Tuning a Cr-Catalyzed Ethylene Oligomerization Product Profile via a Rational Design of the N-aryl PNP Ligands
Abstract
1. Introduction
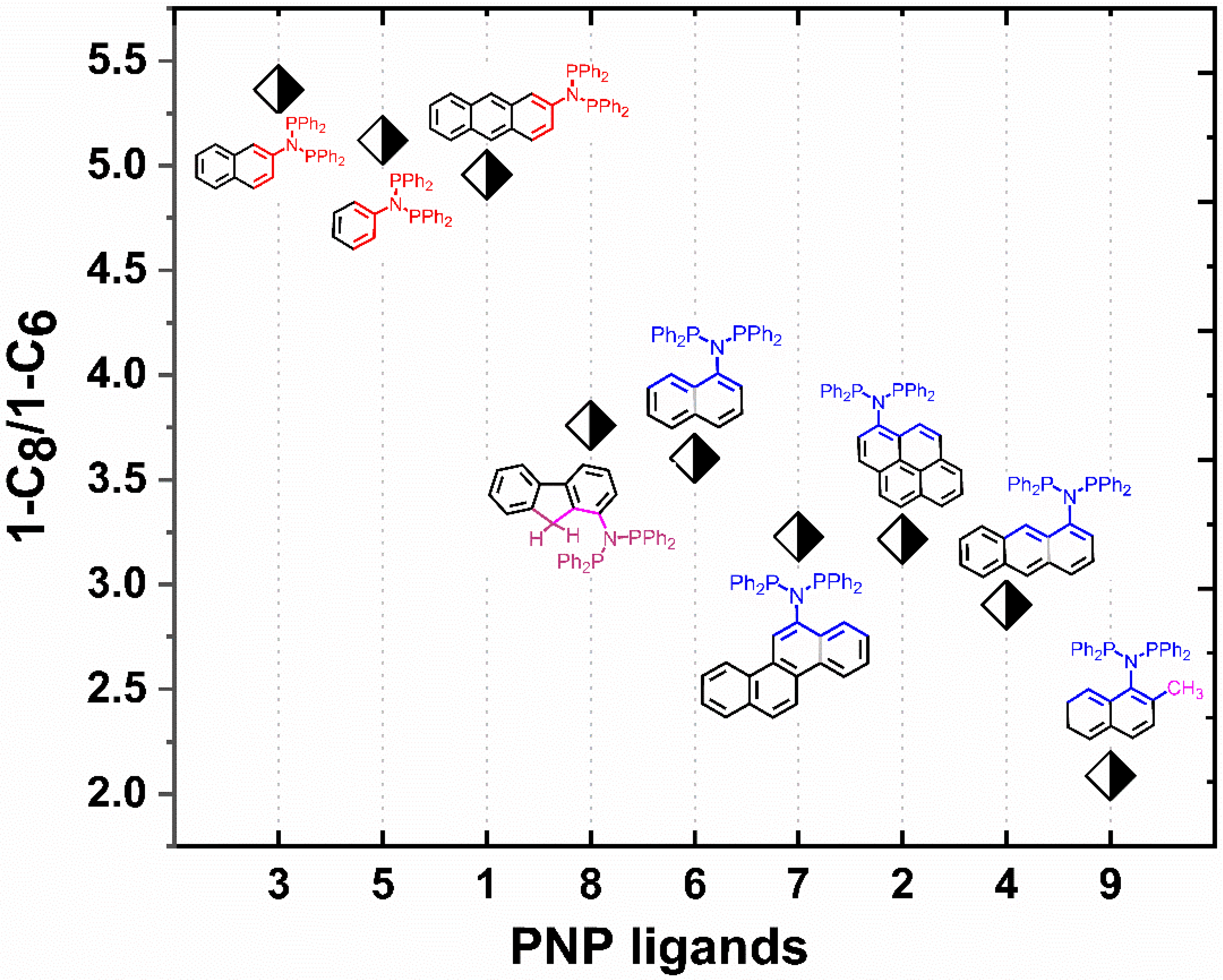
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental Section
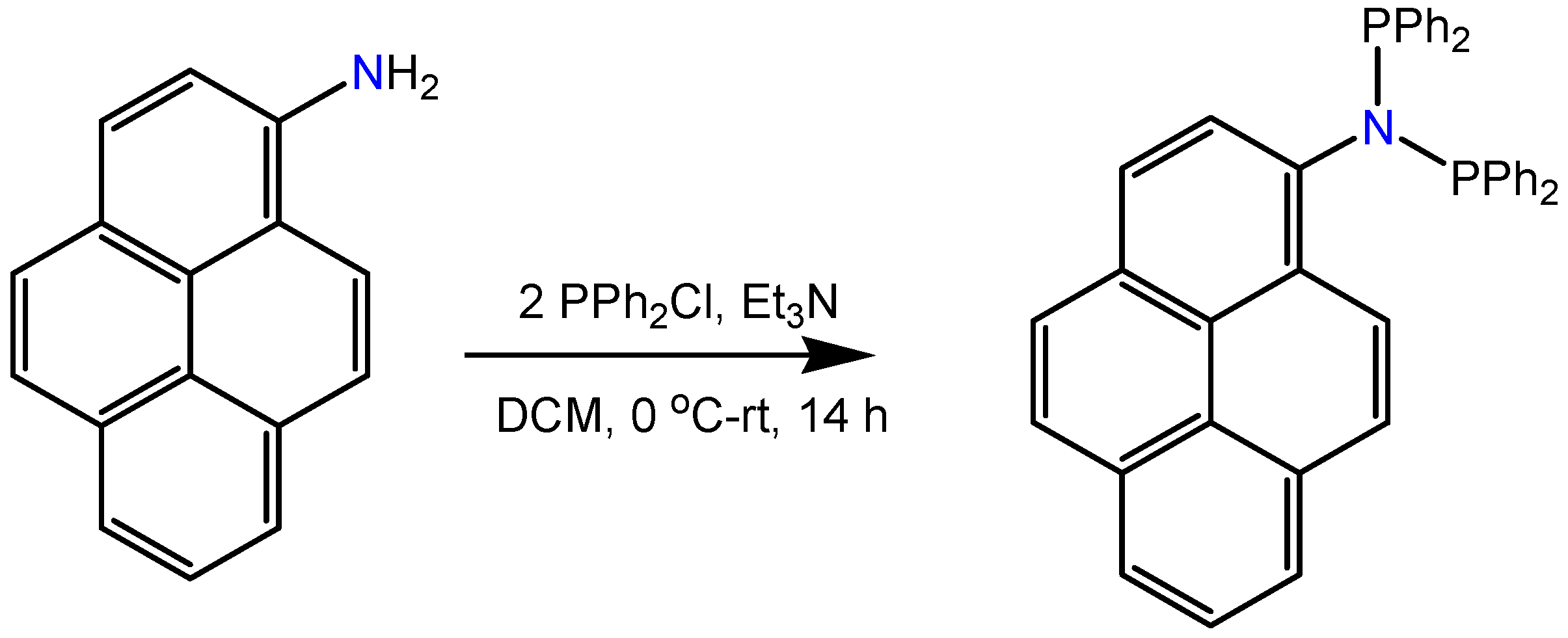
3.1. Ligand Preparation
3.2. General Oligomerization Procedure
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carter, A.; Cohen, S.A.; Cooley, N.A.; Murphy, A.; Scutt, J.; Wass, D.F. High activity ethylene trimerisation catalysts based on diphosphine ligands. Chem. Commun. 2002, 858–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J.T.; Green, M.J.; Hess, F.M.; Morgan, D.H. Advances in selective ethylene trimerization—A critical overview. J. Organomet. Chem. 2004, 689, 3641–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, D.S. Olefin Oligomerization via Metallacycles: Dimerization, Trimerization, Tetramerization, and Beyond. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 2321–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agapie, T. Selective ethylene oligomerization: Recent advances in chromium catalysis and mechanistic investigations. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 861–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, P.W.N.M.; Clément, N.D.; Tschan, M.J.L. New processes for the selective production of 1-octene. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 1499–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belov, G.P. Tetramerization of ethylene to octene-1 (a review). Pet. Chem. 2012, 52, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuil, P.-A.R.; Magna, L.; Olivier-Bourbigou, H. Role of Homogeneous Catalysis in Oligomerization of Olefins: Focus on Selected Examples Based on Group 4 to Group 10 Transition Metal Complexes. Catal. Lett. 2015, 145, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alferov, K.A.; Belov, G.P.; Meng, Y. Chromium catalysts for selective ethylene oligomerization to 1-hexene and 1-octene: Recent results. Appl. Catal. A 2017, 542, 71–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bariashir, C.; Huang, C.; Solan, G.A.; Sun, W.H. Recent advances in homogeneous chromium catalyst design for ethylene tri-, tetra-, oligo- and polymerization. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 385, 208–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, B.-B.; Alam, F.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, L.; Fan, H.; Jing, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, T. Selective Ethylene Tetramerization: An Overview. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2023, 10, 2860–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollmann, A.; Blann, K.; Dixon, J.T.; Hess, F.M.; Killian, E.; Maumela, H.; McGuinness, D.S.; Morgan, D.H.; Neveling, A.; Otto, S.; et al. Ethylene Tetramerization: A New Route to Produce 1-Octene in Exceptionally High Selectivities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 14712–14713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overett, M.J.; Blann, K.; Bollmann, A.; Dixon, J.T.; Haasbroek, D.; Killian, E.; Maumela, H.; McGuinness, D.S.; Morgan, D.H. Mechanistic Investigations of the Ethylene Tetramerisation Reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 10723–10730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blann, K.; Bollmann, A.; de Bod, H.; Dixon, J.T.; Killian, E.; Nongodlwana, P.; Maumela, M.C.; Maumela, H.; McConnell, A.E.; Morgan, D.H.; et al. Ethylene Tetramerisation: Subtle effects exhibited by N-substituted diphosphinoamine ligands. J. Catal. 2007, 249, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killian, E.; Blann, K.; Bollmann, A.; Dixon, J.T.; Kuhlmann, S.; Maumela, M.C.; Maumela, H.; Morgan, D.H.; Nongodlwana, P.; Overett, M.J.; et al. The use of bis(diphenylphosphino)amines with N-aryl functionalities in selective ethylene tri- and tetramerisation. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2007, 270, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K.; Kim, T.-J.; Chung, J.-H.; Hahn, T.-K.; Chae, S.-S.; Lee, H.