Abstract
In the present study, terbium-based metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) based on fcu topology, fcu-Tb- FTZB-MOF, was synthesized using 2-fluoro-4-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)benzoic acid (FTZB) as a linear ligand, and then was characterized using powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) and Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) analysis and to study the texture properties of the Tb-FTZB-MOF. The characterization results confirmed the successful synthesis of the high surface area Tb-FTZB-MOF (1220 m2/g). The synthesized Tb-FTZB-MOF was then applied as a catalytic adsorbent to remove direct violet 31 (DV31) dye as an example of organic pollutants, from a model and real solution. The effect of various operational parameters such as adsorbent loading, contact time, initial DV31 dye concentration, initial solution pH, different water matrix, temperature, and ionic strength have also been evaluated. Solution pH and temperature significantly influenced the adsorption of DV31 dye using Tb-FTZB-MOF, and the results should efficiently remove the DV31 dye at ambient temperature, and at pH value of 8.0 using 35 mg Tb-FTZB-MOF, within few minutes. The process was studied kinetically and found to follow the pseudo-second-order kinetic model, and thermodynamically the process was spontaneous, endothermic, with a positive entropy. Finally, the result showed that Tb-FTZB-MOF was able to adsorb a high percentage of DV31 dye and maintained reasonable efficiency even after five cycles, indicating that Tb-FTZB-MOF could be a promising adsorbent in wastewater remediation.
1. Introduction
Water is an essential element of life. It is a vital resource for all living things as it supports the physiological activities of any biological cell [1]. Although this precious resource covers more than 70% of the earth crust, unfortunately, only a limited portion is portable [2]. This is due to the growing industrialization and the extensive use of chemicals for various purposes in day-to-day life, leading to the release of diverse organic and inorganic pollutants into the water system [3]. In addition, natural phenomena such as storms, volcanoes, earthquakes and algae blooms also result in major changes in the ecological status and quality of water [1]. Water pollution is a severe problem that leads to the onset of numerous fatal diseases, resulting in over 14,000 people every day [1,4]. Moreover, the United Nations (UN) has projected that between 1/2 and 2/3 of the world’s population would experience scarcity of fresh water in 2025 [5].
Among various pollutants, direct organic dye, such as direct violet 31 dye, is one of the most commonly used classes of dyes [6]. They are usually applied to print and dye cellulose fibers and their blends [6]. Generally, dyes have a low fixation degree on the textile substrate, and about 10–15% is unexhausted and remains as a waste in the bath [7]. However, direct dyes are considered as one of the most refractory pollutants due to their toxicity and stability, which are non-biodegradable because of their complex molecular structure [8,9]. Thus, their removal from wastewaters is an issue of significant concern.
Over the past few years, varieties of techniques were used for the treatment of wastewater from organic pollutants such as coagulation [10], photocatalytic treatment [11,12], ultra-filtration [13], membrane [14] and adsorption [15], especially from organic dyes such as direct violet dyes [16,17,18,19,20]. Among the various treatment technologies, adsorption is a green process that has received significant attention from environmentalists and researchers [9,18,21]. This is because the process is promising, efficient, technically feasible and economically viable for wastewater treatment [22,23,24]. However, the properties of the adsorbent material utilized had a significant impact on the effectiveness of the adsorption process [25]. For instance, to efficiently remove the pollutant, an adsorbent must have a large surface area or pore structure and a good equilibrium uptake time [26].
Nevertheless, metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are a new class of porous materials with tunable structure and high specific surface area [21]. They are arrays of inorganic nodes (clusters of ions or single ions) bridged by organic linkers, and more than 20,000 MOFs have been reported within the past decade [27,28,29,30]. MOFs are considered superior to other porous materials due to their open metal sites, high/tunable porosity, pore functionality, various pore compositions/architectures, etc. [31]. They are effective in the removal and sensing of hazardous materials [32] such as organic compounds [33,34,35], aromatic molecules [36], dyes [37,38], metal ions [39], and fluoride ions [40,41]. However, the adsorption performance rare earth (RE) based MOFs with face-centered cubic (fcu) topology deserves to be explored among the MOFs.
The research work focus on the facile synthesis of Tb-FTZB-MOF and its application for environmental remediation is stile scare in the literature, and more research needs to be done to explore the extraordinary capabilities of the Tb-FTZB-MOF for the remediation and attain sustainable environment through the removal and elimination of different pollutants from the polluted water. Therefore, this research work focuses on exploiting the synthesis, and application of Tb-FTZB-MOF for the removal of organic pollutants, namelyDV31 dye from a model and real water sample.
In the current study, Tb-FTZB-MOF (Figure 1) was synthesized, characterized, and then applied as a catalytic adsorbent to remove DV31 dye from an aqueous solution. The prepared Tb-FTZB-MOF was characterized using different characterization techniques to confirm the chemical and crystal structure. In addition, the effect of various operational parameters such as adsorbent loading, contact time, initial DV31 dye concentration, initial solution pH, different water matrix, temperature and ionic strength were also investigated. The kinetics of the DV31 dye removal using Tb-FTZB-MOF was explored for the understanding of the removal process. Additionally, the application of the Tb-FTZB-MOF for the removal of DV31 dye from different environmental samples was explored as well as the recyclability of the solid adsorbent.
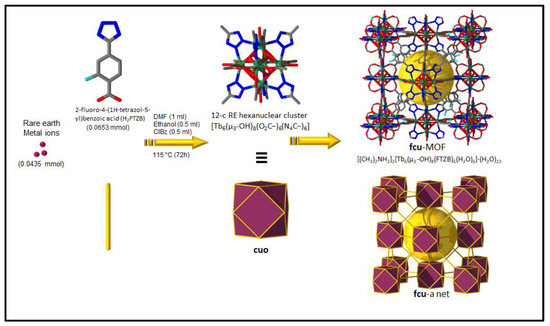
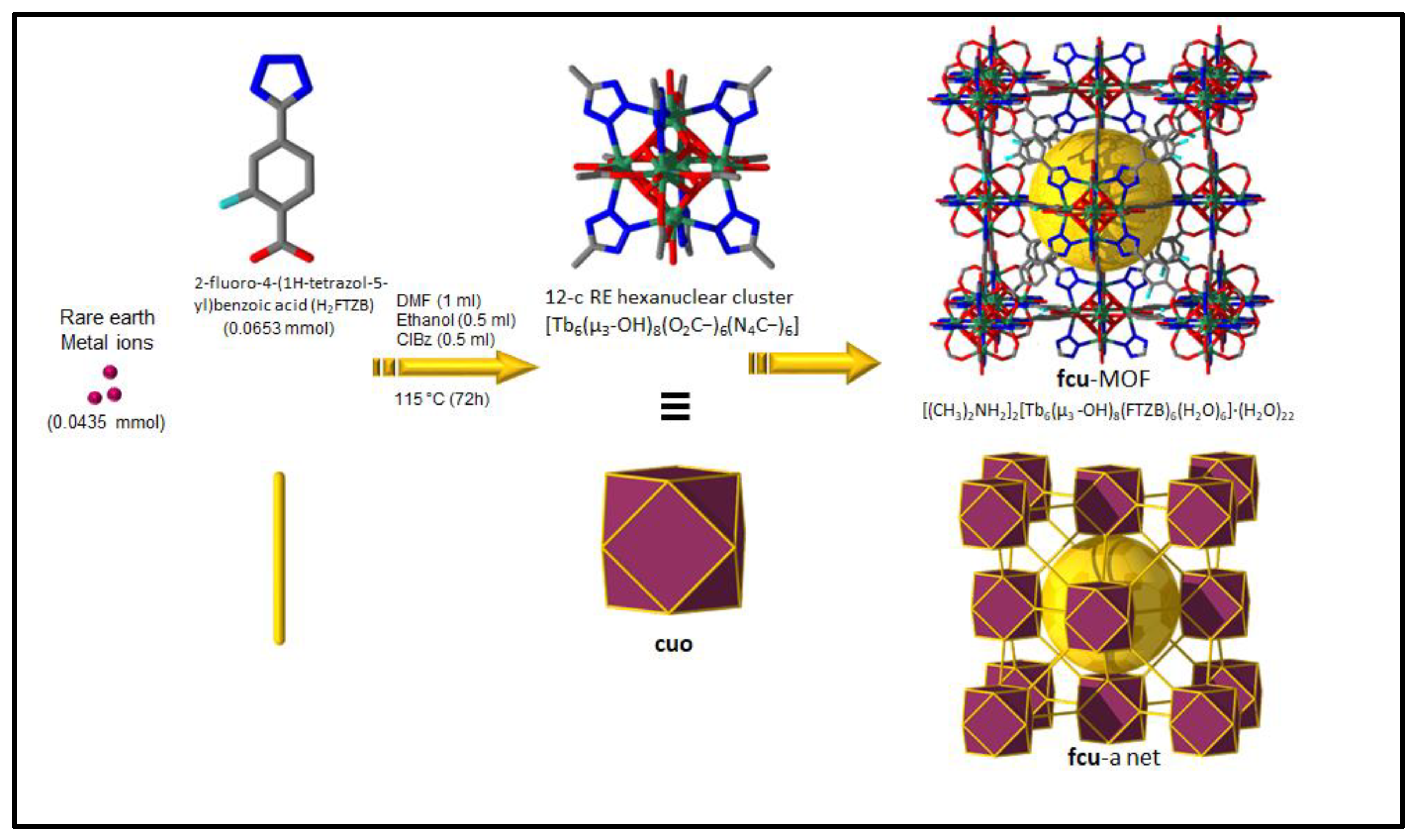
Figure 1.
Schematic showing the assembly of Tb-FTZB-MOF.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Tb-FTZB-MOF
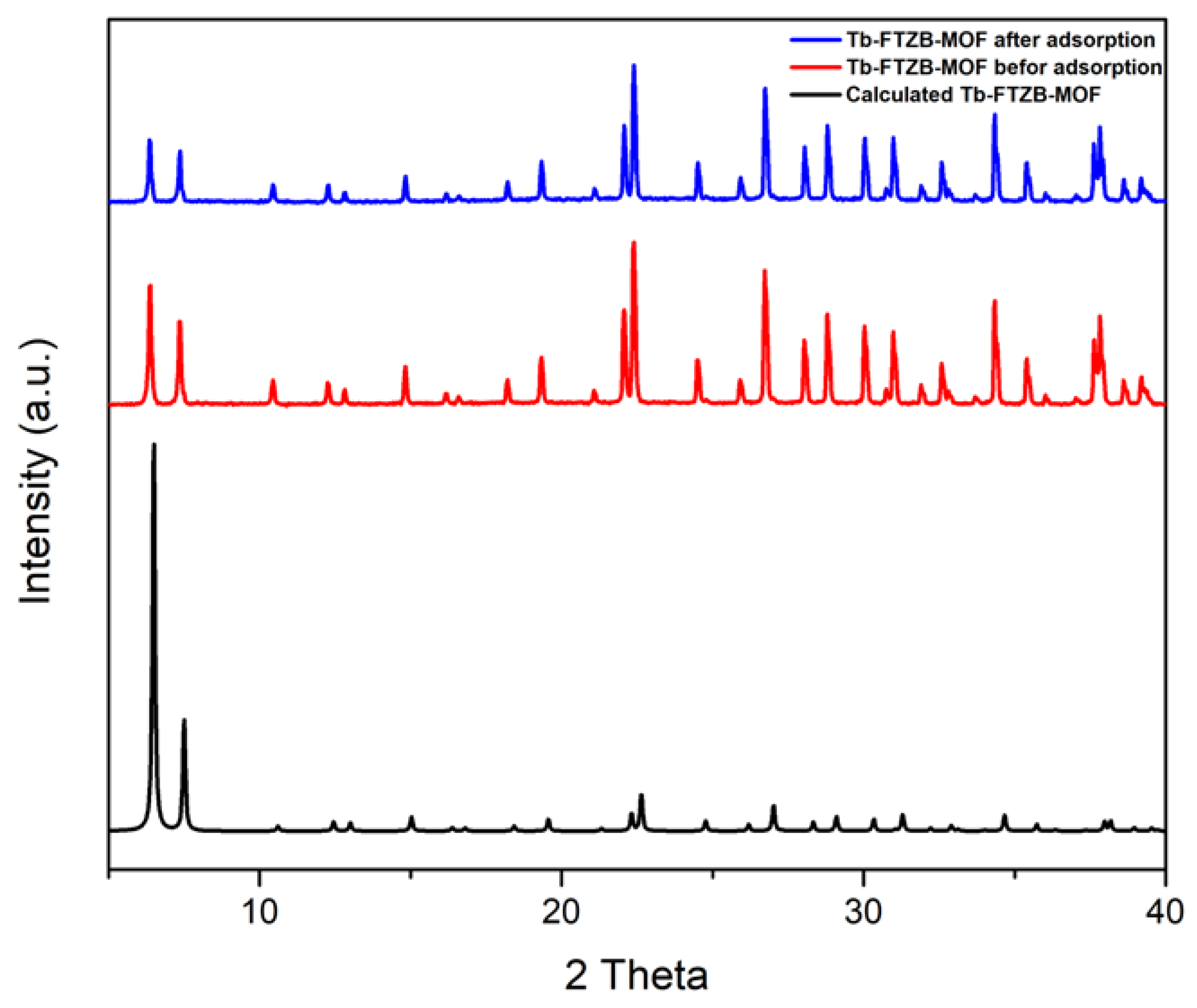
Figure 2 shows the PXRD patterns of the Tb-FTZB-MOF in comparison to calculated PXRD, which confirm the purity of the prepared sample. Additionally, it demonstrated the PXRD patterns before and after adsorption of the DV 31 dye, which were similar to the calculated pattern, and it is clear that the PXRD pattern before and after the adsorption did not change. However, the PXRD peaks for Tb-FTZB-MOF became less intense after adsorption of DV31 dye, and such reduction in the diffraction intensity may be indicative of a decrease in degree of crystallinity of the Tb-FTZB-MOF [42].
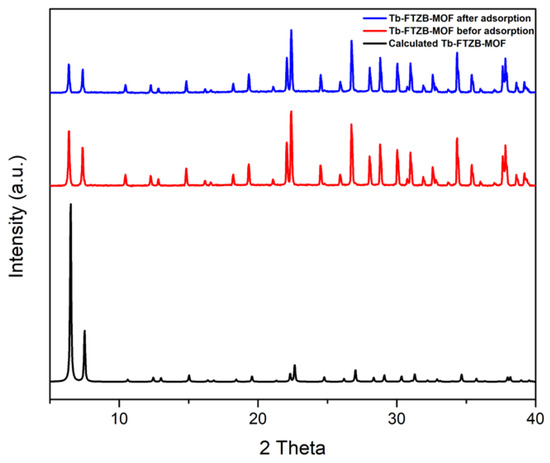
Figure 2.
PXRD patterns for Tb-FTZB-MOF before and after the adsorption of DV31 dye.
