Abstract
A series of the Cr-containing erbium substituted yttrium iron garnet ferrites (ECYIG) was synthesized with distinct Cr amounts, herein referred to as Y3(Er0.02Fe5Cr1−x)O12, where x refers to Cr amounts from 0 to 0.05. The catalytic performance of the solids was investigated in ethylbenzene oxidation in the presence of hydrogen peroxide to assess the role of Cr and Er present in the YIG garnet lattice for fine chemistry compound production. Raman spectroscopy, HRTEM, EPR and FTIR revealed that the insertion of Er (at a fixed amount of 2%) in dodecahedral sites had a great impact on the catalytic activity of the garnets. Both Er3+ and Y3+ in the lattice simultaneously provided structural stability to the garnet structure in any harsh environment. XPS and EPR indicated that the Cr3+ ions replaced those of Fe3+ located in both octahedral and tetrahedral sites of the YIG garnets. The Cr3+ ions acted as electronic promoter to increase the oxidation rate of the Fe3+ active species responsible for activating the EB molecule. SEM-EDS demonstrated that the solids having Cr amounts lower than 4% experienced the most severe deactivation due to the Cr leaching and strong carbon species adsorption on the surface of the catalysts, which decreased their efficiency in the reaction.
1. Introduction
Since garnets are thought to be modified by various synthetic routes to improve their physicochemical properties, yttrium iron garnet (YIG) ferrite structures have become the focus of a wide range of applications [1,2,3]. With numerous potential advantages, such as good chemical stability of the rigid framework, facile tuning of composition, and controllable morphology and texture, the modified garnets can be applied as efficient catalysts, comparative to their conventional bulk and nanostructured iron oxide counterparts [2,3,4,5,6].
YIG garnet-like compounds are known as natural minerals possessing compact arrays of oxygen atoms, in which the cations occupy the center of the corresponding oxygen polyhedron [2,7,8]. Moreover, these materials have a nearly cubic symmetry and general formula of A3B2C3O12, where A is the yttrium ions usually located in the dodecahedral site, and B is an atom in the octahedral position, including Fe and Cr trivalent ions [2,7,8,9,10]. C is an atom, such as Fe, located in tetrahedral sites of the garnet [2,7]. In YIG garnets, Y3+ ions at the dodecahedron sites can be replaced by trivalent rare earth cations; for instance, Er, Ho, Pr, Ce, La, Gd and Yb [2,11,12,13,14,15]. As these cations have similar ionic radii, e.g., Y3+ (0.96 Å) and Er3+ (0.95 Å), it is expected that there is no drastic change due to cation substitution in the structure of YIG garnets. On the contrary, partial substitution of Y3+ cations in the YIG garnet by trivalent or divalent ions, i.e., Fe3+ (0.65 Å), Cr3+(0.62 Å), Mo3+ (0.69 Å) and Al3+ (0.53 Å) or Zn2+ (0.74 Å), ultimately results in structural distortions and high internal stresses of the lattices [1,5,13]. Such a variety of compositions also makes it possible for the garnet to act as an acid-base or redox catalyst, and its Er effects on oxidation catalysts are especially well documented [5,13].
Therefore, the insertion of metals into the YIG garnet sub-lattices highlights new and peculiar characteristics arising from the structural distortions of the YIG rhombic dodecahedron lattice, when compared with pristine YIG [9,10,11]. Prompted by the aforesaid physicochemical properties, the modified garnet offers impressive advantages as an alternative to enhance the catalytic activity of methane decomposition, condensation of aldehydes with o-phenylenediamines and o-aminophen to benzimidazole and benzoxazole derivatives, ethylbenzene oxidation, partial oxidation of methane, and other reactions [2,5,13].
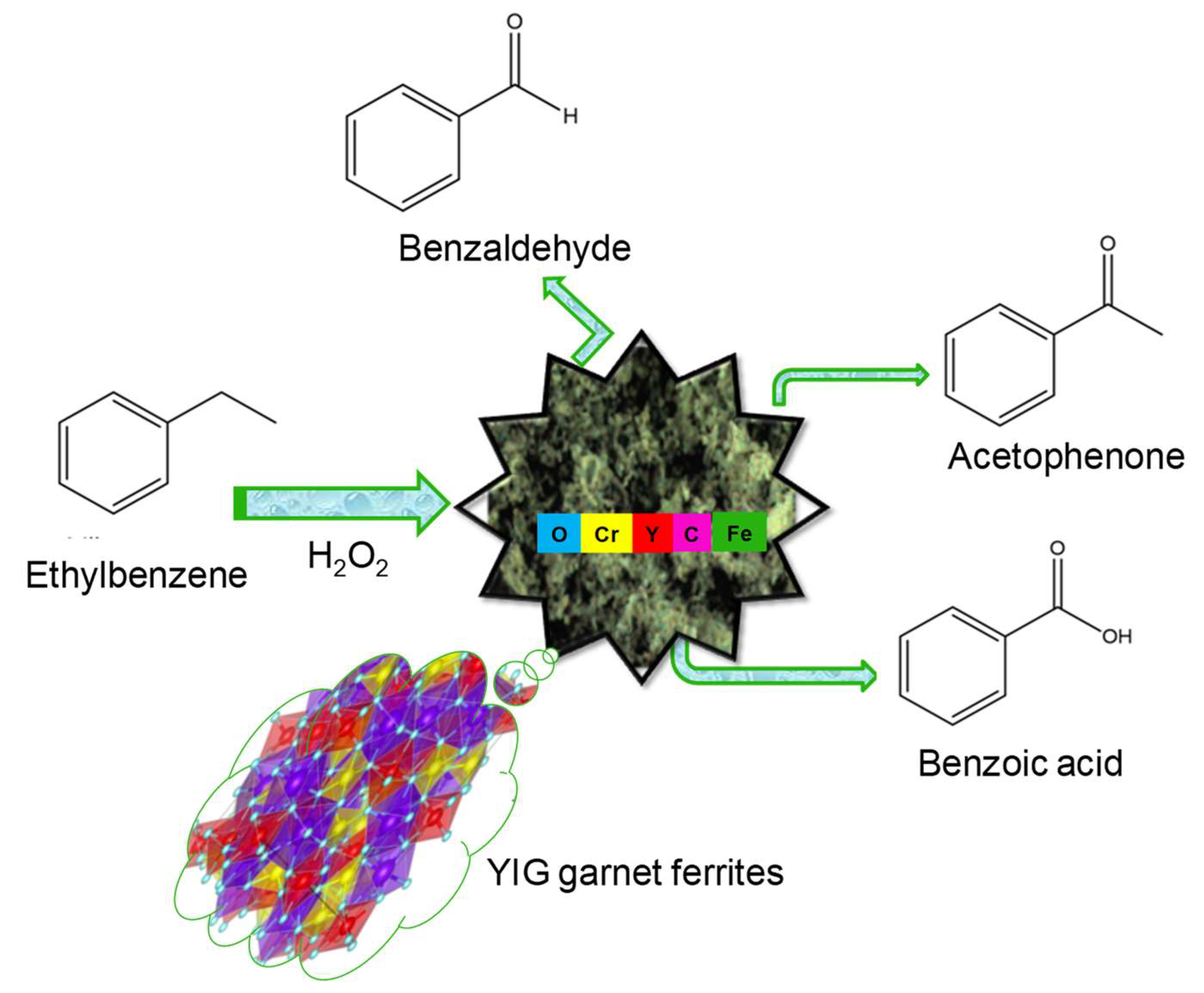
So far, many efforts have been made to improve the catalytic performance of the solids in hydrocarbon oxidation reactions, particularly in the selective oxidation of aromatic hydrocarbons [16,17,18,19,20,21]. Following this trend, Fe-based oxides usually emerge as a suitable option as catalysts among various metal transition candidates for the selective oxidation of ethylbenzene (EB). The reaction is represented in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Scheme of the ethylbenzene oxidation reaction in the presence of H2O2 catalyzed by the YIG garnet ferrites.
The selective EB oxidation reaction is an aromatic alkyl C-H bond oxidation that produces acetophenone, 1-phenyl ethanol, benzaldehyde and benzoic acid. These compounds are of industrial importance for fine chemicals and pharmaceutical products [7,19,20,21,22,23,24]. Among the various transition metal catalysts applied in the EB oxidation reaction, the iron-based oxides open up avenues for developing a new generation of solids. This could be due to the Fe3+/Fe4+ redox pair acting as transition state in the presence of H2O2 at relatively low reaction temperatures, as observed in the selective oxidation of styrene [25]. However, phase transitions, sintering and growth of particles, besides leaching of the Fe sites, are worth mentioning here, as having negative impacts on the catalytic activity.
In recent advances in the selective oxidation of ethylbenzene in the presence of H2O2 as oxidant, Fe3+/Fe2+ ions present in the YIG garnet have exerted a role as active sites for the title oxidation reaction. The synergistic effect derived from the interactions among Fe, Ni, Co and Zn cations hosted in the garnet lattice gives effective performances in the selective EB oxidation reaction [5]. Although there being successful achievements in modifying the YIG garnet compositions, their modest catalytic efficiencies are due to the phase transformation and leaching of the active metal catalysts during EB oxidation reaction.
Inspired by solving these drawbacks for the EB oxidation reaction, we report herein the modification of YIG garnets innovatively by Er and Cr cations to improve the redox ability of the active site for the title reaction. It is expected that the insertion of the trivalent Er and Cr cations in the garnets can not only give new insights into the effect of structures on preventing the Fe phase transformation, but also promote a positive synergistic effect in improving stability of the Fe sites against leaching of the active sites during the catalytic runs.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Summary of the Main Physiochemical Features of the Fresh YIG Catalysts
The details of the physicochemical characterizations of the fresh yttrium iron garnet ferrites are given in Table 1. A common feature of the yttrium iron garnet ferrites is the presence of a YIG phase, namely Y3Fe5O12 [2,8]. Regarding the EYIG and CYIG catalysts, the YIG phase was prevalent with the samples having Y2.98Er0.02Fe5O12 and Y3Fe4.98Cr0.02O12 compositions, respectively. Moreover, the YIG garnets consisted mostly of narrow and crystalline diffraction peaks from YIG cubic structure, independent of the Cr and Er presence [2]. Indeed, low amounts of Er were included in the YIG structure to avoid impurities segregation and the substitution of Y3+ cations previously located in dodecahedral sites by Er3+, as well. Even though the samples had high Cr amounts, the diffraction peaks of chromium oxide species were not detected [2]. These results suggested that Er and Cr species were either included into the YIG cubic lattice or in an amorphous state, being too small to generate XRD peaks.

Table 1.
Physicochemical characterizations of the fresh yttrium iron garnet ferrite catalysts studied.
Additionally, the estimated crystal size values suggested that within a standard deviation, the sizes were in the range of 53–67 nm. This was an indication that the Cr addition resulted in internal stress and its effect on the YIG structure deformation, but did not promote significant crystal growth.
FTIR results exhibited one broad absorption band at around 3448 cm−1 due to the ν(O–H) stretching vibration form having adsorbed water molecules, whereas the out of plane bending vibration for δ(O–H) was visible at 1696 cm−1 [2,5]. Moreover, narrow absorption bands at about 565, 598 and 661 cm−1 arose from M−O stretching vibrations in all fresh catalysts [2,5].
2.2. Effect of the Reaction Time on the Catalytic Activity in EB Oxidation with H2O2
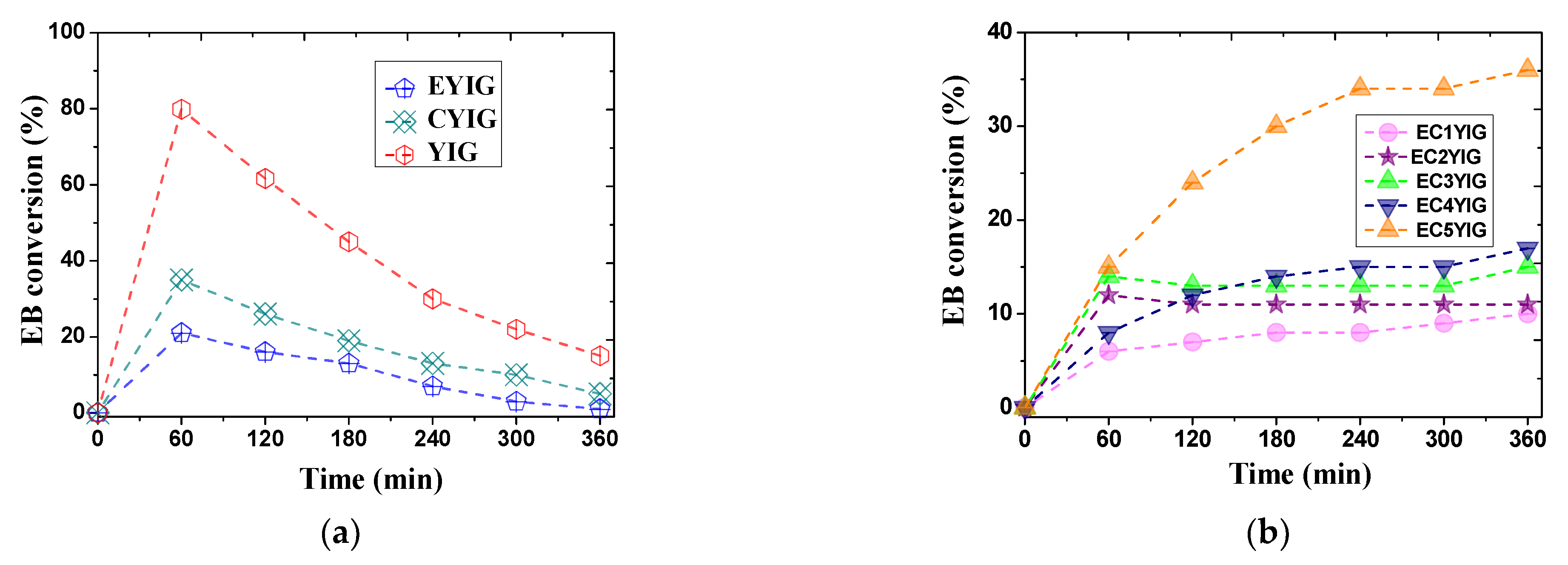
Catalytic results of the yttrium iron garnet ferrites in the EB oxidation reaction in the presence of H2O2 are depicted in Figure 2. At the beginning of the reaction, the EB conversion increased slightly within 60 min for EYIG and CYIG catalysts achieving values of 21 and 35%, respectively. During this period, the EB conversion over YIG catalyst exhibited a greater increment achieving the value of ca. 80% (Figure 2a). This suggested that the adsorption of EB molecule on the Fe active sites of the garnets seemed to occur in the early stages of reaction. The reaction time continued to extend from 60 to 300 min, while EB conversions declined gradually for all catalysts reaching values lower than 5% within 360 min of reaction for samples containing Cr or Er only, that is to say, the CYIG and EYIG catalysts (Figure 2a). In the case of the YIG catalyst, EB conversion achieved 15%, which was likely a consequence of the contribution of the Fe active site in the garnet for oxidizing EB molecules. In all cases, the sudden EB conversions dropped after 120 min, which might have been due to the catalyst deactivation, as shown later by spent catalyst characterizations.
