Performance of Iron-Functionalized Activated Carbon Catalysts (Fe/AC-f) on CWPO Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Result and Discussion
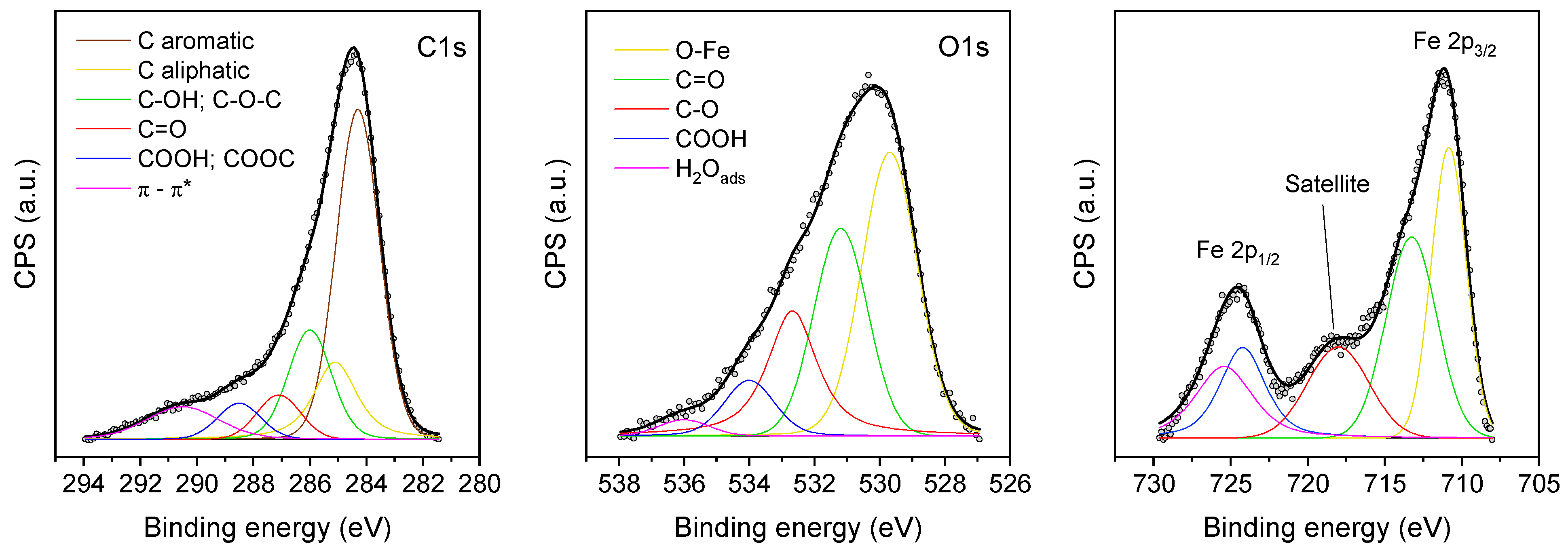
2.1. Physicochemical Characterization Studies
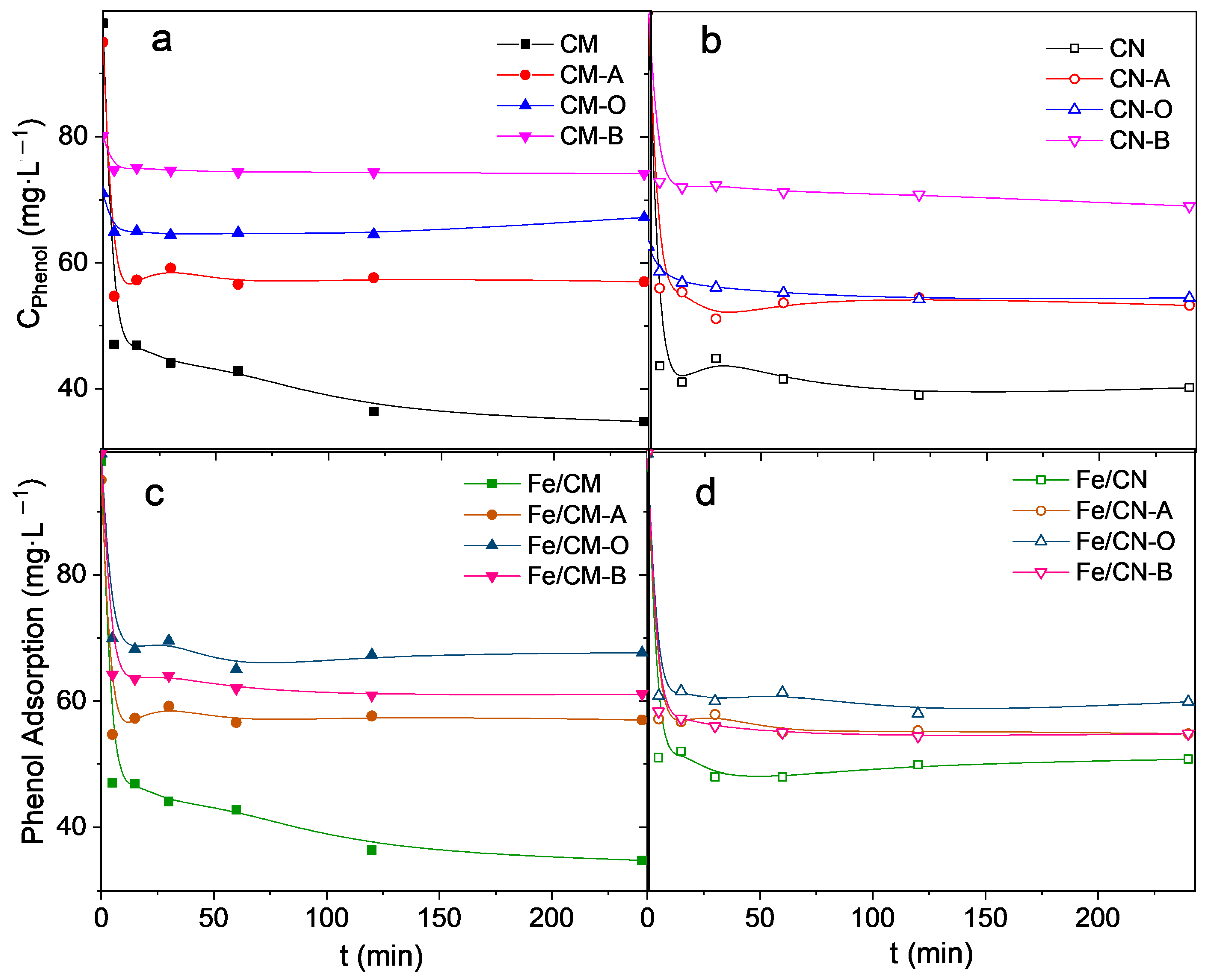
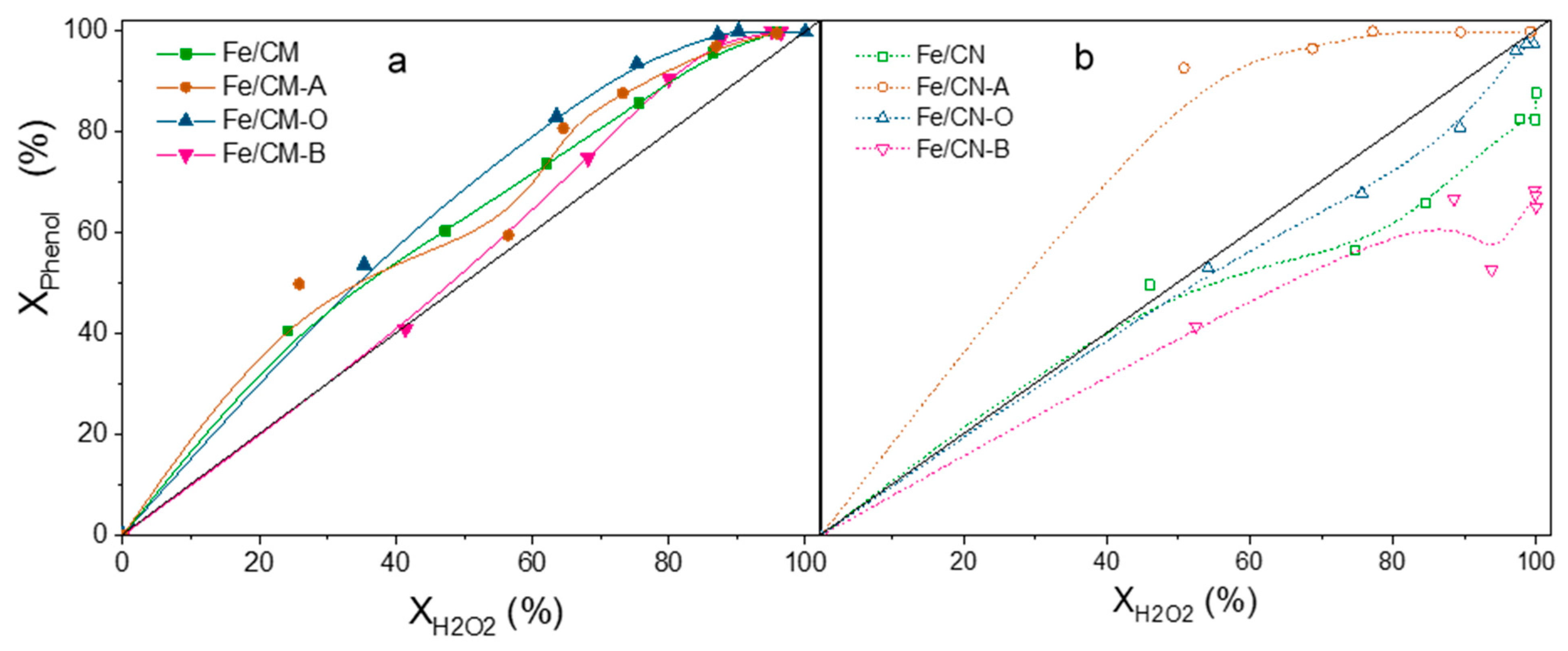
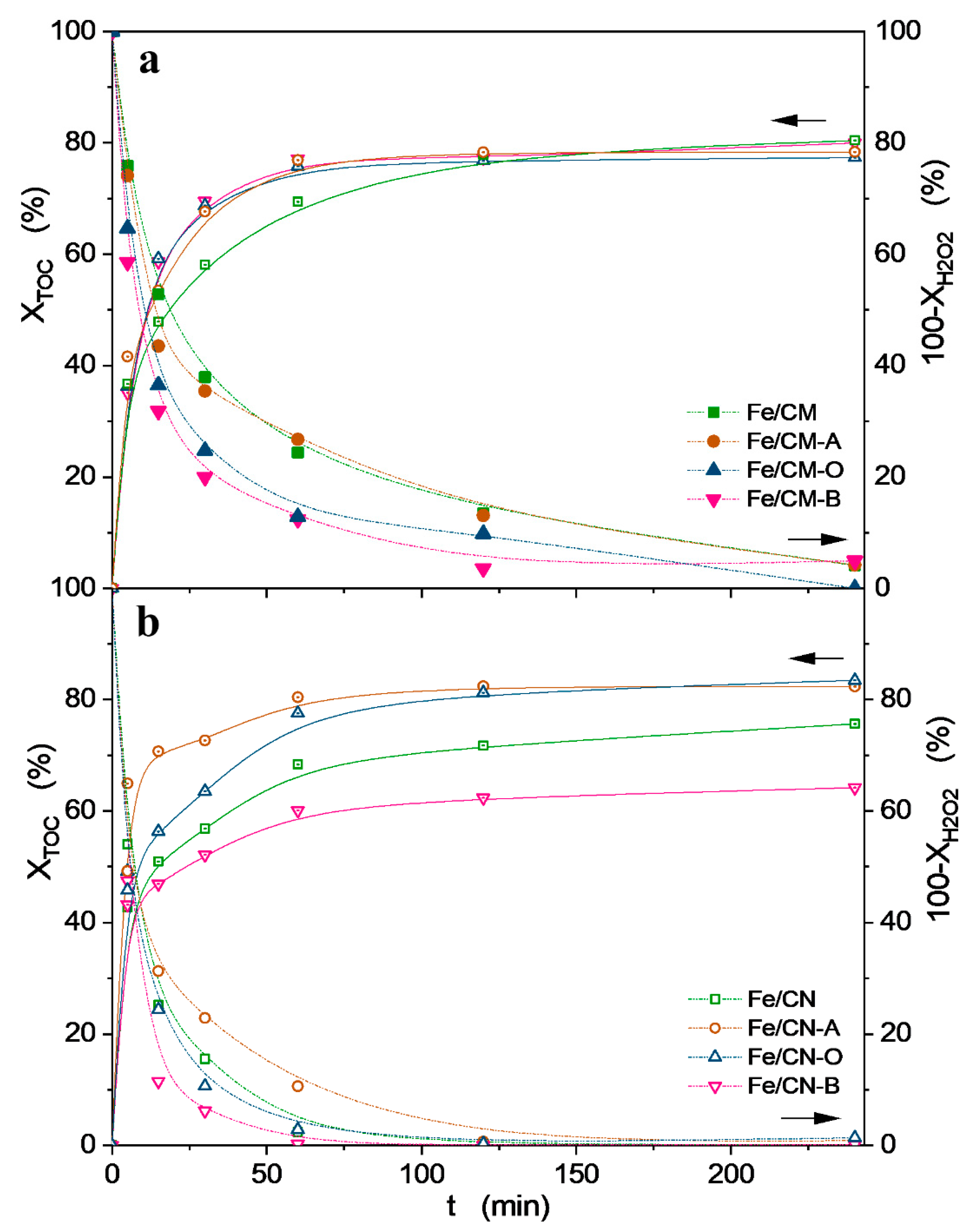
2.2. Catalytic Activity
2.3. CWPO in WWTP Effluent and Landfill Leachate Matrices
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
3.2. Functionalization of Activated Carbons
3.3. Catalysts Preparation
3.4. Catalysts Characterization
3.5. Catalytic Activity: CWPO
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Serrano, E.; Munoz, M.; de Pedro, Z.M.; Casas, J.A. Efficient removal of the pharmaceutical pollutants included in the EU Watch List (Decision 2015/495) by modified magnetite/H2O2. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 376, 120265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, M.; Nieto-Sandoval, J.; Serrano, E.; De Pedro, Z.M.; Casas, J.A. CWPO intensification by induction heating using magnetite as catalyst. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda-Márquez, J.J.; Sillanpää, M.; Pocostales, P.; Acevedo, A.; Manzano, M.A. Post-treatment of biologically treated wastewater containing organic contaminants using a sequence of H2O2 based advanced oxidation processes: Photolysis and catalytic wet oxidation. Water Res. 2015, 71, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Costa, A.L.; Zazo, J.A.; Rodríguez, J.J.; Casas, J.A. Microwave-assisted catalytic wet peroxide oxidation. Comparison of Fe catalysts supported on activated carbon and Γ-alumina. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 218, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaouadi, A.; Adhoum, N. Heterogeneous catalytic wet peroxide oxidation of paraquat in the presence of modified activated carbon. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2010, 97, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulou, M.; Brienza, M.; Contesini, B.R.; de Freitas, A.P.B.R.; de Freitas, L.V.; Esteves, B.M.; Fernandez-Ibañez, P.; Galeano, L.A.; Garcia, A.M.; Gil, A.; et al. Advanced Oxidation Processes: Applications in Drinking Water Treatment; Barcelo, D., Kostianoy, A.G., Gil, A., Galeano, L.A., Vicente, M.A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 67, ISBN 978-3-319-76881-6. [Google Scholar]
- Zazo, J.A.; Casas, J.A.; Mohedano, A.F.; Rodríguez, J.J. Catalytic wet peroxide oxidation of phenol with a Fe/active carbon catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2006, 65, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvino-Casilda, V.; Lopez-Peinado, A.J.; Duran-Valle, C.J.; Martin-Aranda, R.M. Last decade of research on activated carbons as catalytic support in chemical processes. Catal. Rev. Sci. Eng. 2010, 52, 325–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Romero, C.L.; Revelo, D.; Caicedo, A.; Botina, M.; García-Mora, A.M.; Torres-Palma, R.A.; Galeano, L.A.; Sánchez-Ortiz, I.A. Evaluation of the acute toxicity on daphnia magna throughout the catalytic wet peroxide oxidation of dissolved natural organic matter. