Neodymium-Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Catalytic Cathode for Enhanced Efficiency of Microbial Desalination Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results & Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Nd-Doped ZnO Catalyst for MDC
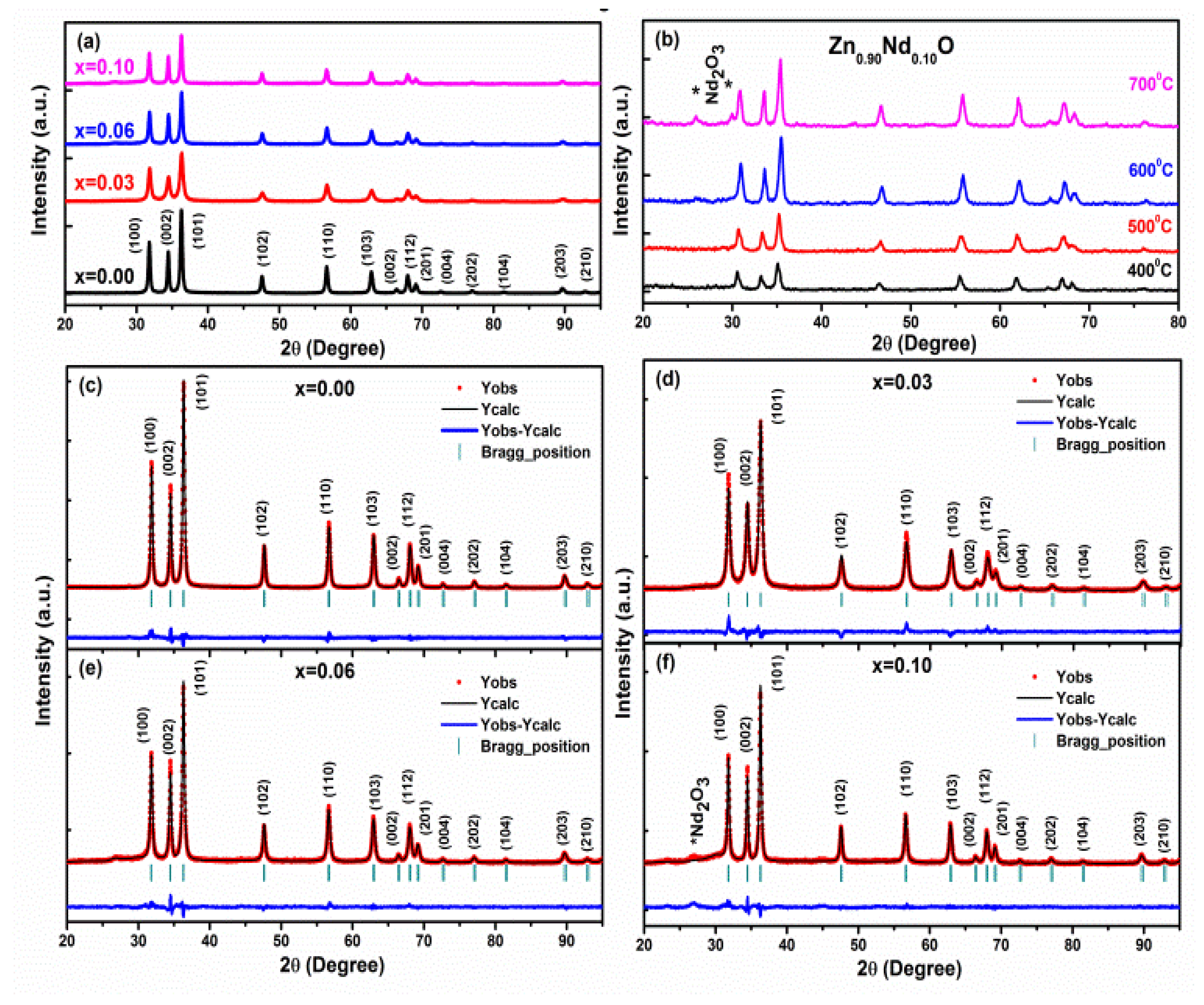
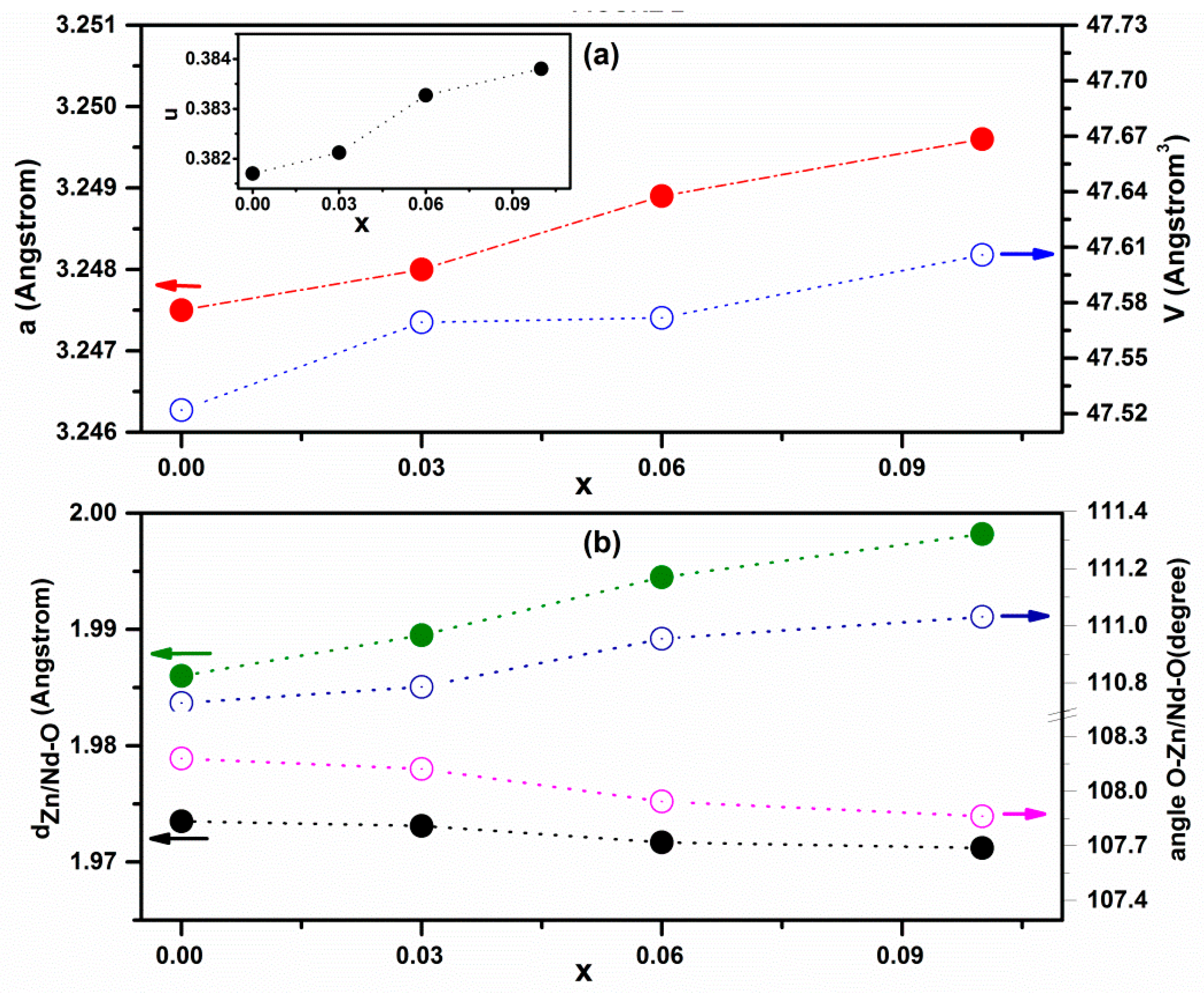
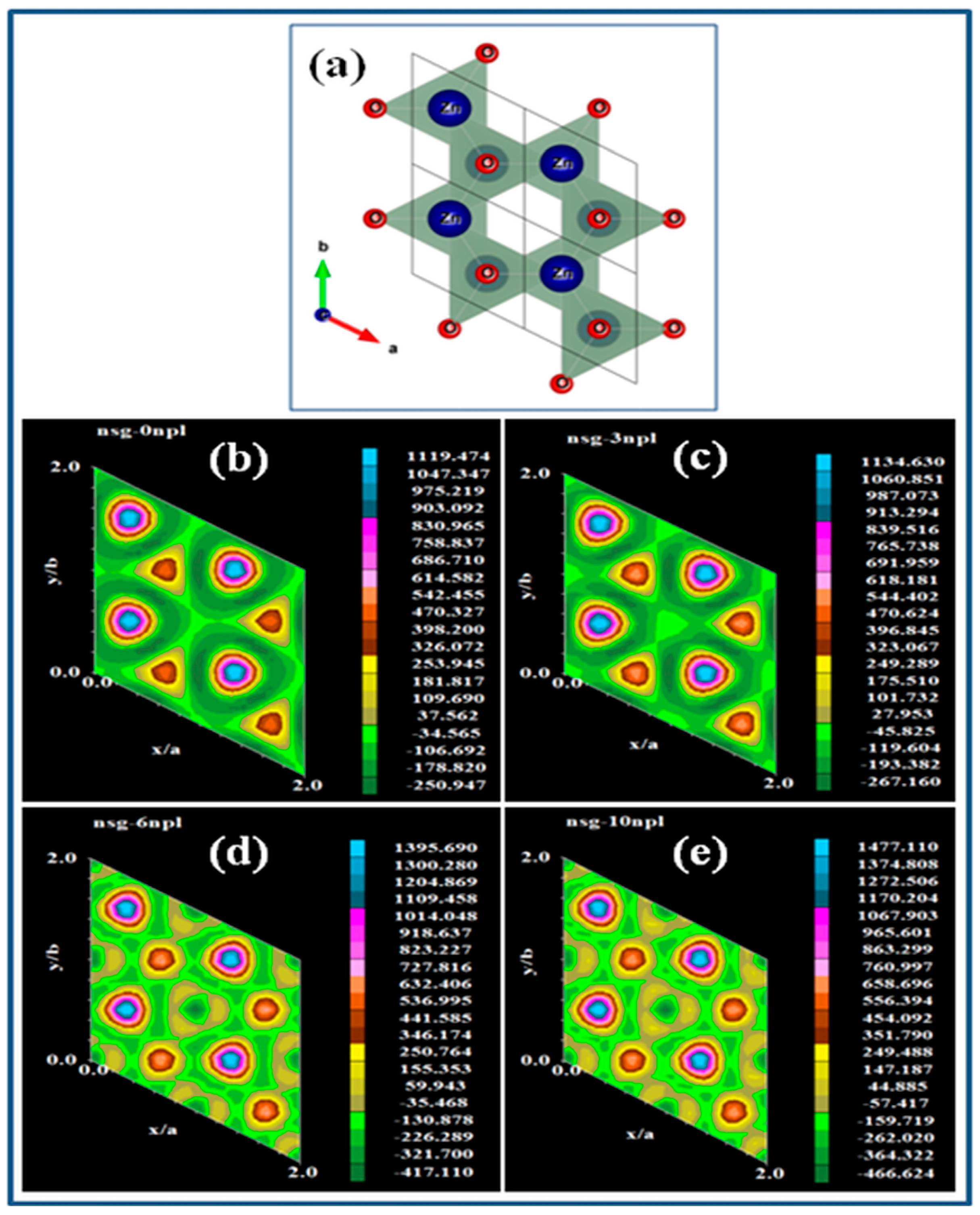
2.1.1. X-ray Diffraction Technique
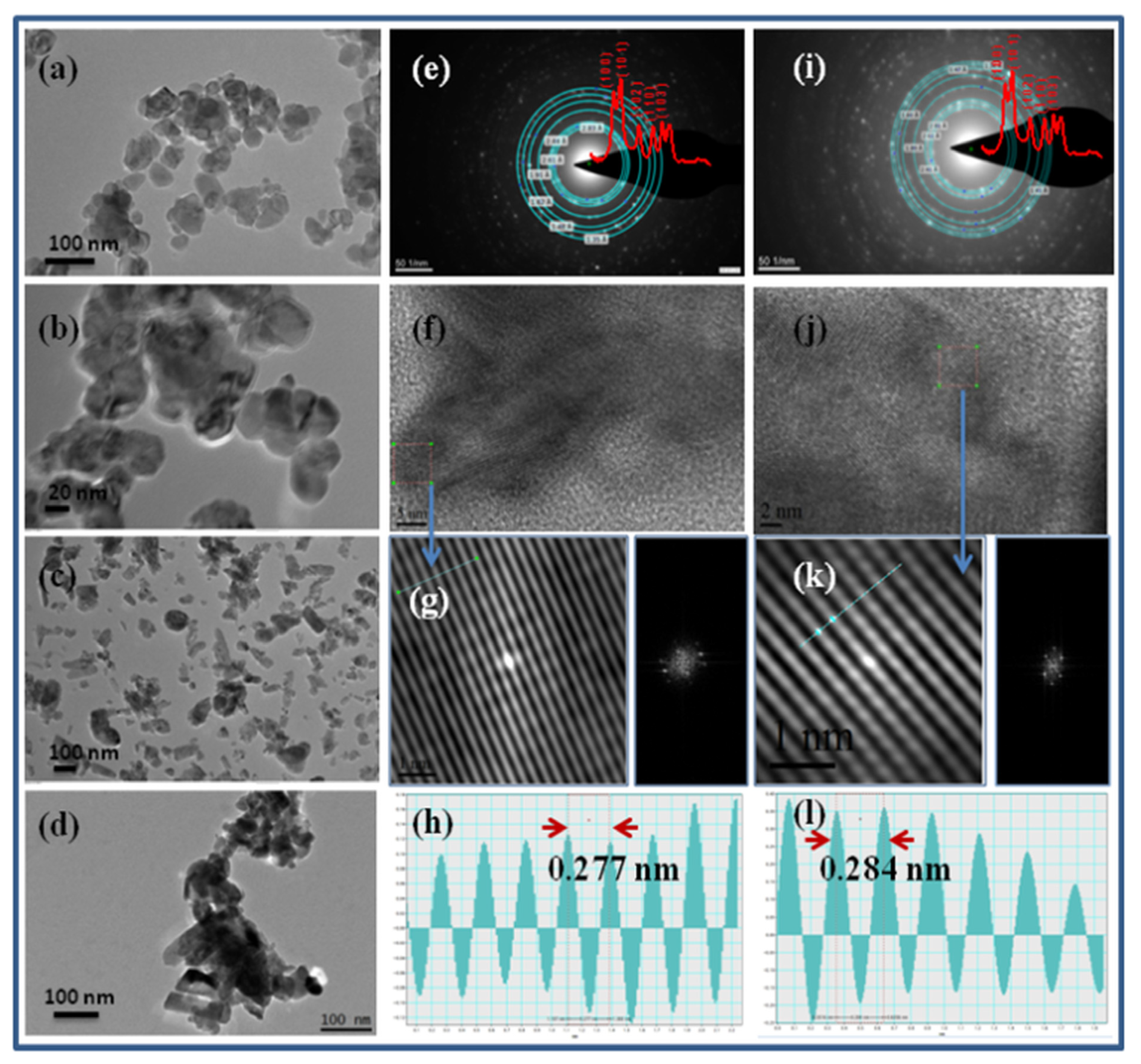
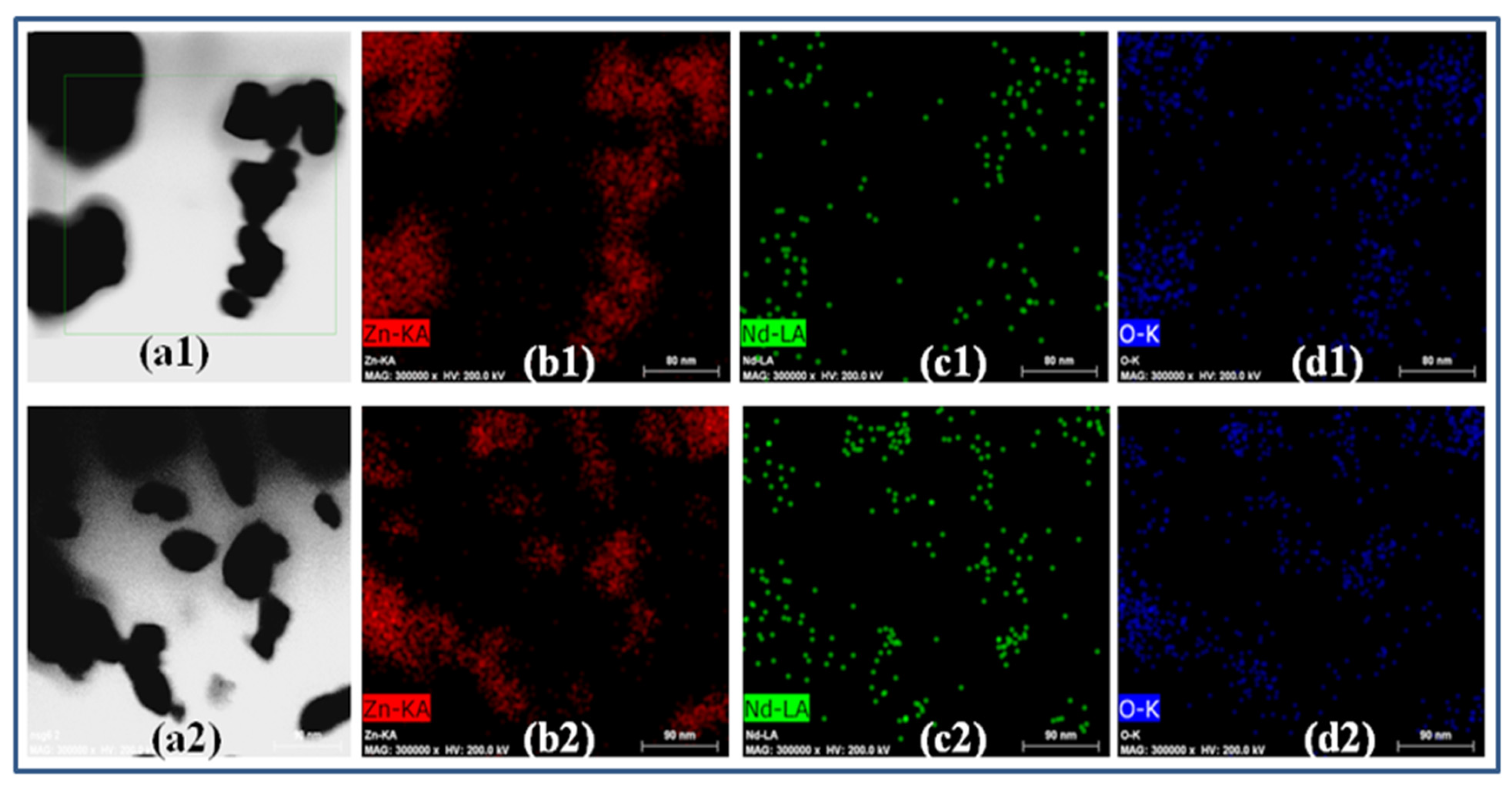
2.1.2. TEM
2.1.3. Photoluminescence Spectrum
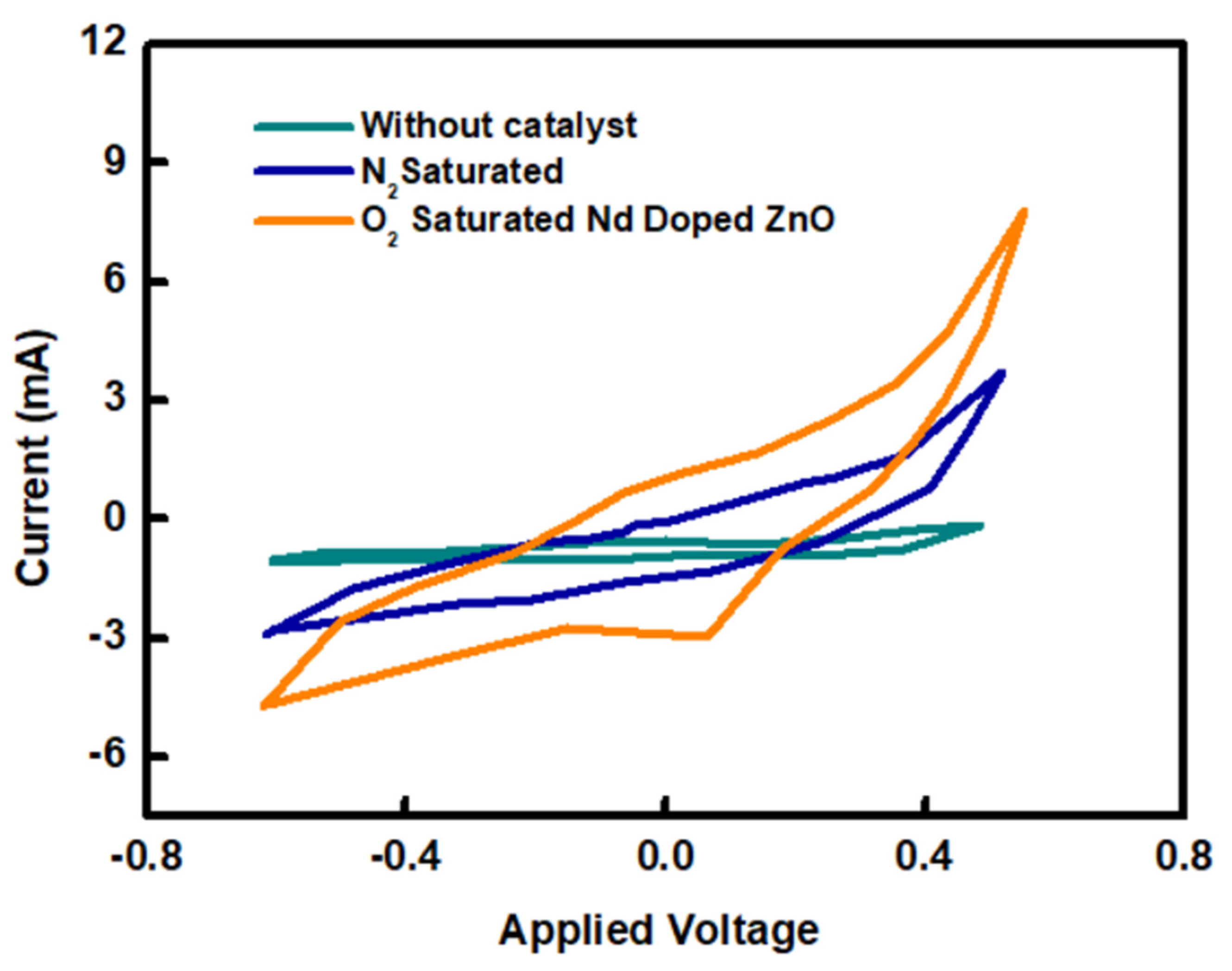
2.2. Cyclic Voltammetry
2.3. Desalination Efficiency with and without the Presence of Nd-Doped ZnO as the Catalyst
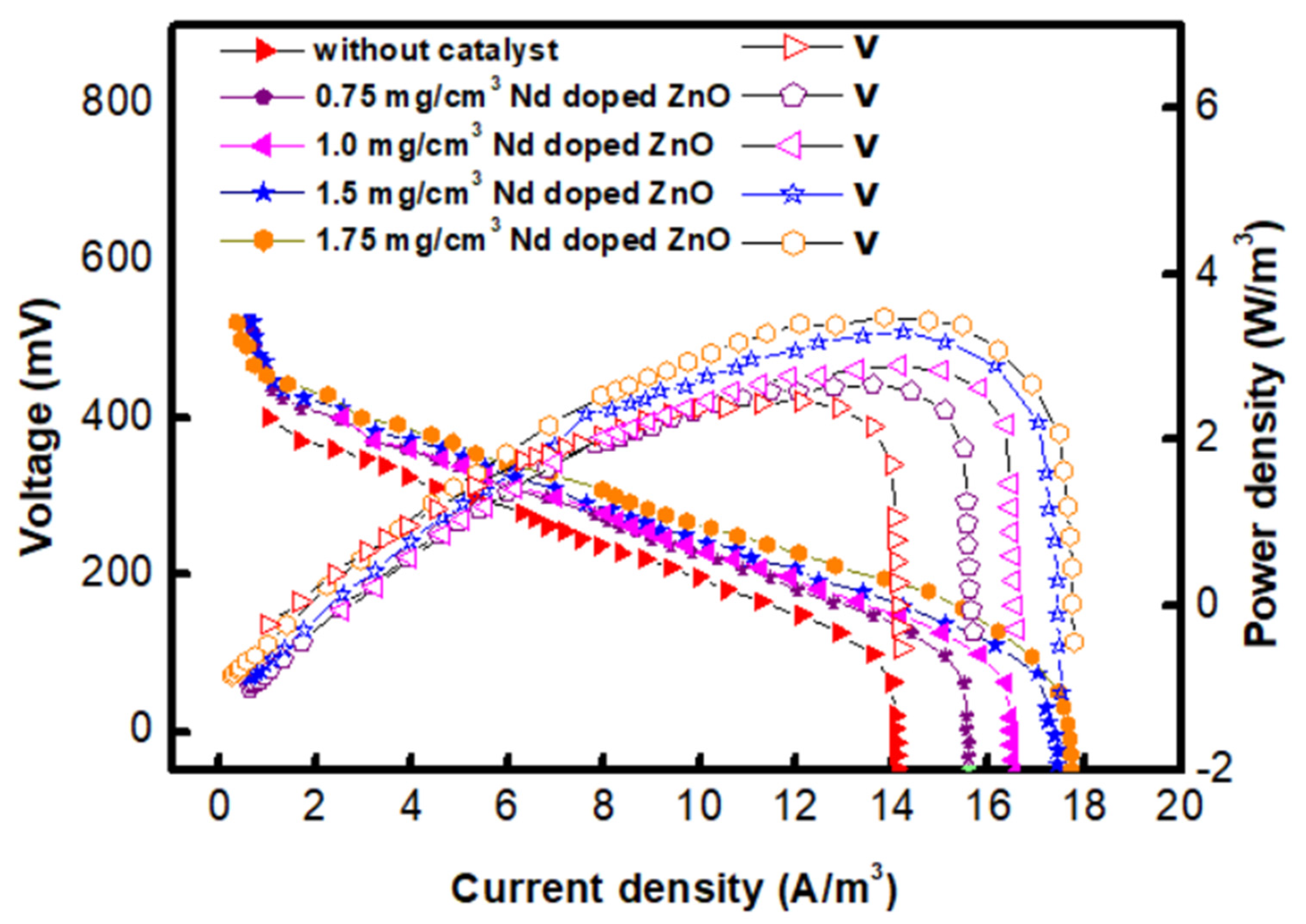
2.4. Polarization Studies
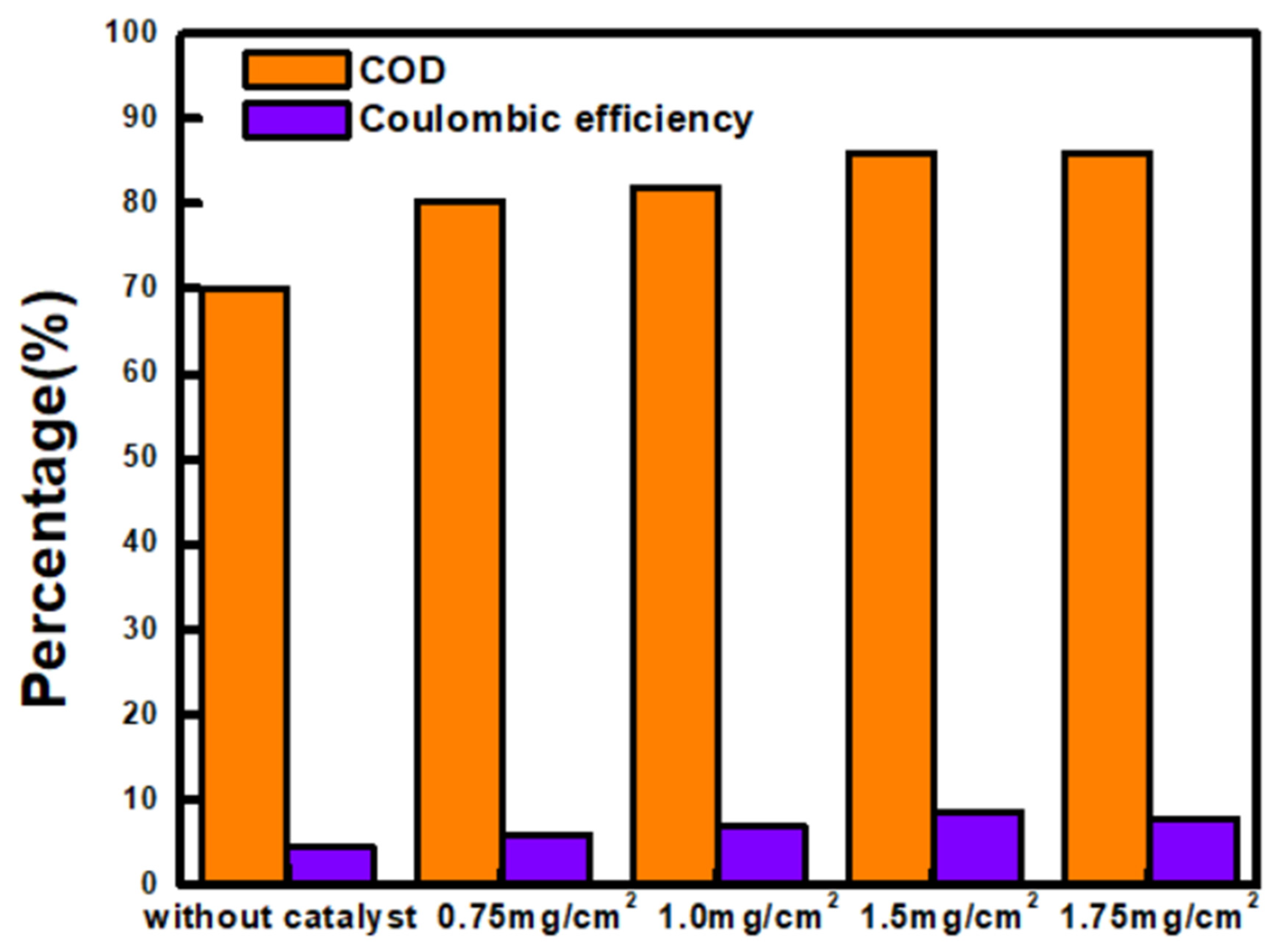
2.5. COD Removal and Coulombic Efficiency
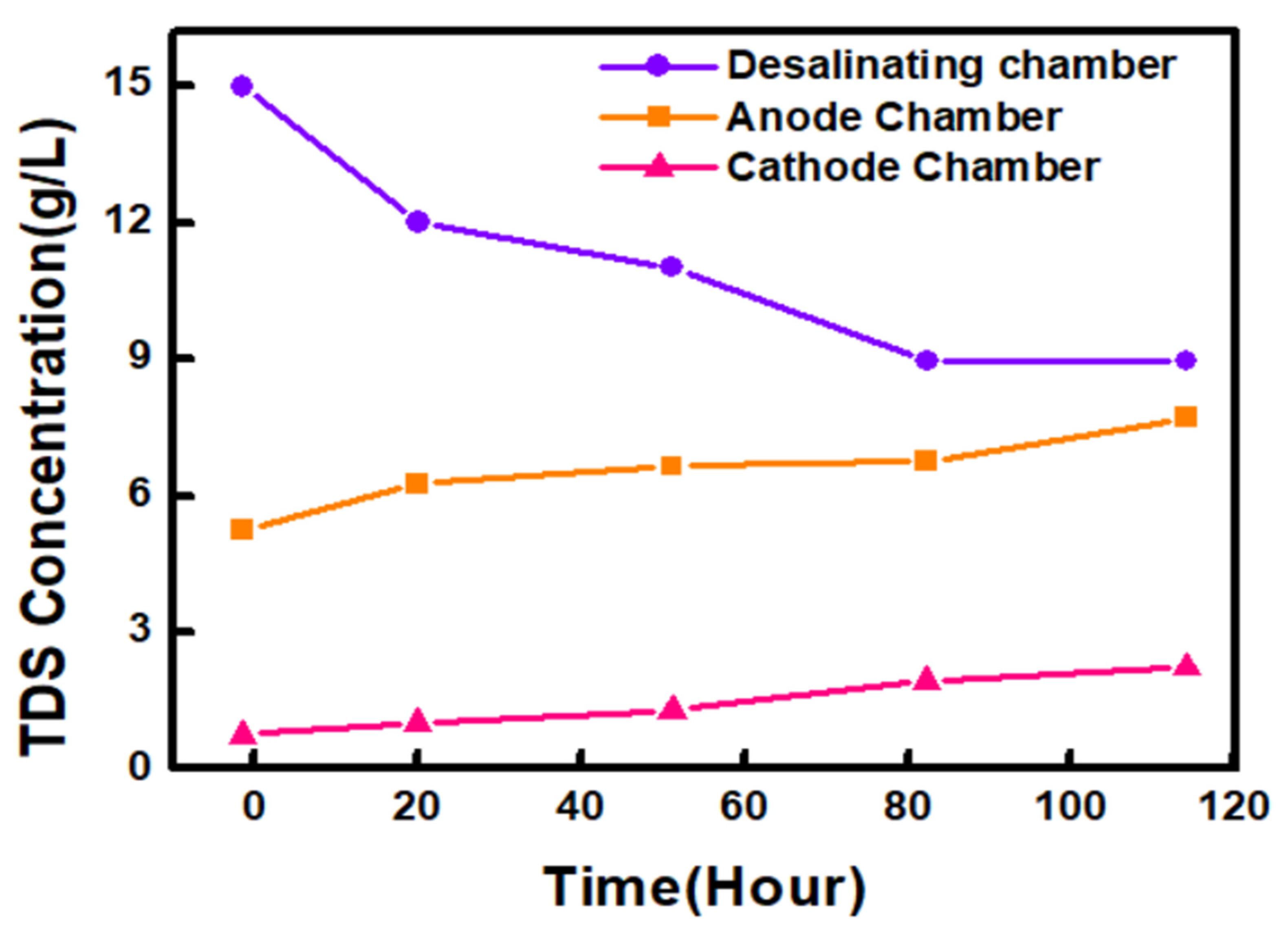
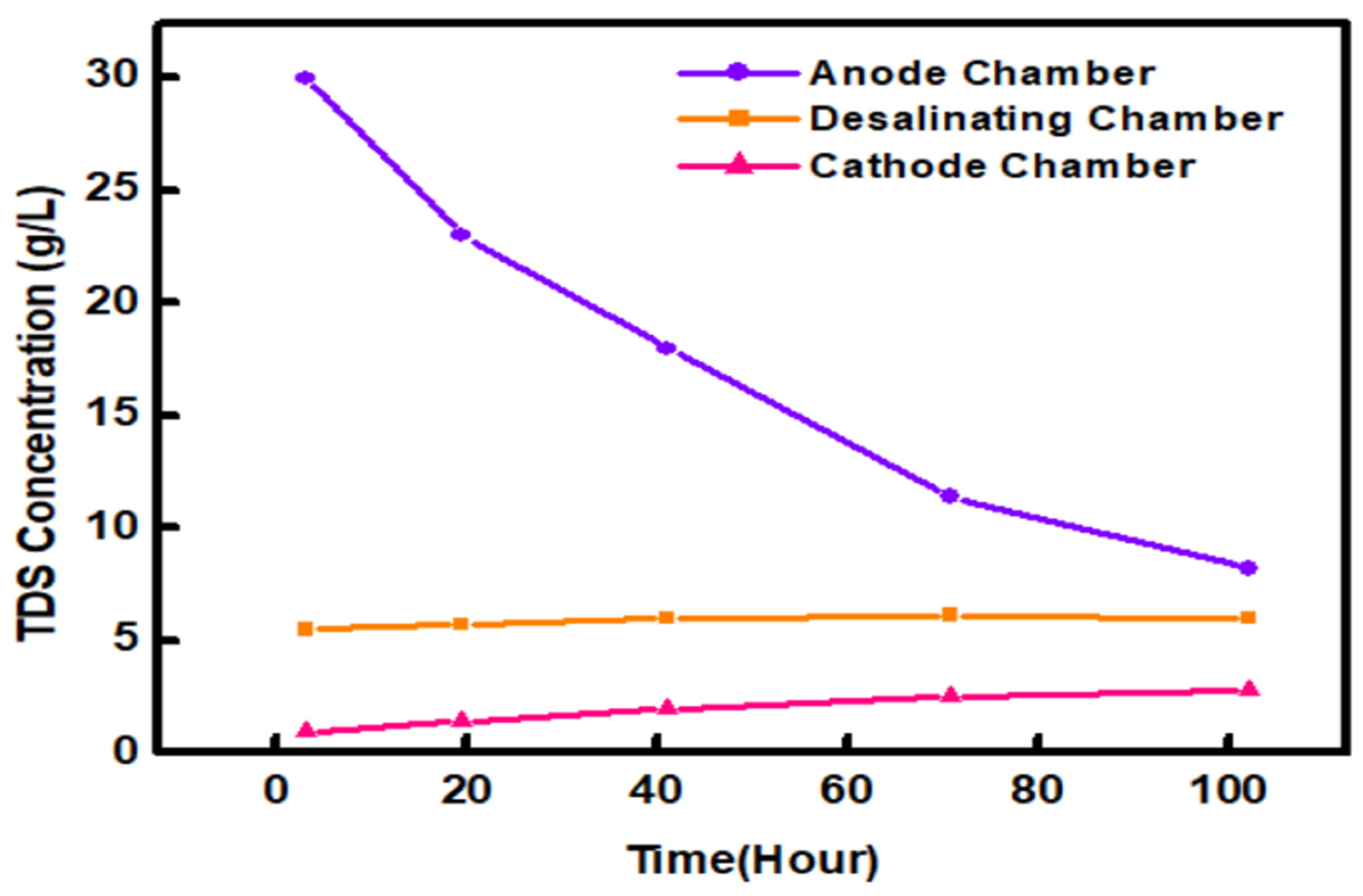
2.6. Effect of the TDS Concentration on the System Performance
3. Materials and Methods
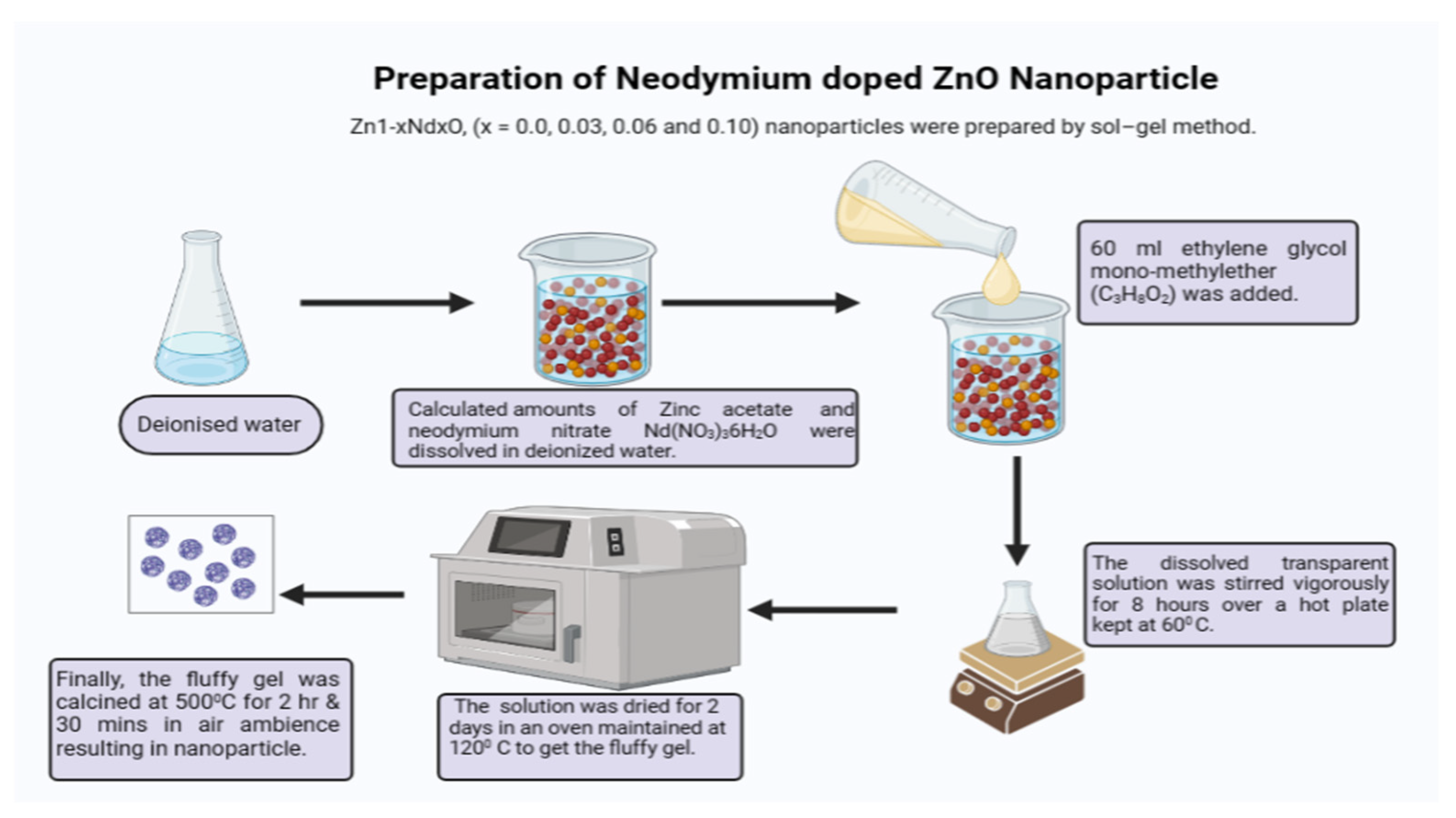
3.1. Process of Synthesis of Neodymium Metal Doped Zinc Oxide
3.2. Preparation of Cathode
3.3. Fabrication of MDC
3.4. MDCs Operation
3.5. Analysis and Calculations
3.6. Characterization of Catalyst