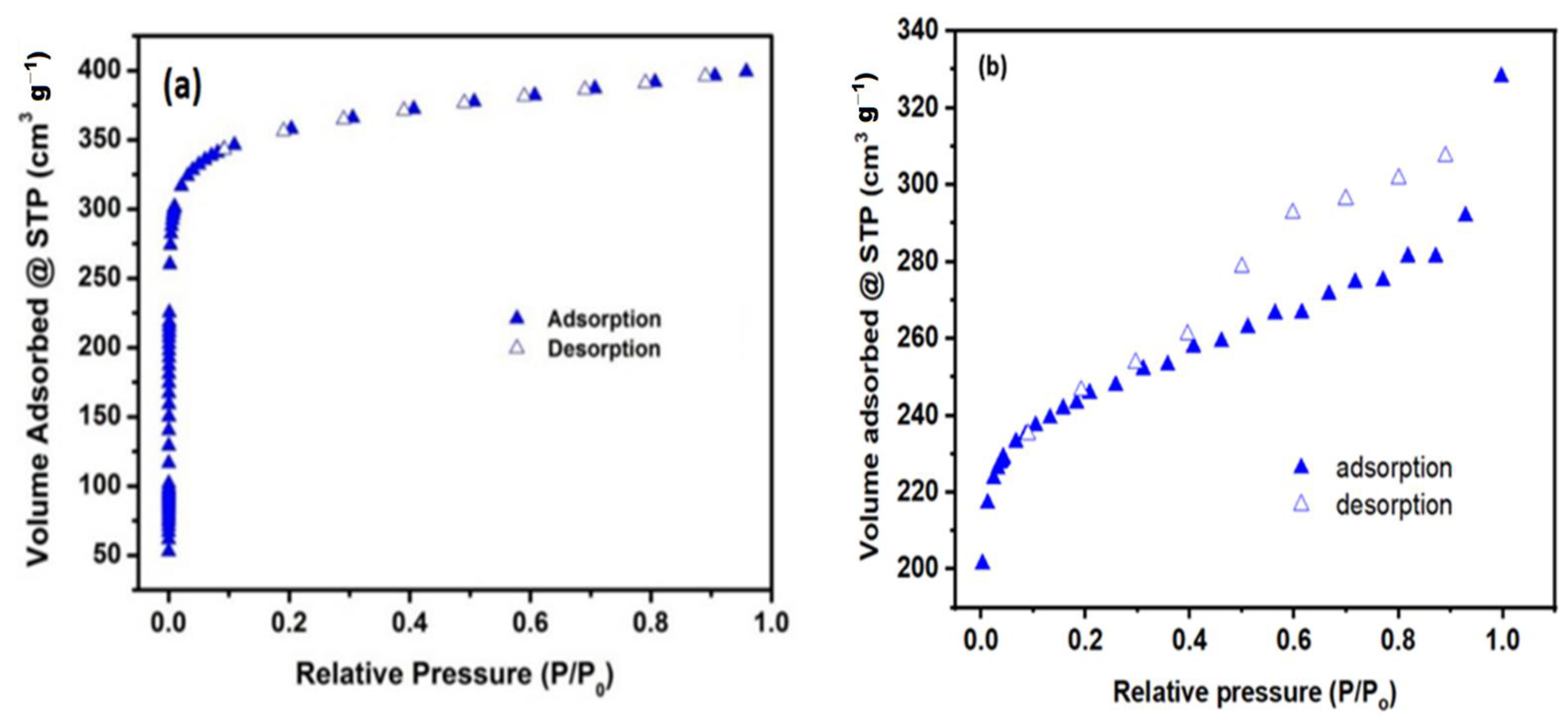
N2 adsorption–desorption isotherm curves of Tb-FTZB-MOF before and after the adsorption of DV31 dye are shown in Figure 3, as well as the calculated BET surface area (m2/g) and pore volume (cm2/g) from N2 isotherm are presented (Table 1). The BET surface area of freshly prepared Tb-FTZB-MOF was 1220 m2/g, but decreased to 959.0 m2/g after adsorption of DV31 dye, and likewise, a slight decrease in pore volume after adsorption of DV31 dye was also observed, which may be attributed to the blocking of the active sites of Tb-FTZB-MOF by DV31 dye molecules.
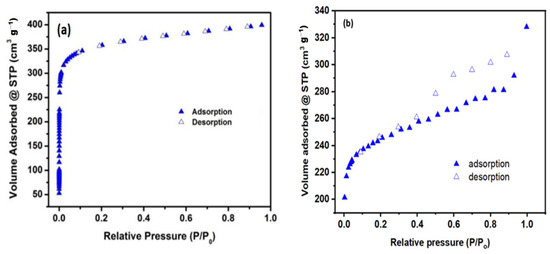
Figure 3.
Adsorption isotherms collected before adsorption (a), and after adsorption (b) of DV31 dye using Tb-FTZB-MOF.

Table 1.
Surface area and pore volume of Tb-FTZB-MOF.
2.2. Adsorption Process
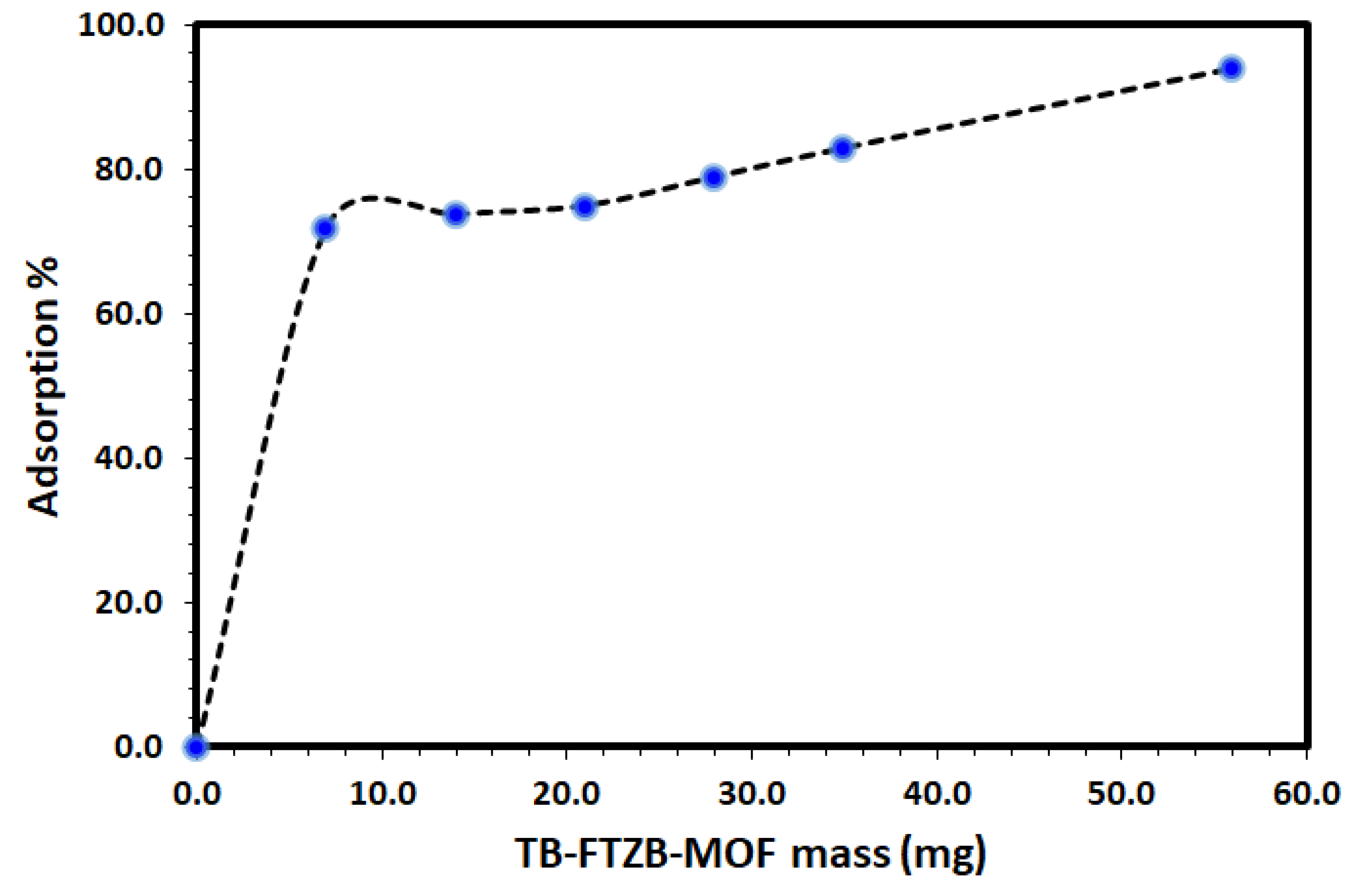
The effect of various operational parameters may affect the removal of the DV31 dye from a solution using Tb-FTZB-MOF was explored in order to determine the performance of Tb-FTZB-MOF as a solid adsorbent for the removal of DV31 dye under different conditions. The effect of Tb-FTZB-MOF mass on the removal of DV31 from aqueous solution via adsorption was studied using 7–56 mg of Tb-FTZB-MOF, and the results are shown in Figure 4. The adsorption of DV31 using Tb-FTZB-MOF was found to increase with increase in MOF mass, and such effect is attributed to the increase of the Tb-FTZB-MOF surface area and the availability of more sorption sites due to the increase in mass [43]. Furthermore, due to the negligible increase in percentage adsorption, after increase in MOF mass from 35–56 mg, the rest of the study was conducted using 35 mg of Tb-FTZB-MOF.
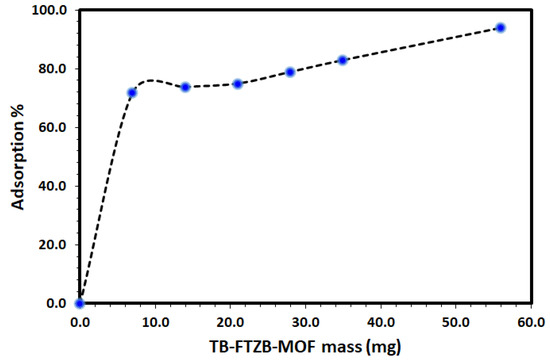
Figure 4.
Effect of Tb-FTZB-MOF mass on the removal of DV31 from aqueous solution. (Experimental conditions: 10 mL solution, 120 min, pH 8.0, and DV31 dye conc. 25 mg/L).
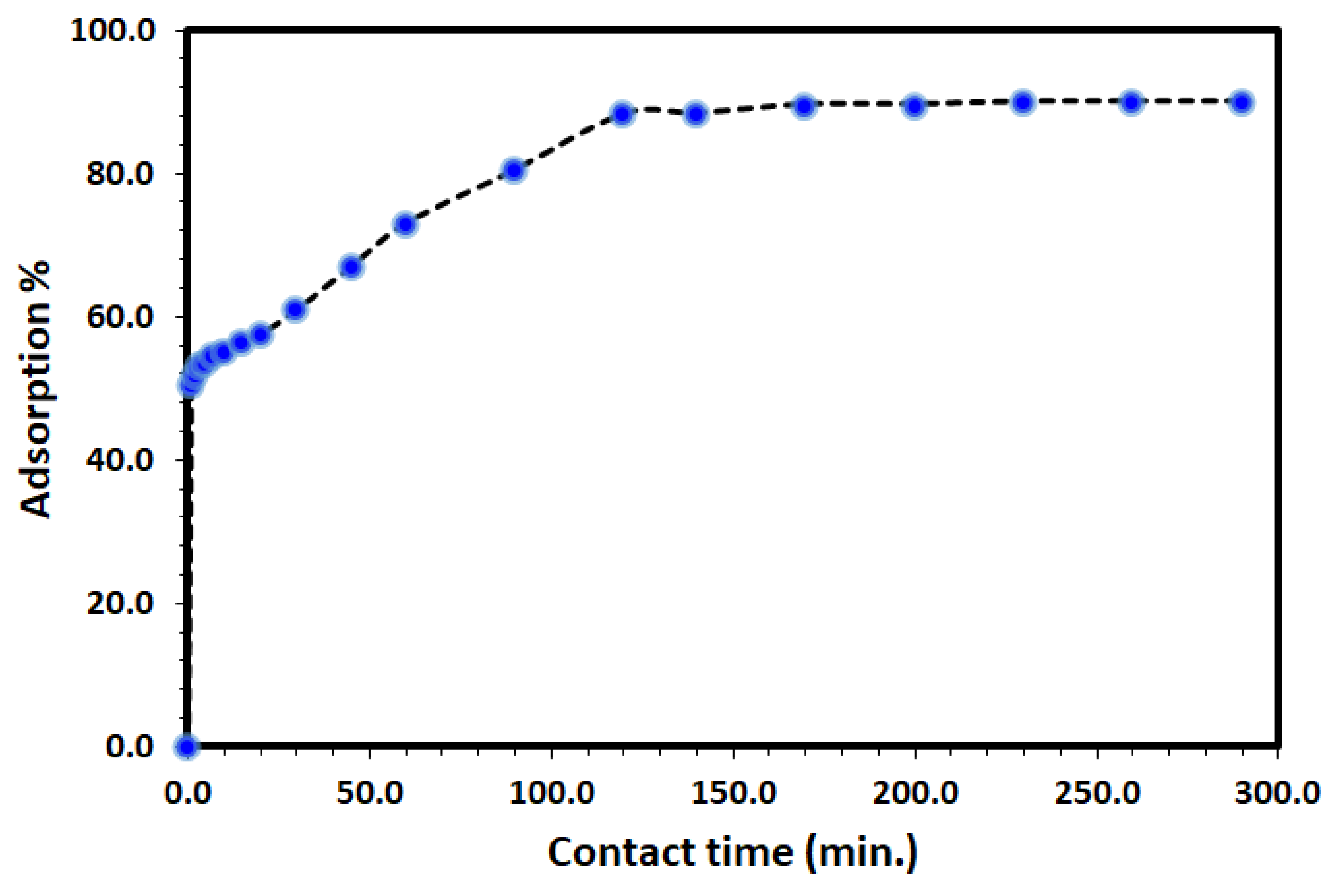
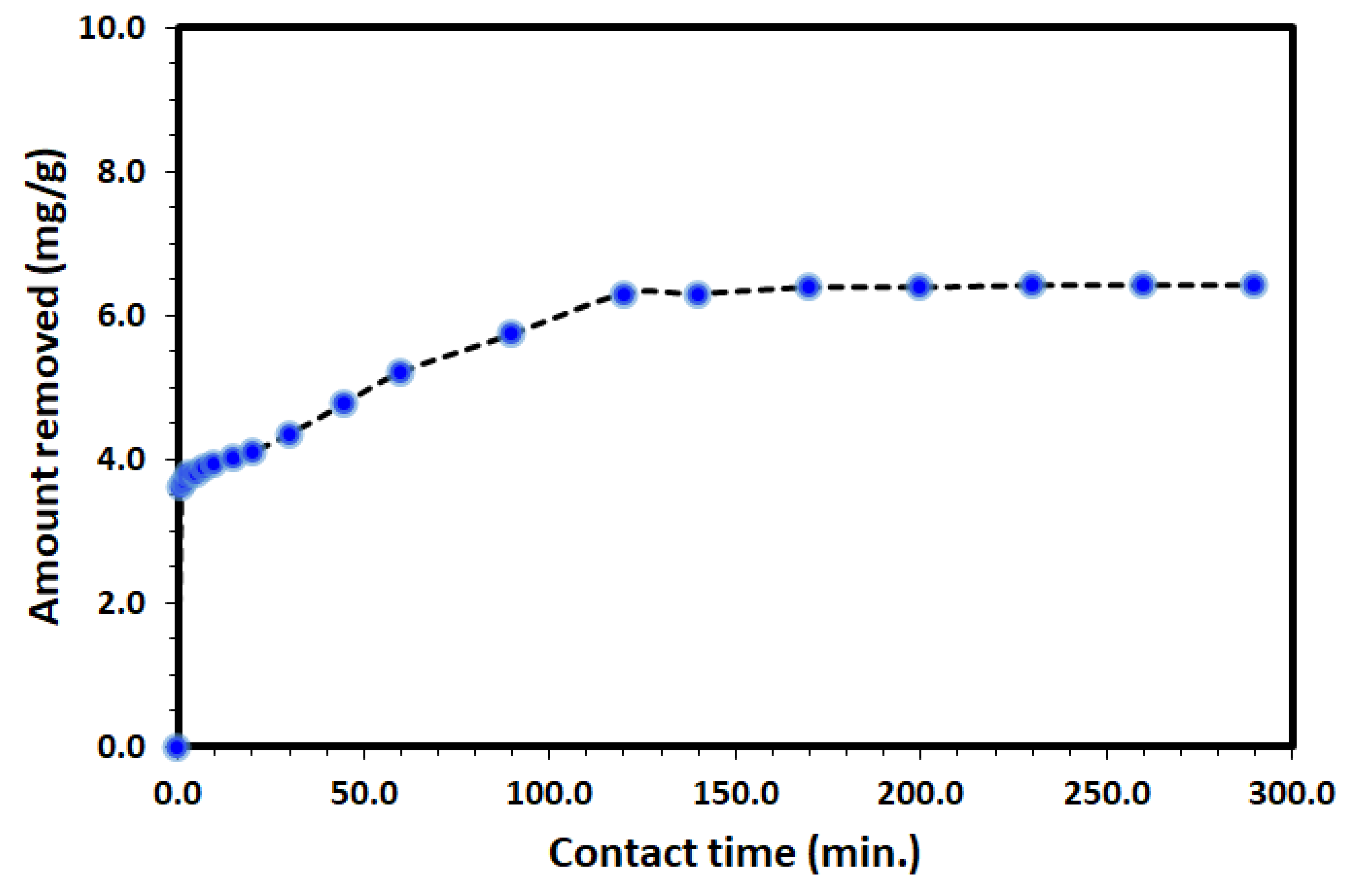
The uptake of DV31 from an aqueous solution using Tb-FTZB-MOF has been examined at different time intervals and the results are shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6. Based on the results obtained, the percentage and amount of DV31 adsorbed on the surface of Tb-FTZB-MOF rises with the prolonged time. The process was divided into two stages; the first stage (fast adsorption) was observed below 120 min with % adsorption of 88.3%, and removal capacity of 6.31 mg DV31 per gram of Tb-FTZB-MOF. However, from 120–300 min, no significant change in DV31 concentration was observed (slow adsorption); with % adsorption of 90.0%, and removal capacity of 6.42 mg DV31 per gram of Tb-FTZB-MOF, and this performance indicates that the active sites of Tb-FTZB-MOF gradually becomes saturated [44].
