Recent Advances in Platinum and Palladium Solvent Extraction from Real Leaching Solutions of Spent Catalysts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
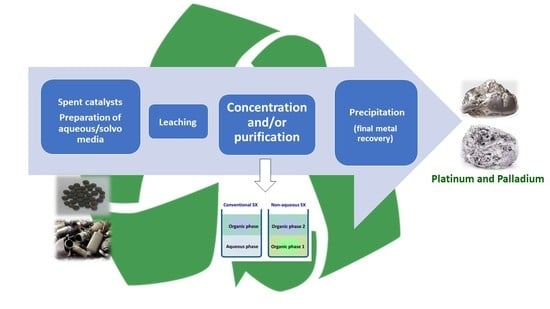
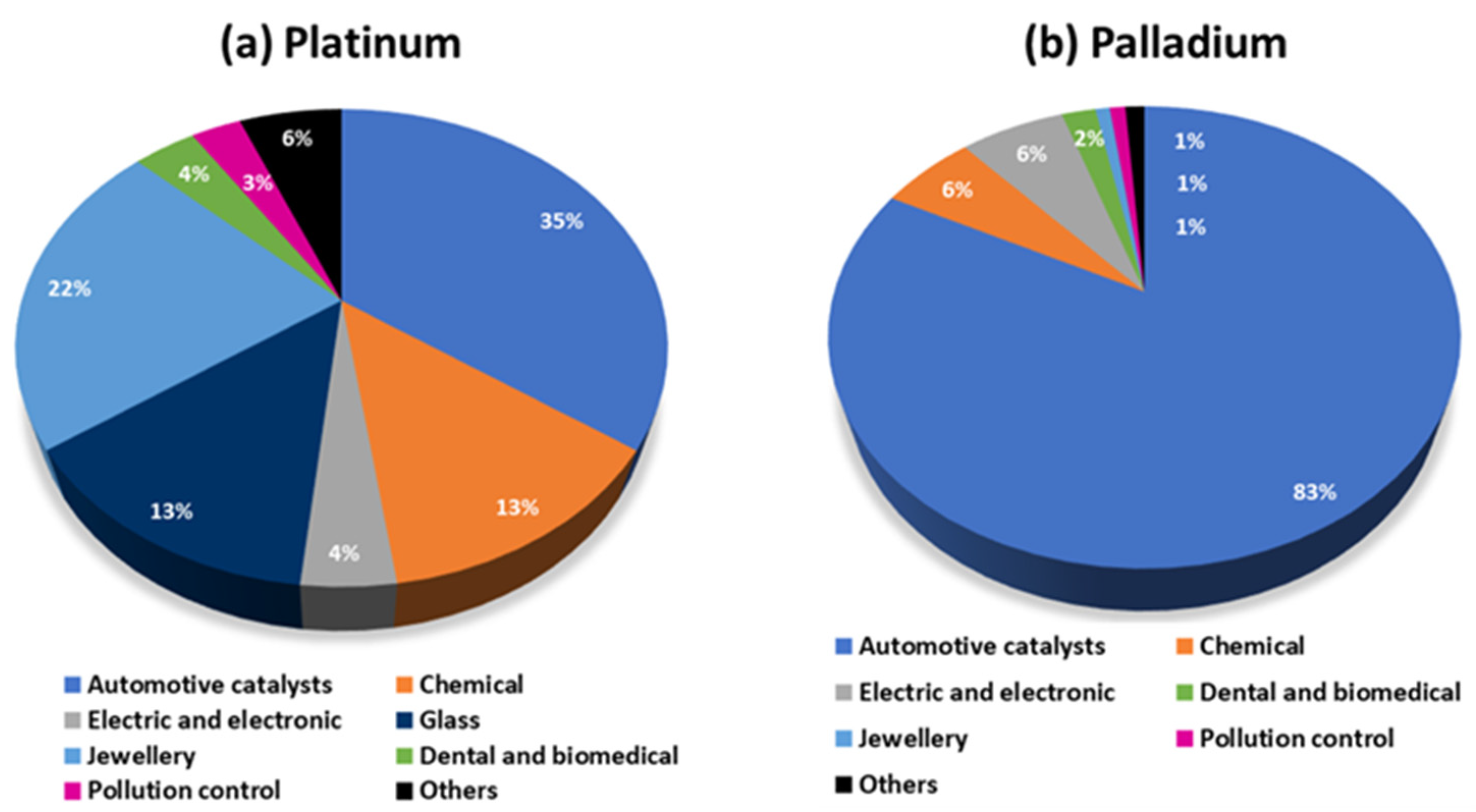
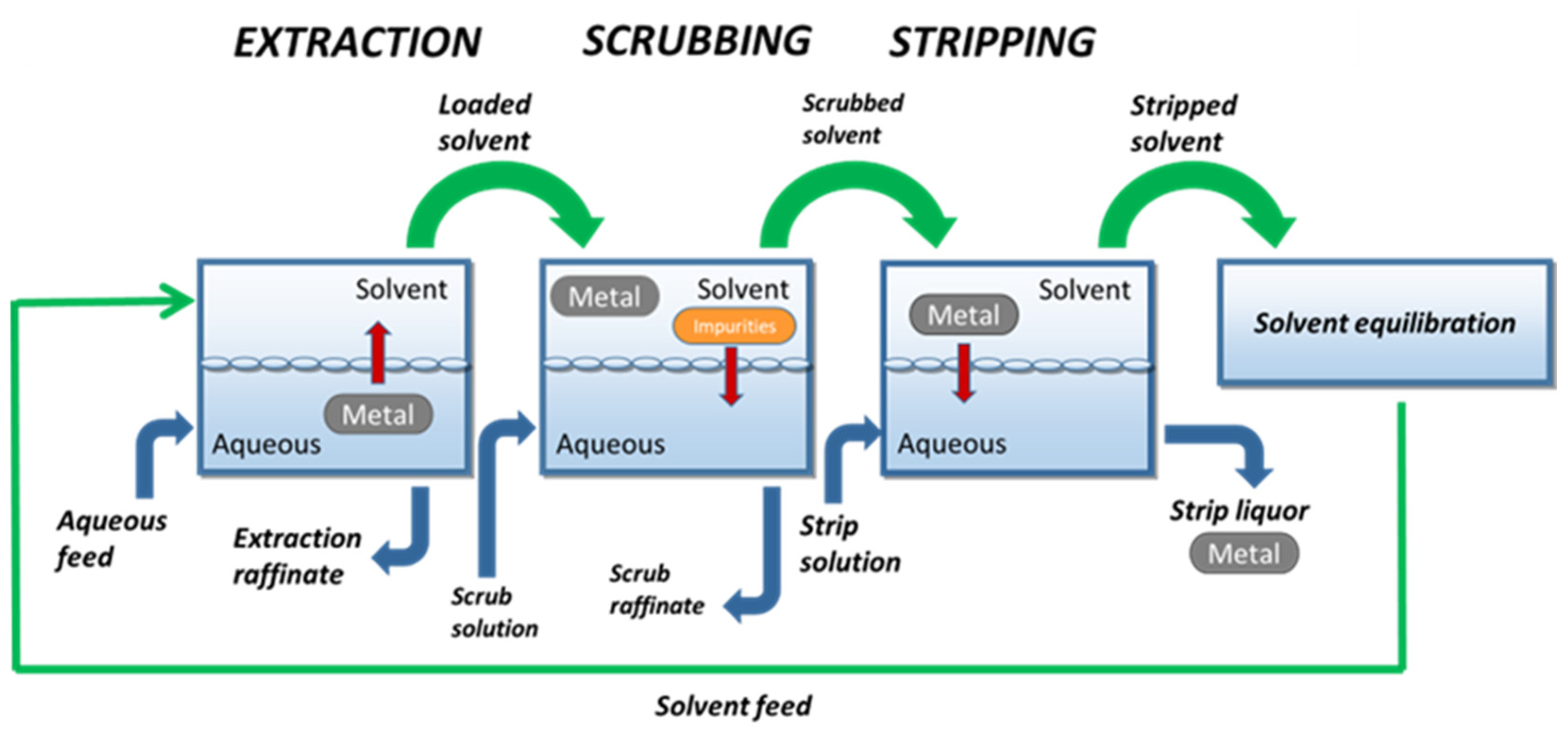
2. Hydrometallurgy
- The oxidation and coordination numbers;
- The size, charge, and structure of chlorocomplexes;
- The kinetics of ligand exchange reactions of the type MXn + L → MXn−1L + X.
3. Solvometallurgy
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson Matthey. Available online: https://matthey.com/pgm-market-report-2022 (accessed on 31 May 2023).
- Hagelüken, C. Recycling the platinum group metals: A European perspective. Platinum Metals Rev. 2012, 56, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS, Science for a Changing World. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/fs/2014/3064/pdf/fs2014-3064.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- Løvika, A.N.; Hagelüken, C.; Wägera, P. Improving supply security of critical metals: Current developments and research in the EU. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2018, 15, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission, Study on the Critical Raw Materials for the EU. Available online: https://single-market-economy.ec.europa.eu/system/files/2023-03/Study%202023%20CRM%20Assessment.pdf (accessed on 5 June 2023).
- European Commission, Funding & Tender Opportunities. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/funding-tenders/opportunities/portal/screen/programmes/h2020 (accessed on 5 June 2023).