-S.; Cheong, M.; Kang, S.O. Bimetallic Ethylene Tetramerization Catalysts derived from Chiral DPPDME Ligands: Syntheses, Structural Characterizations, and Catalytic Performance of [(DPPDME)CrCl3]2 (DPPDME = S,S- and R,R-chiraphos and meso-achiraphos). Organometallics 2010, 29, 5805–5811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wu, W.; Zhang, G.; Xu, S.; Shi, M. Switchable Ethylene Tri-/Tetramerization with High Activity: Subtle Effect Presented by Backbone- Substituent of Carbon-Bridged Diphosphine Ligands. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 2311–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, F.; Zhang, L.; Wei, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Dong, C.; Jiang, T. Catalytic Systems Based on Chromium (III) Silylated-Diphosphinoamines for Selective Ethylene Tri-/Tetramerization. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 10836–10845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.H.; Lee, H.M.; Jeong, M.S.; Ryu, J.Y.; Lee, J.; Lee, B.Y. Methylaluminoxane-Free Chromium Catalytic System for Ethylene Tetramerization. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, X.; Yang, C.; Niu, B.; Ning, Y. The effect of N-aryl bisphosphineamine ligands on the selective ethylene tetramerization. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2008, 279, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, S.; Jaseer, E.A.; Garcia, N.; Elanany, M.; Khawaji, M.; Xu, W.; Lin, S.; Alasiri, H.; Akhtar, M.N.; Theravalappil, R. A rational approach towards selective ethylene oligomerization via PNP-ligand design with an N-triptycene functionality. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 10044–10047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaseer, E.A.; Garcia, N.; Barman, S.; Khawaji, M.; Xu, W.; Alasiri, H.; Peedikakkal, A.M.P.; Akhtar, M.N.; Theravalappil, R. Highly Efficient Ethylene Tetramerization Using Cr Catalysts Constructed with Trifluoromethyl-Substituted N-Aryl PNP Ligands. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 16333–16340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, S.; Garcia, N.; Jaseer, E.A.; Elanany, M.; Khawaji, M.; Alasiri, H.; Peedikakkal, A.M.P.; Akhtar, M.N.; Theravalappil, R. Unveiling meta-Alkyloxy/-Silyloxy-Substituted N-Aryl PNP Ligands for Efficient Cr-Catalyzed Ethylene Tetramerization. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 26437–26443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.H.; Fuller, J.T.; Kilgore, U.J.; Sydora, O.L.; Bischof, S.M.; Ess, D.H. Computational Transition-State Design Provides Experimentally Verified Cr(P,N) Catalysts for Control of Ethylene Trimerization and Tetramerization. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 1138–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
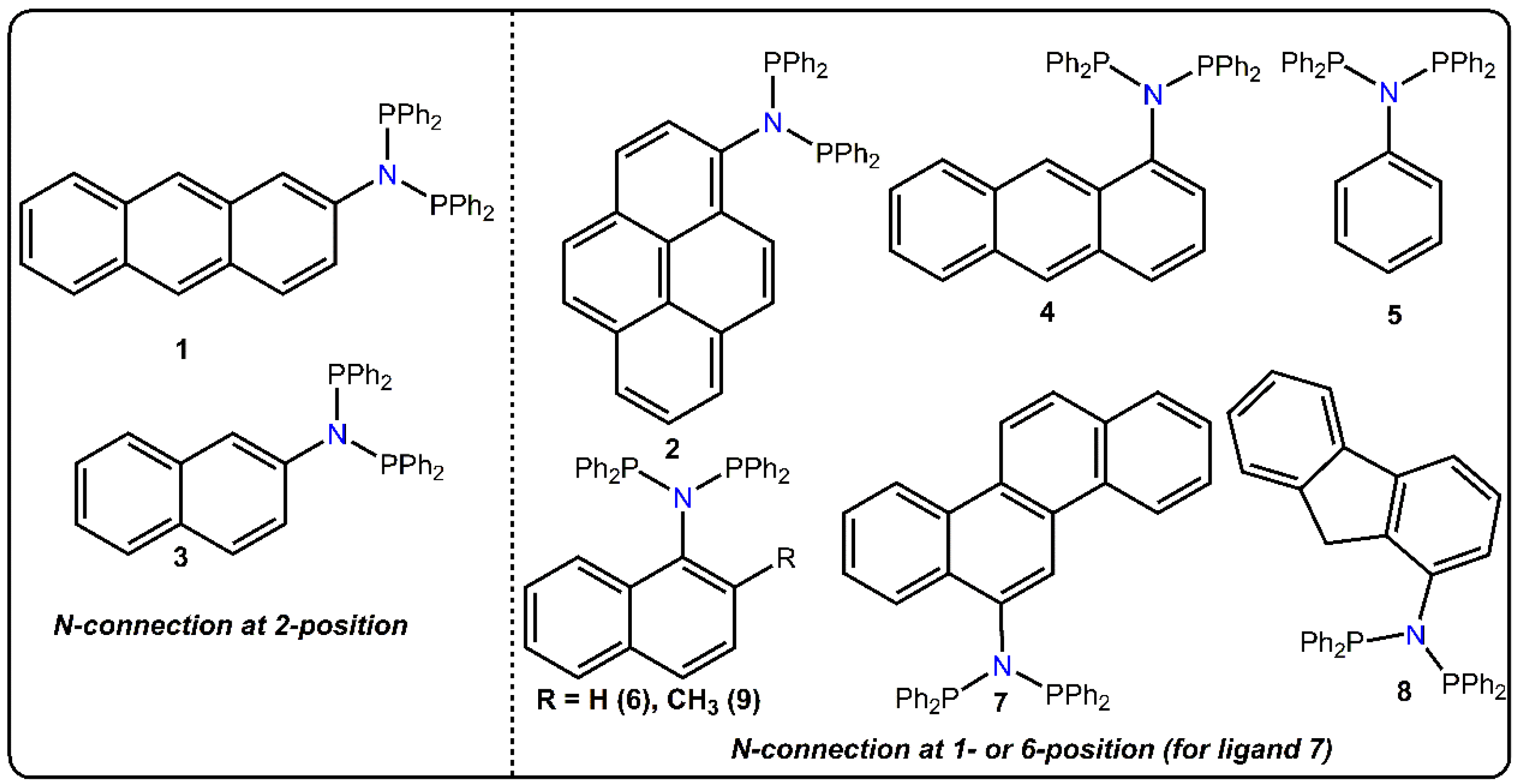
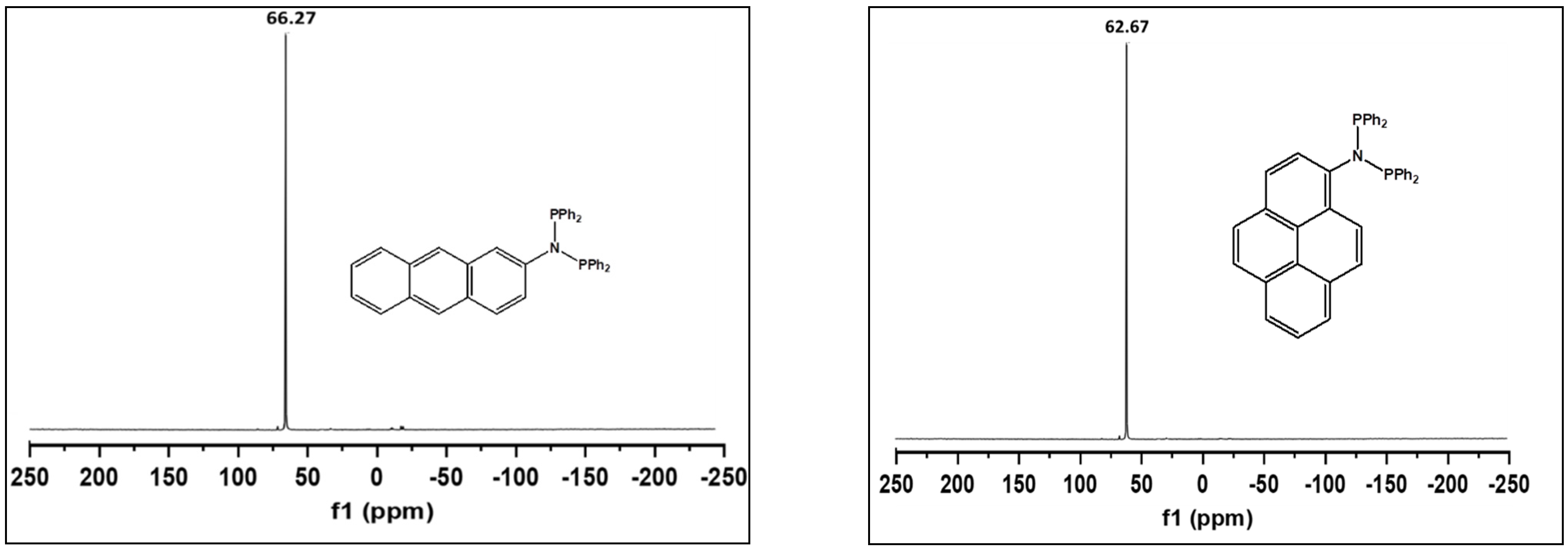


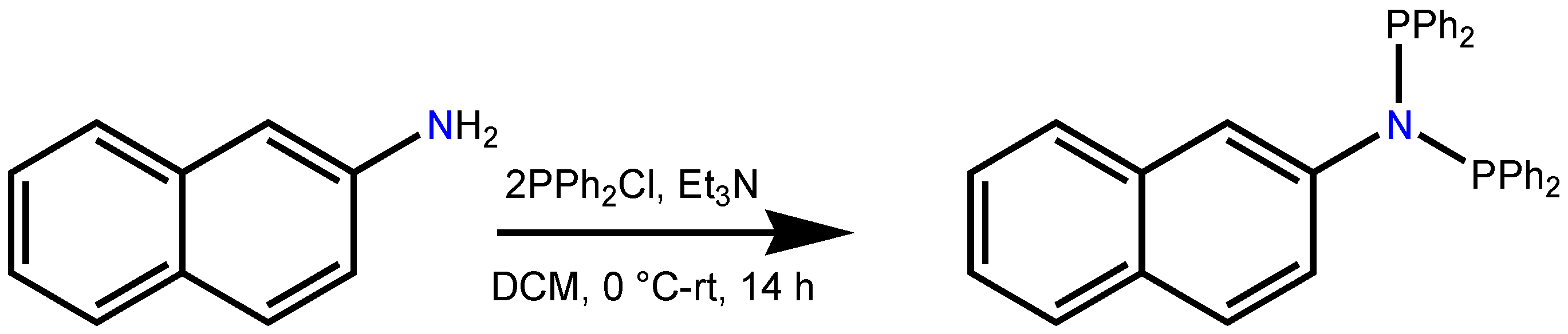

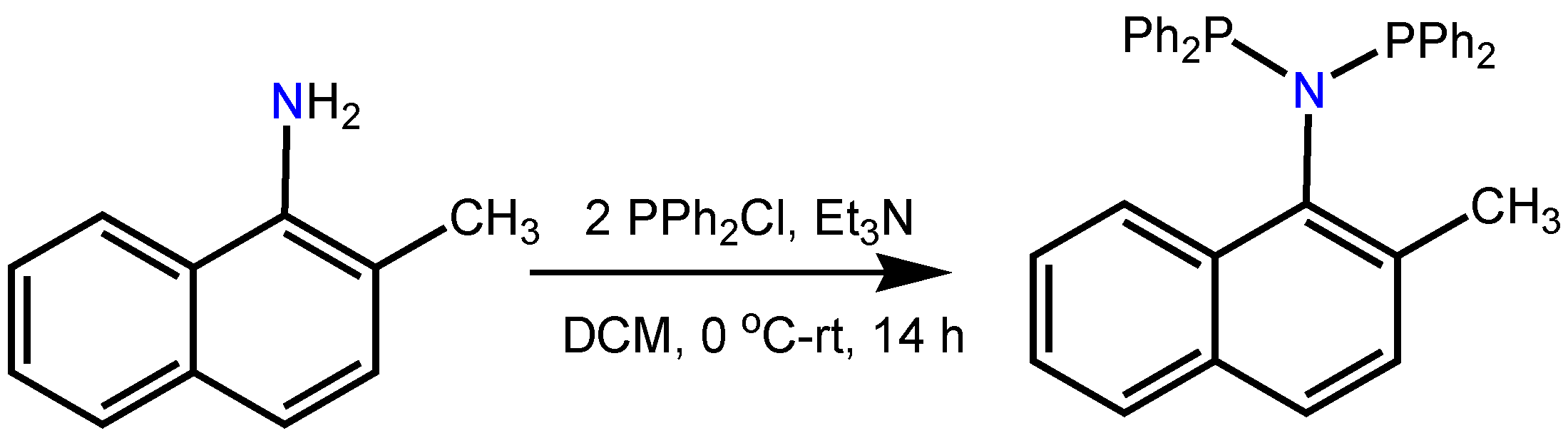


| Ligand | 31P NMR (ppm) | Ligand | 31P NMR (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 66.27 | 7 | 63.60 |