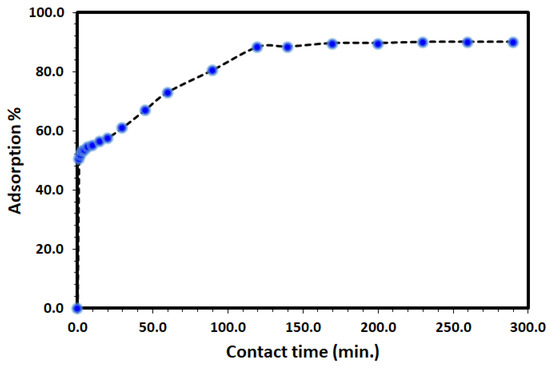
Figure 5.
Effect of contact time on the removal of DV31 using Tb-FTZB-MOF from aqueous solution. (Experimental conditions: 35 mg Tb-FTZB-MOF, 10 mL solution, pH 8.0 and DV31 dye conc. 25 mg/L).
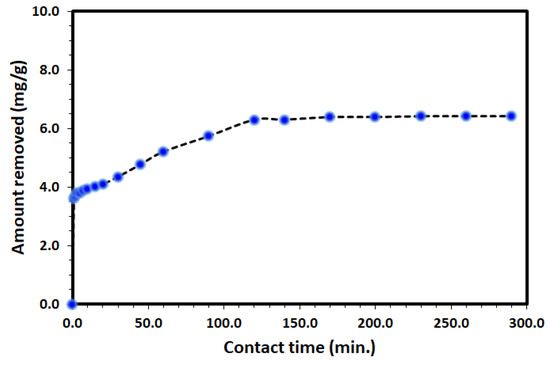
Figure 6.
Variation of the amount of DV31 dye adsorbed per unit mass of Tb-FTZB MOF (qt) with time. (Experimental conditions: 35 mg Tb-FTZB-MOF, 10 mL solution, pH 8.0 and DV31 dye conc. 25 mg/L).
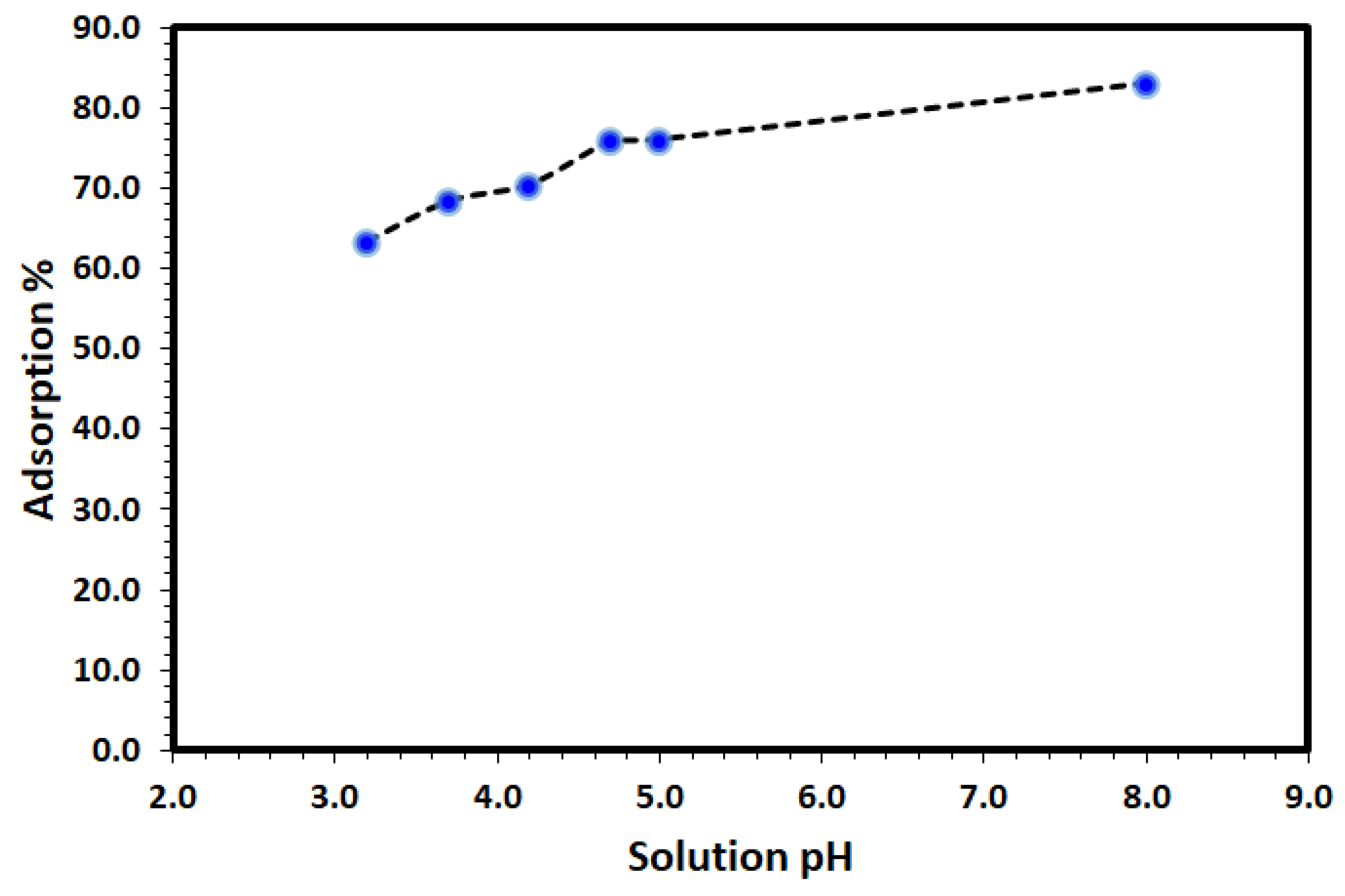
Solution pH is a controlling factor on the removal and environmental remediation of organic pollutants such as DV31 dye from water using adsorption process. Therefore, the effect of initial solution pH on the removal of DV31 dye using Tb-FTZB-MOF was studied. The results are shown in Figure 7, and it was observed that the efficiency of the removal was found to increase with increase in pH of the solution due to the electrostatic attraction between the anionic form of the DV31 dye and the Tb-FTZB-MOF positive surface. The low removal efficiency recorded at low pHs could be due to competition effect between the hydronium ions (H3O+) and the DV31 dye molecules for the adsorption active sites of Tb-FTZB-MOF surface, while the high removal efficiency recorded at high pHs could be due to electrostatic attraction. Previously, it have also reported that a negatively charged site on an adsorbent does not favor the adsorption of anionic dyes due to electrostatic repulsion [45].
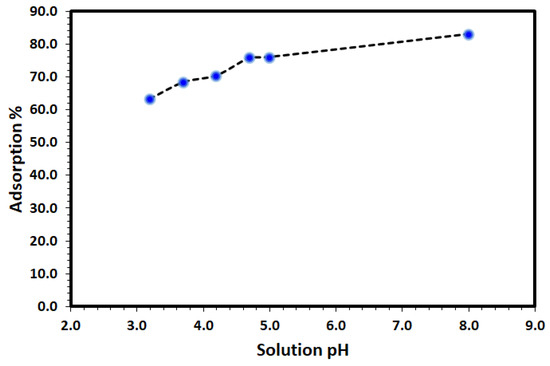
Figure 7.
Effect of solution pH on the removal of DV31 from aqueous solution using Tb-FTZB-MOF. (Experimental conditions: 35 mg Tb-FTZB-MOF, 10 mL solution, 120 min and DV31 dye conc. 25 mg/L).
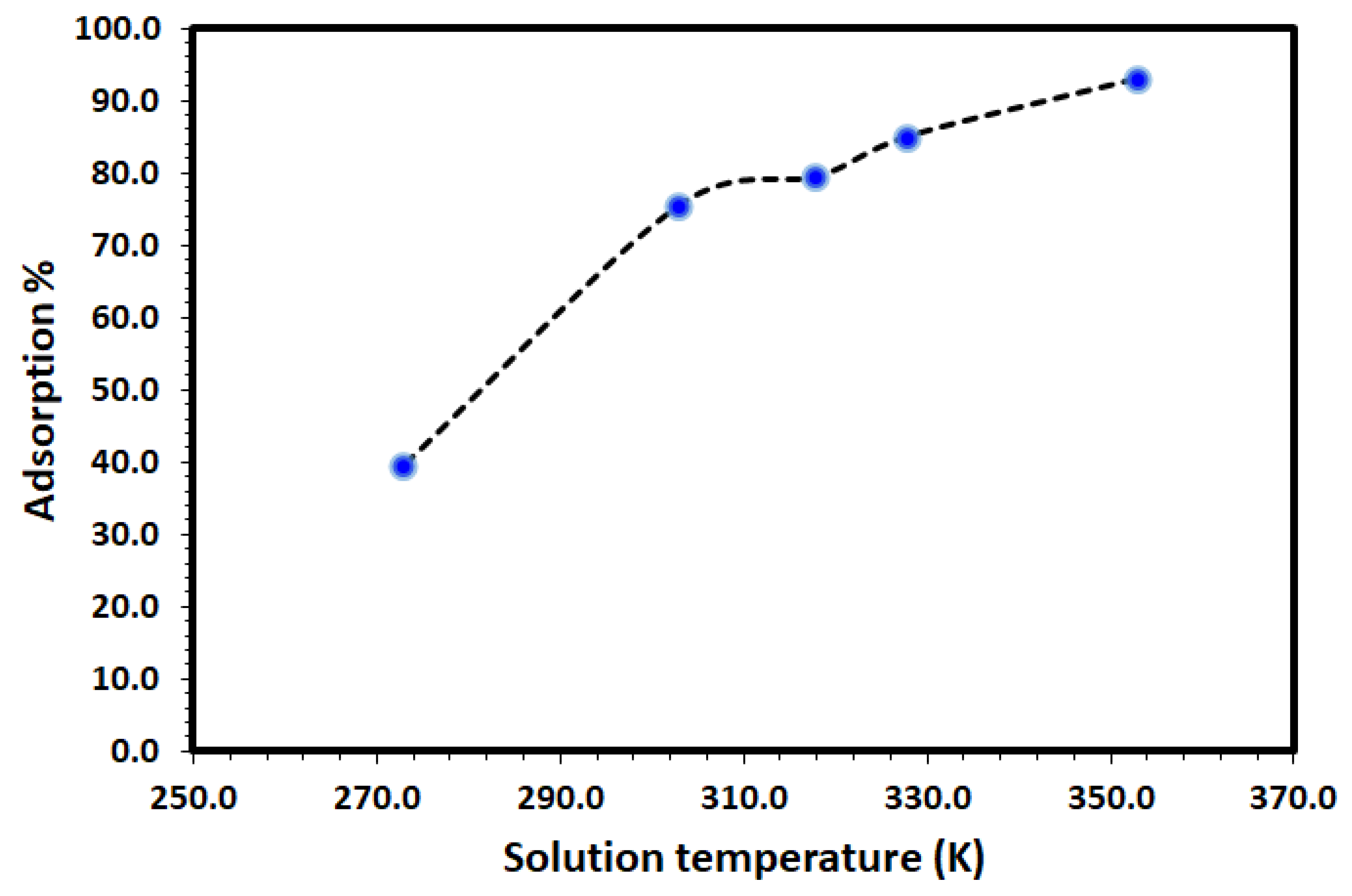
The effect of temperature on the adsorption of DV31 using Tb-FTZB-MOF was studied and the results are shown in Figure 8. It is clear from the figure that, the percentage of DV31 adsorbed on Tb-FTZB-MOF increases with increase in temperature, indicating the endothermic nature of the adsorption process. This is attributed to the increase in mobility and diffusion of DV31 molecules, as more DV31 molecules could acquire sufficient energy to interact with the Tb-FTZB-MOF surface [46]. Moreover, increase in temperature would result in pore size enlargement due to the activated diffusion, thereby creating more surface for adsorption [47].
