One-Pot Synthesis of Nano CuO-ZnO Modified Hydrochar Derived from Chitosan and Starch for the H2S Conversion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Basic Physical and Chemical Properties of Hydrochars
2.2. H2S Adsorption Performance
2.2.1. Effect of Hydrochar Species
2.2.2. Effect of Auxiliary Agents on H2S Removal
2.2.3. Effect of Adsorption Temperature on H2S Removal
2.3. Adsorption Mechanism
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Adsorbent
3.3. Characterization of Hydrochar
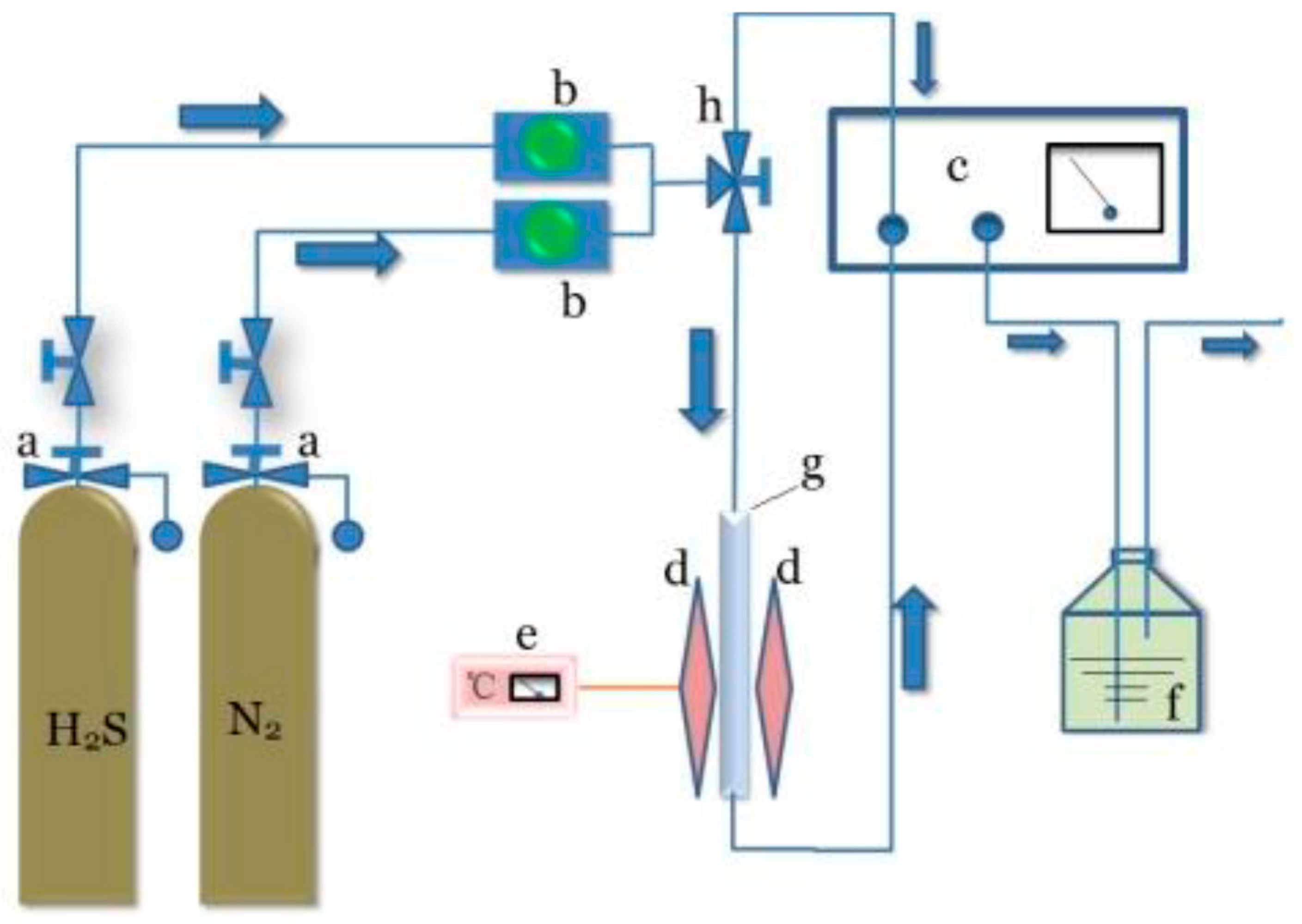
3.4. Batch H2S Adsorption Experiments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coenen, K.; Gallucci, F.; Hensen, E.; Annaland, M.V.S. Adsorption behavior and kinetics of H2S on a potassium-promoted hydrotalcite. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2018, 43, 20758–20771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Arriaga, V.; Alvarez-Ramirez, J.; Amaya, M.; Sosa, E. H2S and O2 influence on the corrosion of carbon steel immersed in a solution containing 3M diethanolamine. Corros. Eng. 2010, 52, 2268–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.H.; Wang, S.D.; Wu, D.Y.; Yuan, Q. Experimental and simulation study of hydrogen sulfide adsorption on impregnated activated carbon under anaerobic conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eow, J.S. Recovery of sulfur from sour acid gas: A review of the technology. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2010, 21, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Yao, Y.; Li, D.; Wu, F.; Zhang, C.; Gao, B. Facile low-temperature one-step synthesis of pomelo peel biochar under air atmosphere and its adsorption behaviors for Ag(I) and Pb(II). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dou, G.Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.F.; Wang, H.L.; Hao, Z.P. Selective catalytic oxidation of H2S over iron oxide supported on alumina-intercalated Laponite clay catalysts. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 260, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasyerli, S. Cerium–manganese mixed oxides for high temperature H2S removal and activity comparisons with V–Mn, Zn–Mn, Fe–Mn sorbents. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2008, 47, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khudenko, B.M.; Gitman, G.M.; Wechsler, T.E.P. Oxygen Based Claus Process for Recovery of Sulfur from H2S Gases. J. Environ. Eng. 1993, 119, 1233–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garces, H.F.; Galindo, H.M.; Garces, L.J.; Hunt, J.; Morey, A.; Suib, S.L. Low temperature H2S dry-desulfurization with zinc oxide. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 127, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, Y.Y.; Qu, S.Q.; Da, J.W.; Hao, Z.P. H2S-Selective Catalytic Oxidation: Catalysts and Processes. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 1053–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Cai, T.; Liu, Z. Hydrochar and pyrochar for sorption of pollutants in wastewater and exhaust gas: A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgwater, A.V.; Meier, D.; Radlein, D. An Overview of Fast Pyrolysis of Biomass. Org. Geochem. 1999, 30, 1479–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Shan, G.C.; Sun, Y.F. Catalytic fast pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass: Critical role of zeolite catalysts. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 139, 110707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, B.; Leifeld, J.; Knicker, H.; Dufey, J.E.; Deforce, K.; Cornélis, J.-T. Long term change in chemical properties of preindustrial charcoal particles aged in forest and agricultural temperate soil. Org. Geochem. 2017, 107, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, F.C.; Volpe, M.; Fiori, L.; Manni, A.; Cordiner, S.; Mulone, V.; Rocco, V. Spent coffee enhanced biomethane potential via an integrated hydrothermal carbonizationanaerobic digestion process. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 256, 102–109. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.X.; Yao, S.; Wang, Y.Y.; Lu, H.H.; Brar, S.K.; Yang, S.M. Bio- and hydrochars from rice straw and pig manure: Inter-comparison. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 235, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, X.; Chen, B.L.; Chen, Z.M.; Zhu, L.Z.; Schnoor, J.L. Insight into Multiple and Multi-level Structures of Biochars and Their Potential Environmental Applications: A Critical Review. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2018, 52, 5027–5047. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P.Z.; Li, Y.X.; Meng, T.; Zhang, R.C.; Song, M.; Ren, J. Removal of sulfonamide antibiotics and human metabolite by biochar and biochar/H2O2 in synthetic urine. Water Res. 2018, 147, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.G.; Balasubramanian, R. Upgrading of waste biomass by hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) and low temperature pyrolysis (LTP): A comparative evaluation. Appl. Energy 2014, 114, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titirici, M.M.; White, R.J.; Falco, C.; Sevilla, M. Black perspectives for a green future: Hydrothermal carbons for environment protection and energy storage. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 6796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, G. Near critical and supercritical water. Part I. Hydrolytic and hydrothermal processes. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2009, 47, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Yang, T.X.; Zhu, N.M.; Li, D.; Chen, Z.L.; Lang, Q.Q.; Liu, Z.G.; Jiao, W.T. Enhanced adsorption of Pb(II) onto modified hydrochar: Modeling and mechanism analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 288, 121593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, S.; Sen, T.K.; Phan, C. Synthesis and characterization of slow pyrolysis pine cone bio-char in the removal of organic and inorganic pollutants from aqueous solution by adsorption: Kinetic, equilibrium, mechanism and thermodynamic. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 246, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simsir, H.; Eltugral, N.; Karagoz, S. Hydrothermal carbonization for the preparation of hydrochars from glucose, cellulose, chitin, chitosan and wood chips via low-temperature and their characterization. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 246, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Gao, W.; Kang, X.M.; Dong, Y.Q.; Liu, P.F.; Yan, S.X.; Yu, B.; Guo, L.; Cui, B.; El-Aty, A.M.A. Structural changes in corn starch granules treated at different temperatures. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 118, 106760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin, K.; Karagöz, S.; Bektaş, S. A review of hydrothermal biomass processing. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 40, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almughamisi, M.S.; Khan, Z.A.; Alshitari, W.; Elwakeel, K.Z. Recovery of chromium(VI) oxyanions from aqueous solution using Cu(OH)2 and CuO embedded chitosan adsorbents. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.W.; Huang, G.Q.; Qi, S. Properties of AC and 13X zeolite modified with CuCl2 and Cu(NO3)2 in phosphine removal and the adsorptive mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 316, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Liu, Z.Y.; Yang, Z.H. Polymer-Controlled Growth of CuO Nanodiscs in the Mild Aqueous Solution. Chin. J. Chem. 2009, 27, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Gao, Y.; Wang, B.; Rozynek, Z.; Fossum, J.O. Carbonate-Assisted Hydrothermal Synthesis of Nanoporous CuO Microstructures and Their Application in Catalysis. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 5, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mureddu, M.; Ferino, I.; Rombi, E.; Cutrufello, M.G.; Deiana, P.; Ardu, A.; Musinu, A.; Piccaluga, G.; Cannas, C. ZnO/SBA-15 composites for mid-temperature removal of H2S: Synthesis, performance and regeneration studies. Fuel 2012, 102, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhage, P.; Samokhvalov, A.; Repala, D.; Duin, E.C.; Bowman, M.; Tatarchuk, B.J. Copper-Promoted ZnO/SiO2 Regenerable Sorbents for the Room Temperature Removal of H2S from Reformate Gas Streams. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 8388–8396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.R.; Lin, Y.T.; Xu, Z.C.; Wang, B.; Zhu, T.Y. Oxidation mechanisms of H2S by oxygen and oxygen-containing functional groups on activated carbon. Fuel Process. Technol. 