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 198, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luis, A.M.; Lombraña, J.I.; Menéndez, A.; Sanz, J. Analysis of the toxicity of phenol solutions treated with H2O2/UV and H2O2/Fe oxidative systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 1928–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameta, S.C. Introduction. Adv. Oxid. Process. Wastewater Treat. Emerg. Green Chem. Technol. 2018, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosso-Kankeu, E. Photocatalysts in Advanced Oxidation Processes for Wastewater Treatment, 1st ed.; Fosso-Kankeu, E., Pandley, S., Sinha Ray, S., Eds.; Scrivener Publishing, Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; ISBN 978-1-119-63139-2. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhu, R.; Xi, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, G.; He, H. Strategies for enhancing the heterogeneous fenton catalytic reactivity: A review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 255, 117739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, M.; de Pedro, Z.M.; Casas, J.A.; Rodriguez, J.J. Preparation of magnetite-based catalysts and their application in heterogeneous Fenton oxidation—A review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 176–177, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, O.S.G.P.; Rodrigues, C.S.D.; Madeira, L.M.; Pereira, M.F.R. Heterogeneous fenton-like degradation of p-nitrophenol over tailored carbon-based materials. Catalysts 2019, 9, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Costa, A.L.; Zazo, J.A.; Rodriguez, J.J.; Casas, J.A. Intensification of catalytic wet peroxide oxidation with microwave radiation: Activity and stability of carbon materials. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 209, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, M.T.; Ribeiro, R.S.; Gomes, H.T.; Faria, J.L.; Silva, A.M.T. Screening of activated carbons for the treatment of highly concentrated phenol solutions using catalytic wet peroxide oxidation: The effect of iron impurities on the catalytic activity. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, R.S.; Silva, A.M.T.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Faria, J.L.; Gomes, H.T. Catalytic wet peroxide oxidation: A route towards the application of hybrid magnetic carbon nanocomposites for the degradation of organic pollutants. A review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 187, 428–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani-Bagha, A.R.; Balchi, T. Catalytic Wet Peroxide Oxidation; Ameta, S.C., Rakshit Ameta, J.R.N., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: London, UK; Oxford, UK; San Diego, CA, USA; Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; ISBN 9780128105252. [Google Scholar]
