Design of a New Chemoenzymatic Process for Producing Epoxidized Monoalkyl Esters from Used Soybean Cooking Oil and Fusel Oil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
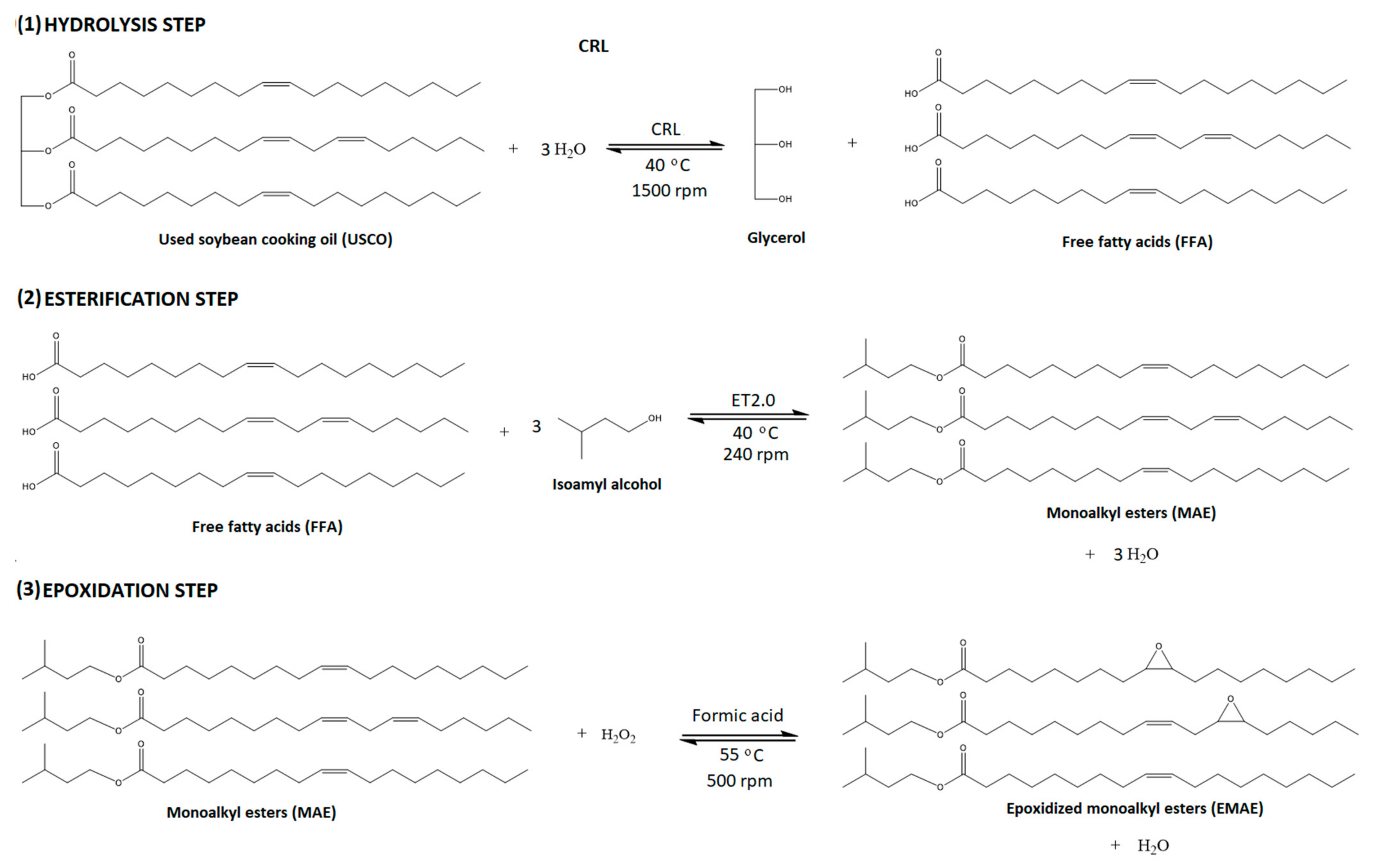
2.1. FFA Production from Enzymatic Hydrolysis of USCO: Screening the Lipase Sources
2.2. Comparative Performance of Soluble or Immobilized Lipase ET2.0 on MAE Production via Esterification in Solvent-Free Systems
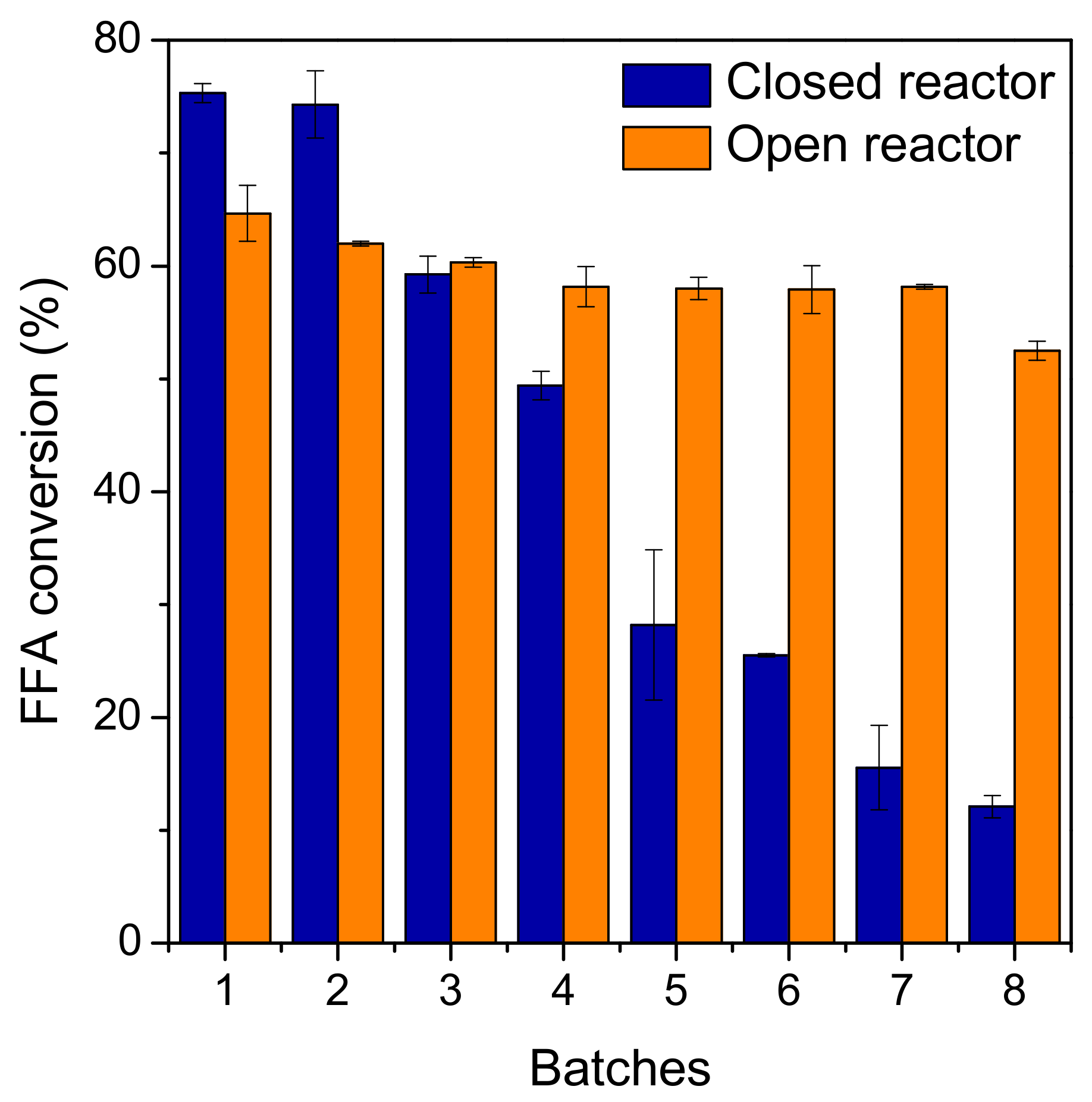
2.3. Biocatalyst Reusability Studies
2.4. In Situ Epoxidation of Monoalkyl Esters
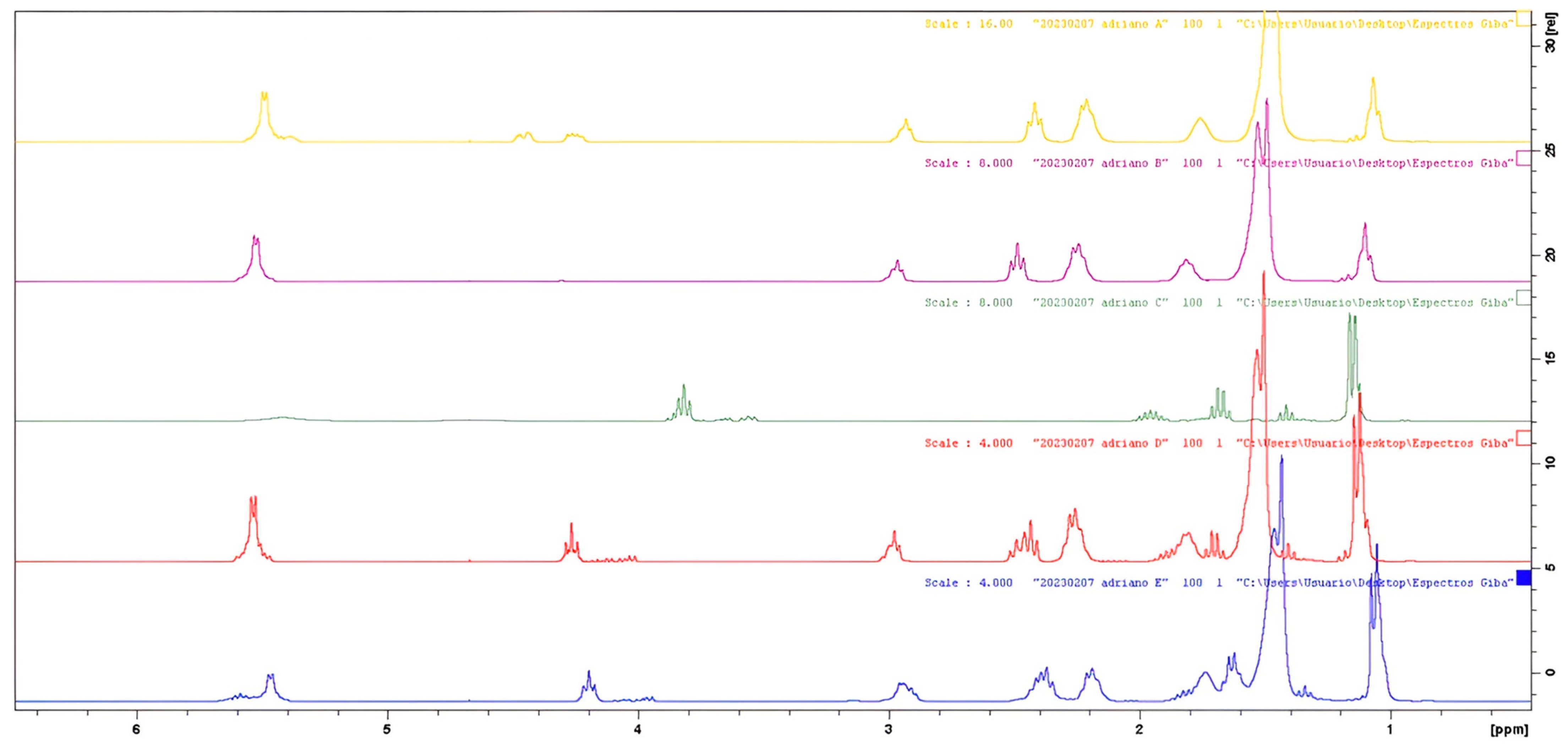
2.5. H NMR Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Fusel Oil Dehydration