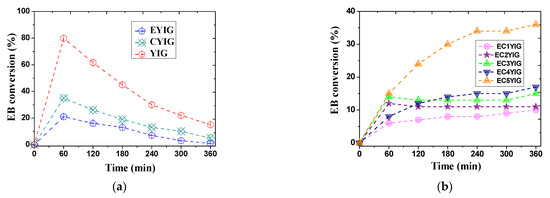
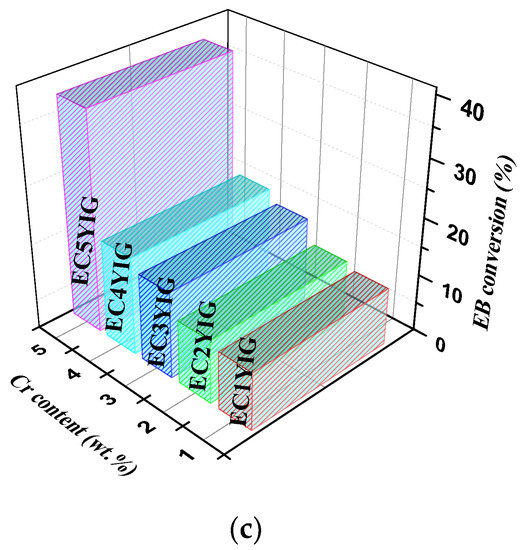
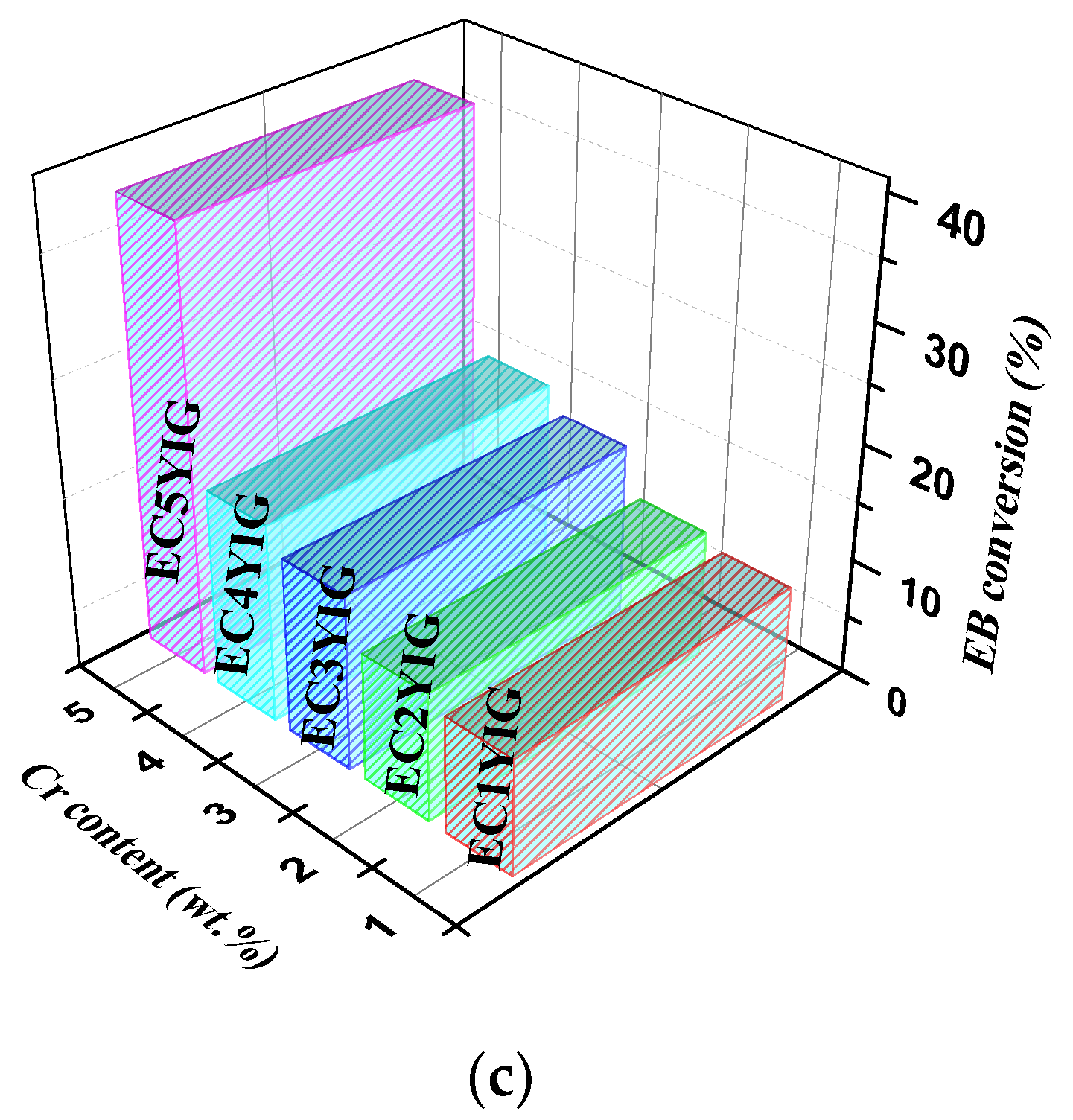
Figure 2.
The reaction time-dependence conversion for yttrium iron garnet ferrites in the oxidation of ethylbenzene with H2O2: (a) YIG, CYIG and ECYIG catalysts (b) ECYIG series of garnets with distinct amounts of chromium (c) The relationship between EB conversions and Cr content present in the yttrium iron garnet ferrites in ethylbenzene oxidation with H2O2. Reaction conditions: EB to H2O2 molar ratio of 1 using 1.3 mol of acetone as solvent, temperature of 50 °C and a catalyst mass of 50 mg within 360 min of reaction.
In spite of the YIG and CYIG catalysts having a Y3Fe5O12 phase, namely YIG (Table 1), their EB conversions were modest. On the other hand, the EYIG sample, possessing Er substituted in the Y sites in the YIG garnet structure, was inactive in 360 min of reaction. Hence, the differences in the catalytic activity of the garnets were most likely attributed to their compositions and the concomitant presence of Cr and Er in the YIG lattice.
The catalytic evaluation at different reaction times was investigated for ECYIG catalysts (Figure 2b). At shorter reaction times, EB conversions were negligible whatever the ECYIG catalyst investigated. Then, there was a sharp rising for almost all the catalysts at 120 min reaching a EB conversion of more than 6%. A further increase in the reaction time revealed that the EB conversions were nearly unchanged for all catalysts. This suggested that Cr could partially vanish from the YIG structure in samples possessing high Cr contents, and, in turn, reduce the activity of the solids. Contrarily, EC5YIG was an exception, since its EB conversion increased from 24% at 120 min and beyond this time to 36%, possibly due to the availability of Cr and Fe in the YIG active phase exposed to the reactant that allowed more EB molecules to be converted per time period. Hence, EC5YIG was more stable toward Cr leaching than the other samples possessing lower Cr contents, as shown further by spent catalyst characterizations.
Of importance, a dissimilar shape of the curve corresponding to the EB conversion versus reaction time was demonstrated by the YIG sample (Figure 2a), wherein EB conversion decreased drastically from 80% at 60 min to 30% at 240 min, followed by a gradual decrement after 300 min. In view of this catalytic performance scenario, the presence of Cr3+, Er3+, Y3+ and Fe3+ ions was essential for very stable catalytic activity during the EB oxidation reaction. It is commonly accepted that the Cr3+ and Fe3+ ions are Lewis acidic centers that might promote an electron transfer during redox mechanisms at the surface of solids during oxidation reactions [26,27,28].
Besides, the Y3+ ions (0.96 Å) positioned in the dodecahedral sites were partially replaced by Er3+ ions (0.95 Å) owing to the proximity of their ionic radii, while Cr3+ species (0.62 Å) substituted tetrahedral Fe3+ ions (0.65 Å), causing increase in lattice constants. Hence, both Er 3+ and Y3+ in the garnet lattice simultaneously stabilized the structure in any harsh environment, while Cr3+ ions acted as electronic promoters to increase the oxidation rate, as the most oxidized intermediate to activate the EB molecule. Therefore, EC5YIG catalyst possessing the highest Cr content exhibited the major activity among the catalysts studied due to the formation of Fe3+/Fe4+ active species that had too short lifetimes, as demonstrated in early studies on Fe-based catalysts for hydrocarbon oxidation reactions [5,22]. Another important advantage of the EC5YIG garnet catalyst was the fact that the Cr3+ may transfer its electron to Fe during the EB oxidation reaction, as shown in previous studies [5]. Thus, the continuous redox cycle contributes to the high catalytic performance of the solid.
The EB oxidation with H2O2 in the presence of YIG as catalyst is a reaction that obeys an electron transfer mechanism, where Fe3+ sites coming from the Y3Fe5O12 adsorb the H2O2, and a Fe4+–O. metal-oxy radical might form on the catalyst surface. Once formed, the Fe4+ species gives an intermediate Fe4+-EB complex, and when EB is adsorbed on the YIG surface the latter intermediate is transformed into another complex, which is oxidized to the desired products [19].
As yttrium is not an active site for the reaction, the Fe3+ was oxidized to Fe4+, the latter species being highly active in the reaction. Figure 2a illustrates that the YIG gave a relatively low EB conversion of ca. 15% within 360 min. After introducing either Cr or Er, the EYIG and CYIG catalysts had poorer catalytic performances than the YIG with a decline of ca. 70% for the same interval. This could be explained by the fact that some of the active Fe sites in YIG phase were replaced by Cr in both tetrahedral and octahedral sites of the YIG structure, due to the proximity of their ionic radii, as stated before. Even if Cr had the major reduction potential compared to that of Fe to trigger redox reactions, the H2O2 was a stronger oxidant than Fe, and, thus, the Fe3+/Fe2+ sites in the garnet were prone to form the active EB-Fe4+ complex during the reaction. Oppositely, it seemed that, in the absence of Er, the synergetic effects among Cr and Fe were not established. As a consequence, Cr3+ site reduction and Fe3+/Fe2+ oxidation to Fe4+/Fe3+ were not fast enough to enhance EB oxidation.
2.3. Impact of the Cr Amounts on the Catalytic Activity and Recyclability
It is noteworthy that EB conversions seemed to increase within 360 min, when the amount of Cr3+ incorporated in the YIG catalysts increased and Er was also present (Figure 2c). An exception was found for the EC1YIG substituted sample of low Cr content. That is to say, samples having Cr contents inferior to 4% suffered from severe Cr leaching during the reaction and, thereby, there was a reduction of the catalyst active sites with less EB molecules to compete for the adsorption for reactive sites, e.g., minor EB conversion. Furthermore, the homogenous filtrate solution. containing the catalytically active Cr species for samples possessing Cr content lower than 4%, was allowed to react for 1h and no catalytic activity was observed. Further spent catalyst confirmed these results, showing that leaching of metal active centers monitored by EDS did not take place significantly over EC5YIG.
Moreover, high EB conversions were observed over EC3YIG and EC4YIG, especially on the EC5YIG chromium-richer samples. Meanwhile, EC1YIG having low amounts of chromium showed an eightfold decrease of the EB conversion compared to that of EC5YIG possessing a Cr content of ca. 5%.
In the cubic structure of the garnet the incorporated Cr3+ ions may furnish electrons to the Fe3+/Fe2+ redox pair at the octahedral (tetrahedral) sites of the garnet. Thus, the combination of high amounts of structural Cr3+ ions and Fe present in the YIG garnet resulted in a definitive role in the present catalyst system.
Additionally, the selectivity to the products obtained are shown in Table 2. The data for product distribution during the oxidation of EB with H2O2 catalyzed by EYIG and CYIG are not shown, since both catalysts had poor catalytic activities in the EB oxidation reaction within 360 min.

Table 2.
Selectivity to the products of the oxidation of EB reaction in the presence of H2O2 using acetone as solvent. Reaction conditions: EB to H2O2 molar ratio of 1 using 1.3 mol of acetone as solvent, temperature of 50 °C and a catalyst mass of 50 mg within 360 min of reaction.
Among all the ECYIG catalysts, acetophenone, benzoic acid and other products were obtained. Trace amounts of benzaldehyde and 1-fenilacetaldehyde and products coming from acetophenone self-condensation reactions arose among the detected products over YIG and EC1YIG. It is important to note that the amount of acetophenone was low in samples possessing high Cr contents, i.e., EC3YIG, EC4YIG and EC5YIG, with benzoic acid and other products being formed as the major components. Hence, other products, including ethylbenzene condensation products, acetophenone oligomers and benzyl benzoate, were preferentially formed. This suggested that side reactions prevailed when high Cr contents were used, due to the high EB conversion achieved. Phenylethanol was the expected product of the partial oxidation of ethylbenzene [21,29]. However, phenylethanol was further oxidized to acetophenone due to the consecutive oxidation reaction. In addition, benzyl benzoate was formed through the consecutive oxidation reaction of benzaldehyde [30].
Ethylbenzene oxidation with H2O2 is a free-radical reaction [5,21,22], in which electron-deficient Fe species may induce adsorption of the H2O2 to form the hydroxyl radicals. The formation of high-valence metal oxygenated species Fe4+-OH abstracts the α-hydrogen from ethylbenzene to produce the ethylbenzene hydroperoxide intermediate, as demonstrated for Fe-based catalyst [21,22]. Then, the ethylbenzene hydroperoxide intermediate is efficiently converted to 1-phenylethanol, which is later oxidized to acetophenone. As Cr enhances the oxidation ability of Fe species, the benzaldehyde can be converted into benzoic acid at a certain stage of the reaction. Moreover, the formation of benzoic acid was observed in this work in a similar fashion as in the presence of oxidizing H2O2 over Cu-based catalysts [30]. Benzaldehyde is still important to produce the condensation products because of the typical reactivity of aldehydes for aldol condensations and Claisen-Schmidt reactions in the presence of either Cr or Fe active sites [2,31,32,33]. However, benzaldehyde was obtained in very low amounts in the product distribution over all catalysts studied.
