Influence of Secondary Porosity Introduction via Top-Down Methods on MOR, ZSM-5, and Y Zeolites on Their Cumene Cracking Performance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
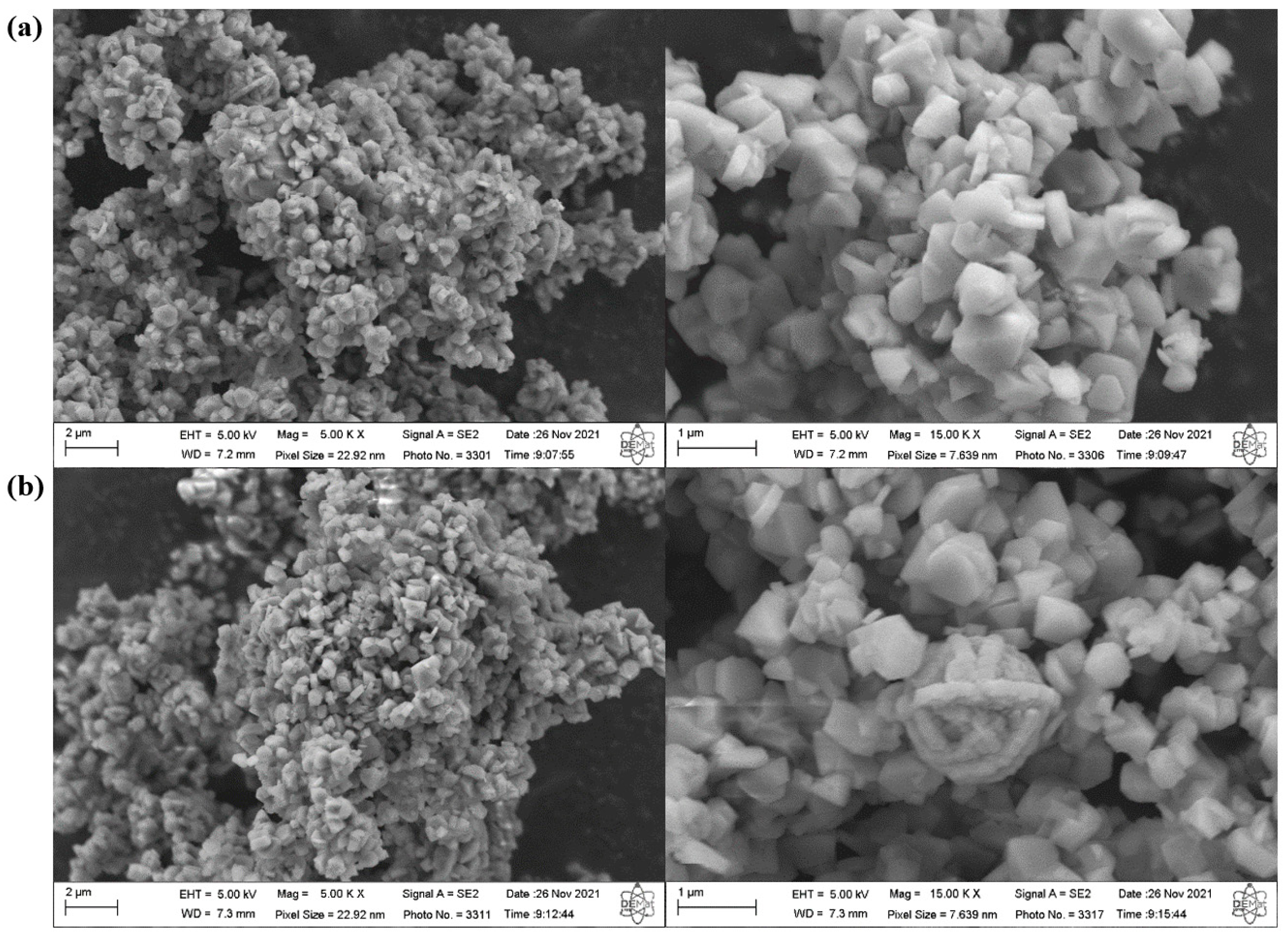
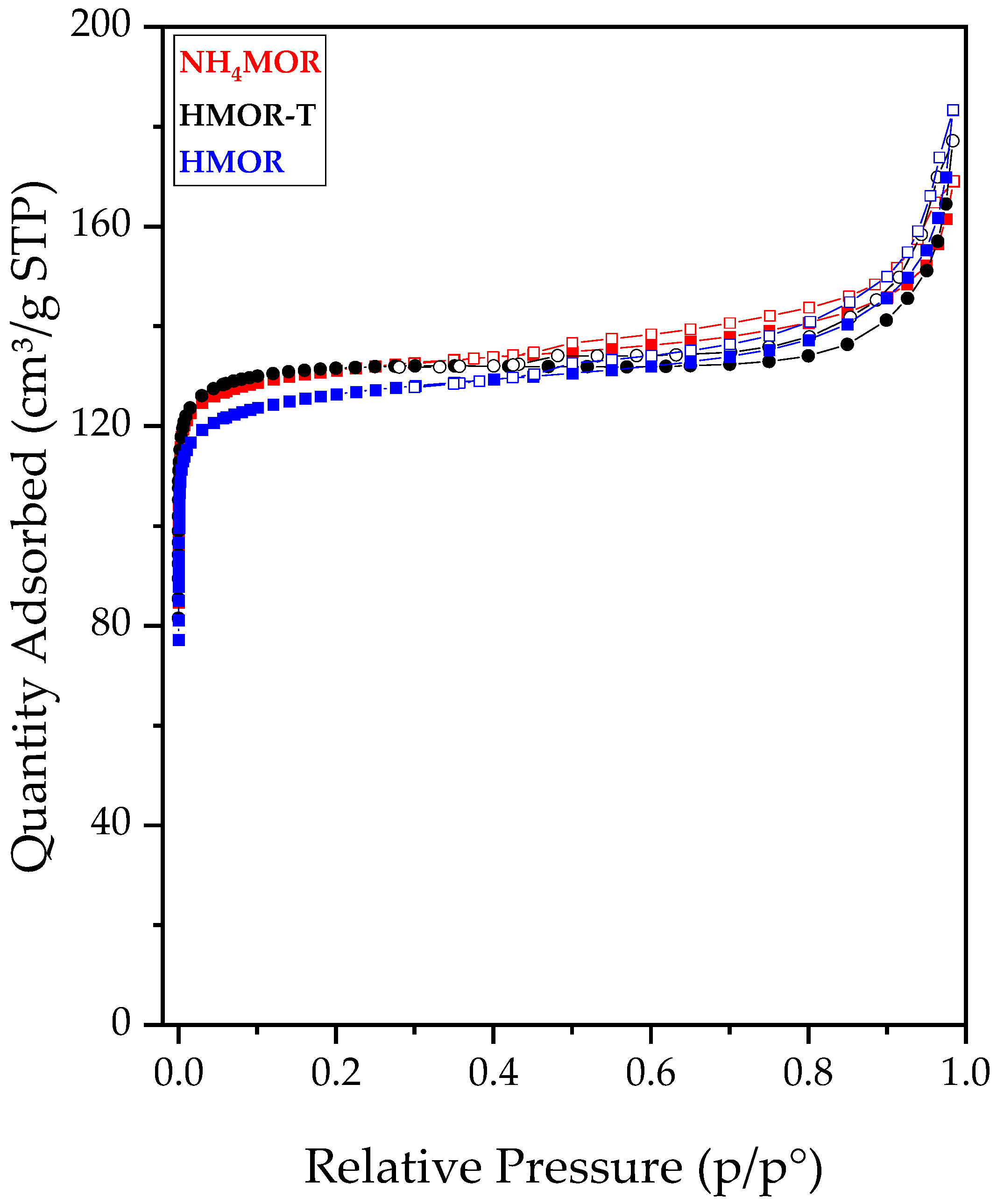
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Mordenite Zeolite with Secondary Porosity
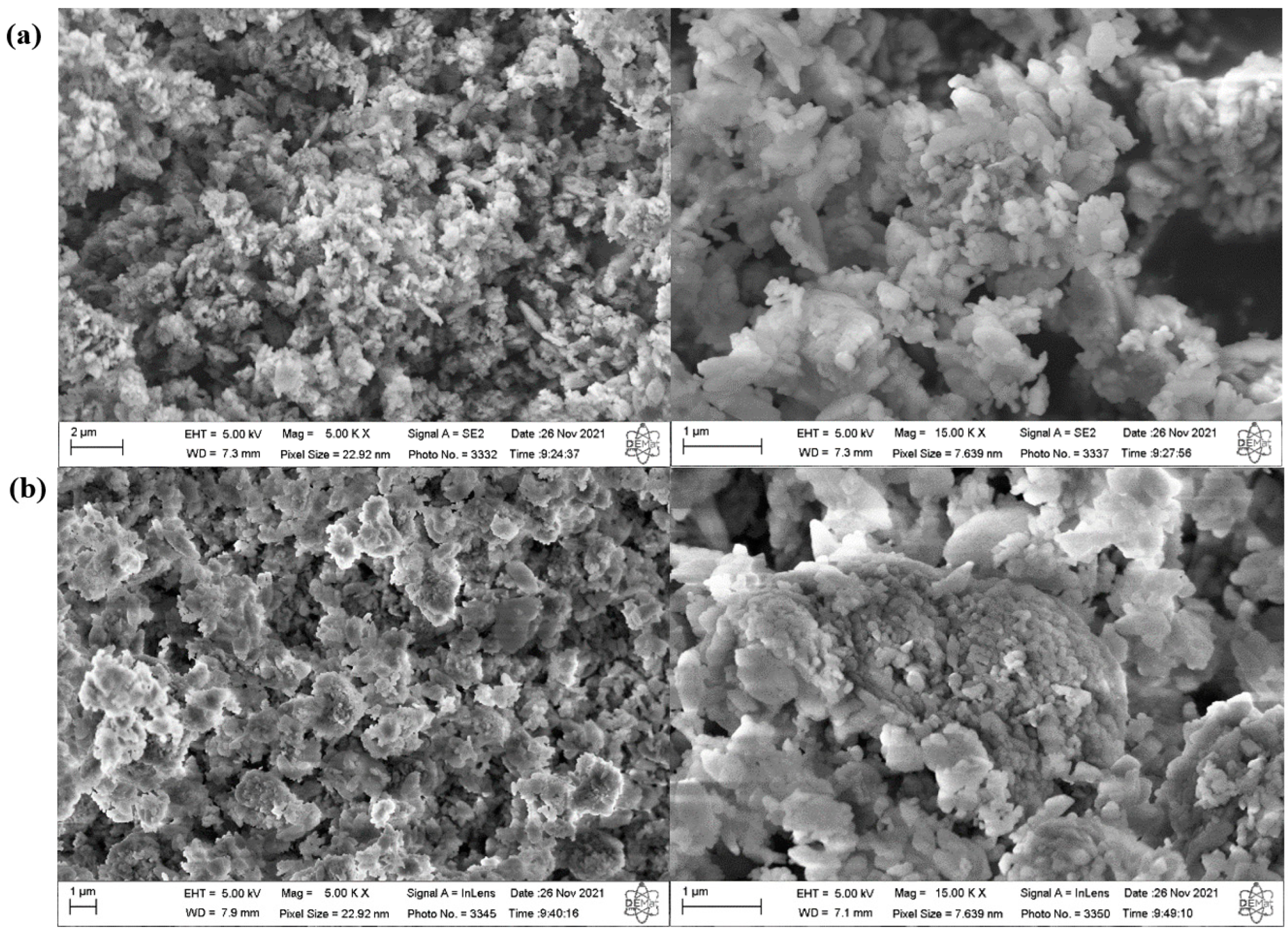
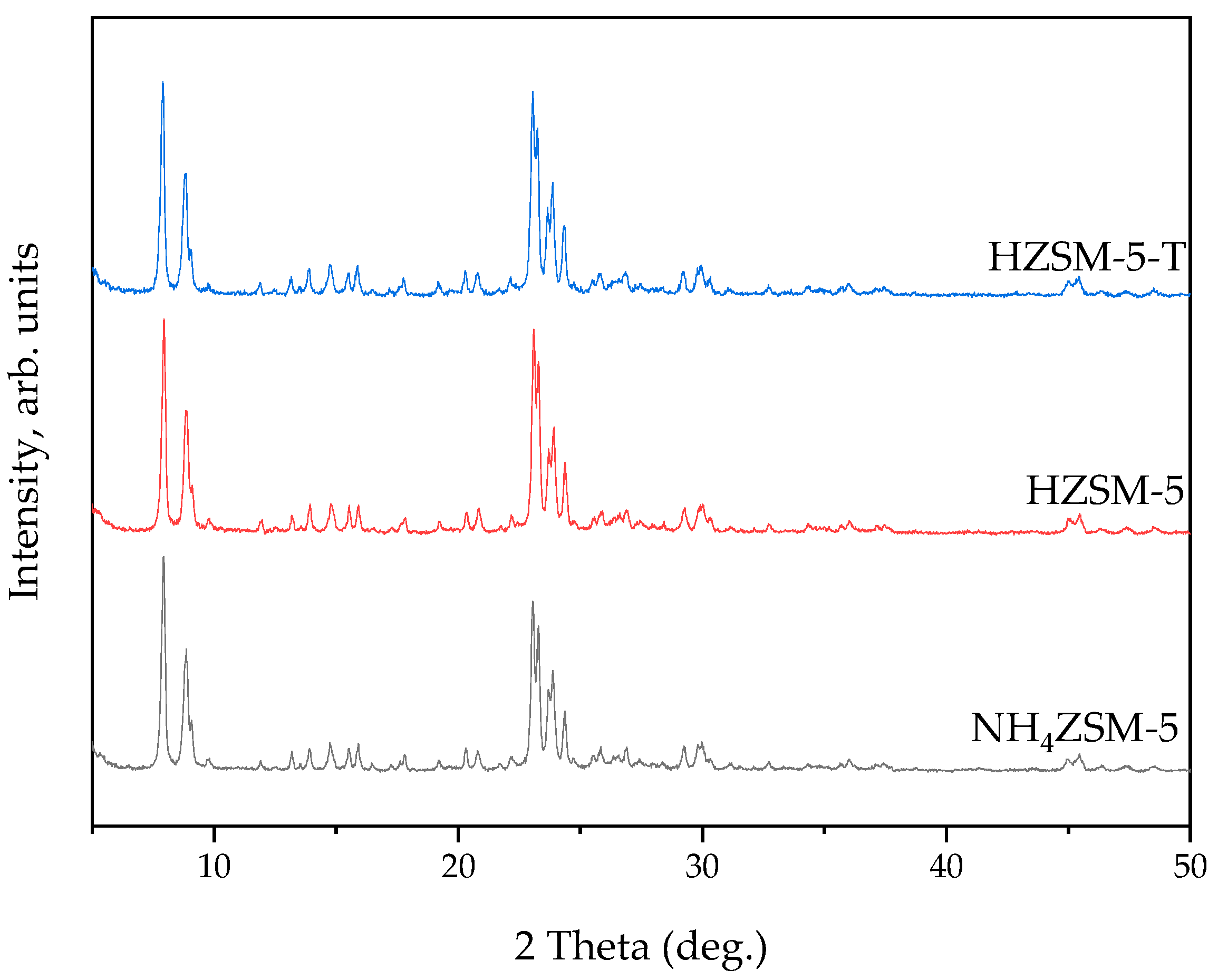
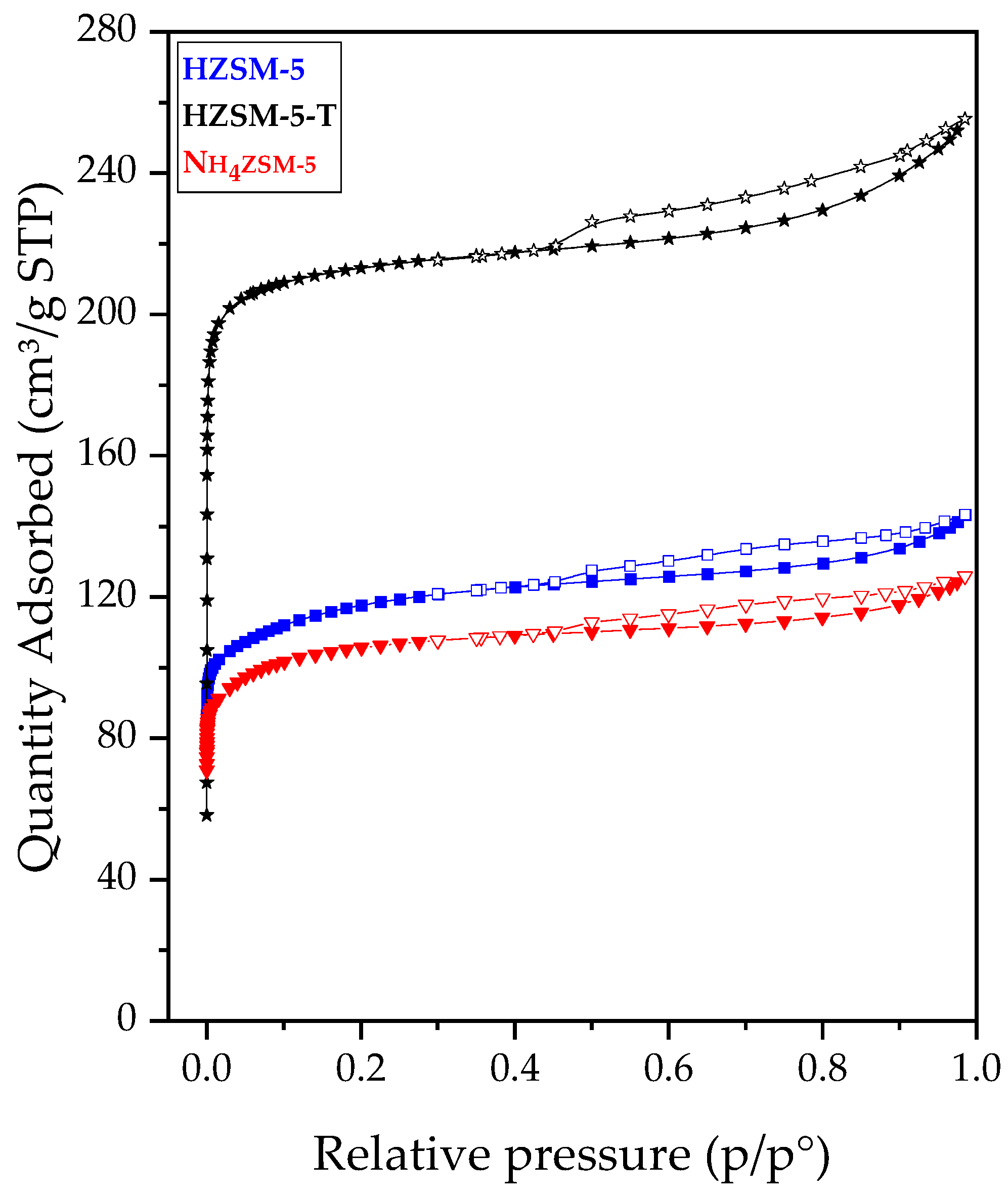
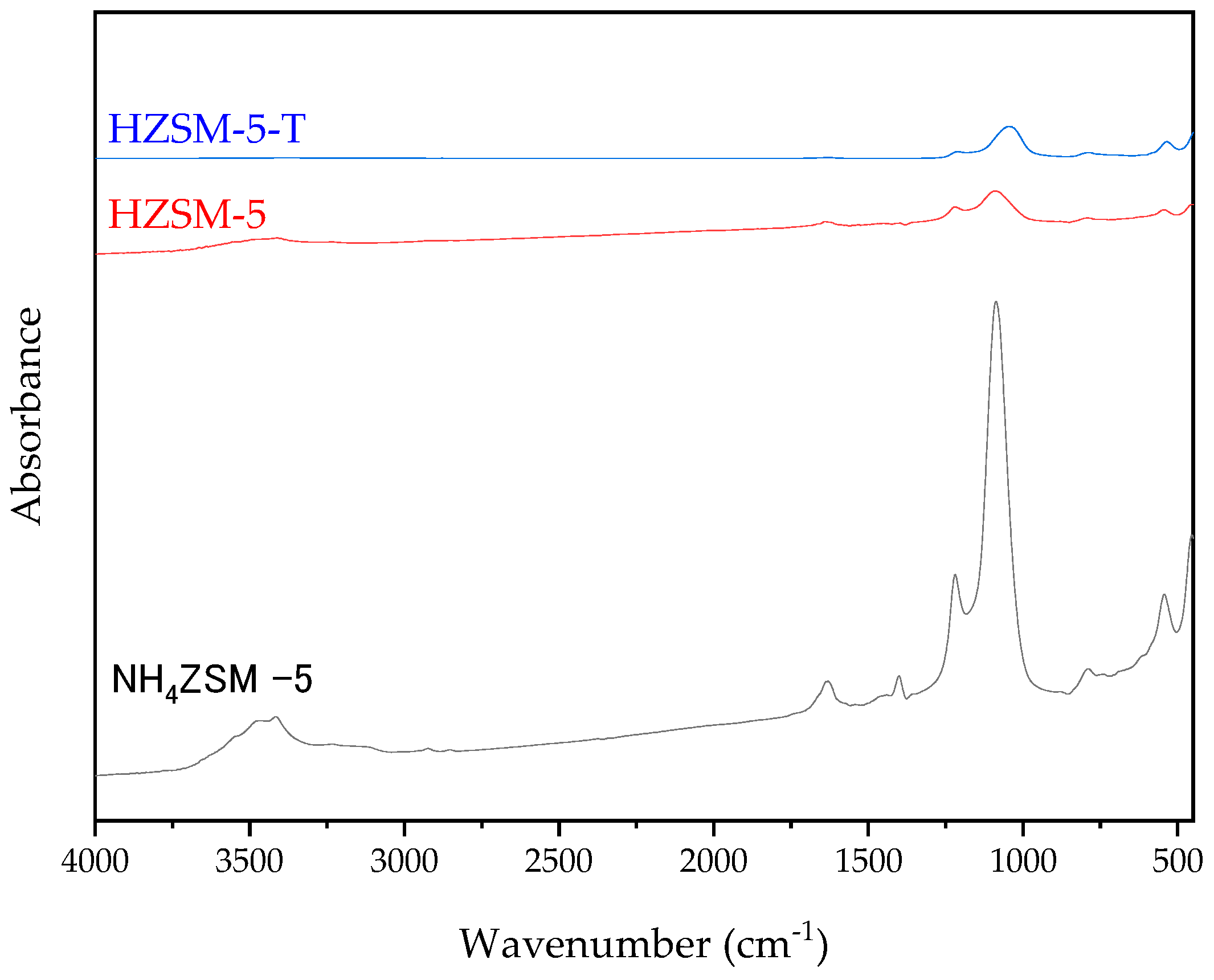
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization of ZSM-5 Zeolite with Secondary Porosity
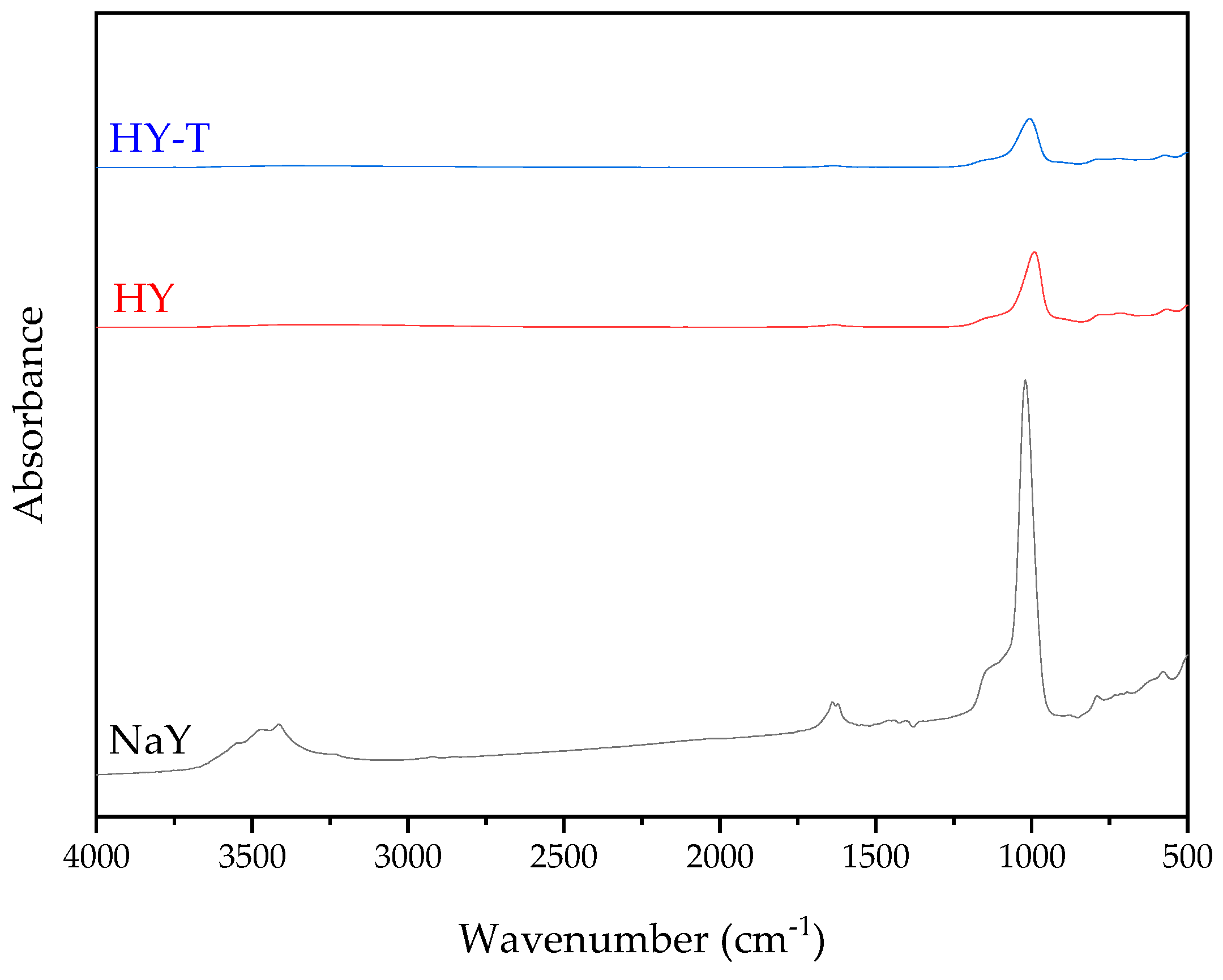
2.3. Synthesis and Characterization of Zeolite Y with Secondary Porosity
2.4. Catalytic Evaluation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of Zeolites with Secondary Porosity
3.3. Catalyst Characterizations
3.4. Catalytic Reaction
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Braga, A.A.C.; Morgon, N.H. Descrições estruturais cristalinas de zeólitos. Quim. Nova 2007, 30, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ramírez, J.; Mitchell, S.; Verboekend, D.; Milina, M.; Michels, N.L.; Krumeich, F.; Marti, N.; Erdmann, M. Expanding the Horizons of Hierarchical Zeolites: Beyond Laboratory Curiosity towards Industrial Realization. ChemCatChem 2011, 3, 1731–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, E.T.C.; Weckhuysen, B.M. Fluid catalytic cracking: Recent developments on the grand old lady of zeolite catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 7342–7370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gola, A.; Rebours, B.; Milazzo, E.; Lynch, J.; Benazzi, E.; Lacombe, S.; Delevoye, L.; Fernandez, C. Effect of leaching agent in the dealumination of stabilized Y zeolites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2000, 40, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Bordiga, S.; Prins, R.; van Bokhoven, J.A. Effect of framework Si/Al ratio and extra-framework aluminum on the catalytic activity of Y zeolite. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2007, 333, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krisnandi, Y.K.; Saragi, I.R.; Sihombing, R.; Ekananda, R.; Sari, I.P.; Griffith, B.E.; Hanna, J.V. Synthesis and characterization of crystalline NaY-Zeolite from Belitung Kaolin as catalyst for n-Hexadecane cracking. Crystals 2019, 9, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verboekend, D.; Vilé, G.; Pérez-Ramírez, J. Hierarchical y and USY zeolites designed by post-synthetic strategies. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 916–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Kanoh, H.; Kaneko, K. Developments and structures of mesopores in alkaline-treated ZSM-5 zeolites. Adsorption 2006, 12, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, C.; Corma, A. Inorganic molecular sieves: Preparation, modification and industrial application in catalytic processes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 1558–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groen, J.C.; Peffer, L.A.A.; Moulijn, J.A.; Pérez-Ramírez, J. On the introduction of intracrystalline mesoporosity in zeolites upon desilication in alkaline medium. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2004, 69, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moliner, M.; González, J.; Portilla, M.T.; Willhammar, T.; Rey, F.; Llopis, F.J.; Zou, X.; Corma, A. A New aluminosilicate molecular sieve with a system of pores between those of ZSM-5 and beta zeolite. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 9497–9505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Lakiss, L.; Gilson, J.P.; Thomas, K.; Goupil, J.M.; Fernandez, C.; Valtchev, V. Chemical equilibrium controlled etching of MFI-type zeolite and its influence on zeolite structure. acidity, and catalytic activity. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 2759–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Vidal-Moya, A.; Miguel, P.J.; Dedecek, J.; Boronat, M.; Corma, A. Selective Introduction of Acid Sites in Different Confined Positions in ZSM-5 and Its Catalytic Implications. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 7688–7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.H.; Sun, M.H.; Wang, Z.; Yang, W.; Xie, Z.; Su, B.L. Hierarchically structured zeolites: From design to application. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 11194–11294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Gao, M.; Yan, W.; Yu, J. Regulation of the Si/Al ratios and Al distributions of zeolites and their impact on properties. Chem. Sci. 2022, 14, 1935–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Yang, J.; Dong, S.; Ma, L.; Dai, Q.; Guo, J. Zeolite preparation from industrial solid waste: Current status. applications, and prospects. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 128957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, F.F.; Loiola, A.R.; Pergher, S.B.C.; Braga, T.P. Challenges, prospects and comprehensive evolution of zeolite-based materials for the catalytic conversion of glycerol: A review. Catal. Today 2025, 444, 114998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidis, S.; Kalogiannis, K.; Iliopoulou, E.F.; Lappas, A.A.; Triguero, J.M.; Navarro, M.T.; Chica, A.; Rey, F. Mesopore-modified mordenites as catalysts for catalytic pyrolysis of biomass and cracking of vacuum gasoil processes. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 1647–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silaghi, M.C.; Chizallet, C.; Raybaud, P. Challenges on molecular aspects of dealumination and desilication of zeolites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 191, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Zhang, J.; Shen, Z.; Li, T.; Luo, J.; Yang, T. Isomerization performance of n-hexane in hydrogen atmosphere over the multistage porous composite NixPy-MCM-41/MOR catalyst. J. Energy Inst. 2024, 114, 101652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benamar, M.; Sachse, A.; Miqueu, C.; Batonneau-Gener, I. Textural characterization of zeolites with complex pore systems: The case of dealuminated mordenite zeolites. Mater. Today Chem. 2024, 36, 101974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Yu, C.; Ren, K.; Yang, P. Synthesis of hierarchical mordenite by solvent-free method for dimethyl ether carbonylation reaction. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 4734–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Kanoh, H.; Abrams, L.; Kaneko, K.; Zeolites, M.-M. Mesopore-Modified Zeolites: Preparation, Characterization, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 896–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Martínez, J.; Johnson, M.; Valla, J.; Li, K.; Ying, J.Y. Mesostructured zeolite Y—High hydrothermal stability and superior FCC catalytic performance. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fan, Y.; Shi, G.; Liu, H.; Bao, X. Preparation of hydrotreating catalysts via an oxalic acid-assisted hydrothermal deposition method. J. Catal. 2008, 260, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Yu, C.; Yu, L.; Miao, S.; Zou, M.; Jin, C.; Zhang, D.; Xu, L.; Huang, S. Bridging Dealumination and Desilication for the Synthesis of Hierarchical MFI Zeolites. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 12553–12556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M.; Thommes, M.; Schwieger, W. Hierarchically-Ordered Zeolites: A Critical Assessment. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2001841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Groen, J.C.; Yue, W.; Zhou, W.; Coppens, M.O. Facile synthesis of ZSM-5 composites with hierarchical porosity. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paixão, V.; Carvalho, A.P.; Rocha, J.; Fernandes, A.; Martins, A. Modification of MOR by desilication treatments: Structural. textural and acidic characterization. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 131, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Gilson, J.P.; Valtchev, V. Mesoporous zeolites by fluoride etching. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2015, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Yang, H.; Yan, W. Catalytic cracking of n-hexane to light alkene over ZSM-5 zeolite: Influence of hierarchical porosity and acid property. Mol. Catal. 