Abstract
Peroxymonosulfate-based advanced oxidation processes (PMS-AOPs) relying on non-radical pathways offer advantages such as resistance to interference, efficient oxidant utilization, and selective degradation of pollutants. In this study, an Fe, N co-doped activator (Fe-N-C1.5) was synthesized using a simple mixed solvent pyrolysis method. The Fe-N-C1.5 exhibited excellent PMS activation activity. A total of 100% of paracetamol (PCT, 10 ppm) was degraded in the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system in 7 min. Furthermore, this oxidation system maintained effective PCT removal even in the presence of background ions and in real water matrices. In addition, the leached Fe concentration after 60 min was only 0.084 mg/L, and 94% of PCT could still be removed during the fourth cyclic use of the catalyst. Quenching experiments, electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR), and electrochemical analysis revealed that the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS/PCT system predominantly relies on non-radical pathways, including singlet oxygen (1O2) and catalyst-interface-mediated electron transfer process (ETP). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis and KSCN toxicity experiment confirmed that the graphitic N, carbonyl (C=O), and Fe-Nx were the main PMS activation sites. This study provides an understanding of degradation mechanisms of the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS/PCT system and offers insights into the design of iron–carbon composite catalysts that carry out non-radical PMS activation.
1. Introduction
Paracetamol (PCT) is a widely used analgesic and antipyretic owing to its safety, tolerability, and minimal side effects [1,2]. However, approximately 58–68% of ingested PCT is not absorbed and utilized by the human body [3,4] and is excreted directly into the municipal wastewater treatment system [5]. Due to its low biodegradability, traditional biological treatment processes do not efficiently treat PCT [3]. According to reports, in municipal wastewater treatment plants of various regions, the PCT concentrations remained between 0.27 and 300 μg/L [6,7,8]. If PCT is not adequately treated, its release into the environment will present toxicological risks to aquatic organisms, including hepatotoxicity, genotoxicity, and endocrine disruption [8]. Furthermore, PCT bioaccumulation, through the food chain, poses a threat to human health. Therefore, developing a rapid and effective PCT degradation treatment strategy is urgent.
Peroxymonosulfate-based advanced oxidation processes (PMS-AOPs) are a promising remediation technology for PCT degradation, due to their rapid generation of various reactive oxygen species (ROS) with high oxidation-reduction potentials [9,10,11]. Radical-based PMS-AOPs show significant cost-effectiveness and high efficiency, as they do not require additional energy input while enabling the rapid generation of strongly oxidizing radicals [12]. However, its application is limited by natural organic matter, background ions, and pH [13]. In addition, the reaction of halide ions with free radicals results in the formation of halogen radicals, which further react with organics to form more toxic organohalides [14]. In contrast, the non-radical-based PMS-AOPs exhibit a broader pH operational range, higher selectivity for pollutants, more improved oxidant utilization efficiency, and more sustained degradation capacity [15]. They can be carried out on the catalyst surface to directly oxidize organics with electron-rich groups without additional oxidant consumption and radical generation [16,17]. Moreover, non-radical-based PMS-AOPs hinder the formation of halogen free radicals, minimizing the production of halogenated disinfection by-products. Therefore, developing suitable catalysts that efficiently activate PMS for selectively degrading organic pollutants through non-radical pathway is crucial for facilitating the efficient PCT removal by the PMS-AOPs system.
Most carbon materials, such as biochar [18], carbon nanotubes [19], and graphene oxide [20], exhibit poor PMS activation activities and stabilities due to their low degree of graphitization and high impedance [21]. In contrast, metal materials exhibit better activation capacity and stability [22]; however, metal ion leaching during the reaction process poses an additional environmental threat [23]. To improve the stability and activation ability of materials and reduce metal leaching, researchers have proposed metal composite materials, which incorporate both metal and non-metal elements into carbon materials [24,25]. On one hand, the doping of metal and non-metal elements can break the structural inertness of the carbon network, enhancing the electron transfer capacity of materials while also inducing the formation of structural defects that increase the number of active sites [26]. For instance, doping carbon materials with electron-rich nitrogen can create Lewis basic sites, which tend to bind with transition metal atoms, forming strong M-Nx coordination sites with high catalytic activity (M, representing Lewis acids) [27,28]. On the other hand, carbon materials disperse and anchor metal atoms, preventing particle aggregation, avoiding the loss of metal active sites, and reducing metal leaching [24].
Iron is an excellent candidate for the preparation of metal composites due to its abundant natural reserves and environmental friendliness [29,30]. A large number of Fe/C composite catalysts have been designed and applied to AOPs. Wu et al. developed a carbon-dot-modified iron-based MOF material as persulfate (PS) activator for PCT degradation. In total, 100% of PCT was removed in the iron-based MOF/PS system in 20 min [31]. Zhu et al. synthesized an Fe-N-C catalyst by anchoring Fe onto a covalent triazine framework. The Fe-N-C exhibited efficient PMS activation, and the Fe-N-C/PMS system achieved 100% PCT degradation across a broad pH range (2.6–10.67) [32]. However, iron–carbon composite materials reported in previous studies still face several challenges on their practical applications. Zhuo et al. developed a magnetic biochar catalyst with dual active sites of Fe3C and Fe4N, but the synthesis process required high energy consumption [33]. Huang et al. designed an Fe(BDC)(DMF,F)-OA/PS system that exhibited significant iron leaching (up to 1.51 mg/L) after 120 min of reaction [34]. Furthermore, due to limitations in quencher selection and experimental design, the mechanistic understanding of high-valent metal oxides, singlet oxygen, and electron transfer pathways remains controversial in previous studies [24,35]. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct further research for enhancing the understanding of the oxidation mechanisms in Fe/C composite/persulfate systems.
In this study, an Fe-N-C catalyst was synthesized through a simple and low-energy mixed-solvent pyrolysis method to construct a non-radical-dominated PMS oxidation system for PCT degradation. By regulating the Fe/C mass ratio in the precursor, the catalytic performance of Fe-N-C was optimized while achieving extremely low Fe leaching. This work systematically explored the operational conditions affecting the performance of the Fe-N-C/PMS system and identified the main reactive species responsible for PCT degradation and the active sites for PMS activation in the Fe-N-C/PMS system through quenching experiments, EPR, electrochemical tests, XPS analysis, and KSCN toxicity experiment. Additionally, this work proposed possible degradation pathways for PCT and evaluated the toxicity of the intermediates. In conclusion, this study provides a comprehensive understanding of the PCT degradation mechanism in the Fe-N-C/PMS system and presents a new approach for developing efficient and stable Fe-N-C catalysts.
2. Result and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Materials
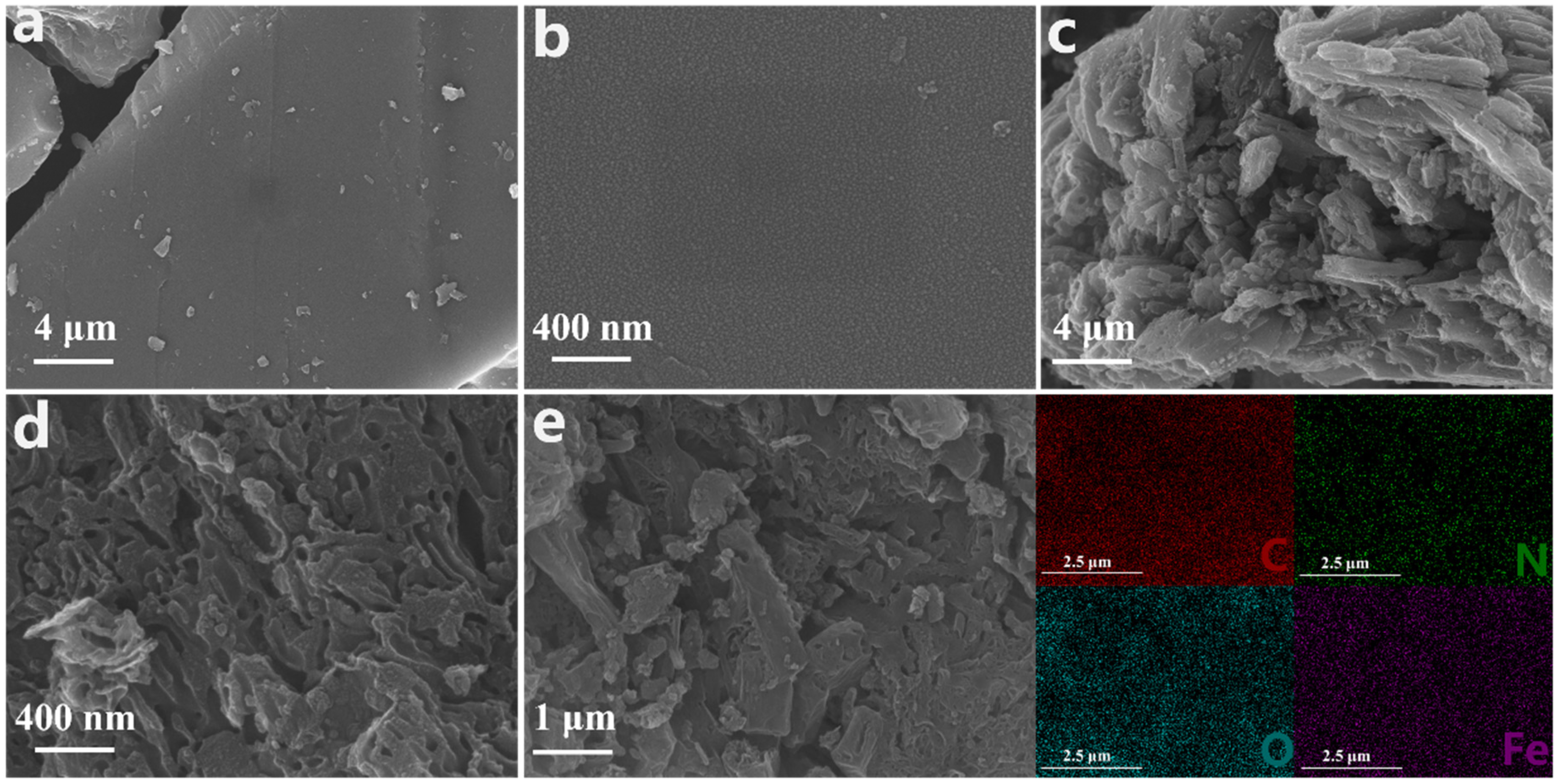
The Fe-N-Cx microstructure was observed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Fe-N-C6, with the lowest Fe:C mass ratio, exhibited a unique carbon block structure with a smooth and dense surface (Figure 1a,b). As the Fe:C mass ratio increased to 2:3, the carbon block surface gradually became rough, fragmented, and more porous (Figure 1c,d), indicating that the Fe:C mass ratio in the precursor had an impact on the catalyst structure. Fe may promote the graphitization of carbon material during pyrolysis [36], thereby affecting the microstructure of the carbon material. Additionally, the rough surface morphology facilitates exposure of additional active sites and enhances reactant accessibility, thereby significantly improving catalytic activity [37]. Interestingly, granular protrusions were observed on the Fe-N-C0.25 surface (Figure S1), which could be attributed to the formation of encapsulated iron oxides from the excess Fe [38]. The energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) elemental mapping images (Figure 1e) of Fe-N-C1.5 showed uniform dispersion of C, N, O, and Fe on the catalyst’s surface.
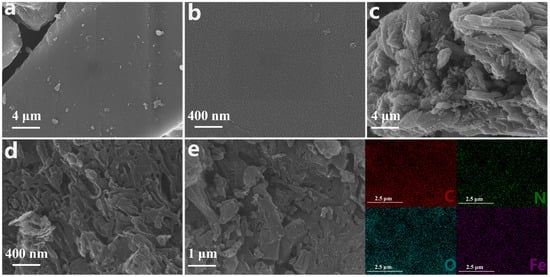
Figure 1.
SEM images of (a,b) Fe-N-C6 and (c,d) Fe-N-C1.5 at different scales; (e) EDS images of Fe-N-C1.5.