- Saguru, C.; Ndlovu, S.; Moropeng, D. A review of recent studies into hydrometallurgical methods for recovering PGMs from used catalytic converters. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 182, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilli, M.L.; Slobozeanu, A.E.; Larosa, C.; Paneva, D.; Yakoumis, I.; Cherkezova-Zheleva, Z. Platinum group metals: Green recovery from spent auto-catalysts and reuse in new catalysts—A review. Crystals 2023, 13, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, G.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, T. A review of recovery of palladium from the spent automobile catalysts. Metals 2022, 12, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T. Solvometallurgy: An emerging branch of extractive metallurgy. J. Sustain. Metall. 2017, 3, 570–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Dewulf, B.; Binnemans, K. Nonaqueous solvent extraction for enhanced metal separations: Concept, systems, and mechanisms. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 17285–17302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, A.P.; Nogueira, C.A. Ionic liquids in the extraction and recycling of critical metals from urban mines. Waste Biomass Valor. 2021, 12, 1725–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardis, F.L.; Grant, R.A.; Sherrington, D.C. A review of methods of separation of the platinum-group metals through their chloro-complexes. React. Funct. Polym. 2005, 65, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, C.A.; Paiva, A.P.; Oliveira, P.C.; Costa, M.C.; Rosa da Costa, A.M. Oxidative leaching process with cupric ion in hydrochloric acid media for recovery of Pd and Rh from spent catalytic converters. J. Hazard. Mat. 2014, 278, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cox, M. Solvent extraction in hydrometallurgy. In Solvent Extraction Principles and Practices, 2nd ed.; Rydberg, J., Cox, M., Musikas, C., Choppin, G.R., Eds.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 455–505. [Google Scholar]
- Paiva, A.P. Recycling of palladium from spent catalysts using solvent extraction—Some critical points. Metals 2017, 7, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sinisalo, P.; Lundström, M. Refining approaches in the platinum group metal processing value chain—A review. Metals 2018, 8, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panda, R.; Jha, M.K.; Pathak, D.D. Commercial processes for the extraction of platinum group metals (PGMs). In Rare Metal Technology 2018; The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series; Kim, H., Wesstrom, B., Alam, S., Ouchi, T., Azimi, G., Neelameggham, N.R., Wang, S., Guan, X., Eds.; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 119–130. [Google Scholar]
- Sethurajan, M.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Fontana, D.; Akcil, A.; Deveci, H.; Batinic, B.; Leal, J.P.; Gasche, T.A.; Kucuker, M.A.; Kuchta, K.; et al. Recent advances on hydrometallurgical recovery of critical and precious elements from end of life electronic wastes—A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 212–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Zheng, H.; Chang, C.-c.; Ekberg, C. Recovery of precious metals from electronic waste and spent catalysts: A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 141, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsawa, T.; Traiwongsa, N.; Pancharoen, U.; Nootong, K. A review of the recovery of precious metals using ionic liquid extractants in hydrometallurgical processes. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 198, 105488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, H.B.; Lee, J.-c.; Suh, Y.-j.; Lee, J. A review on the recycling processes of spent auto-catalysts: Towards the development of sustainable metallurgy. Waste Manag. 2020, 114, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granados-Fernández, R.; Montiel, M.A.; Díaz-Abad, S.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Lobato, J. Platinum recovery techniques for a circular economy. Catalysts 2021, 11, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakoumis, I.; Panou, M.; Moschovi, A.M.; Panias, D. Recovery of platinum group metals from spent automotive catalysts: A review. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2021, 3, 100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, W.; Liu, H.; Yu, F.; Wang, H. Extractant structures and their performance for palladium extraction and separation from chloride media: A review. Miner. Eng. 2021, 163, 106798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xolo, L.; Moleko-Boyce, P.; Makelane, H.; Faleni, N.; Tshentu, Z.R. Status of recovery of strategic metals from spent secondary products. Minerals 2021, 11, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, S.; Ting, Y.-P. Recycling pathways for platinum group metals from spent automotive catalyst: A review on conventional approaches and bio-processes. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 170, 105588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Ding, Y.; Wen, Q.; Liu, B.; Zhang, S. Separation and purification of platinum group metals from aqueous solution: Recent developments and industrial applications. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 167, 105417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Jin, C.; He, W.; Li, G.; Zhu, H.; Huang, J. A review on management of waste three-way catalysts and strategies for recovery of platinum group metals from them. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 305, 114383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupanc, A.; Install, J.; Jereb, M.; Repo, T. Sustainable and selective modern methods of noble metal recycling. Angew. Chem. 2023, 62, e202214453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-c.; Kurniawan, K.; Kim, S.; Nguyen, V.T.; Pandey, B.D. Ionic liquids-assisted solvent extraction of precious metals from chloride solutions. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2023, 52, 242–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Ghahreman, A. Platinum group metals recycling from spent automotive catalysts: Metallurgical extraction and recovery technologies. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 311, 123357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Peng, Z.; Tian, R.; Ye, L.; Zhang, J.; Rao, M.; Li, G. Platinum-group metals: Demand, supply, applications and their recycling from spent automotive catalysts. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pianowska, K.; Kluczka, J.; Benke, G.; Goc, K.; Malarz, J.; Ochmański, M.; Leszczyńska-Sejda, K. Solvent extraction as a method of recovery and separation of platinum group metals. Materials 2023, 16, 4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demopoulos, G.P. Solvent extraction in precious metals refining. J. Metals 1986, 38, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Publications of the International Precious Metals Educational and Scientific Foundation; Stern, E.W. Aqueous Chemistry of Precious Metals Applicable to Refining Processes. pp. 16–50. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Corby-Anderson/publication/346259411_The_IPMI_Journal_-_Volume_1/links/600a368ca6fdccdcb86fd4a9/The-IPMI-Journal-Volume-1.pdf#page=25 (accessed on 9 June 2023).
