Kinetics of Hydrogen Evolution Reaction on Monometallic Bulk Electrodes in Various Electrolytic Solutions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trasatti, S. Work function, electronegativity, and electrochemical behaviour of metals: III. Electrolytic hydrogen evolution in acid solutions. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1972, 39, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nørskov, J.K.; Bligaard, T.; Logadottir, A.; Kitchin, J.R.; Chen, J.G.; Pandelov, S.; Stimming, U. Trends in the Exchange Current for Hydrogen Evolution. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, J23–J26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmickler, W.; Trasatti, S. Comment on “Trends in the Exchange Current for Hydrogen Evolution”. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, L31–L32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaino, P.; Juarez, F.; Santos, E.; Schmickler, W. Volcano plots in hydrogen electrocatalysis-uses and abuses. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, W.; Myint, M.; Chen, J.G.; Yan, Y. Correlating the hydrogen evolution reaction activity in alkaline electrolytes with the hydrogen binding energy on monometallic surfaces. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 1509–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Al-Attas, T.; Roy, S.; Rahman, M.M.; Ghaffour, N.; Thangadurai, V.; Larter, S.; Hu, J.; Ajayan, P.M.; Kibria, G. Seawater electrolysis for hydrogen production: A solution looking for a problem? Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 4831–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilovic, N.; Subbaraman, R.; Strmcnik, D.; Chang, K.-C.; Paulikas, A.P.; Stamenkovic, V.R.; Markovic, N.M. Enhancing the alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction activity through the bifunctionality of Ni(OH)2/metal catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 12495–12498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbaraman, R.; Tripkovic, D.; Chang, K.C.; Strmcnik, D.; Paulikas, A.P.; Hirunsit, P.; Chan, M.; Greeley, J.; Stamenkovic, V.; Markovic, N.M. Trends in activity for the water electrolyser reactions on 3d M(Ni,Co,Fe,Mn) hydr(oxy)oxide catalysts. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremariam, G.K.; Jovanović, A.Z.; Dobrota, A.S.; Skorodumova, N.V.; Pašti, I.A. Hydrogen Evolution Volcano(es)—From Acidic to Neutral and Alkaline Solutions. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubouis, N.; Grimaud, A. The hydrogen evolution reaction: From material to interfacial descriptors. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 9165–9181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auinger, M.; Katsounaros, I.; Meier, J.C.; Klemm, S.O.; Biedermann, P.U.; Topalov, A.A.; Rohwerder, M.; Mayrhofer, K.J. Near-surface ion distribution and buffer effects during electrochemical reactions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 16384–16394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faid, A.Y.; Foroughi, F.; Sunde, S.; Pollet, B. Unveiling hydrogen evolution dependence on KOH concentration for polycrystalline and nanostructured nickel-based catalysts. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2022, 52, 1819–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledezma-Yanez, I.; Wallace, W.D.Z.; Sebastián-Pascual, P.; Climent, V.; Feliu, J.M.; Koper, M.T.M. Interfacial Water Reorganization as a PH-Dependent Descriptor of the Hydrogen Evolution Rate on Platinum Electrodes. Nat. Energy 2017, 2, 17031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, W.; Zhuang, Z.; Gao, M.; Zheng, J.; Chen, J.G.; Yan, Y. Correlating hydrogen oxidation and evolution activity on platinum at different pH with measured hydrogen binding energy. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durst, J.; Siebel, A.; Simon, C.; Hasché, F.; Herranz, J.; Gasteiger, H.A. New insights into the electrochemical hydrogen oxidation and evolution reaction mechanism. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 2255–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossmeisl, J.; Chan, K.; Ahmed, R.; Tripković, V.; Björketun, M.E. PH in atomic scale simulations of electrochemical interfaces. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 10321–10325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Wang, L.; Merinov, B.v.; Goddard, W.A. Explanation of Dramatic pH-Dependence of Hydrogen Binding on Noble Metal Electrode: Greatly Weakened Water Adsorption at High pH. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 7787–7790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Garlyyev, B.; Watzele, S.A.; Sarpey, T.K.; Bandarenka, A.S. Spotlight on the Effect of Electrolyte Composition on the Potential of Maximum Entropy: Supporting Electrolytes Are Not Always Inert. Chem. A Eur. J. 2021, 27, 10016–10020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, A.; Koper, M.T.M. The Interrelated Effect of Cations and Electrolyte pH on the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction on Gold Electrodes in Alkaline Media. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 13452–13462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Rao, R.R.; You, S.; Myint, K.H.; Song, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ding, W.; Giordano, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; et al. Cation- and pH-Dependent Hydrogen Evolution and Oxidation Reaction Kinetics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 1, 1674–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taji, Y.; Zagalskaya, A.; Evazzade, I.; Watzele, S.; Song, K.