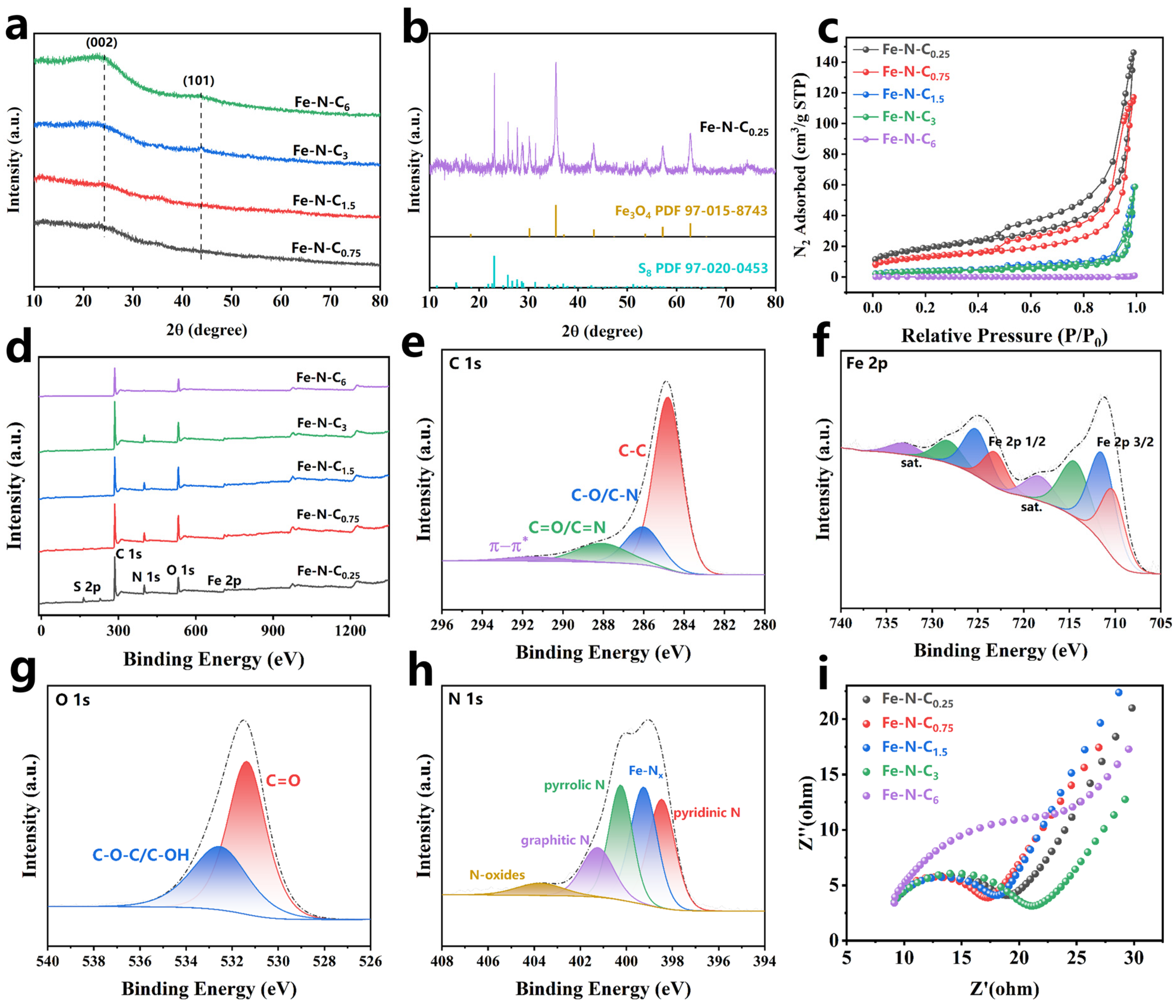
The crystalline phase composition of the catalyst was obtained using X-ray diffraction (XRD). No characteristic peaks for Fe or its oxides were observed for Fe-N-C0.75, Fe-N-C1.5, Fe-N-C3, and Fe-N-C6. This may be due to the low Fe-doping level, which coordinated with C and N during pyrolysis, resulting in its high dispersion within the material [31]. The broad peak at 24° was from the 002 plane, and the weak diffraction peak at 43.8° was from the 101 plane of graphite (Figure 2a), indicating that the synthesized carbon structure was amorphous [39]. In contrast, the higher Fe content in Fe-N-C0.25 led to the formation of iron oxides (Fe3O4, PDF 97-015-8743) during pyrolysis. Additionally, the XRD pattern of Fe-N-C0.25 (Figure 2b) showed characteristic peaks for elemental sulfur (S8, PDF 97-020-0453). The presence of sulfur could be explained by the decomposition of excess sulfate ions into sulfur dioxide (SO2) at high temperatures, which were then reduced to elemental sulfur by the carbon [40].
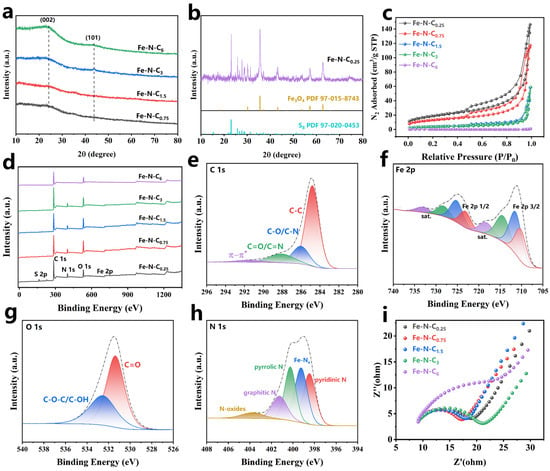
Figure 2.
(a,b) XRD patterns, (c) N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms, (d) XPS survey spectra of Fe-N-Cx; XPS C 1s (e), Fe 2p (f), O 1s (g), and N 1s (h) of Fe-N-C1.5; (i) The Nyquist plots of Fe-N-Cx.
The N2 adsorption–desorption isotherm of the prepared catalysts (Figure 2c) exhibited typical type-IV isotherms with H3-type hysteresis loops, indicating the presence of mesoporous structures (2–50 nm) in the catalyst [41]. The Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) curve (Figure S2) revealed that the prepared catalysts pore structures were primarily composed of mesopores and macropores, with most of the pores having a diameter of around 50 nm. Furthermore, as the Fe:C mass ratio in the precursor increased, the pyrolyzed catalyst had a larger Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area and smaller average pore diameter (Table S2), suggesting that Fe promoted porous structure formation in the material during pyrolysis. In addition, Fe-N-C6 did not exhibit a type-IV isotherm, which was attributed to its low Fe-doping level, resulting in a smooth and flat structure with a smaller specific surface area. The specific surface area has a significant impact on the catalytic activity. Figure S3a shows the relationship between the BET surface area of catalyst and degradation rate constant (Kobs). Compared to Fe-N-C3 and Fe-N-C6, Fe-N-C0.25 and Fe-N-C0.75, which had larger surface areas, exhibited higher Kobs values. This might be attributed to the larger surface area providing more active sites that facilitate the adsorption of PMS and pollutants, thereby enhancing catalytic performance [39].
The Fe content in the catalyst was determined by ICP-OES (Table S3). The Fe loading increased with the Fe:C mass ratio in the precursor, but when the Fe:C mass ratio exceeded 2:3, the Fe loading did not significantly increase. High Fe loading in the iron–carbon composite catalyst provided additional active sites. Figure S3b illustrates an approximately positive correlation between Fe content and Kobs, which might be due to the higher Fe content leading to the formation of more Fe active sites after pyrolysis. These active sites played a crucial role in PMS activation.
High-resolution X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was used to analyze the surface elements and chemical composition of the catalyst. XPS analysis (Figure 2d) revealed that the catalyst surface primarily contains C, N, O, and Fe, which was consistent with the EDS analysis results. Table S4 presents the surface composition results and their relative contents for the different catalysts. The C 1s spectrum (Figure 2e) was deconvoluted into four peaks, C-C bonds (284.8 eV), C-O bonds (286.02 eV), C=O bonds (288.07 eV), and π-π* shake-up satellite (291.44 eV) [17]. Compared to Fe-N-C6, catalysts with higher Fe content (Fe-N-C0.75 and Fe-N-C1.5) showed a higher proportion of C-O and C=O bonds. This result showed that Fe promoted carbon matrix reconstruction during pyrolysis, leading to the formation of more oxygen-containing functional groups [42]. Previous studies have demonstrated that C=O is the active center for PMS activation on catalysts to produce 1O2, with higher C=O content significantly enhancing catalytic activation performance [43].
The Fe 2p spectrum (Figure 2f) could be deconvoluted into Fe2+ (710.21 eV, 723.13 eV) and Fe3+ (711.39 eV, 725.19 eV) [32]. Additionally, four satellite peaks were observed: two corresponding to Fe2+ at 714.36 eV and 728.23 eV, and two corresponding to Fe3+ at 718.27 eV and 733.04 eV. The O 1s spectrum (Figure 2g) could be deconvoluted into C=O (531.37 eV) and C-O-C/C-OH (532.54 eV). Notably, no discernible peaks corresponding to Fe-O bonds (~529.5–530.5 eV) were observed in the O 1s spectrum, suggesting negligible contributions from iron oxides (Fe-O) or iron–carbonate (Fe-O-C) species. This absence aligns with the catalyst preparation protocol, which includes an acid-washing step to remove unstable metallic aggregates, thereby significantly reducing oxygenated iron phases. Previous studies on Fe/C composites have similarly reported that acid-treated catalysts predominantly exhibit oxygen functionalities associated with carbon matrices (C=O and C-O) rather than Fe-bonded oxygen [44].
The N 1s spectrum was deconvoluted into five peaks (Figure 2h), corresponding to pyridinic N (398.47 eV), Fe-Nx (399.25 eV), pyrrolic N (400.25 eV), graphite N (401.25 eV), and N-oxide (403.75 eV) [31,32]. As shown in Table S4, the proportions of Fe-Nx on the surface of the catalyst gradually increased as the Fe:C mass ratio increased, while the proportions of Fe-Nx decreased when the Fe:C mass ratio exceeded 0.75. It was reported that the Fe-Nx site was favorable to alter the electronic distribution on the catalyst surface, enhancing electron transfer capability [31]. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was used to analyze the interfacial charge transfer resistance of the catalysts. The Nyquist plot (Figure 2i) showed that Fe-N-C0.75 had the smallest semicircular arc diameter, indicating it had the lowest charge transfer resistance and the highest electron transfer efficiency compared to other prepared catalysts [45]. This allowed it to serve more effectively as an electron transfer medium, facilitating electron transfer from the pollutants to PMS.
