Template–Free–Induced Synthesis of an Fe–N–C Electrocatalyst with Porous Yolk–Shell Structure Towards Oxygen Reduction Reaction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
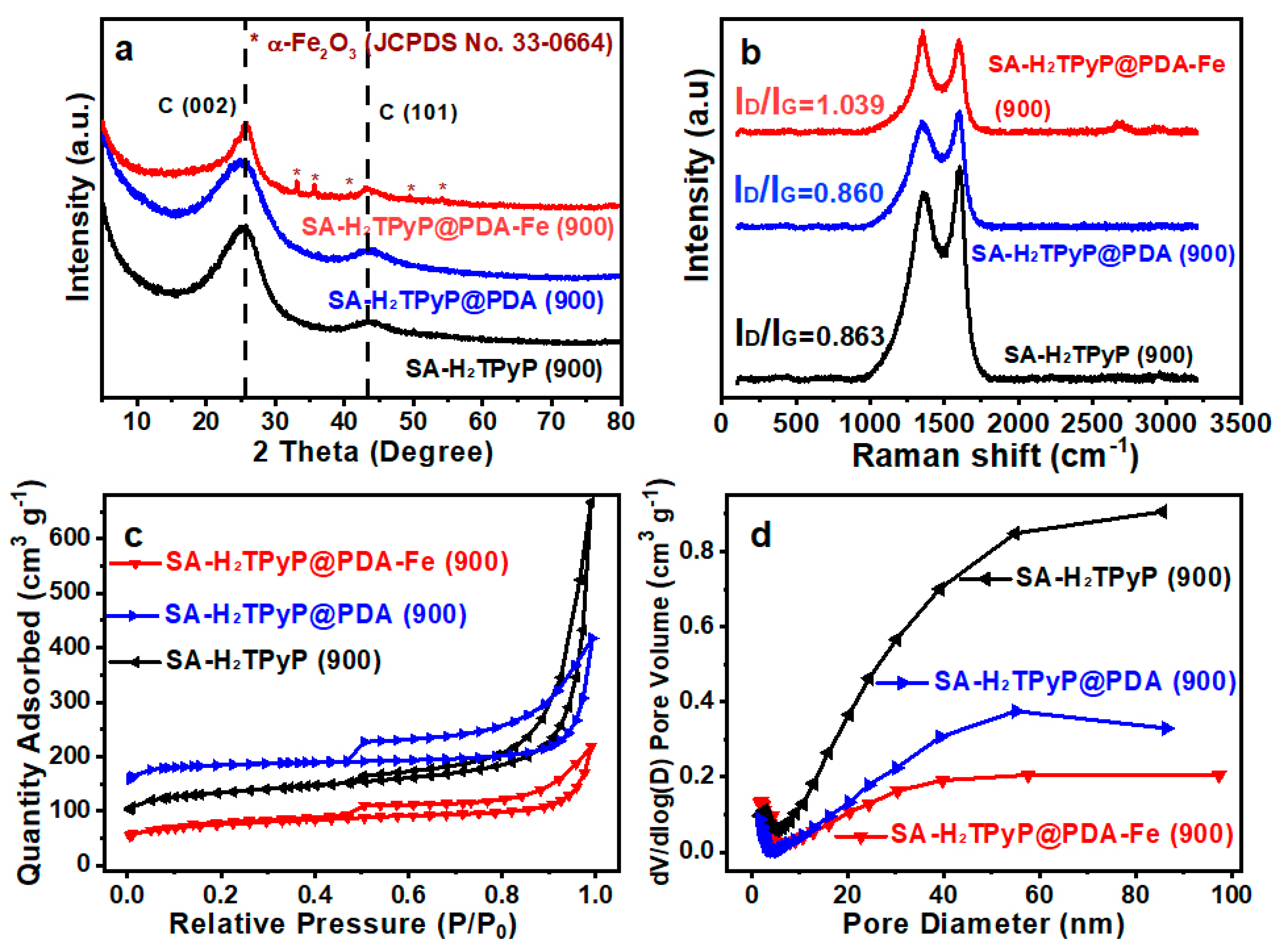
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Synthesis of SA–H2TPyP
3.3. Synthesis of SA–H2TPyP@PDA
3.4. Synthesis of SA–H2TPyP@PDA–Fe (900)
3.5. Characterization
3.6. Electrochemical Measurements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, P.; Liu, B.; Tu, F.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Ma, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Z. Breaking Sabatier’s vertex via switching the oxygen adsorption configuration and reaction pathway on dual active sites for acidic oxygen reduction. Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 3077–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, F.; Wang, L. Joule heating synthesis for single-atomic Fe sites on porous carbon spheres and armchair–type edge defect engineering dominated oxygen reduction reaction performance. Appl. Catal. B–Environ. Energy 2025, 361, 124673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Zhao, T.; Wu, X.; Gao, X.; Huang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Li, P.; Guan, X.; Chen, C.; Liu, X.; et al. Strengthening the oxygen reduction stability and activity of single iron active sites via a simultaneously electronic regulation and structure design strategy. Appl. Catal. B–Environ. Energy 2024, 357, 124254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, H.-C.; Zhu, H.; Chen, K.; Li, T.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Hu, R.; Huang, S.; Zhu, W. Inter–site structural heterogeneity induction of single atom Fe catalysts for robust oxygen reduction. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Li, H.; Fu, S.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Highly efficient nonprecious metal catalysts towards oxygen reduction reaction based on three–dimensional porous carbon nanostructures. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Zhou, R.F.; Chen, X.M.; Tang, Y.H.; Qiao, S.Z. Fe–N decorated hybrids of CNTs grown on hierarchically porous carbon for high–performance oxygen reduction. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6074–6079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Liao, Z.; Yang, W.; Zhou, H.; Fu, C.; Gong, Y.; Chen, L.; Kuang, Y. Different types of nitrogen species in nitrogen–doped carbon material: The formation mechanism and catalytic role on oxygen reduction reaction. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 245, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Shibuya, R.; Akiba, C.; Saji, S.; Kondo, T.; Nakamura, J. Active sites of nitrogen–doped carbon materials for oxygen reduction reaction clarified using model catalysts. Science 2016, 351, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Tian, Z.; Wang, W.; Deng, X.; Tseng, J.-C.; Wang, G. Size–dependent activity of Fe–N–doped mesoporous carbon nanoparticles towards oxygen reduction reaction. Green Carbon 2024, 2, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.-W.; Wei, W.; Wu, Z.-S.; Feng, X.; Müllen, K. Mesoporous metal–nitrogen–doped carbon electrocatalysts for highly efficient oxygen reduction reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16002–16005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeano, C.; Baldizzone, C.; Bongard, H.; Spliethoff, B.; Weidenthaler, C.; Meier, J.C.; Mayrhofer, K.J.; Schüth, F. Carbon–based yolk-shell materials for fuel cell applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhou, R.; Wang, D.-W.; Jiang, S.P.; Yamauchi, Y.; Qiao, S.Z.; Monteiro, M.J.; Liu, J. Hierarchical mesoporous yolk–shell structured carbonaceous nanospheres for high performance electrochemical capacitive energy storage. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 2518–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Zeng, M.; Luo, R.; Shen, J.; Sun, X.; Han, W.; Wang, L. Synthesis of N–doped hollow–structured mesoporous carbon nanospheres for high–performance supercapacitors. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2016, 8, 7194–7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Feng, S.; Song, Y.; Li, W.; Gao, W.; Elzatahry, A.A.; Aldhayan, D.; Xia, Y.; Zhao, D. Synthesis of hierarchically porous carbon spheres with yolk–shell structure for high performance supercapacitors. Catal. Today 2015, 243, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yan, T.; Shi, L.