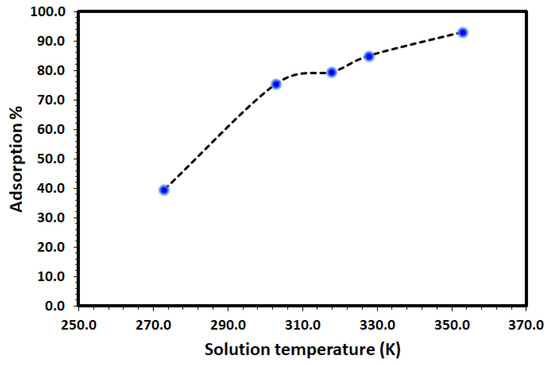
Figure 8.
Effect of solution temperature on the removal of DV31 using Tb-FTZB-MOF (Experimental conditions: 35 mg Tb-FTZB-MOF, 10 mL solution, pH 8, 120 min, and DV31 dye conc. 25 mg/L).
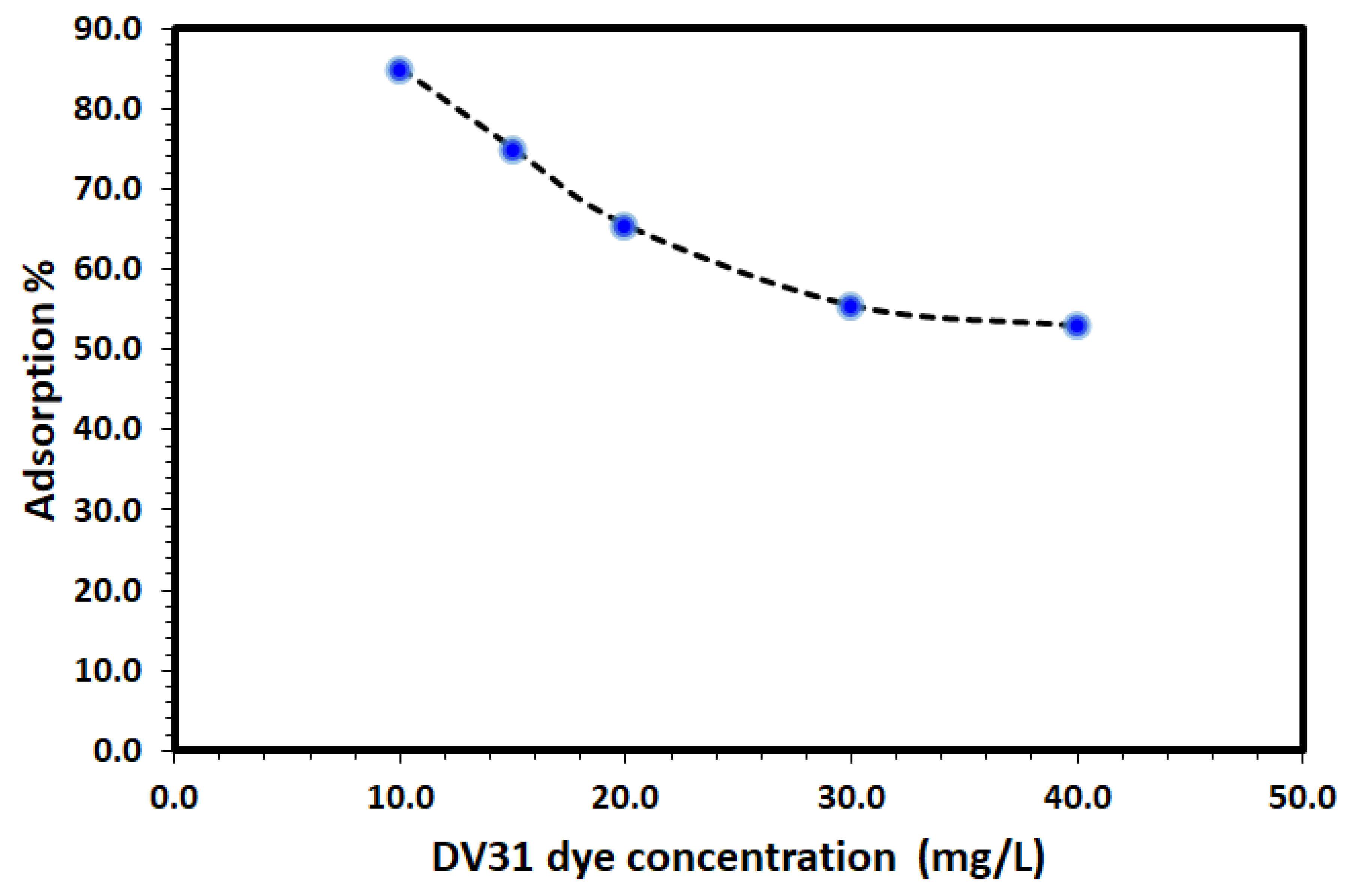
The influence of initial DV31 concentration on the adsorption efficiency using fixed mass of Tb-FTZB-MOF was studied and the results are shown in Figure 9. From the figure, the % removal of DV31 dye via adsorption using fixed amount of Tb-FTZB-MOF was found to decrease with increase in DV31 dye concentration. Such performance is attributed to the unavailability of the Tb-FTZB-MOF active sites under high concentration of DV31 dye [44].
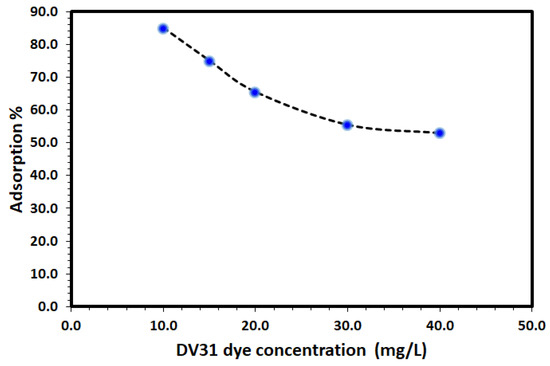
Figure 9.
Effect of initial DV31 concentration temperature on the removal using Tb-FTZB-MOF. (Experimental conditions: 35 mg Tb-FTZB-MOF, 10 mL solution, pH 8, and 120 min).
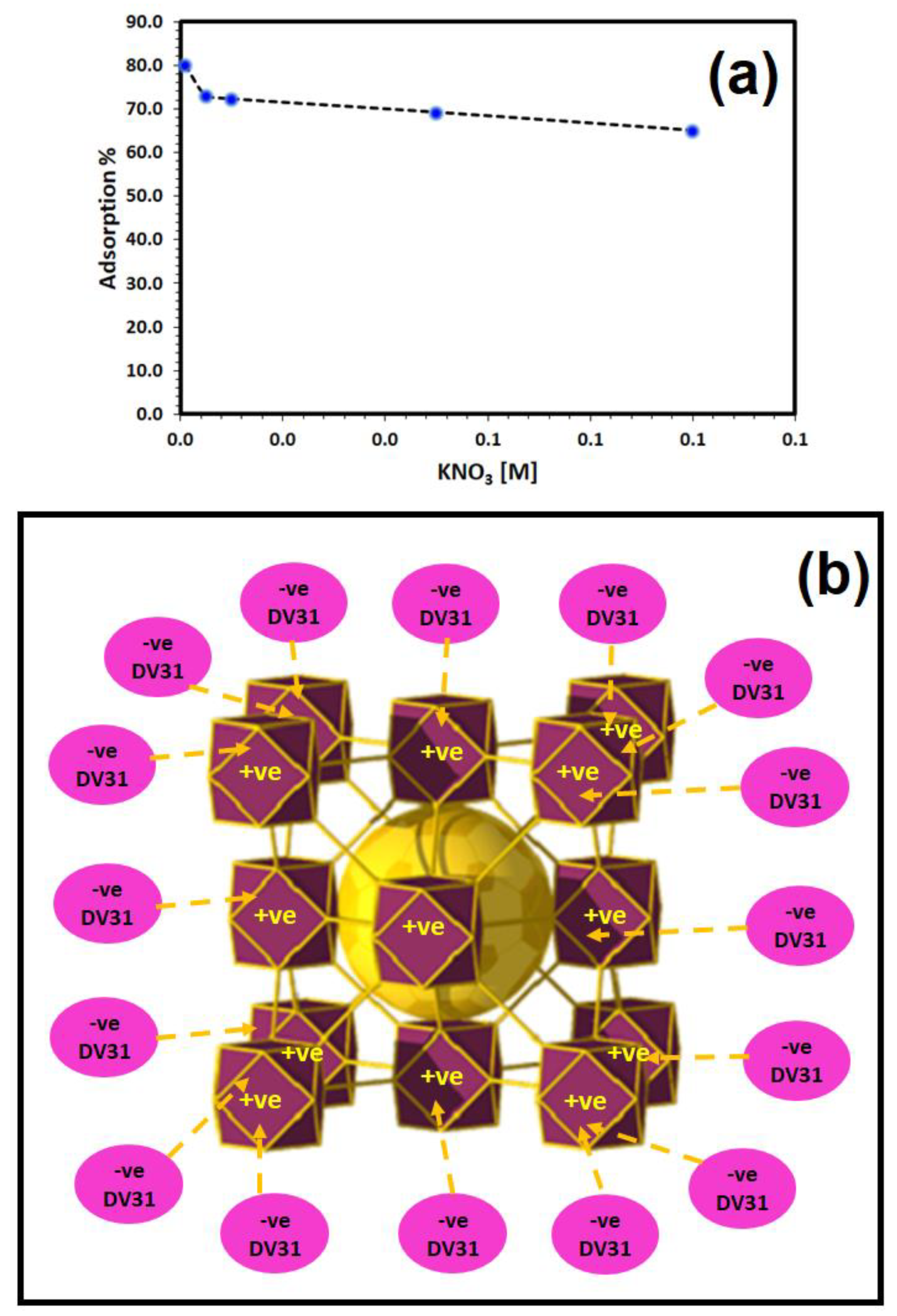
The effect of solution ionic strength on the adsorption of DV31 dye by Tb-FTZB-MOF was studied using different concentrations of KNO3: 0.001–0.1 M, and the results are shown in Figure 10a. From the figure, the percentage removal of DV31 dye using Tb-FTZB-MOF decreased with an increase in concentration of KNO3, indicating that binding efficiency decreases in the presence of KNO3, which may be attributed to the shielding effect due to the high concentration of KNO3 ions (K+ and NO3−), which decreased the electrostatic attraction between the DV31 molecules and the Tb-FTZB-MOF surface, indicating the electrostatic nature of the removal process. Furthermore, DV31 dye might also combine with the ions derived from KNO3 to form a complex, hence limiting its uptake by Tb-FTZB-MOF [48]. The electrostatic nature of the adsorption mechanism between DV31 dye molecules and Tb-FTZB-MOF surface could be explained as Figure 10b.
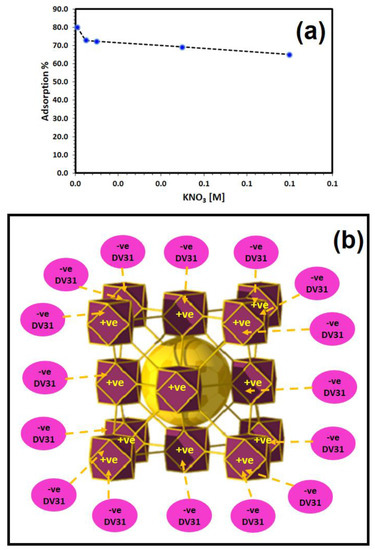
Figure 10.
(a) Effect of ionic strength (KNO3) on the removal of DV31 using Tb-FTZB-MOF (Experimental conditions: 35 mg Tb-FTZB-MOF, 10 mL solution, pH 8, 120 min and DV31 dye conc. 25 mg/L); (b) Schematic representation of the electrostatic nature of the adsorption of DV31 dye molecules by Tb-FTZB-MOF.
2.3. Kinetic Study
There are many kinetic models can be used to describe the adsorption of DV31 dye by Tb-FTZB-MOF from aqueous solution. The kinetics of DV31 removal by Tb-FTZB-MOF were analyzed using different kinetic models; fraction power function [49], Lagergren pseudo-first-order [50], pseudo-second-order [51], and Elovich models [52].
The fractional power function model is a modified form of the Freundlich equation and can be written in its linearized form as follows:
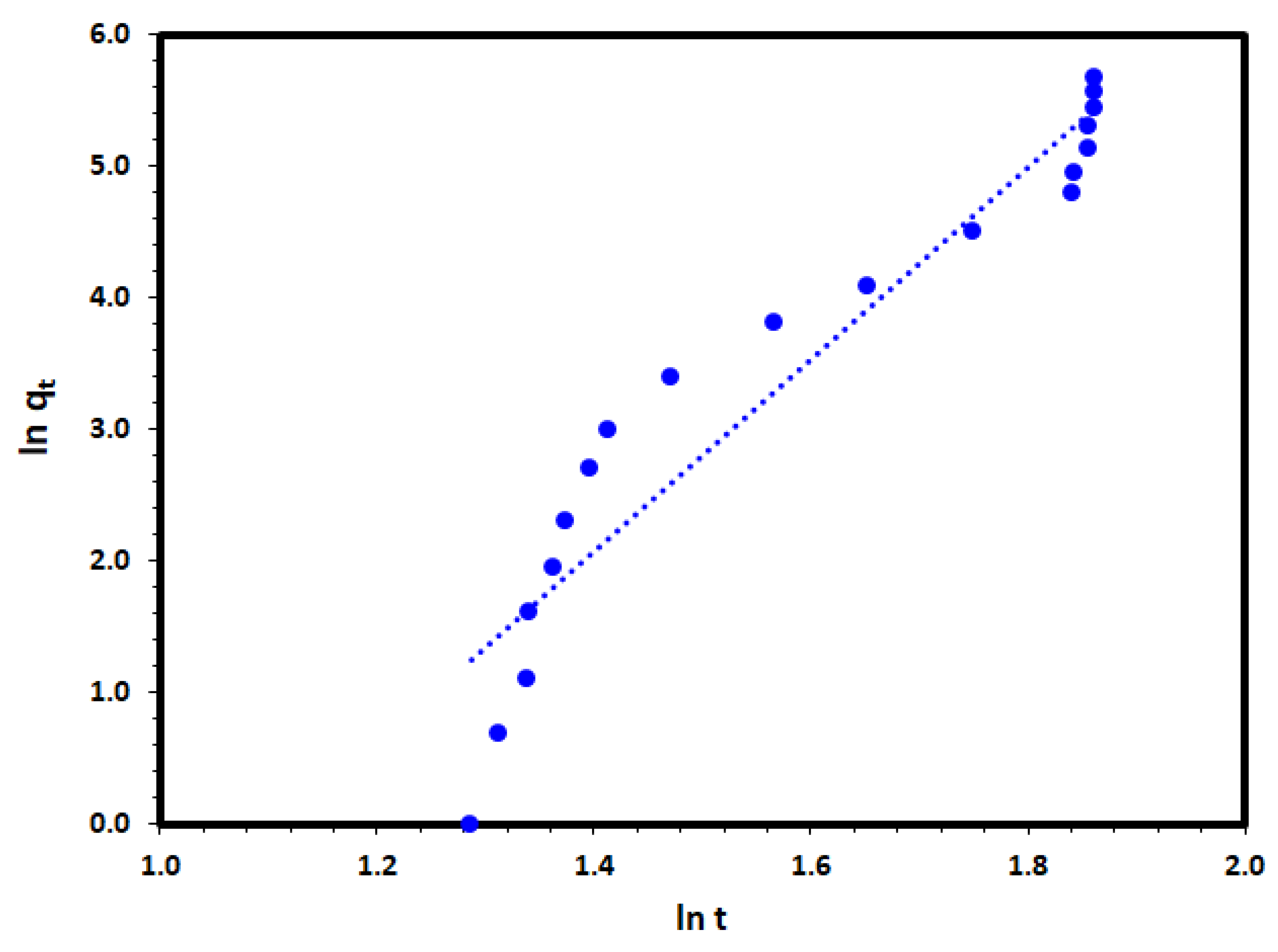
where qt (mg/g) is the amount of DV31 dye removed per unit mass of Tb-FTZB-MOF at any time t while a and b are coefficients with b < 1. The function ab is the specific adsorption rate when t = 1 min. The application of the fractional power equation to the removal date of the DV31 dye on Tb-FTZB-MOF at Figure 11. A linear relationship obtained between ln qt and ln t with very low correlation coefficient of 0.816 as it is presented in Table 2, which may indicate that the fractional power function model was not the appropriate model to describe the adsorption of the DV31 on Tb-FTZB-MOF.