-T.; Xue, S.; Schott, C.; Garlyyev, B.; Alexandrov, V.; Gubanova, E.; et al. Alkali Metal Cations Change the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction Mechanisms at Pt Electrodes in Alkaline Media. Nano Mater. Sci. 2022, in press. [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, M.C.O.; Goyal, A.; Moerland, P.; Koper, M.T.M. Understanding Cation Trends for Hydrogen Evolution on Platinum and Gold Electrodes in Alkaline Media. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 14328–14335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, G.A.; Zeledón, J.A.Z.; Gunasooriya, G.T.K.K.; Dull, S.M.; Perryman, J.T.; Nørskov, J.K.; Stevens, M.B.; Jaramillo, T.F. Acid anion electrolyte effects on platinum for oxygen and hydrogen electrocatalysis. Commun. Chem. 2022, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamy-Pitara, E.; El Mouahid, S.; Barbier, J. Effect of anions on catalytic and electrocatalytic hydrogenations and on the electrocatalytic oxidation and evolution of hydrogen on platinum. Electrochim. Acta 2000, 45, 4299–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.Q.; Liao, L.W.; Zheng, Y.L.; Kang, J.; Chen, Y.X. Temperature Effect on Hydrogen Evolution Reaction at Au Electrode. Chin. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 25, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Vasileff, A.; Qiao, S.Z. The Hydrogen Evolution Reaction in Alkaline Solution: From Theory, Single Crystal Models, to Practical Electrocatalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 7568–7579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, W.; Gasteiger, H.A.; Shao-Horn, Y. Hydrogen Oxidation and Evolution Reaction Kinetics on Platinum: Acid vs. Alkaline Electrolytes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, B1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.M.; Beck, J.R.; Lvov, S.N. Electrochemical kinetics of the hydrogen reaction on platinum in concentrated HCl(aq). Electrochem. Commun. 2015, 57, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanda, D.; Hnát, J.; Dobrota, A.S.; Pašti, I.A.; Paidar, M.; Bouzek, K. The effect of surface modification by reduced graphene oxide on the electrocatalytic activity of nickel towards the hydrogen evolution reaction. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 26864–26874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, F.; Kemppainen, E.; Dorbandt, I.; Bors, R.; Xi, F.; Schlatmann, R.; van de Krol, R.; Calnan, S. Understanding the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction Kinetics of Electrodeposited Nickel-Molybdenum in Acidic, Near-Neutral, and Alkaline Conditions. ChemElectroChem 2020, 8, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrii, O.A.; Tsirlina, G.A. Electrocatalytic activity prediction for hydrogen electrode reaction: Intuition, art, science. Electrochim. Acta 1994, 39, 1739–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divisek, J. Determination of the kinetics of hydrogen evolution by analysis of the potential-current and potential-coverage curves. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1986, 214, 615–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miousse, D.; Lasia, A.; Borck, V. Hydrogen evolution reaction on Ni-Al-Mo and Ni-Al electrodes prepared by low pressure plasma spraying. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1995, 25, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huot, J.-Y. Hydrogen Evolution and Interface Phenomena on a Nickel Cathode in 30 w/o KOH : I. Kinetics Parameters and Electrode Impedance between 303 and 363 K. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1989, 136, 1933–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, D.J.; Janssen, M.; Oezaslan, M. Effect of Monovalent Cations on the HOR/HER Activity for Pt in Alkaline Environment. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, F66–F73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Lu, J.; Zhuang, L.; Liu, P. Calculations of the exchange current density for hydrogen electrode reactions: A short review and a new equation. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2010, 644, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.J.; Ross, P.N.; Markovic, N.M. Temperature dependent surface electrochemistry on Pt single crystals in alkaline electrolytes: Part 2. The hydrogen evolution/oxidation reaction. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2002, 524–525, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, S.; Hamann, C.H. The pH-dependence of the hydrogen exchange current density at smooth platinum in alkaline solution (KOH). J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1975, 60, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.M.F.; Sequeira, C.A.C.; Macciò, D.; Saccone, A.; Figueiredo, J.L. Platinum–rare earth electrodes for hydrogen evolution in alkaline water electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 3137–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Tong, Y. Interface Coupling of Cobalt Hydroxide/Molybdenum Disulfide Heterostructured Nanosheet Arrays for Highly Efficient Hydrazine-Assisted Hydrogen Generation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 3219–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Tong, Y.; Feng, D.; Chen, P. Electronic regulation of platinum species on metal nitrides realizes superior mass activity for hydrogen production. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 622, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukaszewski, M.; Soszko, M.; Czerwiński, A. Electrochemical Methods of Real Surface Area Determination of Noble Metal Electrodes-an Overview. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2016, 11, 4442–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trasatti, S.; Petrii, O.A. Real surface area measurements in electrochemistry. Pure Appl. Chem. 1991, 63, 711–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watzele, S.; Hauenstein, P.; Liang, Y.; Xue, S.; Fichtner, J.; Garlyyev, B.; Scieszka, D.; Claudel, F.; Maillard, F.; Bandarenka, A.S. Determination of Electroactive Surface Area of Ni-, Co-, Fe-, and Ir-Based Oxide Electrocatalysts. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 9222–9230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumüller, D.; Rafailović, L.D.; Jovanović, A.Z.; Skorodumova, N.V.; Pašti, I.A.; Lassnig, A.; Griesser, T.; Gammer, C.; Eckert, J. Hydrogen Evolution Reaction on Ultra-Smooth Sputtered Nanocrystalline Ni Thin Films in Alkaline Media—From Intrinsic Activity to the Effects of Surface Oxidation. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
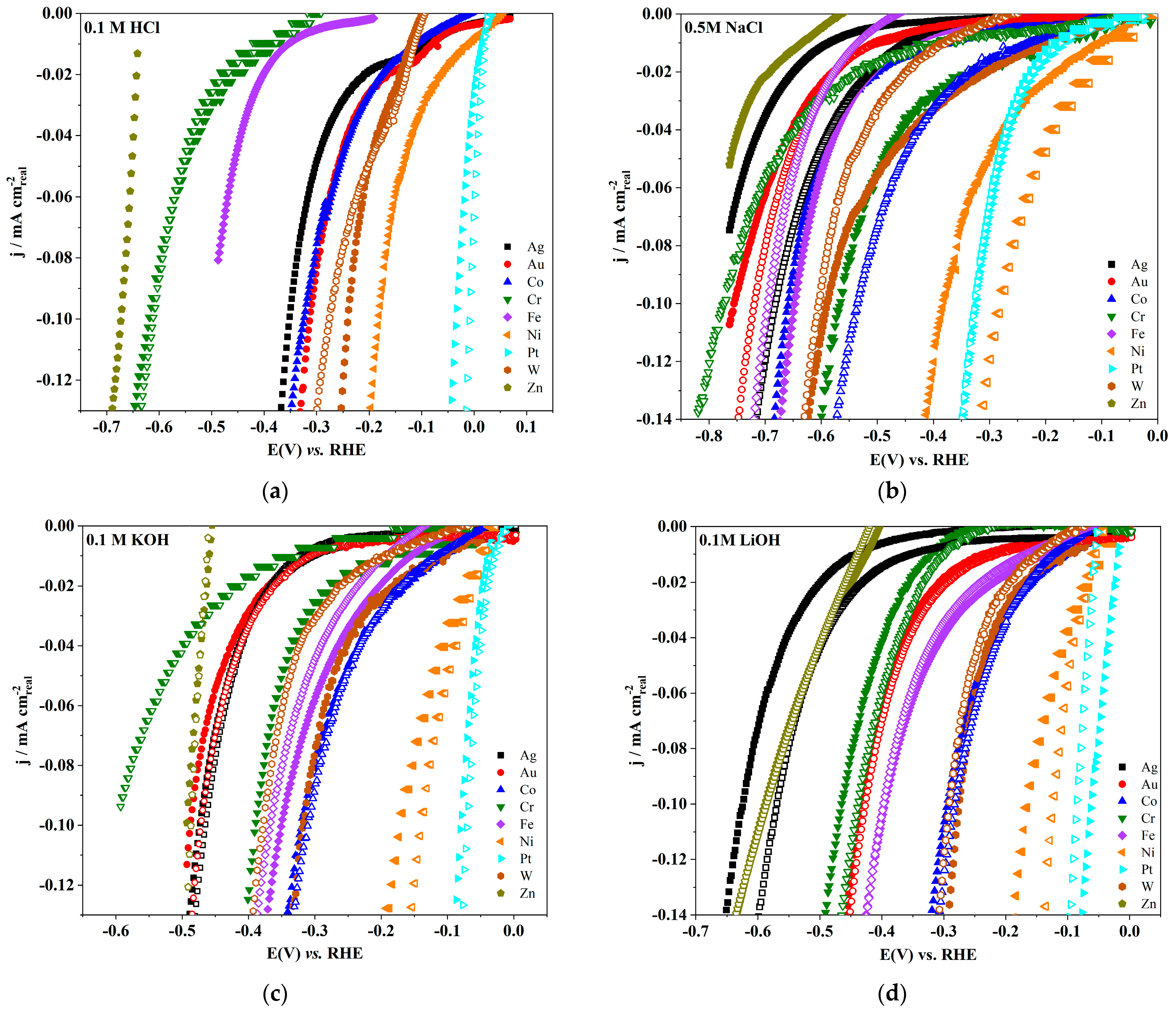
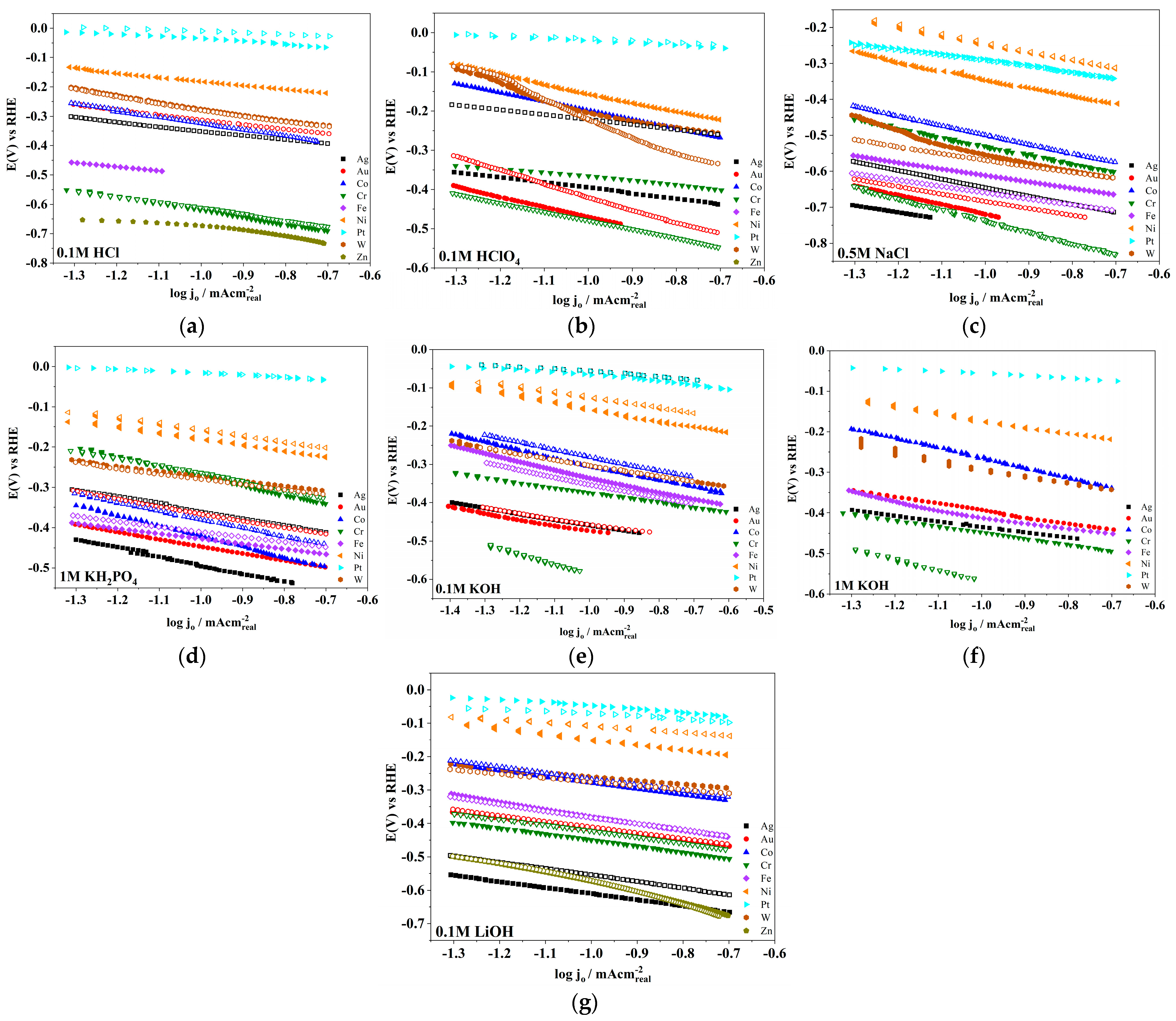
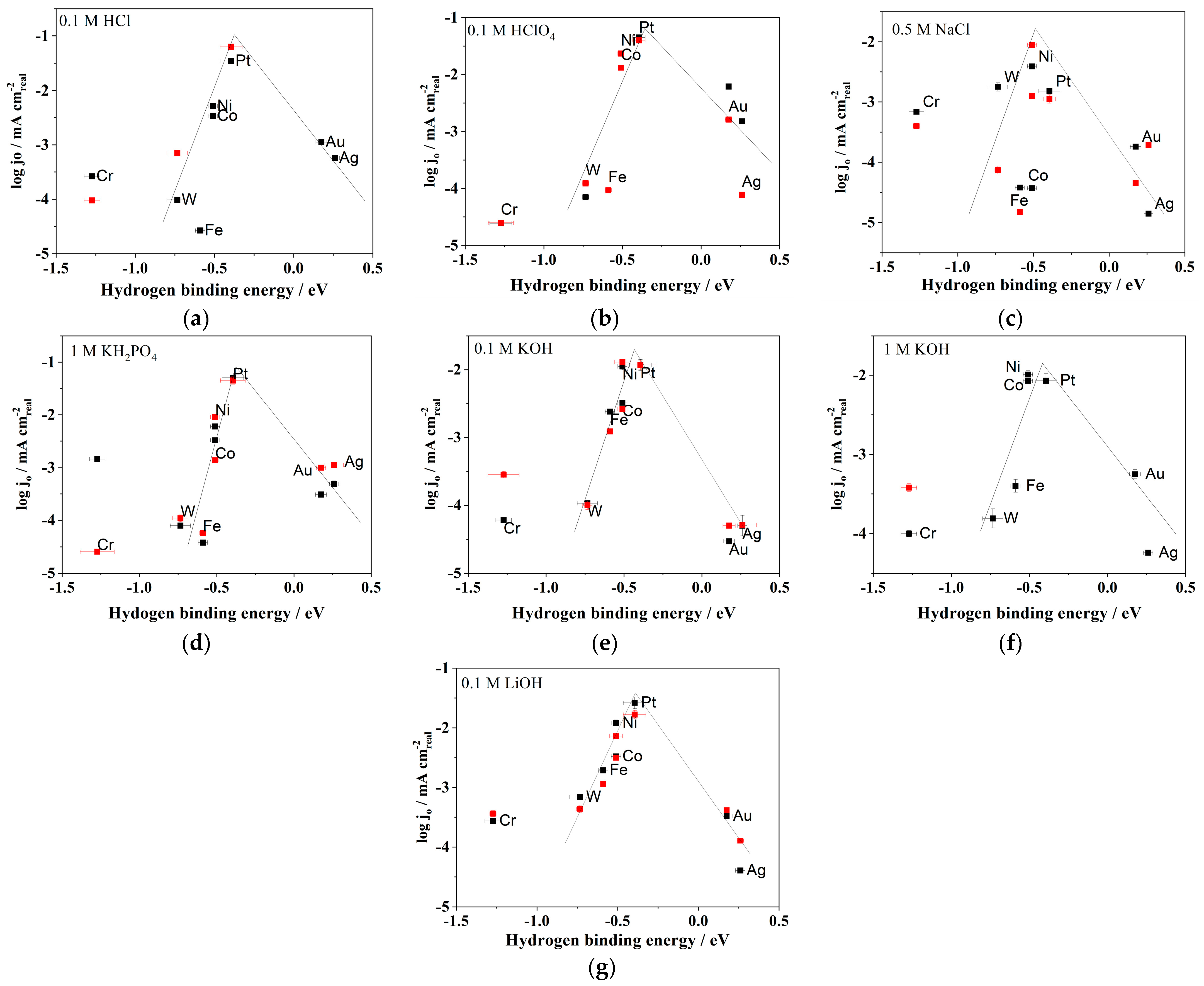
| Electrode | log(jo/mA cm−2) | Tafel Slope (mV dec−1) | Electrolyte | Temperature | Surface Area Used | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag | −(4.11 ± 0.01) | −127 | 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4 | rt | real | this work |
| Au | −(2.79 ± 0.02) | −263 | 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4 | rt | real | this work |
| Au(100) | −4.3 | varies gradually from −60 to −120 mV dec−1 | 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4 | NM | geo | [25] |
| Au(110) | −4.52 | |||||
| Au(111) | −3.6 | |||||
| Au (pc) | −3.85 | |||||
| Au | −2.6 | −118 | 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4 | 278 K | geo | [25] |
| Au | −2.55 | −128.1 | 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4 | 283 K | geo | [25] |
| Au | −2.12 | −133.3 | 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4 | 293 K | geo | [25] |
| Au | −2 | −137.6 | 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4 | 303 K | geo | [25] |
| Au | −1.72 | −146.7 | 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4 | 313 K | geo | [25] |
| Au | −1.66 | −136 | 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4 | 323 K | geo | [25] |
| Co | −(1.88 ± 0.01) | −227 | 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4 | rt | real | this work |
| Cr | −(4.6 ± 0.08) | −102 | 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4 | rt | real | this work |
| Fe | −(4.03 ± 0.02) | −144 | 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4 | rt | real | this work |
| Ni | −(1.63 ± 0.02) | −248 | 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4 | rt | real | this work |
| Pt | −(1.4 ± 0.04) | −53 | 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4 | rt | real | this work |
| Pt(111) | −0.68 | −74 | 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4 | NM | [26] | |
| Pt(111) | 0.17 | - | 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4 | NM | [27] | |
| W | −(3.91 ± 0.02) | −85 | 0.1 mol dm−3 HClO4 | rt | real | this work |