- Esteves, B.M.; Morales-Torres, S.; Maldonado-Hódar, F.J.; Madeira, L.M. Fitting biochars and activated carbons from residues of the olive oil industry as supports of Fe-catalysts for the heterogeneous Fenton-like treatment of simulated olive mill wastewater. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda Márquez, J.J.; Levchuk, I.; Sillanpää, M. Application of catalytic wet peroxide oxidation for industrial and urban wastewater treatment: A review. Catalysts 2018, 8, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena, I.F.; Diaz, E.; Pérez-Farías, C.; Stolte, S.; Moreno-Andrade, I.; Rodriguez, J.J.; Mohedano, A.F. Catalytic wet peroxide oxidation of imidazolium-based ionic liquids: Catalyst stability and biodegradability enhancement. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 376, 120431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M. Removing Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) Assay Interference from Landfill Leachate Treated with Fenton’s Reagents. Bachelor’s Thesis, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Wei, H.; Yu, L.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Gu, B.; Sun, C. Sewage-sludge-derived carbonaceous materials for catalytic wet hydrogen peroxide oxidation of m -cresol in batch and continuous reactors. Environ. Technol. 2016, 37, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, C.M.; Quintanilla, A.; Casas, J.A.; Rodriguez, J.J. Treatment of real winery wastewater by wet oxidation at mild temperature. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 129, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türgay, O.; Ersöz, G.; Atalay, S.; Forss, J.; Welander, U. The treatment of azo dyes found in textile industry wastewater by anaerobic biological method and chemical oxidation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 79, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Lv, B.; Jin, Y.; Li, D. P-Chlorophenol Wastewater Treatment by Microwave-Enhanced Catalytic Wet Peroxide Oxidation. Water Environ. Res. 2010, 82, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhemkhem, A.; Rida, K.; Pizarro, A.H.; Molina, C.B.; Rodriguez, J.J. Iron catalyst supported on modified kaolin for catalytic wet peroxide oxidation. Clay Miner. 2019, 54, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbajo, J.; Quintanilla, A.; Garcia-Costa, A.L.; González-Julián, J.; Belmonte, M.; Miranzo, P.; Osendi, M.I.; Casas, J.A. The influence of the catalyst on the CO formation during catalytic wet peroxide oxidation process. Catal. Today 2021, 361, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, M.; de Pedro, Z.M.; Casas, J.A.; Rodriguez, J.J. Improved wet peroxide oxidation strategies for the treatment of chlorophenols. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 228, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazo, J.A.; Bedia, J.; Fierro, C.M.; Pliego, G.; Casas, J.A.; Rodriguez, J.J. Highly stable Fe on activated carbon catalysts for CWPO upon FeCl3 activation of lignin from black liquors. Catal. Today 2012, 187, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubir, N.A.; Yacou, C.; Motuzas, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.S.; Diniz Da Costa, J.C. The sacrificial role of graphene oxide in stabilising a Fenton-like catalyst GO-Fe3O4. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 9291–9293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, T.W.; Lourenço, L.A.; Brandão, H.d.L.; da Silva, A.; de Souza, S.M.A.G.U.; de Souza, A.A.U. Low-cost iron-doped catalyst for phenol degradation by heterogeneous Fenton. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 359, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, R.S.; Silva, A.M.T.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Faria, J.L.; Gomes, H.T. Removal of 2-nitrophenol by catalytic wet peroxide oxidation using carbon materials with different morphological and chemical properties. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 140–141, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Martinez, M.; Machado, B.F.; Serp, P.; Morales-Torres, S.; Silva, A.M.T.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Faria, J.L.; Gomes, H.T. Carbon nanotubes as catalysts for wet peroxide oxidation: The effect of surface chemistry. Catal. Today 2020, 357, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wei, H.; Liu, P.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Jiang, W.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Sun, C. Effect of structural defects on activated carbon catalysts in catalytic wet peroxide oxidation of m-cresol. Catal. Today 2015, 258, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huaccallo-Aguilar, Y.; Diaz de Tuesta, J.L.; Álvarez-Torrellas, S.; Gomes, H.T.; Larriba, M.; Ovejero, G.; García, J. New insights on the removal of diclofenac and ibuprofen by CWPO using a magnetite-based catalyst in an up-flow fixed-bed reactor. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosu, V.; Arora, S.; Subbaramaiah, V. Simultaneous degradation of nitrogenous heterocyclic compounds by catalytic wet-peroxidation process using box-behnken design. Environ. Eng. Res. 2020, 25, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, A.; Carbajo, J.; Adán, C.; Faraldos, M.; Bahamonde, A.; Casas, J.A.; Rodriguez, J.J. Improved mineralization by combined advanced oxidation processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 174, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navalon, S.; Dhakshinamoorthy, A.; Alvaro, M.; Garcia, H. Heterogeneous Fenton catalysts based on activated carbon and related materials. ChemSusChem 2011, 4, 1712–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonietti, M.; Lopez-Salas, N.; Primo, A. Adjusting the Structure and Electronic Properties of Carbons for Metal-Free Carbocatalysis of Organic Transformations. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinho, M.T.; Silva, A.M.T.; Fathy, N.A.; Attia, A.A.; Gomes, H.T.; Faria, J.L. Activated carbon xerogel-chitosan composite materials for catalytic wet peroxide oxidation under intensified process conditions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1243–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, H.; Yan, Y.; Huang, H. Graphene as efficient and robust catalysts for catalytic wet peroxide oxidation of phenol in a continuous fixed-bed reactor. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaika, A.; Morawa Eblagon, K.; Soares, O.S.G.P.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Figueiredo, J.L. The impact of surface chemistry of carbon xerogels on their performance in phenol removal from wastewaters via combined adsorption-catalytic process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 511, 145467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, B.K.; Sandle, N.K. Effect of different oxidizing agent treatments on the surface properties of activated carbons. Carbon N. Y. 1999, 37, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messele, S.A.; Stüber, F.; Bengoa, C.; Fortuny, A.; Fabregat, A.; Font, J. Phenol degradation by heterogeneous Fenton-like reaction using Fe supported over activated carbon. Procedia Eng. 2012, 42, 1373–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, A.; Hungria, A.B.B.; Duran-Valle, C.J.J.; Faraldos, M.; Bahamonde, A.; Casas, J.A.A.; Rodriguez, J.J.J. On the optimization of activated carbon-supported iron catalysts in catalytic wet peroxide oxidation process. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 181, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, A.; Faraldos, M.; Bahamonde, A.; Casas, J.A.; Zazo, J.A.; Rodríguez, J.J. Role of the activated carbon surface on catalytic wet peroxide oxidation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 8166–8174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Pliego, G.; Garcia-Costa, A.L.; Zazo, J.A.; Liu, S.; Casas, J.A.; Rodriguez, J.J. Cyclohexanoic acid breakdown by two-step persulfate and heterogeneous Fenton-like oxidation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 232, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, A.; Faraldos, M.; Casas, J.A.; Zazo, J.A.; Bahamonde, A.; Rodríguez, J.J. Catalytic wet peroxide oxidation of phenol over Fe/AC catalysts: Influence of iron precursor and activated carbon surface. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2009, 86, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Martinez, M.; Álvarez-Torrellas, S.; García, J.; Silva, A.M.T.; Faria, J.L.; Gomes, H.T. Exploring the activity of chemical-activated carbons synthesized from peach stones as metal-free catalysts for wet peroxide oxidation. Catal. Today 2018, 313, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazo, J.A.; Pliego, G.; García-Muñoz, P.; Casas, J.A.; Rodriguez, J.J. UV-LED assisted catalytic wet peroxide oxidation with a Fe(II)-Fe(III)/activated carbon catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 192, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, C.M.; Ocón, P.; Quintanilla, A.; Casas, J.A.; Rodriguez, J.J. Highly efficient application of activated carbon as catalyst for wet peroxide oxidation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 140–141, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.R.; Shu, H.Y. The reaction kinetics, decomposition pathways and intermediate formations of phenol in ozonation, UV O3 and UV H2O2 processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 1995, 41, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, L.G.; Rajashekhar, K.E. A kinetic model based on non-linear regression analysis is proposed for the degradation of phenol under UV/solar light using nitrogen doped TiO2. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2011, 334, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kylefors, K.; Ecke, H.; Lagerkvist, A. Accuracy of cod test for landfill leachates. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2003, 146, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermosilla, D.; Cortijo, M.; Huang, C.P. Optimizing the treatment of landfill leachate by conventional Fenton and photo-Fenton processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3473–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.M.; Geissen, S.U.; Vogelpohl, A. Landfill leachate treatment by a photoassisted Fenton reaction. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 35, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of Gases in Multimolecular Layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, G.M. Colorimetric Determination of Hydrogen Peroxide. Ind. Eng. Chem. Anal. Ed. 1943, 15, 327–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehlig, J.P.; Hulett, H.R. Spectrophotometric Determination of Iron With o-Phenanthroline and with Nitro-o-phenanthroline. Ind. Eng. Chem. Anal. Ed. 1942, 14, 869–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

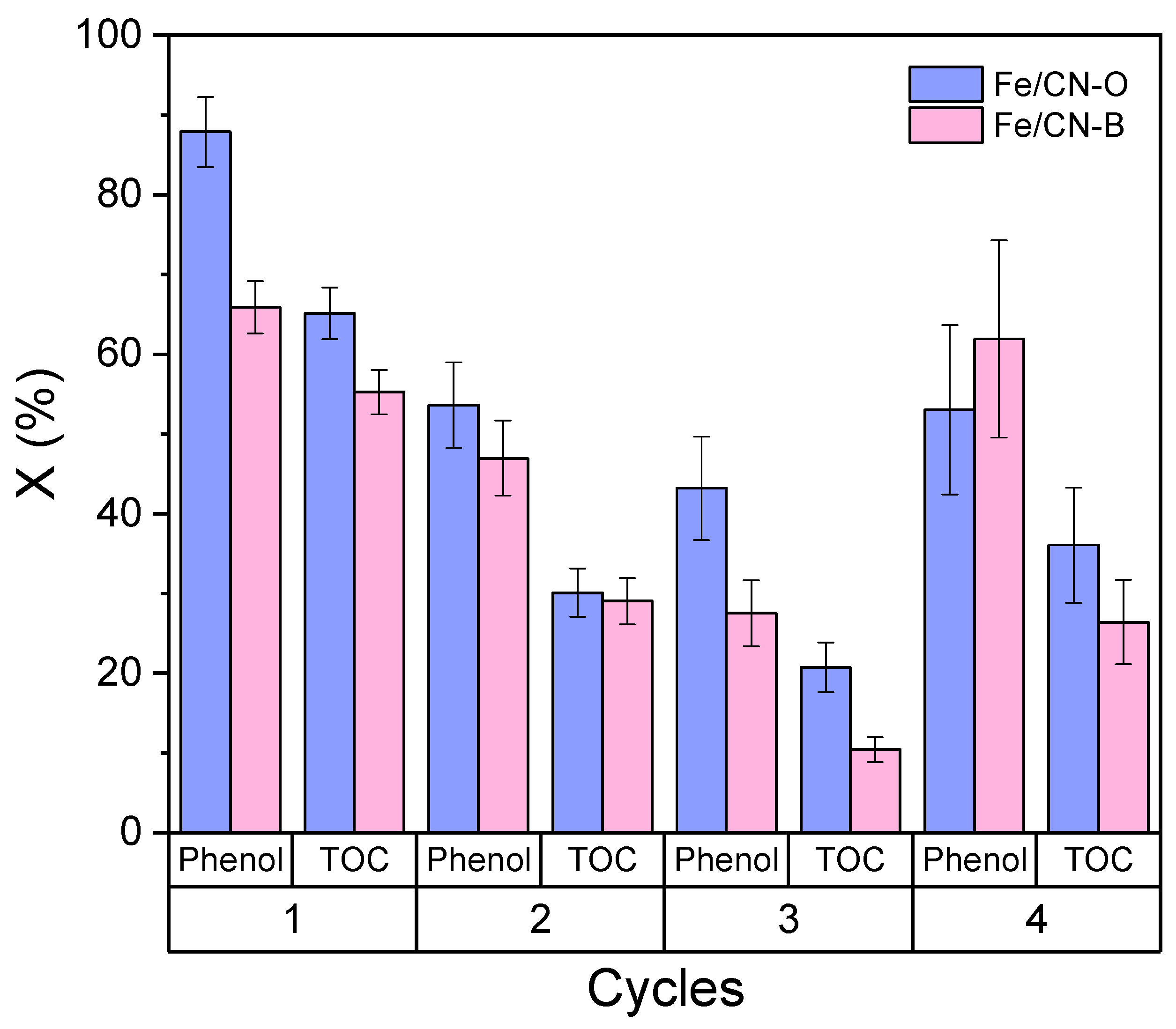
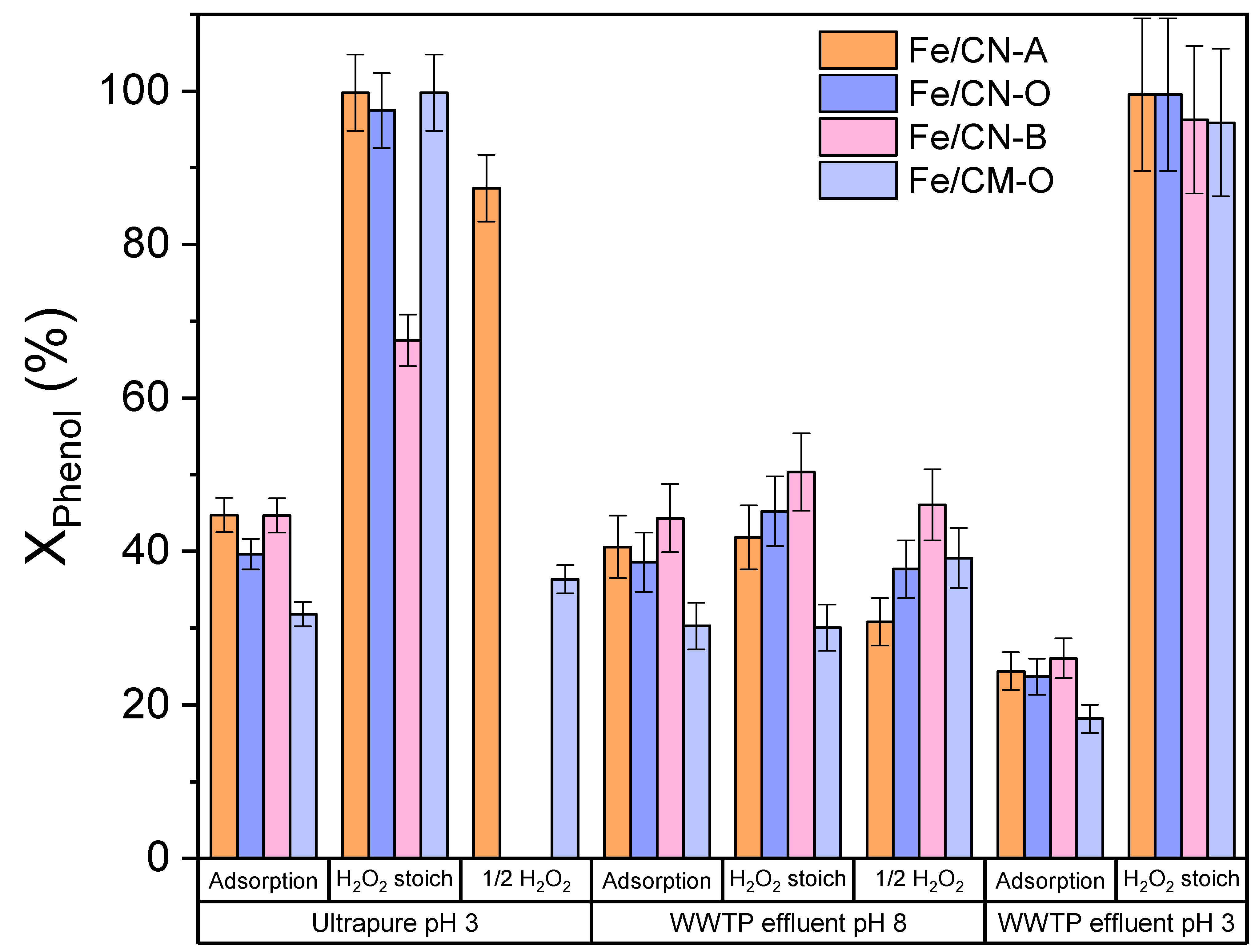
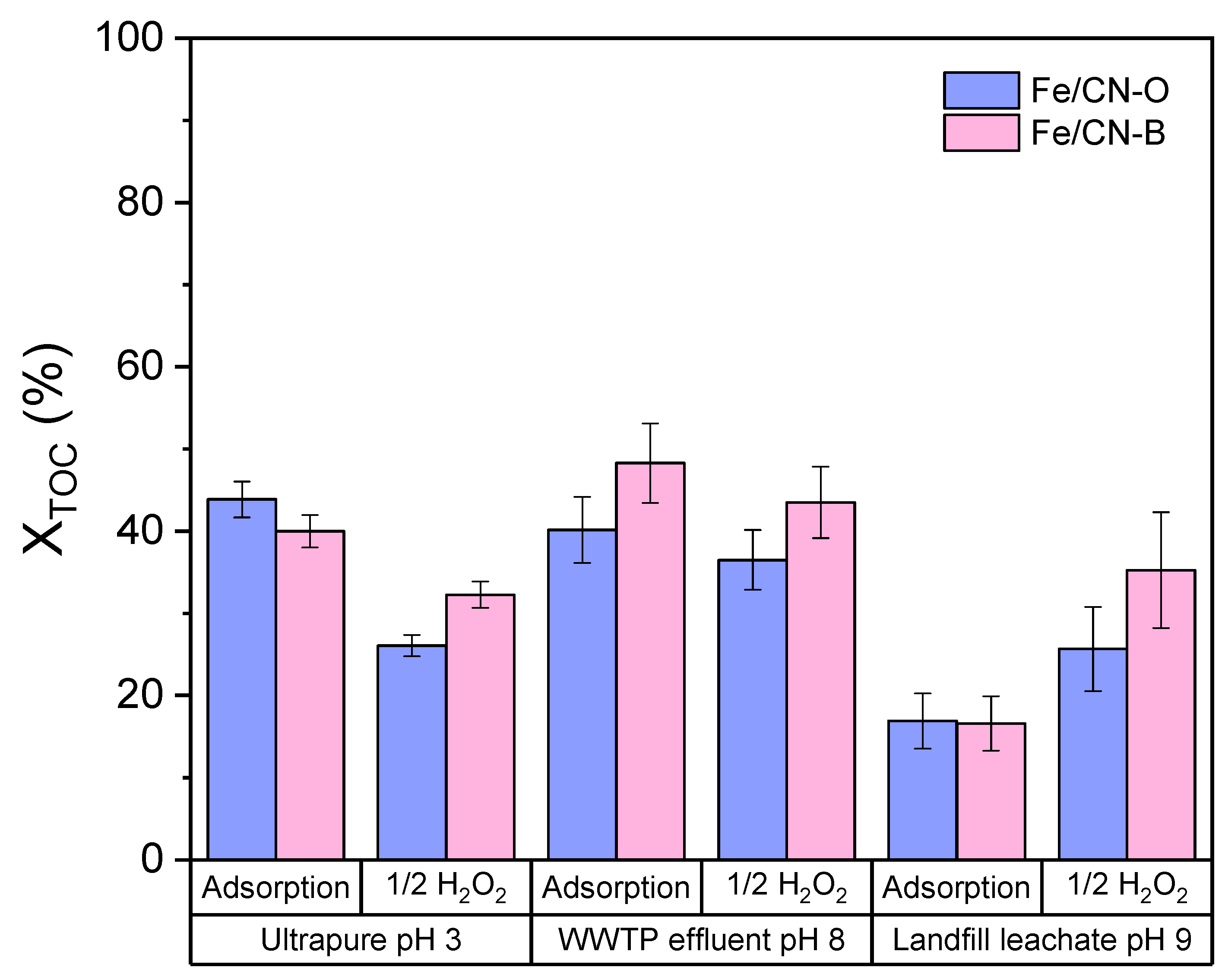
| Sample | SBET (m2·g−1) | AExternal (m2·g−1) | AMicropore (m2·g−1) | VMicropore (cm3·g−1) | VTotal (cm3·g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CM | 967 | 105 | 862 | 0.36 | 0.52 |
| Fe/CM | 934 | 104 | 830 | 0.35 | 0.50 |
| Fe/CM-O | 940 | 169 | 771 | 0.30 | 0.49 |
| Fe/CM-A | 827 | 103 | 724 | 0.33 | 0.43 |
| Fe/CM-B | 888 | 125 | 763 | 0.30 | 0.44 |
| CN | 1297 | 110 | 1187 | 0.47 | 0.57 |
| Fe/CN | 1228 | 193 | 1035 | 0.39 | 0.53 |
| Fe/CN-O | 932 | 176 | 756 | 0.29 | 0.48 |
| Fe/CN-A | 1164 | 141 | 1023 | 0.41 | 0.54 |
| Fe/CN-B | 1202 | 140 | 1062 | 0.42 | 0.55 |
| Catalyst | C | H | N | S | O * | Ashes | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CM | 89.5 ± 1.8 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 3.9 ± 0.4 | 4.7 ± 0.5 | - |
| Fe/CM | 75.4 ± 1.5 | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 12.4 ± 1.3 | 9.3 ± 0.9 | 4.3 ± 0.4 |