- Ramachandra Reddy, B.; Raju, B.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, H.K. Process for the separation and recovery of palladium and platinum from spent automobile catalyst leach liquor using LIX 84I and Alamine 336. J. Hazard. Mat. 2010, 180, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho, R.S.; Afonso, J.C.; Dias da Cunha, J.W.S. Recovery of platinum from spent catalysts by liquid–liquid extraction in chloride medium. J. Hazard. Mat. 2010, 179, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, P.; Paiva, A.P. Novel solvent extraction route for the mutual separation of platinum, palladium, and rhodium in hydrochloric acid media. Solvent Extr. Ion. Exch. 2010, 28, 49–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traeger, J.; König, J.; Städtke, A.; Holdt, H.-J. Development of a solvent extraction system with 1,2-bis(2-methoxyethylthio)benzene for the selective separation of palladium(II) from secondary raw materials. Hydrometallurgy 2012, 127–128, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.; Singh, I. Extraction and separation of platinum, palladium and rhodium using Cyanex 923 and their recovery from real samples. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 134–135, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.-Y.; Nikoloski, A.N.; Wang, M.W. Microfluidic solvent extraction of platinum and palladium from a chloride leach solution using Alamine 336. Miner. Eng. 2013, 45, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, P.P.; Lee, M.S. Recovery of platinum from chloride leaching solution of spent catalysts by solvent extraction. Mater. Trans. 2013, 54, 74–80. [Google Scholar]
- Gandhi, M.R.; Yamada, M.; Kondo, Y.; Sato, R.; Hamada, F. Synthesis and characterization of dimethylthiocarbamoyl-modified thiacalix[n]arenes for selective Pd(II)-ion extraction. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 2559–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Gandhi, M.R.; Kondo, Y.; Sato, R.; Hamada, F. Synthesis and characterisation of p-diethylaminomethylthiacalix[4]arene for selective recovery of platinum from automotive catalyst residue. Supramol. Chem. 2014, 26, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, M.R.; Yamada, M.; Kondo, Y.; Shibayama, A.; Hamada, F. Selective extraction of Pd(II) ions from automotive catalyst residue in Cl− media by O-thiocarbamoyl-functionalized thiacalix[n]arenes. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 151, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Gandhi, M.R.; Kondo, Y.; Shibayama, A.; Hamada, F. Feasibility studies on palladium extraction from leach liquors of automotive catalysts using p-diethylphosphonomethylthiacalix[6]arene. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 1964–1973. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, M.; Gandhi, M.R.; Sato, R.; Kaneta, Y.; Kimura, N. Comparative study on palladium(II) extraction using thioamide-modified acyclic and cyclic extractants. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 8914–8921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, M.R.; Yamada, M.; Kondo, Y.; Shibayama, A.; Hamada, F. Rapid and selective extraction of Pd(II) ions using the SCS type pincer ligand 1,3-bis(dimethylthiocarbamoyloxy)benzene, and its Pd(II) extraction mechanism. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, M.R.; Yamada, M.; Kaneta, Y.; Hu, Y.; Shibayama, A. Calix[4]arene-based n-dialkylamino extractants for selective platinum group metal separation from automotive catalysts. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 1052–1057. [Google Scholar]