2019, 189, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, D.G.; Montagnaro, F.; Balsamo, M.; Erto, A.; Deorsola, F.A.; Lisi, L.; Cimino, S. Synergic effect of Zn and Cu oxides dispersed on activated carbon during reactive adsorption of H2S at room temperature. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 257, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-J.; Na, C.W.; Hwang, I.-S.; Lee, J.-H. One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of CuO–ZnO composite hollow spheres for selective H2S detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 168, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutillara, Y.; Tombeur, J.L.; De Weireld, G.; Lodewyckx, P. In-situ copper impregnation by chemical activation with CuCl2 and its application to SO2 and H2S capture by activated carbons. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 372, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

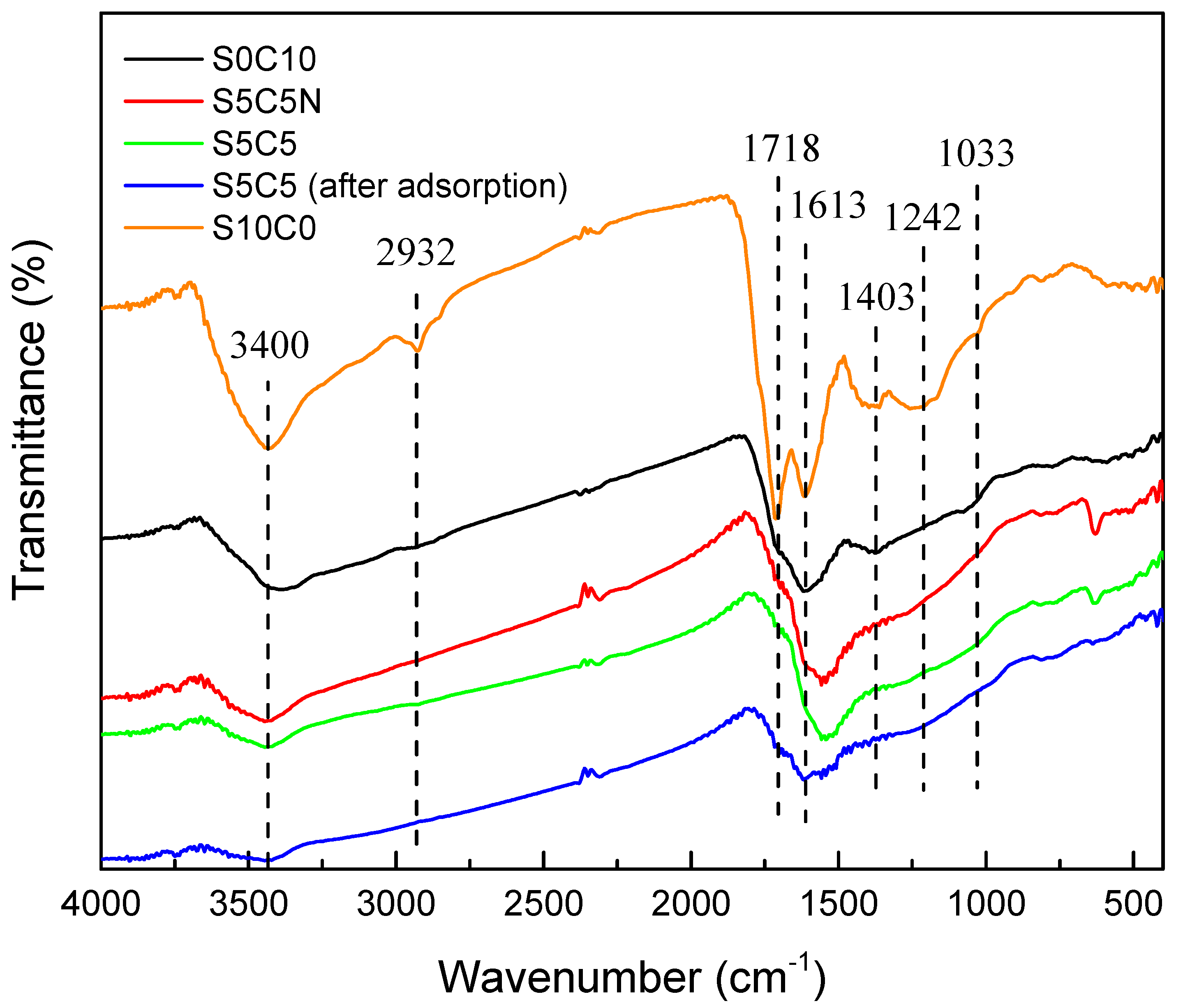




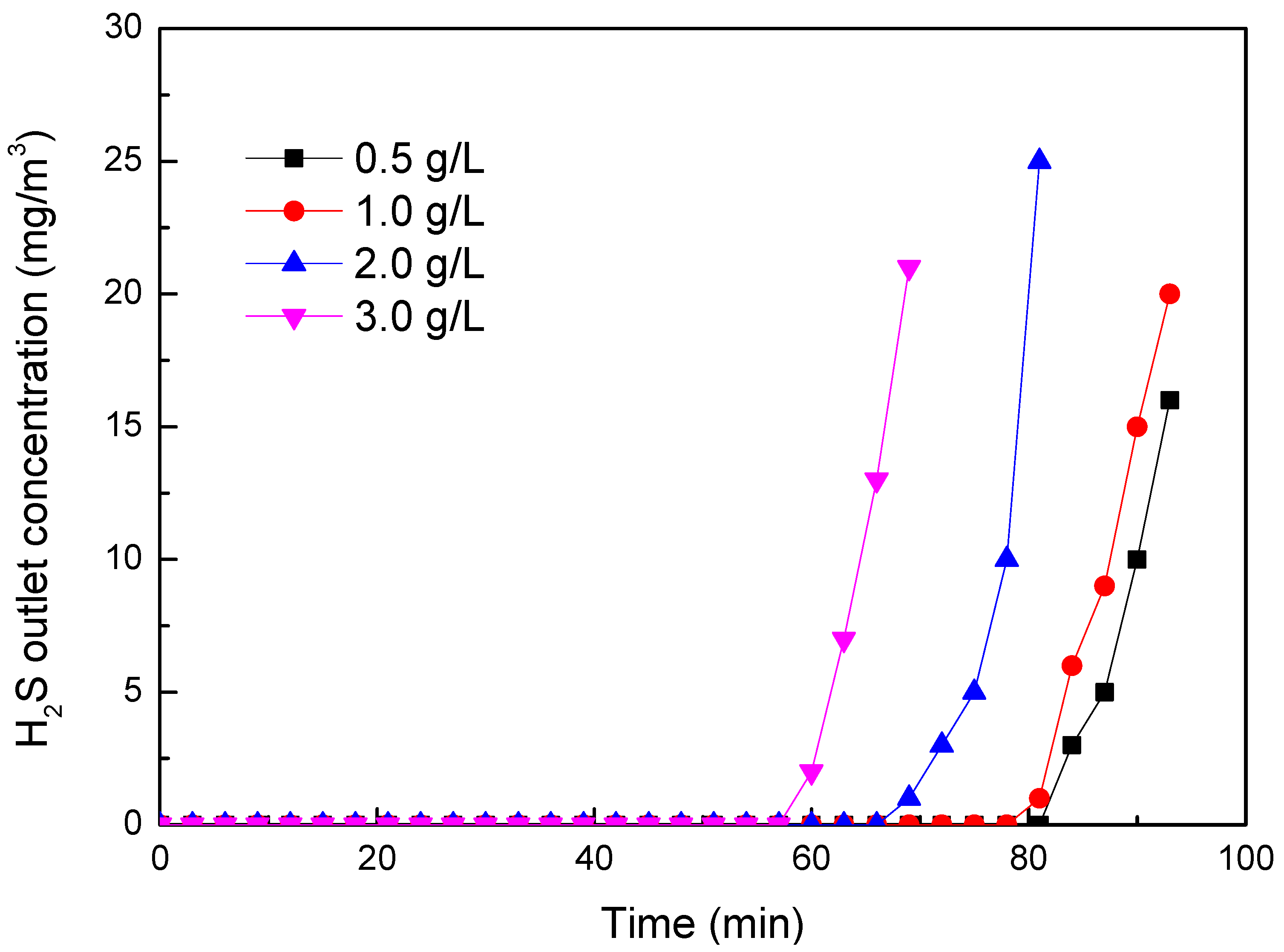
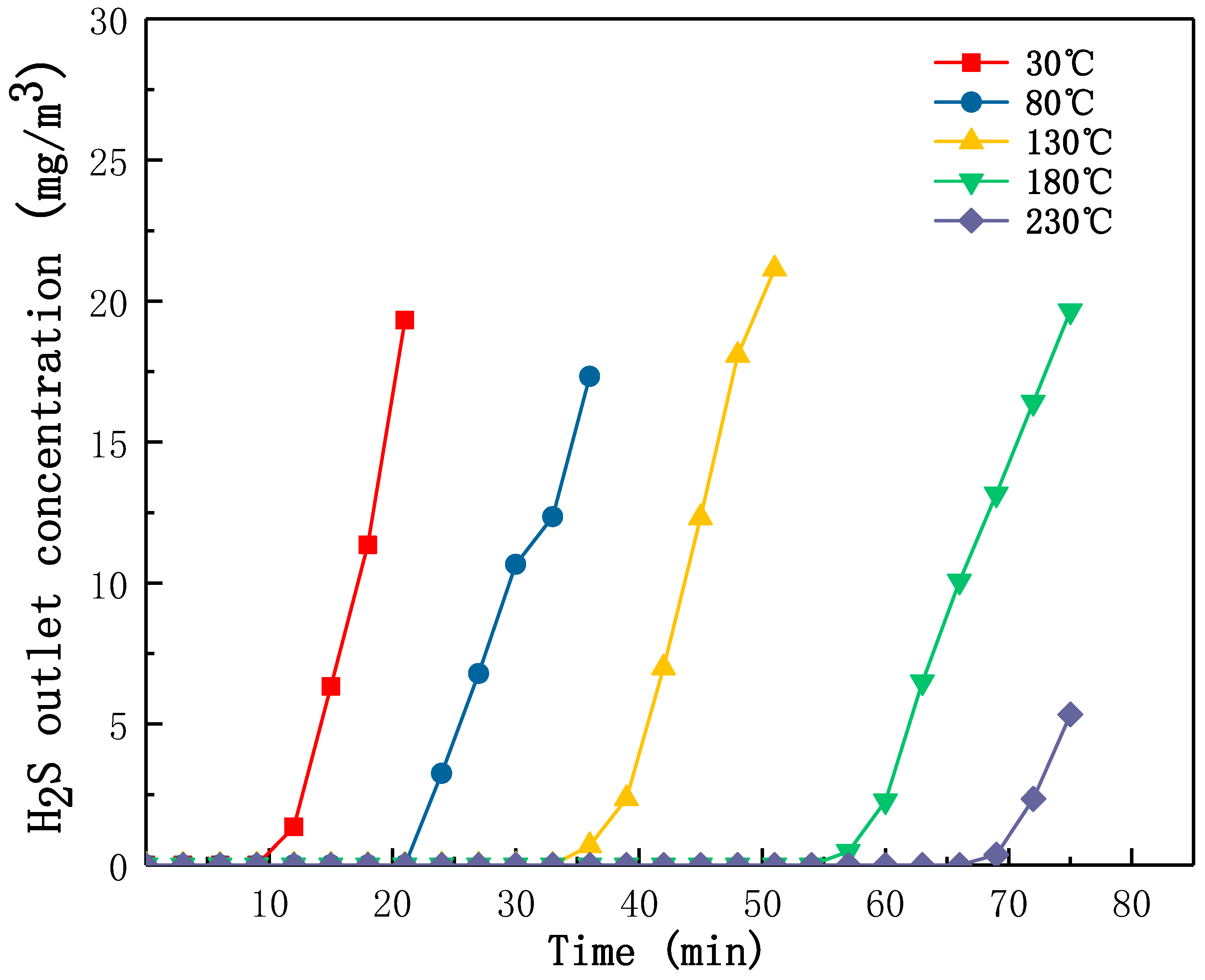
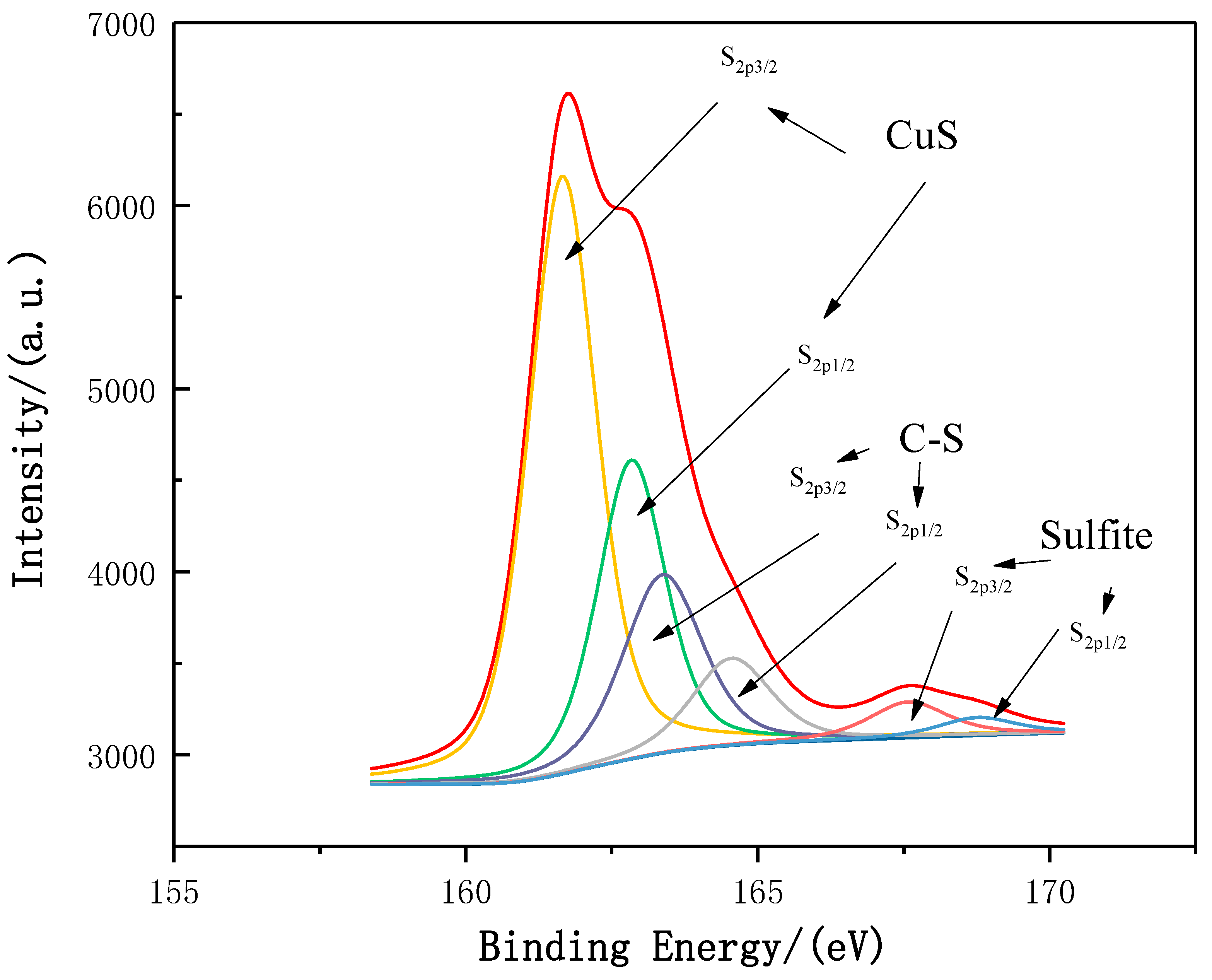


| Hydrochar | Yield (%) | SSA | PV | APD | Elemental Composition (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | Zn | Cu | N | |||||
| S5C5 | 14.83 | 30.102 | 0.071 | 8.9264 | 48.49 | 38.73 | 0.34 | 6.68 | 2.58 |
| S10C0 | 11.01 | 12.939 | 0.041 | 1.2464 | 36.42 | 54.34 | 0.37 | 5.57 | 0.05 |
| S3C7 | 29.89 | 16.456 | 0.069 | 1.456 | 38.85 | 42.07 | 0.36 | 6.97 | 5.93 |
| S7C3 | 14.44 | 17.244 | 0.073 | 1.6234 | 43.20 | 45.37 | 0.66 | 5.10 | 1.18 |
| S0C10 | 32.37 | 14.653 | 0.046 | 1.093 | 43.33 | 39.64 | 0.41 | 6.35 | 7.13 |