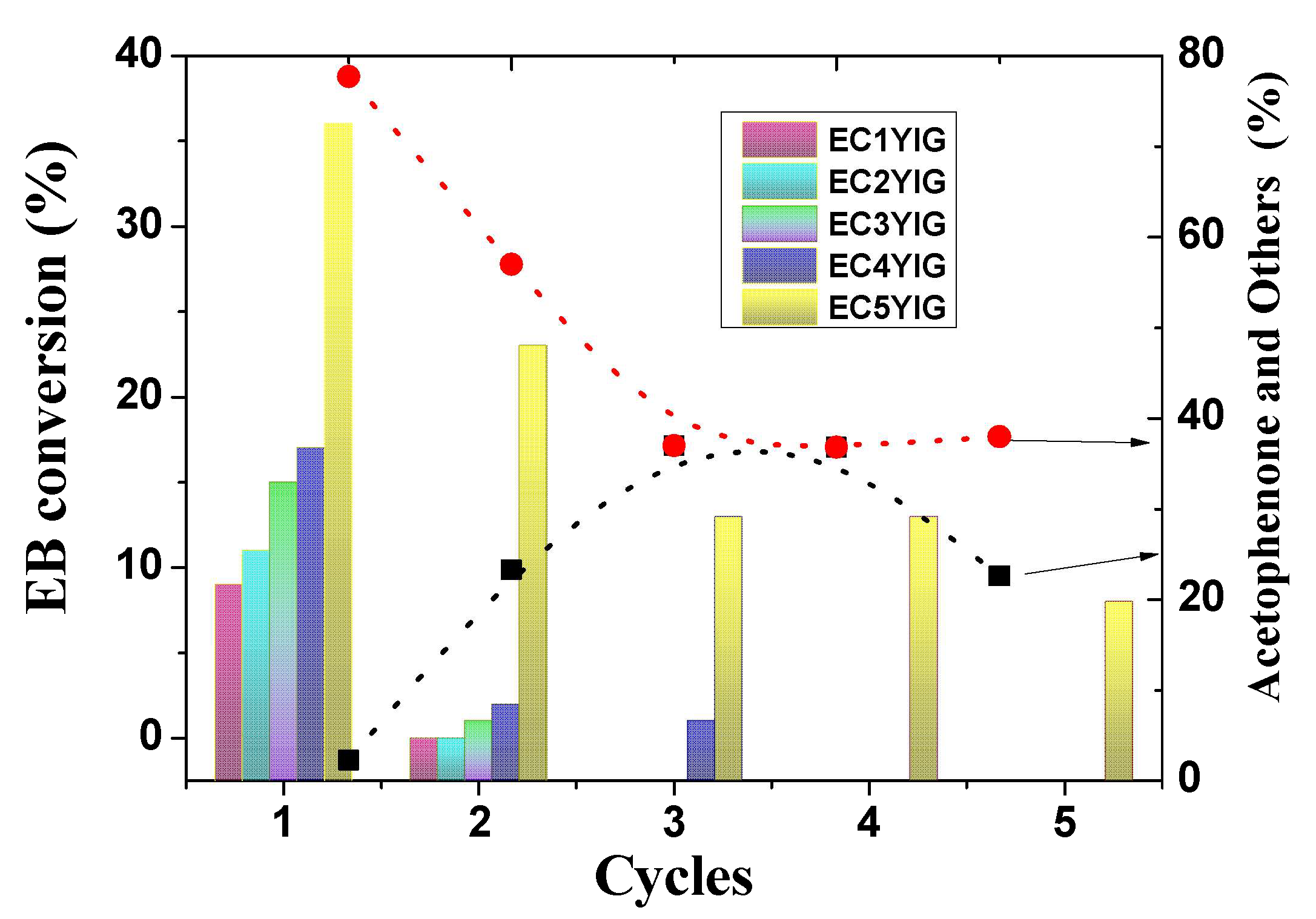
The recyclability of the most active solid towards EB oxidation in the presence of H2O2 is illustrated in Figure 3. The solids were removed from the catalytic runs, washed with ethanol and finally dried, before reuse. It is also worth noting that the EC1YIG, EC2YIG and EC3YIG catalysts had activity for the first cycle of recyclability. Due to the modest catalytic performance of the samples with Cr content below 3%, it is reasonable to suppose that Cr ions were leached from the YIG structure after the first run. Accordingly, chemical analyses confirmed that Cr contents of EC2YIG and EC3YIG were inferior to 0.6% in the second cycle of reuse. Another possibility was that there was not enough Cr to maintain the catalytic stability of the solids. On the contrary, EC4YIG and E5CYIG catalysts gave EB conversions superior to 17% and more than 2.3% production of acetophenone and other products.
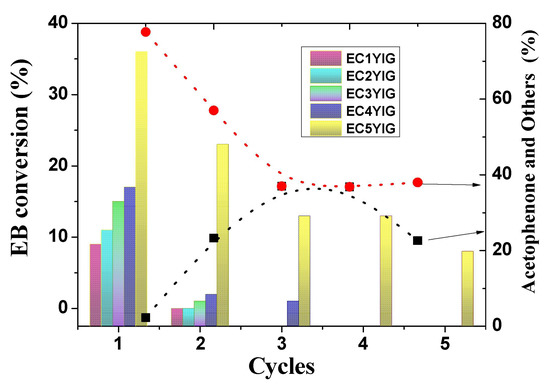
Figure 3.
Recyclability of the solids in the EB oxidation in the presence of H2O2. Reaction conditions: EB to H2O2 molar ratio of 1 using 1.3 mol of acetone as solvent, temperature of 50 °C and a catalyst mass of 50 mg. The symbols (▪) and (•) indicate the selectivity to acetophenone and other products, respectively.
Thereafter, EC4YIG showed significant deactivation in the second cycle of reuse, limiting activity at least three times due to the leaching out of Cr and Fe ions. It seemed to be mainly due to a very small fraction of Cr and Fe species present in the YIG structure restricting accessibility to EB and H2O2 reactants for only two cycles of use. Besides, the filtrate was submitted to another reaction for 1h and no catalytic activity was observable.
On the other hand, the EC5YIG catalyst depicted an opposite trend with EB conversion and others products of 23% and 21%, respectively, after the second catalytic run. The catalytic activity did not change significantly, even after three consecutive catalytic cycles of use. The ICP-OES analysis of the resulting filtrate obtained after the third use in the reaction indicated the presence of Cr in traces. A significant drop in the catalytic activity of EC5YIG was seen after the fifth use, which could be ascribed to the reduction in the amount of active sites, due to Cr and Fe loss during the reaction.
2.4. Structure by Raman, FTIR and XRD and Valence States by EPR
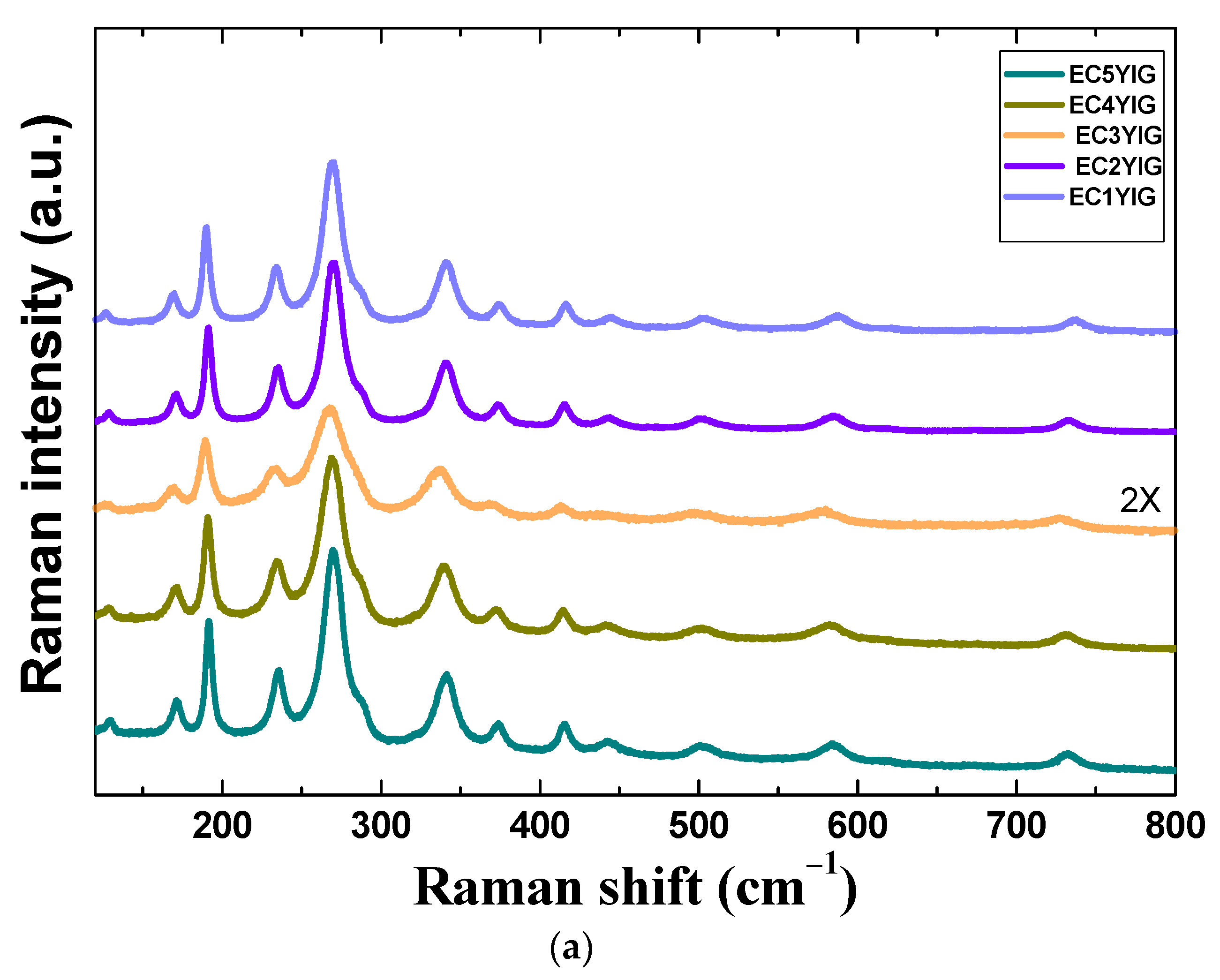
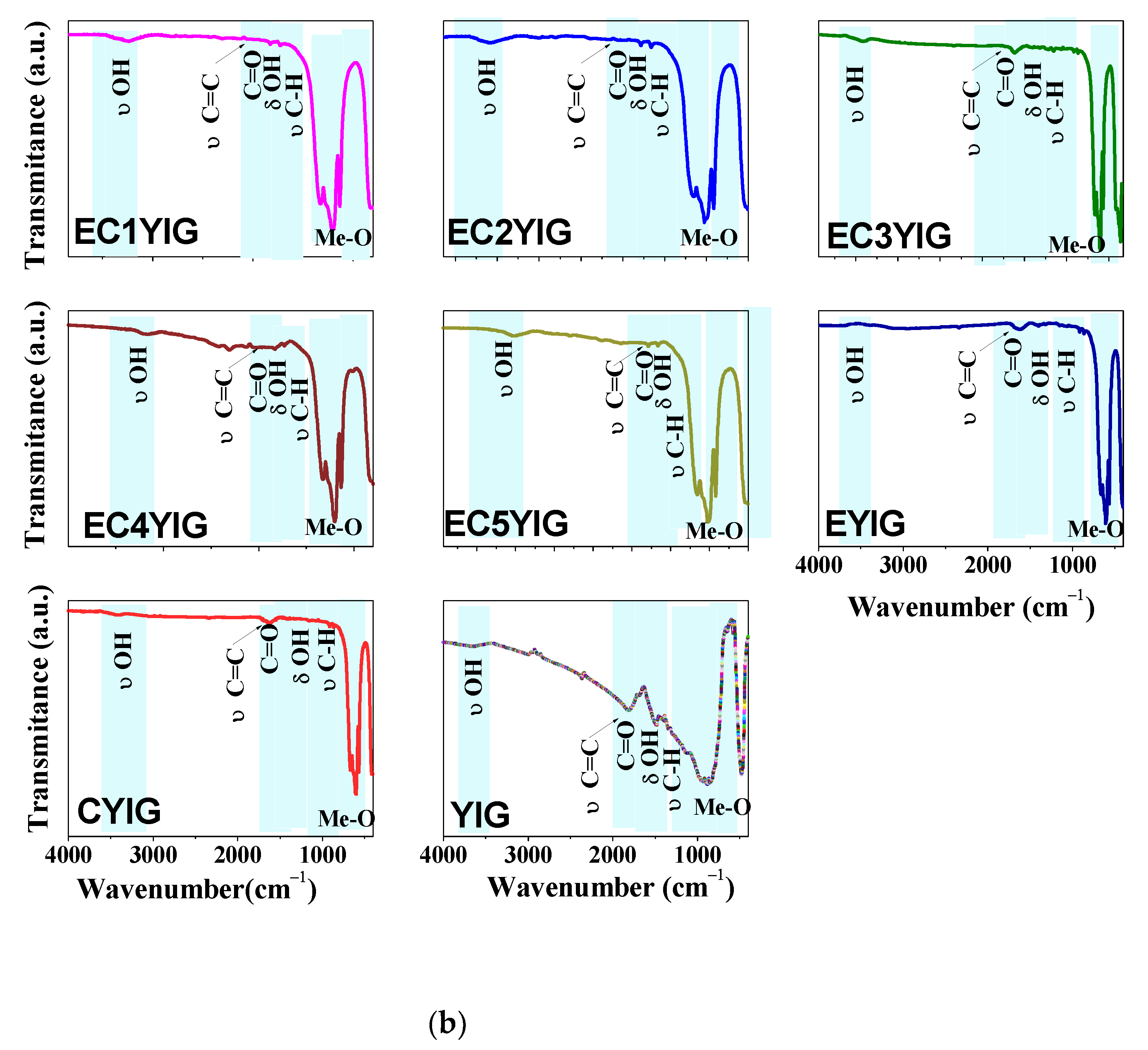
The structural features and chemical states of spent yttrium iron garnet ferrites are shown in Figure 4.