| Electrode | log(jo/mA cm−2) | Tafel Slope (mV dec−1) | Electrolyte | Temperature | Surface Area Used | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag | −(3.24 ± 0.03) | −156 | 0.1 mol dm−3 HCl | rt | real | this work |
| Au | −(2.95 ± 0.02) | −160 | 0.1 mol dm−3 HCl | rt | real | this work |
| Co | −(2.47 ± 0.03) | −219 | 0.1 mol dm−3 HCl | rt | real | this work |
| Cr | −(3.58 ± 0.03) | −240 | 0.1 mol dm−3 HCl | rt | real | this work |
| Fe | −(4.57 ± 0.01) | −139 | 0.1 mol dm−3 HCl | rt | real | this work |
| Ni | −(2.29 ± 0.04) | −140 | 0.1 mol dm−3 HCl | rt | real | this work |
| Pt | −(1.46 ± 0.05) | −77 | 0.1 mol dm−3 HCl | rt | real | this work |
| Pt | 0.2 | - | 1 mol dm−3 HCl | NM | geo | [28] |
| Pt | 0.079 | - | 7.72 mol dm−3 HCl | NM | geo | [28] |
| W | −(4.01 ± 0.03) | −84 | 0.1 mol dm−3 HCl | rt | real | this work |
| Electrode | log(jo/mA cm−2) | Tafel Slope (mV dec−1) | Electrolyte | Temperature | Surface Area Used | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag | −(4.24 ± 0.03) | −134 | 1 mol dm−3 KOH | rt | real | this work |
| Ag | −(4.3 ± 0.15) | −139 | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | rt | real | this work |
| Ag | −(4.3 ± 0.3) | −(134 ± 9) | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | NM | geo | [5] |
| Au | −(3.25 ± 0.06) | −175 | 1 mol dm−3 KOH | rt | real | this work |
| Au | −(4.53 ± 0.01) | −134 | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | rt | real | this work |
| Au | −(3.2 ± 0.6) | −(168 ± 9) | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | NM | [5] | |
| Au | −2.85 | −167.7 | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | 278 K | geo | [25] |
| Au | −2.82 | −159.8 | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | 283 K | geo | [25] |
| Au | −2.72 | −155.4 | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | 293 K | geo | [25] |
| Au | −2.55 | −157.4 | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | 303 K | geo | [25] |
| Au | −2.26 | −167.5 | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | 313 K | geo | [25] |
| Au | −1.74 | −139.7 | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | 323 K | geo | [25] |
| Au | −1.54 | −141.4 | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | 333 K | geo | [25] |
| Co | −(2.07 ±0.02) | −248 | 1 mol dm−3 KOH | rt | real | this work |
| Co | −(2.49 ± 0.03) | −204 | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | rt | real | this work |
| Co | −(2.5 ± 0.4) | −(126 ± 6) | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | NM | [5] | |
| Cr | −(4.0 ±0.04) | −149 | 1 mol dm−3 KOH | rt | real | this work |
| Cr | −4.22 | −117 | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | rt | real | this work |
| Fe | −(3.4 ±0.08) | −172 | 1 mol dm−3 KOH | rt | real | this work |
| Fe | −(2.62 ± 0.02) | −206 | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | rt | real | this work |
| Fe | −(1.9 ± 0.4) | −(131 ± 12) | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | NM | [5] | |
