TiO2-Supported Catalysts in Low-Temperature Selective Reduction of NOx with NH3: A Review of Recent Progress
Abstract
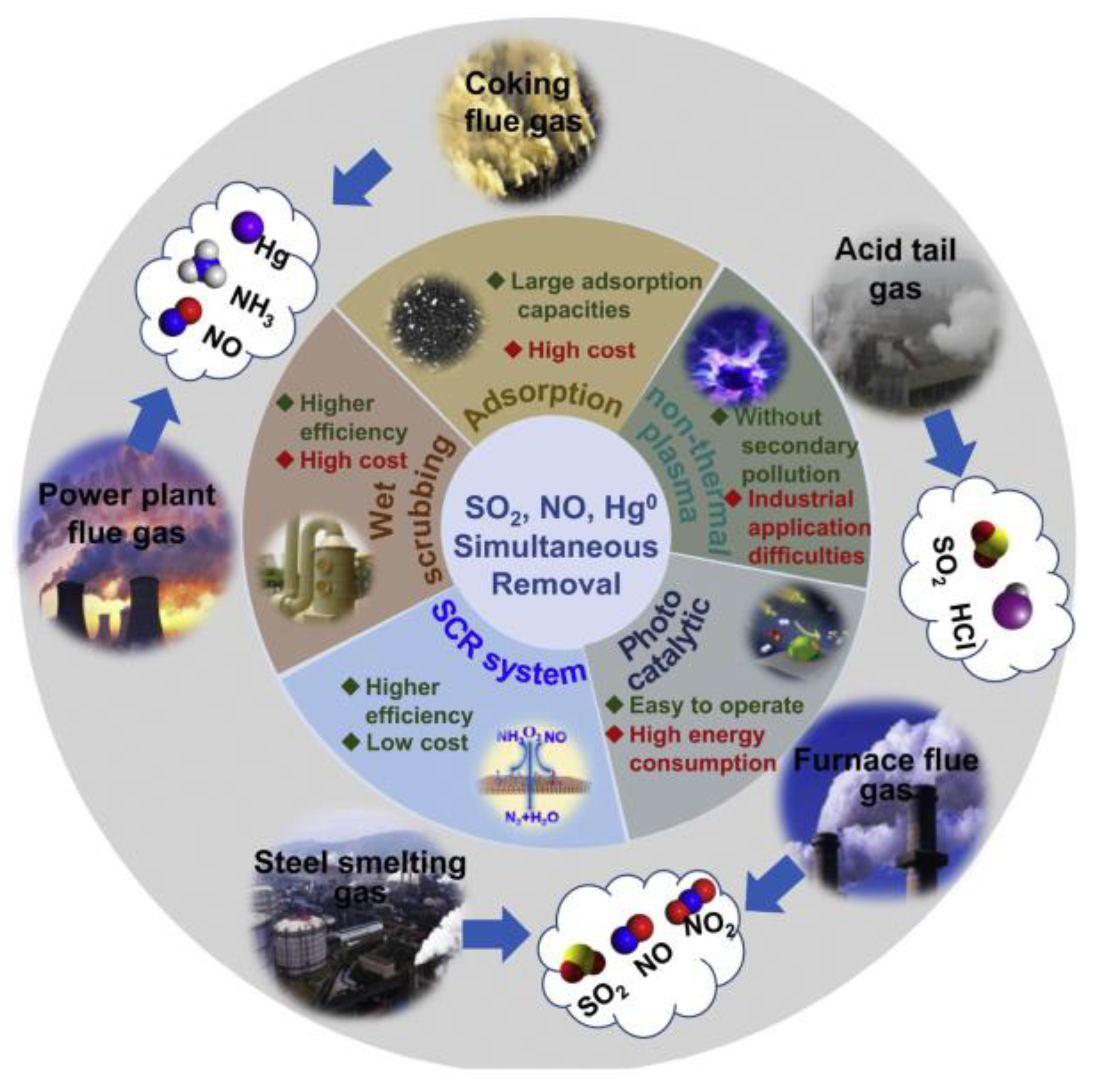
:1. Introduction

2. Effect of TiO2 Support Morphological Regulation on Catalysts
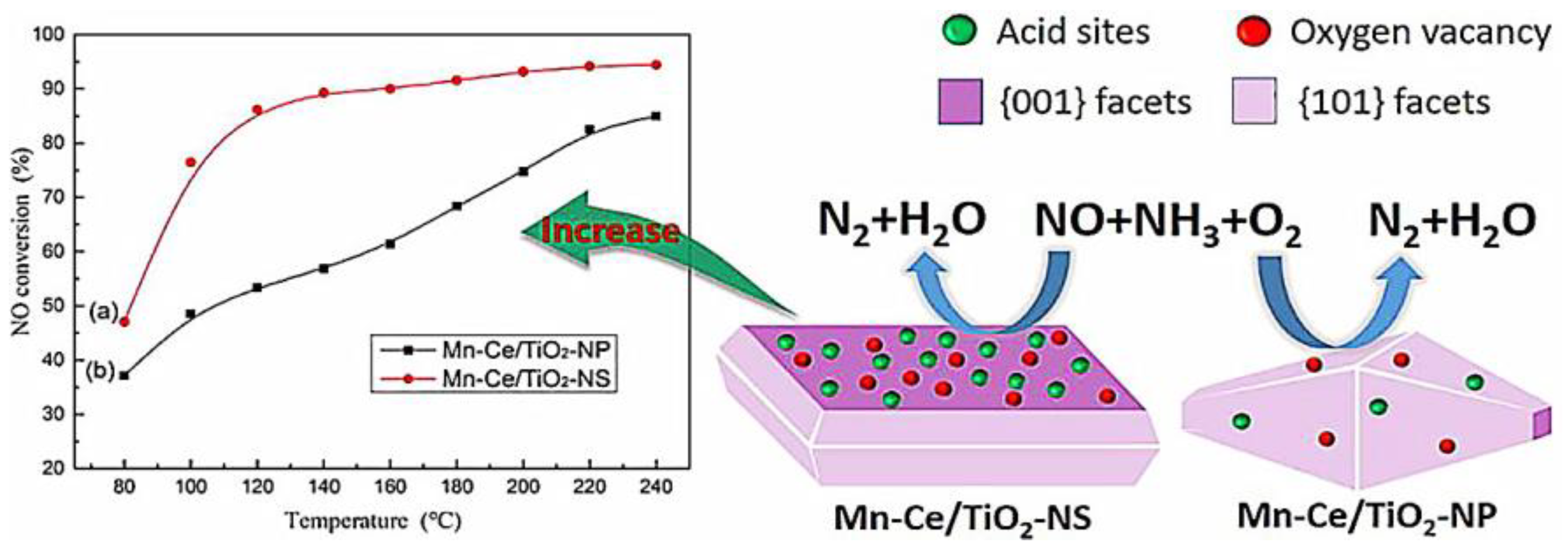
2.1. Mechanism and Properties of SCR Catalysts with Different Crystal Faces
2.2. Resistance to H2O/SO2 of TiO2 Catalysts with Different Crystal Faces
3. Effect of TiO2 Structure on Catalyst
3.1. Pore Structure
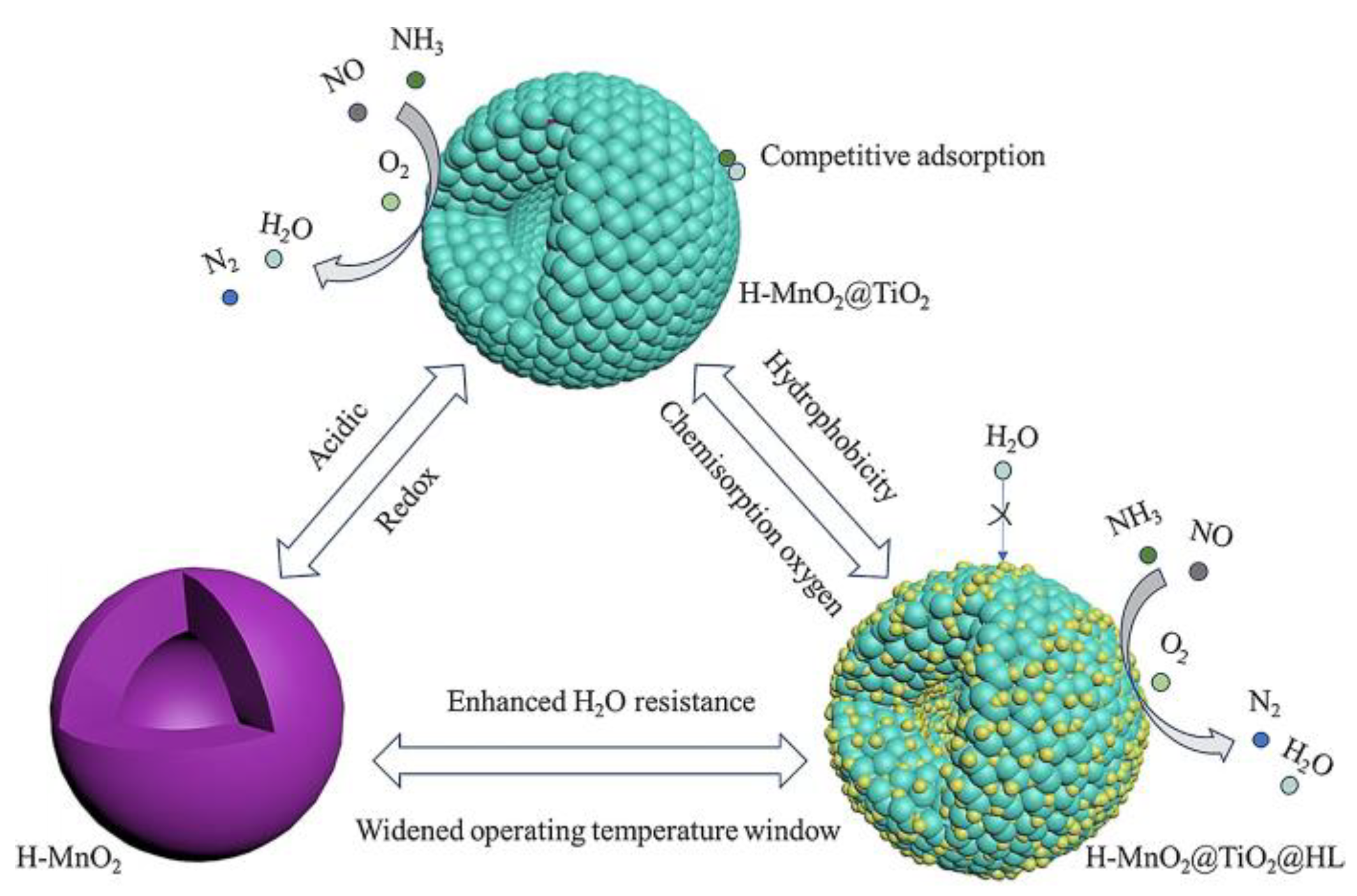
3.2. Core-Shell Structure
4. The Effect TiO2-X Composite Structural Support on SCR Catalyst Performance
4.1. TiO2 Composite Metal Oxide as the Support
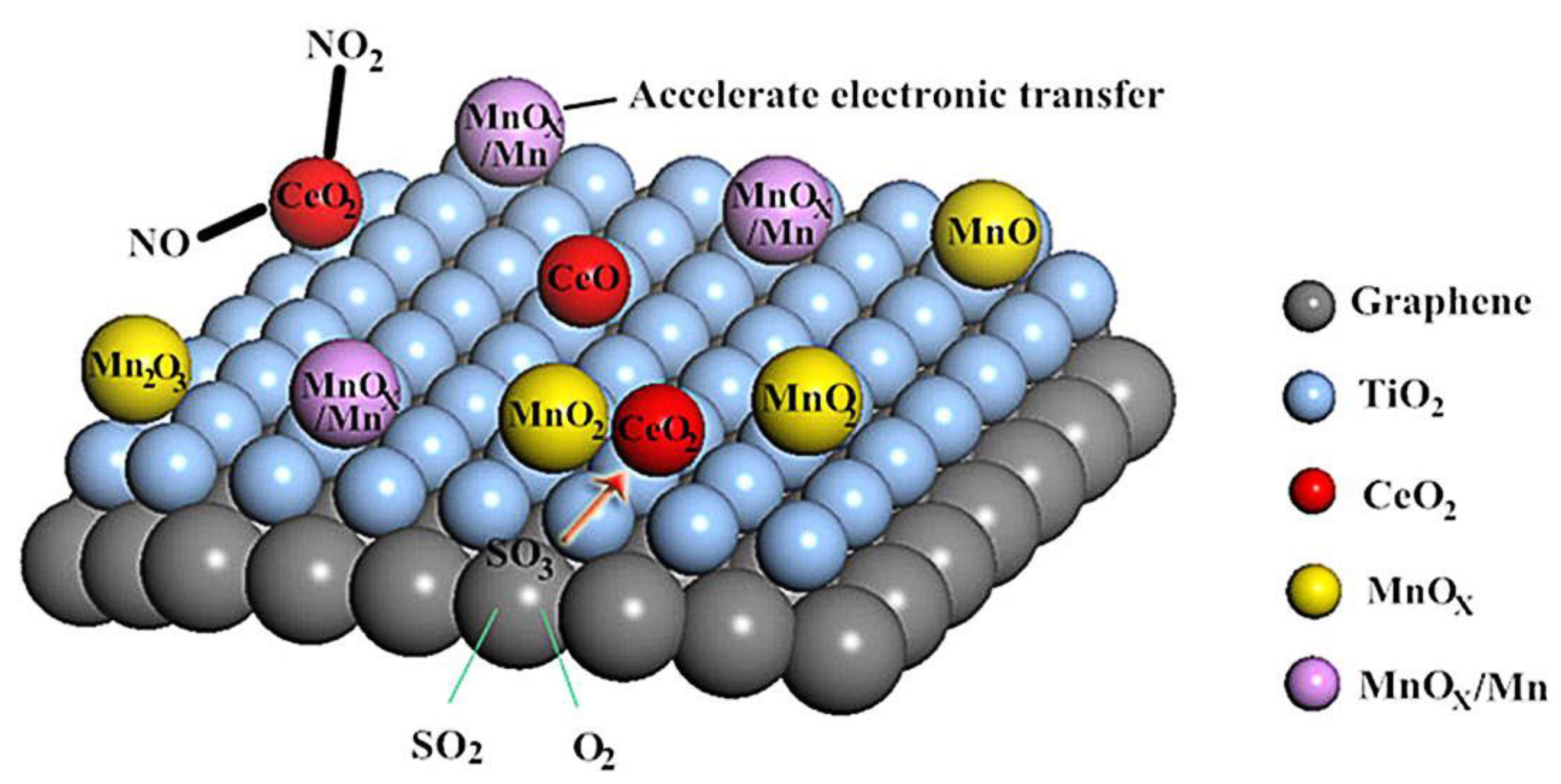
4.2. TiO2 Composite Carbon Material as the Support
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Richter, A.; Burrows, J.P.; Nüß, H.; Granier, C.; Niemeier, U. Increase in tropospheric nitrogen dioxide over China observed from space. Nature 2005, 437, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, F.; Rao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, W.; Mei, H. The new challenges for the development of NH3-SCR catalysts under new situation of energy transition in power generation industry. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 35, 108931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Ba, K.; Li, F.; Wang, Q.; Ma, Q.; Yuan, X.; Mu, R.; Hong, J.; Zuo, J. Life cycle assessment of ultra-low treatment for steel industry sintering flue gas emissions. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 725, 138292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Zou, D.; Li, H. Environmental regulation and green technical efficiency: A process-level data envelopment analysis from Chinese iron and steel enterprises. Energy 2023, 277, 127662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masera, K.; Hossain, A.K. Modified selective non-catalytic reduction system to reduce NOx gas emission in biodiesel powered engines. Fuel 2021, 298, 120826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caneghem, J.; De Greef, J.; Block, C.; Vandecasteele, C. NOx reduction in waste incinerators by selective catalytic reduction (SCR) instead of selective non catalytic reduction (SNCR) compared from a life cycle perspective: A case study. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 4452–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.B.; Lim, Y.-I.; Eom, W.-H.; Kim, S.-J.; Yoo, K.-S. Experiment and CFD simulation of hybrid SNCR–SCR using urea solution in a pilot-scale reactor. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2010, 34, 1580–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Park, J.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Srivastava, K.; Gu, S.; Shanks, B.H.; Roling, L.T.; Li, W. Electrocatalytic Nitrate Reduction on Oxide-Derived Silver with Tunable Selectivity to Nitrite and Ammonia. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 8431–8442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Peng, Q.; Jiaqiang, E.; Xie, B.; Wei, J.; Yin, R.; Fu, G. Mechanism, performance and modification methods for NH3-SCR catalysts: A review. Fuel 2023, 331, 125885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Guan, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Zhou, S.; Chen, G.; Guo, R.; Pan, W.; Wu, J.; Li, F.; Ren, J. The impact of catalyst structure and morphology on the catalytic performance in NH3-SCR reaction: A review. Fuel 2024, 361, 130541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Kong, T.; Yu, S.; Li, L.; Yang, F.; Dong, L. Influence of different supports on the physicochemical properties and denitration performance of the supported Mn-based catalysts for NH3-SCR at low temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 402, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Schill, L.; Gao, Q.; Mossin, S.; Riisager, A. The effect of dopants (Fe, Al) on the low-temperature activity and SO2 tolerance in solvothermally synthesized MnOx NH3-SCR catalysts. Fuel 2024, 358, 130111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ji, J.; Tan, W.; Song, W.; Wang, X.; Wei, X.; Guo, K.; Zhang, W.; Tang, C.; Dong, L. Enhancing low-temperature NH3-SCR performance of Fe–Mn/CeO2 catalyst by Al2O3 modification. J. Rare Earths 2022, 40, 1454–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, W.; Wu, H. Efficient Mnox-Ceo2/Ti-Bearing Blast Furnace Slag Catalyst for Nh3-Scr of No at Low Temperature: Study of Support Treating and Mn/Ce Ratio. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Gui, K.; Zha, X. DRIFTS study of γFe2 O3 nano-catalyst for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 94, 1668–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeidi, M.; Hamidzadeh, M. Co-doping a metal (Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, and Zn) on Mn/ZSM-5 catalyst and its effect on the catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides with ammonia. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2017, 43, 2143–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, Y.; Su, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, M.; Gao, M.; Yang, M.; Wang, F.; Zhang, X.; Shen, B. Low temperature denitrification and mercury removal of Mn/TiO2-based catalysts: A review of activities, mechanisms, and deactivation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 297, 121544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Cui, S.; Guo, H.; Ma, X. Study on the role of Mn species in low temperature SCR on MnOx/TiO2 through experiment and DFT calculation. Mol. Catal. 2018, 445, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Guo, X.; Cheng, X.; Yu, J.; Fang, B. A review of Mn-based catalysts for low-temperature NH3-SCR: NOx removal and H2O/SO2 resistance. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 7052–7080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Luo, N.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, G.; Chu, F.; Yang, R.; Tang, X.; Wang, G.; Gao, F.; Huang, X. Recent advances in low-temperature NH3-SCR of NOx over Ce-based catalysts: Performance optimizations, reaction mechanisms and anti-poisoning countermeasures. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 476, 146889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Tang, P.; Xu, C.; Zhu, B.; He, Y.; Duan, T.; He, J.; Zhang, G.; Cui, P. Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) as a super support for Mn–Ce based NH3-SCR catalyst: Improvement of catalytic performance and H2O/SO2 tolerance for NO removal. J. Energy Inst. 2023, 108, 101201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Shen, H.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, T.; Guo, F.; Zhang, Q.; Duan, M. Enhancement low-temperature NH3-SCR activity of the Fe-Mn-Mo/TiO2 catalyst and its DFT calculations and kinetics. Mol. Catal. 2023, 551, 113657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Dang, Y.; Li, M.; Zhu, C.; Liu, F.; Tang, W.; Weng, J.; Ruan, M.; Suib, S.L.; Gao, P.-X. Synergistic promotion of transition metal ion-exchange in TiO2 nanoarray-based monolithic catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2022, 12, 5397–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannuzzi, C.; Mino, L.; Bordiga, S.; Pedersen, A.H.; Houghton, J.M.; Vennestrøm, P.N.R.; Janssens, T.V.W.; Berlier, G. Optimization of high surface area VOx/TiO2 catalysts for low-temperature NH3-SCR for NOx abatement. J. Catal. 