- Senthil, K.; Akiba, U.; Fujiwara, K.; Hamada, F.; Kondo, Y. High selectivity and extractability of palladium from chloride leach liquors of an automotive catalyst residue by azothiacalix[4]arene derivative. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 169, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil, K.; Akiba, U.; Fujiwara, K.; Hamada, F.; Kondo, Y. New heterocyclic dithioether ligands for highly selective separation and recovery of Pd(II) from acidic leach liquors of spent automobile catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 1036–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, M.R.; Yamada, M.; Haga, K.; Shibayama, A. Synthesis of pincer-type extractants for selective extraction of palladium from PGMs: An improved liquid-liquid extraction approach to current refining processes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paiva, A.P.; Ortet, O.; Carvalho, G.I.; Nogueira, C.A. Recovery of palladium from a spent industrial catalyst through leaching and solvent extraction. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 371, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Gandhi, M.R.; Kaneta, Y.; Kimura, N.; Katagiri, H. Thiodiphenol-based n-dialkylamino extractants for selective platinum group metal separation from automotive catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Kaneta, Y.; Gandhi, M.R.; Kunda, U.M.R.; Shibayama, A. Calix[4]arene-based amino extractants containing n-alkyl moieties for separation of Pd(II) and Pt(IV) from leach liquors of automotive catalysts. Metals 2018, 8, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamada, M.; Gandhi, M.R.; Shibayama, A. Rapid and selective recovery of palladium from platinum group metals and base metals using a thioamide-modified calix[4]arene extractant in environmentally friendly hydrocarbon fluids. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Firmansyah, M.L.; Kubota, F.; Yoshida, W.; Goto, M. Application of a novel phosphonium-based ionic liquid to the separation of platinum group metals from automobile catalyst leach liquor. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 3845–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makua, L.; Langa, K.; Saguru, C.; Ndlovu, S. PGM recovery from a pregnant leach solution using solvent extraction and cloud point extraction: A preliminary comparison. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2019, 119, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Gandhi, M.R.; Kunda, U.M.R.; Mori, T.; Haga, K.; Shibayama, A. Recovery of Pd(II) from leach solutions of automotive catalysts by solvent extraction with new thiophosphate extractants. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 191, 105221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzelewska-Piekut, M.; Paukszta, D.; Regel-Rosocka, M. Hydrometallurgical recovery of platinum group metals from spent automotive converters. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2021, 57, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, A.; Nogueira, C.A.; Paiva, A.P. Recovery of platinum from a spent automotive catalyst through chloride leaching and solvent extraction. Recycling 2021, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiecka, Z.; Rzelewska-Piekut, M.; Regel-Rosocka, M. Recovery of platinum group metals from spent automotive converters by leaching with organic and inorganic acids and extraction with quaternary phosphonium salts. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 280, 119933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, A.P.; Piedras, F.V.; Rodrigues, P.G.; Nogueira, C.A. Hydrometallurgical recovery of platinum-group metals from spent auto-catalysts—Focus on leaching and solvent extraction. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 286, 120474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Ohira, T.; Watanabe, N.; Katagiri, H.; Shibayama, A.; Hamada, F. Recovery of Pd(II) by solvent extraction with a dithiophenol-based extractant from the undiluted leachate of spent automotive catalysts followed by water scrubbing and thiourea stripping. Hydrometallurgy 2023, 215, 105986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiecka, Z.; Rzelewska-Piekut, M.; Reis, M.T.A.; Ismael, M.R.C.; Wieszczycka, K.; Regel-Rosocka, M. Pd(II) and Pt(IV) dispersive or non-dispersive extraction from model and real leach solutions with alkoxyimine-1-propylpyridinium derivatives. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 317, 123800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortet, O.; Santos, M.S.C.S.; Paiva, A.P. Palladium(II) extraction from concentrated chloride media: Reactions involving thioamide derivatives. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 1461–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortet, O.; Santos, M.S.C.S.; Paiva, A.P. Palladium(II) and N,N′-dimethyl-N,N′-dicyclohexylthiodiglycolamide—The extracted species from concentrated chloride solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 170, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Cyanamid Co. Cyanex® 471X Extractant Sales Brochure—Technical Information Sheet; Cyanamid: Wayne, NJ, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Nikoloski, A.N.; Ang, K.-L.; Li, D. Recovery of platinum, palladium and rhodium from acidic chloride leach solution using ion exchange resins. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 152, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S.; Rajesh, N. Augmenting the adsorption of palladium from spent catalyst using a thiazole ligand tethered on an amine functionalized polymeric resin. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.-y.; Nishihama, S.; Yoshizuka, K. Recovery of platinum and palladium from spent automobile catalyst by solvent-impregnated resins. Solvent Extr. Ion. Exch. 2018, 36, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Kimura, S.; Gandhi, M.R.; Shibayama, A. Environmentally friendly Pd(II) recovery from spent automotive catalysts using resins impregnated with a pincer-type extractant. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanaridi, O.; Sahoo, A.R.; Limbeck, A.; Naghdi, S.; Eder, D.; Eitenberger, E.; Csendes, Z.; Schnürch, M.; Bica-Schröder, K. Toward the recovery of platinum group metals from a spent automotive catalyst with supported ionic liquid phases. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ye, M.; Liu, Z.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y. Selective Pt recovery from spent catalyst enabled by hierarchical porous poly(imine dioxime)/polyethylenimine composite membrane for recycled Pt/C catalyst. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 310, 123125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, S.; Srivastava, R.R.; Kim, H.; Cheema, H.A. Hydrometallurgical recycling of palladium and platinum from exhausted diesel oxidation catalysts. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 248, 117029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzelewska-Piekut, M.; Wolańczyk, Z.; Nowicki, M.; Regel-Rosocka, M. Precipitation of Pt, Pd, Rh, and Ru nanoparticles with non-precious metals from model and real multicomponent solutions. Molecules 2023, 28, 5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.R.P.; Paredes, X.; Cristino, A.F.; Santos, F.J.V.; Queirós, C.S.G.P. Ionic liquids—A review of their toxicity to living organisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicol, G.; Goosey, E.; Yildiz, D.S.; Loving, E.; Nguyen, V.T.; Riaño, S.; Yakoumis, I.; Martinez, A.M.; Siriwardana, A.; Unzurrunzaga, A.; et al. Platinum group metals recovery using secondary raw materials (PLATIRUS): Project overview with a focus on processing spent autocatalyst. Johns. Matthey Technol. Rev. 2021, 65, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Riaño, S.; Binnemans, K. Separation of precious metals by split-anion extraction using water-saturated ionic liquids. Green. Chem. 2020, 22, 8375–8388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Riaño, S.; Aktan, E.; Deferm, C.; Fransaer, J.; Binnemans, K. Solvometallurgical recovery of platinum group metals from spent automotive catalysts. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Government, Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment, and Water. National Pollutant Inventory. Available online: https://www.dcceew.gov.au/environment/protection/npi/substances/fact-sheets/acetonitrile#tabs-2 (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- Solvomet. Available online: https://solvomet.eu/about-solvomet/ (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T. Ionic liquids and deep-eutectic solvents in extractive metallurgy: Mismatch between academic research and industrial applicability. J. Sustain. Metall. 2023, 9, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T. The twelve principles of circular hydrometallurgy. J. Sustain. Metall. 