ln qt = ln a + b ln t
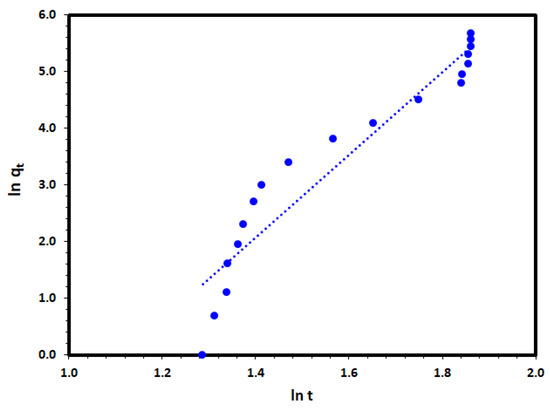
Figure 11.
Fractional power kinetic model plot for the DV31 dye adsorption by Tb-FTZB-MOF.

Table 2.
Different kinetic model parameters for the adsorption of DV31 dye using Tb-FTZB-MOF.
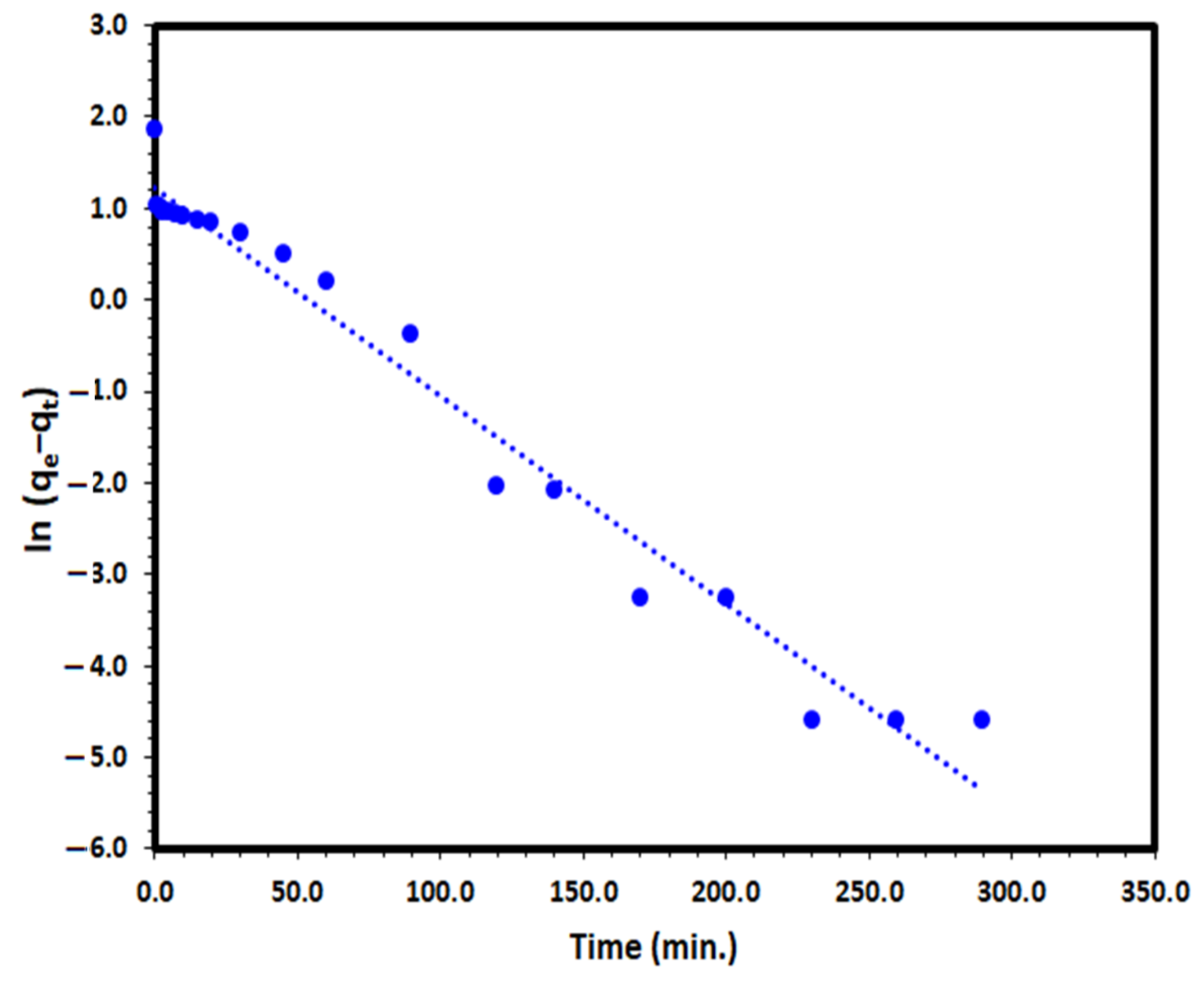
Lagergren pseudo-first-order (PFO) kinetic model is one of the most frequent used models to define the adsorption from aqueous solution by solid adsorbent such as Tb-FTZB-MOF:
where k1 (min−1) is the PFO kinetic rate coefficient, and qe and qt are the values of the amount adsorbed per unit mass at equilibrium and at any time t, respectively. The plot of ln (qe−qt) versus t for the DV31 dye under investigation converged well with a straight line Figure 12 and good correlation coefficient of 0.973, which indicates that the PFO model could be the appropriate way to describe the adsorption of the DV31 dye by Tb-FTZB-MOF.
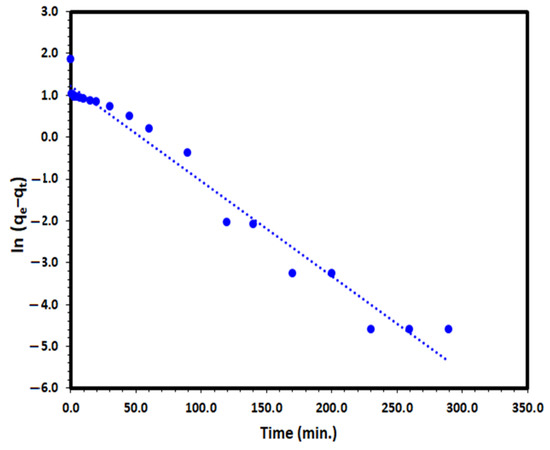
Figure 12.
Pseudo-first-order kinetic model plot for the adsorption of DV31 using Tb-FTZB-MOF.
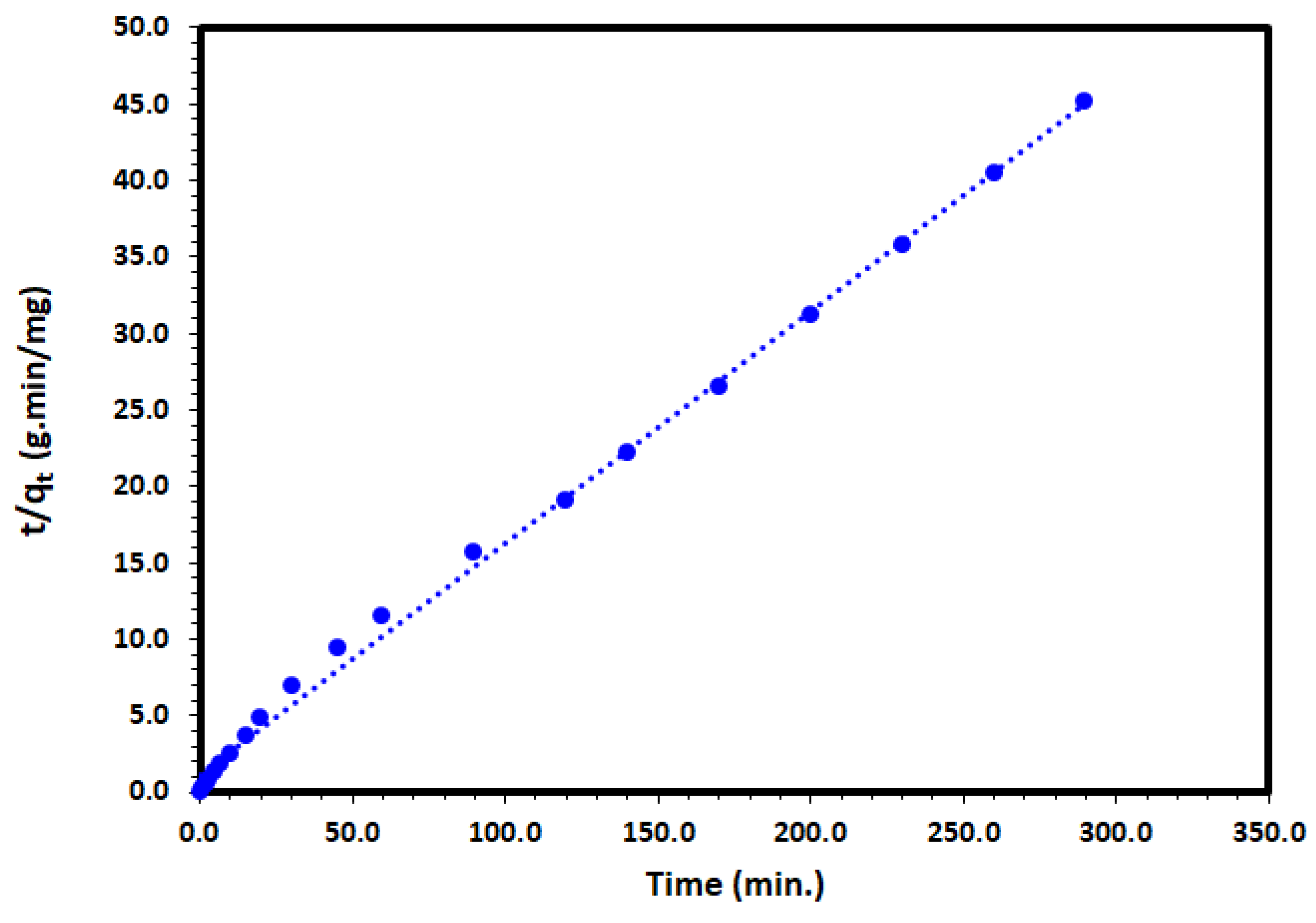
The pseudo-second-order (PSO) kinetic model was selected to describe the adsorption of the DV31 dye by Tb-FTZB-MOF. The linearized form of the PSO rate equation is as follows:
where k2 (g/mg·min) is the PSO rate coefficient. Applying the PSO rate equation and plotting of t/qt and t to the adsorption of DV31 dye experimental data converged very well for the DV31 with excellent correlation coefficient of 0.997 and straight line (Figure 13, Table 2), which may have indicated the suitability of the pseudo-second-order rate equation to describe the DV31 dye adsorption by Tb-FTZB-MOF from aqueous solution.
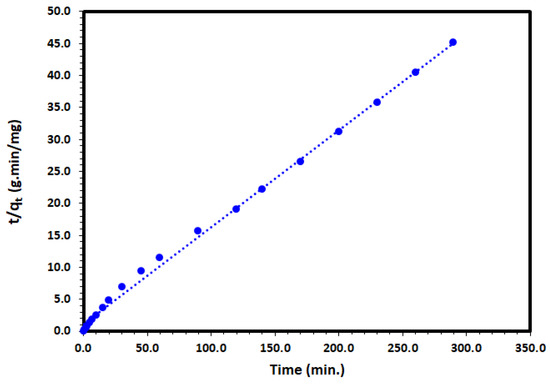
Figure 13.
Pseudo-second-order kinetic model plot for the adsorption of DV31 using Tb-FTZB-MOF.