2023, 421, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettireddy, P.R.; Ettireddy, N.; Mamedov, S.; Boolchand, P.; Smirniotis, P.G. Surface characterization studies of TiO2 supported manganese oxide catalysts for low temperature SCR of NO with NH3. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2007, 76, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fan, Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, L.; Zhou, L.; Luo, X.; Zou, J.; Dai, W. Promoting the catalytic activity and SO2 resistance of CeO2 by Ti-doping for low-temperature NH3-SCR: Increasing surface activity and constructing Ce3+ sites. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 473, 145272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimino, S.; Totarella, G.; Tortorelli, M.; Lisi, L. Combined poisoning effect of K+ and its counter-ion (Cl− or NO3−) on MnOx/TiO2 catalyst during the low temperature NH3-SCR of NO. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Sun, X.; Wang, C.; Song, X.; Wang, F.; Li, K.; Ning, P. Supported catalysts for simultaneous removal of SO2, NOx, and Hg0 from industrial exhaust gases: A review. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 2963–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-C.; Nian, J.-N.; Teng, H. Mesoporous nanotube aggregates obtained from hydrothermally treating TiO2 with NaOH. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 253, 1898–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Mei, S.; Quaresma, S.; Norby, P.; Ferreira, J. In situ-templated hydrothermal synthesis of Fe-doped anatase nanorods. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 1479–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, D.; Fabbri, F.; Falini, G.; Baravelli, V.; Magnani, A.; Torri, C.; Maskrot, H.; Leconte, Y. The activity of nanopowder and mesoporous titanium catalysts for the analysis of fatty acids in triglycerides by pyrolysis methylation with dimethyl carbonate. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2008, 82, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadou, I.; Papadopoulou, C.; Matralis, H.K.; Voyiatzis, G.A.; Lycourghiotis, A.; Kordulis, C. Preparation, Characterization, and Catalytic Properties for the SCR of NO by NH3 of V2 O5/TiO2 Catalysts Prepared by Equilibrium Deposition Filtration. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 8459–8468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourikas, K.; Fountzoula, C.; Kordulis, C. Monolayer Binary Active Phase (Mo−V) and (Cr−V) Supported on Titania Catalysts for the Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) of NO by NH3. Langmuir 2004, 20, 10663–10669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giakoumelou, I.; Fountzoula, C.; Kordulis, C.; Boghosian, S. Molecular structure and catalytic activity of V2O5/TiO2 catalysts for the SCR of NO by NH3: In situ Raman spectra in the presence of O2, NH3, NO, H2, H2O, and SO2. J. Catal. 2006, 239, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Gao, Y.; Moreno, E.M.; Kunst, M.; Muhler, M.; Wang, Y.; Idriss, H.; Wöll, C. Photocatalytic Activity of Bulk TiO2 Anatase and Rutile Single Crystals Using Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 138302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourikas, K.; Kordulis, C.; Lycourghiotis, A. Titanium Dioxide (Anatase and Rutile): Surface Chemistry, Liquid–Solid Interface Chemistry, and Scientific Synthesis of Supported Catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 9754–9823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; He, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X. Anatase TiO2 hollow microspheres with exposed {001} facets: Facile synthesis and enhanced photocatalysis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 5863–5868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Lyu, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, Q.; Zhong, Z. New insight on N2O formation over MnOx/TiO2 catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Mol. Catal. 