| 2 | 62.67 | 8 | 57.73 |
| 3 | 68.52 | 9 | 62.43 |
| 4 | 64.21 |
| Entry | Ligand | Productivity (kg·gCr−1·h−1) b | Product Selectivity (wt%) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solvent | C6 | 1-C6 in C6 (%) | 1-C6 | C6 Cyclics c | C8 | 1-C8 in C8 (%) | 1-C8 | 1-C6 + 1-C8 | C10+ | PE | |||
| 1 | 1 | Cy | 435 | 21.5 | 57.7 | 12.4 | 9.1 | 74.1 | 91.6 | 67.9 | 80.2 | 2.6 | 1.8 |
| 2 | 1 | MeCY | 290 | 23.9 | 61.1 | 14.6 | 9.3 | 71.8 | 88.1 | 63.3 | 77.9 | 1.7 | 2.6 |
| 3 | 1 | PhCl | 1479 | 24.2 | 57.4 | 13.9 | 10.3 | 72.1 | 95.6 | 68.9 | 82.8 | 2.0 | 1.7 |
| 4 | 2 | Cy | 450 | 25.1 | 64.5 | 16.2 | 8.9 | 71.7 | 90.2 | 64.7 | 80.9 | 1.6 | 1.5 |
| 5 | 2 | MeCY | 511 | 26.3 | 58.9 | 15.5 | 10.8 | 70.7 | 91.9 | 65.0 | 80.5 | 1.8 | 1.2 |
| 6 | 2 | PhCl | 1774 | 29.5 | 70.5 | 20.8 | 8.7 | 68.4 | 97.8 | 66.9 | 87.7 | 1.3 | 0.8 |
| 7 a | 1 | PhCl | 1005 | 21.4 | 56.9 | 12.2 | 9.2 | 72.1 | 98.0 | 70.7 | 82.9 | 5.1 | 1.5 |
| 8 a | 2 | PhCl | 1214 | 27.1 | 62.4 | 16.9 | 10.2 | 68.0 | 98.4 | 66.9 | 83.8 | 3.5 | 1.4 |
| Entry | Productivity (kg·gCr−1·h−1) a | Product Selectivity (wt%) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure (Bar) | C6 | 1-C6 in C6 (%) | 1-C6 | C6 Cyclics b | C8 | 1-C8 in C8 (%) | 1-C8 | 1-C6 + 1-C8 | C10+ | PE | ||
| 1 | 10 | 161 | 42.2 | 91.8 | 38.7 | 3.5 | 37.4 | 96.2 | 36.0 | 74.7 | 0.0 | 20.4 |