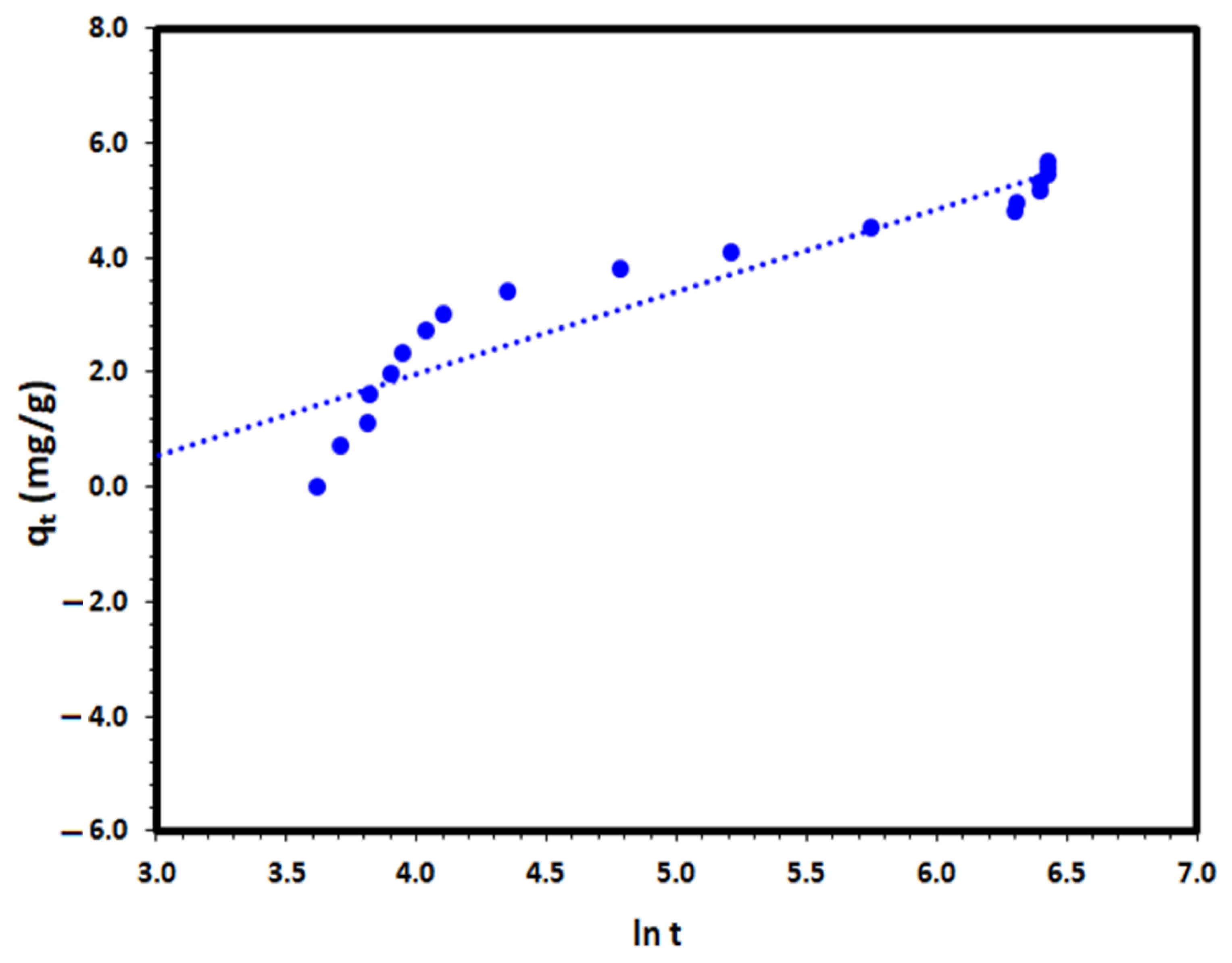
The Elovich equation is another kinetic model that describes the adsorption of adsorbate, such as DV31 dye by a solid adsorbent such as Tb-FTZB-MOF in an aqueous medium [52], and its linear form is as follows:
where α and β are the Elovich coefficients that represent the initial adsorption rate (g/(mg·min)) and the desorption coefficient (mg/(g·min)), respectively. The Elovich coefficients, α and β, were calculated from the slope and intercept of qt versus ln t to the experimental data and the results are presented at Figure 14. The correlation coefficient of the Elovich plot was not satisfactory with a value of 0.886, as presented in Table 2, which indicates the inappropriateness of the Elovich equation for the description of the removal process under investigation.
qt = β ln (αβ) + β ln t
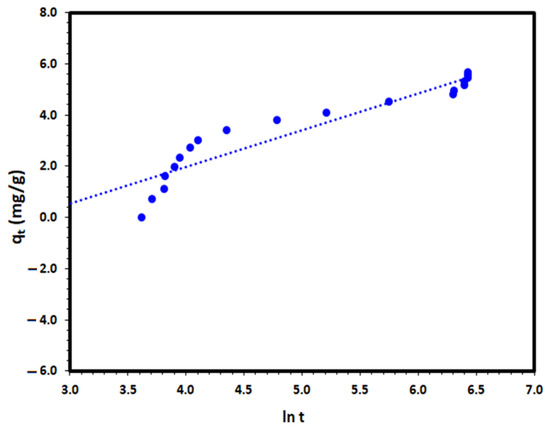
Figure 14.
Elovich kinetic model plot for the DV31 dye adsorption from an aqueous solution by Tb-FTZB-MOF.
By comparing the results on Table 2 obtained from application of different kinetic models to the experimental data at Figure 6,the fractional power function model, Lagergren pseudo-first-order model, pseudo-second-order model, and Elovich equation, it can be concluded that the removal via adsorption pathway of DV31 dye from an aqueous solution by Tb-FTZB-MOF could be expressed well by either the PFO or PSO kinetic models due to their high convergence as well as the excellent correlation coefficients: 0973, and 0.997, respectively. Moreover, to validate the suitability of either PFO or PSO kinetic models, two different statistical tests were used; the chi-square test [53]; Equation (5), the sum of the squares of errors (SSE) [54]; and Equation (6), as shown in the following:
where qe,calc and qe,exp are the calculated and experimental amount of DV31 removed (mg) per unit mass of Tb-FTZB-MOF at equilibrium presented in Table 2. The achieved χ2 values and the SSE values were 2.653 and 0.003, and 9.08 and 0.020, for the PFO kinetic model, and the PSO kinetic model was applied, respectively, indicating the suitability of the PSO kinetic model for describing the removal process, compared with the PFO kinetic model. Accordingly, it could be concluded that DV31 dye removal by Tb-FTZB-MOF from solutions were well described by the PSO compared to PFO.
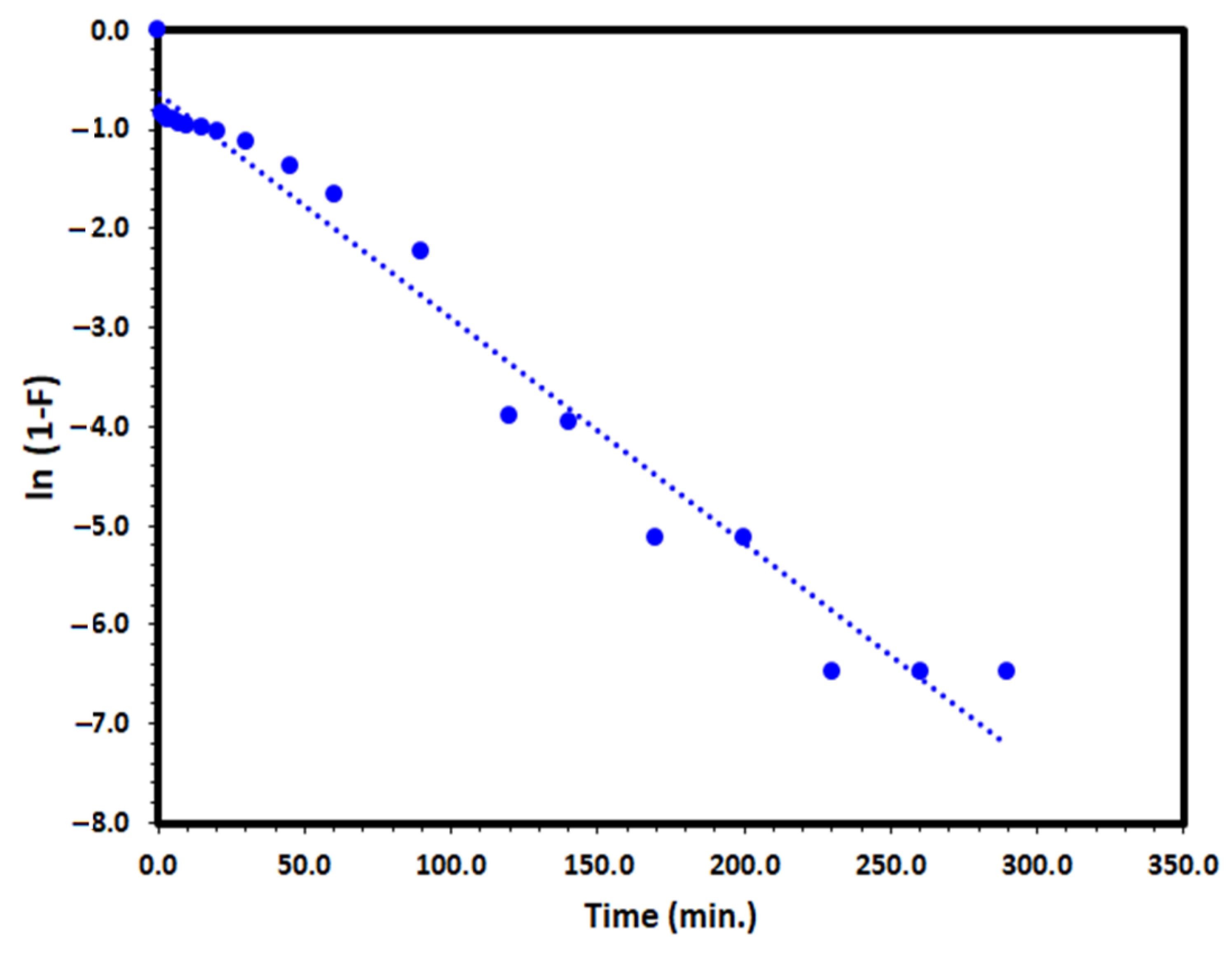
Moreover, the adsorption usually occurs in four distinctive steps; bulk diffusion, mass action, liquid film diffusion, and finally, intra-particle diffusion, which is classified as a pore and surface diffusion. This part of the study emphases on the determination of the rate determining step for the adsorption/diffusion process. Liquid film diffusion is another kinetic model that assumes that the flow of the adsorbate molecules through a liquid film surrounding the solid adsorbent is the slowest step in the adsorption process and determines the kinetics of the rate processes. The liquid film diffusion model is given by the following equation [55]:
where F is the fractional attainment of equilibrium (F = qt/qe), and kfd (min−1) is the film diffusion rate coefficient. The application of the liquid film diffusion model plot of −ln (1−F) versus t to the adsorption of DV31 dye by Tb-FTZB-MOF converged well and a straight line through the origin was obtained with a correlation coefficient value of 0.972 as it is presented in Figure 15 and Table 2, which may indicate that the liquid film diffusion model could be the rate determining step.
ln (1−F) = −kfd * t
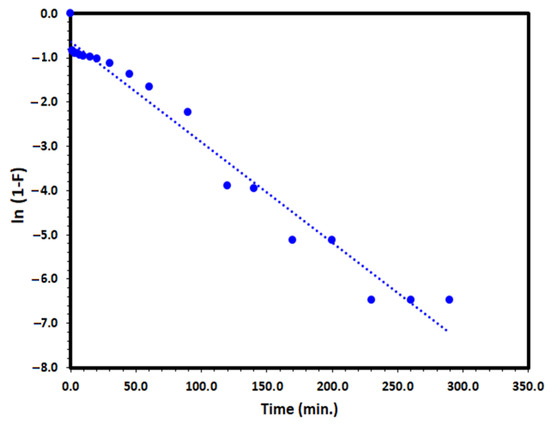
Figure 15.
Liquid film diffusion model plot for the adsorption of DV31 using Tb-FTZB-MOF.
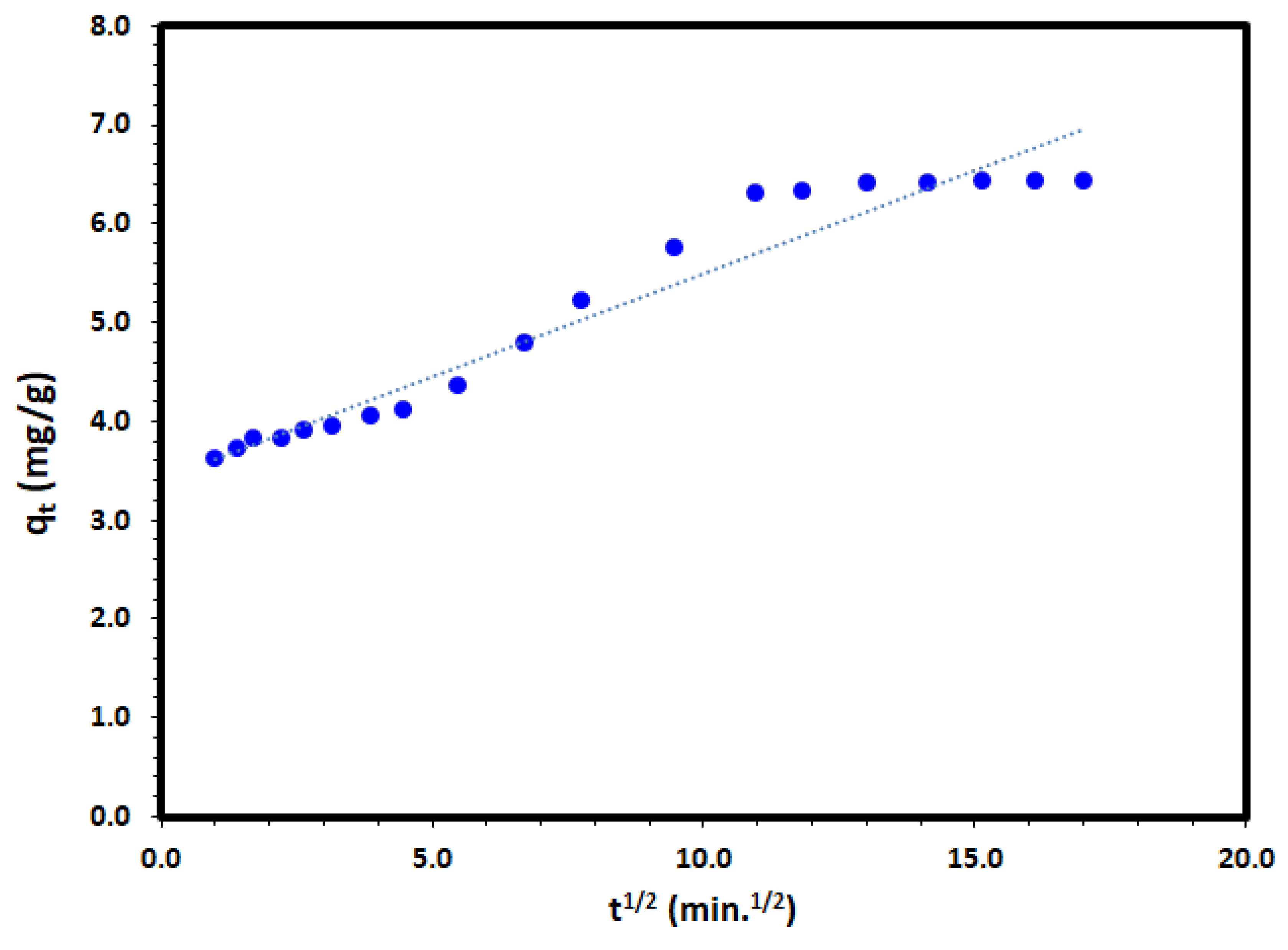
The intra-particle diffusion model [56] could be expressed as follows:
where kid is the intra-particle diffusion rate constant (mg/g.min1/2); and C (mg/g) is a constant proportional to the thickness of the boundary layer. Applying the intra-particle diffusion model to the experimental data and plot of qt versus t to the adsorption of DV31 dye by Tb-FTZB-MOF converged well and a straight line through the origin as it is presented in Figure 16 and Table 2; after the first minute, was obtained with a correlation coefficient value of 0.944, which may indicate that the intra-particle diffusion model could be the rate determining step. However, in this study, the removal diffusion kinetics may be controlled by both film diffusion and intra-particle diffusion simultaneously.
