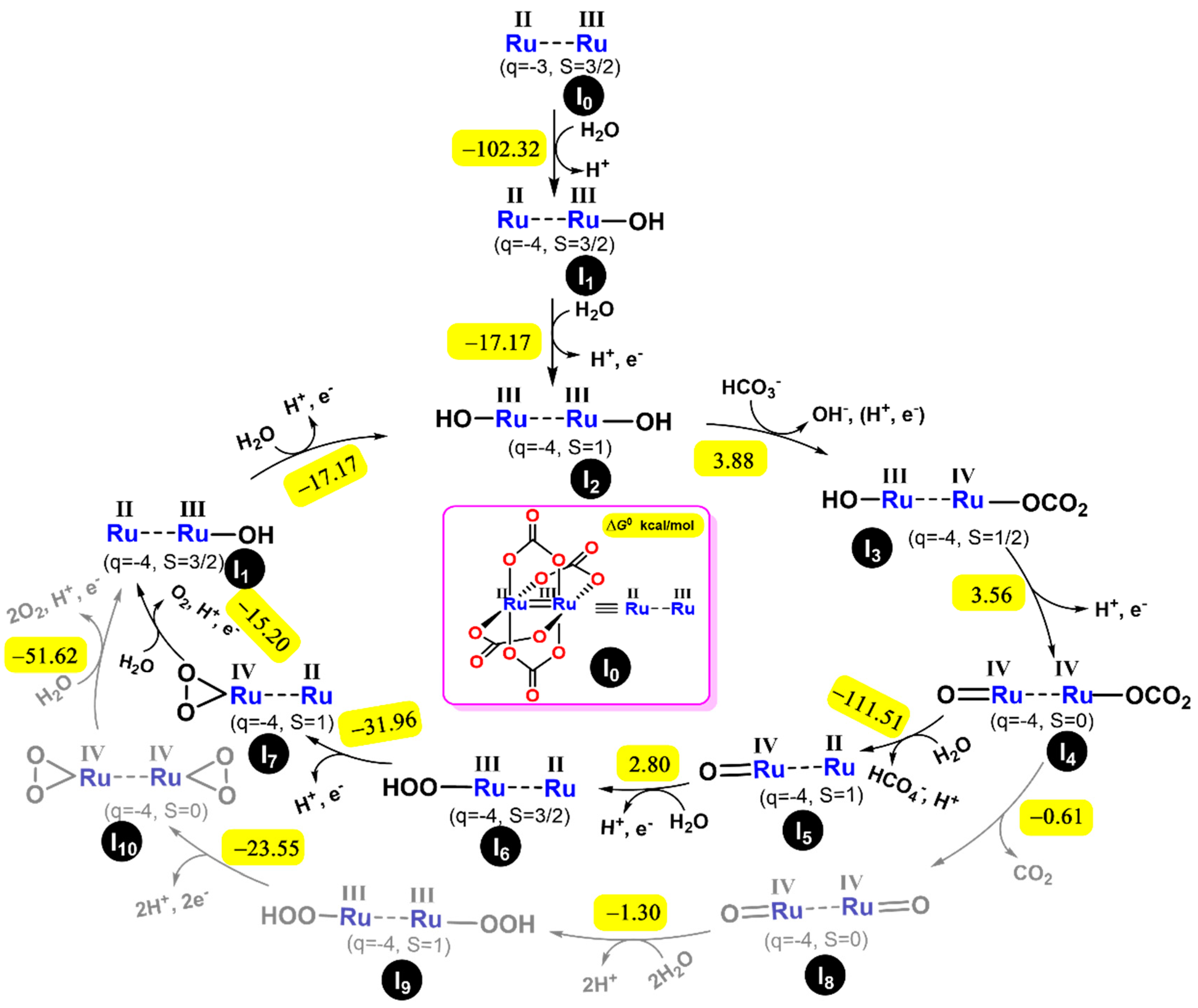
2.3. Theoretical Analysis of the Mechanism
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Electrochemistry Methods
3.2. Computational Details
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shatskiy, A.; Kärkäs, M.D.; Åkermark, B. The Art of Splitting Water: Storing Energy in a Readily Available and Convenient Form. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 2019, 2020–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dresselhaus, M.S.; Thomas, I.L. Alternative energy technologies. Nature 2001, 414, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ort, D.R.; Yocum, C.F.; Heichel, I.F. (Eds.) Oxygenic photosynthesis: The light reactions. In Advances in Photosynthesis and Respiration; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996; Volume 4, ISBN 978-0-7923-3683-9. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, T.J.; Huynh, M.H.V.; Thorp, H.H. The possible role of proton-coupled electron transfer (PCET) in water oxidation by photosystem II. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 5284–5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Kraft, M.; Xu, R. Metal-free carbonaceous electrocatalysts and photocatalysts for water splitting. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 3039–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Zheng, M.; Lin, J.; Meng, X.; Ding, Y. Amorphous Ni–Fe double hydroxide hollow nanocubes enriched with oxygen vacancies as efficient electrocatalytic water oxidation catalysts. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 1044–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuzumi, S.; Lee, Y.M.; Nam, W. Kinetics and mechanisms of catalytic water oxidation. Dalt. Trans. 2019, 48, 779–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Suntivich, J.; May, K.J.; Perry, E.E.; Shao-Horn, Y. Synthesis and Activities of Rutile IrO2 and RuO2 Nanoparticles for Oxygen Evolution in Acid and Alkaline Solutions. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Shah, S.S.A.; Wei, Z. Recent developments in metal phosphide and sulfide electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution reaction. Chin. J. Catal. 2018, 39, 1575–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, B.M.; Gray, H.B.; Müller, A.M. Earth-Abundant Heterogeneous Water Oxidation Catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 14120–14136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasylenko, D.J.; Palmer, R.D.; Berlinguette, C.P. Homogeneous water oxidation catalysts containing a single metal site. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parent, A.R.; Sakai, K. Progress in base-metal water oxidation catalysis. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 2070–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indra, A.; Menezes, P.W.; Driess, M. Uncovering structure-activity relationships in manganese-oxide-based heterogeneous catalysts for efficient water oxidation. ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, B.; Sun, L. Iron-Based Molecular Water Oxidation Catalysts: Abundant, Cheap, and Promising. Chem. Asian J. 2019, 14, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärkäs, M.D.; Åkermark, B. Water oxidation using earth-abundant transition metal catalysts: Opportunities and challenges. Dalt. Trans. 2016, 45, 14421–14461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Spiccia, L. Water oxidation catalysts based on abundant 1st row transition metals. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2013, 257, 2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risch, M.; Klingan, K.; Zaharieva, I.; Dau, H. Water Oxidation by Co-Based Oxides with Molecular Properties. Mol. Water Oxid. Catal. Key Top. New Sustain. Energy Convers. Schemes 2014, 9781118413, 163–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oversteeg, C.H.M.; Doan, H.Q.; De Groot, F.M.F.; Cuk, T. In situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy of transition metal based water oxidation catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 102–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, O.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Das, S.K. Cobalt based functional inorganic materials: Electrocatalytic water oxidation. J. Chem. Sci. 2018, 130, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, S.G.; Illés, E.; Mizrahi, A.; Meyerstein, D. Cobalt Carbonate as an Electrocatalyst for Water Oxidation. Chem. A Eur. J. 2020, 26, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.W.; Liu, W.J.; Zhong, D.C.; Lu, T.B. Nickel complexes as molecular catalysts for water splitting and CO2 reduction. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 378, 237–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariela, B.; Yaniv, W.; Dror, S.; Haya, K.; Yael, A.; Eric, M.; Dan, M. The role of carbonate in electro-catalytic water oxidation by using Ni(1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane) 2+. Dalt. Trans. 2017, 46, 10774–10779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Lei, Y.J.; Xin, Z.J.; Lu, Y.B.; Wang, H.Y. Water splitting based on homogeneous copper molecular catalysts. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2018, 355, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, D.W.; Xie, Y.; Concepcion, J.J. O-O bond formation in ruthenium-catalyzed water oxidation: Single-site nucleophilic attack: Vs. O-O radical coupling. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 6170–6193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbucci, I.; Macchioni, A.; Albrecht, M. Iridium Complexes in Water Oxidation Catalysis. Iridium(III) Optoelectron. Photonics Appl. 2017, 617–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheu, R.; Ertem, M.Z.; Gimbert-Suriñach, C.; Sala, X.; Llobet, A. Seven Coordinated Molecular Ruthenium-Water Oxidation Catalysts: A Coordination Chemistry Journey. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 3453–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakemore, J.D.; Crabtree, R.H.; Brudvig, G.W. Molecular Catalysts for Water Oxidation. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 12974–13005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gersten, S.W.; Samuels, G.J.; Meyer, T.J. Catalytic oxidation of water by an oxo-bridged ruthenium dimer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1982, 104, 4029–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Sun, L. Artificial photosynthesis: Opportunities and challenges of molecular catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2216–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stull, J.A.; Stich, T.A.; Hurst, J.K.; Britt, R.D. Electron paramagnetic resonance analysis of a transient species formed during water oxidation catalyzed by the complex ion [(bpy)2Ru(OH2)]2O4+. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 4578–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Siems, W.F.; Koike, T.; Hurst, J.K. Mechanisms of water oxidation catalyzed by the cis,cis-[(bpy)2Ru(OH2)]2O4+ ion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9786–9795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moonshiram, D.; Jurss, J.W.; Concepcion, J.J.; Zakharova, T.; Alperovich, I.; Meyer, T.J.; Pushkar, Y. Structure and electronic configurations of the intermediates of water oxidation in blue ruthenium dimer catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 4625–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, H.; Hurst, J.K. Resonance raman, optical spectroscopic, and EPR characterization of the higher oxidation states of the water oxidation catalyst, cis,cis-[(bpy)2Ru(OH2)]2O4+. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 5303–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moonshiram, D.; Alperovich, I.; Concepcion, J.J.; Meyer, T.J.; Pushkar, Y. Experimental demonstration of radicaloid character in a RuV=O intermediate in catalytic water oxidation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3765–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cape, J.L.; Hurst, J.K. Detection and mechanistic relevance of transient ligand radicals formed during [Ru(bpy)2(OH2)]2O4+-catalyzed water oxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 827–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafpour, M.M.; Renger, G.; Hołyńska, M.; Moghaddam, A.N.; Aro, E.M.; Carpentier, R.; Nishihara, H.; Eaton-Rye, J.J.; Shen, J.R.; Allakhverdiev, S.I. Manganese Compounds as Water-Oxidizing Catalysts: From the Natural Water-Oxidizing Complex to Nanosized Manganese Oxide Structures. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2886–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyer, B.A.; Meyer, T.J. Properties of the oxo/aqua system (bpy)2(py)RuO2+/(bpy)2(py)Ru(OH2)2+. Inorg. Chem. 1981, 20, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, B.A.; Meyer, T.J. Oxobis(2,2’-bipyridine)pyridineruthenium(IV) ion, [(bpy)2(py)Ru:O]2+. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1978, 100, 3601–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Thummel, R.P. Mononuclear ruthenium polypyridine complexes that catalyze water oxidation. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 6591–6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagliardi, C.J.; Vannucci, A.K.; Concepcion, J.J.; Chen, Z.; Meyer, T.J. The role of proton coupled electron transfer in water oxidation. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 7704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenson, D.L.; Barry, B.A. Proton-coupled electron transfer in photosystem II: Proton inventory of a redox active tyrosine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 10567–10573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizrahi, A.; Meyerstein, D. Plausible roles of carbonate in catalytic water oxidation. In Advances in Inorganic Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 343–360. [Google Scholar]
- Patra, S.G.; Mizrahi, A.; Meyerstein, D. The Role of Carbonate in Catalytic Oxidations. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 2189–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenken, S.; Neta, P.; Stanbury, D.M.; Armstrong, D.A.; Ruscic, B.; Koppenol, W.H.; Huie, R.E.; Merényi, G.; Wardman, P.; Lymar, S.V. Standard electrode potentials involving radicals in aqueous solution: Inorganic radicals (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilberg, S.; Mizrahi, A.; Meyerstein, D.; Kornweitz, H. Carbonate and carbonate anion radicals in aqueous solutions exist as CO3(H2O)62− and CO3(H2O)6− respectively: The crucial role of the inner hydration sphere of anions in explaining their properties. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 9429–9435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ji, L.; Chen, Z. In Situ Rapid Formation of a Nickel–Iron-Based Electrocatalyst for Water Oxidation. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 6987–6992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorobrykh, A.; Dasgupta, J.; Kolling, D.R.J.; Terentyev, V.; Klimov, V.V.; Dismukes, G.C. Evolutionary Origins of the Photosynthetic Water Oxidation Cluster: Bicarbonate Permits Mn2+ Photo-oxidation by Anoxygenic Bacterial Reaction Centers. ChemBioChem 2013, 14, 1725–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobart, D.E.; Samhoun, K.; Young, J.P.; Norvell, V.E.; Mamantov, G.; Peterson, J.R. Stabilization of praseodymium(IV) and terbium(IV) in aqueous carbonate solution. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. Lett. 1980, 16, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroidov, S.; Shevela, D.; Shutova, T.; Samuelsson, G.; Messinger, J. Mobile hydrogen carbonate acts as proton acceptor in photosynthetic water oxidation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6299–6304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevela, D.; Nöring, B.; Koroidov, S.; Shutova, T.; Samuelsson, G.; Messinger, J. Efficiency of photosynthetic water oxidation at ambient and depleted levels of inorganic carbon. Photosynth. Res. 2013, 117, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Meyer, T.J. Copper(II) Catalysis of Water Oxidation. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 700–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winikoff, S.G.; Cramer, C.J. Mechanistic analysis of water oxidation catalyzed by mononuclear copper in aqueous bicarbonate solutions. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 2484–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizrahi, A.; Maimon, E.; Cohen, H.; Kornweitz, H.; Zilbermann, I.; Meyerstein, D. Mechanistic Studies on the Role of [CuII(CO3)n]2−2n as a Water Oxidation Catalyst: Carbonate as a Non-Innocent Ligand. Chem. A Eur. J. 2018, 24, 1088–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Wang, N.; Lei, H.; Guo, D.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Lai, W.; Cao, R. Electrocatalytic Water Oxidation by a Water-Soluble Copper(II) Complex with a Copper-Bound Carbonate Group Acting as a Potential Proton Shuttle. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 13368–13375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuttassery, F.; Sebastian, A.; Mathew, S.; Tachibana, H.; Inoue, H. Promotive Effect of Bicarbonate Ion on Two-Electron Water Oxidation to Form H2O2 Catalyzed by Aluminum Porphyrins. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 1939–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haygarth, K.S.; Marin, T.W.; Janik, I.; Kanjana, K.; Stanisky, C.M.; Bartels, D.M. Carbonate radical formation in radiolysis of sodium carbonate and bicarbonate solutions up to 250 °C and the mechanism of its second order decay. J. Phys. Chem. A 2010, 114, 2142–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, A.J.; Wilkinson, G.; Motevalli, M.; Hursthouse, M.B. Reactions of tetra-µ-carboxylato-diruthenium(II,II) compounds. X-Ray crystal structures of Ru2(µ-O2CCF3)4(thf)2, Ru2(µ-O2CR)4. J. Chem. Soc. Dalt. Trans. 1987, 2723–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, A.J.; Motevalli, M.; Hursthouse, M.B.; Wilkinson, G. The synthesis and structure of the unusual polymeric compound {Na3[Ru2(µ-O2CO)4]·6H2O}n. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1986, 2, 433–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, F.A.; Labella, L.; Shang, M. Further study of tetracarbonato diruthenium(II,III) compounds. Inorg. Chem. 1992, 31, 2385–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, F.A.; Murillo, C.A.; Walton, R.A. Multiple Bonds between Metal Atoms; Cotton, F.A., Murillo, C.A., Walton, R.A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; ISBN 0-387-25084-0. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, R.S. Theory and Application of Cyclic Voltammetry for Measurement of Electrode Reaction Kinetics. Anal. Chem. 1965, 37, 1351–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.J.; Caulton, K.G.; Cotton, F.A. Structure of tetra-n-butyratodiruthenium chloride, a compound with a strong metal-metal bond. Inorg. Chem. 1969, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadalupe Hernández, J.; Huerta-Aguilar, C.A.; Thangarasu, P.; Höpfl, H. A ruthenium(iii) complex derived from N,N′-bis(salicylidene)ethylenediamine as a chemosensor for the selective recognition of acetate and its interaction with cells for bio-imaging: Experimental and theoretical studies. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 10815–10827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, T.; Nishimura, S.; Mochizuki, T.; Ando, T.; Miyazato, Y. Mechanism of Water Oxidation Catalyzed by a Dinuclear Ruthenium Complex Bridged by Anthraquinone. Catalysts 2017, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockris, J.O. The Electrocatalysis of Oxygen Evolution on Perovskites. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1984, 131, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Zhao, G. Water Oxidation on Spinel NiCo2O4 Nanoneedles Anode: Microstructures, Specific Surface Character, and the Enhanced Electrocatalytic Performance. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 25939–25946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goberna-Ferrón, S.; Peña, B.; Soriano-López, J.; Carbó, J.J.; Zhao, H.; Poblet, J.M.; Dunbar, K.R.; Galán-Mascarós, J.R. A fast metal–metal bonded water oxidation catalyst. J. Catal. 2014, 315, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakemore, J.D.; Schley, N.D.; Olack, G.W.; Incarvito, C.D.; Brudvig, G.W.; Crabtree, R.H. Anodic deposition of a robust iridium-based water-oxidation catalyst from organometallic precursors. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schley, N.D.; Blakemore, J.D.; Subbaiyan, N.K.; Incarvito, C.D.; D’Souza, F.; Crabtree, R.H.; Brudvig, G.W. Distinguishing Homogeneous from Heterogeneous Catalysis in Electrode-Driven Water Oxidation with Molecular Iridium Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 10473–10481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Groves, J.T. Efficient water oxidation catalyzed by homogeneous cationic cobalt porphyrins with critical roles for the buffer base. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 15579–15584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannucci, A.K.; Meyer, T.J.; Dares, C.J.; Coggins, M.K.; Zhang, M.-T. Electrocatalytic Water Oxidation by a Monomeric Amidate-Ligated Fe(III)–Aqua Complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 5531–5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koepke, S.J.; Light, K.M.; Vannatta, P.E.; Wiley, K.M.; Kieber-Emmons, M.T. Electrocatalytic Water Oxidation by a Homogeneous Copper Catalyst Disfavors Single-Site Mechanisms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 8586–8600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Bruner, C.O. Catalytic Water Oxidation by a Bio-inspired Nickel Complex with a Redox-Active Ligand. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 13638–13641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.Y.; Chen, S.C.; Su, X.J.; Jiao, L.; Zhang, M.T. Redox-Active Ligand Assisted Multielectron Catalysis: A Case of CoIII Complex as Water Oxidation Catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Bozoglian, F.; Mandal, S.; Stewart, B.; Privalov, T.; Llobet, A.; Sun, L. A molecular ruthenium catalyst with water-oxidation activity comparable to that of photosystem II. Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional exchange-energy approximation with correct asymptotic behavior. Phys. Rev. A 1988, 38, 3098–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Yang, W.; Parr, R.G. Development of the Colle-Salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16, Revision C.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Grimme, S.; Antony, J.; Ehrlich, S.; Krieg, H. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 154104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marenich, A.V.; Cramer, C.J.; Truhlar, D.G. Universal Solvation Model Based on Solute Electron Density and on a Continuum Model of the Solvent Defined by the Bulk Dielectric Constant and Atomic Surface Tensions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 6378–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, T.; Tew, D.P.; Handy, N.C. A new hybrid exchange–correlation functional using the Coulomb-attenuating method (CAM-B3LYP). Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 393, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Species | Configuration | Spin | q a | d bRu1-Ru2 | d cRu1-O1/Ru2-O2 | ρ dRu1/Ru2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I0 | RuII-RuIII d6-d5 | 3/2 | −3 | 2.235(2.260) e | - | 1.052/1.074 |
| I1 | RuII-RuIII d6-d5 | 3/2 | −4 | 2.334 | -/2.070 | 0.968/0.762 |
| I2 | RuIII-RuIII d5-d5 | 1 | −4 | 2.318 | 2.087/2.038 | 0.960/0.923 |
| I3 | RuIII-RuIV d5-d4 | 1/2 | −4 | 2.458 | 2.059/1.928 | 1.160/1.058 |
| I4 | RuIV-RuIV d4-d4 | 0 | −4 | 2.458 | 1.752/1.969 | 1.084/0.991 |
| I5 | RuIV-RuII d4-d6 | 1 | −4 | 2.422 | 1.850/- | 0.839/1.027 |
| I6 | RuIII-RuII d5-d6 | 3/2 | −4 | 2.303 | 2.023/- | 0.712/0.979 |
| I7 | RuIV-RuII d4-d6 | 1 | −4 | 2.347 | 2.094/- | 0.731/1.128 |
| I8 | RuIV-RuIV d4-d4 | 0 | −4 | 2.444 | 1.769/1.769 | 1.002/1.002 |
| I9 | RuIII-RuIII d5-d5 | 1 | −4 | 2.342 | 2.043/2.135 | 0.394/0.462 |
| I10 | RuIV-RuIV d4-d4 | 0 | −4 | 2.523 | 2.080/2.080 | 0.788/0.785 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patra, S.G.; Mondal, T.; Sathiyan, K.; Mizrahi, A.; Kornweitz, H.; Meyerstein, D. Na3[Ru2(µ-CO3)4] as a Homogeneous Catalyst for Water Oxidation; HCO3− as a Co-Catalyst. Catalysts 2021, 11, 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11020281
Patra SG, Mondal T, Sathiyan K, Mizrahi A, Kornweitz H, Meyerstein D. Na3[Ru2(µ-CO3)4] as a Homogeneous Catalyst for Water Oxidation; HCO3− as a Co-Catalyst. Catalysts. 2021; 11(2):281. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11020281
Chicago/Turabian StylePatra, Shanti Gopal, Totan Mondal, Krishnamoorthy Sathiyan, Amir Mizrahi, Haya Kornweitz, and Dan Meyerstein. 2021. "Na3[Ru2(µ-CO3)4] as a Homogeneous Catalyst for Water Oxidation; HCO3− as a Co-Catalyst" Catalysts 11, no. 2: 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11020281
APA StylePatra, S. G., Mondal, T., Sathiyan, K., Mizrahi, A., Kornweitz, H., & Meyerstein, D. (2021). Na3[Ru2(µ-CO3)4] as a Homogeneous Catalyst for Water Oxidation; HCO3− as a Co-Catalyst. Catalysts, 11(2), 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11020281