3.3. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of USCO: Screening the Lipase Preparations
3.4. Immobilization of Lipase Eversa® Transform 2.0 via Physical Adsorption on PSty-DVB Beads
3.5. General Procedure for the Enzymatic Esterification of FFA and Fusel Oil in a Solvent-Free System
3.6. Heterogeneous Biocatalyst Reusability Tests
3.7. General Procedure for the In Situ Epoxidation of Monoalkyl Esters from USCO and Fusel Oil
3.8. Analytical Methods
3.8.1. Iodine Value (IV)
3.8.2. Relative Conversion Percentage of Double Bonds
3.8.3. Acid Value (AV)
3.8.4. Maximum Theoretical Epoxy Oxygen Content (OOCtheor.)
3.8.5. Experimental Epoxy Oxygen Content (OOCexp.)
3.8.6. Relative Conversion Percentage to Oxirane (ROC)
3.8.7. Selectivity (S)
3.9. 1H NMR Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, Z.; Mahmud, A.R.; Maneengam, A.; Nassani, A.A.; Haffar, M.; Cong, P.T. Non linear effect of Biomass, fossil fuels and renewable energy usage on the economic Growth: Managing sustainable development through energy sector. Fuel 2022, 326, 124943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renewable Chemicals|Opportunities & Forecast To 2030. Available online: https://www.psmarketresearch.com/market-analysis/renewable-chemicals-market# (accessed on 7 December 2022).