| 2 | 30 | 1076 | 32.0 | 74.4 | 23.8 | 8.2 | 63.0 | 96.8 | 61.0 | 84.8 | 0.8 | 4.2 |
| 3 | 45 | 1774 | 29.5 | 70.5 | 20.8 | 8.7 | 68.4 | 97.8 | 66.9 | 87.7 | 1.3 | 0.8 |
| Entry | Productivity (kg·gCr−1·h−1) a | Product Selectivity (wt%) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | C6 | 1-C6 in C6 (%) | 1-C6 | C6 Cyclics b | C8 | 1-C8 in C8 (%) | 1-C8 | 1-C6 + 1-C8 | C10+ | PE | ||
| 1 | 30 | 431 | 24.5 | 62.7 | 15.4 | 9.1 | 70.9 | 94.6 | 67.1 | 82.4 | 2.0 | 2.6 |
| 2 | 45 | 1774 | 29.5 | 70.5 | 20.8 | 8.7 | 68.4 | 97.8 | 66.9 | 87.7 | 1.3 | 0.8 |
| 3 | 60 | 1206 | 38.1 | 79.1 | 30.1 | 8.0 | 59.9 | 97.0 | 58.1 | 88.2 | 0.4 | 1.5 |
| Entry | Ligand | Productivity (kg·gCr−1·h−1) a | Product Selectivity (wt%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C6 | 1-C6 in C6 (%) | 1-C6 | C6 Cyclics b | C8 | 1-C8 in C8 (%) | 1-C8 | 1-C6 + 1-C8 | C10+ | PE | |||
| 1 | 5 | 1323 | 22.8 | 61.5 | 14.0 | 8.8 | 74.1 | 96.8 | 71.7 | 85.8 | 2.0 | 1.0 |
| 2 | 6 | 702 | 26.7 | 69 | 18.4 | 8.3 | 68.4 | 96.9 | 66.3 | 84.7 | 2.1 | 2.8 |
| 3 | 3 | 1177 | 22.2 | 60.7 | 13.5 | 8.7 | 74.6 | 97.1 | 72.4 | 85.9 | 2.2 | 1.1 |
| 4 | 1 | 1479 | 24.2 | 57.3 | 13.9 | 10.3 | 72.1 | 95.6 | 68.9 | 82.8 | 2.0 | 1.7 |
| 5 | 2 | 1774 | 29.5 | 70.5 | 20.8 | 8.7 | 68.4 | 97.8 | 66.9 | 87.7 | 1.3 | 0.8 |
| 6 | 4 | 1452 | 30.4 | 74.9 | 22.8 | 7.6 | 67.6 | 98 | 66.2 | 89.0 | 1.0 | 0.9 |
| 7 | 7 | 1505 | 29.8 | 67.8 | 20.2 | 9.6 | 67.4 | 96.8 | 65.2 | 85.4 | 1.5 | 1.2 |