2022, 525, 112356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Meng, T.; Xu, B.; Gao, F.; Ding, Y.; Yu, L.; Fan, Y. Advanced MnOx/TiO2 Catalyst with Preferentially Exposed Anatase {001} Facet for Low-Temperature SCR of NO. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 5807–5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Q.; Zhong, L.; Ma, L.; Yu, S.; Zhang, C.; Fang, Q.; Chen, G. Natures of (001) and (101) surfaces of original and MnO2-loaded anatase: A comparative study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 489, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Zhong, L.; Zhang, C.; Fang, Q.; Chen, G. Effect of preferential exposure of anatase TiO2 {001} facets on the performance of Mn-Ce/TiO2 catalysts for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 369, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Lai, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Ding, Y.; Sun, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, Q. Distinguishing the roles of anatase TiO2 nanocrystals with {101}, {010} or {001} facets catalyzed O3/H2O2 for low-temperature NO oxidation. Mol. Catal. 2023, 549, 113513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Cao, L.; Wu, X.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Z.; Ran, R.; Si, Z.; Weng, D.; Wang, B. Protection Effect of Ammonia on CeNbTi NH3-SCR Catalyst from SO2 Poisoning. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.; Hu, Y.; Xue, J.; Wang, X.; Liao, W. SO2 poisoning and regeneration of Mn-Ce/TiO2 catalyst for low temperature NOx reduction with NH3. J. Rare Earths 2012, 30, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.; Liu, F.; Shan, W.; He, H. Improvement of Nb Doping on SO2 Resistance of VOx/CeO2 Catalyst for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 7803–7809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, T.; Lu, B.; Shen, K. Sulfur-poisoning and thermal reduction regeneration of holmium-modified Fe-Mn/TiO2 catalyst for low-temperature SCR. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2017, 45, 1356–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Asakura, K.; He, H.; Liu, Y.; Shan, W.; Shi, X.; Zhang, C. Influence of calcination temperature on iron titanate catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Catal. Today 2011, 164, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; He, H.; Yu, Y. Deactivation of a Ce/TiO2 Catalyst by SO2 in the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO by NH3. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 4426–4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Guo, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Y.; Su, F.; Gao, S.; Xu, G. Sulfur poisoning resistant mesoporous Mn-base catalyst for low-temperature SCR of NO with NH3. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2010, 95, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, Q.; Gao, T.; Yu, S.; Tan, P.; Fang, Q.; Chen, G. Promoting mechanism of SO2 resistance performance by anatase TiO2 {001} facets on Mn-Ce/TiO2 catalysts during NH3-SCR reaction. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2022, 251, 117438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Cen, W. Mechanism of Ce-Modified Birnessite-MnO2 in Promoting SO2 Poisoning Resistance for Low-Temperature NH3-SCR. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 4125–4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Lotina, A.; Iglesias-Juez, A.; Monte, M.; Ávila, P. MnO2-supported catalytic bodies for selective reduction of NO with NH3: Influence of NO2 and H2O. Mol. Catal. 2020, 491, 111004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Fang, D.; Zheng, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Tan, P.; Fang, Q.; Chen, G. An in-depth revelation of a novel facilitation mechanism of H2O on the NH3-SCR reaction of Mn-Ce/TiO2 catalyst with exposed anatase {001} facets. Fuel 2024, 366, 131382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Zhang, H.; Duan, X.; Sun, H.; Shao, G.; Wang, S. Porous Carbons: Structure-Oriented Design and Versatile Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Schill, L.; Fehrmann, R.; Riisager, A. Recent developments of core–shell structured catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with ammonia. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2023, 10, 727–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Arandiyan, H.; Scott, J.; Bagheri, A.; Dai, H.; Amal, R. Recent advances in ordered meso/macroporous metal oxides for heterogeneous catalysis: A review. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 8825–8846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, C.; Zheng, J.; Duan, A.; Jiang, G. Easy synthesis of three-dimensionally ordered macroporous La1−xKxCoO3 catalysts and their high activities for the catalytic combustion of soot. J. Catal. 2011, 282, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Xie, J.; Fang, D.; Han, D.; He, F.; Li, F.; Qi, K. Effects of surface physicochemical properties on NH3-SCR activity of MnO2 catalysts with different crystal structures. Chin. J. Catal. 2017, 38, 1925–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, G.; Zang, P.; Li, G.; Wang, Y. Insights into the structure-activity relationships of highly efficient CuCe oxides for the low temperature CO oxidation and CO-SCR. J. Energy Inst. 2022, 104, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Chen, L.; Li, Y. Ordered macroporous MOF-based materials for catalysis. Mol. Catal. 2022, 529, 112568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Mi, R.; Li, D.; Yong, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, K. Effect of initial support particle size of MnOx/TiO2 catalysts in the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 4682–4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, S.; Song, I.; Lee, H.; Cho, S.J.; Kim, D.H. Effect of pore structure of TiO2 on the SO2 poisoning over V2O5/TiO2 catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Catal. Today 2018, 303, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Huang, X.; Tang, Z.; Wang, Q. Ordered mesoporous TiO2 framework confined CeSn catalyst exhibiting excellent high activity for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 at low temperature. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Han, Y.; Hu, Y.; Shen, K.; Ding, S.; Zhang, Y. Preparation and NH3-SCR catalytic performance of CeTiO catalysts with different pore structures. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2024, 52, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, X.; Tang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, F.; Liu, H. Recent advances and perspectives in the resistance of SO2 and H2O of cerium-based catalysts for NOx selective catalytic reduction with ammonia. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 2053–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Yang, L.; Huang, B.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Sheng, Z.; Dong, F. MnOx–CeO2 @TiO2 core–shell composites for low temperature SCR of NOx. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 15161–15168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Dong, C.; Hu, X.; Zhang, J.; Xue, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X. Effect of the Fe2O3@TiO2 core-shell structure on CO catalytic oxidation and SO2 poisoning resistance. Mol. Catal. 2023, 547, 113308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Liu, J.; Huang, D.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, K.; Li, Z.; Zhu, W.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, J. Interface Engineering of a Bifunctional Cu-SSZ-13@CZO Core–Shell Catalyst for Boosting Potassium Ion and SO2 Tolerance. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 11281–11293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Zhang, T.; Dang, H.; Chen, X.; You, Y.; Schwank, J.W.; Li, J. Fe2O3@SiTi core–shell catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3: Activity improvement and HCl tolerance. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 3313–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting-ting, X.; Gang-gang, L.; Kai-hua, Z.; Xin-yan, Z.; Xin, Z.; Shao-qing, Z. Effective reduction of nitric oxide over a core–shell Cu-SAPO-34@Fe-MOR zeolite catalyst. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 638–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Lian, C.; Wang, J.; Ling, L.; Qiao, W. Carbon Nanotube@Microporous Carbon Core–Shell Nanowires for NO Oxidation: The Multiple Roles of Micropore Structure. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 12061–12070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Guo, R.; Pan, W.; Sun, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Shi, X. SCR of NOx by NH3 over MnFeOx@TiO2 catalyst with a core-shell structure: The improved K resistance. J. Energy Inst. 2019, 92, 1364–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, R. Core-shell structure effect on CeO2 and TiO2 supported WO3 for the NH3-SCR process. Mol. Catal. 2020, 485, 110822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Han, W.; Tang, Z. The water resistance enhanced strategy of Mn based SCR catalyst by construction of TiO2 shell and superhydrophobic coating. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 131334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
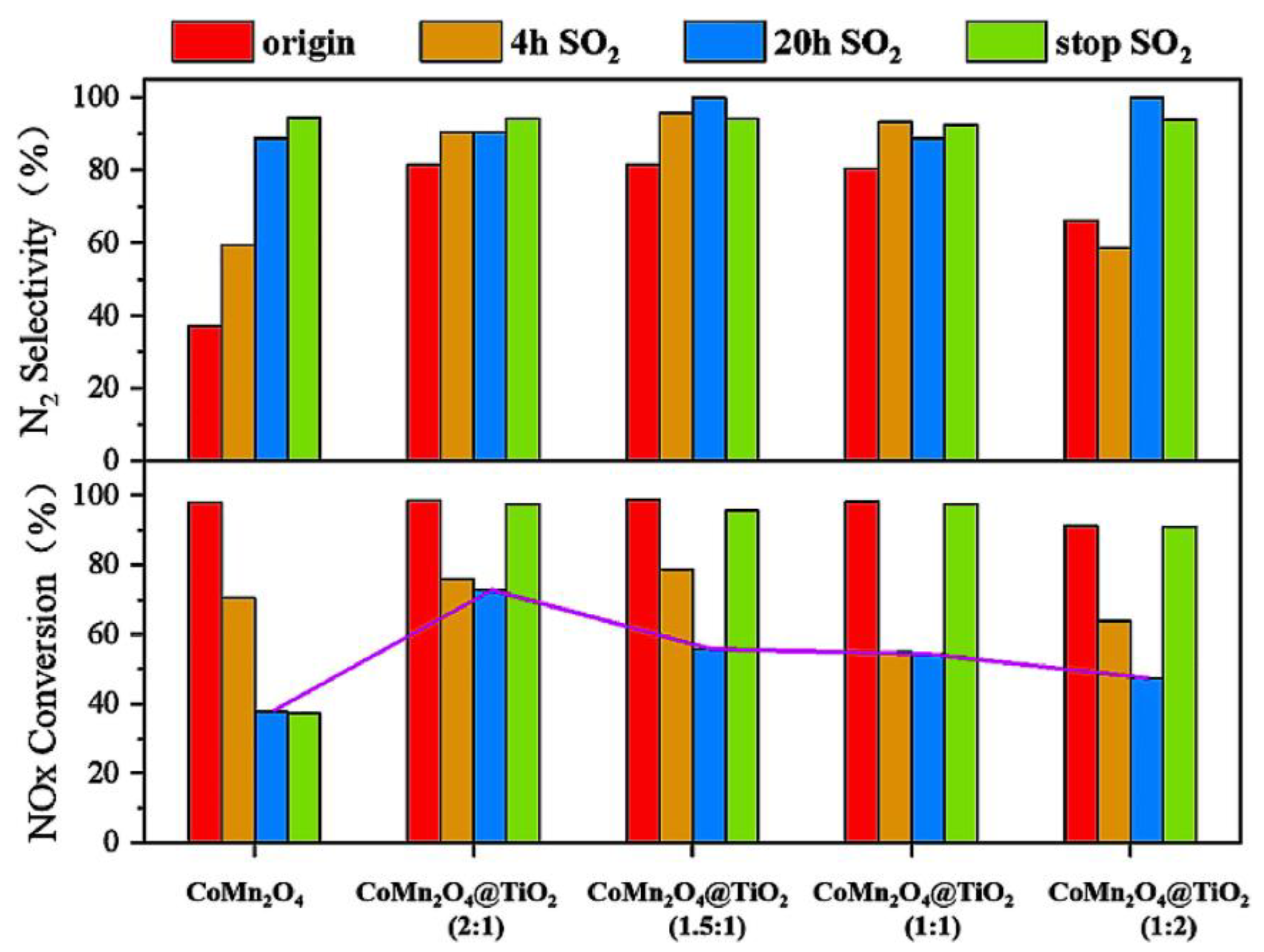
- Qi, Z.; Gao, F.; Ko, S.; Tang, X.; Yi, H.; Liu, H.; Luo, N.; Du, Y. Synthesis of novel Co(3-x)MnxO4@TiO2 core-shell catalyst for low-temperature NH3-SCR of NOx with enhanced SO2 tolerance. Chem. Phys. Impact 2022, 5, 100120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P. Effect of multi-layered nanosheets γ-Al2O3 with (110) facets on zinc deactivation resistance for Ce–Ti SCR catalyst. J. Energy Inst. 2022, 101, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Zhou, Y.; Pan, W.; Hong, J.; Zhen, W.; Jin, Q.; Ding, C.; Guo, S. Effect of preparation methods on the performance of CeO2/Al2O3 catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2013, 19, 2022–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, D.; Qin, Q.; Huang, C.; Tao, L.; Li, C.; Qiu, J.; Wang, J.; Han, X.; Gu, S.; Chen, Z.; et al. Regulating the distribution of iron active sites on γ-Fe2O3 via Mn-modified α-Fe2O3 for NH3-SCR. Appl. Catal. B Environ. Energy 2024, 349, 123869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, H.-H.; Wey, M.-Y. Study of SO2 adsorption and thermal regeneration over activated carbon-supported copper oxide catalysts. Carbon 2004, 42, 2269–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagrande, L.; Lietti, L.; Nova, I.; Forzatti, P.; Baiker, A. SCR of NO by NH3 over TiO2-supported V2O5–MoO3 catalysts: Reactivity and redox behavior. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 1999, 22, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lietti, L.; Forzatti, P.; Bregani, F. Steady-State and Transient Reactivity Study of TiO2-Supported V2O5−WO3 De-NOx Catalysts: Relevance of the Vanadium−Tungsten Interaction on the Catalytic Activity. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1996, 35, 3884–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Bare, S.R.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Banares, M.A.; Wachs, I.E. Preparation and in-Situ Spectroscopic Characterization of Molecularly Dispersed Titanium Oxide on Silica. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 5653–5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datye, A.K.; Srinivasan, S.; Allard, L.F.; Peden, C.H.F.; Brenner, J.R.; Thompson, L.T. Oxide Supported MoS2 Catalysts of Unusual Morphology. J. Catal. 1996, 158, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimova, T. New selective Mo and NiMo HDS catalysts supported on Al2O3–MgO(x) mixed oxides. Catal. Today 1998, 43, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhu, S.; Qiu, T.; Shen, S. A novel catalyst of CeO2/Al2O3 for selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3. Catal. Commun. 2009, 11, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, S.; Jung, S.M.; Avila, P.; Grange, P.; Blanco, J. Influence of NH3 and NO oxidation on the SCR reaction mechanism on copper/nickel and vanadium oxide catalysts supported on alumina and titania. Catal. Today 2002, 75, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camposeco, R.; Castillo, S.; Mejía-Centeno, I.; Navarrete, J.; Nava, N. Boosted surface acidity in TiO2 and Al2O3-TiO2 nanotubes as catalytic supports. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 356, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camposeco, R.; Castillo, S.; Mejía-Centeno, I. Performance of V2O5/NPTiO2–Al2O3-nanoparticle- and V2O5/NTiO2–Al2O3-nanotube model catalysts in the SCR–NO with NH3. Catal. Commun. 2015, 60, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Xu, M.; Lu, Y.; Yang, B.; Ji, W.; Xue, Z.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Xu, H. Simultaneous catalytic removal of NO, mercury and chlorobenzene over WCeMnOx/TiO2–ZrO2: Performance study of microscopic morphology and phase composition. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Wang, Y.; Pang, D.; Ouyang, F.; Zhang, C. SO42−–Mn–Co–Ce supported on TiO2/SiO2 with high sulfur durability for low-temperature SCR of NO with NH3. Catal. Commun. 2016, 78, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Jin, D.; Yang, H.; Lu, S.; Potter, P.M.; Du, C.; Peng, Y.; Li, X.; Yan, J. Low-Temperature Catalytic Decomposition of 130 Tetra- to Octa-PCDD/Fs Congeners over CuOX and MnOX Modified V2O5/TiO2–CNTs with the Assistance of O3. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 11424–11432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, N.M.; Kim, M.-S.; Baker, R.T.K. Carbon Nanofibers: A Unique Catalyst Support Medium. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 13108–13111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planeix, J.M.; Coustel, N.; Coq, B.; Brotons, V.; Kumbhar, P.S.; Dutartre, R.; Geneste, P.; Bernier, P.; Ajayan, P.M. Application of Carbon Nanotubes as Supports in Heterogeneous Catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 7935–7936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, M.; Ren, S.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, Q. Unveiling the effect of Al2O3 on PbCl2 resistance over Mn-Ce/AC catalyst for low-temperature NH3-SCR of NO. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2022, 140, 104535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Hou, X.; Yang, H.; Ma, Z.; Zheng, J.; Liu, F.