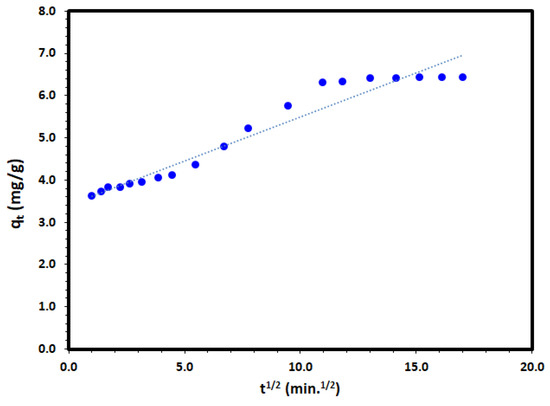
Figure 16.
Intra-particle diffusion model plot for the adsorption of DV31 using Tb-FTZB-MOF.
2.4. Environmental Applications
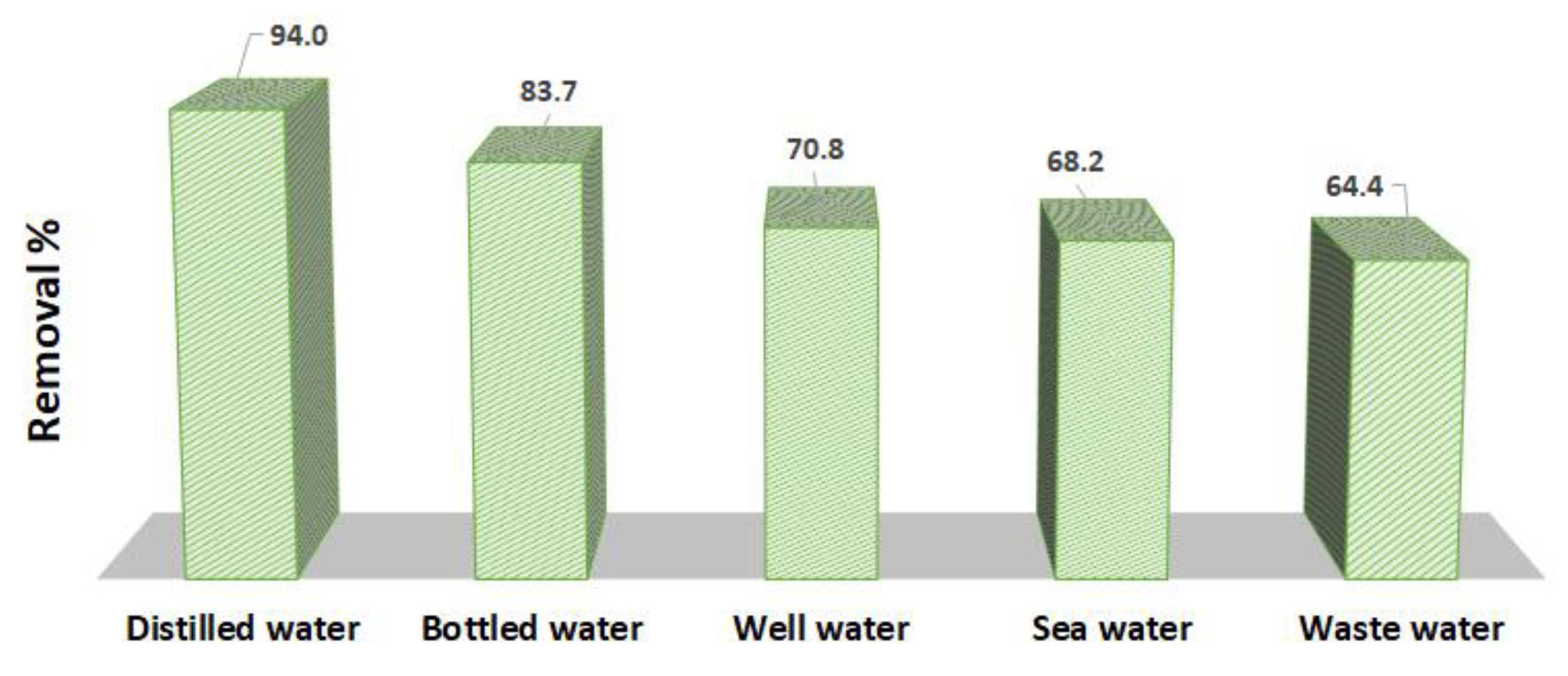
In order to further validate the efficiency of the Tb-FTZB-MOF as adsorbent for the removal of DV31 dye, five different water samples were used, and the results are shown in Figure 17. The concentrations of DV31 dye were measured after the samples collection, and were found to be below the detection limit, which is considered to be zero. Therefore, the real water samples were spiked with concentrated DV31 dye to acquire final concentration of 25.0 mg/L to simulate a pollution scenario and to explore the possible application of Tb-FTZB-MOF as a potential solid material for the remediation of water pollution. Tb-FTZB-MOF was mixed with the spiked real samples, and the removal percentages of DV31 dye were 94.0%, 83.7%, 70.8%, 68.2%, and 64.4%, for the distilled water, bottled water, well water, sea water, and wastewater samples, respectively. It noteworthy to mention that the low removal percent of the DV31 dye for the sea water, well water and wastewater by the solid Tb-FTZB-MOF could be attributed mainly due to the excessive concentrations of Na+, K+, Mg2+, and Ca2+ presented in the selected water samples, as compared to the other real water samples. These ions present at such high concentrations resulted in a shielding and screening effect, which decreased the DV31 dye removed by the solid Tb-FTZB-MOF. These results showed that most of the DV31 dye were removed from the real environmental water samples using the Tb-FTZB-MOF.
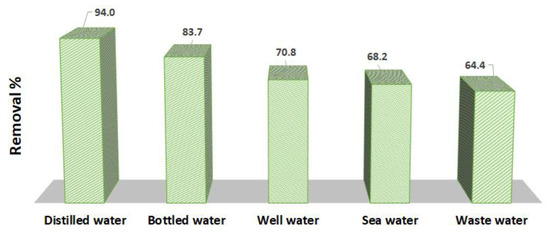
Figure 17.
Removal of DV31 from environmental water using Tb-FTZB-MOF. (Experimental conditions: 56 mg Tb-FTZB-MOF, 10 mL solution, pH 8, 120 min, and DV31 dye conc. 25 mg/L).
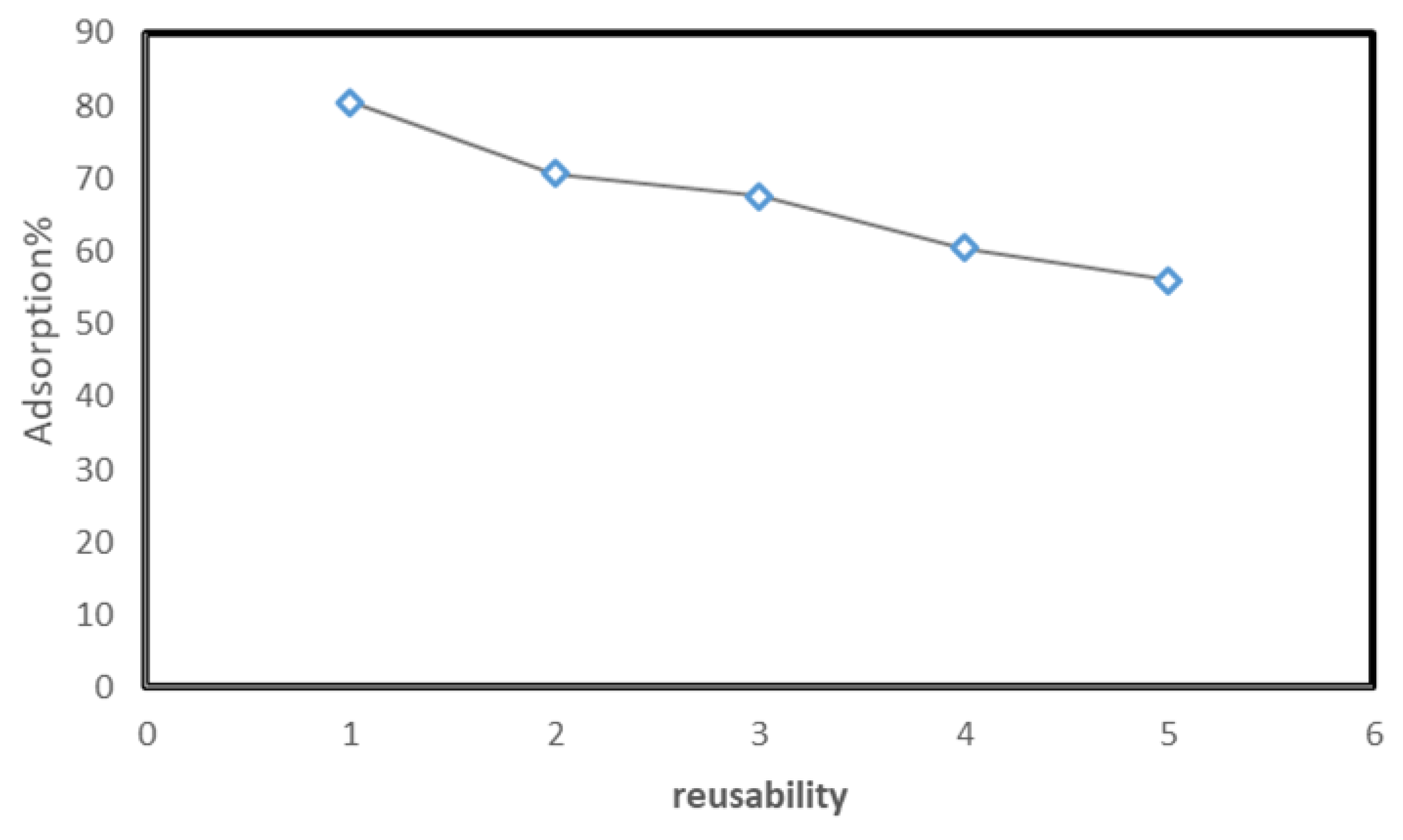
2.5. Reusability Studies
The reusability of a solid adsorbent is vital for practical application. It is a very essential aspect in adsorption from both environment and economical point of view. Sequel to that, the recycling efficiency of Tb-FTZB-MOF for the adsorption of DV31 dye was studied in five consecutive cycles, and it was observed that the percentage removal of DV31 using Tb-FTZB-MOF decreased slightly, even after the fifth cycle with high removal efficiency (Figure 18). This indicates that Tb-FTZB-MOF is a reusable adsorbent for the environmental remediation. Additionally, based on Figure 2, the PXRD pattern of the Tb-FTZB-MOF did not changed much after the adsorption of the DV31 dye, indicating the high stability of the Tb-FTZB-MOF for the environmental remediation application.
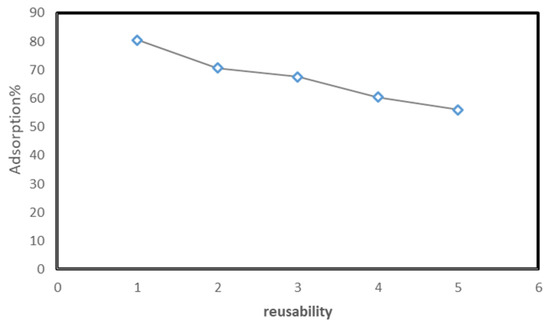
Figure 18.
Reusability of Tb-FTZB-MOF adsorbent in the removal of DV31 dye from solution. (Experimental conditions: 35 mg Tb-FTZB-MOF, 10 mL, pH 8, 120 min, and DV31 dye conc. 25 mg/L).
2.6. Thermodynamic Studies
The thermodynamic parameters, entropy change (ΔS), enthalpy change (ΔH), and Gibbs free energy change (ΔG), are very crucial to exploring and obtaining predictions of spontaneity and thermodynamic feasibility of any the physical or chemical process, such as the removal of DV31 dye from aqueous solution by Tb-FTZB-MOF as solid adsorbent. The following equations were used to calculate the thermodynamic parameters [57]:
where Kd is the thermodynamic distribution coefficient calculated using the amount DV31 dye removed at equilibrium (mg DV31 dye per g of Tb-FTZB-MOF), and Ct is the equilibrium concentration of DV31 dye at the solution (mg/L) [57]. A straight line was observed upon plotting of ln Kd vs. 1/T as presented in Figure 17, and the straight-line slope and intercept were used to enumerate the ΔH and ΔS, respectively.
ΔG = ΔH − TΔS
Thermodynamic parameters for the removal of Dv31 dye by the Tb-FTZB-MOF were calculated, and ∆H, ∆S, and ∆G values were +29.3 kJ/mole, +151 J/mole.K, and −16.5 kJ/mole, respectively. It could be observed that the enthalpy change has a positive value indicating the endothermic nature of the removal process, which was unfavorable to the removal process. Meanwhile, the entropy change has a positive value, indicating the increase in the degrees of freedom at the liquid-solid interface as a result of the DV31 dye adsorbed to Tb-FTZB-MOF solid surface, in favor the spontaneity of the removal process. Accordingly, the free energy change has a negative change that would be expected for a spontaneous removal process. In contrast, the positive values of the ∆H, and ∆S and the negative value of the ∆G present that DV31 dye removal by Tb-FTZB-MOF from aqueous solution is an entropy-driven process. In addition, the value of the ∆H usually indicates the physical nature of the adsorption, as the value is lower than 40 kJ/mol [58].
Based on the above mentioned results, the maximum removal capacities of DV31 dye (25.0 mg/L), obtained using 0.035 g/L loading of Tb-FTZB-MOF within 120.0 min were 6.44 mg/g, which is very competitive with other removal methods based on the removal capacity and the treatment time as presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Removal capacity of DV31 dye by various removal techniques.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
All chemicals were analytical grade and used without further purification. Terbium (III) nitrate pentahydrate (Tb(NO3)3·5H2O) was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (Oakville, ON, Canada) 2-fluoro-4-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl) benzoic acid (H2FTZB) was prepared according to the literature [59]. Ethanol and dimethylformamide were supplied by Fisher chemicals (Hampton, NH, United States). Sodium hydroxide and nitric acid were obtained from QReC chemicals (Mueang Chon Buri Chonburi 20130, Thailand). Potassium nitrate and chlorobenzene were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (Oakville, ON, Canada), while direct violet 31 dye was obtained from the Hangzhou Emperor chemical (Xiao Shan City, China). Distilled water was used during the preparation of all solutions.
3.2. Synthesis of Tb-FTZB-MOF
Tb-FTZB-MOF was synthesized using a similar method reported by [59]. Briefly, Tb(NO3)3·5H2O (0.0435 mmol), H2FTZB (0.0653 mmol), DMF (1.0 mL), C2H5OH (0.5 mL), and chlorobenzene (0.5 mL) were combined in a scintillation vial (20 mL) and sealed. The mixture was then heated at 115 °C for 72 h and cooled to room temperature. The crystals were then collected and dried in air.