| Ni | −(1.99 ± 0.05) | −174 | 1 mol dm−3 KOH | rt | real | this work |
| Ni | −(1.95 ± 0.05) | −132 | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | rt | real | this work |
| Ni | −(2.1 ± 0.5) | −(135 ± 32) | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | NM | geo | [5] |
| Ni foam | −1.17 | −144 | 1 mol dm−3 KOH | NM | geo | [29] |
| Ni | −2.60 | −121 | 1 mol dm−3 KOH | NM | geo | [30] |
| Ni metal with possible surface state of NiOx | −0.99 | −(146 ± 19) | 1 mol dm−3 KOH | geo | [31] | |
| Raney Ni (250) | 0.95 | 84 | 25% KOH | NM | geo | [32] |
| Ni metal with possible surface state of NiHx | −1.77 | 105–125 | 1.3 mol dm−3 KOH | NM | geo | [33] |
| Ni metal with possible surface state of NiHx | −1.45 | −115 | 30 (w%) KOH | NM | [34] | |
| Pt | −(2.07 ± 0.09) | −52 | 1 mol dm−3 KOH | rt | real | this work |
| Pt | −(1.93 ± 0.08) | −72 | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | rt | real | this work |
| Pt | −(0.2 ± 0.01) | −(113 ± 1) | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | NM | geo | [5] |
| Pt | −(0.24 ± 0.07) | - | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | NM | geo | [35] |
| Pt (poly) | −0.16 | - | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | NM | geo | [27] |
| Pt | −1–0.96 | - | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | 298 K | geo | [36] |
| Pt(111) | −2 | - | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | 275 K | geo | [37] |
| Pt(111) | −1.46 | - | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | 293 K | geo | [37] |
| Pt(111) | −1 | - | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | 313 K | geo | [37] |
| Pt(111) | −0.52 | - | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | 333 K | geo | [37] |
| Pt(110) | −0.9 | - | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | 275 K | geo | [37] |
| Pt(110) | −0.52 | - | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | 293 K | geo | [37] |
| Pt(110) | −0.25 | - | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | 313 K | geo | [37] |
| Pt(110) | −0.17 | - | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | 333 K | geo | [37] |
| Pt(110) | −1.3 | - | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | 275 K | geo | [37] |
| Pt | 0.02 | - | 1 mol dm−3 KOH | rt | geo | [38] |
| Pt(100) | −0.83 | −460 | 8 mol dm−3 KOH | NM | geo | [39] |
| W | −(3.81 ± 0.03) | −114 | 1 mol dm−3 KOH | rt | real | this work |
| W | −(3.97 ± 0.03) | −107 | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | rt | real | this work |
| W | −(4.2 ± 0.4) | −(90 ± 7) | 0.1 mol dm−3 KOH | NM | [5] |
| Electrode | log(jo/mA cm−2) | Tafel Slope (mV dec−1) | Electrolyte | Temperature | Surface Area Used | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag | −(4.39 ± 0.01) | −180 | 0.1 mol dm−3 LiOH | rt | real | this work |
| Au | −(3.48 ± 0.01) | −169 | 0.1 mol dm−3 LiOH | rt | real | this work |