- Biomass Explained—U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). Available online: https://www.eia.gov/energyexplained/biomass/ (accessed on 7 December 2022).
- Berenblyum, A.S.; Danyushevsky, V.Y.; Kuznetsov, P.S.; Katsman, E.A.; Shamsiev, R. Catalytic methods for the manufacturing of high-production volume chemicals from vegetable oils and fats (review). Pet. Chem. 2016, 56, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baena, A.; Orjuela, A.; Rakshit, S.K.; Clark, J.H. Enzymatic hydrolysis of waste fats, oils and greases (FOGs): Status, prospective, and process intensification alternatives. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2022, 175, 108930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannu, A.; Garroni, S.; Porras, J.I.; Mele, A. Available Technologies and Materials for Waste Cooking Oil Recycling. Processes 2020, 8, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foo, W.H.; Chia, W.Y.; Tang, D.Y.Y.; Koay, S.S.N.; Lim, S.S.; Chew, K.W. The conundrum of waste cooking oil: Transforming hazard into energy. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zainal, N.A.; Zulkifli, N.W.M.; Gulzar, M.; Masjuki, H.H. A review on the chemistry, production, and technological potential of bio-based lubricants. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 80–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.K.; McAuley, K.B.; Peppley, B.A. Biolubricants through renewable hydrocarbons: A perspective for new opportunities. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 113, 109261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolina, I.C.A.; Gomes, R.A.B.; Mendes, A.A. Biolubricant Production from Several Oleaginous Feedstocks Using Lipases as Catalysts: Current Scenario and Future Perspectives. BioEnergy Res. 2021, 14, 1039–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, B.R.; Cermak, S.C.; Doll, K.M.; Kenar, J.A.; Sharma, B.K. A review of fatty epoxide ring opening reactions: Chemistry, recent advances, and applications. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2022, 99, 801–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemlou, M.; Daver, F.; Ivanova, E.P.; Adhikari, B. Polyurethanes from seed oil-based polyols: A review of synthesis, mechanical and thermal properties. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 142, 111841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belousov, A.S.; Esipovich, A.L.; Kanakov, E.A.; Otopkova, K.V. Recent advances in sustainable production and catalytic transformations of fatty acid methyl esters. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2021, 5, 4512–4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, A.A.; Soares, C.M.F.; Tardioli, P.W. Recent advances and future prospects for biolubricant base stocks production using lipases as environmentally friendly catalysts: A mini-review. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 39, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Liu, D. Preparation of Epoxidized Fatty Acid Methyl Ester with in situ Auto-Catalyzed Generation of Performic Acid and the Influence of Impurities on Epoxidation. Waste Biomass Valorization 2018, 9, 1881–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuy, N.T.; Lan, P.N. Epoxidation of vietnam rubber seed oil by using peroxophosphatotungstate catalyst complex based on Na2WO4/H3PO4/H2O2 with the presence of phase-transfer catalyst. Mol. Catal. 2021, 509, 111645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, D.; Zhao, X. Conversion of fatty acid methyl ester to epoxy plasticizer by auto-catalyzed in situ formation of performic acid: Kinetic modeling and application of the model. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 259, 120791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Ma, F.; Liu, J.; Song, R.-M.; Fu, Z.; Dai, J.-S.; Li, C.; Wen, Y.-L. Development of a new rejuvenator for aged SBS modified asphalt binder. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 380, 134986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhusudhana, A.M.; Mohana, K.N.S.; Hegde, M.B.; Nayak, S.R.; Rajitha, K.; Kumar, M.C.S. Functionalized graphene oxide dispersed polyvinyl alcohol-epoxidized linseed oil composite: An eco-friendly and promising anticorrosion coating material. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 650, 129382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaglieri, C.; Alarcon, R.T.; de Moura, A.; Bannach, G. Vegetable oils as monomeric and polymeric materials: A graphical review. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2022, 5, 100343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.-Y.; Dou, Q. “In situ” compatibilization of poly(L-lactic acid)/epoxidized soybean oil bio-blends by reactive additives. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 188, 115698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xu, S.; Wang, W.; Ran, X.; Ching, Y.C.; Sui, X.; Wei, Y.; Wang, R.; Al-Hada, N.M. Preparation and characterization of bioplastics from silylated cassava starch and epoxidized soybean oils. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 300, 120253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armanasco, F.; D’Hers, S.; Chiacchiarelli, L.M. Kinetic and chemorheological modeling of thermosetting polyurethanes obtained from an epoxidized soybean oil polyol crosslinked with glycerin. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e53194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Biresaw, G.; Cermak, S.C.; Isbell, T.A.; Ngo, H.L.; Chen, L.; Durham, A.L. Fatty Acid Estolides: A Review. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2020, 97, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polaczek, K.; Kurańska, M.; Prociak, A. Open-cell bio-polyurethane foams based on bio-polyols from used cooking oil. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 359, 132107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De María, P.D.; Sánchez-Montero, J.M.; Sinisterra, J.V.; Alcántara, A.R. Understanding Candida rugosa lipases: An overview. Biotechnol. Adv. 2006, 24, 180–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, R.R.; Arana-Peña, S.; da Rocha, T.N.; Miranda, L.P.; Berenguer-Murcia, A.; Tardioli, P.W.; dos Santos, J.C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Liquid lipase preparations designed for industrial production of biodiesel. Is it really an optimal solution? Renew. Energy 2021, 164, 1566–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, R.R.; Virgen-Ortiz, J.J.; Berenguer-Murcia, A.; da Rocha, T.N.; dos Santos, J.C.; Alcántara, A.R.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Biotechnological relevance of the lipase A from Candida antarctica. Catal. Today 2021, 362, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fregolente, P.B.; Fregolente, L.; Maciel, M.R.; Carvalho, P.O. Screening of microbial lipases and evalutaion of their potential to produce glycerides with high gamma linolenic acid concentration. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2009, 40, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabi, G.J.; Gama, R.S.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Cancino-Bernardi, J.; Mendes, A.A. Decyl esters production from soybean-based oils catalyzed by lipase immobilized on differently functionalized rice husk silica and their characterization as potential biolubricants. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2022, 157, 110019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Pedroza, J.D.J.; Sánchez-Ramírez, E.; Segovia-Hernández, J.G.; Hernández, S.; Orjuela, A. Recovery of alcohol industry wastes: Revaluation of fusel oil through intensified processes. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2021, 163, 108329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massa, T.; Raspe, D.; Feiten, M.; Cardozo-Filho, L.; da Silva, C. Fusel Oil: Chemical Composition and an Overview of Its Potential Application. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2023, 34, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, R.R.; Silva, A.S.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Ferreira-Leitão, V.S. Solvent-free esterifications mediated by immobilized lipases: A review from thermodynamic and kinetic perspectives. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 5696–5711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryglewicz, S.; Muszyński, M.; Nowicki, J. Enzymatic synthesis of rapeseed oil-based lubricants. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2013, 45, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerón, A.A.; Boas, R.N.V.; Biaggio, F.C.; de Castro, H.F. Synthesis of biolubricant by transesterification of palm kernel oil with simulated fusel oil: Batch and continuous processes. Biomass Bioenergy 2018, 119, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marty, A.; Dossat, V.; Condoret, J.S. Continuous operation of lipase-catalyzed reactions in nonaqueous solvents: Influence of the production of hydrophilic compound. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1997, 56, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombié, S.; Tweddell, R.; Condoret, J.-S.; Marty, A. Water activity control: A way to improve the efficiency of continuous lipase esterification. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1998, 60, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, G.; Condoret, J.S.; Monsan, P.; Marty, A. Esterification by immobilized lipase in solvent-free media: Kinetic and thermodynamic arguments. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2002, 78, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Séverac, E.; Galy, O.; Turon, F.; Pantel, C.A.; Condoret, J.-S.; Monsan, P.; Marty, A. Selection of CalB immobilization method to be used in continuous oil transesterification: Analysis of the economical impact. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2011, 48, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrutia, P.; Arrieta, R.; Alvarez, L.; Cardenas, C.; Mesa, M.; Wilson, L. Immobilization of lipases in hydrophobic chitosan for selective hydrolysis of fish oil: The impact of support functionalization on lipase activity, selectivity and stability. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wancura, J.H.; Fantinel, A.L.; Ugalde, G.A.; Donato, F.F.; de Oliveira, J.V.; Tres, M.V.; Jahn, S.L. Semi-continuous production of biodiesel on pilot scale via enzymatic hydroesterification of waste material: Process and economics considerations. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 285, 124838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, W.C.; Luiz, J.H.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Hirata, D.B.; Mendes, A.A. Eco-friendly production of trimethylolpropane triesters from refined and used soybean cooking oils using an immobilized low-cost lipase (Eversa>® Transform 2.0) as heterogeneous catalyst. Biomass Bioenergy 2021, 155, 106302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Júnior, J.G.G.; Mattos, F.R.; Sabi, G.J.; Carvalho, W.C.; Luiz, J.H.; Cren, C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Mendes, A.A. Design of a sustainable process for enzymatic production of ethylene glycol diesters via hydroesterification of used soybean cooking oil. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Júnior, J.M.; Mattos, F.; Costa, G.; Zurlo, A.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Mendes, A. Improved catalytic performance of lipase Eversa® Transform 2.0 via immobilization for the sustainable production of flavor esters—Adsorption process and environmental assessment studies. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Wu, Z.; Gao, N.; Xu, H.; Wang, D.; Zhou, F.; Nie, Y. Novel packed bed reactor designed for Prileschajew epoxidation of fatty acid methyl ester: Intensification of mass/heat transfer. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2022, 176, 108960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, F.; Kozell, V.; Petrucci, C.; Marrocchi, A.; Gu, Y.; Gelman, D.; Vaccaro, L. Formic acid, a biomass-derived source of energy and hydrogen for biomass upgrading. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 2646–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, Z.S.; Zlatanić, A.; Lava, C.C.; Sinadinović-Fišer, S. Epoxidation of soybean oil in toluene with peroxoacetic and peroxoformic acids— kinetics and side reactions. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2002, 104, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, P.D.; Patwardhan, A.V.; Kulkarni, R.D. Kinetic study of in situ epoxidation of mustard oil. Mol. Catal. 2021, 511, 111748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Lipase from Thermomyces lanuginosus: Uses and prospects as an industrial biocatalyst. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2010, 62, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feiten, M.C.; Rosa, C.D.; Treichel, H.; Furigo, A.; Zenevicz, M.C.; de Oliveira, D.; Oliveira, J.V. Batch and fed-batch enzymatic hydrolysis of soybean oil under ultrasound irradiation. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2014, 3, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenevicz, M.C.P.; Jacques, A.; Furigo, A.F.; Oliveira, J.V.; de Oliveira, D. Enzymatic hydrolysis of soybean and waste cooking oils under ultrasound system. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2016, 80, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.C.; Ayub, M.A.Z. Effects of the combined use of Thermomyces lanuginosus and Rhizomucor miehei lipases for the transesterification and hydrolysis of soybean oil. Process. Biochem. 2011, 46, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souza, J.E.S.; Monteiro, R.R.C.; Rocha, T.G.; Moreira, K.S.; Cavalcante, F.T.T.; Braz, A.K.D.S.; de Souza, M.C.M.; dos Santos, J.C.S. Sonohydrolysis using an enzymatic cocktail in the preparation of free fatty acid. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Kim, B.H.; No, D.S.; Yoon, S.W.; Lee, M.-W.; Im, D.J.; Kim, I.-H. Lipase-catalyzed synthesis of 2-ethylhexyl palmitate in a solvent free system using step changes in temperature. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 177, 108261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facin, B.; Quinto, E.; Valerio, A.; de Oliveira, D.; Oliveira, J.; Fernandez-Lorente, G. Strategies for the immobilization of Eversa® Transform 2.0 lipase and application for phospholipid synthesis. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Páez, B.; Medina, A.; Rubio, F.; Moreno, P.; Grima, E. Modeling the effect of free water on enzyme activity in immobilized lipase-catalyzed reactions in organic solvents. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2003, 33, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carvalho, P.D.O.; Contesini, F.; Bizaco, R.; Calafatti, S.A.; Macedo, G. Optimization of enantioselective resolution of racemic ibuprofen by native lipase from Aspergillus niger. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 33, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, K.C.; Cassimiro, D.M.; Avelar, M.H.; Hirata, D.B.; de Castro, H.F.; Fernández-Lafuente, R.; Mendes, A.A. Characterization of the catalytic properties of lipases from plant seeds for the production of concentrated fatty acids from different vegetable oils. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2013, 49, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.D.; Aracri, F.M.; Cren, C.; Mendes, A.A. Isotherm, kinetic, mechanism and thermodynamic studies of adsorption of a microbial lipase on a mesoporous and hydrophobic resin. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 311, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, D.; Weatherley, L. The effect of reaction conditions upon lipase catalysed hydrolysis of high oleate sunflower oil in a stirred liquid–liquid reactor. Process. Biochem. 2001, 36, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lage, F.A.; Bassi, J.J.; Corradini, M.C.; Todero, L.M.; Luiz, J.H.; Mendes, A.A. Preparation of a biocatalyst via physical adsorption of lipase from Thermomyces lanuginosus on hydrophobic support to catalyze biolubricant synthesis by esterification reaction in a solvent-free system. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2016, 84, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudrant, J.; Woodley, J.M.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Parameters necessary to define an immobilized enzyme preparation. Process. Biochem. 2020, 90, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard Test Method for Determination of the Iodine Value of Fats and Oils. Available online: https://www.astm.org/d5554-95.html (accessed on 3 December 2022).