2.2. The Performance of Catalysts
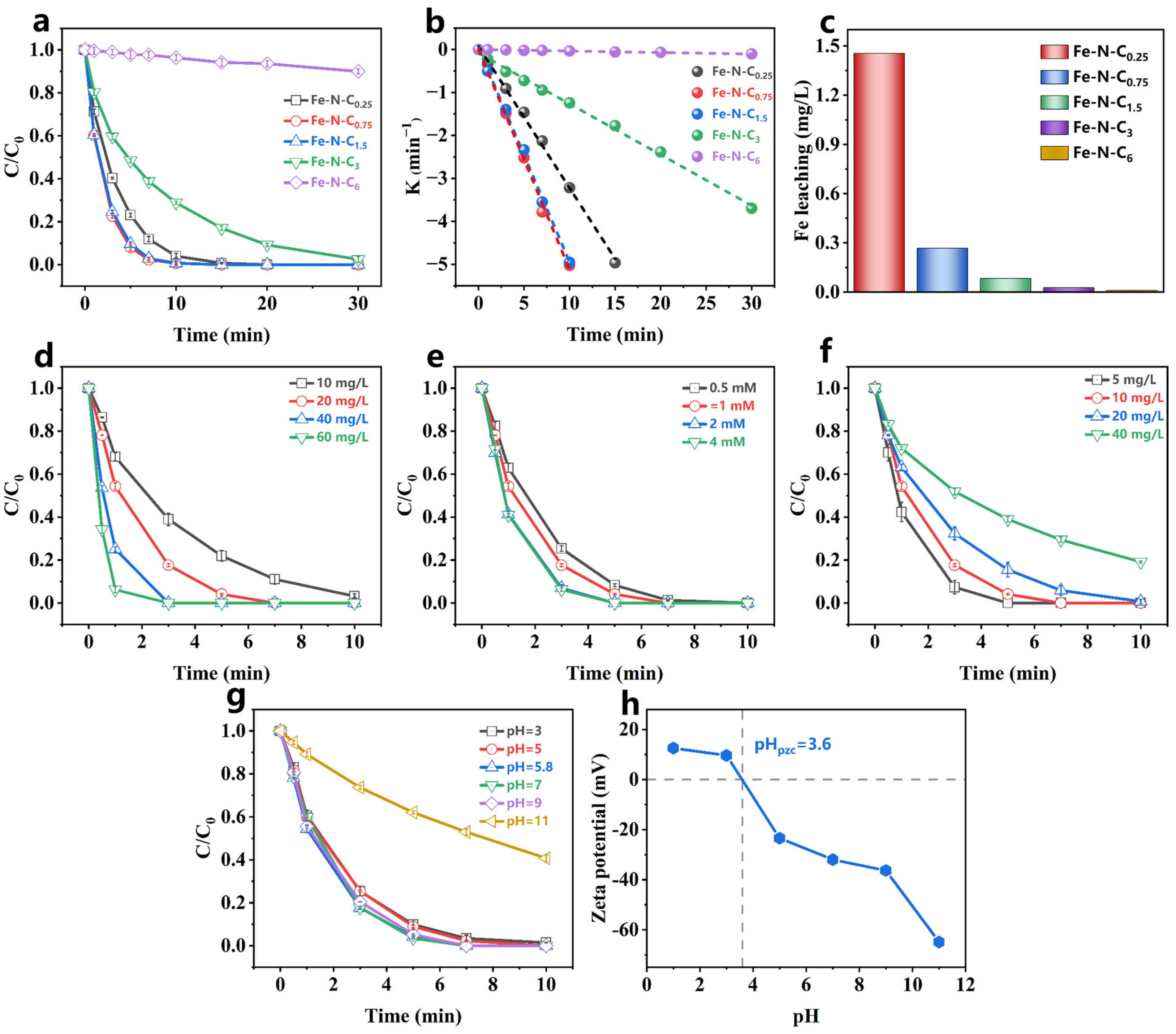
The PMS activation performance of the catalyst was investigated using PCT as the target pollutant. The synthesized catalysts showed negligible PCT adsorption (less than 5%) (Figure S4). In the PMS-only system, PCT removal was almost nonexistent within 30 min (Figure S5), indicating that PMS alone could not degrade PCT through self-decomposition, which is consistent with previous studies [39]. However, when the catalyst was introduced, PCT degradation was significantly enhanced. As shown in Figure 3a, both the Fe-N-C0.75/PMS and Fe-N-C1.5/PMS systems removed 99% of PCT in 10 min. The Kobs for the Fe-N-C3/PMS system was 0.118 min−1 (Figure 3b), while the Kobs of the Fe-N-C0.25/PMS system was approximately three times higher. In contrast, the Fe-N-C6/PMS system removed only 10% of PCT in 30 min. These results demonstrate that the catalyst performance is proportional to the Fe-doping ratio within a certain range, with higher Fe content generating more active sites. Moreover, the decreased performance of Fe-N-C0.25 might be attributed to the formation of excessive unstable iron clusters during pyrolysis, which were removed during acid washing, leading to a reduction in active sites. The Fe-N-Cx (x = 0.75–6) systems exhibited low iron leaching after a 60 min reaction (0.007–0.268 mg/L) (Figure 3c), all within the emission standards for drinking water, surface water, and ground water (GB 5749-2006 [46], GB 3838-2002 [47], and GB/T 14848-2017 III [48]). Among the synthesized catalysts, the reaction rates for Fe-N-C0.75 and Fe-N-C1.5 were similar, and the iron leaching in the Fe-N-C1.5 system was only one-third of the Fe-N-C0.75 system. Additionally, the Fe-N-C1.5 also could efficiently active PDS. As shown in Figure S5, the Fe-N-C1.5/PDS system removed 80% of PCT in 30 min. Compared to some previously reported catalysts (Table S5), the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system demonstrated the highest PMS activation, with the lowest iron leaching. Therefore, Fe-N-C1.5 was selected as the PMS activator for subsequent experiments.
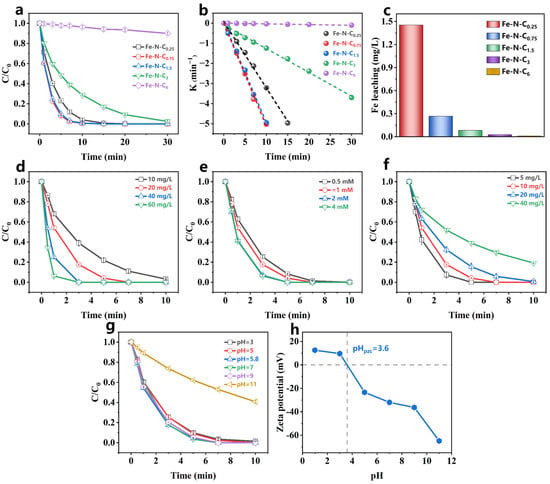
Figure 3.
(a) Activation performance, (b) the corresponding rate constants, and (c) the Fe leaching at 60 min for Fe-N-Cx. ([catalyst] = 30 mg/L, [PMS] = 1.5 mM, [PCT] = 50 mg/L, pH0 = 5.8 (without pH adjustment), temperature = 25–30 °C); PCT degradation in Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system under different (d) catalyst dosage, (e) PMS dosage, (f) PCT concentration, and (g) initial pH; (h) Zeta potential of Fe- N-C1.5. [catalyst] = 20 mg/L, [PCT] = 10 mg/L, [PMS] = 1 mM, pH0 = 5.8 (without pH adjustment), temperature = 25–30 °C.
2.3. Effect of Different Factors on PCT Degradation
Previous studies reported that catalyst dosage had a significant impact on PCT degradation [49]. Therefore, the PCT degradation rates at various catalyst dosages were examined. As shown in Figure 3d and Figure S6a, the PCT degradation rate was accelerated with increasing catalyst dosage, exhibiting a linear correlation (Figure S7). This indicated that increasing the catalyst dosage provides more available active sites, thereby facilitating PMS activation.
The effect of PMS dosage on PCT degradation was also investigated. The Kobs increased significantly from 0.5957 min−1 to 0.9002 min−1 as the PMS dosage increased from 0.5 mM to 2 mM (Figure S6b). However, when the PMS dosage exceeded 2 mM, the enhancement of PCT degradation became negligible (Figure 3e). This result suggested that 2 mM PMS was sufficient for the available active sites on the 0.02 g/L Fe-N-C1.5.
Furthermore, the effect of PCT concentration was examined (Figure 3f). As shown in Figure S6c, the Kobs gradually decreased as the PCT concentration increased, suggesting that the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system effectively treated PCT concentrations less than 20 mg/L.
pH is a critical factor limiting the practical application of advanced oxidation technology. Therefore, the effect of different initial pHs on PCT degradation by the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system was explored. The oxidation system maintained efficient PCT removal over an initial pH from 3 to 9 (Figure 3g). However, PCT degradation was significantly inhibited when the initial pH was 11. To further explore the mechanism of pH impact on PMS activation, the Fe-N-C1.5 surface charge characteristics at different pH levels were investigated. Figure 3h shows that the zero point of charge (pHzpc) of Fe-N-C1.5 was 3.6, and the zeta potential decreased as the initial pH increased. This suggested that Fe-N-C1.5 carried negative charge at pH ≥ 3.6. When the initial pH of the solution was 3–9, the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system pH rapidly stabilized in the range of 2.94–3.39 after PMS addition (Table S6). In this pH range, the Fe-N-C1.5 carried a positive charge, facilitating the adsorption of the negatively charged HSO5−. In contrast, when the initial pH was 11, the pH of the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system decreased to 10.11 after PMS addition. At this pH, Fe-N-C1.5 carried a negative charge, and PCT underwent deprotonation (pKa = 9.86) [50]. Thus, at initial pH ≥ 11, electrostatic repulsion existed between the Fe-N-C1.5 and PMS that hindered PMS activation, leading to a decrease in the PCT degradation rate.
2.4. Feasibility of Practical Application of Catalysts
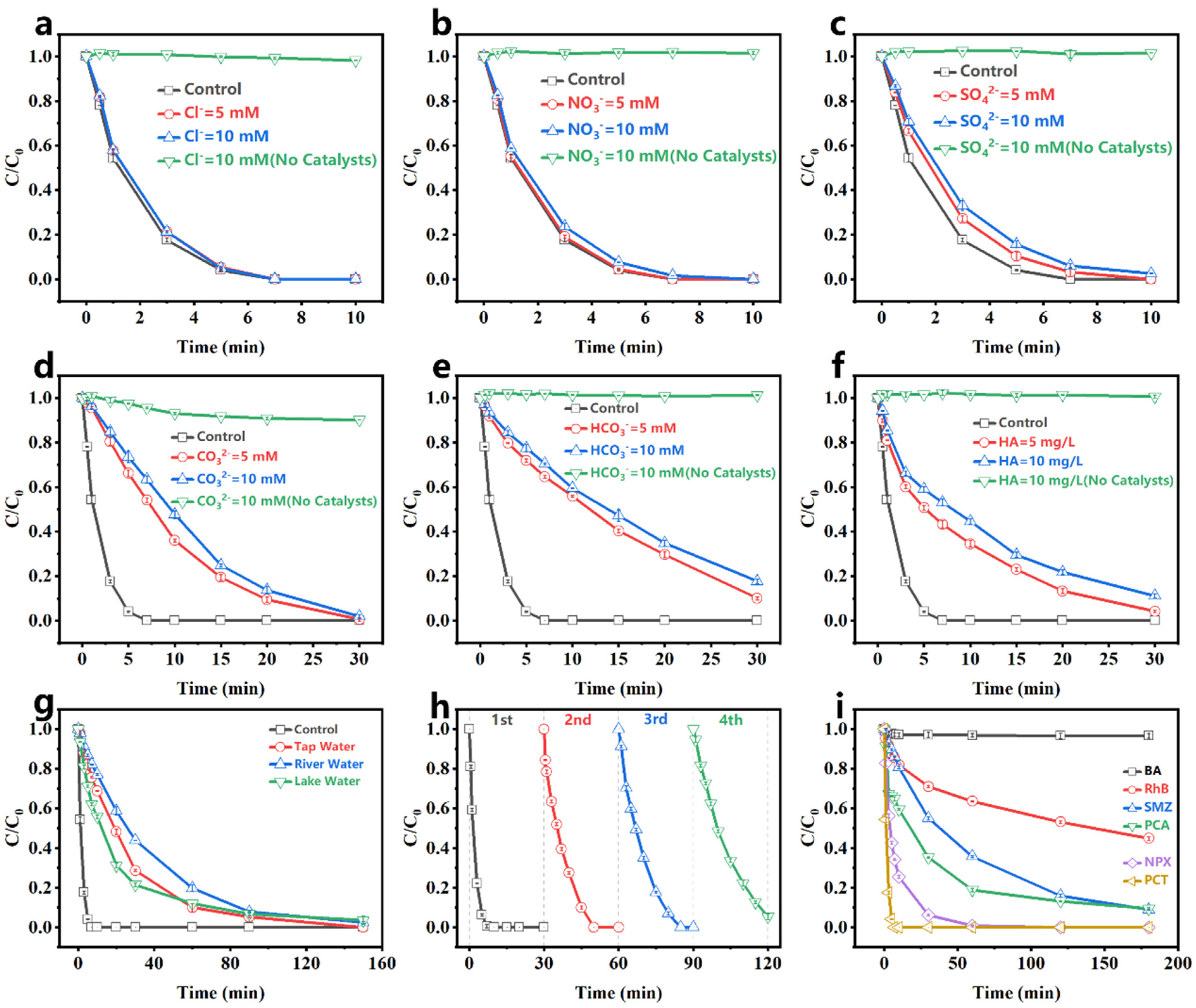
Many background ions (Cl−, NO3−, SO42−, CO32−, HCO3−) and humic acid (HA) exist in environmental water. The impacts of these background ions on PCT degradation in the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system were investigated. As shown in Figure 4a–c, Cl−, NO3−, and SO42− showed insignificant inhibition for PCT degradation, while CO32− and HCO3− significantly inhibited PCT degradation (Figure 4d,e), as both ions raise the pH, which was unfavorable for PMS activation. Moreover, Figure 4f shows that HA inhibited PCT degradation, likely due to the fact that HA competes with PCT for the active sites and active species of the catalyst. Despite the varying degrees of inhibition caused by adding these interfering ions, PCT was still largely removed in 30 min. This result demonstrated that the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system had good resistance to ion interference.
