Simultaneous Oxidation of Emerging Pollutants in Real Wastewater by the Advanced Fenton Oxidation Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Physicochemical Characterization of the Influent (Real Wastewater) and Effluent Generated by the Advanced Fenton Oxidation Process
2.2. Simultaneous Oxidation of the Emerging Pollutants by the Advanced Fenton Oxidation Process
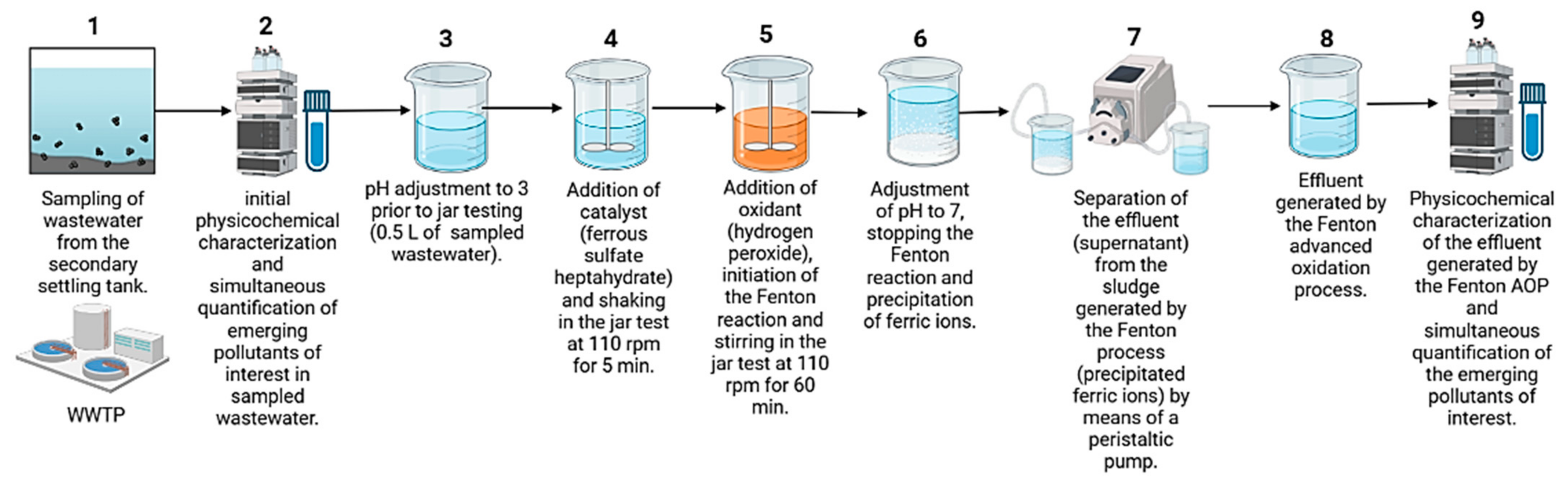
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Real Wastewater Sampling
3.2. Characterization of the Real Wastewater (Influent) and Effluent Generated by the Advanced Fenton Oxidation Process
3.3. Quantification of the Emerging Pollutants of Concern
3.3.1. Solid Phase Extraction (SPE)
3.3.2. Quantification of Emerging Contaminants of Interest
3.4. Experimental Setup (Advanced Fenton Oxidation Process)
3.5. Oxidation Percentage
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vasilachi, I.C.; Asiminicesei, D.M.; Fertu, D.I.; Gavrilescu, M. Occurrence and Fate of Emerging Pollutants in Water Environment and Options for Their Removal. Water 2021, 13, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Narvaez, O.M.; Peralta-Hernandez, J.M.; Goonetilleke, A.; Bandala, E.R. Treatment technologies for emerging contaminants in water: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 323, 361–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jari, Y.; Roche, N.; Necibi, M.C.; El Hajjaji, S.; Dhiba, D.; Chehbouni, A.G. Emerging Pollutants in Moroccan Wastewater: Occurrence, Impact, and Removal Technologies. J. Chem. 2022, 2022, 9727857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lama, G.; Meijide, J.; Sanromán, A.; Pazos, M. Heterogeneous Advanced Oxidation Processes: Current Approaches for Wastewater Treatment. Catalysts 2022, 12, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arman, N.Z.; Salmiati, S.; Aris, A.; Salim, M.R.; Nazifa, T.H.; Muhamad, M.S.; Marpongahtun, M. A Review on Emerging Pollutants in the Water Environment: Existences, Health Effects and Treatment Processes. Water 2021, 13, 3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracamontes-Ruelas, A.R.; Ordaz-Díaz, L.A.; Bailón-Salas, A.M.; Ríos-Saucedo, J.C.; Reyes-Vidal, Y.; Reynoso-Cuevas, L. Emerging Pollutants in Wastewater, Advanced Oxidation Processes as an Alternative Treatment and Perspectives. Processes 2022, 10, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, J.P.P.; Tabelini, C.H.B.; Aguiar, A. A Review of Gallic Acid-Mediated Fenton Processes for Degrading Emerging Pollutants and Dyes. Molecules 2023, 28, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roznere, I.; An, V.; Robinson, T.; Banda, J.A.; Watters, G.T. Contaminants of emerging concern in the Maumee River and their effects on freshwater mussel physiology. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0280382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagklis, D.P.; Bampos, G. Tertiary Wastewater Treatment Technologies: A Review of Technical, Economic, and Life Cycle Aspects. Processes 2022, 10, 2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufail, A.; Price, W.E.; Mohseni, M.; Pramanik, B.K.; Hai, F.I. A critical review of advanced oxidation processes for emerging trace organic contaminant degradation: Mechanisms, factors, degradation products, and effluent toxicity. J. Water Process. Eng. 2021, 40, 101778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, V.K.; Saidulu, D.; Majumder, A.; Srivastava, A.; Gupta, B.; Gupta, A.K. Emerging contaminants in wastewater: A critical review on occurrence, existing legislations, risk assessment, and sustainable treatment alternatives. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necibi, M.C.; Dhiba, D.; El Hajjaji, S. Contaminants of Emerging Concern in African Wastewater Effluents: Occurrence, Impact and Removal Technologies. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deblonde, T.; Cossu-Leguille, C.; Hartemann, P. Emerging pollutants in wastewater: A review of literature. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2011, 214, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogoi, A.; Mazumder, P.; Tyagi, V.K.; Tushara Chaminda, G.G.; An, A.K.; Kumar, M. Occurrence and fate of emerging contaminants in water environment: A review. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 6, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.H.; Reinhard, M.; Gin, K.Y.H. Occurrence and fate of emerging contaminants in municipal wastewater treatment plants from different geographical regions-a review. Water Res. 2018, 133, 182–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez, L.A.; Pascual, J.M.; Martínez, M.d.M.M.; Poyatos Capilla, J.M. Effectiveness of Advanced Oxidation Processes in Wastewater Treatment: State of the Art. Water 2021, 13, 2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Jiao, Y.; Xu, X.; Pan, Y.; Su, C.; Duan, X.; Sun, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Shao, Z. Superstructures with Atomic-Level Arranged Perovskite and Oxide Layers for Advanced Oxidation with an Enhanced Non-Free Radical Pathway. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 1899–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fast, S.A.; Gude, V.G.; Truax, D.D.; Martin, J.; Magbanua, B.S. A Critical Evaluation of Advanced Oxidation Processes for Emerging Contaminants Removal. Environ. Process. 2017, 4, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Yi, H.; Lai, C.; Liu, X.; Huo, X.; An, Z.; Li, L.; Fu, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, M.; et al. Critical review of advanced oxidation processes in organic wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 130104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, V.S.; Pare, B.; Gupta, P.; Jonnalagadda, S.B.; Shrivastava, R. A Review on Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) for Wastewater Remediation. Asian J. Chem. 2020, 32, 2677–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.B.; Pereira, L.O.; Moura, S.G.; Magalhães, F. Degradation of organic contaminants in effluents—Synthetic and from the textile industry—By Fenton, photocatalysis, and H2O2 photolysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 6299–6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousset, E.; Loh, W.H.; Lim, W.S.; Jarry, L.; Wang, Z.; Lefebvre, O. Cost comparison of advanced oxidation processes for wastewater treatment using accumulated oxygen-equivalent criteria. Water Res. 2021, 200, 117234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekin, H.; Bilkay, O.; Ataberk, S.S.; Balta, T.H.; Ceribasi, I.H.; Sanin, F.D.; Dilek, F.B.; Yetis, U. Use of Fenton oxidation to improve the biodegradability of a pharmaceutical wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, S.; Malakahmad, A. Optimization of Fenton process for refinery wastewater biodegradability augmentation. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 30, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Gao, Y.; Yang, M. Extended Fenton’s process: Toward improving biodegradability of drilling wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 79, 1790–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, N.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Pillai, S.C. Heterogeneous Fenton catalysts: A review of recent advances. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litter, M.I.; Slodowicz, M. An overview on heterogeneous Fenton and photoFenton reactions using zerovalent iron materials. J. Adv. Oxid. Technol. 2017, 20, 20160164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshini, M.; Das, I.; Ghangrekar, M.M.; Blaney, L. Advanced oxidation processes: Performance, advantages, and scale-up of emerging technologies. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 316, 115295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOM-001-SEMARNAT-2021 (Which Establishes the Permissible Limits of Pollutants in Wastewater Discharges into Receiving Bodies Owned by the Nation). Available online: https://www.dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=5645374&fecha=11/03/2022#gsc.tab=0 (accessed on 8 February 2023).