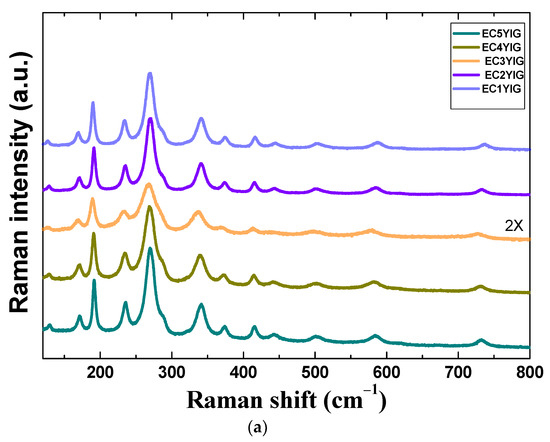
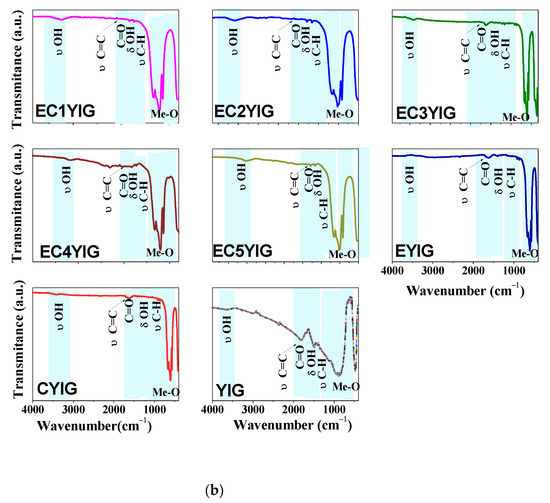
Figure 4.
Structural features of spent yttrium iron garnet ferrites by (a) Raman and (b) FTIR measurements. For Raman spectrum of EC3YIG, the signal intensity was amplified by two times. Reaction conditions: EB to H2O2 molar ratio of 1 using 1.3 mol of acetone as solvent, temperature of 50 °C and a catalyst mass of 50 mg within 360 min of reaction.
Raman spectroscopy is an indispensable tool to investigate the structural features of yttrium iron garnet ferrites. The Raman spectra of selected spent samples are depicted in Figure 4a. Raman spectra of spent yttrium iron garnet ferrites are characterized by well-defined bands with spectral features similar to those of the cubic yttrium iron garnet YIG phase [2,8]. As is well known, the YIG crystallizes in the cubic crystal system belonging to space group Iad3 (Oh10) and there are twenty Fe atoms in the primitive body-centered cubic unit cell.
The main Raman active modes were visible in the spectra of the selected spent garnet from 150–800 cm−1. All solids exhibited the external modes or lattice of polyhedral units below 250 cm−1. Accordingly, the Er mode at about 126 cm−1 was assigned to the translational motion of Y3+ ions at the dodecahedral site, whereas the T2g modes were visible close to 170, 189 and 223 cm−1. These vibration modes are characteristic of translational motions coming from tetrahedral sites of YIG [2,11]. Moreover, the internal modes, due to the translational vibrations of the cations in tetrahedral and dodecahedral sites, arose at about 270 cm−1 for T2g and Er modes, as found elsewhere [5]. Independently of the Cr presence, no significant spectral change occurred after the catalytic test.
Raman bands at 319 and 370 cm−1 corresponded to the bending of Y and Fe cations in tetrahedral (24d) and dodecahedral units (24c) and vibration oscillations of FeO4 tetrahedron [34,35,36]. It is already known that these modes are attributable to the displacements of lighter oxygen ions in Fe3+ polyhedral units in the YIG garnet [35]. Above 400 cm−1, the stretching of Fe–O bonds in tetrahedral and octahedral sites appeared in all solids [35,37]. These observations implied that the crystalline YIG phase was not affected by running the catalytic tests, since the spectral dependence of Fe or Cr was almost the same as that of the fresh sample [5].
For samples possessing Cr contents lower than 2%, Raman modes below 270 cm−1 had blue shifted after the catalytic test. There were no remarkable differences among the Raman spectra of fresh and spent YIG [2,5] and those observed in Figure 4a.
That is to say, Cr incorporation onto the YIG in the 1 and 2% amounts gave a hardening of the modes as a consequence of the Cr leaching from the garnet lattice. Thus, if, on one hand, a small amount of Cr insertion led to YIG lattice expansion, the Cr leaching provokes a further shrinkage of YIG lattice where Fe cations were accommodated in the vacant sites to preserve the structure. Similar phenomena have been reported previously for Cr doping in YIG garnets [36,37]. Moreover, to give further insight into surface compositions and corroborate these results, EDS and XPS analyses were performed.
FTIR spectra of the spent yttrium iron garnet ferrites are illustrated in Figure 4b. The band located at about 3410–3640 cm−1 was due to the stretching vibrations of either structural OH groups or physisorbed water in all solids [8,11,19]. At 1635 cm−1, the weak band assigned the δ(OH) groups from water molecules, which was attributable to the water formed during the reaction [19,22]. When comparing the spectra of fresh YIG samples [5,10], the OH bands could suggest the presence of structural OH groups from the garnets. The adsorption band at 1350 cm−1 along with that at 1434 cm−1 might be associated with the deformation of C-H bond vibrations coming from either acetophenone or benzaldehyde adsorbed on the catalyst surface [5,38]. It is noteworthy that C–H stretching was observed at 1080 and 1040 cm−1, as found elsewhere [39].
The bands at around 2810 and 2400 cm−1 in the FTIR spectra appeared to come from the adsorbed CO2 during the measurements. Moreover, these absorption bands were in the same region as those from CH2 asymmetric stretching and CH3 symmetric stretching vibrations of ethylbenzene aromatic rings [19,38,39]. The presence of these absorption bands suggested that a strong adsorption of EB molecules might have taken place, resulting in the decrease of the catalytic performances of the solids, especially those of samples possessing Cr contents lower than 3%.
Furthermore, the band at around 1690 cm−1 was due to the symmetric and asymmetric stretching of C=O groups coming from benzaldehyde, acetophenone or benzoic acid [40,41]. It is important is to note that these findings indicated that the band at 1602 cm−1, together with a weak band at 1540 cm−1, corresponded to the stretching of the C=C π-type bonding interaction of ethylbenzene and oligomers products with Fe and Cr sites [5,41,42,43]. Two weak bands arose near 1081 and 934 cm−1 and were consistent with the absorption bands of the stretching vibration of single C=O bonds [40]. Additionally, the strong infrared absorption band located at low wavenumber regions widened from 900 to 400 cm−1 and the band located at 729 cm−1 was due to the symmetrical out of-plane bending vibration C-H bonds on the benzene ring [41]. Three other absorption bands were also evident in all the spectra at approximately 475, 565, 598 and 661 cm−1 belonging to the Me-O (Me=Fe, Er, Cr or Y) stretching vibrations [5,8,11]. All of these bands were characteristic of the stretching mode of the tetrahedral site in the YIG structure [2,8]. Importantly, both Y-OH and Fe-OH coordination polyhedral band vibrations arose near 475 cm−1, in agreement with the literature [32]. Due to the replacement of Fe3+ with Cr3+ in the tetrahedral sites in the YIG structure, these bands exhibited a fairly significant shift towards high wavenumber as the Cr amount increased. However, the intensities did not appear to be affected by the Cr amount, after the reaction.
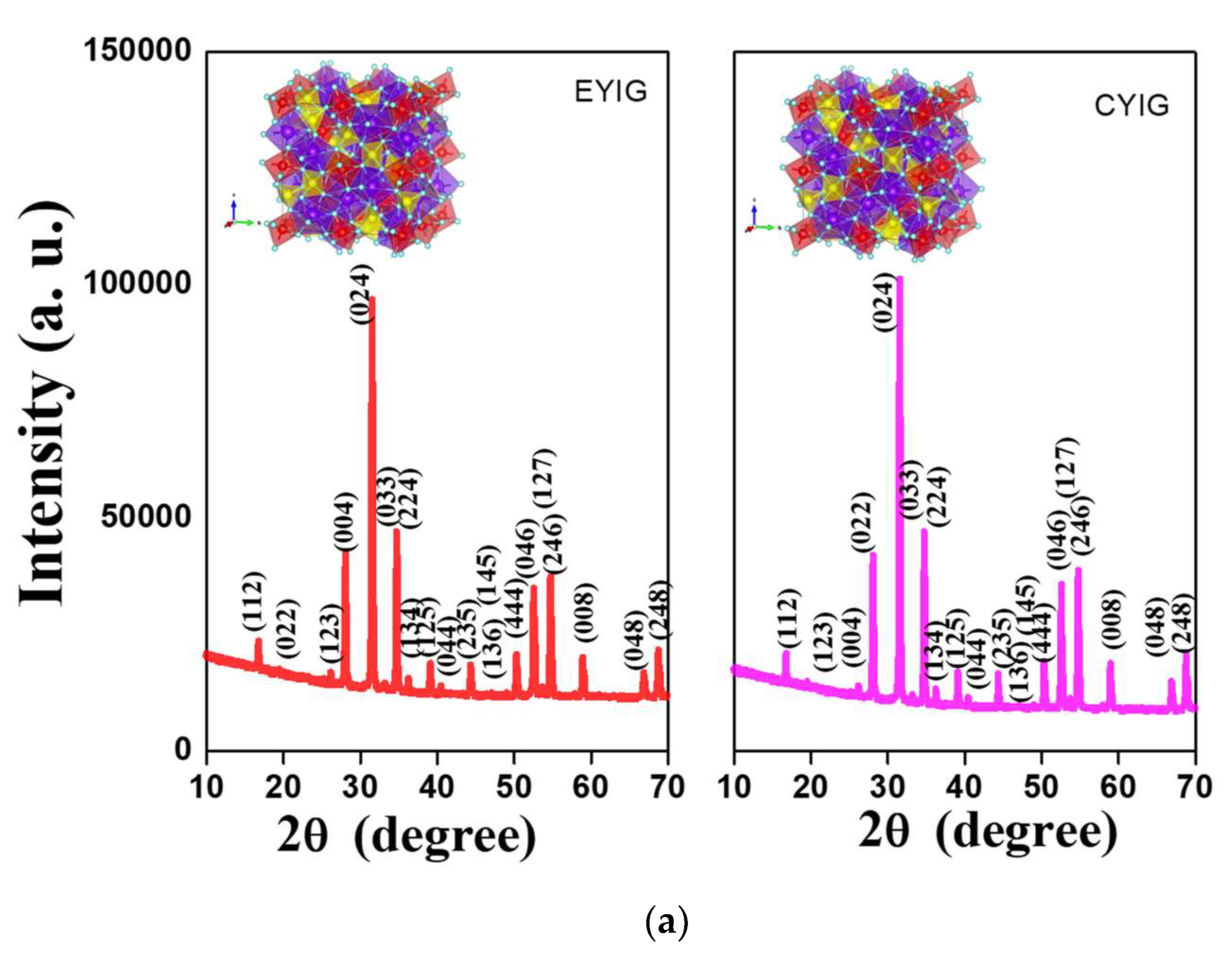
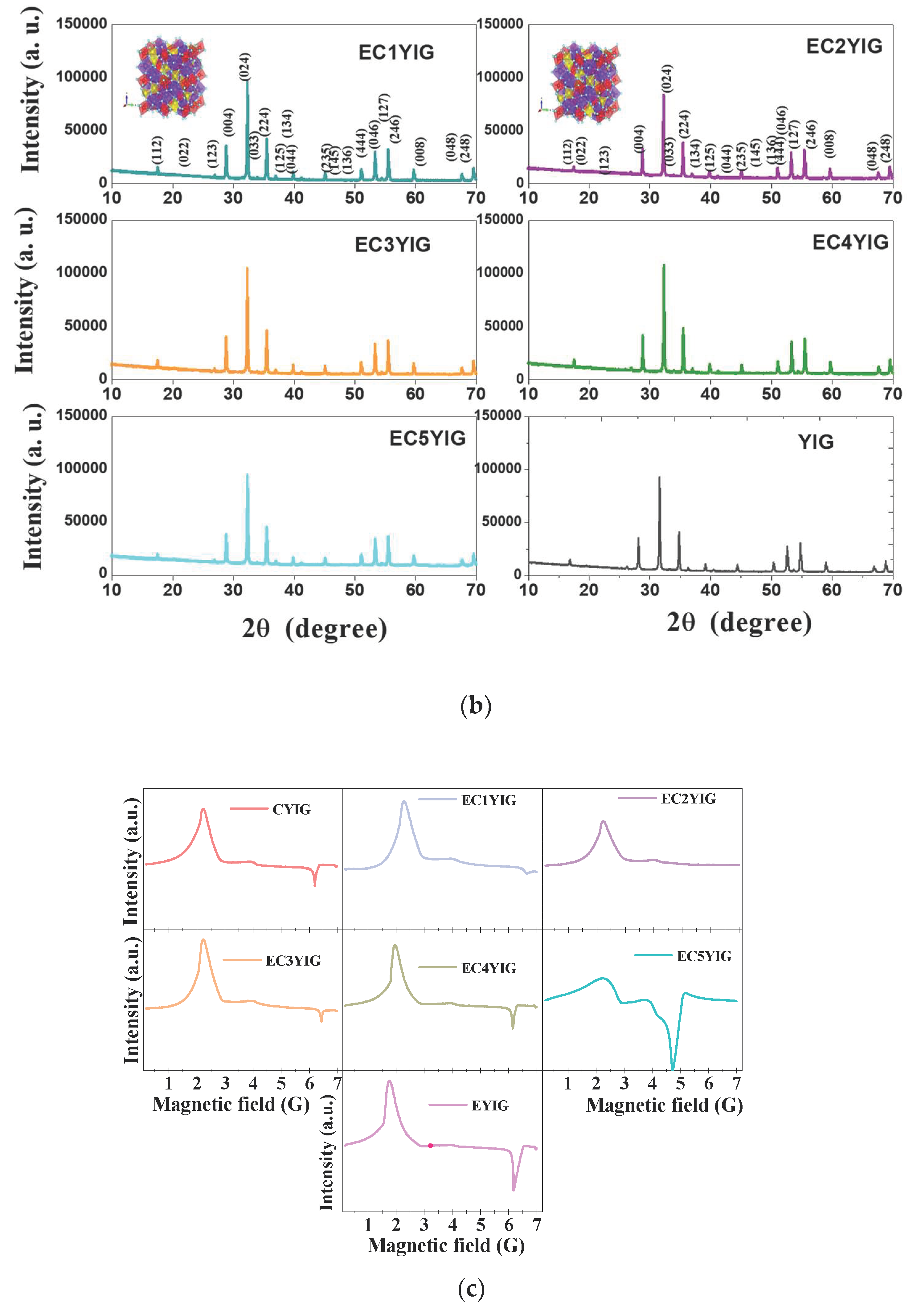
The diffraction patterns of the spent garnets exclusively depicted narrow and intense reflections (Figure 5a,b), which were indexed to the Y3Fe5O12 e.g., YIG as the only crystalline phase present. The cubic structures of the garnet obtained from VESTA [43] were included at the top of the Figures. As described previously [5,8,10], yttrium iron garnet ferrite has a cubic lattice belonging to the Iad3 space group (JCPDS no 43–0507). Similarly, to the fresh solids [2] the well-developed diffracting domains of the spent samples evidenced no signs of phase transformation after the catalytic tests.