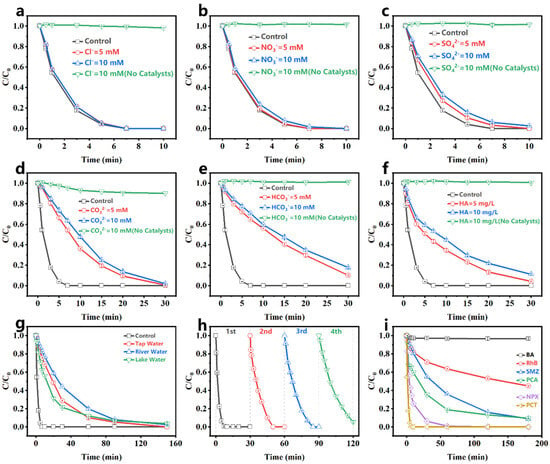
Figure 4.
Effect of (a) Cl−, (b) NO3−, (c) SO42−, (d) CO32−, (e) HCO3−, (f) HA on the degradation of PCT; (g) PCT degradation by the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system in different real water bodies; (h) cycle experiments; (i) degradation of different pollutants. [catalyst] = 20 mg/L, [PCT] = 10 mg/L, [PMS] = 1 mM, pH0 = 5.8 (without pH adjustment), temperature = 25–30 °C.
To more comprehensively assess the practical applicability of the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system, its degradation performance was evaluated in tap water (South China University of Technology), artificial lake water (South China University of Technology), and river water (the Zhujiang River). As shown in Figure 4g, 97% of PCT was removed in 150 min in the natural water matrix, which was lower than in DI water. This was attributed to the presence of abundant interfering ions and organic matter in natural waters, which compete with PCT for active sites and consume reactive oxygen species. Additionally, the mineralization capability of the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system was assessed, showing a TOC removal rate of 16.14% at 120 min (Figure S8).
The stability of the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system was investigated through cycle experiments. Figure 4h shows the degradation performance of the system over four cycles. In the first cycle, PCT was completely degraded in 10 min, and all subsequent cycles showed slower reaction rates than the previous one. In the fourth cycle, only 94% of PCT was degraded in 30 min, which might be due to the large amount of intermediate product adsorption occupying the catalyst active sites and hindering PMS reacting at those sites [32]. The absence of significant changes in the Fe-N-C1.5 XRD pattern after four cycles (Figure S9) further demonstrated the excellent stability of Fe-N-C1.5.
The degradation of different pollutants via the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system was evaluated. Due to their varying chemical structures and properties, the degradation mechanisms and rates differed significantly. As shown in Figure 4i, the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system demonstrated varying degradation rates for benzoic acid (BA), rhodamine B (RhB), p-chloroaniline (PCA), sulfamethazine (SMZ), naproxen (NPX), and paracetamol (PCT). Among them, the degradation rates of electron-rich pollutants (PCT, NPX) with electron-donating groups such as hydroxyl and alkoxy groups were faster, while there was basically no degradation for BA with electron-withdrawing groups. This was likely due to the lower ionization potential of the electron-donating groups, such as hydroxyl and alkoxy groups, which were more susceptible to electron capture by the oxidation of activated PMS [51]. Furthermore, the cycle experiments for PCT, NPX, PCA, and SMZ (Figure S10) revealed that the system maintains excellent removal efficiency (>98%) for both PCT and NPX after four consecutive cycles, while the removal efficiency for PCA and SMZ decreased to approximately 65%. These results demonstrated that the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system exhibits selective degradation capability towards various contaminants while maintaining superior stability.
2.5. Mechanism Discussion for PCT Degradation
2.5.1. Identification of Reactive Species
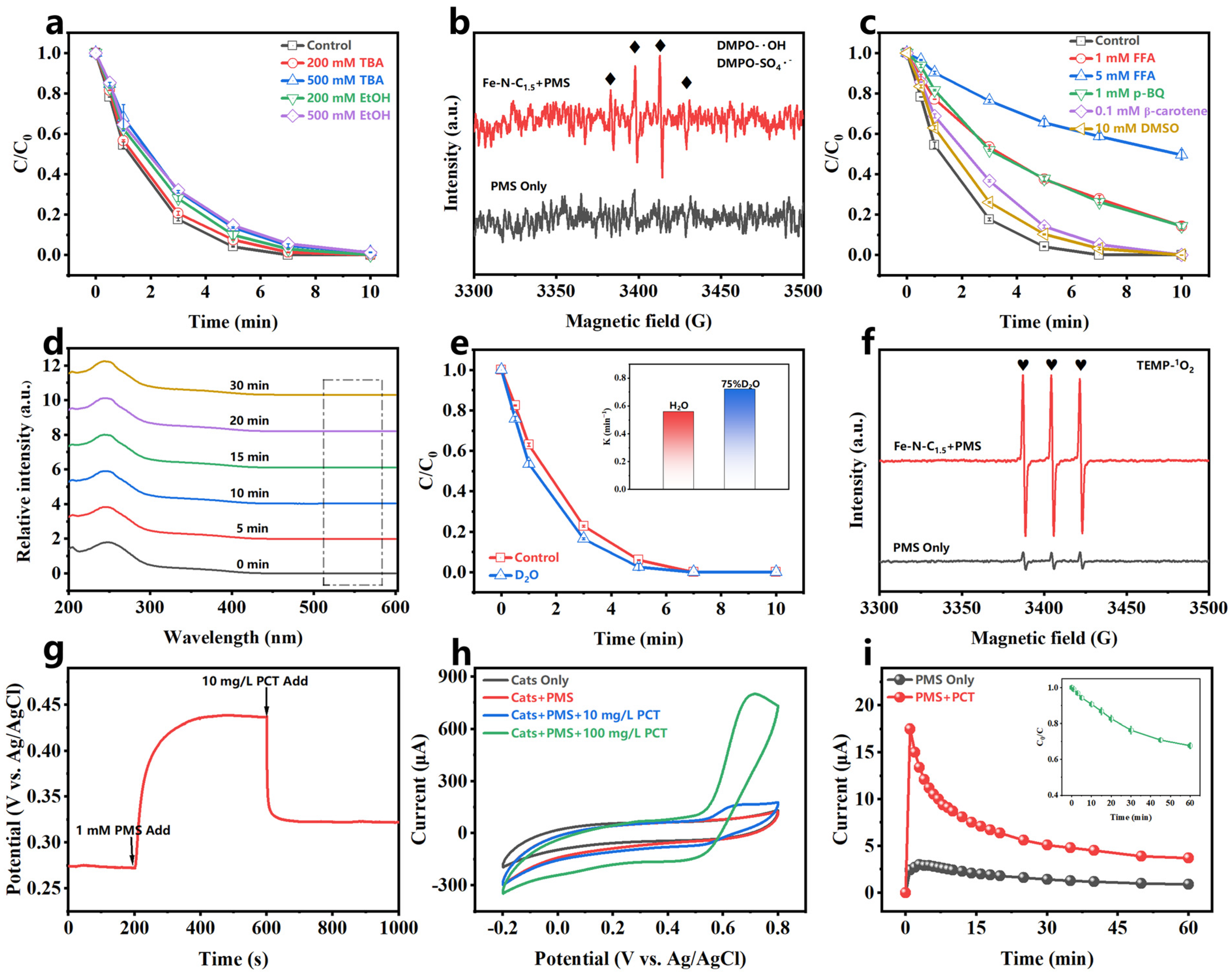
Quenching experiments were conducted to identify the reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated in the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system. Ethanol (EtOH) and tert-butyl alcohol (TBA) are commonly used to identify hydroxyl radicals (•OH) and sulfate radicals (SO4•−) in the system [52]. EtOH is an effective quencher for both •OH and SO4•− (KEtOH/•OH = 1.9 × 109 M−1s−1, KEtOH/SO4•− = 7.7 × 107 M−1s−1) [53,54], while TBA reacts much faster with •OH than SO4•− (KTBA/•OH = 6.0 × 108 M−1s−1, KTBA/SO4•− = 7.6 × 105 M−1s−1) [15]. As shown in Figure 5a, both EtOH and TBA insignificantly inhibited PCT degradation, indicating PCT degradation was not primarily dependent on •OH or SO4•−. 5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide (DMPO), a radical scavenger, was used to capture •OH and SO4•− in the system [55]. As shown in Figure 5b, the appearance of only a weak 1:2:2:1 signal peak further confirmed that •OH and SO4•− were not the primary active species in the system.
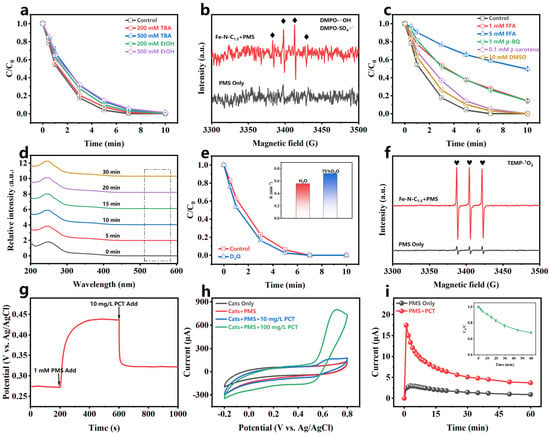
Figure 5.
(a) Quenching experiments of EtOH and TBA; (b) EPR in the presence of DMPO; (c) quenching experiments of FFA, p-BQ, β-carotene, and DMSO; (d) NBT experiments; (e) effect of reaction solvents (H2O and D2O); (f) EPR in the presence of TEMP; (g) OCPT, (h) CV; and (i) GOP experiment for the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS/PCT system. [catalyst] = 20 mg/L, [PCT] = 10 mg/L, [PMS] = 1 mM, pH0 = 5.8 (without pH adjustment), temperature = 25–30 °C.
O2•− is a common radical in PMS systems. Since p-benzoquinone (p-BQ) reacts with O2•− at a high rate (Kp−BQ/O2•− = 0.9 − 1.0 × 109 M−1s−1) [56], it was used as a quencher to identify O2•− in the system. After adding 1 mM p-BQ, PCT degradation was significantly inhibited (Figure 5c). However, it has been reported that p-BQ can directly consume PMS [57], resulting in a reduced degradation rate. To further identify the O2•− contribution, the O2•− was detected by monitoring the absorption intensity of nitro blue tetrazolium (NBT) at 560 nm in the UV–visible spectrum [41,58]. Figure 5d shows that no NBT absorption peak appeared after 30 min of reaction, confirming the absence of O2•− in the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system.
Furfuryl alcohol (FFA) was used for quenching singlet oxygen (1O2) (KFFA/1O2 = 1.2 × 108 M−1s−1) [15]. As shown in Figure 5c, after adding FFA, PCT degradation in the system was significantly inhibited, and the inhibitory effect increased as the FFA concentration increased. In the presence of 5 mM FFA, only 50% of PCT was removed in 10 min. However, there is debate that high FFA concentrations may directly react with PMS [59], reducing the reaction rate. β-carotene, a 1O2-quenching agent that does not consume PMS, was used to further evaluate the 1O2 contribution. Figure 5c shows that even at low concentrations (β-carotene: PMS = 0.2:1), the addition of β-carotene significantly inhibited PCT degradation. This result indicated that 1O2 was a crucial ROS in PCT degradation. Since 1O2 has a longer lifetime in D2O (60 μs) than in H2O (3.5 μs), a solvent exchange experiment was conducted to further confirm its presence [60]. Figure 5e shows an accelerated PCT degradation rate in D2O (from 0.5601 min−1 to 0.7211 min−1), further confirming the generation of 1O2 in the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system and its involvement in PCT degradation. 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine (TEMP) was used as a spin trap agent for 1O2. As shown in Figure 5f, a weak TEMPO triplet signal (1:1:1) appeared in the PMS-only system. In contrast, the intensity of the triplet signal increased significantly in the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system, providing further evidence for the generation of 1O2 in the system.