- Sudakin, D.L.; Trevathan, W.R. DEET: A review and update of safety and risk in the general population. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swale, D.R.; Bloomquist, J.R. Is DEET a dangerous neurotoxicant? Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 2068–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrelli, A.; DellaGreca, M.; Iesce, M.R.; Lavorgna, M.; Temussi, F.; Schiavone, L.; Crisculo, E.; Parrella, A.; Previtera, L.; Isidori, M. Ecotoxicological evaluation of caffeine and its derivatives from a simulated chlorination step. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bahlmann, A.; Brack, W.; Schneider, R.J.; Krauss, M. Carbamazepine and its metabolites in wastewater: Analytical pitfalls and occurrence in Germany and Portugal. Water Res. 2014, 57, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sol, D.; Menéndez-Manjón, A.; Arias-García, P.; Laca, A.; Laca, A.; Rancaño, A.; Díaz, M. Occurrence of Selected Emerging Contaminants in Southern Europe WWTPs: Comparison of Simulations and Real Data. Processes 2022, 10, 2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, G.S.; Kaur, S.; Pulicharla, R.; Brar, S.K.; Cledón, M.; Verma, M.; Surampalli, R.Y. Triclosan: Current Status, Occurrence, Environmental Risks and Bioaccumulation Potential. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 5657–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Velázquez, K.; Villanueva-Rodríguez, M.; Mejía-González, G.; Herrera-López, D. Removal of 17α-ethinylestradiol and caffeine from wastewater by UASB-Fenton coupled system. Environ. Technol. 2021, 42, 3771–3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Shoda, M. Removal of COD and color from livestock wastewater by the Fenton method. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 1314–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, M.S.; Peres, J.A. Removal of COD from olive mill wastewater by Fenton’s reagent: Kinetic study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Nie, J.; Wu, S.; Wang, D. Removal of COD and decolorizing from landfill leachate by Fenton’s reagent advanced oxidation. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2014, 16, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedinzadeh, N.; Shariat, M.; Monavari, S.M.; Pendashteh, A. Evaluation of color and COD removal by Fenton from biologically (SBR) pre-treated pulp and paper wastewater. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 116, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakika, D.C.; Sarto, S.; Mindaryani, A.; Hidayat, M. Decreasing COD in Sugarcane Vinasse Using the Fenton Reaction: The Effect of Processing Parameters. Catalysts 2019, 9, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polo-López, M.I.; Nahim-Granados, S.; Fernández-Ibáñez, P. Homogeneous Fenton and Photo-Fenton Disinfection of Surface and Groundwater. In Applications of Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) in Drinking Water Treatment, 1st ed.; Gil, A., Galeano, L., Vicente, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2018; Volume 67, pp. 155–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Orgániz, A.; Becerril Bravo, J.E.; Llompart, M.; Dagnac, T.; Lamas, J.P.; Vázquez, L.; Sampedro-Rosas, L. Emerging pollutants and antibiotics removed by conventional activated sludge followed by ultraviolet radiation in a municipal wastewater treatment plant in Mexico. Water Qual. Res. J. Canada 2021, 56, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, M.; de Pedro, Z.M.; Casas, J.A.; Rodriguez, J.J. Triclosan breakdown by Fenton-like oxidation. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 198–199, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cokay, E.; Oztamer, M. Degradation of triclosan by photo-fenton oxidation. J. Sci. Eng. 2017, 19, 583–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Miao, D.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Gao, S. Removal of triclosan in a Fenton-like system mediated by graphene oxide: Reaction kinetics and ecotoxicity evaluation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 673, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klamerth, N.; Rizzo, L.; Malato, S.; Maldonado, M.I.; Aguera, A.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Degradation of fifteen emerging contaminants at mg.L−1 initial concentrations by mild solar photo-Fenton in MWTP effluents. Water Res. 2010, 44, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekikot, B.; Mammeri, L.; Talbi, K.; Benssassi, M.E.; Abdessemed, A.; Sehili, R. Homogeneous modified Fenton-like oxidation using FeIII-gallic acid complex for ibuprofen degradation at neutral pH. Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 234, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.C.-F.; Leung, K.S.-Y. Redox mediators and irradiation improve fenton degradation of acesulfame. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Üstün Odabaşı, S.; Maryam, B.; Büyükgüngör, H. Fenton oxidation of carbamazepine in wastewater with fewer reagents. Sigma J. Eng. Nat. Sci. 2018, 36, 289–298. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, T.D.; Martini, W.S.; Santos, M.D.R.; Matos, M.A.C.; Rocha, L.L. Caffeine Oxidation in Water by Fenton and Fenton-Like Processes: Effects of Inorganic Anions and Ecotoxicological Evaluation on Aquatic Organisms. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2015, 26, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NMX-AA-003-1980 (Mexican Standard for Wastewater Sampling). Available online: https://agua.org.mx/biblioteca/nmx-aa-003-1980-aguas-residuales-muestreo/ (accessed on 4 February 2023).