| Fe/CM-O | 72.0 ± 1.4 | 1.4 ± 0.2 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 18.6 ± 1.9 | 6.6 ± 0.7 | 3.9 ± 0.3 |
| Fe/CM-A | 79.8 ± 1.6 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 11.1 ± 1.1 | 6.3 ± 0.6 | 3.6 ± 0.3 |
| Fe/CM-B | 72.4 ± 1.4 | 1.6 ± 0.2 | 2.4 ± 0.3 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 14.6 ± 1.5 | 7.3 ± 0.7 | 4.4 ± 0.4 |
| CN | 86.7 ± 1.8 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 2.7 ± 0.4 | 8.3 ± 0.3 | - |
| Fe/CN | 81.2 ± 1.6 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 5.7 ± 0.6 | 10.9 ± 1.1 | 3.8 ± 0.3 |
| Fe/CN-O | 71.8 ± 1.4 | 1.5 ± 0.2 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 17.9 ± 1.8 | 7.6 ± 0.8 | 4.3 ± 0.4 |
| Fe/CN-A | 74.4 ± 1.5 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 1.5 ± 0.2 | 15.1 ± 1.6 | 7.3 ± 0.7 | 4.1 ± 0.4 |
| Fe/CN-B | 75.2 ± 1.5 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 2.4 ± 0.3 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 12.9 ± 1.3 | 7.9 ± 0.8 | 4.5 ± 0.4 |
| Binding E (eV) | ID | Fe/CM | Fe/CM-O | Fe/CM-A | Fe/CM-B | Fe/CN | Fe/CN-O | Fe/CN-A | Fe/CN-B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 530.0 | O-Fe | 19.5 | 16.2 | 20.6 | 33.3 | 28.5 | 19.6 | 17.9 | 41.2 |
| 531.5 | C=O | 29.6 | 26.8 | 30.9 | 31.3 | 31.3 | 30.5 | 35.5 | 28.0 |
| 532.9 | C-O | 27.5 | 28.9 | 25.7 | 21.6 | 23.5 | 27.9 | 26.4 | 21.2 |
| 534.0 | COOH | 16.4 | 19.5 | 16.7 | 10.4 | 12.6 | 16.3 | 13.8 | 7.6 |
| 536.0 | H2O ads | 7.0 | 8.6 | 6.1 | 3.4 | 4.1 | 5.7 | 6.4 | 2.0 |
| Catalyst | Fe 2p3/2 (eV) | Fe 2p1/2 (eV) | Sat-Fe3+ (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe/CM | 711.3 | 724.5 | 718.3 |
| Fe/CM-O | 711.4 | 724.5 | 718.3 |
| Fe/CM-A | 711.4 | 724.6 | 718.2 |
| Fe/CM-B | 711.1 | 724.6 | 718.1 |
| Fe/CN | 711.1 | 724.5 | 718.2 |
| Fe/CN-O | 711.3 | 724.7 | 718.4 |
| Fe/CN-A | 711.4 | 724.6 | 718.3 |
| Fe/CN-B | 711.1 | 724.5 | 718.4 |
| Catalyst | (O/C)bulk | (O/C)XPS | (Fe/C)bulk | (Fe/C)XPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CM | 0.044 | 0.029 | 0 | 0 |
| Fe/CM | 0.164 | 0.081 | 0.057 | 0.005 |
| Fe/CM-O | 0.258 | 0.159 | 0.054 | 0.007 |
| Fe/CM-A | 0.139 | 0.108 | 0.045 | 0.005 |
| Fe/CM-B | 0.202 | 0.139 | 0.061 | 0.017 |
| CN | 0.031 | 0.046 | 0 | 0 |
| Fe/CN | 0.070 | 0.105 | 0.047 | 0.010 |
| Fe/CN-O | 0.249 | 0.107 | 0.060 | 0.008 |
| Fe/CN-A | 0.203 | 0.121 | 0.055 | 0.009 |
| Fe/CN-B | 0.172 | 0.183 | 0.060 | 0.043 |
| Material | Phenol Removal: Adsorption (1) | Phenol Removal: Total (2) (ads + CWPO) | Phenol Mineralization (3) (CWPO) | H2O2 Consumption (4) | H2O2 Direct Decomposition (5) | Ferel (6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | XH2O2 (%) | (XH2O2)direct (%) | (%) | |||
| AC | ||||||
| CM | 54 ± 2 | 64 ± 3 | 5–15 | 55 ± 3 | 80 ± 3 | - |
| CN | 51 ± 2 | 53 ± 2 | 2-6 | 28 ± 2 | 100 ± 3 | - |
| AC-f | ||||||
| CM-A | 47 ± 2 | 47 ± 2 | 0–4 | 5 ± 1 | 76 ± 3 | - |
| CM-O | 41 ± 2 | 41 ± 2 | 0–4 | 3 ± 1 | 45 ± 3 | - |