2023, 9, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izatt, N.E.; Bruening, R.L.; Krakowiak, K.E.; Izatt, S.R. Contributions of Professor Reed M. Izatt to molecular recognition technology: From laboratory to commercial application. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 3405–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izatt, S.R.; Bruening, R.L.; Izatt, N.E. Metal separations and recovery in the mining industry. JOM 2012, 64, 1279–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Publications of the International Precious Metals Educational and Scientific Foundation; Izatt, S.R.; Bruening, R.L.; Izatt, N.E.; Izatt, R.M. Precious Metal Separation and Recovery from Primary and Secondary Sources Using SUPERLIG® Molecular Recognition Technology Processes. pp. 51–81. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Corby-Anderson/publication/346259411_The_IPMI_Journal_-_Volume_1/links/600a368ca6fdccdcb86fd4a9/The-IPMI-Journal-Volume-1.pdf#page=60 (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- Wilson, A.M.; Grant, R.A.; Gordon, R.J.; Love, J.B.; Morrison, C.A.; Macruary, K.J.; Nichol, G.S.; Tasker, P.A. Ditopic extractants to separate palladium(II) and platinum(IV) chloridometalates via inner or outer sphere binding. Solvent Extr. Ion. Exch. 2023, 41, 401–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narita, H.; Morisaku, K.; Tamura, K.; Tanaka, M.; Shiwaku, H.; Okamoto, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Yaita, T. Extraction properties of palladium(II) in HCl solution with sulfide-containing monoamide compounds. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 3636–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

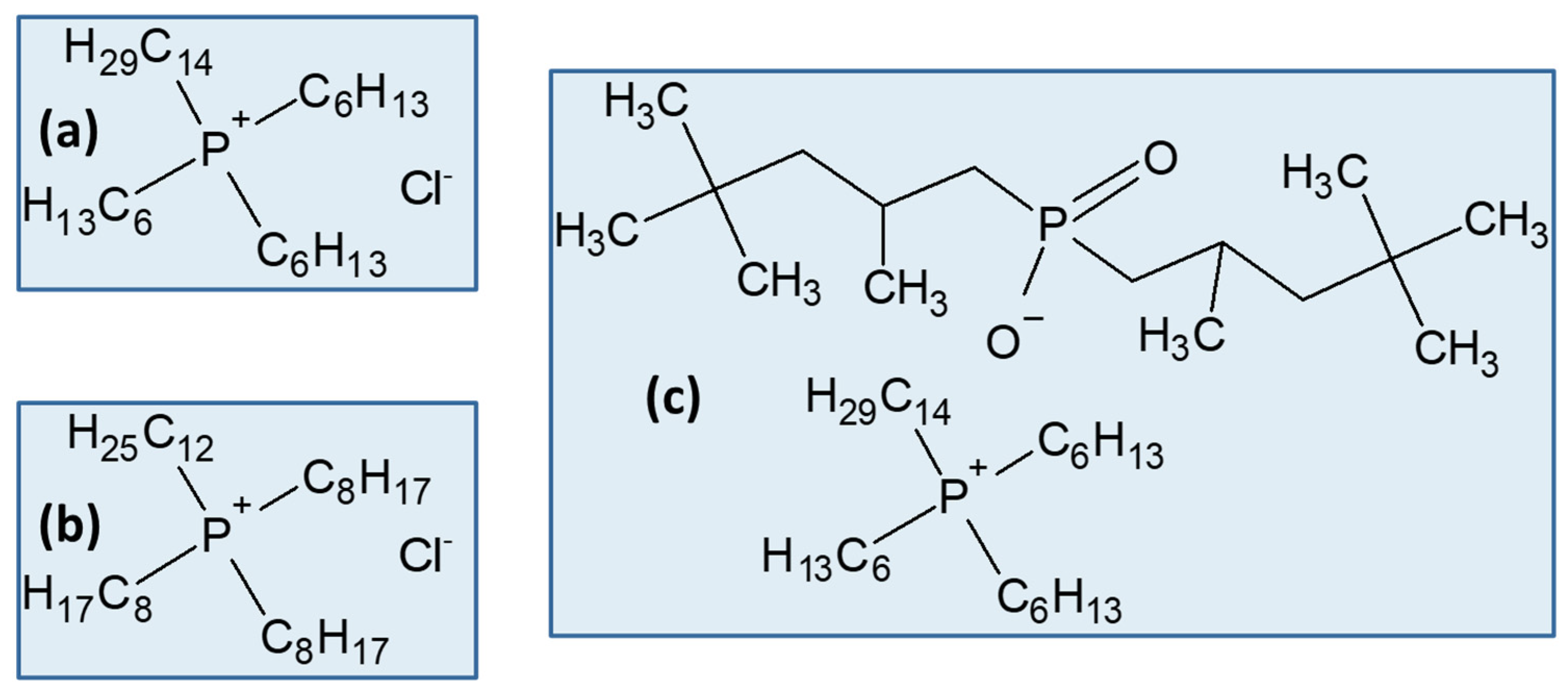

| Metals | Oxidation States | d-Electron Configurations | Coordination Numbers | Structure Configurations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pd | +2 (+4) | d8 (d6) | 4 | 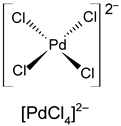 |
| Pt | +2, +4 | d8, d6 | 4, 6 | 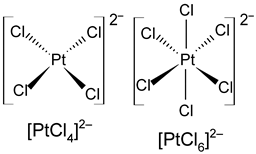 |
| Target Metal(s) | Extractant(s) | Catalysts/Leaching Media for SX Application | SX Data | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pd, Pt | LIX84I (2-hydroxy-5-nonylacetophenone oxime) and Alamine 336 (trioctyl-decylamines) | First-generation SAC/ 3 M HCl | LIX84I: 100% Pd extraction; 100% stripping with acidic TU; good selectivity Alamine 336: 100% Pt extraction; 100% stripping with acidic TU; Fe co-extraction, easily scrubbed | [37] |
| Pt | Alamine 336; Aliquat 336 (trioctylmethyl ammonium chloride) | Monometallic (Pt/Al2O3); multimetallic (PtSnIn/Al2O3)/1.4 and 0.5 M Cl−, respectively | >99.4% extraction; reductive stripping to Pt(II) by Na2S2O3; good selectivity | [38] |
| Pt | N,N’–dimethyl–N,N’–diphenyltetradecyl-malonamide (DMDPHTDMA) | SAC/5M HCl | 99.5% extraction in presence of Sn; ≈79% stripping with (HCl + NaClO3) + NaOH; reasonable selectivity | [39] |
| Pd | 1,2-bis(2-methoxyethylthio) benzene | SAC/2 M Cl− | 100% extraction; 100% stripping with acidic TU; excellent selectivity | [40] |
| Pd | Cyanex 923 (trialkylphosphine oxides, mainly with hexyl and octyl groups) | Alumina and coated ceramic honeycomb catalysts/5 M H2SO4 | 98.6% extraction; 100% stripping with HClO4; excellent selectivity over Al | [41] |
| Pd, Pt | Alamine 336 (Microfluidic SX) | SAC/pH 1.42 | Pd and Pt co-extraction | [42] |
| Pt | Aliquat 336 | Spent petroleum refining catalyst/3 M HCl | 100% extraction of Pt and Fe; 100% Fe scrubbing with dilute HCl; 100% Pt stripping by HClO4 | [43] |
| Pd | Thiacalix[6]arene and thiacalix[4]arene derivatives | SAC/pH 0.8 | 99.3% extraction; 100% stripping with TU; excellent selectivity, slight Zr co-extraction | [44] |
| Pt | Thiacalix[4]arene derivative | SAC/pH 0.8 | 88% extraction; 20% Pd co-extraction | [45] |
| Pd | Thiacalix[6]arene and thiacalix[4]arene derivatives | SAC/1 M HCl | 99% extraction; slight co-extraction of Zr, Pt, and Al | [46] |
| Pd | Thiacalix[6]arene derivative | SAC/pH 1.5 | 98% extraction; 98% stripping with acidic TU; 22% co-extraction of Zr | [47] |
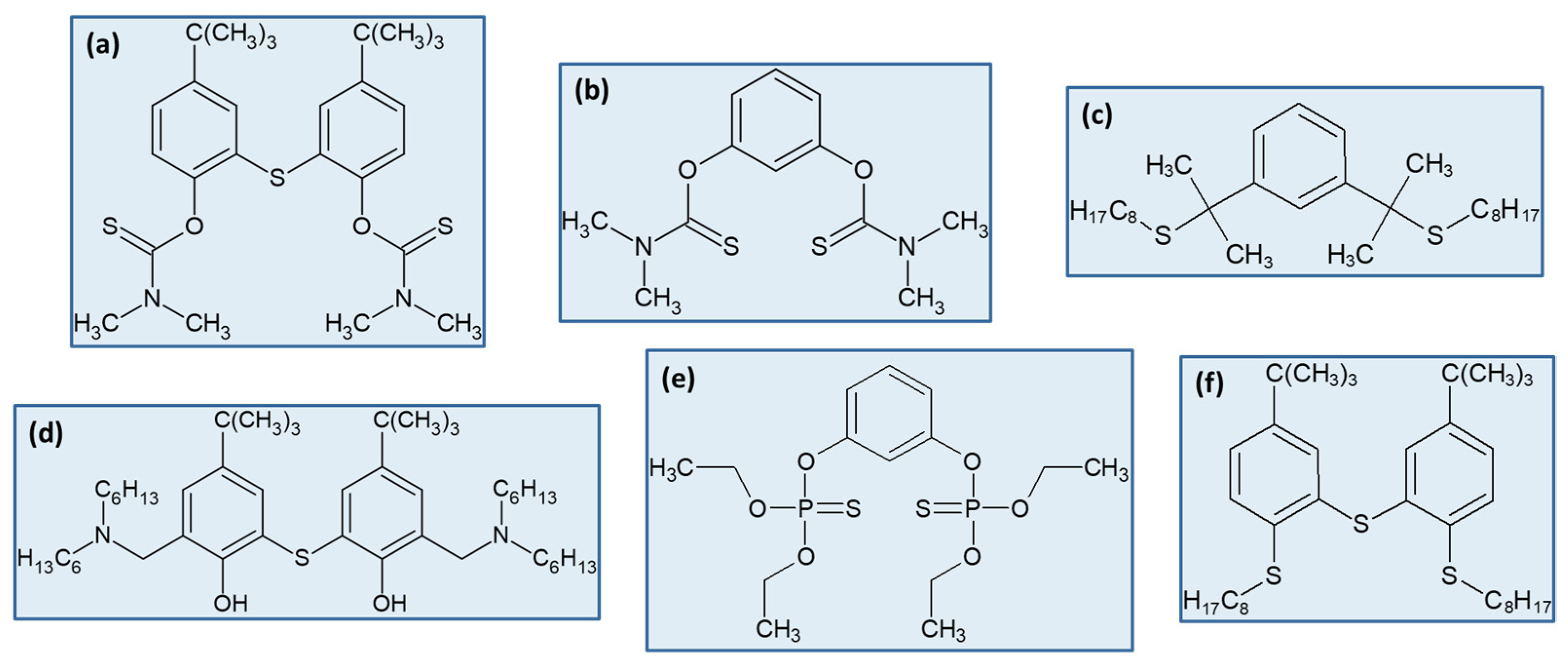
| Pd | Acyclic thioamide derivative | SAC/0.1 M HCl | 96% extraction; 99.5% stripping with acidic TU; excellent selectivity | [48] |