High-valent metal oxide species are commonly present in metal composite catalyst systems and participate in the direct oxidation of pollutants. To verify the generation and role of high-valent metal oxide species (Fe(IV)=O, Fe(V)=O), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was introduced as a quencher. The addition of 10 mM DMSO had negligible effects on PCT degradation (Figure 5c). This suggested that Fe(IV)=O and Fe(V)=O were not the primary ROS for PCT degradation.
Based on the above results, the electron transfer process (ETP) likely plays a crucial role in PCT degradation in the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system. K2Cr2O7, a solution-phase ETP scavenger [61,62], was employed to identify solution-phase ETP’s contribution in the system. Figure S11 shows that 100% of PCT was degraded in 30 min, even with the addition of 10 mM K2Cr2O7, suggesting that the solution-phase ETP was an insignificant role for PCT removal in this system. The PMS decomposition experiments were performed (Figure S12). The PMS concentration decreased slightly (approximately 8%) after 10 min when either the catalyst or PCT were present, while it significantly decreased 22% when both the catalyst and PCT were present. This result implied a catalyst interface-mediated ETP [39]. Electrochemical tests can directly detect electron transfer in the system to further identify the role of catalyst-interface-mediated ETPs. As shown in Figure 5g, the addition of PMS to the catalyst-coated carbon electrode system led to a rapid increase in potential, reaching a stable plateau, indicating the catalyst interacts with PMS to elevate its potential. After adding PCT, the potential quickly decreased, suggesting the high-potential catalyst directly captures electrons from PCT, thereby proving electron transfer [63,64]. Similar results were observed in the chronoamperometry (i-t) experiment (Figure S13), where the current density showed significant changes upon the sequential addition of PMS and PCT. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) clearly showed the redox processes of the pollutants on the catalyst surface [65]. After adding PMS, the curve shows no significant changes, but after adding PCT, a pair of redox peaks appeared, with the peak current increasing as the PCT concentration increased (Figure 5h), further illustrating that the system captured the electrons from PCT through electron transfer. The galvanic oxidation process (GOP) system developed by Huang et al. provides a more intuitive demonstration of the electron transfer [66]. As shown in Figure 5i, after adding PMS and PCT to the two half-cells, respectively, the current in the external circuit increased, and the PCT began to degrade gradually. This confirmed that the system degraded the PCT via catalyst-mediated electron transfer.
In catalyst-interface-mediated ETP systems, the PMS usually interacts with the surface sites of the catalyst, forming surface-bonded active complexes that have higher redox potentials [67]. Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy (Figure S14) confirmed the formation of the metastable complex in the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system. Compared to PMS alone, the FTIR spectrum of the system showed a red shift in the S-O absorption peak from 1120 cm−1 to 1132 cm−1. This shift was attributed to the interaction between Fe-N-C1.5 and PMS, which weakened the electron density of the S-O bond in the metastable complex [68].
Furthermore, ionic strength experiments were conducted to explore whether the interaction between the catalyst, PMS, and PCT during electron transfer occurs through an inner-sphere or outer-sphere process. The ionic strength of the system was adjusted by introducing varying NaClO4 concentrations to modulate the interference from background ions [15]. When the NaClO4 concentration ranged from 1 to 50 mM, the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system was able to completely remove PCT in 7 min (Figure S15), indicating that ionic strength had minimal impact on PCT degradation. This result demonstrated that the electron transfer in the system predominantly follows an inner-sphere mechanism.
The above experimental results indicated that the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system primarily degrades PCT through two non-radical pathways: (i) 1O2- and (ii) catalyst-interface-mediated ETPs.
2.5.2. Identification of Reactive Sites and Analysis of PCT Degradation Mechanisms
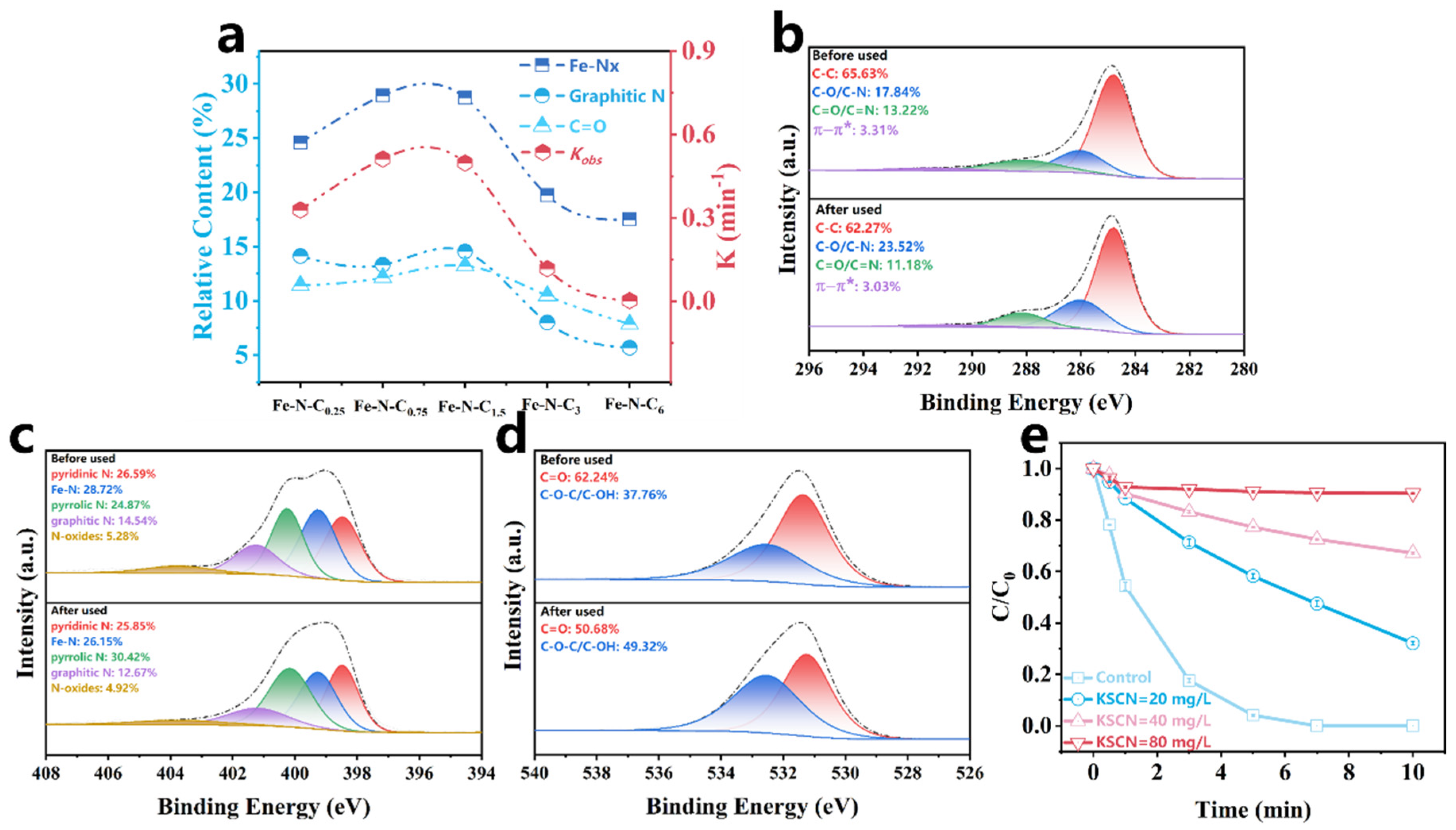
The XPS results and the Kobs of Fe-N-Cx showed the relative content of Fe-Nx, graphitic N, and C=O on the catalyst surface positively correlated with Kobs (Table S4 and Figure 6a). Specifically, the Kobs gradually increased as the relative content of Fe-Nx, graphitic N, and C=O increased, indicating that these sites play important roles in PMS activation. To further explore the primary active sites for PMS activation, the catalyst surface before and after the reaction was analyzed by XPS. As shown in Figure 6b–d, the relative content of Fe-Nx decreased from 28.72% to 26.15%, graphitic N decreased from 14.54% to 12.67%, and C=O content declined from 70.14% to 61.28% after the reaction. These results further demonstrated that Fe-Nx, graphitic N, and C=O sites play significant roles for PMS activation. It was reported that N atoms could alter the electronic arrangement of the carbon network, introducing hybrid nitrogen sites such as pyridinic N, pyrrolic N, and graphitic N. Pyrrolic N and pyridinic N, with lone pairs of electrons, could coordinate with the Fe atom, forming Fe-Nx sites that have a strong affinity for PMS [69]. Due to differences in electronegativity between elements, local polarization electric fields exist at Fe-Nx sites, which promote electron transfer on the Fe-N-C1.5 electronic bridge [17], thereby facilitating the rapid activation of PMS. Additionally, graphitic N also serves as a reactive site in the catalytic reaction. The more electronegative N in graphitic N has a stronger electron-withdrawing ability, which induces the adjacent carbon atoms to become positively charged, generating electron-deficient C active sites that promote nucleophilic attack by PMS [70]. When one electron from PMS transfers to the electron-deficient C+ site, a peroxyl radical intermediate (SO5•−) is generated, which easily reacts to form 1O2 [39]. Similarly, the carbonyl (C=O), with its electrophilic nature, also induces nucleophilic attack by PMS, leading to the generation of 1O2 [43]. To further identify the contribution of Fe-Nx for PMS activation, a KSCN toxicity experiment was conducted. As shown in Figure 6e, the addition of KSCN significantly inhibited PCT degradation, confirming that Fe-Nx served as a critical site for PMS activation.
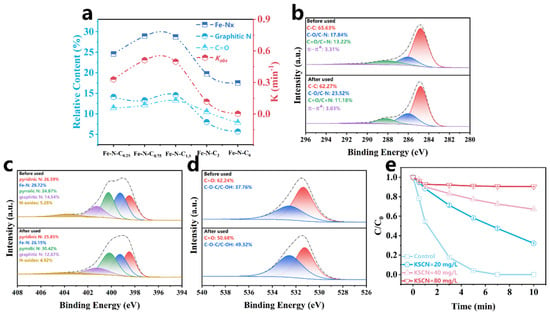
Figure 6.
(a) Structure–property relationships between different species and the Kobs; XPS C 1s (b), N 1s (c), O 1s (d) of the Fe-N-C1.5 before and after use; (e) effects of different concentrations of KSCN on Fe-N-C1.5/PMS/PCT system.