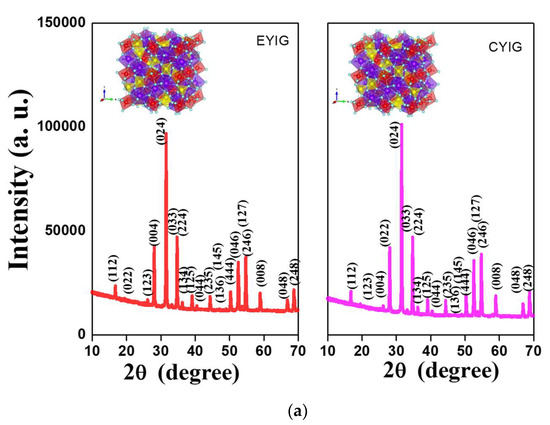
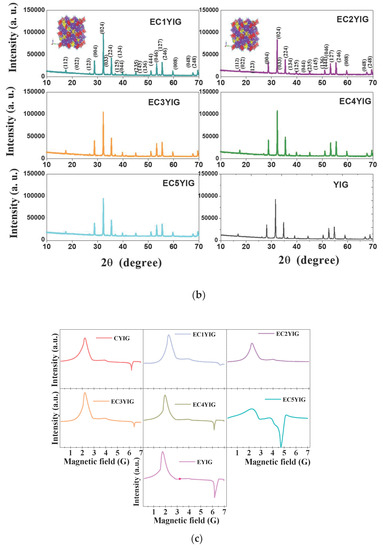
Figure 5.
Structural features and valence states of spent yttrium iron garnet ferrites by (a,b) XRD and (c) EPR measurements. The included figure in the XRD is the structure of YIG. Reaction conditions: EB to H2O2 molar ratio of 1 using 1.3 mol of acetone as solvent, temperature of 50 °C and a catalyst mass of 50 mg within 360 min of reaction.
The average crystallite sizes were determined from the intensity of the peak centered at the plane of about 2θ = 35.5° (420) of the YIG phase. Crystallite sizes varied from 54 to 69 nm, irrespective of the spent yttrium iron garnet ferrites, which confirmed the defined crystalline features and structural stability of the solid, after the reaction. These results were in accordance with those of Raman and FTIR and suggested that the structural features of the solids persevered and the spent garnets were almost stable against phase transformation, independent of their catalytic behavior.
Additionally, solids based on Fe are known to be efficient materials for use in oxidation processes [44,45]. Thus, it was important to correlate the chemical states of the yttrium iron garnet ferrite catalysts with the catalytic properties. A reliable assessment of the structure and chemical states of the metals in YIG garnet was given by EPR measurements of the spent solids (Figure 5c).
The EPR spectra of typical yttrium iron garnet ferrites are described in detail in our previous works [5]. Accordingly, the presence of Fe3+ ions, irrespective of the spent catalyst, are illustrated by the broad and asymmetric signals of the EPR spectra (Figure 5c). The spent YIG catalyst depicted two strong signals at low magnetic field with free energy values (g) of approximately 2.10 and 4.2, which were attributed to Fe2+ in ferromagnetic environments and Fe3+ isolated sites in either tetrahedral or rhombic FeO6 octahedral sites, respectively [5]. The spent Cr-containing YIG samples had a much better signals resolution than their EYIG and CYIG counterparts due to the distribution of the Fe species on the solid surface, as found elsewhere [26,46]. Moreover, the g value of 1.29 found at high magnetic field for YIG assigned the transitions in both octahedral and tetrahedral sites [5,27]. These signals were observed in all the EPR spectra. When Fe ions were substituted by Cr ions in large amounts in YIG, there was a shift to low magnetic field regions of the signal at g = 2.10, whereas that of 1.29 moved towards high magnetic fields. The EC5YIG sample was an exception since its g = 1.29 signal remained unchanged in terms of positions.
This behavior is expected to provide valuable indications on the Fe of d-sites being not completely compensated, when Cr is introduced in the samples giving deviations from linear changes in the magnetic moment, as in the case of metals substitution in some materials [46,47,48].
Again, the presence of Cr in the samples strongly influenced the chemical environments of the YIG garnets. Hence, the broad signal of the ECYIG spent samples could be due to the presence of Cr4+ and Cr3+ ions with g value of 1.98, as demonstrated in Cr oxides having high oxidized species [49]. These environments were likely to occur owing to the H2O2 oxidant present in the reaction.
A plausible explanation for these observations is that small extra-framework Cr2O3 or Fe2O3 particles formed as clusters or nanoparticles, and may have been leached during the reaction and deposited on the solid surface, as later seen by MEV-EDS, TEM and XPS analyses. This was especially true considering the fact that spent samples that incorporated Cr(III) amounts lower than 3% had a bad performance in EB oxidation due to leaching of Cr or Fe species.
On the contrary, catalytic performances of EC4YIG and EC5YIG possessing higher Cr amounts were attributed to their high catalytic stabilities during the reaction. These results suggested that Er and Cr species were either included into the YIG cubic lattice or the particles of these species were amorphous or too small to be detected by XRD.
2.5. Morphological and Surface Properties
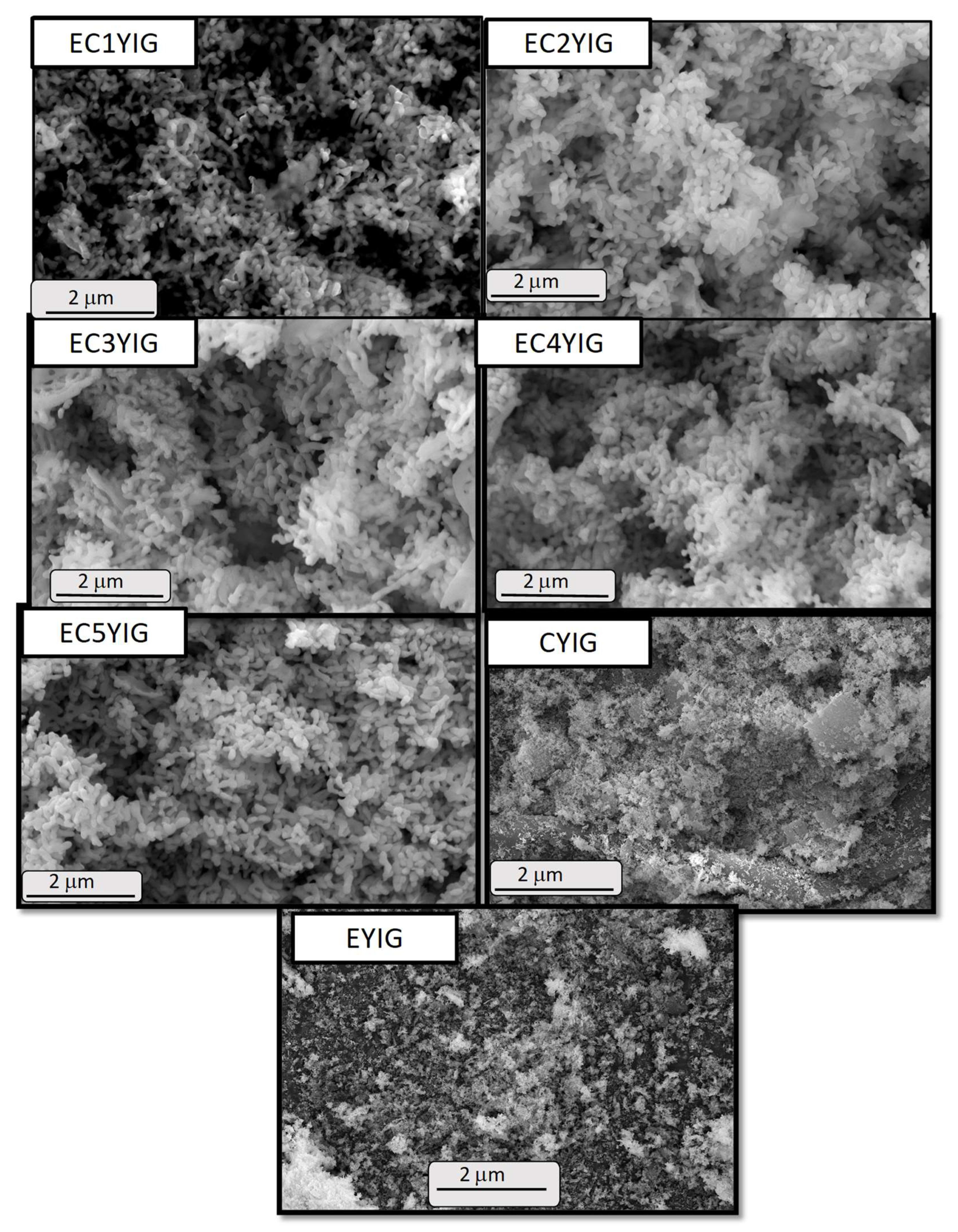
The morphological and structural features of the spent yttrium iron garnet ferrites were assessed by SEM-EDS and TEM measurements. Figure 6 shows well defined particles for all the spent solids. The former YIG sample displayed rod shaped particles with smooth surface morphology, as expected for fresh yttrium iron garnet ferrites ([2,8,39] and references herewith). This illustrated the fact that the YIG particles were not damaged during the catalytic runs, independent of the presence of Cr and Er. Some of these small particles tended to agglomerate, increasing their densification in some areas. Contrarily, EDS images exhibited the elemental compositions and distributions for the samples whose behaviors differed markedly among EYIG, CYIG and ECYIG spent samples (Figure 7a). Accordingly, all the spent samples presented compositional percentages of Y, Fe and O that suggested a uniform distribution of these elements on the solid surface. This was sound proof of the lack of impurities in the composition of the original fresh garnets, before the catalytic test.
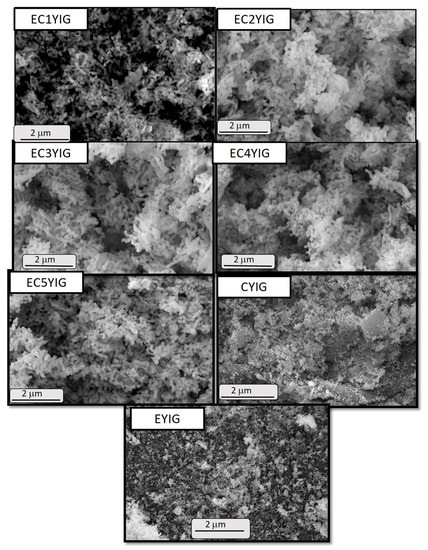
Figure 6.
SEM micrographs of the spent yttrium iron garnet ferrites. Reaction conditions: EB to H2O2 molar ratio of 1 using 1.3 mol of acetone as solvent, temperature of 50 °C and a catalyst mass of 50 mg within 360 min of reaction.
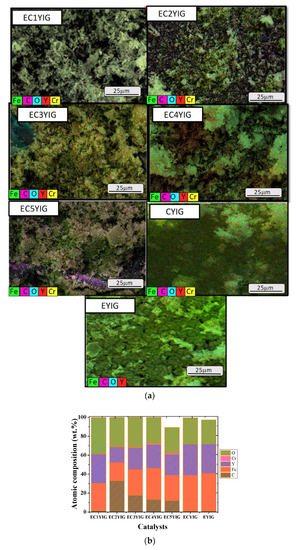
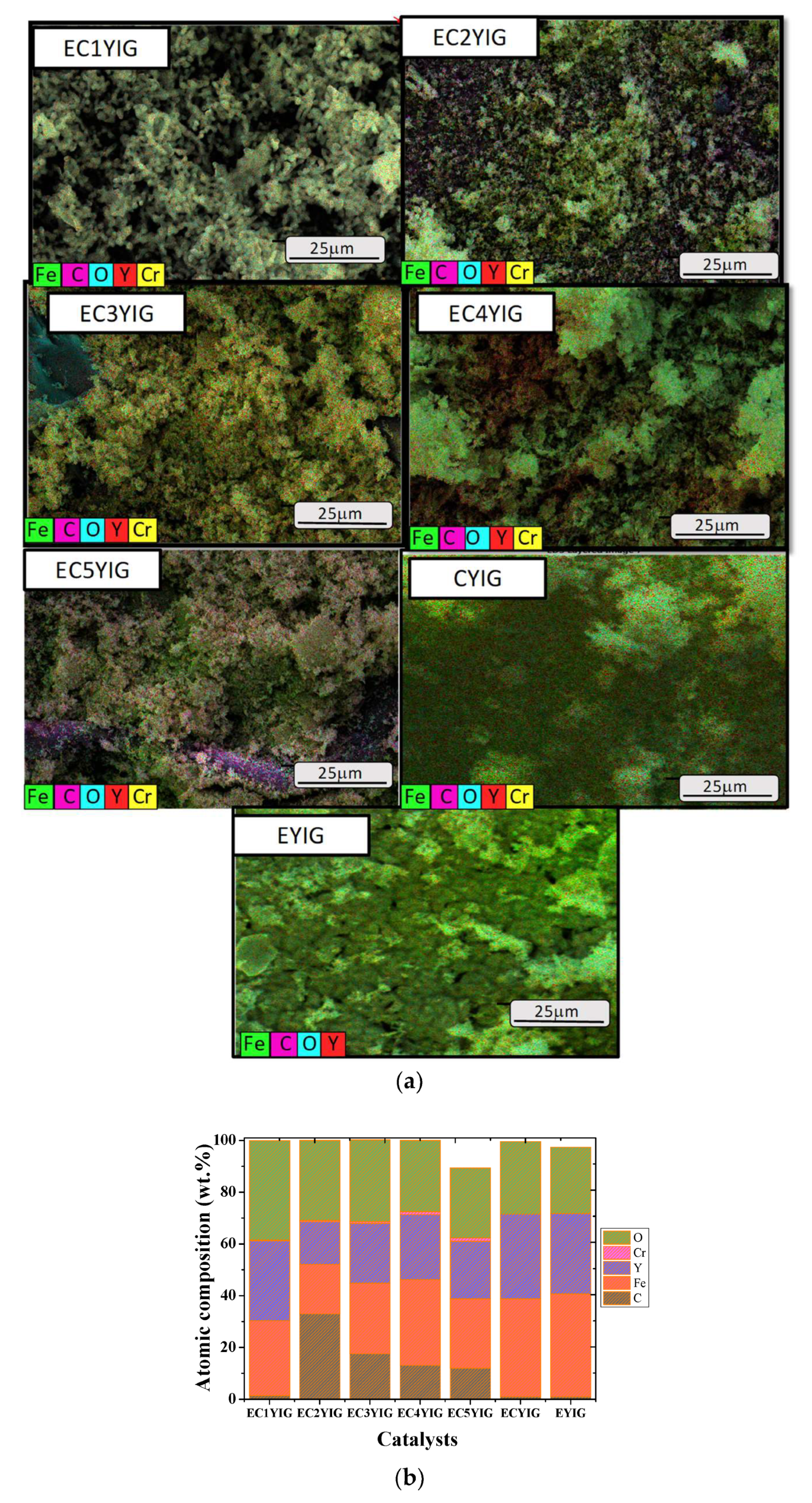
Figure 7.