- NMX-AA-008-SCFI-2011 (Water Analysis—pH Determination). Available online: http://www.economia-nmx.gob.mx/normas/nmx/2010/nmx-aa-008-scfi11.pdf (accessed on 4 February 2023).
- NMX-AA-007-SCFI-2013 (Water Analysis-Temperature Measurement in Natural, Waste and Treated Wastewater). Available online: http://legismex.mty.itesm.mx/normas/aa/aa007-2014_01. (accessed on 4 February 2023).
- NMX-AA-006-SCFI-2010 (Water Analysis-Determination of Floating Matter in Wastewater and Sewage Water). Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/166765/NMX-AA-006-SCFI-2010.pdf (accessed on 4 February 2023).
- NMX-AA-004-SCFI-2013 (Water Analysis-Measurement of Settleable Solids in Natural, Waste and Wastewater). Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/166763/NMX-AA-004-SCFI-2013.pdf (accessed on 4 February 2023).
- HACH (HACH Methods Manual). Available online: https://www.hach.com/resources/water-analysis-handbook (accessed on 4 February 2023).
- NMX-AA-034-SCFI-2015 (Water Analysis-Measurement of Dissolved Solids and Salts in Natural, Waste and Treated Wastewater). Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/166146/nmx-aa-034-scfi-2015.pdf (accessed on 4 February 2023).
- NMX-AA-042-SCFI-2015 (Water Analysis-Enumeration of Total Coliform Organisms, Fecal Coliform Organisms (Thermotolerant) and Escherichia Coli-Most Probable Number Method in Multiple Tubes). Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/166147/nmx-aa-042-scfi-2015.pdf (accessed on 4 February 2023).
- NMX-AA-051-SCFI-2016 (Water Analysis—Measurement of Metals by Atomic Absorption in Natural Waters Atomic Absorption in Natural Waters, Drinking Water, Wastewater and Treated Wastewater). Available online: http://www.economia-nmx.gob.mx/normas/nmx/2010/nmx-aa-051-scfi-2016.pdf (accessed on 4 February 2023).
- Babuponnusami, A.; Muthukumar, K. A review on Fenton and improvements to the Fenton process for wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 557–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J. Comparative study on sulfamethoxazole degradation by Fenton and Fe(II)-activated persulfate process. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 48670–48677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Modi, H.J. Fenton Treatment: A Review on Treatment of Waste Water. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 7, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karale, R.S.; Manu, B.; Shrihari, S. Fenton and Photo-Fenton Oxidation Processes for Degradation of 3-Aminopyridine from Water. APCBEE Procedia 2014, 9, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valderrama, M.; Javier, C.; del Águila, M.; Miche, E.; Pio, C.; Erika, L. Fenton process optimization in the treatment of landfill leachates lixiviated. Rev. Soc. Quim. Perú. 2016, 82, 454–466. [Google Scholar]
- Pignatello, J.J.; Oliveros, E.; MacKay, A. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Organic Contaminant Destruction Based on the Fenton Reaction and Related Chemistry. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 36, 1–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastanek, F.; Spacilova, M.; Krystynik, P.; Dlaskova, M.; Solcova, O. Fenton Reaction–Unique but Still Mysterious. Processes 2023, 11, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, P.B. Tratamiento de Aguas Residuales de la Industria Cosmética Mediante el Proceso Fenton y con el Sistema Fe/𝛾-Al2O3/H2O2. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Madrid, Spain, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Taco Ugsha, M.; Mayorga Llerena, E. Aplicación del proceso Fenton en la disminución de materia orgánica en aguas residuales de la industria termoeléctrica. Quím. Cent. 2013, 3, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Determination | Influent (Sampled Real Wastewater) | Effluent Generated by the Advanced Fenton Oxidation Process | Percentage Removal (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.01 | 7.12 ± 0.07 | ND |