| S5C5N | 9.7 | 8.162 | 0.042 | 0.891 | 49.38 | 36.97 | 0.42 | 5.59 | 2.05 |
| Sample | Carbon Precursor (Dosage) | Auxiliary Agent | Metal Oxide Precursor (Dosage) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S5C5 | Starch (3.60 g) + Chitosan (3.60 g) | Cationic polyacrylamide solution | ZnCl2 (0.84 g) + CuCl2 (0.84 g) |
| S10C0 | Starch (7.20 g) | ||
| S3C7 | Starch (2.16 g) + Chitosan (5.04 g) | ||
| S7C3 | Starch (5.04 g) + Chitosan (2.16 g) | ||
| S0C10 | Chitosan (7.20 g) | ||
| S5C5N | Starch (3.60 g) + Chitosan (3.60 g) | None |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zang, L.; Zhou, C.; Dong, L.; Wang, L.; Mao, J.; Lu, X.; Xue, R.; Ma, Y. One-Pot Synthesis of Nano CuO-ZnO Modified Hydrochar Derived from Chitosan and Starch for the H2S Conversion. Catalysts 2021, 11, 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11070767
Zang L, Zhou C, Dong L, Wang L, Mao J, Lu X, Xue R, Ma Y. One-Pot Synthesis of Nano CuO-ZnO Modified Hydrochar Derived from Chitosan and Starch for the H2S Conversion. Catalysts. 2021; 11(7):767. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11070767
Chicago/Turabian StyleZang, Lihua, Chengxuan Zhou, Liming Dong, Leilei Wang, Jiaming Mao, Xiaomin Lu, Rong Xue, and Yunqian Ma. 2021. "One-Pot Synthesis of Nano CuO-ZnO Modified Hydrochar Derived from Chitosan and Starch for the H2S Conversion" Catalysts 11, no. 7: 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11070767
APA StyleZang, L., Zhou, C., Dong, L., Wang, L., Mao, J., Lu, X., Xue, R., & Ma, Y. (2021). One-Pot Synthesis of Nano CuO-ZnO Modified Hydrochar Derived from Chitosan and Starch for the H2S Conversion. Catalysts, 11(7), 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11070767