| CM-B | 14 ± 1 | 19 ± 1 | 3–7 | 5 ± 1 | 8 ± 3 | - |
| CN-A | 47 ± 2 | 47 ± 2 | 0 | 23 ± 2 | 100 ± 3 | - |
| CN-O | 51 ± 2 | 50 ± 2 | 0–4 | 34 ± 2 | 99 ± 3 | - |
| CN-B | 18 ± 1 | 18 ± 1 | 0–4 | 9 ± 1 | 80 ± 3 | - |
| Fe/AC-f | ||||||
| Fe/CM | 39 ± 2 | 80 ± 2 | 41 ± 4 | 96 ± 2 | - | 11 ± 1 |
| Fe/CM-A | 40 ± 2 | 78 ± 2 | 38 ± 4 | 87 ± 2 | - | 4 ± 1 |
| Fe/CM-O | 24 ± 2 | 77 ± 2 | 53 ± 4 | 90 ± 2 | - | 26 ± 2 |
| Fe/CM-B | 40 ± 2 | 80 ± 2 | 40 ± 4 | 88 ± 2 | - | 6 ± 1 |
| Fe/CN | 39 ± 2 | 76 ± 2 | 37 ± 4 | 100 ± 2 | - | 8 ± 1 |
| Fe/CN-A | 33 ± 2 | 82 ± 2 | 49 ± 4 | 89 ± 2 | - | 24 ± 2 |
| Fe/CN-O | 26 ± 1 | 83 ± 2 | 57 ± 3 | 97 ± 2 | - | 4 ± 1 |
| Fe/CN-B | 32 ± 1 | 64 ± 2 | 32 ± 3 | 100 ± 2 | - | 0.8 ± 0.2 |
| Parameter | WWTP Effluent | Landfill Leachate |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.2 ± 0.1 | 8.2 ± 0.1 |
| Conductivity, mS·cm−1 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 17.3 ± 0.1 |
| UV-254, cm−1 | colorless | 27.5 ± 0.1 |
| Color, mgPt·L−1 | - | 17300 ± 200 |
| COD, mgO2·L−1 | n.d. | 5000 ± 500 |
| BOD5, mgO2·L−1 | n.d. | 150 ± 50 |
| BOD5/COD | n.d. | 0.03 ± 0.01 |
| TOC, mgC·L−1 | 5 ± 1 | 2000 ± 10 |
| TS, mg·L−1 | n.d. | 21300 ± 1000 |
| TSS, mg·L−1 | n.d. | 1370 ± 20 |
| TDS, mg·L−1 | 1020 ± 20 | 18970 ± 230 |
| Alkalinity, mgCaCO3·L−1 | 440 ± 20 | 13250 ± 100 |
| TNb, mgN·L−1 | 16 ± 2 | 1600 ± 10 |
| Chloride, mg·L−1 | 210 ± 50 | 3000 ± 150 |
| Sulfate, mg·L−1 | 370 ± 20 | 120 ± 30 |
| Aluminum, mg·L−1 | n.d. | 5.5 ± 0.1 |
| Iron, mg·L−1 | n.d. | 8.5 ± 0.1 |
| Chromium, mg·L−1 | n.d. | 1.9 ± 0.1 |
| Sodium, mg·L−1 | 290 ± 60 | 2150 ± 220 |
| Potassium, mg·L−1 | 48 ± 1 | 1220 ± 120 |
| Magnesium, mg·L−1 | 52 ± 5 | 98 ± 6 |
| Calcium, mg·L−1 | 150 ± 14 | 134 ± 4 |
| Silicon, mg·L−1 | n.d. | 15 ± 1 |
| Zinc, mg·L−1 | n.d. | 0.6 ± 0.1 |
| Nickel, mg·L−1 | n.d. | 0.3 ± 0.1 |
| Copper, mg·L−1 | n.d. | 0.03 ± 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mesa Medina, S.; Rey, A.; Durán-Valle, C.; Bahamonde, A.; Faraldos, M. Performance of Iron-Functionalized Activated Carbon Catalysts (Fe/AC-f) on CWPO Wastewater Treatment. Catalysts 2021, 11, 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11030337
Mesa Medina S, Rey A, Durán-Valle C, Bahamonde A, Faraldos M. Performance of Iron-Functionalized Activated Carbon Catalysts (Fe/AC-f) on CWPO Wastewater Treatment. Catalysts. 2021; 11(3):337. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11030337
Chicago/Turabian StyleMesa Medina, Sara, Ana Rey, Carlos Durán-Valle, Ana Bahamonde, and Marisol Faraldos. 2021. "Performance of Iron-Functionalized Activated Carbon Catalysts (Fe/AC-f) on CWPO Wastewater Treatment" Catalysts 11, no. 3: 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11030337
APA StyleMesa Medina, S., Rey, A., Durán-Valle, C., Bahamonde, A., & Faraldos, M. (2021). Performance of Iron-Functionalized Activated Carbon Catalysts (Fe/AC-f) on CWPO Wastewater Treatment. Catalysts, 11(3), 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11030337