3.3. Characterizations
The crystal structure of Tb-FTZB-MOF was characterized using the X-ray powder diffractometer (BRUKER D8, Billerica, MA, United States) with Cu-Kα radiation. Specific surface area of Tb-FTZB-MOF was determined using Micromeritics ASAP 2020 V 4.01 (Norcross, GA, United States) at liquid nitrogen temperature (−196 °C).
3.4. Adsorption Experiment
A stock solution of DV31 Dye (25 mg/L) was prepared, and subsequently, 10 mL of the prepared dye solution was treated with certain amount of the adsorbent (Tb-FTZB-MOF) for 2 h without agitation. After the experiment, the amount of DV31 dye adsorbed was monitored using SHIMADZU CPS-240A UV-VIS spectroscopy (Kyoto, Japan). The effect of experimental conditions, such as Tb-FTZB-MOF loading (7–56 mg), solution pH (3–8), DV31 dye concentration (10–40 ppm), solution temperature (273 K–353 K), and ionic strength using KNO3 (0.001 M–0.1 M) were studied in order to determine the performance of Tb-FTZB-MOF towards the adsorption of DV31 dye under different conditions. The efficiency of the Tb-FTZB-MOF towards removal adsorption of DV31 dye was calculated using Equation (1), and the adsorption capacity (qt, mg.g−1) was calculated using Equation (2).
where C0 and Ct are the concentrations of DV31 dye in solution (g L−1) at time t = 0 and t, respectively. V is the volume of the solution (L), and m is the mass of the dry adsorbent used (g).
3.5. Real Water Samples Collection
To confirm the applicability of the Tb-FTZB-MOF as solid adsorbent for the environmental remediation of polluted real water with DV31 dye different real water samples were collected. Wastewater sample was collected from the Membrane Bio-Reactor Technology Wastewater Treatment Plant (MBR 6000 STP) at King Abdulaziz University (KAUWW), Jeddah City (Latitude deg. North 21.487954, Longitude deg. East 39.236748). Well water samples were collected from a deep well at Abdraboh AL-Beladi Farm; Khulais Province, Saudi Arabia (Latitude deg. North 22.124376, Longitude deg. East 39.500618), in addition to distilled water samples from the distillation unit of King Abdulaziz University laboratories, Safa water samples (commercial bottled water), and Red Sea water samples. All real water samples were filtered through 45.0 µm Millipore filter paper and kept in Teflon® bottles and stored at 5 °C in dark.
4. Conclusions
The synthesis of terbium-based metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) based on fcu topology, fcu-Tb- FTZB-MOF, using 2-fluoro-4-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)benzoic acid (FTZB) as a linear ligand was studied, and it was characterized using powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) and Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) analysis, which showed the successful preparation of the Tb-FTZB-MOF. The synthesized Tb-FTZB-MOF was used for the environmental remediation as a catalytic adsorbent to remove direct violet 31 (DV31) dye from aqueous model and real solution. The effect of various operational parameters such as adsorbent loading, contact time, initial DV31 dye concentration, initial solution pH, different water matrix, temperature, and ionic strength have also been evaluated, and the results should make efficient the removal of the DV31 dye at ambient temperature, and at pH value of 8.0 using 35 mg Tb-FTZB-MOF, within few minutes. The removal of the DV31 dye by the Tb-FTZB-MOF was explored and studied kinetically and the results revealed that the removal process followed the pseudo-second-order kinetic model. Additionally, the removal process was studied thermodynamically, and the process was spontaneous (negative Gibbs free energy change) and endothermic (positive enthalpy change) with a positive entropy, indicating an entropy-driven process. Finally, the result showed that Tb-FTZB-MOF adsorbent was able to adsorb high percentage of DV31 and maintained reasonable efficiency even after five cycles, indicating the potential application of the Tb-FTZB-MOF a promising adsorbent in wastewater remediation application.
Author Contributions
Data curation, A.D.A. and M.A.S., methodology; M.A.S. and D.A..; investigation, A.D.A. and M.A.S.; validation, M.A.S.; supervision, M.A.S. and D.A.; formal analysis, M.A.S. and D.A..; visualization, A.D.A. and M.A.S.; resources, M.A.S.; writing—original draft, A.D.A., M.A.S.; writing—review and editing, M.A.S. and D.A.; funding acquisition M.A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR), King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia under grant no. (S: 38-130-1440).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This project was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR) at King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, under grant no. S: 38-130-1440. The authors, therefore, acknowledge with thanks DSR and Saudi Basic Industries Corporation (Sabic) for technical and financial support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Anju, A.; Ravi, S.P.; Bechan, S. Water pollution with special reference to pesticide contamination in India. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2010, 2010, 432–448. [Google Scholar]
- Dechnik, J.; Janiak, C.; De, S. Aluminium fumarate metal-organic framework: A super adsorbent for fluoride from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 303, 10–20. [Google Scholar]
- Rasalingam, S.; Peng, R.; Koodali, R.T. Removal of hazardous pollutants from wastewaters: Applications of TiO2-SiO2 mixed oxide materials. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, P. Investing in Tomorrow’s Liquid Gold. Available online: http://finance.yahoo.com/columnist/article/trenddesk/pp3748 (accessed on 16 November 2013).
- Barlow, M.; Clarke, T. Blue Gold: The Battle Against Corporate Theft of the World’s Water; Routledge: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wawrzkiewicz, M.; Polska-Adach, E.; Hubicki, Z. Polacrylic and polystyrene functionalized resins for direct dye removal from textile effluents. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 2122–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastiano, R.; Contiello, N.; Senatore, S.; Righetti, P.G.; Citterio, A. Analysis of commercial Acid Black 194 and related dyes by micellar electrokinetic chromatography. Dye Pigment. 2012, 94, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Lee, J.; Chen, H.; Zheng, Y. Preparation and catalytic performance of copper-containing magnetic catalysts for degradation of azo dye (direct violet). Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 3069–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadaf, S.; Bhatti, H.N.; Arif, M.; Amin, M.; Nazar, F.; Sultan, M. Box–Behnken design optimization for the removal of Direct Violet 51 dye from aqueous solution using lignocellulosic waste. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 56, 2425–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Quan, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y. Reduction of acute toxicity and genotoxicity of dye effluent using Fenton-coagulation process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 274, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanpour, M.; Hatami, M. Photocatalytic performance of aerogels for organic dyes removal from wastewaters: Review study. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 309, 113094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, A.; Bibi, I.; Majid, F.; Kamal, K.; Taj, B.; Raza, M.A.S.; Khaliq, N.; Katubi, K.M.; Ezzine, S.; Alwadai, N.; et al. Mn doped SrFe12O19 fabricated via facile microemulsion route and solar-light-driven photocatalytic removal of crystal violet dye. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2022, 646, 414303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, W.; Guan, K.; Peng, C.; Wu, J. Freeze-casting of alumina ultra-filtration membranes with good performance for anionic dye separation. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 11901–11904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradihamedani, P. Recent advances in dye removal from wastewater by membrane technology: A review. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 2603–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, S.; Derakhshankhah, H.; Jaymand, M. Simultaneous removal of cationic dyes from simulated industrial wastewater using sulfated alginate microparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 363, 119880. [Google Scholar]
- Saria, Y.; Taher, T.; Hariani, P.L.; Lesbani, A. Synthesis of Zn/Al layered double hydroxides as adsorbent for congo red and direct violet removal from aqueous solution. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Chemistry, Chemical Process and Engineering (IC3PE), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 14 August 2018; Volume 2026, p. 020043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Rahim, W.M.; El-Ardy, O.A.; Mohammad, F.H. The effect of pH on bioremediation potential for the removal of direct violet textile dye by Aspergillus niger. Desalination 2009, 249, 1206–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadaf, S.; Bhatti, H.N.; Nausheen, S.; Amin, M. Application of a novel lignocellulosic biomaterial for the removal of Direct Yellow 50 dye from aqueous solution: Batch and column study. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2015, 47, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahinez, H.; Abdelkader, O.; Leila, Y.; Tran, H.N. One-stage preparation of palm petiole-derived biochar: Characterization and application for adsorption of crystal violet dye in water. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 100872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Ngwabebhoh, F.A.; Saha, N.; Saha, T.; Saha, P. Gellan gum/bacterial cellulose hydrogel crosslinked with citric acid as an eco-friendly green adsorbent for safranin and crystal violet dye removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Chen, M.; Wang, H.; Zeng, G.; Huang, D.; Cheng, M.; Liu, Y.; Xue, W.; Wang, Z. The application of different typological and structural MOFs-based materials for the dyes adsorption. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 380, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Du, M.; Li, H.; Zhou, T. Removal of direct dyes from aqueous solution by oxidized starch cross-linked chitosan/silica hybrid membrane. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Mittal, J.; Malviya, A.; Gupta, V. Adsorptive removal of hazardous anionic dye “Congo red” from wastewater using waste materials and recovery by desorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 340, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, S.; Sen, T. Review on Dye Removal from Its Aqueous Solution into Alternative Cost Effective and Non-Conventional Adsorbents. J. Chem. Process Eng. 2013, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Taher, T.; Huda, N.; Palapa, N.R.; Mohadi, R.; Lesbani, A. Preparation of MgAl LDH intercalated by α-PW12O403- for adsorptive removal of direct violet dye from aqueous solution. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Science, Mathematics, Environment, and Education, Surakarta, Indonesia, 26–28 July 2019; Volume 2194, p. 020125. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad-Rezaei, R.; Khalilzadeh, B.; Rahimi, F.; Rezaee, P.; Gupta, S. Application of low-cost adsorbents for dye removal—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2313–2342. [Google Scholar]
- Abdollahi, N.; Moussavi, G.; Giannakis, S. A review of heavy metals’ removal from aqueous matrices by Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs): State-of-the art and recent advances. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, Y.; Li, X.; Xia, Q.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Xiao, J.; Li, Z. Adsorptive and photocatalytic removal of Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) in water by metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 337, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadra, B.N.; Ahmed, I.; Lee, H.J.; Jhung, S.H. Metal-organic frameworks bearing free carboxylic acids: Preparation, modification, and applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 450, 214237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Lin, K.-Y.A.; Oh, W.-D.; Lisak, G. Metal-organic frameworks for pesticidal persistent organic pollutants detection and adsorption—A mini review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A.; Hasan, Z.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorptive removal of hazardous materials using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs): A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 244, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.K.; Sim, Y.; Carboni, M.L.; Meyer, D.; Mathews, N. Generating metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) from photovoltaic modules for wastewater remediation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, S.; Horcajada, P. Metal–Organic Frameworks for the Removal of Emerging Organic Contaminants in Water. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 8378–8415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.K.; Bhadra, B.N.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorptive removal of hazardous organics from water and fuel with functionalized metal-organic frameworks: Contribution of functional groups. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, S.; Bajpai, P.; Mittal, J.; Arora, C. Utilisation of cobalt doped Iron based MOF for enhanced removal and recovery of methylene blue dye from waste water. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 314, 113642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A.; Jung, B.K.; Hasan, Z.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorption and removal of phthalic acid and diethyl phthalate from water with zeolitic imidazolate and metal–organic frameworks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 282, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqadami, A.A.; Naushad, M.; Alothman, Z.; Ahamad, T. Adsorptive performance of MOF nanocomposite for methylene blue and malachite green dyes: Kinetics, isotherm and mechanism. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 223, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xiong, B.; Li, J.; Qian, L.; Liu, L.; Liu, Z.; Fang, P.; He, C. Dependence of Dye Molecules Adsorption Behaviors on Pore Characteristics of Mesostructured MOFs Fabricated by Surfactant Template. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 31441–31451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqadami, A.A.; Naushad, M.; Alothman, Z.A.; Ghfar, A.A. Novel metal–organic framework (MOF) based composite material for the sequestration of U (VI) and Th (IV) metal ions from aqueous environment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 2017, 9, 36026–36037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Zhou, C.; Xia, W.; Liang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xiong, W.; Cheng, M.; Wang, Z. Recent advances in metal–organic framework-based materials for removal of fluoride in water: Performance, mechanism, and potential practical application. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Xia, W.; Qu, X.; Wang, C.; Wenjun, W.; Liang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Xiong, W.; Cheng, M.; Song, B.; et al. Structure–performance correlation guided cerium-based metal–organic frameworks: Superior adsorbents for fluoride removal in water. Chemosphere 2023, 312, 137335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Dash, S.K.; Parida, K. Kinetics, isotherm, and thermodynamic study for ultrafast adsorption of Azo dye by an efficient sorbent: Ternary Mg/(Al + Fe) Layered double hydroxides. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 2532–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. Removal of Rhodamine B with Fe-supported bentonite as heterogeneous photo-Fenton catalyst under visible irradiation. Appl. Catal. B: Environmental. 2015, 178, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, S. Adsorption of methylene blue in water onto activated carbon by surfactant modification. Water 2020, 12, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Viraraghavan, T. Removal of Congo Red from an solution by fungus Aspergillus niger. Adv. Environ. Research. 2002, 7, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkoc, E.; Nuhoglu, Y. Potential of tea factory waste for chromium (VI) removal from solutions: Thermodynamic and kinetic studies. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 54, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demiral, H.; Demiral, I.; Tümsek, F.; Karabacakoğlu, B. Adsorption of chromium (VI) from solution by activated carbon derived from olive bagasse and applicability of different adsorption models. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 144, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Asheh, S.; Banat, F.; Abu-Aitah, L. The removal of methylene blue dye from solutions using activated and non-activated bentonites. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2003, 21, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khambhaty, Y.; Mody, K.; Basha, S.; Jha, B. Kinetics equilibrium and thermodynamic studies on biosorption of hexavalent chromium by dead fungal biomass of marine Aspergillus niger. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 145, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption geloster stoffe Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens. Handlingar 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G.; Wase, D.A.J.; Forster, C.F. Study of the sorption of divalent metal Study of the sorption of divalent metal ions on to peat. Adsorp. Sci. Technol. 2000, 18, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Application of Kinetic Models to the Sorption of Copper(II) on to Peat. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2002, 20, 797–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagdonavicius, V.B.; Nikulin, M.S. Chi-squared goodness-of-fit test for right censored data. Int. J. Appl. Math. Stat. 2011, 24, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Karri, R.R.; Sahu, J.N.; Jayakumar, N.S. Optimal isotherm parameters for phenol adsorption from aqueous solutions onto coconut shell based activated carbon: Error analysis of linear and non-linear methods. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 80, 472–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, G.E.; Adamson, A.W.; Myers, L.S. The exchange adsorption of ions from aqueous solutions by organic zeolites II kinetics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1947, 69, 2836–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, W.J.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1963, 89, 31–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owija, N.Y.; Salam, S.K.M.A. Removal of cadmium ions from aqueous solution by Zero valent iron nanoparticles: Equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 342, 117462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, P.; De Paula, J. Physical Chemistry for the Life Sciences; W. H. Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, D.; Cairns, A.J.; Belmabkhout, Y.; Wojtas, L.; Liu, Y.; Alkordi, M.H.; Eddaoudi, M. Tunable Rare-Earth fcu-MOFs: A Platform for Systematic Enhancement of CO2 Adsorption Energetics and Uptake. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 7660–7667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).