2.6. PCT Degradation Pathway and the Intermediates Toxicity Assessment
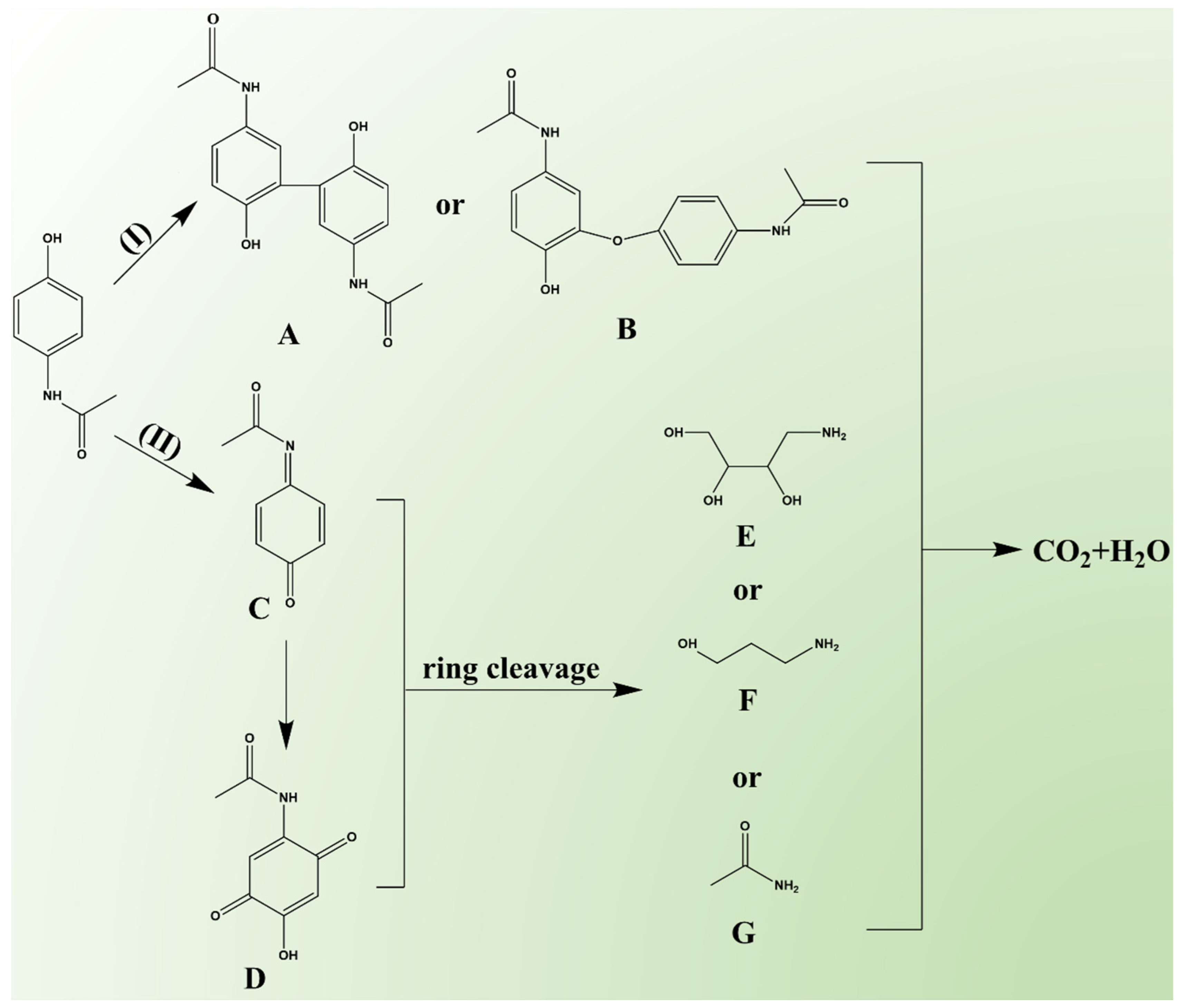
The intermediates generated during PCT degradation in the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system were detected using HPLC-MS (detailed information is provided in Table S8 and Figure S16), based on which two possible degradation pathways were proposed (Figure 7). It was reported that the radical pathway contributes to the formation of biphenyl and diphenyl ether [71]. In Pathway I, PCT was attacked by •OH and SO4•−, leading to the formation of phenoxy radicals, which subsequently produced compound A (2,2′-dihydroxy-5,5′-diacetyldiaminebiphenyl, m/z = 300) or compound B (2-hydroxy-4′,5-diacetamido-diphenyl ether, m/z = 300) [31,41]. In Pathway II, PCT underwent hydrogen abstraction, forming compound C (N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine, m/z = 149) [72]. Compound C, after hydroxylation and hydrogen abstraction, was oxidized to form compound D (2-hydroxy-5-acetamido-1,4-benzoquinone, m/z = 181) [73]. Due to the instability of their quinoid structure, compounds C and D were prone to ring-opening reactions [71,74,75], generating small aliphatic hydrocarbon derivatives, such as compound E (4-aminobutane-1,2,3-triol, m/z = 121), compound F (3-aminopropanol, m/z = 75), and compound G (acetamide, m/z = 59). Finally, these substances were further mineralized to CO2 and H2O.
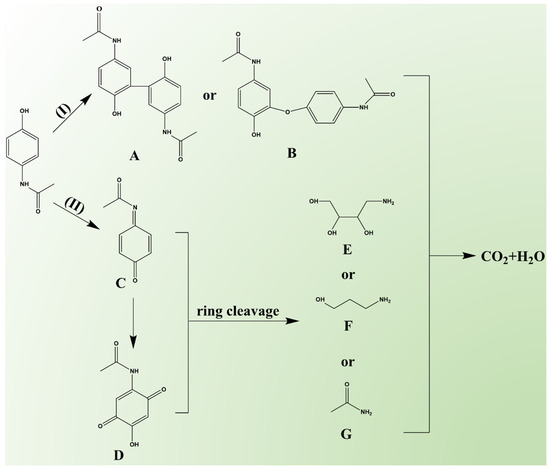
Figure 7.
The proposed PCT degradation pathways in the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system.
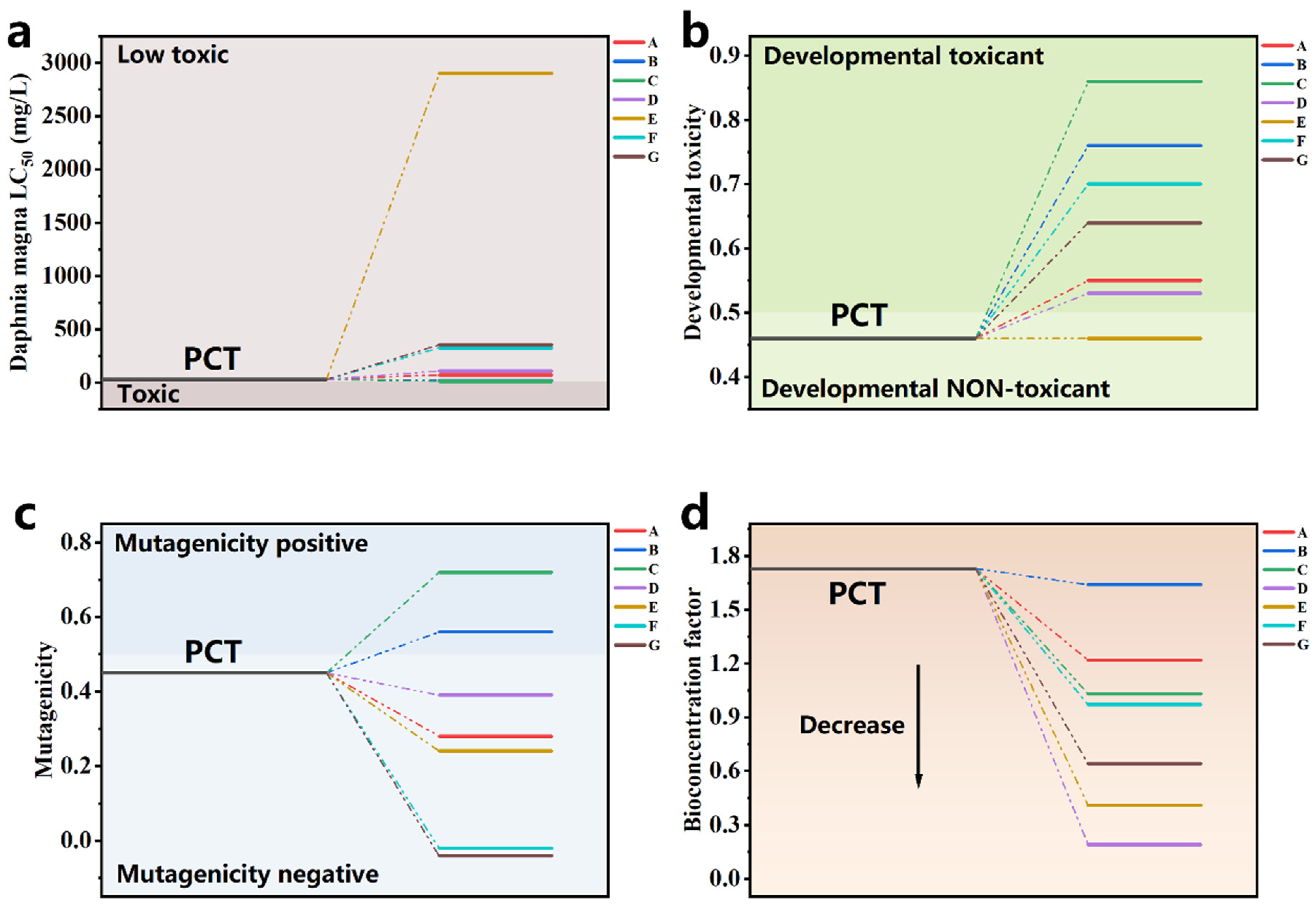
The toxicity of the PCT degradation intermediates was assessed using a Toxicity Estimation Software Tool (T.E.S.T version 5.1.2) based on the QASR method to evaluate their environmental impact. Four indicators were selected for evaluation: acute toxicity LC50 to Daphnia magna, developmental toxicity, bioconcentration factor, and mutagenicity (Figure 8) [3,76,77]. The acute toxicity LC50 of PCT to Daphnia magna was 27.14 mg/L, classifying it as a low-toxicity substance (LC50 > 10 mg/L) according to the aquatic toxicity classification. The other intermediates were also found to be low-toxicity substances, with most intermediates showing an increase in LC50 relative to PCT, indicating that the degradation effectively reduced the pollutants’ acute toxicity in the system. However, for developmental toxicity, all intermediates except compound E exhibited higher toxicity. Additionally, intermediates B and C were found to be mutagenic, indicating that PCT degradation in the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system produced toxic intermediates. Fortunately, all intermediates showed lower bioconcentration factors, suggesting that although some intermediates possess higher toxicity, their accumulation is much lower than that of PCT. As a result, the system’s overall toxicity may decrease over the course of degradation. However, to ensure the safety of treated water, further oxidation and mineralization are required to eliminate these toxic intermediates.
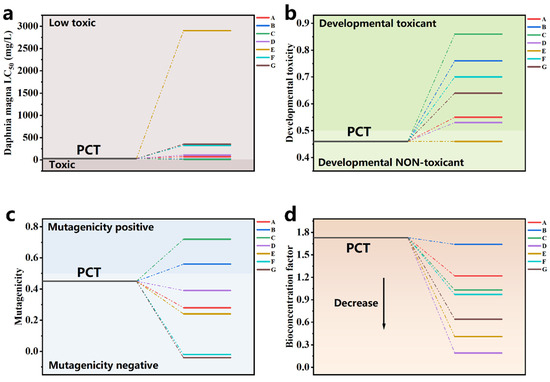
Figure 8.
(a) Daphnia magna LC50, (b) developmental toxicity, (c) mutagenicity, and (d) bioaccumulation factor of PCT and degradation intermediates in the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Catalyst Synthesis
Details of the chemicals used in this work are provided in the Text S1. Fe-N-Cx was synthesized using a simple co-pyrolysis method. Ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (1 mmol) was added to 25 mL of deionized water to obtain solution A. 1,10-phenanthroline (x mmol, x = 0.25, 0.75, 1.5, 3, 6) was added to 25 mL of ethanol to obtain solution B. Solution A was added dropwise to stirred solution B. The mixed solution was dried under vacuum at 60 °C for 48 h to produce the Fe-N precursor. The Fe-N precursor was calcined at 600 °C for 2 h under a N2 atmosphere to obtain Fe, N co-doped metal composites. Finally, the metal composites were washed with 1 M HCl solution for 2 h to remove unstable metal particles which aggregated on the surface of the metal composites. The acid-treated material was dried at 60 °C for 24 h to obtain stable composites, referred to as Fe-N-Cx.
3.2. Characterizing Methods
The characterization details are provided in the Text S2–S4.
3.3. Batch Experiments
All degradation experiments were conducted at room temperature in a 250 mL beaker with magnetic stirring. The degradation process was initiated by adding catalyst (30 mg/L) and PMS (1.5 mM) to a 50 mg/L PCT solution. At set intervals, a 0.5 mL sample was withdrawn from the reaction mixture and filtered through a 0.45 μm filter, then transferred into a vial containing 0.5 mL of sodium thiosulfate (0.05 M) to quench the oxidation reaction. Adsorption experiments followed the same procedure as above but without the PMS addition. All experiments were conducted in duplicate, and the mean values with their corresponding standard deviations are presented.
The pseudo-first-order kinetic degradation rate constant for the degradation experiments was calculated using the following equation:
where Ct represents the residual pollutant concentration and C0 the initial pollutant concentration, while Kobs is the rate constant for the target pollutant degradation.