| 8 | 8 | 1309 | 25.3 | 75.6 | 19.1 | 6.2 | 72.5 | 99.0 | 71.8 | 90.9 | 0.9 | 1.3 |
| 9 | 9 | 1234 | 33.7 | 91.2 | 30.7 | 3.0 | 64.4 | 99.5 | 64.1 | 94.8 | 0.4 | 1.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barman, S.; Jaseer, E.A.; Garcia, N.; Elanany, M.; Khawaji, M.; Maity, N.; Musa, A. Tuning a Cr-Catalyzed Ethylene Oligomerization Product Profile via a Rational Design of the N-aryl PNP Ligands. Catalysts 2024, 14, 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14070441
Barman S, Jaseer EA, Garcia N, Elanany M, Khawaji M, Maity N, Musa A. Tuning a Cr-Catalyzed Ethylene Oligomerization Product Profile via a Rational Design of the N-aryl PNP Ligands. Catalysts. 2024; 14(7):441. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14070441
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarman, Samir, E. A. Jaseer, Nestor Garcia, Mohamed Elanany, Motaz Khawaji, Niladri Maity, and Abdulrahman Musa. 2024. "Tuning a Cr-Catalyzed Ethylene Oligomerization Product Profile via a Rational Design of the N-aryl PNP Ligands" Catalysts 14, no. 7: 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14070441
APA StyleBarman, S., Jaseer, E. A., Garcia, N., Elanany, M., Khawaji, M., Maity, N., & Musa, A. (2024). Tuning a Cr-Catalyzed Ethylene Oligomerization Product Profile via a Rational Design of the N-aryl PNP Ligands. Catalysts, 14(7), 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14070441