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D. Creating nitrogen–doped hollow multiyolk@shell carbon as high performance electrodes for flow–through deionization capacitors. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 3329–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, S.; Cui, Q.; Wang, K.; Bai, Z.; Yang, L.; Qiao, J. Template–free synthesis of hierarchical yolk–shell Co and N codoped porous carbon microspheres with enhanced performance for oxygen reduction reaction. J. Power Sources 2015, 288, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Zhang, W. Synthesis, self-assembly and applications of functional polymers based on porphyrins. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 95, 65–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, P.; Dong, H.; Zhen, Y.; Liu, M.; Hu, W. Porphyrin supramolecular 1D structures via surfactant-assisted self-assembly. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 5379–5387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Chen, P.; Liu, M. Evolution of various porphyrin nanostructures via an oil/aqueous medium: Controlled self–assembly, further organization, and supramolecular chirality. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 9644–9652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Medforth, C.J.; Shelnutt, J.A. Porphyrin nanotubes by ionic self–assembly. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 15954–15955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Lv, Y.; Li, J.; Hao, Z.; Tang, C.; Wei, X.; Su, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, A. Interwoven molecular chains obtained by ionic self–assembly of two iron (III) porphyrins with opposite and mismatched charges. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 34203–34211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Tang, C.; Hao, Z.; Lv, Y.; Yang, R.; Wei, X.; Deng, W.; Wang, A.; Yi, B.; Song, Y. Carbonization of self–assembled nanoporous hemin with a significantly enhanced activity for the oxygen reduction reaction. Faraday Discuss. 2014, 176, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Xie, Y.; Huang, J. Highly effective dual transition metal macrocycle based electrocatalyst with macro–/mesoporous structures for oxygen reduction reaction. Catalysts 2017, 7, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Rong, F.; Yao, Y.; Fan, W.; Li, M.; Yang, Q. Co NP/NC hollow nanoparticles derived from yolk–shell structured ZIFs@polydopamine as bifunctional electrocatalysts for water oxidation and oxygen reduction reactions. J. Energy Chem. 2018, 27, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, X.; Noonan, O.; Zhou, L.; Yu, C. Tailored yolk-shell Sn@C nanoboxes for high–performance lithium storage. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1606023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Yu, L.; Yang, B.; Li, C.; Fang, C.; Guo, W.; Xiao, F.X.; Lin, Y. Fe–N–C core–shell catalysts with single low-spin Fe(II)–N4 species for oxygen reduction reaction and high–performance proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Energy Chem. 2024, 93, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Bao, H.; Wang, J.-Q.; Zheng, L.; Sun, S.; Wang, Z.L.; Sun, C. 3D N–doped ordered mesoporous carbon supported single-atom Fe–N–C catalysts with superior performance for oxygen reduction reaction and zinc-air battery. Appl. Catal. B–Environ. 2021, 280, 119411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhakemy, A.Z.; Wang, G.; Chen, K.; Hassan, A.E.; Wen, Z. Boosting Zn–air battery performance: Fe single–atom anchored on F, N co–doped carbon nanosheets for efficient oxygen reduction. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1010, 177166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Liang, J.; Yi, J.-D.; Shi, P.-C.; Huang, Y.-B.; Cao, R. Porous nitrogen/halogen dual–doped nanocarbons derived from imidazolium functionalized cationic metal–organic frameworks for highly efficient oxygen reduction reaction. Sci. China Mater. 2019, 62, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Gu, J.; Zheng, X.; Liu, M.; Qiu, X.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Chen, Z.; Ji, X.; Li, J. Defect–rich and ultrathin N doped carbon nanosheets as advanced trifunctional metal-free electrocatalysts for the ORR, OER and HER. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhao, H.; Yan, G.; Huang, G.; Ge, C.; Forsyth, M.; Howlett, P.C.; Wang, X.; Fang, J. Ternary heteroatomic doping induced microenvironment engineering of low Fe–N4–loaded carbon nanofibers for bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysis. Small 2024, 20, 2304844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Xie, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, G. The promotional effect of multiple active sites on Fe–based oxygen reduction electrocatalysts for a zinc–air battery. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 26573–26579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Song, Y.; Zhang, G.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Guo, X. Pyrolysis of self–assembled iron porphyrin on carbon black as core/shell structured electrocatalysts for highly efficient oxygen reduction in both alkaline and acidic medium. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1604356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Jin, X.; Tong, L.; Xu, R.; Kong, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Engineering CoN4 and FeN4 dual sites with adjacent nanoclusters on flexible porous carbon fibers for enhanced electrocatalytic oxygen reduction and evolution. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 2418489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, V.; Nsanzimana, J.M.V.; Hu, H.; Choi, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, J.-M. Highly efficient oxygen reduction reaction activity of N–doped carbon–cobalt boride heterointerfaces. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2100157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramm, U.I.; Herrmann–Geppert, I.; Behrends, J.; Lips, K.; Fiechter, S.; Bogdanoff, P. On an easy way to prepare metal–nitrogen doped carbon with exclusive presence of MeN4–type sites active for the ORR. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2016, 138, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa, Y.J.; Seo, D.-J.; Woo, J.; Lim, J.T.; Cheon, J.Y.; Yang, S.Y.; Lee, J.M.; Kang, D.; Shin, T.J.; Shin, H.S. A general approach to preferential formation of active Fe–Nx sites in Fe–N/C electrocatalysts for efficient oxygen reduction reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 15046–15056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; More, K.L.; Johnston, C.M.; Zelenay, P. High-performance electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction derived from polyaniline, iron, and cobalt. Science 2011, 332, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Muthukrishnan, A.; Nagata, S.; Nabae, Y. Tafel slope analysis from inherent rate constants for oxygen reduction reaction over N–doped carbon and Fe-N-doped carbon electrocatalysts. Catal. Surv. Asia 2023, 27, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, P.; Wan, Y.; Wang, D.; Xu, H.; Liu, L.; Xiao, L.; Li, R.; Wang, G.; et al. Atomically dispersed Fe–N–C catalyst with densely exposed Fe-N4 active sites for enhanced oxygen reduction reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 485, 149529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa, Y.J.; Park, C.; Jeong, H.Y.; Park, S.H.; Lee, Z.; Kim, K.T.; Park, G.-G.; Joo, S.H. Carbon nanotubes/heteroatom-doped carbon core–sheath nanostructures as highly active, metal-free oxygen reduction electrocatalysts for alkaline fuel cells. Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 4186–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Sun, F.; Xiang, Z.; Shen, Z.; Yun, J.; Cao, D. ZIF-derived in situ nitrogen-doped porous carbons as efficient metal-free electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 7, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, A.-W. Noble-Metal-Free Fe–N/C Catalyst for Highly Efficient Oxygen Reduction Reaction under Both Alkaline and Acidic Conditions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 11027–11033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.-H.; Xu, B.-Q. Mesoporous carbon material co-doped with nitrogen and iron (Fe–N–C): High-performance cathode catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction in alkaline electrolyte. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 8617–8622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, A.; Zhu, X.; Han, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, B.; Shan, Y. Ordered Hierarchically Micro- and Mesoporous Fe–Nx-Embedded Graphitic Architectures as Efficient Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 1793–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Zhu, J.; Feng, L.; Liu, C.; Xing, W. Meso/Macroporous Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Architectures with Iron Carbide Encapsulated in Graphitic Layers as an Efficient and Robust Catalyst for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Both Acidic and Alkaline Solutions. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2521–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Zou, R.; An, L.; Xia, D.; Guo, S. A metal–organic framework route to in situ encapsulation of Co@Co3O4@C core@ bishell nanoparticles into a highly ordered porous carbon matrix for oxygen reduction. Energ Environ Sci. 2015, 8, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wen, Z.; Cui, S.; Ci, S.; Mao, S.; Chen, J. An Advanced Nitrogen-Doped Graphene/Cobalt-Embedded Porous Carbon Polyhedron Hybrid for Efficient Catalysis of Oxygen Reduction and Water Splitting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 25, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, B.Y.; Yan, Y.; Li, N.; Wu, H.B.; Lou, X.W.; Wang, X. A metal–organic framework-derived bifunctional oxygen electrocatalyst. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 15006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Zhou, J.; Leung, M.K.H. Bubble-like Fe-encapsulated N,S-codoped carbon nanofibers as efficient bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysts for robust Zn-air batteries. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 2175–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyasato, S.M. Early Microstructural Evolution and Deformation Behavior in Solution Heat Treated Aluminum-Lithium Alloys; University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, B.; Zhao, Y.; Du, X.; Li, D.; Ding, S.; Li, Y.; Xiao, C.; Song, Z. Electron injection induced phase transition of 2H to 1T MoS2 by cobalt and nickel substitutional doping. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 411, 128567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibraheem, S.; Yasin, G.; Kumar, A.; Mushtaq, M.A.; Ibrahim, S.; Iqbal, R.; Tabish, M.; Ali, S.; Saad, A. Iron-cation-coordinated cobalt-bridged-selenides nanorods for highly efficient photo/electrochemical water splitting. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 304, 120987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample | SBET (m2 g−1) | Smic (m2 g−1) | Vt (cm3 g−1) | Dave (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA–H2TPyP@PDA–Fe (900) | 241 | 110 | 0.34 | 5.60 |
| SA–H2TPyP@PDA (900) | 542 | 460 | 0.65 | 4.76 |
| SA–H2TPyP (900) | 408 | 236 | 1.03 | 10.11 |
| Site | δiso (mm s−1) a | ΔEQ (mm s−1) b | Assignment | Relative Absorption Area | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sing | −0.22 | - | Superparamagnetic Fe | 8.18% | [36,37] |
| D1 | 0.21 | 3.91 | Low–spin, FeII–N4 | 7.53% | |
| D2 | 0.37 | 2.67 | Intermediate–spin porph–type FeII–N4 | 19.09% | |
| D3 | 0.44 | 1.07 | Intermediate–spin Pc–type FeII–N4 | 47.32% | |
| Sext | 0.39 | −0.18 | α–Fe2O3 | 17.87% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Chen, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Xu, L.; Xie, Y. Template–Free–Induced Synthesis of an Fe–N–C Electrocatalyst with Porous Yolk–Shell Structure Towards Oxygen Reduction Reaction. Catalysts 2025, 15, 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15040384
Wang L, Chen L, Li Z, Zhang S, Wang H, Xu L, Xie Y. Template–Free–Induced Synthesis of an Fe–N–C Electrocatalyst with Porous Yolk–Shell Structure Towards Oxygen Reduction Reaction. Catalysts. 2025; 15(4):384. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15040384
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lili, Li Chen, Zhiwen Li, Shaohua Zhang, Hezhen Wang, Ling Xu, and Yan Xie. 2025. "Template–Free–Induced Synthesis of an Fe–N–C Electrocatalyst with Porous Yolk–Shell Structure Towards Oxygen Reduction Reaction" Catalysts 15, no. 4: 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15040384
APA StyleWang, L., Chen, L., Li, Z., Zhang, S., Wang, H., Xu, L., & Xie, Y. (2025). Template–Free–Induced Synthesis of an Fe–N–C Electrocatalyst with Porous Yolk–Shell Structure Towards Oxygen Reduction Reaction. Catalysts, 15(4), 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15040384