- Suzuki, A.H.; Botelho, B.G.; Oliveira, L.S.; Franca, A.S. Sustainable synthesis of epoxidized waste cooking oil and its application as a plasticizer for polyvinyl chloride films. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 99, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOCS Te 1a-64—Acid Value (2017) PDF|PDF|Titration|Chemistry. Available online: https://pt.scribd.com/document/451524050/AOCS-Te-1a-64-Acid-Value-2017-pdf (accessed on 4 December 2022).
- GB/T 1677-2008: PDF in English. Available online: https://www.chinesestandard.net/PDF.aspx/GBT1677-2008 (accessed on 4 December 2022).

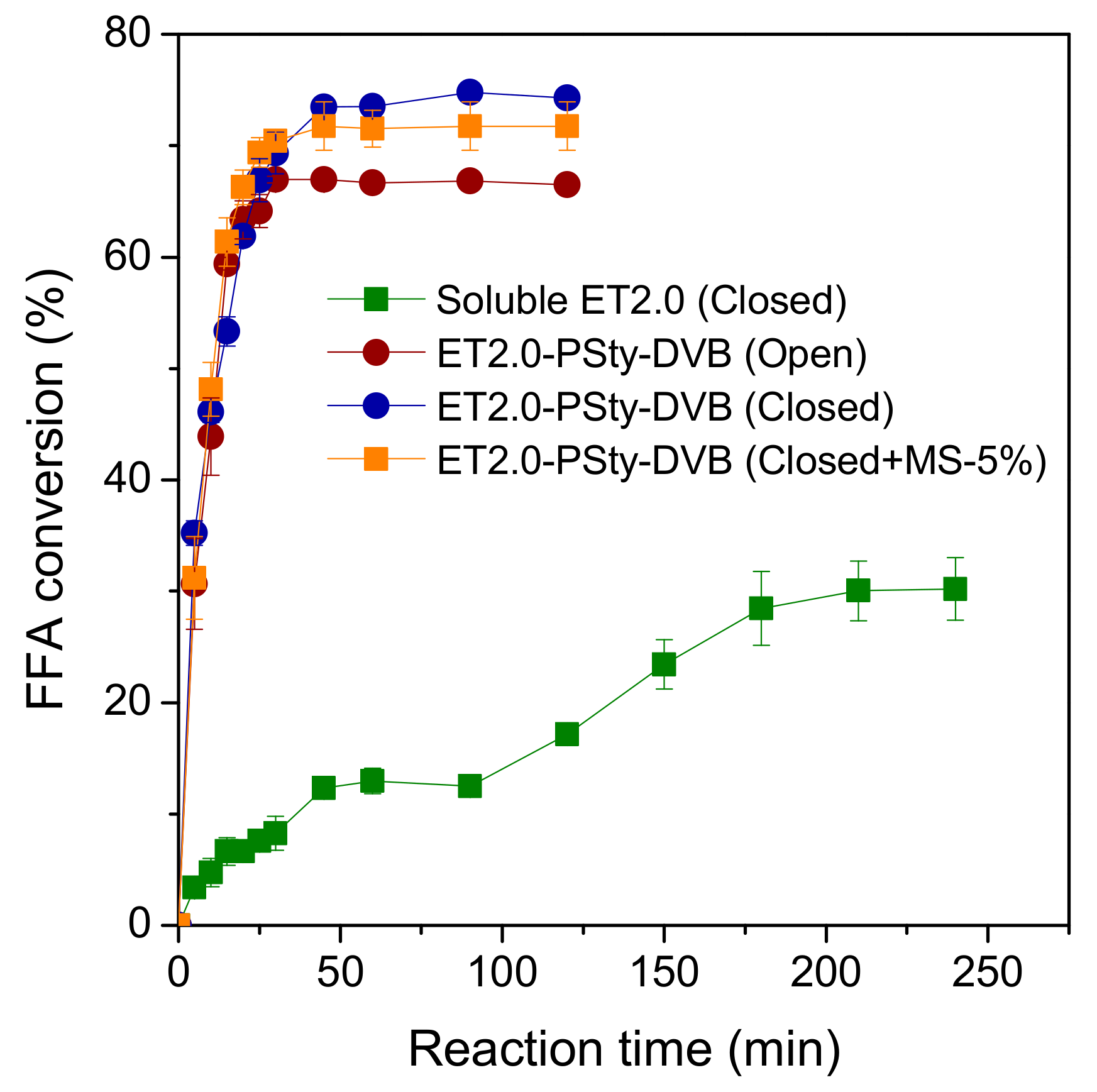
| Reaction System | Y a (%) | te b (min) | PFFA c (µmolFFA·min−1·mgprot−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soluble ET2.0 d (Closed reactor) | 30.2 ± 2.7 | 210 | 0.8 |
| ET2.0-PSty-DVB e (Open reactor) | 64.3 ± 2.3 | 30 | 12.4 |
| ET2.0-PSty-DVB e (Closed reactor) | 73.5 ± 0.4 | 45 | 9.4 |
| ET2.0-PSty-DVB e (Closed reactor + MS f-5%) | 71.8 ± 2.2 | 45 | 9.2 |
| Properties | Units | MAE a | EMAE b | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Open Reactor | Closed Reactor | Open Reactor | Closed Reactor | ||
| IV c | gI2 per 100 g | 110.2 ± 1.7 | 109.8 ± 1.1 | 73.5 ± 0.9 | 72.6 ± 1.4 |
| X d | % | - | - | 33.3 | 33.9 |
| AV e | mKOH·g−1 | 5.1 ± 0.3 | 5.8 ± 0.3 | 7.1 ± 0.4 | 7.3 ± 0.2 |
| OOCtheor. f | % | - | - | 6.50 | 6.47 |
| OOCexp. g | % | - | - | 1.75 ± 0.01 | 1.78 ± 0.03 |
| ROC h | % | - | - | 26.9 | 27.5 |
| S i | Dimensionless | - | - | 0.81 | 0.81 |
| Properties | Eversa® Transform 2.0 | CRL | CALA | RJL | ANL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Thermomyces lanuginosus | Candida rugosa | Candida sp. | Rhizopus javanicus | Aspergillus niger |