| Temperature (°C) | 25 | 25.35 ± 0.35 | ND |
| Floating matter | Absence | Absence | ND |
| Settleable solids (mL/L) | Absence | Absence | ND |
| COD (mg/L) | 54 ± 1.41 | 26.50 ± 7.78 | 50.93 ± 14.40 |
| TSS (mg/L) | 45 ± 21.21 | 17.50 ± 5.00 | 72 ± 7.54 |
| Total phosphates (mg/L) | 0.7 | 1.55 ± 1.63 | ND |
| Total nitrogen (mg/L) | 2.5 | 2.8 | ND |
| FC (*MPN/100 mL) | 111,200 | 1 | 99.9% |
| Iron total (mg/L) | *ND | 4.41 ± 0.38 | ND |
| Determination | Method or Technique | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| pH | NMX-AA-008-SCFI-2011 | [53] |
| Temperature | NMX-AA-007-SCFI-2013 | [54] |
| Floating matter | NMX-AA-006-SCFI-2010 | [55] |
| Settleable solids | NMX-AA-004-SCFI-2013 | [56] |
| Chemical oxygen demand (COD) | HACH® | [57] |
| Total suspended solids (TSS) | NMX-AA-034-SCFI-2015 | [58] |
| Total phosphates | HACH® | [57] |
| Total nitrogen | HACH® | [57] |
| Fecal coliforms (FC) | NMX-AA-042-SCFI-2015 | [59] |
| Total iron | NMX-AA-051-SCFI-2016 | [60] |
| Chromatograph | ||
|---|---|---|
| Column | ACQUITY Premier CSH C18 1.7 µm, 2.1 × 150 mm | |
| Flow (mL/min) | 0.4 | |
| Sample temperature (°C) | 7 | |
| Column temperature (°C) | 40 | |
| Mobile phase A composition | water (Milli-Q) with 10 mM ammonium formate (chromatographic grade) plus 0.1% formic acid (chromatographic grade). | |
| Mobile phase B composition | Methanol–Acetonitrile (50% v/v–50% v/v) | |
| Injection volume (L) | 10 | |
| Elution (min) | A (%) | B (%) |
| 0 | 2 | 98 |
| 0.5 | 2 | 98 |
| 14 | 90 | 10 |
| 16 | 95 | 5 |
| 16.5 | 2 | 98 |
| 19 | 2 | 98 |
| Mass spectrometer | ||
| Ionization source | Electrospray (ESI) | |
| Polarity | ES+ and ES− | |
| Source temperature (°C) | 150 | |
| Capillary voltage (kV) | 3 | |
| Cone gas flow (L/h) | 50 | |
| Desolventizing temperature (°C) | 500 | |
| Desolvation gas flow (L/h) | 100 | |
| Coalition gas (argon) | 0.15 mL/min | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bracamontes-Ruelas, A.R.; Reyes-Vidal, Y.; Irigoyen-Campuzano, J.R.; Reynoso-Cuevas, L. Simultaneous Oxidation of Emerging Pollutants in Real Wastewater by the Advanced Fenton Oxidation Process. Catalysts 2023, 13, 748. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13040748
Bracamontes-Ruelas AR, Reyes-Vidal Y, Irigoyen-Campuzano JR, Reynoso-Cuevas L. Simultaneous Oxidation of Emerging Pollutants in Real Wastewater by the Advanced Fenton Oxidation Process. Catalysts. 2023; 13(4):748. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13040748
Chicago/Turabian StyleBracamontes-Ruelas, Alexis Rubén, Yolanda Reyes-Vidal, José Rafael Irigoyen-Campuzano, and Liliana Reynoso-Cuevas. 2023. "Simultaneous Oxidation of Emerging Pollutants in Real Wastewater by the Advanced Fenton Oxidation Process" Catalysts 13, no. 4: 748. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13040748
APA StyleBracamontes-Ruelas, A. R., Reyes-Vidal, Y., Irigoyen-Campuzano, J. R., & Reynoso-Cuevas, L. (2023). Simultaneous Oxidation of Emerging Pollutants in Real Wastewater by the Advanced Fenton Oxidation Process. Catalysts, 13(4), 748. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13040748