3.4. Analytical Methods
The concentration of the target pollutant was determined via HPLC (Agilent1200, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA), with details listed in Table S1. The leached Fe ion concentration was determined using a UV–Vis spectrophotometer (UV-2550, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) via the 1,10-phenanthroline colorimetric method. The zeta potential was obtained with a nanoparticle size and zeta potential analyzer (Malvern Zetasizer Nano ZS90, Malvern Panalytical, Worcestershire, UK). The concentration of PMS in the PMS decomposition experiments was determined using the 2,2′-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt (ABTS) colorimetric method, using the detailed procedures provided in Text S5. The radicals generated in the system were measured via a paramagnetic resonance spectrometer (EPR, Bruker EMXPlus-10/12, Bruker, Rheinstetten, Germany), using DMPO and TEMP as radical scavengers. The total organic carbon (TOC) was measured using a TOC analyzer (Jena Multi N/C 3100, Analytik Jena GmbH + Co. KG., Jena, Germany). Electrochemical analyses were performed using an electrochemical workstation (CHI760E, Shanghai Chenhua Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), with detailed methods given (Text S6). The galvanic oxidation process (GOP) experiment (details provided in Text S7) was conducted to further confirm electron transfer, with the current measured with an ammeter. Degradation intermediates were analyzed using an Agilent 1290 ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry system (HPLC-MS, Bruker maXis impact, Bruker, Bremen, Germany), with detailed information presented in Text S8.
4. Conclusions
In this study, an efficient and stable Fe-N-C1.5 catalyst was synthesized via a simple mixed solvent–pyrolysis method to activate PMS for PCT degradation. The Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system exhibited exceptional performance, achieving 100% PCT (10 mg/L) removal in 7 min with low catalyst doses (20 mg/L) and PMS (1 mM). Moreover, the system demonstrated outstanding anti-interference capabilities and practical applicability, effectively degrading PCT in the presence of various inorganic anions and in different real environmental water matrices. The cycle experiments further confirmed the stability of the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system. Mechanistic analysis revealed that PCT degradation primarily occurred via two non-radical pathways: 1O2 and catalyst-interface-mediated ETP. PMS was rapidly activated at Fe-Nx, graphitic nitrogen, and C=O, generating singlet oxygen or forming an active PMS complex species, which subsequently oxidized PCT. In addition, two degradation pathways for PCT were proposed, and the toxicity of the potential intermediates was assessed. The results indicated that some intermediates exhibited more ecological toxicity than PCT, highlighting the need for further mineralization to eliminate these harmful byproducts. In summary, this study deepens an understanding of the PCT degradation mechanism by the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system and offers a promising strategy for organic contaminant removal from water.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/catal15030217/s1, Text S1. Chemicals. Text S2. Characterizing methods. Text S3. The determination of Fe content in activators by ICP-OES. Text S4. The experimental method of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). Text S5. Measurement of PMS concentration by the ABTS colorimetric method. Text S6. Electrochemical measurements. Text S7. The experimental method of galvanic oxidation processes (GOP). Text S8. Analytical method of LC-MS. Table S1. HPLC analysis parameters for different pollutants. Table S2. BET surface area, pore volume and pore size of Fe-N-Cx. Table S3. ICP-OES test of different catalysts. Table S4. The surface element chemical states of different catalysts. (XPS analysis) Table S5. Comparison of reported iron-based catalysts. Table S6. Comparison of the solution pH before and after adding PMS. Table S7. Comparison of the surface element chemical states before and after reaction of Fe-N-C1.5. (XPS analysis). Table S8. The intermediate products of PCT degradation. Figure S1. (a, b) SEM images of Fe-N-C0.25. Figure S2. Pore size distribution of Fe-N-C0.25 (a), Fe-N-C0.75 (b), Fe-N-C1.5 (c), Fe-N-C3 (d) and Fe-N-C6 (e). Figure S3. Structure-property relationships between the Kobs and (a) SBET, (b) Fe content. Figure S4. Adsorption performance of Fe-N-Cx. [catalyst] = 30 mg/L, [PCT] = 50 mg/L, pH0 = 5.8 (without pH adjustment), room temperature. Figure S5. PCT degradation in different systems. [catalyst] = 20 mg/L, [PCT] = 10 mg/L, [PMS] = 1 mM, [PDS] = 1 mM, pH0 = 5.8 (without pH adjustment), room temperature. Figure S6. The first-order reaction rate constants of PCT degradation under different catalyst dosage (a), PMS dosage (b), PCT concentration (c). Figure S7. Catalyst dosages and linear fitting of first-order reaction rate constants. Figure S8. TOC removal of PCT degradation in the Fe-N-C1.5/PMS system. Figure S9. XRD patterns of Fe-N-C1.5 before and after use. Figure S10. Cycle experiments for PCT, NPX, PCA, and SMZ. (reaction time per cycle: 180 min). Figure S12. PMS decomposition in different systems. [catalyst] = 20 mg/L, [PCT] = 10 mg/L, [PMS] = 1 mM, pH0 = 5.8 (without pH adjustment), room temperature. Figure S13. I-t experiment of Fe-N-C1.5/PMS/PCT system. Figure S14. FTIR of Fe-N-C1.5 only, PMS only and Fe-N-C1.5/PMS. Figure S15. Effects of different concentrations of NaClO4 on Fe-N-C1.5/PMS/PCT system. [catalyst] = 20 mg/L, [PCT] = 10 mg/L, [PMS] = 1 mM, pH0 = 5.8 (without pH adjustment), room temperature. Figure S16. Chromatogram and mass spectrum of substances at 5 min. Refs. [32,34,66,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85] are cited in the Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
Y.Z. (Yujun Zhuo): Writing—original draft, investigation, formal analysis, methodology; H.M.: formal analysis, methodology, writing—review and editing; Y.Z. (Yongqing Zhang): writing—review and editing, supervision, funding acquisition; Y.C.: investigation, methodology, validation; J.C.: investigation, validation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51572089), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0400708) and Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2023A1515012378).
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Chidiac, A.S.; Buckley, N.A.; Noghrehchi, F.; Cairns, R. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) overdose and hepatotoxicity: Mechanism, treatment, prevention measures, and estimates of burden of disease. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2023, 19, 297–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.M. Acetaminophen (APAP) hepatotoxicity—Isn’t it time for APAP to go away? J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 1324–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Gong, Z.; Xiang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. Influence of entropy on catalytic performance of high-entropy oxides (NiMgZnCuCoOx) in peroxymonosulfate-mediated acetaminophen degradation. Chemosphere 2024, 362, 142610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón, F.J.; Cayuela, M.L.; Sánchez-Monedero, M.A. Paracetamol degradation pathways in soil after biochar addition. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 307, 119546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantzi, L.; Reppas, C.; Dressman, J.B.; Amidon, G.L.; Junginger, H.E.; Midha, K.K.; Shah, V.P.; Stavchansky, S.A.; Barends, D.M. Biowaiver monographs for immediate release solid oral dosage forms: Acetaminophen (paracetamol). J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.-l.; Liu, Z.-h.; Ma, Q.-g.; Dai, L.; Dang, Z. Occurrence, removal and risk evaluation of ibuprofen and acetaminophen in municipal wastewater treatment plants: A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 891, 164600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanbari, F.; Giannakis, S.; Lin, K.-Y.A.; Wu, J.; Madihi-Bidgoli, S. Acetaminophen degradation by a synergistic peracetic acid/UVC-LED/Fe(II) advanced oxidation process: Kinetic assessment, process feasibility and mechanistic considerations. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parolini, M. Toxicity of the Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) acetylsalicylic acid, paracetamol, diclofenac, ibuprofen and naproxen towards freshwater invertebrates: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Ren, X.; Duan, X.; Sarmah, A.K.; Zhao, X. Remediation of environmentally persistent organic pollutants (POPs) by persulfates oxidation system (PS): A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 863, 160818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Wang, X.; Fu, L.; Peng, X.; Pan, C.; Mao, Q.; Wang, C.; Yan, J. Nonradicals induced degradation of organic pollutants by peroxydisulfate (PDS) and peroxymonosulfate (PMS): Recent advances and perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 142794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matzek, L.W.; Carter, K.E. Activated persulfate for organic chemical degradation: A review. Chemosphere 2016, 151, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Hu, L.; Li, L.; Zheng, Q.; Xin, Y.; Zhang, G. Recent advances in persulfate-based advanced oxidation processes for organic wastewater treatment. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 4461–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; von Gunten, U.; Kim, J.-H. Persulfate-Based Advanced Oxidation: Critical Assessment of Opportunities and Roadblocks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3064–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhu, H.; Croué, J.-P. Production of Sulfate Radical from Peroxymonosulfate Induced by a Magnetically Separable CuFe2O4 Spinel in Water: Efficiency, Stability, and Mechanism. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 2784–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, W.; Cheng, C.; Shao, P.; Luo, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Duan, X. Origins of Electron-Transfer Regime in Persulfate-Based Nonradical Oxidation Processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 78–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zeng, G.; Deng, Y.; Dong, H.; Feng, H.; Wang, J.; Peng, B. Enhanced activation process of persulfate by mesoporous carbon for degradation of aqueous organic pollutants: Electron transfer mechanism. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 231, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hayat, W.; Wu, X.; Meng, H.; Wu, Q. Selective degradation of organic pollutants by highly dispersed Fe, Ni anchored on nitrogen carbon activating persulfate system: Electron transfer promotion, the impact of pollutant redox and adsorption properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 490, 151585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, W.; Liu, B.; Wu, Q.; Luo, H.; Zhao, Q.; Si, Q.; Sseguya, F.; Ren, N. Edge-nitrogenated biochar for efficient peroxydisulfate activation: An electron transfer mechanism. Water Res. 2019, 160, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y. Non-photochemical production of singlet oxygen via activation of persulfate by carbon nanotubes. Water Res. 2017, 113, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhai, H.; Luo, W.; Liu, W.; Zhuang, Z.; Ji, M. Multifunctional sites on reduced graphene oxide synergistically improving the degradation of diclofenac in peroxydisulfate systems. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Xiao, S.; Zhong, H.; Yan, M.; Yang, X. Activation of persulfates by carbonaceous materials: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 418, 129297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Duan, X.; Xu, X.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Qiu, H.; Wang, S.; Cao, X. Persulfate Oxidation of Sulfamethoxazole by Magnetic Iron-Char Composites via Nonradical Pathways: Fe(IV) Versus Surface-Mediated Electron Transfer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 10077–10086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Niu, X.; Zhang, D.; Lv, M.; Ye, X.; Ma, J.; Lin, Z.; Fu, M. Metal-based catalysts for persulfate and peroxymonosulfate activation in heterogeneous ways: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Lai, C.; Liu, S.; Wang, D.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Xu, F.; Nie, J. Metal-carbon hybrid materials induced persulfate activation: Application, mechanism, and tunable reaction pathways. Water Res. 2023, 234, 119808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyekunle, D.T.; Gendy, E.A.; Ifthikar, J.; Chen, Z. Heterogeneous activation of persulfate by metal and non-metal catalyst for the degradation of sulfamethoxazole: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 437, 135277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lai, C.; Li, B.; Liu, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, C.; Qin, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Yi, H.; et al. Heteroatom doping in metal-free carbonaceous materials for the enhancement of persulfate activation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 131655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Nie, X.; Ji, X.; Quan, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Yu, H.; Guo, X. Enhanced heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate by Co and N codoped porous carbon for degradation of organic pollutants: The synergism between Co and N. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Chen, Y.; Su, R.; Liu, Z.; He, J.; Zhou, W.; Gu, M.; Yan, M.; Li, Q. In situ synthesis of Fe-N co-doped carbonaceous nanocomposites using biogas residue as an effective persulfate activator for remediation of aged petroleum contaminated soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 128963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Zou, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Long, X.; Yu, J.; Jiao, F. Iron-based catalysts for persulfate-based advanced oxidation process: Microstructure, property and tailoring. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 421, 127845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Cheng, M.; Zhong, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Liang, Q. Iron-mediated activation of persulfate and peroxymonosulfate in both homogeneous and heterogeneous ways: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhu, J.; Hayat, W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Jiang, R. Fe-N coordination moieties regulate the defect formation in carbon nanomaterial for efficient peroxydisulfate activation: Significant role of surface complex. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, L.; Hayat, W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, S. The efficient degradation of paracetamol using covalent triazine framework-derived Fe-N-C activated peroxymonosulfate via a non-radical pathway: Analysis of high-valent iron oxide, singlet oxygen and electron transfer. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 310, 123034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, S.-N.; Sun, H.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Ren, H.-Y.; Xing, D.-F.; Ren, N.-Q.; Liu, B.-F. A magnetic biochar catalyst with dual active sites of Fe3C and Fe4N derived from floc: The activation mechanism for persulfate on degrading organic pollutant. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 455, 140702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Wang, Y.; Wan, J.; Ma, Y.; Chi, H.; Xu, Y.; Qiu, S. Facile construction of highly reactive and stable defective iron-based metal organic frameworks for efficient degradation of Tetrabromobisphenol A via persulfate activation. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Guo, Z.; Song, Y. Recent advance of Fe-based bimetallic persulfate activation catalysts for antibiotics removal: Performance, mechanism, contribution of the key ROSs and degradation pathways. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 487, 150514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Yao, D.; Cao, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, H.; Yuan, Q.; Yi, B. Preparation and formation mechanism of biomass-based graphite carbon catalyzed by iron nitrate under a low-temperature condition. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 318, 115555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Xiong, W.; Yang, Z.; Tong, J.; Jia, M.; Xiang, Y.; Sun, S.; Xu, Z. Fe3O4-supported N-doped carbon channels in wood carbon form etching and carbonization: Boosting performance for persulfate activating. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 457, 141317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jia, Y.; Zhou, M.; Su, X.; Sun, J. High-efficiency degradation of organic pollutants with Fe, N co-doped biochar catalysts via persulfate activation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 397, 122764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, H.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, L. Cu/N co-doped biochar activating PMS for selective degrading paracetamol via a non-radical pathway dominated by singlet oxygen and electron transfer. Chemosphere 2024, 357, 141858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Zhou, H.; Li, W.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Xiong, Y.; He, D.; Chen, L.; Mu, S. In situ derived Fe/N/S-codoped carbon nanotubes from ZIF-8 crystals as efficient electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction and zinc–air batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 20093–20099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, H.; Liu, Y.; Hayat, W.; Wu, X. Efficient degradation of acetaminophen by activated peroxymonosulfate using Mn/C composites: Performance and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 341, 126768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Cai, X.; Zhang, X.; Xie, X. Relying on the non-radical pathways for selective degradation organic pollutants in Fe and Cu co-doped biochar/peroxymonosulfate system: The roles of Cu, Fe, defect sites and ketonic group. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 279, 119697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, P.; Tian, J.; Yang, F.; Duan, X.; Gao, S.; Shi, W.; Luo, X.; Cui, F.; Luo, S.; Wang, S. Identification and Regulation of Active Sites on Nanodiamonds: Establishing a Highly Efficient Catalytic System for Oxidation of Organic Contaminants. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Xu, H.; Wang, L.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, T. Nonradical Oxidation of Pollutants with Single-Atom-Fe(III)-Activated Persulfate: Fe(V) Being the Possible Intermediate Oxidant. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14057–14065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Guo, P.; Huang, Z.; Sun, J.; Lei, Y.; Xu, J. Enhanced stability and conductivity of montmorillonite and sucrose loaded Fe-MOFs for degradation of chlortetracycline hydrochloride via electrochemically activated persulfate. Appl. Clay Sci. 2024, 249, 107231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5749-2006; Standards for Drinking Water Quality. Ministry of Health of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- GB 3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the PRC: Beijing, China, 2002.