| Pd | 1,3-bis (dimethylthio-carbamoyloxy)-benzene | SAC/1 M HCl | 99.9% extraction; > 99% stripping with acidic TU; excellent selectivity | [49] |
| Pd | Calix[4]arene-based n-dialkylamino extractants | SAC/0.06 M HCl | 88–92% extraction; 90–99% stripping with acidic TU; reasonable selectivity | [50] |
| Pd | Azothiacalix[4]arene derivative | SAC/1 M HCl | 99.7% extraction; >99% stripping with acidic TU; <10% Pt and La co-extraction | [51] |
| Pd | Heterocyclic dithioether ligands | SAC/0.5 M HCl | 99.9% extraction; >99% stripping with acidic TU; 11–17% Pt, 3–8% Rh, <4% other metals co-extraction | [52] |
| Pd | Sulphur–carbon–sulphur (SCS) pincer ligands | SAC/≈ 0.1 M HCl | 99.9% extraction; >99.9% stripping with acidic TU; excellent selectivity | [53] |
| Pd | Thioamide and thiodiglycolamide derivatives | Spent petrochemical catalyst/2M HCl (MgCl2 + NH4Cl) + H2O2 | 95–100% extraction; 98–99.5% stripping with acidic TU; Al slowly accumulates in the solvents | [54] |
| Pd, Pt | Thiodiphenol-based n-dialkylamino extractants | SAC/0.1 M HCl | 99.5% Pd, 99.3% Pt extraction; 99% Pd and Pt stripping with acidic TU; <3% other metals co-extraction | [55] |
| Pd, Pt | Calix[4]arene-based amino extractants containing n-alkyl moieties | SAC/pH 1.22 | 93–98% Pd, 92–94% Pt extraction; 95–99% Pd, 91–93% Pt stripping with acidic TU; <6% other metals co-extraction | [56] |
| Pd | Thioamide-modified calix[4]arene derivative | SAC/0.06 M HCl | 99.9% extraction; 99.9% stripping with acidic TU; <2% other metals co-extraction | [57] |
| Pd | Phosphonium-based ionic liquid | SAC/5 M HCl | 90% extraction, 50% Fe co-extracted; Fe scrubbing by Na2SO3, Pd stripping by TU; small amounts of other metals co-extracted | [58] |
| Pd, Pt | Alamine 308 (trioctylamine); Cloud-point extraction | SAC/unknown [HCl] | 81% Pd, 95% Pt | [59] |
| Pd | Thiophosphate-based extractant | SAC/0.06 M HCl | 99.9% extraction; 99% stripping with acidic TU; <1% other metals co-extraction | [60] |
| Pt, Rh | Cyphos IL 101 (trihexyl-tetradecyl- phosphonium chloride) | SAC/10.7 M HCl + 1 M H2SO4 + H2O2 | 100% Pt, 0% Rh, 100% Fe, 100% Zn, 47% Pb extraction; 19% Pt and 100% Fe stripping with HNO3 | [61] |
| Pt | Thiodiglycolamide derivative | SAC/HCl + H2O2 (8 M HCl) | 100% extraction; 100% Fe co-extraction; Fe scrubbing by water and Pt stripping by acidic TU did not work | [62] |
| Pd, Pt | Cyphos IL 101 | SAC/10.7 M HCl + 1 M H2SO4 + H2O2 | 100% Pt, 100% Pd, 100% Fe, 96% Mg, 95% Zn, 84% Cu extraction; Pd stripping with acidic TU and Pt stripping with HNO3 | [63] |
| Pd, Pt | Cyanex 471X (triisobutylphosphine sulphide) and Cyphos IL 101 | SAC/HCl + H2O2 (6 M HCl) | Cyanex 471X: 100% Pd extraction; 46% stripping with acidic TU; 99% Fe, scrubbed with water. Cyphos IL 101: 99% Pt, 100% Pd; 100% Fe, 100% Zn co-extraction; stripping inefficient | [64] |
| Pd | Dithiophenol-based extractant bearing 3 S atoms | SAC/HCl + H2O2 [HCl] ≈ 8 M | 100% Pd, 4% Al, 11% Cr, 24% Fe, 3% Ni, 9% Rh, 1% Ce extraction; Fe scrubbing with water, 100% Pd stripping with acidic TU | [65] |
| Pd, Pt | Pyridinium salt derivatives | SAC/aqua regia + H2O2 (half diluted); HCl + H2SO4+ H2O2 (half diluted) [H+] < 6 M | One compound: 80% Pd, 0% Pt extraction; another compound: 70% Pt, 0% Pd; Fe and Zn co-extraction; Pd stripping by acidic TU | [66] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paiva, A.P. Recent Advances in Platinum and Palladium Solvent Extraction from Real Leaching Solutions of Spent Catalysts. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13071146
Paiva AP. Recent Advances in Platinum and Palladium Solvent Extraction from Real Leaching Solutions of Spent Catalysts. Catalysts. 2023; 13(7):1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13071146
Chicago/Turabian StylePaiva, Ana Paula. 2023. "Recent Advances in Platinum and Palladium Solvent Extraction from Real Leaching Solutions of Spent Catalysts" Catalysts 13, no. 7: 1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13071146
APA StylePaiva, A. P. (2023). Recent Advances in Platinum and Palladium Solvent Extraction from Real Leaching Solutions of Spent Catalysts. Catalysts, 13(7), 1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13071146