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Bavel, J. The World Population Explosion: Causes, Backgrounds and Projections for the Future. Facts Views Vis. Obgyn. 2013, 5, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saeed, H.M.; Husseini, G.A.; Yousef, S.; Saif, J.; Al-Asheh, S.; Abu Fara, A.; Azzam, S.; Khawaga, R.; Aidan, A. Microbial Desalination Cell Technology: A Review and a Case Study. Desalination 2015, 359, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunwar, S.; Roy, A.; Bhusal, U.; Gacem, A.; Abdullah, M.M.; Sharma, P.; Yadav, K.K.; Rustagi, S.; Chatterjee, N.; Deshwal, V.K.; et al. Bio-Fabrication of Cu/Ag/Zn Nanoparticles and Their Antioxidant and Dye Degradation Activities. Catalysts 2023, 13, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawalbeh, M.; Al-Othman, A.; Singh, K.; Douba, I.; Kabakebji, D.; Alkasrawi, M. Microbial Desalination Cells for Water Purification and Power Generation: A Critical Review. Energy 2020, 209, 118493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imoro, A.Z.; Mensah, M.; Buamah, R. Developments in the Microbial Desalination Cell Technology: A Review. Water-Energy Nexus 2021, 4, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Salama, E.-S.; Thakur, N.; Alghamdi, H.; Jeon, B.-H.; Li, X. Advances in the Biomass Valorization in Bioelectrochemical Systems: A Sustainable Approach for Microbial-Aided Electricity and Hydrogen Production. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 465, 142546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Logan, B.E. Microbial Desalination Cells for Energy Production and Desalination. Desalination 2013, 308, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jingyu, H.; Ewusi-Mensah, D.; Norgbey, E. Desalination and Water Treatment Microbial Desalination Cells Technology: A Review of the Factors Affecting the Process, Performance and Efficiency. Desalination Water Treat. 