(a) Elementary maps and secondary electron images convolution. (b) Composition taken from EDS spectra of the spent yttrium iron garnet ferrites. Reaction conditions: EB to H2O2 molar ratio of 1 using 1.3 mol of acetone as solvent, temperature of 50 °C and a catalyst mass of 50 mg within 360 min of reaction.
Furthermore, carbon was detected in the EDS scans for all solids, which directly corresponded to the adsorbed hydrocarbons e.g., ethylbenzene, oligomers, benzaldehyde, among others, as evidenced by the functional groups in the FTIR measurements.
Small agglomerates of particles have high amounts of carbon especially if samples possessing low Cr amounts are taken into account. This can be ascribed to Cr ion accumulation/segregation on the solid surface generating sites where carbon adsorption is prevalent. Particularly, the EDS image of CYIG (Figure 7a) evidenced the C species adsorbed on the solid surface, as well as the agglomerates of particles with rough surfaces. These particles appeared to contain only Fe, Y and O, that is to say they lacked Cr species, indicative of leaching and explaining the poor catalytic performance of the sample in the oxidation reaction. In the case of EYIG, the Fe/(Fe + Y) ratio was of 0.22, which indicated an enrichment of Fe on the solid surface, inconsistent with the expected Fe/(Fe + Y) ratio of 0.55 [5,8]. This effect was likely due to the leaching of Fe species during the catalytic runs deactivating the solid. In addition, Er was not visible on the sample surface since Er ion distribution on the dodecahedral sites in the structure was likely.
For ECYIG samples possessing Cr contents lower than 3%, the Fe percentages based on the Fe/(Fe + Y) stoichiometric ratios were within an error of 1–2%. However, the Cr percentages were lower than the theoretical calculations of a 1–3% range for all E1CYIG, E2CYIG and E3CYIG samples. This fact, associated with that of the formation of the rough particle clusters, evidenced the deactivation of solids by Cr being leached out of the YIG structure during the catalytic runs. Another point was that both Cr and Fe did not remain well dispersed on the solid surface and the appearance of C in high amounts (Figure 7b) revealed that there was a strong adsorption of carbon species on the Fe active sites from reactant and products during the reaction. On the contrary, negligible effects on the morphologies of the EC4YIG and EC5YIG spent samples (Figure 6) were depicted, except for low amounts of Cr and large carbon amounts for the former samples.
One particular particle of EC5YIG appeared to primarily contain Fe with a small amount of Cr, consistently confirming the presence of both metals in the solid structure. It is worth mentioning that the expected Y3+ and Fe3+ molar ratio was of 3/5 for YIG but as the Cr3+ substitution increased, its percentage experienced a drop. The implication of these observations on the composition of the sample and valence state is discussed later, when the XPS spectra are analyzed. It is possible that there were several factors explaining the best performance of EC5YIG but the stability of Cr and Fe leaching was the dominant factor responsible for the high activity observed in the sample.
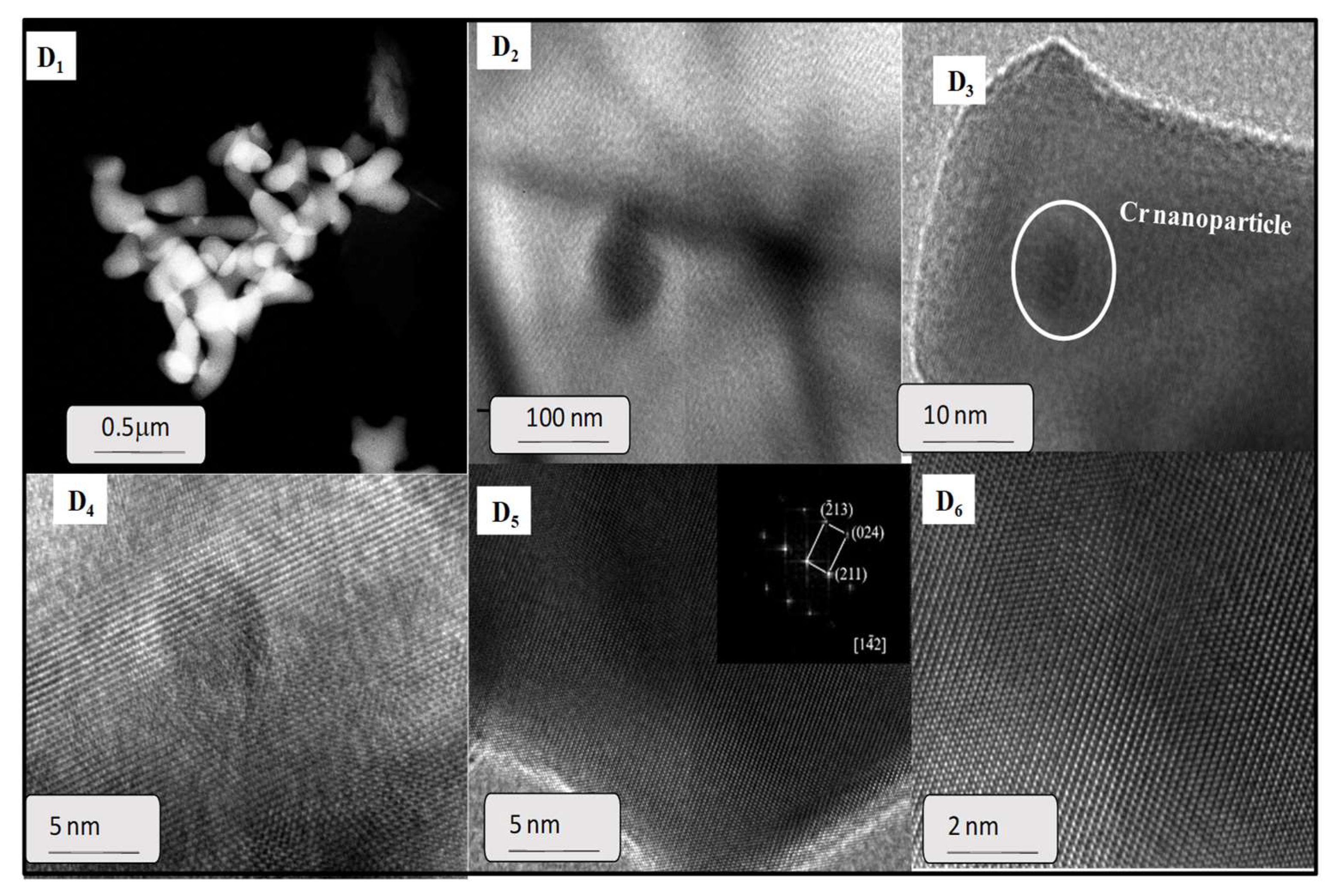
TEM images also revealed the morphology and microstructure of a representative spent yttrium iron garnet ferrite (Figure 8). It is clearly observed that the typical TEM micrograph of spent EC5YIG sample consisted of rod like nanoparticles, some of them being agglomerated (Figure 8D1). This was consistent with the morphological features of the garnets assessed by SEM analyses [15,39,50]. Some of these regions appeared with isolated nanoparticles, as shown in Figure 8D2.
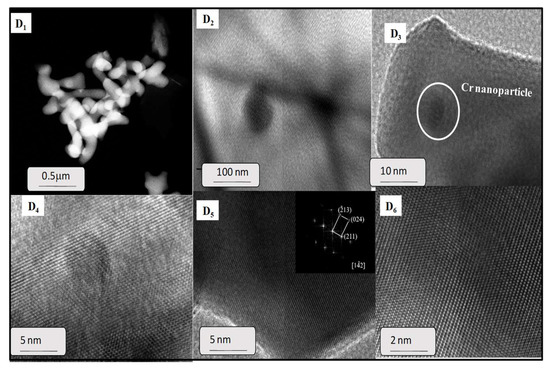
Figure 8.
TEM images of the EC5YIG spent sample (D1,D2,D3,D4,D5,D6) after the catalytic test. The high magnification HRTEM images are accompanied with fast Fourier transform (FFT) where the crystal planes are shown to be in the (142) direction in the included (D5). Reaction conditions: EB to H2O2 molar ratio of 1 using 1.3 mol of acetone as solvent, temperature of 50 °C and a catalyst mass of 50 mg within 360 min of reaction.
The HRTEM images showed that these nanoparticles were crystalline (Figure 8D3) having small sizes. This was in line with the crystallite size estimated by XRD measurements. Of importance, the agglomeration of the particles may have been a result of the magnetic interaction between nanoparticles during the TEM measurements but the piling up of the particles might have been due, to some extent, to the leaching effects occurring during the catalytic test. Furthermore, the hypothesis that the agglomeration of the EC5YIG was a consequence of blur, owing to being off the focal plane, cannot be neglected.
As revealed by XRD, the relative crystallinity of the samples resulted in well-defined lattice fringes owing to their polycrystalline nature (Figure 8D4). Moreover, the fringe d-spacing of the lattice planes was obtained from the bright field high resolution HRTEM micrograph (Figure 8D5).
Remarkably, the lattice spacing of 0.26 corresponded to the crystallographic plane of Cr2O3 segregated nanoparticles, in line with the findings in [51]. The fringes associated with a certain region of the solid showed lattice spacings of 0.277 and 0.250 nm, corresponding to the (420) and (422) planes of the YIG garnets. In addition, the finite Fourier transform (FFT) method in the figure inset of center right shows the clear lattice fringes, confirming the polycrystalline nature of the sample (Figure 8D5 inset and Figure 8D6).
Thus, SEM-EDS and TEM results illustrated that the YIG structure was retained after the catalytic test and some Cr oxide was segregated from the EC5YIG sample but in a lower amount and having no obvious influence on the catalytic performance of the solid. On the other hand, the relatively low catalytic activity of the samples with lower Cr amounts could be due to their having less resistance against Cr leaching, as shown by the SEM-EDS results.
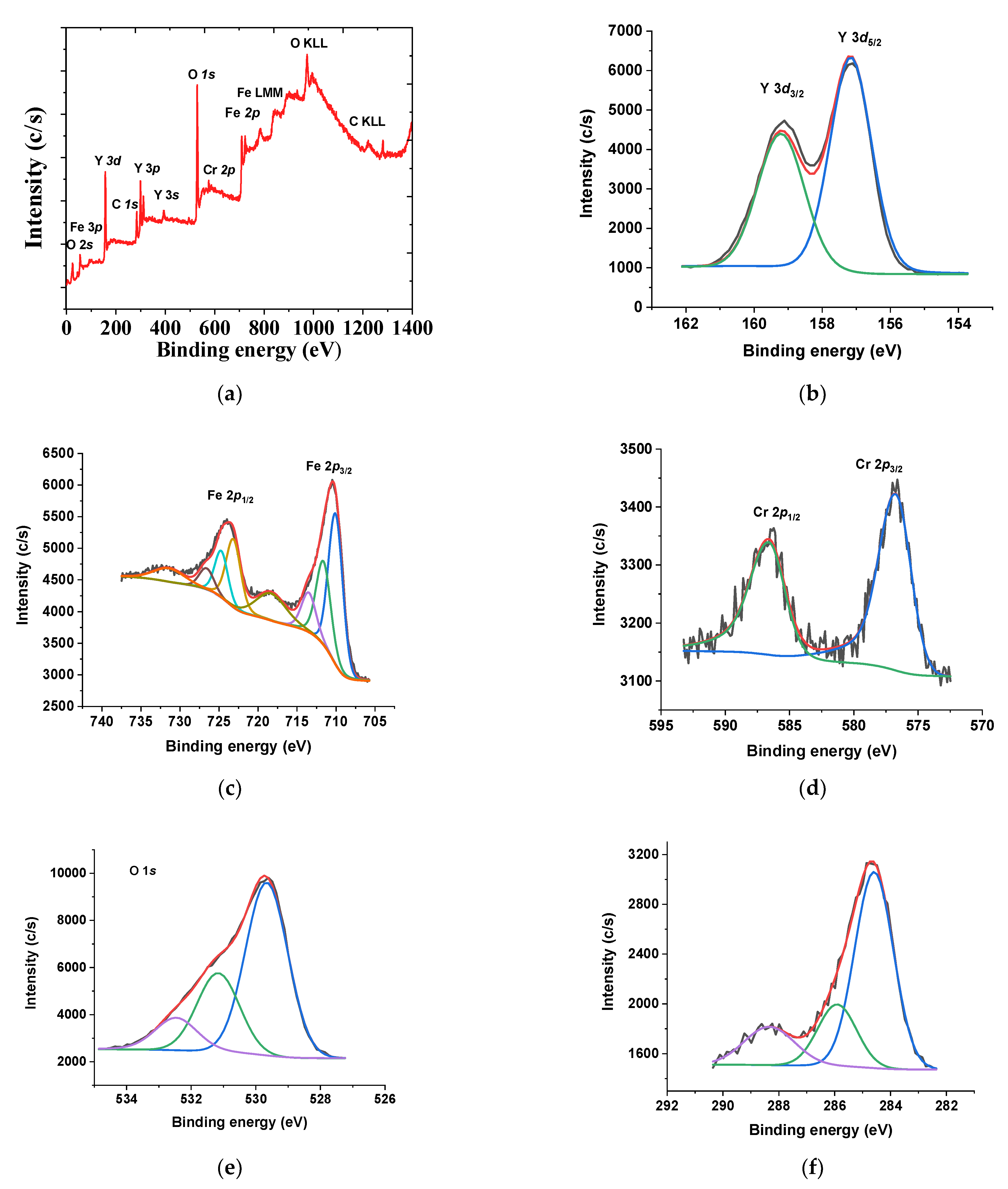
XPS analyses were performed to study the chemical state and surface elemental composition of the selected spent garnets (Figure 9). The survey spectrum of YIG garnet depicted the characteristic peaks of the O 1s, C 1s, Cr 2p, Y 3d and Fe 2p core levels (Figure 9a), as an indication of the presence of the constituent elements on the surface of the garnet. The curve-fitting parameters corresponding to the high resolution core level spectra are shown in Table 3.
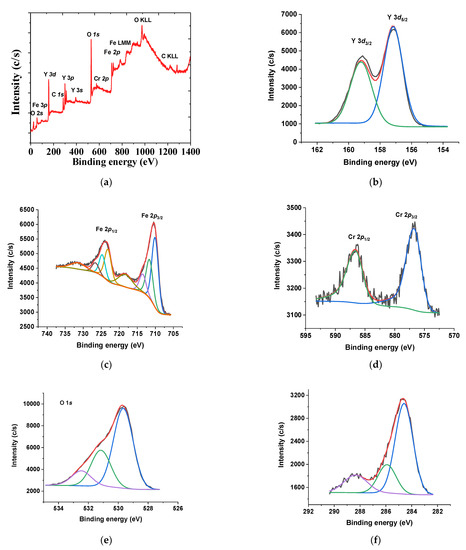
Figure 9.
