Physicochemical Features and NH3-SCR Catalytic Performance of Natural Zeolite Modified with Iron—The Effect of Fe Loading
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Physicochemical Properties of the Materials
2.1.1. Chemical Composition, Crystal Structure, and Morphology of the Materials
2.1.2. Textural Properties of the Materials
2.1.3. Characteristic Chemical Groups in the Materials
2.1.4. Speciation of the Active Phase
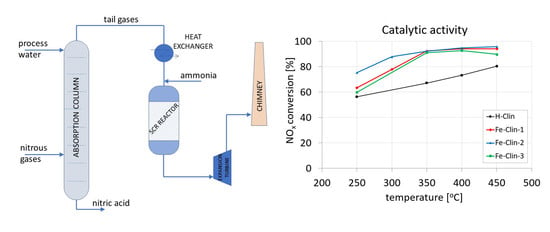
2.2. NH3-SCR Catalytic Tests Performed with Industrial Gas Mixture
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Catalysts Preparation
3.2. Catalysts Characterization
3.3. Catalytic Tests in Real Gas Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forzatti, P. Present Status and Perspectives in De-NOx SCR Catalysis. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2001, 222, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Integrated Pollution Prevention and Control Reference Document on Best Available Techniques for the Manufacture of Large Volume Inorganic Chemicals—Ammonia, Acids and Fertilisers; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, D.W.; Park, K.H.; Ha, H.P.; Hong, S.C. The Role of Molybdenum on the Enhanced Performance and SO2 Resistance of V/Mo-Ti Catalysts for NH3-SCR. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 481, 1167–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damma, D.; Ettireddy, P.R.; Reddy, B.M.; Smirniotis, P.G. A Review of Low Temperature NH3-SCR for Removal of NOx. Catalysts 2019, 9, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Bian, C.; Ming, S.; Guo, L.; Zhang, S.; Pang, L.; Liu, P.; Chen, Z.; Li, T. The Opportunities and Challenges of Iron-Zeolite as NH3-SCR Catalyst in Purification of Vehicle Exhaust. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2020, 607, 117865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husnain, N.; Wang, E.; Li, K.; Anwar, M.T.; Mehmood, A.; Gul, M.; Li, D.; Mao, J. Iron Oxide-Based Catalysts for Low-Temperature Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2019, 35, 239–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Du, Y. Fabrication of Carbon Doped Cu-Based Oxides as Superior NH3-SCR Catalysts via Employing Sodium Dodecyl Sulfonate Intercalating CuMgAl-LDH. J. Catal. 2022, 407, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Kuma, R.; Masaki, S.; Sugishima, N. TiO2-SiO2 and V2O5/TiO2-SiO2 Catalyst: Physico-Chemical Characteristics and Catalytic Behavior in Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO by NH3. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2005, 60, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Cai, S.; Gao, M.; Hasegawa, J.Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Shi, L.; Zhang, D. Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3 by Using Novel Catalysts: State of the Art and Future Prospects. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 10916–10976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, Z.; Xu, L.; Ohnishi, T.; Yanaba, Y.; Ogura, M.; Wakihara, T.; Okubo, T. Understanding the High Hydrothermal Stability and NH3-SCR Activity of the Fast-Synthesized ERI Zeolite. J. Catal. 2020, 391, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrozova, P.; Kynicky, J.; Urubek, T.; Nguyen, V.D. Synthesis and Modification of Clinoptilolite. Molecules 2017, 22, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szymaszek-Wawryca, A.; Díaz, U.; Samojeden, B.; Motak, M. Catalytic Performance of One-Pot Synthesized Fe-MWW Layered Zeolites (MCM-22, MCM-36, and ITQ-2) in Selective Catalytic Reduction of Nitrogen Oxides with Ammonia. Molecules 2022, 27, 2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymaszek, A.; Samojeden, B.; Motak, M. Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with Ammonia (NH3-SCR) over Transition Metal-Based Catalysts-Influence of the Catalysts Support. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2019, 55, 1429–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakdareh, A.M.; Falamaki, C.; Ghasemian, N. Hydrothermally Grown Nano-Manganese Oxide on Clinoptilolite for Low-Temperature Propane-Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2018, 20, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemian, N.; Falamaki, C.; Kalbasi, M.; Khosravi, M. Enhancement of the Catalytic Performance of H-Clinoptilolite in Propane-SCR-NOx Process through Controlled Dealumination. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 252, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemian, N.; Nourmoradi, H. The Study of the Performance of Iranian Clinoptilolite Zeolite in Removal of Nitrogen Oxide (NOx) from Stack of Industries by Using Selective Catalytic Reduction System (SCR). J. Ilam Univ. Med. Sci. 2015, 23, 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemian, N.; Falamaki, C.; Kalbasi, M. Clinoptilolite Zeolite as a Potential Catalyst for Propane-SCR-NOx: Performance Investigation and Kinetic Analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saramok, M.; Szymaszek, A.; Inger, M.; Antoniak-Jurak, K.; Samojeden, B.; Motak, M. Modified Zeolite Catalyst for a NOx Selective Catalytic Reduction Process in Nitric Acid Plants. Catalysts 2021, 11, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boroń, P.; Chmielarz, L.; Gurgul, J.; Łątka, K.; Gil, B.; Marszałek, B.; Dzwigaj, S. Influence of Iron State and Acidity of Zeolites on the Catalytic Activity of FeHBEA, FeHZSM-5 and FeHMOR in SCR of NO with NH3 and N2O Decomposition. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 203, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Qin, X.; Peng, Y.; Wang, C.; Chang, H.; Chen, J.; Li, J. Effect of Fe Precursors on the Catalytic Activity of Fe/SAPO-34 Catalysts for N2O Decomposition. Catal. Commun. 2019, 128, 105706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burris, L.E.; Juenger, M.C. The Effect of Acid Treatment on the Reactivity of Natural Zeolites Used as Supplementary Cementitious Materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 79, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.; Liu, Q.L.; Dong, Y.B.; He, Y.H.; Wang, L. Physicochemical Properties and Mechanism Study of Clinoptilolite Modified by NaOH. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 218, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Habib, A.H.; Gee, S.H.; Hong, Y.K.; McHenry, M. Spin Orientation, Structure, Morphology, and Magnetic Properties of Hematite Nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 17A315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessouri, A.; Boukoussa, B.; Bengueddach, A.; Hamacha, R. Synthesis of Iron-MFI Zeolite and Its Photocatalytic Application for Hydroxylation of Phenol. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2018, 44, 2475–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of Gases, with Special Reference to the Evaluation of Surface Area and Pore Size Distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vassileva, P.; Voikova, D. Investigation on Natural and Pretreated Bulgarian Clinoptilolite for Ammonium Ions Removal from Aqueous Solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doula, M.K. Synthesis of a Clinoptilolite-Fe System with High Cu Sorption Capacity. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gu, Y.; Lin, H.; Jie, B.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, X. Bicarbonate-Enhanced Iron-Based Prussian Blue Analogs Catalyze the Fenton-like Degradation of p-Nitrophenol. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 608, 2884–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, M.; Díaz, U.; Palomares, A.E.; Chmielarz, L. Cu and Fe Modified Derivatives of 2D MWW-Type Zeolites (MCM-22, ITQ-2 and MCM-36) as New Catalysts for DeNOx Process. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 168–169, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkuna, O.; Leboda, R.; Skubiszewska-Ziȩba, J.; Vrublevs’ka, T.; Gun’ko, V.M.; Ryczkowski, J. Structural and Physicochemical Properties of Natural Zeolites: Clinoptilolite and Mordenite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 87, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Lingfa, P. Sodium Bentonite and Kaolin Clays: Comparative Study on Their FT-IR, XRF, and XRD. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 22, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobzaru, C.; Marinoiu, A.; Cernatescu, C. Sorption of Vitamin C on Acid Modified Clinoptilolite. Rev. Roum. Chim. 2015, 60, 241–247. [Google Scholar]