| Formulation | Liquid | Powder | Liquid | Powder | Powder |
| Hydrolytic activity a (U·g−1) | 19,856.7 | 16,156.8 | 806.4 | 27,436.5 | 20,224.9 |
| Protein b (mg·g−1) | 35.8 | 24.5 | 16.1 | 74.9 | 12.7 |
| Specific activity c (U·mgprot−1) | 554.6 | 659.5 | 50.1 | 366.3 | 1592.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mattos, F.R.; Júnior, J.M.; Sabi, G.J.; Garcia, P.H.D.; Carvalho, P.O.; Luiz, J.H.H.; Mendes, A.A. Design of a New Chemoenzymatic Process for Producing Epoxidized Monoalkyl Esters from Used Soybean Cooking Oil and Fusel Oil. Catalysts 2023, 13, 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13030543
Mattos FR, Júnior JM, Sabi GJ, Garcia PHD, Carvalho PO, Luiz JHH, Mendes AA. Design of a New Chemoenzymatic Process for Producing Epoxidized Monoalkyl Esters from Used Soybean Cooking Oil and Fusel Oil. Catalysts. 2023; 13(3):543. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13030543
Chicago/Turabian StyleMattos, Fernanda R., José Miguel Júnior, Guilherme J. Sabi, Pedro H. D. Garcia, Patrícia O. Carvalho, Jaine H. H. Luiz, and Adriano A. Mendes. 2023. "Design of a New Chemoenzymatic Process for Producing Epoxidized Monoalkyl Esters from Used Soybean Cooking Oil and Fusel Oil" Catalysts 13, no. 3: 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13030543
APA StyleMattos, F. R., Júnior, J. M., Sabi, G. J., Garcia, P. H. D., Carvalho, P. O., Luiz, J. H. H., & Mendes, A. A. (2023). Design of a New Chemoenzymatic Process for Producing Epoxidized Monoalkyl Esters from Used Soybean Cooking Oil and Fusel Oil. Catalysts, 13(3), 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13030543