(a) XPS survey spectrum, (b) Y 3d, (c) Fe 2p (d) Cr 2p, (e) O 1s and (f) C 1s core levels for spent EC1YIG samples. Reaction conditions: EB to H2O2 molar ratio of 1 using 1.3 mol of acetone as solvent, temperature of 50 °C and a catalyst mass of 50 mg within 360 min of reaction.

Table 3.
Binding energies values (in eV) of the constituent elements of the studied catalysts and Y/Fe and Cr/C atomic ratios determined by XPS.
The Y 3d core-level spectrum was fitted in a doublet of Y 3d5/2 and Y 3d3/2 components (Figure 9b). The corresponding binding energies of 157.1 eV and 159.1 eV were due to Y3+ ions in dodecahedral position certifying the maintenance of the YIG structure [37,50]. The Y 3d core-level of the fresh garnet was similar to that of the spent solids, as illustrated in a previous work [35]. Besides, the Fe 2p core level was resolved into two components, due to the multiplet splitting phenomena corresponding to the Fe 2p3/2 and Fe 2p1/2 doublet (Figure 9c). The deconvolution of the Fe 2p3/2 main peak showed three contributions at 710.0 and 711.6 eV assigned to Fe3+ in different co-ordinations [5,35,36]. The doublet Fe 2p1/2 showed a similar curve fitting. A satellite peak at 718.3 eV indicated the existence of Fe3+ ions on the solid surface and in the extra-framework [37]. There were significant BE shifts for the samples studied (Table 3). In agreement, EPR measurements suggested the occurrence of Fe3+ in either octahedral sites of the YIG garnet structure or extra-framework α-Fe2O3 [5]. The later phase was not detectable by XRD due to its nanometric size.
The Cr 2p core level spectrum (Figure 9d) exhibited a doublet separated by 9.9 eV due to spin–orbit coupling. That is to say, the Cr 2p3/2 and Cr 2p1/2 doublet was visible at 576.8 eV and 586.6 eV, respectively. This corresponded to the presence Cr3+ oxidation state in the garnets [51]. On the basis of existing literature, the Er 3d5/2 signal was observed at 168.7 eV as Er3+ ions [50,52]. However, the Er 3d signal was absent, as the Y 3d lines appeared in a region close to that of Er, e.g., 164–172 eV, when using Al-Kα radiation. Furthermore, the Er contents in all samples were of ca. 2%, mostly substituted in the dodecahedral sites before being occupied by the Y position and, thus, the identification of Er on the surface, either by XPS or EDS, was hardly observed.
The O 1s core levels spectra clearly displayed contributions at 529.7, 531.4 eV and 532.9 eV for all solids (Figure 9e). Importantly, the main and most intense peak at 529.7 eV came from the lattice oxygen of the Fe−O and Y−O bonds [36,37,50]. At 532.9 eV, both surface hydroxyl group and adsorbed water molecules appeared concomitantly with the C–OH and/or C–O–C groups, as shown previously [5,36].
The C 1s core level spectra were decomposed in three contributions (Figure 9f) that corresponded to carbon atoms in different functional groups coming from the adsorbed carbon species during the reaction. For instance, the main functional groups appeared as a prominent peak from C-C/C=C bond groups (284.8 eV), most probably from ethylbenzene or acetophenone adsorbed on the solid surface, in addition to adventitious carbon [5]. Another contribution was ascribed to the C-OH groups (285.8 eV). This observation was in agreement with a previous study that demonstrated the adsorption of these compounds after the reaction [5,53]. Furthermore, the deconvoluted XPS spectra of C 1s (binding energy at 284.7 eV) and O 1s (binding energy at 531.47 eV) confirmed these assumptions.
C-O groups along with surface carbonates (288.8 eV) were identified, which implied the adsorption of ethylbenzene, oligomers, benzaldehyde or carboxyl acid on the solid surface. Literature reports that carbonate species interact easily with trivalent lanthanides, such as Y3+ ions, to form surface lanthanide carbonates having BE values in the 288.5–290.0 eV range [5].
Furthermore, the surface atomic composition in atomic % of CYIG sample was 38.06, 46.45, 1.06, 5.63 and 8.79% for C, O, Cr, Fe and Y, respectively. Hence, the surface Y/Fe atomic ratio for CYIG was found to be close to 1.5. Assuming that the atomic Y/Fe ratios of the spent Cr-containing YIG samples were of ca. 1.1, it seemed that there was an enrichment of Fe on the surface, since the atomic Y/Fe ratio determined by ICP-OES was of 0.6. This was due to the segregation of α-Fe2O3 as suggested by EPR and XPS. When associating these data with the Cr/C ratio of ca.0.02 for CYIG, the Cr amounts increased on the surface as a result of Cr leaching and strong carbon adsorption on the solid surface. This could be the reason for the deactivation of EC1YIG, EC2YIG and EC3YIG catalysts within 360 min of reaction, as depicted previously.
These XPS results suggested the existence of Cr and C species on solid surfaces in good agreement with SEM-EDS and EDS results. Indeed, the Cr loading amounts verified on the solid surface confirmed its leaching from the YIG garnet structure during the catalytic runs, which explained the inferior catalytic performance for samples possessing Cr contents lower than 4%.
Moreover, the stability of yttrium iron garnet ferrite possessing Cr content of 5% made it a promising catalyst for EB oxidation, compared with other catalysts evaluated in the title reaction [5,16,53].
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
Iron(III) nitrate nonahydrate (Fe(NO3)3·9H2O, yttrium nitrate hexahydrate (Y(NO3)3·6H2O, erbium(III) nitrate pentahydrate (Er(NO3)3·5H2O) and chromium(III) nitrate hexahydrate (Cr(NO3)3.9H2O),acetone (CH3COCH3 99.0%) and aqueous ammonium solution were purchased from Vetec (Vetec, São Paulo, Brazil). Ethylbenzene (C6H5C2H5 anhydrous, 99.8%) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2, 30 wt.% in water) were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich ((Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany). All reagents were purchased from commercial suppliers and used without further purification.
3.2. Synthesis of the YIG Catalyst
The Yttrium iron garnets (YIG) were synthesized by the sol-gel method in the same conditions as described elsewhere [8,10,11]. The method consisted of the simultaneous addition of iron (III) nitrate nonahydrate (Fe(NO3)3·9H2O, 0.01 mol) and yttrium nitrate hexahydrate (Y(NO3)3·6H2O, 0.006 mol) in distilled water (25 mL). After stirring, the solutions turned from cloudy to a transparent color and the amount of the iron was adjusted to the desired molar ratio of iron to yttrium of 5:3. Further, anhydrous citric acid (C6H8O7, 0.1 mol) was incorporated to the resulting solution and stirring was continued for 3 h to chelate Y and Fe ions and simultaneously reduce some Fe(III) to Fe(II) ions. The following step consisted of heating the solution at 95 °C under vigorous stirring for an additional 5 h to remove water in the solution to form a gel. Aging of the solution was performed for 48 h at room temperature, and then the gel obtained was recovered by centrifugation with subsequent drying at 150 °C at 0.5 °C. min−1 for 36 h. The sample was later annealed for 1 h at 350 °C with a heating rate of 1 °C min−1, and then calcined at 900 °C in air for 2 h. The reference solid having the composition of Y3Fe5O12 was denoted as YIG sample.
3.3. Synthesis of the Er and Cr Containing Yttrium Iron Garnet Ferrites
The introduction of Er and Cr in YIG was performed during the synthesis in the presence of erbium (III) nitrate pentahydrate (Er(NO3)3·5H2O) and chromium (III) nitrate hexahydrate (Cr(NO3)3.9H2O) precursors. Briefly, aqueous solutions of yttrium, iron, erbium and chromium nitrates were mixed dropwise and vigorously stirred. Subsequently, citric acid solution was added and the pH of the solution was 2. Then, the solution was kept under constant stirring and heated at 95 °C for 5 h until the formation of a yellow-green gel. Afterwards, the gel formed was dried and calcined at 900 °C under the same conditions mentioned above. The corresponding catalysts were generally referred to herein as Y3(Er0.02 Fe5Cr1−x)O12, where x refers to the numbers 0, 0.01, 0.02, 0.03, 0.04 or 0.05. The erbium lanthanide x value was fixed at 0.02. The catalysts possessing only Cr or Er were named as EYIG and CYIG for Y2.98Er0.02Fe5O12 and Y3Fe4.98Cr0.02O12, respectively.
The Cr-containing catalysts were denoted as EC1YIG, EC2YIG, EC3YIG, EC4YIG, EC5YIG referring to the Y2.98Er0.02Fe4.99Cr0.01O12, Y2.98Er0.02Fe4.98Cr0.02O12, Y2.98Er0.02Fe4.97Cr0.03O12, Y2.98Er0.02Fe4.96Cr0.04O12 and Y2.98Er0.02Fe4.95Cr0.05O12. The detailed description of the catalysts is summarized in Table 1.
3.4. Characterizations
Raman spectra of selected spent samples were collected with a LabRAM HR Horiba spectrometer. The thermoelectrically cooled charge-coupled device (CCD) was used as detection system at 785 nm excitation wavelength. A 50 times objective lens was used during the experiments. The measurements were conducted using a resolution of 2 cm−1 with 8 accumulations per second for each spectrum.
The surface functional groups of the spent garnet were investigated by Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) on a Bruker Vertex 70 V apparatus (Bruker, Rheinstetten, Germany). The spectra were recorded in transmittance mode in the range of 4000–400 cm−1 using a resolution of 4 cm−1. Before the measurements, samples diluted in KBr pellets were prepared using a ratio of 1:100 for sample: KBr.
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS) element mappings of the spent catalysts were obtained in a INSPEC Quanta 200 FEG electron microscope (FEI Quanta, Hillsboro, OR, USA) at 2 kV, which was equipped with and EDS system. The catalysts were coated by sputtering of a thin silver layer, prior to the analyses.
The morphology and mean particle size of the spent garnets were examined by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) in a Tecnai 20 FEI microscope (FEI Quanta, Hillsboro, OR, USA) operating at 200 kV. Previously, the catalysts were ultrasonically suspended in acetone with the final suspensions later being deposited onto a grid with amorphous carbon film.
Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectra were recorded on a Bruker spectrometer (Bruker, Rheinstetten, Germany) operating at X band microwave frequencies at 9.5 GHz. Prior to the measurements, the samples were placed in an EPR quartz tube under helium flow at room temperature, and then transferred to the spectrometer cavity. The g factor was determined using DPPH as the standard from the integrated X-band spectra.
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis was performed with a Physical Electronics VersaProbe II Scanning XPS Microprobe (Minneapolis, MN, USA) equipped with a monochromatic X-ray Al Kα radiation at a vacuum of 10−7 Pa. The binding energies were referenced to the C 1s peak from adventitious carbon with at 284.8 eV.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of the samples were recorded with 2θ values from 20 to 80° on a X-ray diffractometer Shimadzu XRD6000 (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) with Cu Kα radiation source (λ = 1.540 Å). A nickel filter was used and a current of 130 kV, along with a voltage of 25 mA, applied. The crystallite sizes were calculated through the Scherrer equation from the prominent 2θ = 35.5° (420) reflection [5,11].
The chemical analyses of Fe, Er, Y and Cr contents were determined with inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES) in a Varian apparatus. About 200 mg of catalysts was dissolved in aqua regia solution and heated to evaporate the solvent. Then, the residual powder was diluted in nitric acid solution to perform the analyses.
3.5. Catalytic Tests
The catalytic activity of the solids was conducted in the liquid phase oxidation of ethylbenzene (EB) reaction using H2O2 as oxidant. About 50 mg of the catalysts were placed in a batch glass reactor surrounding by coated body jacket and equipped with a reflux condenser in a water bath. The EB oxidation reaction was initiated by introducing 1 mol of ethylbenzene (C6H5C2H5) and 1 mol of diluted hydrogen peroxide (H2O2, 30 wt.% in water) using 1.3 mol of acetone as solvent (CH3COCH3) to the batch reactor under stirring. Caution: mixing high concentrated H2O2 with acetone could lead to explosion. The use of a solvent with weak polarity was necessary to increase the reactivity of EB, in comparison with the solvent-free reaction conditions [18,21,51]. The temperature was set at 50 °C and the reaction was carried out for 6 h under stirring. The composition of reactants and products were determined removing aliquots of the reaction mixture and performing chromatographic analyses using a GCrom gas chromatograph coupled with a flame ionization detector (FID). The ethylbenzene conversions were obtained by the following equation [21,22]:
where EBin and EBout correspond to the inlet and outlet concentration of ethylbenzene, respectively.
Selectivity to the products S (i) was calculated according to the following equation [54,55]:
where mols product (i) formed and molsEBconsumed correspond to the mols of a specific product i formed and ethylbenzene consumed in the reaction, respectively.
Blank tests in the absence of the catalysts were carried out in the reaction system under the same conditions as the catalytic tests with conversion values lower than 3%. The catalyst reusability experiments were conducted over the most active solid in 1–5 time-scaled runs. Previously, about 50 mg of fresh catalyst was added in the reactor for the first catalytic run and then filtered off, washed, dried and included again in the presence of the reactants for the recyclability experiments. To maintain the same catalyst mass during the various cycles of use, about 25 mg of the catalysts were added to the previous system, if one considered the expected loss during the experiments. The carbon balance was 100%.
4. Conclusions
The Y3+ ions in the dodecahedral sites of YIG garnets were partially replaced by Er3+ ions, stabilizing the structure, during the EB oxidation reaction in the presence of H2O2 as oxidant. When adding distinct amounts of Cr in both tetrahedral and octahedral sites of the garnet that had before been occupied by Fe3+ ions, the EB conversions increased almost linearly to the Cr amounts ranging from 0–5%. Thus, Cr3+ ions acted as electronic promoters to increase the oxidation rate of the Fe3+/Fe4+ active species to transform the EB molecule, especially for Cr amounts more than 4%.
In view of the high stability of EC5YIG catalyst possessing the highest Cr amount, the major activity among the catalysts studied was observed to be due to the Fe3+ active species as Cr3+ continuously transferring electrons to Fe during the reaction, allowing reuse without Cr leaching out of the solid. The catalytic properties of the iron containing garnets in the study were improved by adding chromium to the YIG structure with the consequent enhancement of EB oxidation conversion.