- Long, R.; Yang, R. Characterization of Fe-ZSM-5 Catalyst for Selective Catalytic Reduction of Nitric Oxide by Ammonia. J. Catal. 2000, 194, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doula, M.K.; Ioannou, A. The Effect of Electrolyte Anion on Cu Adsorption-Desorption by Clinoptilolite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2003, 58, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayati-Ashtiani, M. Use of FTIR Spectroscopy in the Characterization of Natural and Treated Nanostructured Bentonites (Montmorillonites). Part. Sci. Technol. 2012, 30, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzybek, J.; Gil, B.; Roth, W.J.; Skoczek, M.; Kowalczyk, A.; Chmielarz, L. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy Characterization of Co and Fe-MCM-56 Catalysts for NH3-SCR and N2O Decomposition: An in Situ FTIR Study. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 196, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, F.C.; Rodriguez-Iznaga, I.; Berlier, G.; Ferro, D.T.; Conception-Rosabal, B.; Pertanovskii, V. Fe Speciation in Iron Modified Natural Zeolites as Sustainable Environmental Catalysts. Catalysts 2019, 9, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]












| Sample | Fe2O3 (%) | SiO2 (%) | Al2O3 (%) | Na2O (%) | MgO (%) | SO3 (%) | K2O (%) | CaO (%) | TiO (%) | MnO (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clin | 2.1 | 74.7 | 12.1 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.04 | 3.2 | 3.7 | 0.2 | 0.07 |
| H-Clin | 2.0 | 80.5 | 11.4 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.03 | 3.0 | 1.7 | 0.2 | 0.03 |
| Fe-Clin-1 | 8.6 | 71.0 | 10.1 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 5.00 | 2.6 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0.01 |
| Fe-Clin-2 | 11.1 | 69.2 | 10.0 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 4.59 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0.01 |
| Fe-Clin-3 | 11.9 | 66.7 | 9.4 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 7.41 | 2.3 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 0.01 |
| Sample | SBET a (m2·g−1) | SExt b (m2·g−1) | Vmeso c (cm3·g−1) | Dmeso c (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clin | 16 | 7 | 0.025 | 17.0 |
| H-Clin | 30 | 9 | 0.281 | 28.2 |
| Fe-Clin-1 | 15 | 10 | 0.277 | 20.8 |
| Fe-Clin-2 | 12 | 13 | 0.262 | 20.8 |
| Fe-Clin-3 | 10 | 10 | 0.224 | 22.3 |
| Selectivity Towards N2 (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | 250 °C | 300 °C | 350 °C | 400 °C | 450 °C |
| Fe-Clin-1 | 99.2 | 98.2 | 96.7 | 96.9 | 100.0 |
| Fe-Clin-2 | 99.6 | 98.6 | 97.7 | 94.6 | 100.0 |
| Fe-Clin-3 | 98.3 | - | 97.1 | 93.1 | 100.0 |
| Sample | Description of the Sample |
|---|---|
| Clin | Raw clinoptilolite |
| H-Clin | Protonated clinoptilolite |
| Fe-Clin-1 | The catalyst obtained by single impregnation with Fe precursor |
| Fe-Clin-2 | The catalyst obtained by dual impregnation with Fe precursor |
| Fe-Clin-3 | The catalyst obtained by triple impregnation with Fe precursor |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saramok, M.; Inger, M.; Antoniak-Jurak, K.; Szymaszek-Wawryca, A.; Samojeden, B.; Motak, M. Physicochemical Features and NH3-SCR Catalytic Performance of Natural Zeolite Modified with Iron—The Effect of Fe Loading. Catalysts 2022, 12, 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12070731
Saramok M, Inger M, Antoniak-Jurak K, Szymaszek-Wawryca A, Samojeden B, Motak M. Physicochemical Features and NH3-SCR Catalytic Performance of Natural Zeolite Modified with Iron—The Effect of Fe Loading. Catalysts. 2022; 12(7):731. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12070731
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaramok, Magdalena, Marek Inger, Katarzyna Antoniak-Jurak, Agnieszka Szymaszek-Wawryca, Bogdan Samojeden, and Monika Motak. 2022. "Physicochemical Features and NH3-SCR Catalytic Performance of Natural Zeolite Modified with Iron—The Effect of Fe Loading" Catalysts 12, no. 7: 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12070731
APA StyleSaramok, M., Inger, M., Antoniak-Jurak, K., Szymaszek-Wawryca, A., Samojeden, B., & Motak, M. (2022). Physicochemical Features and NH3-SCR Catalytic Performance of Natural Zeolite Modified with Iron—The Effect of Fe Loading. Catalysts, 12(7), 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12070731