2017, 87, 140–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Lin, G.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, T.; Shan, G.; Yang, M.; Wang, J. A Review of Oxygen Reduction Mechanisms for Metal-Free Carbon-Based Electrocatalysts. Npj Comput Mater 2019, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goswami, C.; Hazarika, K.K.; Bharali, P. Transition Metal Oxide Nanocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2018, 1, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.H.; Saha, S.; Hwang, J.-H.; Hosen, M.A.; Ahn, Y.-T.; Park, Y.-K.; Khan, M.A.; Jeon, B.-H. Integrative Biohydrogen- and Biomethane-Producing Bioprocesses for Comprehensive Production of Biohythane. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 365, 128145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mamun, A.; Ahmad, W.; Baawain, M.S.; Khadem, M.; Dhar, B.R. A Review of Microbial Desalination Cell Technology: Configurations, Optimization and Applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 183, 458–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anusha, G.; Noori, M.T.; Ghangrekar, M.M. Application of Silver-Tin Dioxide Composite Cathode Catalyst for Enhancing Performance of Microbial Desalination Cell. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2018, 1, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, R.; Xiang, L.; Komarneni, S. Synthesis, Properties and Applications of ZnO Nanomaterials with Oxygen Vacancies: A Review. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 7357–7377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, S.; Kumar, M.; Chhoker, S.; Katyal, S.C.; Awana, V.P.S. Structural, Vibrational, Optical and Magnetic Properties of Sol–Gel Derived Nd Doped ZnO Nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2013, 24, 5102–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.K.; Shukla, S.; Sharma, K.K.; Kumar, V. A Review on ZnO: Fundamental Properties and Applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 49, 3028–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujihara, S.; Ogawa, Y.; Kasai, A. Tunable Visible Photoluminescence from ZnO Thin Films through Mg-Doping and Annealing. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 2965–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahy, B.; Aslam, M.; Bahadur, D. Effect of Fe Doping Concentration on Optical and Magnetic Properties of ZnO Nanorods. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 115601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Singh, P.; Kamni. Study of Synthesis Mechanism, Structural, Optical and Luminescent Properties of Bluish-Violet Rare Earth Doped KSrVO4: Nd3+ Nano Powders. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2022, 276, 115564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vempaty, A.; Kumar, A.; Pandit, S.; Gupta, M.; Mathuriya, A.S.; Lahiri, D.; Nag, M.; Kumar, Y.; Joshi, S.; Kumar, N. Evaluation of the Datura Peels Derived Biochar-Based Anode for Enhancing Power Output in Microbial Fuel Cell Application. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2023, 47, 102560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, S.; Khanna, S.; Mathuriya, A.S. Analysis of Pyridine-2-Carbaldehyde Thiosemicarbazone as an Anti-Biofouling Cathodic Agent in Microbial Fuel Cell. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shatnawi, M.; Alsmadi, A.M.; Bsoul, I.; Salameh, B.; Alna’washi, G.A.; Al-Dweri, F.; El Akkad, F. Magnetic and Optical Properties of Co-Doped ZnO Nanocrystalline Particles. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 655, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, A.; Goswami, N. Structural and Vibrational Properties of ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized by the Chemical Precipitation Method. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostructures 2014, 58, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, A.; Goswami, N. Probing the Dominance of Interstitial Oxygen Defects in ZnO Nanoparticles through Structural and Optical Characterizations. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 14569–14578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, B.; Noori, M. Carbon Supported Nickel-Phthalocyanine/MnO x as Novel Cathode Catalyst for Microbial Fuel Cell Application. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 23085–23094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Siddiqui, T.; Pandit, S.; Roy, A.; Gacem, A.; Souwaileh, A.A.; Mathuriya, A.S.; Fatma, T.; Sharma, P.; Rustagi, S.; et al. Application of Biogenic TiO2 Nanoparticles as ORR Catalysts on Cathode for Enhanced Performance of Microbial Fuel Cell. Catalysts 2023, 13, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pema, T.; Kumar, A.; Tripathi, B.; Pandit, S.; Chauhan, S.; Singh, S.; Dikshit, P.K.; Mathuriya, A.S.; Gupta, P.K.; Lahiri, D.; et al. Investigating the Performance of Lithium-Doped Bismuth Ferrite [BiFe1−xLixO3]-Graphene Nanocomposites as Cathode Catalyst for the Improved Power Output in Microbial Fuel Cells. Catalysts 2023, 13, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, H.; Ghangrekar, M.M. Multi-Chamber Microbial Desalination Cell for Improved Organic Matter and Dissolved Solids Removal from Wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 70, 1948–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jafary, T.; Al-Mamun, A.; Alhimali, H.; Baawain, M.S.; Rahman, S.; Tarpeh, W.A.; Dhar, B.R.; Kim, B.H. Novel Two-Chamber Tubular Microbial Desalination Cell for Bioelectricity Production, Wastewater Treatment and Desalination with a Focus on Self-Generated PH Control. Desalination 2020, 481, 114358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Pandit, S.; Thapa, B.S.; Pant, M. Biodegradation of Congo Red Using Co-Culture Anode Inoculum in a Microbial Fuel Cell. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample | Williamson Hall Method | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UDM | UDSM | UDEDM | |||||||
| D (nm) | ε × 10−3 | D (nm) | ε × 10−3 | σ (MPa) | D (nm) | ε × 10−3 | σ (MPa) | u (KJm−3) | |
| x = 0.00 | 30 | 1.82 | 27 | 1.74 | 215.28 | 26 | 1.80 | 222.26 | 196.15 |
| x = 0.03 | 28 | 1.77 | 24 | 1.646 | 210.78 | 24 | 1.74 | 220.45 | 192.41 |
| x = 0.06 | 34 | 0.6131 | 30 | 0.5681 | 71.64 | 30 | 0.596 | 75.16 | 22.425 |
| x = 0.10 | 48 | 0.3419 | 54 | 0.3172 | 40.002 | 55 | 0.3327 | 41.96 | 6.982 |
| Nd-Doped ZnO Concentration (mg/cm2) | COD Removal (%) | CE (%) | PD (W/m3) | DC Voltage (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.75 | 80.4 | 6.02 | 1.28 | 515 |
| 1.0 | 82.01 | 7.04 | 1.98 | 545 |
| 1.5 | 86.08 | 8.8 | 2.28 | 585 |
| 1.75 | 86.01 | 8.02 | 3.65 | 603 |
| Without catalyst | 70.9 | 4.56 | 0.78 | 475 |
| TDS Concentration 15 (g/L) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Time (t) | Anode | Desalination | Cathode |
| 0 | 6 | 15 | 0.2 |
| 20 | 6.25 | 12 | 1 |
| 40 | 6.65 | 10.4 | 1.25 |
| 80 | 6.75 | 8.2 | 1.75 |
| 100 | 7.03 | 6.14 | 2.23 |
| TDS Concentration 30 (g/L) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Time (t) | Anode | Desalination | Cathode |
| 0 | 5.5 | 30 | 0.24 |
| 20 | 5.75 | 23 | 1.38 |
| 40 | 6 | 18 | 2.03 |
| 80 | 6.12 | 11.4 | 2.5 |