- GB/T 14848-2017; Standard for Groundwater Quality. State Bureau of Technical Supervision: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Wang, L.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Huang, S.; Zhou, S. MOFs-derived Mn/C composites activating peroxymonosulfate for efficient degradation of sulfamethazine: Kinetics, pathways, and mechanism. Surf. Interfaces 2023, 36, 102551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussavi, G.; Momeninejad, H.; Shekoohiyan, S.; Baratpour, P. Oxidation of acetaminophen in the contaminated water using UVC/S2O82− process in a cylindrical photoreactor: Efficiency and kinetics of degradation and mineralization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 181, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Gao, P.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, S.; Wang, G.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, S. Insights into the pollutant electron property inducing the transformation of peroxymonosulfate activation mechanisms on manganese dioxide. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 317, 121753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.; He, Z.; Hu, Y.; Liang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y. FeOOH@MoS2 as a highly effective and stable activator of peroxymonosulfate-based advanced oxidation processes for pollutant degradation. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 27, 101465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Luo, H.; Sheng, B.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, J. Cu2+/Cu+ cycle promoted PMS decomposition with the assistance of Mo for the degradation of organic pollutant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 411, 125050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Jiang, M.; Gao, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Boczkaj, G.; Liu, Z.; Ma, J.; Li, Z. 3D mesoporous α-Co(OH)2 nanosheets electrodeposited on nickel foam: A new generation of macroscopic cobalt-based hybrid for peroxymonosulfate activation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Jia, S.; Zhang, Y.; Nian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Han, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ren, H.; Wu, S.; Yao, K.; et al. Catalytic reactivity of Co3O4 with different facets in the hydrogen abstraction of phenol by persulfate. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 270, 118819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wu, P.; Liu, J.; Chen, M.; Ahmed, Z.; Zhu, N. Efficient removal of bisphenol A by superoxide radical and singlet oxygen generated from peroxymonosulfate activated with Fe0-montmorillonite. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 350, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, E.-T.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.; Park, H.-D.; Lee, J. Identifying the Nonradical Mechanism in the Peroxymonosulfate Activation Process: Singlet Oxygenation Versus Mediated Electron Transfer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7032–7042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Ren, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhang, W.; Shan, C.; Hua, M.; Lv, L.; Pan, B. The nature and catalytic reactivity of UiO-66 supported Fe3O4 nanoparticles provide new insights into Fe-Zr dual active centers in Fenton-like reactions. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 286, 119943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tian, J.; Xiao, F.; Huang, R.; Gao, S.; Cui, F.; Wang, S.; Duan, X. Structure-dependent catalysis of cuprous oxides in peroxymonosulfate activation via nonradical pathway with a high oxidation capacity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.-C.E.; Zhu, M.-P.; Duan, X.; Wang, S.; Yuan, B.; Fu, M.-L. The mechanistic difference of 1T-2H MoS2 homojunctions in persulfates activation: Structure-dependent oxidation pathways. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 297, 120460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Tang, L.; Pang, Y.; Zeng, G.; Feng, H.; Zou, J.; Wang, J.; Feng, C.; Zhu, X.; Ouyang, X.; et al. Hierarchical porous biochar from shrimp shell for persulfate activation: A two-electron transfer path and key impact factors. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 260, 118160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, W.; Chen, Y.; Jia, C.Q. Single-atom Co-N3 sites induce peroxymonosulfate activation for acetaminophen degradation via nearly 100% internal electron transfer process. Appl. Catal. B Environ. Energy 2025, 366, 125038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yang, W. Adsorption and catalysis of peroxymonosulfate on carbocatalysts for phenol degradation: The role of pyrrolic-nitrogen. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 319, 121891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, C.; Miao, F.; Zhang, H.; Luo, X.; Wang, S.; Duan, X. Electro-Induced Carbon Nanotube Discrete Electrodes for Sustainable Persulfate Activation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 14019–14029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, S.; Guan, Z.; Xia, D.; Yang, F.; Xu, H.; Huang, M.; Li, D. Polarized heterogeneous CuO-CN for peroxymonosulfate nonradical activation: An enhancement mechanism of mediated electron transfer. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 127619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.Z.; Zhang, H. Direct Electron-Transfer-Based Peroxymonosulfate Activation by Iron-Doped Manganese Oxide (δ-MnO2) and the Development of Galvanic Oxidation Processes (GOPs). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12610–12620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Nie, C.; Wang, X.; Ye, H.; Li, D.; Ao, Z. Alkaline lignin-derived N-doped biochars as peroxymonosulfate activators for acetaminophen degradation: Performance and catalytic bridging mediated Electron-Transfer mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 323, 124418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Ren, W.; Wang, C.; Fan, Y.; Deng, B.; Lin, H.; Zhang, H. Peroxymonosulfate activated with waste battery-based Mn-Fe oxides for pollutant removal: Electron transfer mechanism, selective oxidation and LFER analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 394, 124864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wu, T.; Yang, C.; Ma, C.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, Z.; Cao, S.; Geng, W.; Wang, Y.; Yao, Y.; et al. Activity Trends and Mechanisms in Peroxymonosulfate-Assisted Catalytic Production of Singlet Oxygen over Atomic Metal-N-C Catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 22513–22521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Lyu, L.; Zeng, Q.; Xing, X.; Hu, C. Electronic Structure Modulation of Graphitic Carbon Nitride by Oxygen Doping for Enhanced Catalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants through Peroxymonosulfate Activation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 14371–14380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Lai, C.; Liu, S.; Li, B.; Qin, L.; Liu, X.; Yi, H.; Fu, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, M.; et al. Activation of persulfate by swine bone derived biochar: Insight into the specific role of different active sites and the toxicity of acetaminophen degradation pathways. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 151059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ye, Q.; Gan, J. Degradation and transformation products of acetaminophen in soil. Water Res. 2014, 49, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematollahi, D.; Shayani-Jam, H.; Alimoradi, M.; Niroomand, S. Electrochemical oxidation of acetaminophen in aqueous solutions: Kinetic evaluation of hydrolysis, hydroxylation and dimerization processes. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 7407–7415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvandi, M.; Nourmoradi, H.; Nikoonahad, A.; Aghayani, E.; Abbas Mirzaee, S. LED visible light assisted photo-oxidation of acetaminophen using one-step synthesis of Cu,Fe@g-C3N4 nanosheet—Activated persulfate system in aqueous solutions. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 105251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, S.-N.; Ren, H.-Y.; Cao, G.-L.; Xie, G.-J.; Xing, D.-F.; Ren, N.-Q.; Liu, B.-F. Highly efficient activation of persulfate by encapsulated nano-Fe0 biochar for acetaminophen degradation: Rich electron environment and dominant effect of superoxide radical. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 440, 135947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Hao, X.; Sun, X.; Du, P.; Liu, W.; Fu, J. Highly active WO3@anatase-SiO2 aerogel for solar-light-driven phenanthrene degradation: Mechanism insight and toxicity assessment. Water Res. 2019, 162, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Duan, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Li, B. Efficient diclofenac removal by superoxide radical and singlet oxygen generated in surface Mn(II)/(III)/(IV) cycle dominated peroxymonosulfate activation system: Mechanism and product toxicity. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 133742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Dai, B.; Shen, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gan, L. Wood induced preparation of Fe3C decorated biochar for peroxymonosulfate activation towards bisphenol a degradation with low ion leaching. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 340, 117978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, S.A.; Najafi, H.; Asasian-Kolur, N.; Ebrahimian Pirbazari, A.; Sharifian, S. The efficiency of a granular Fe-based metal-organic framework for the persulfate oxidative degradation of levofloxacin, an emerging antibiotic in wastewater. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 405, 125119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Bin, Q.; Shen, Y.; Huang, J.; He, D.; Chen, W. In-situ formed N-doped bamboo-like carbon nanotubes encapsulated with Fe nanoparticles supported by biochar as highly efficient catalyst for activation of persulfate (PS) toward degradation of organic pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 402, 126090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, J.; Zeng, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Sun, Y.; Fan, G. Enhanced activation of persulfate by bimetal and nitrogen co-doped biochar for efficient degradation of refractory organic contaminants: The role of the second metal. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2024, 193, 112191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Duan, X.; Shang, Y.; Gao, B.; Xu, X. Engineered carbon supported single iron atom sites and iron clusters from Fe-rich Enteromorpha for Fenton-like reactions via nonradical pathways. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 287, 119963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; He, C.; Pang, J.; Zhang, L.; Tang, F.; Yang, X. Recognizing the relevance of non-radical peroxymonosulfate activation by co-doped Fe metal-organic framework for the high-efficient degradation of acetaminophen: Role of singlet oxygen and the enhancement of redox cycle. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499, 156081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liang, Q.; Xing, Y.; Sun, M.; Luo, H. Magnetic Fe/N-codoped carbon derived from modified Fe-base MOFs: Synergism of multiple active sites for peroxymonosulfate activation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ma, T.; Shang, Y.; Gao, B.; Jin, B.; Dan, H.; Li, Q.; Yue, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. In-situ pyrolysis of Enteromorpha as carbocatalyst for catalytic removal of organic contaminants: Considering the intrinsic N/Fe in Enteromorpha and non-radical reaction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 250, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).