2018, 448, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groen, J.C.; Peffer, L.A.A.; Moulijn, J.A.; Pérez-Ramírez, J. Mechanism of hierarchical porosity development in MFI zeolites by desilication: The role of aluminium as a pore-directing agent. Chem. A Eur. J. 2005, 11, 4983–4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groen, J.C.; Peffer, L.A.A.; Moulijn, J.A.; Pérez-Ramírez, J. Role of intrinsic zeolite properties on mesopore formation by desilication of MFI structures. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2005, 156, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tromp, M.; Van Bokhoven, J.A.; Oostenbrink, M.T.G.; Bitter, J.H.; De Jong, K.P.; Koningsberger, D.C. Influence of the generation of mesopores on the hydroisomerization activity and selectivity of n-hexane over Pt/mordenite. J. Catal. 2000, 190, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Donk, S.; Janssen, A.H.; Bitter, J.H.; De Jong, K.P. Generation, characterization, and impact of mesopores in zeolite catalysts. Catal. Rev. Sci. Eng. 2003, 45, 297–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, M.S.; Taarning, E.; Egeblad, K.; Christensen, C.H. Catalysis with hierarchical zeolites. Catal. Today 2011, 168, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, R. Structural effects of hierarchical pores in zeolite composite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 122, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M.; Machoke, A.G.; Schwieger, W. Catalytic test reactions for the evaluation of hierarchical zeolites. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 3313–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, R.; Wu, G.; Guan, N.; Li, L. Plate-Like ZSM-5 Zeolites as Robust Catalysts for the Cracking of Hydrocarbons. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 11415–11424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloise, A.; Marino, A.; Dalena, F.; Giorgianni, G.; Migliori, M.; Frusteri, L.; Cannilla, C.; Bonura, G.; Frusteri, F.; Giordano, G. Desilicated ZSM-5 zeolite: Catalytic performances assessment in methanol to DME dehydration. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 302, 110198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, L.; Nimlos, M.R.; Robichaud, D.J.; Kim, S. Diffusion of aromatic hydrocarbons in hierarchical mesoporous H-ZSM-5 zeolite. Catal. Today 2018, 312, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Sun, S.Z.; Liu, Y.X.; Liu, X.M.; Mintova, S.; Yan, Z.F. Combined alkali dissolution and re-assembly approach toward ZSM-5 mesostructures with extended lifetime in cumene cracking. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2018, 529, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valtchev, V.; Gilson, J.-P.; Qin, Z. Method for the Preparation of Synthetic Crystalline Zeolite Materials with Enhanced Pore Volume. U.S. Patent 10,647,585, 12 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kostyniuk, A.; Bajec, D.; Prašnikar, A.; Likozar, B. Catalytic hydrocracking; hydrogenation, and isomerization reactions of model biomass tar over (W/Ni)-zeolites. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 101, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachse, A.; Grau-Atienza, A.; Jardim, E.O.; Linares, N.; Thommes, M.; García-Martínez, J. Development of Intracrystalline Mesoporosity in Zeolites through Surfactant-Templating. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 4289–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachse, A.; García-Martínez, J. Surfactant-Templating of Zeolites: From Design to Application. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 3827–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Stosic, D.; Liu, X.M.; Yan, Z.F.; Mintova, S. Strategy towards enhanced performance of zeolite catalysts: Raising effective diffusion coefficient versus reducing diffusion length. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Ma, J.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, T.; Kang, Y.; Li, R. Hierarchical structure and catalytic properties of a microspherical zeolite with intracrystalline mesopores. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 5712–5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Ma, J.; Xiao, H.; Hao, W.; Li, R. Mesoporous EU-1 zeolite with enhanced accessibility and diffusion for bulky molecular reaction. Mater. Res. Bull. 2018, 100, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah, J.; Yan, P.; Kennedy, E.; Drewery, M.; Stockenhuber, M. Novel hierarchical core-shell BEA@NanoZSM-5 zeolite for improved cracking performance for 1,3,5-triisopropylbenzene and n-hexadecane. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 328, 111399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Dai, M.; Yang, B.; Li, P.; Wang, C.; Wu, G.; Jiang, X.; Yu, S.; Li, W.; Li, X.; et al. The effect of hierarchical pore structure SAPO-34 catalyst on the diffusion and reaction behavior in MTO reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Yang, Q.H.; Zeng, S.Q.; Sang, X.Y.; Zhai, W.M.; Nie, H. Synthesis of amorphous silica-alumina with enhanced specific surface area and acidity by pH-swing method and its catalytic activity in cumene cracking. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 337, 111897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Ren, H.; Zhao, Y.; Jia, J. Mechanism and Catalytic Behavior of Quaternary Ammonium Salts in Oxidative Desulfurization. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2009, 27, 1338–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groen, J.C.; Moulijn, J.A.; Pérez-Ramírez, J. Alkaline posttreatment of MFI zeolites. From accelerated screening to scale-up. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 4193–4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groen, J.C.; Jansen, J.C.; Moulijn, J.A.; Pérez-Ramírez, J. Optimal aluminum-assisted mesoporosity development in MFI zeolites by desilication. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 13062–13065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowska, K.; Wach, A.; Olejniczak, Z.; Kuśtrowski, P.; Datka, J. Hierarchic zeolites: Zeolite ZSM-5 desilicated with NaOH and NaOH/tetrabutylamine hydroxide. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 167, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, R.B.; Neto, M.M.S.; Oliveira, D.S.; Santos, A.G.D.; Souza, L.D.; Caldeira, V.P.S. Obtainment of hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolites by alkaline treatment for the polyethylene catalytic cracking. Adv. Powder Technol. 2021, 32, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ramírez, J.; Abelló, S.; Bonilla, A.; Groen, J.C. Tailored mesoporosity development in zeolite crystals by partial detemplation and desilication. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Groen, J.C.; Yue, W.; Zhou, W.; Coppens, M.O. Single-template synthesis of zeolite ZSM-5 composites with tunable mesoporosity. Chem. Commun. 2007, 43, 4653–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, M.; Shinomiya, S.Y.; Tateno, J.; Nara, Y.; Kikuchi, E.; Matsukata, M. Formation of uniform mesopores in ZSM-5 zeolite through treatment in alkaline solution. Chem. Lett. 2000, 29, 882–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessau, R.M.; Valyocsik, E.W.; Goeke, N.H. Aluminum zoning in ZSM-5 as revealed by selective silica removal. Zeolites 1992, 12, 776–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verboekend, D.; Pérez-Ramírez, J. Desilication mechanism revisited: Highly mesoporous all-silica zeolites enabled through pore-directing agents. Chem. A Eur. J. 2011, 17, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafra, L.; Vidal-Moya, J.A.; Blasco, T. Structural characterization of zeolites by advanced solid state NMR spectroscopic methods. In Annual Reports on NMR Spectroscopy; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanov, A.G. Basics of Solid-State NMR for Application in Zeolite Science: Material and Reaction Characterization; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groen, J.C.; Peffer, L.A.A.; Moulijn, J.A.; Pérez-Ramírez, J. Mesoporosity development in ZSM-5 zeolite upon optimized desilication conditions in alkaline medium. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2004, 241, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatamian, M.; Irani, M. Preparation and characterization of nanosized ZSM-5 zeolite using kaolin and investigation of kaolin content. crystallization time and temperature changes on the size and crystallinity of products. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2009, 6, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Tu, C.; Zheng, J.; Luo, Y.; Da, Z. Influence of Acid Wash on the Structural and Catalytic Properties of the Hierarchical Zeolite Y. ChemistrySelect 2016, 1, 934–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallezot, P.; Beaumont, R.; Barthomeuf, D. Crystal structure of a dealuminated Y-type zeolite. J. Phys. Chem. 1974, 78, 1550–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolatto, L.B. Desenvolvimento de Materiais Estruturados Hierarquicamente a Partir de Zeólitas do tipo Y. Riella, H.G., Ed.; BDTD: Florianópolis, Brazil, 2019; Available online: https://bdtd.ibict.br/vufind/Record/UFSC_016d6ecfe930b1890a8ea2b3dd861d1d (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- Paulista, A.P.F.; Barbosa, F.F.; Júnior, M.A.D.N.; Cavalcanti, W.E.C.; de O, J.; Torres, M.M.; Pergher, S.B.C.; Braga, T.P. Synthesis of carbon nanotubes via CCVD of ethylbenzene over SrFe12O19/SiO2 oxide and their application for photodegradation of the remazol red dye. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 323, 129559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Samples | FRX (%) | DRX | NMR | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Na2O | C (%) | Si/Al | SAR | |
| NH4MOR | 87.1 | 8.7 | 1.3 | 100 | 8.2 | 16.5 |
| HMOR | 87.3 | 8.6 | 1.3 | 108 | 9.4 | 18.8 |
| HMOR-T | 89.1 | 7.1 | 1.3 | 82.2 | 11.4 | 22.8 |
| Samples | BET | t-Plot Harkins-Jura-de-Boer | Gurvich VTP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBET (m2/g) | Vo (cm3/g) | Vm (cm3/g) | St (m2/g) | Vt (cm3/g) | |
| NH4MOR | 529 | 0.169 | 0.081 | 81 | 0.250 |
| HMOR | 536 | 0.164 | 0.090 | 103 | 0.254 |
| HMOR-T | 507 | 0.159 | 0.104 | 89 | 0.263 |
| Samples | Pyridine Acidity in IR (µmol·g−1) 150 °C | Pyridine Acidity in IR (µmol·g−1) 450 °C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sites of Brønsted [HPy] | Lewis Sites [LPy] | Sites of Brønsted [HPy] | Lewis Sites [LPy] | |
| HMOR | 833 | 143.3 | 130 | 158.5 |
| HMOR-T | 708 | 135.3 | 201 | 78.5 |
| Samples | FRX (%) | DRX | NMR | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Na2O | C (%) | Si/Al | SAR | |
| NH4ZSM-5 | 93.1 | 6.9 | 1.10 | 100 | 14.4 | 28.8 |
| HZSM-5 | 91.7 | 8.3 | 1.40 | 105.9 | 21.1 | 42.1 |
| HZSM-5-T | 92.9 | 7.1 | 1.20 | 103 | 24.2 | 48.4 |
| Samples | BET | t-Plot Harkins-Jura-de-Boer | Gurvich VTP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBET (m2/g) | Vo (cm3/g) | Vm (cm3/g) | St (m2/g) | Vt (cm3/g) | |
| NH4ZSM-5 | 406 | 0.096 | 0.070 | 165 | 0.166 |
| HZSM-5 | 446 | 0.113 | 0.106 | 165 | 0.219 |
| HZSM-5-T | 858 | 0.271 | 0.119 | 144 | 0.390 |
| Samples | Pyridine Acidity in IR (µmol·g−1) 150 °C | Pyridine Acidity in IR (µmol·g−1) 450 °C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sites of Brønsted [HPy] | Lewis Sites [LPy] | Sites of Brønsted [HPy] | Lewis Sites [LPy] | |
| HZSM-5 | 813.0 | 156.9 | 348.1 | 79.1 |