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, Z. Promotional effect of CeOX for NO reduction over V2O5/TiO2-carbon nanotube composites. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2012, 356, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, S.; Alphin, M.S.; Sivachandiran, L.; Singh, P.; Damma, D.; Smirniotis, P.G. TiO2-carbon nanotubes composite supported MnOx-CuO catalyst for low-temperature NH3-SCR of NO: Investigation of SO2 and H2O tolerance. Fuel 2022, 307, 121886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, S.; Alphin, M.S. Low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3 over Cu modified V2O5/TiO2–carbon nanotube catalyst. React. Kinet. Mech. Cat. 2020, 129, 787–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, J.-R.; Kim, M.-J.; Lee, S.-J.; Ryu, I.-S.; Yoon, H.C.; Jeong, S.K.; Lee, K.; Jeon, S.G. The influence of CNTs addition on Mn-Ce/TiO2 catalyst for low-temperature NH3-SCR of NO. Catal. Commun. 2021, 152, 106282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Hung, P.C.; Lu, S.; Chang, M.B. Catalytic decomposition of gaseous PCDD/Fs over V2O5/TiO2-CNTs catalyst: Effect of NO and NH3 addition. Chemosphere 2016, 159, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Song, C.; Jia, S.; Tong, Z.; Tang, X.; Teng, Y. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOX with NH3 over cerium and manganese oxides supported on TiO2–graphene. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 260, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Catalyst | Mn-Ce/TiO2-NS (001) | Mn-Ce/TiO2-NP (101) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| the NO conversion | No SO2 at 180 °C | 91.2% | 68.1% | |
| 200 ppm SO2 at 180 °C | 81.7% | 50.6% | ||
| BET (m2/g) | normal conditions | 39.7 | 33.7 | |
| After SO2 poisoning | 39.6 | 23.1 | ||
| The acid situation | Brønsted acid (lmol/g) | Before SO2 poisoning | 2.058 | 2.872 |
| After SO2 poisoning | 19.243 | 23.617 | ||
| Lewis acid (lmol/g) | Before SO2 poisoning | 43.536 | 23.105 | |
| After SO2 poisoning | 42.506 | 30.845 | ||
| Catalyst | Three-Dimensionally Ordered Macroporous–Mesoporous (3DOM-m) CeTiOx | Three-Dimensionally Ordered Macroporous (3DOM) CeTiOx | Three-Dimensionally Ordered Mesoporous (3DOm) CeTiOx | Disordered Mesoporous (DM) CeTiOx |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The NO conversion (above 90%)/°C | 250–400 °C | 300–400 °C | 275–400 °C | 325–400 °C |
| Surface area A/(m2·g−1) | 107.3 | 60.9 | 57.6 | 49.3 |
| Pore volume v/(cm3·g−1) | 0.217 | 0.119 | 0.348 | 0.097 |
| Average pore size d/nm | 8.1 | 7.4 | 5.4 | 7.5 |
| Brønsted acid (μmol/g) | 104 | 43.9 | 66 | 32.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bian, X.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, W.; Yang, Y. TiO2-Supported Catalysts in Low-Temperature Selective Reduction of NOx with NH3: A Review of Recent Progress. Catalysts 2024, 14, 558. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14090558
Bian X, Wang J, Bai Y, Li Y, Wu W, Yang Y. TiO2-Supported Catalysts in Low-Temperature Selective Reduction of NOx with NH3: A Review of Recent Progress. Catalysts. 2024; 14(9):558. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14090558
Chicago/Turabian StyleBian, Xue, Jing Wang, Yuting Bai, Yanping Li, Wenyuan Wu, and Yuming Yang. 2024. "TiO2-Supported Catalysts in Low-Temperature Selective Reduction of NOx with NH3: A Review of Recent Progress" Catalysts 14, no. 9: 558. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14090558
APA StyleBian, X., Wang, J., Bai, Y., Li, Y., Wu, W., & Yang, Y. (2024). TiO2-Supported Catalysts in Low-Temperature Selective Reduction of NOx with NH3: A Review of Recent Progress. Catalysts, 14(9), 558. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14090558