| 100 | 6.02 | 8.2 | 2.65 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chauhan, S.; Rai, S.; Pandit, S.; Roy, A.; Gacem, A.; El-Hiti, G.A.; Yadav, K.K.; Ravindran, B.; Cheon, J.-K.; Jeon, B.-H. Neodymium-Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Catalytic Cathode for Enhanced Efficiency of Microbial Desalination Cells. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13081164
Chauhan S, Rai S, Pandit S, Roy A, Gacem A, El-Hiti GA, Yadav KK, Ravindran B, Cheon J-K, Jeon B-H. Neodymium-Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Catalytic Cathode for Enhanced Efficiency of Microbial Desalination Cells. Catalysts. 2023; 13(8):1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13081164
Chicago/Turabian StyleChauhan, Sunil, Shweta Rai, Soumya Pandit, Arpita Roy, Amel Gacem, Gamal A. El-Hiti, Krishna Kumar Yadav, Balasubramani Ravindran, Ji-Kwang Cheon, and Byong-Hun Jeon. 2023. "Neodymium-Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Catalytic Cathode for Enhanced Efficiency of Microbial Desalination Cells" Catalysts 13, no. 8: 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13081164
APA StyleChauhan, S., Rai, S., Pandit, S., Roy, A., Gacem, A., El-Hiti, G. A., Yadav, K. K., Ravindran, B., Cheon, J.-K., & Jeon, B.-H. (2023). Neodymium-Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Catalytic Cathode for Enhanced Efficiency of Microbial Desalination Cells. Catalysts, 13(8), 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13081164