| HZSM-5-T | 892.7 | 168.7 | 411.7 | 104.9 |
| Samples | FRX (%) | DRX | NMR | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Na2O | C (%) | Si/Al | SAR | |
| NaY | 67.7 | 21.1 | 8.8 | 100 | 2.7 | 5.3 |
| HY | 71.9 | 22.9 | 2.9 | 90.2 | 3.7 | 7.5 |
| HY-T | 73.7 | 20.8 | 2.9 | 108 | 3.4 | 6.8 |
| Samples | BET | t-Plot Harkins-Jura-de-Boer | Gurvich VTP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBET (m2/g) | Vo (cm3/g) | Vm (cm3/g) | St (m2/g) | Vt (cm3/g) | |
| NaY | 796 | 0.259 | 0.053 | 100 | 0.312 |
| HY | 524 | 0.163 | 0.055 | 94 | 0.218 |
| HY-T | 858 | 0.266 | 0.124 | 158 | 0.390 |
| Samples | Pyridine Acidity in IR (µmol·g−1) 150 °C | Pyridine Acidity in IR (µmol·g−1) 450 °C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sites of Brønsted [HPy] | Lewis Sites [LPy] | Sites of Brønsted [HPy] | Lewis Sites [LPy] | |
| HY | 614.6 | 269.3 | 7.9 | 3.3 |
| HY-T | 625.4 | 501.1 | no acidity activity considerated | 5.4 |
| Materials | Meaning |
|---|---|
| NH4MOR | Commercial Mordenite Zeolite |
| HMOR | Calcined Commercial Mordenite Zeolite |
| HMOR-T | Commercial Mordenite Zeolite after treatment, cation exchange and calcination |
| NH4ZSM-5 | Commercial ZSM-5 Zeolite |
| HZSM-5 | Calcined Commercial ZSM-5 zeolite |
| HZSM-5-T | Commercial ZSM-5 zeolite after treatment, cation exchange and calcination |
| NaY | Commercial Zeolite Y |
| HY | Zeolite Y after cation exchange and calcination |
| HY-T | Commercial Zeolite Y after treatment, cation exchange and calcination |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Souza, J.C.; Mello, M.I.S.; Barbosa, F.F.; Souza, I.M.S.; Sachse, A.; Pergher, S.B.C. Influence of Secondary Porosity Introduction via Top-Down Methods on MOR, ZSM-5, and Y Zeolites on Their Cumene Cracking Performance. Catalysts 2025, 15, 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15020146
Souza JC, Mello MIS, Barbosa FF, Souza IMS, Sachse A, Pergher SBC. Influence of Secondary Porosity Introduction via Top-Down Methods on MOR, ZSM-5, and Y Zeolites on Their Cumene Cracking Performance. Catalysts. 2025; 15(2):146. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15020146
Chicago/Turabian StyleSouza, Josué C., Mariele I. S. Mello, Felipe F. Barbosa, Iane M. S. Souza, Alexander Sachse, and Sibele B. C. Pergher. 2025. "Influence of Secondary Porosity Introduction via Top-Down Methods on MOR, ZSM-5, and Y Zeolites on Their Cumene Cracking Performance" Catalysts 15, no. 2: 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15020146
APA StyleSouza, J. C., Mello, M. I. S., Barbosa, F. F., Souza, I. M. S., Sachse, A., & Pergher, S. B. C. (2025). Influence of Secondary Porosity Introduction via Top-Down Methods on MOR, ZSM-5, and Y Zeolites on Their Cumene Cracking Performance. Catalysts, 15(2), 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15020146