| Co | −(2.48 ± 0.01) | −189 | 0.1 mol dm−3 LiOH | rt | real | this work |
| Cr | −(3.56 ± 0.02) | −177 | 0.1 mol dm−3 LiOH | rt | real | this work |
| Fe | −(2.71 ± 0.01) | −222 | 0.1 mol dm−3 LiOH | rt | real | this work |
| Ni | −(1.92 ± 0.05) | −162 | 0.1 mol dm−3 LiOH | rt | real | this work |
| Pt | −(1.58 ± 0.1) | −81 | 0.1 mol dm−3 LiOH | rt | real | this work |
| Pt | −0.056 | - | 0.1 mol dm−3 LiOH | rt | NM | [35] |
| W | −(3.16 ± 0.03) | −120 | 0.1 mol dm−3 LiOH | rt | real | this work |
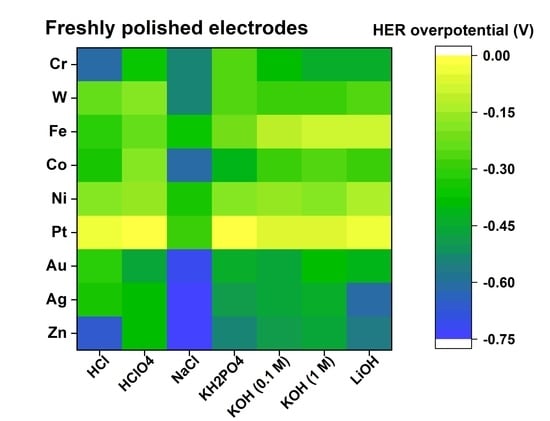
| HCl | HClO4 | NaCl | KH2PO4 | KOH (0.1 mol dm−3) | KOH (1 mol dm−3) | LiOH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrode | HER overpotential for freshly polished electrodes (in V) | ||||||
| Ag | −0.35 | −0.39 | −0.73 | −0.49 | −0.46 | −0.43 | −0.61 |
| Au | −0.31 | −0.47 | −0.72 | −0.44 | −0.47 | −0.39 | −0.42 |
| Co | −0.33 | −0.20 | −0.62 | −0.42 | −0.30 | −0.26 | −0.28 |
| Cr | −0.62 | −0.37 | −0.53 | −0.27 | −0.38 | −0.45 | −0.45 |
| Fe | −0.32 | −0.25 | −0.37 | −0.22 | −0.12 | −0.10 | −0.09 |
| Ni | −0.18 | −0.16 | −0.35 | −0.18 | −0.16 | −0.18 | −0.15 |
| Pt | −0.03 | −0.02 | −0.29 | −0.01 | −0.06 | −0.06 | −0.05 |
| W | −0.24 | −0.20 | −0.55 | −0.27 | −0.30 | −0.29 | −0.26 |
| Zn | −0.67 | −0.40 | −0.73 | −0.55 | −0.48 | −0.46 | −0.57 |
| HER overpotential after oxidation of the polished electrodes (in V) | |||||||
| Ag | - | −0.42 | −0.65 | −0.36 | −0.45 | - | −0.55 |
| Au | - | −0.22 | −0.68 | −0.37 | −0.46 | - | −0.41 |
| Co | - | - | −0.50 | −0.38 | −0.30 | - | −0.27 |
| Cr | −0.61 | −0.48 | −0.74 | −0.26 | −0.58 | - | −0.42 |
| Fe | - | - | −0.48 | −0.20 | −0.16 | - | −0.13 |
| Ni | - | - | −0.24 | −0.16 | −0.13 | - | −0.11 |
| Pt | −0.01 | −0.01 | −0.29 | −0.02 | −0.06 | - | −0.07 |
| W | −0.27 | −0.22 | −0.57 | −0.28 | −0.36 | - | −0.28 |
| Zn | - | - | - | −0.54 | −0.48 | - | −0.57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gebremariam, G.K.; Jovanović, A.Z.; Pašti, I.A. Kinetics of Hydrogen Evolution Reaction on Monometallic Bulk Electrodes in Various Electrolytic Solutions. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13101373
Gebremariam GK, Jovanović AZ, Pašti IA. Kinetics of Hydrogen Evolution Reaction on Monometallic Bulk Electrodes in Various Electrolytic Solutions. Catalysts. 2023; 13(10):1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13101373
Chicago/Turabian StyleGebremariam, Goitom K., Aleksandar Z. Jovanović, and Igor A. Pašti. 2023. "Kinetics of Hydrogen Evolution Reaction on Monometallic Bulk Electrodes in Various Electrolytic Solutions" Catalysts 13, no. 10: 1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13101373
APA StyleGebremariam, G. K., Jovanović, A. Z., & Pašti, I. A. (2023). Kinetics of Hydrogen Evolution Reaction on Monometallic Bulk Electrodes in Various Electrolytic Solutions. Catalysts, 13(10), 1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13101373