Author Contributions
J.V.C.d.C., R.d.C.F.B., G.D.S., Y.G., S.T.-C., A.J.R.C. and J.M.S. performed the experiments and methodology; A.C.O., E.P.-H., R.P.-G., E.R.-C. and E.R.-A. analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript; G.D.S. and R.P.-G. designed and performed the experiments and analyzed the data, as well. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We are grateful to the CNPq Grant (406629/2018-8). E.R.C. and E.R.A thank to project RTI2018-099668-BC22 and PID2021-126235OB-C32 of Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades, and project UMA18-FEDERJA-126 and P20_00375 of Junta de Andalucía and FEDER funds.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The collaborative assistance of Central Analítica da Universidade Federal do Ceará with the SEM-EDS analyses is acknowledged. J.V.C. thanks CAPES for the master scholarship. RCFB is grateful to the CAPES for financial support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Norkus, M.; Laurikenas, A.; Vistorskaj, D.; Mazeik, K.; Baltrunas, D.; Skaudzius, R.; Beganskiene, A.; Kareiv, A. Investigation of substitution effects of the first four lanthanides (La, Ce, Pr and Nd) in yttrium iron garnet. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 903, 163978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, L.R.F.; Milani, R.; Oliveira, D.M.; Guerra, Y.; Padrón-Hernández, E.; Franco, A., Jr.; Viana, B.C.; Santos, F.E.P.; Peña-Garcia, R. Competitive effect of dopants on magnetic and structural properties in yttrium iron garnet co-doped with Er and Cr. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 18584–18591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Chen, L.; Li, Z. Study on the Structure, Magnetic Properties and Mechanism of Zn-Doped Yttrium Iron Garnet Nanomaterial Prepared by the Sol-gel Method. Gels 2022, 8, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Han, Y.; Tian, M.; Huang, C.; Wang, C.; Lin, J.; Hou, B.; Su, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; et al. Promoted methane conversion to syngas over Fe-based garnets via chemical looping. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 278, 119305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo, J.V.C.D.; Pinheiro, A.L.G.; Oliveira, A.C.; de Castro, M.O.; Soares, J.M.; Padron-Hernandez, E.; Peña-Garcia, R.; Saraiva, G.D.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Rodríguez-Aguado, E. Comparison of the catalytic performance of YIG garnets and Fe-containing oxides catalysts for oxidation of ethylbenzene. Ceram. Int. 2020, 47, 6279–6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaji, U.; Chinnapaiyan, S.; Chen, S.-M.; Govindasamy, M.; Filho, J.I.O.; Khushaim, W.; Mani, V. Design and Fab-rication of Yttrium Ferrite Garnet-Embedded Graphitic Carbon Nitride: A Sensitive Electrocatalyst for Smartphone-Enabled Point-of-Care Pesticide (Mesotrione) Analysis in Food Samples. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2021, 13, 24865–24876. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.; Yan, W.; Qin, J.; Bi, L. Dysprosium Substituted Ce: YIG Thin Films for Temperature Insensitive Integrated Optical Isolator Applications. Materials 2022, 15, 1691. [Google Scholar]
- Peña-Garcia, R.; Guerra, Y.; Santos, F.; Almeida, L.; Padrón-Hernández, E. Structural and magnetic properties of Ni-doped yttrium iron garnet nanopowders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 492, 165650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, M.A.; Azis, R.S.; Osman, N.H.; Hassan, J.; Zangina, T. Structural and magnetic properties of yttrium iron garnet (YIG) and yttrium aluminum iron garnet (YAlG) nanoferrite via sol-gel synthesis. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, R.F.; Guerra, Y.; Padrón-Hernández, E.; Rodrigues, A.R.; Santos, F.E.P.; Peña-Garcia, R. Structural and magnetic properties of yttrium iron garnet nanoparticles doped with copper obtained by sol gel method. Mater. Lett. 2019, 236, 547. [Google Scholar]
- Peña-Garcia, R.; Guerra, Y.; Oliveira, D.; Franco, A.; Padrón-Hernández, E. Local atomic disorder and temperature dependence of saturation magnetization in yttrium iron garnet. Ceram. Int. 2019, 46, 5871–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.N.; Yousaf, M.; Khan, S.; Nazir, M.; Ahmad, M.; Khan, M.A. Structural and electromagnetic evaluations of YIG rare earth doped (Gd, Pr, Ho, Yb) nanoferrites for high frequency applications. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 17032–17040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakimia, F.; Fallah-Mehrjardia, M.; Golrasan, E. Yttrium Aluminum Garnet (YAG: Al5Y3O12) as an Efficient Catalyst for the Synthesis of Benzimidazole and Benzoxazole Derivatives. Chem. Methodol. 2020, 4, 234–244. [Google Scholar]
- Cerrato, E.; Gaggero, E.; Calza, P.; Paganini, M.C. The role of Cerium, Europium and Erbium doped TiO2 photocatalysts in water treatment: A mini-review. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2022, 10, 100268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, Z.Y.; Lee, K.C.; Soleimani, H.; Beh, H.G. Experimental Study of Electromagnetic-Assisted Rare-Earth Doped Yttrium Iron Garnet (YIG) Nanofluids on Wettability and Interfacial Tension Alteration. Energies 2019, 12, 3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Xi, N.; Li, G.; Dong, P.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Wang, P.; Zhao, Y. Hydrotalcite-based CoxNiyAl1Ox mixed oxide as a highly efficient catalyst for selective ethylbenzene oxidation. Mol. Catal. 2021, 508, 111579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Fang, J.; Xu, D.; Li, J.; Li, B.; Zhao, H.; Dong, Z. Multistep protection strategy for preparation of atomically dispersed Fe–N catalysts for selective oxidation of ethylbenzene to acetophenone. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2022, 12, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, G.; Hu, C. Selective ring C-H bonds activation of toluene over Fe/activated carbon catalyst. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2013, 377, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, A.L.G.; Oliveira, A.P.S.; De Sousa, F.F.; Soares, J.M.; Saraiva, G.D.; Oliveira, A.C.; Lang, R. CeFe-Based Bead Nanocomposites as Catalysts for Oxidation of Ethylbenzene Reaction. Catalysts 2018, 8, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramu, R.; Hail, W.; Wann, M.; Janmanchi, D.; Tsai, Y.-F.; Liu, C.-C.; Mou, C.-Y.; Yu, S.S.-F. Mechanistic study for the selective oxidation of benzene and toluene catalyzed by Fe(ClO4)2 in an H2O2-H2O-CH3CN system. Mol. Catal. 2017, 441, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, A.D.B.S.; Pinheiro, L.G.; Filho, J.M.; Oliveira, A. Studies on styrene selective oxidation over iron-based catalysts: Reaction parameters effects. Fuel 2015, 150, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.P.S.; Gomes, I.S.; Neto, A.S.; Oliveira, A.C.; Filho, J.M.; Saraiva, G.D.; Soares, J.M.; Tehuacanero-Cuapa, S. Catalytic performance of MnFeSi composite in selective oxidation of styrene, ethylbenzene and benzyl alcohol. Mol. Catal. 2017, 436, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavallaei, H.; Jafarpour, M.; Feizpour, F.; Rezaeifard, A.; Farrokhi, A. A Cooperative Effect in a Novel Bimetallic Mo–V Nanocomplex Catalyzed Selective Aerobic C–H Oxidation. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 3601–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, D.; Faraji, A.; Arshadi, M.; Fierro, J. Characterization and catalytic activity of a novel Fe nano-catalyst as efficient heterogeneous catalyst for selective oxidation of ethylbenzene, cyclohexene, and benzylalcohol. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2013, 372, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardeshi, S.K.; Pawar, R.Y. SrFe2O4 complex oxide an effective and environmentally benign catalyst for selective oxi-dation of styrene. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2011, 334, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachemaoui, M.; Molina, C.; Belver, C.; Bedia, J.; Mokhtar, A.; Hamacha, R.; Boukoussa, B. Metal-Loaded Mesoporous MCM-41 for the Catalytic Wet Peroxide Oxidation (CWPO) of Acetaminophen. Catalysts 2021, 11, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholdeeva, O.; Skobelev, I.Y.; Ivanchikova, I.D.; Kovalenko, K.A. Hydrocarbon oxidation over Fe- and Cr-containing metal-organic frameworks MIL-100 and MIL-101–a comparative study. Catal. Today 2014, 238, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, A.H.M.; Sousa, F.F.; Honorato, S.B.; Ayala, A.P.; Filho, J.M.; Sousa, F.W.; Pinheiro, A.N.; Araujo, J.C.S.; Nas-Cimento, R.F.; Valentini, A.; et al. Ethylbenzene to chemicals: Catalytic conversion of ethylbenzene into styrene over metal-containing MCM-41. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2010, 315, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutmann, B.; Elsner, P.; Roberge, D.; Kappe, C.O. Homogeneous Liquid-Phase Oxidation of Ethylbenzene to Aceto-phenone in Continuous Flow Mode. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 2669–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, V.K.; Thankachan, P.P.; Prasad, R. Oxidation of benzyl alcohol and styrene using H2O2 catalyzed by tetraazamacrocycle complexes of Cu(II) and Ni(II) encapsulated in zeolite-Y. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2010, 381, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annatha, H.; Manayil, J.C.; Thompson, J.; Marra, A.C.; Raja, R. Contrasting structure-property relationships in amorphous, hierarchical and microporous aluminophosphate catalysts for Claisen-Schmidt condensation reactions. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2021, 627, 118376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarinol, C.; Dimakatso, A.; Maheso, J.; Bingwa, N.; Meijboom, R. Highly tunable selectivity to benzaldehyde over Pd/ZrO2 catalysts in Oppenauer oxidation of benzyl alcohol using acetone as H-acceptor. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2021, 61, 118022. [Google Scholar]
- Tamizhdurai, P.; Narayanan, S.; Kumaran, R.; Mangesh, V.L.; Kavitha, C.; Lakshmi, N.V.; Ragupathi, C.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Ouladsman, M.; Manie, G. Catalytic activity of ratio-dependent SBA-15 supported cerium/Pt catalysts for highly selective oxidation reaction of benzyl alcohol to benzaldehyde. Adv. Powder Technol. 2021, 32, 4286–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borade, R.B.; Shirsath, S.E.; Vats, G.; Gaikwad, A.S.; Patange, S.M.; Kadam, S.B.; Kadam, R.H.; Kadam, A.B. Poly-crystalline to preferred-(100) single crystal texture phase transformation of yttrium iron garnet nanoparticles. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caland, J.; Medrano, C.P.; Caytuero, A.; Baggio-Saitovitch, E.; Litterst, F.; Soares, J.M.; Cabrera-Baez, M.; Padrón-Hernández, E.; Marques, T.; Guerra, Y.; et al. Preferential site occupancy of Ni ions and oxidation state of Fe ions in the YIG crystal structure obtained by sol-gel method. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 849, 156657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Kuanr, B.K. Magnetic and crystallographic properties of rare-earth substituted yttrium-iron garnet. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 748, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Liu, X.; Han, Y.; Kan, X.; Feng, S.; Lv, Q.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, C. Investigation of the structural and magnetic properties of Y2.8Ca0.2Fe5-Al M O12 (M = Mn and Cr, x = y + z). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 556, 169291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsenova, H.; Bludau, N.; Haag, W.O.; Karge, H.G. In situ IR spectroscopic study of the adsorption behaviour of ethylbenzene and diethylbenzenes related to ethylbenzene disproportionation over HY zeolite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1988, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Guo, C.; Ji, R.; Fang, C.; Zeng, Y. Low-temperature synthesis and microstructure-property study of single-phase yttrium iron garnet (YIG) nanocrystals via a rapid chemical coprecipitation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 125, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, S.-I.; Onodera, Y.; Yoshida, H.; Arai, M. Selective hydrogenation of acetophenone with supported Pd and Rh catalysts in water, organic solvents, and CO2-dissolved expanded liquids. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 4934–4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Song, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; He, Z.; Bai, P.; Yan, Z. High-performance benzyl alcohol oxidation catalyst: Au-Pd alloy with ZrO2 as promoter. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 537, 148059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, Y.; Niklewski, M.; Wuhn, A.; Ranke, M.W.; Weiss, W.; Woll, C.; Schologl, R. Interaction of ethylbenzene and styrene with iron oxide model catalyst at low coverages: A NEXAFS study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2000, 2, 5314–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Lv, D.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Xia, Q.; Li, Z. Enhanced Adsorption Performance of Aromatics on a Novel Chromium-Based MIL-101@Graphite Oxide Composite. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 13985–13990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momma, K.; Izumi, F. VESTA 3 for three-dimensional visualization of crystal, volumetric and morphology data. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2011, 44, 1272–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Yao, H.; Hu, J.; Cao, G.; Ji, J.; Tian, J.; Pan, J. Evolution of “Spinodal decomposition”-like structures during the oxidation of Zr(Fe,Nb)2 under subcritical environment. Scr. Mater. 2010, 187, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Yao, H.; Cheng, X.; Hu, J.; Cao, G.; Yuan, G. Oxidation behavior and chemical evolution of architecturally arranged Zr/Si multilayer at high temperature. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 399, 126205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, M.J.; Krzystek, J.; Brunel, L.-C.; Hendrickson, D.N. High-Frequency EPR Study of the Ferrous Ion in the Reduced Rubredoxin Model [Fe(SPh)4]2−. Inorg. Chem. 2000, 39, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáez, M.R.; Divakar, D.; Aranzabal, A.; González-Velasco, J.R.; Marcos, J.A.G. Catalytic oxidation of trichloroethylene over Fe-ZSM-5: Influence of the preparation method on the iron species and the catalytic behavior. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 180, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Ram, S. Optical and electron paramagnetic resonance properties of native Cr2O3 surface over CrO2. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322, 1484–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhamali, M.; Ibrahim, N.B.; Radiman, S. Oxygen vacancy-dependent microstructural, optical and magnetic properties of sol-gel Tb0.2Er1Y2.8Fe5O12 films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2000, 497, 166048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Zuo, C. Cr2O3/carbon nanosheet composite with enhanced performance for lithium ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 40243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Sharma, V.; Sarwab, A.; Kumar, A.; Surbhi; Goyal, R.; Sachdev, K.; Annapoornic, S.; Asokan, K.; Kanjilal, D. Understanding the origin of ferromagnetism in Er-doped ZnO system. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 89242–89249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.P.S.; Gomes, I.S.; Oliveira, A.C.; Filho, J.M.; Saraiva, G.D.; Soares, J.M.; Sousa, F.F.; Campos, A. Styrene Oxi-dation to Valuable Compounds over Nanosized FeCo-Based Catalysts: Effect of the Third Metal Addition. Catalysts 2017, 7, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Li, S.; Zhai, S.-R.; An, Q.-D.; Li, M.-H.; Song, Y.; Song, X.-W. Designed synthesis of multifunctional Fe3O4@SiO2–NH2@CS–Co(II) towards efficient oxidation of ethylbenzene. Mater. Res. Bull. 2014, 60, 665–673. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Liu, H.; Li, G.; Hu, C. Partial oxidation of ethylbenzene by H2O2 on VOx/HZSM-22 catalyst. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 55463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).