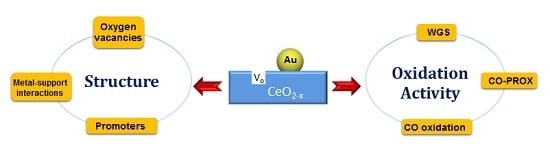
Au/CeO2 Catalysts: Structure and CO Oxidation Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Preparation of Au/CeO2 Catalysts
3. Characterization of Au/CeO2 Catalysts Involved in Oxidation Reactions
4. Au/CeO2 Catalysts: Structure and Oxidation Activity
4.1. Oxidation Reactions Catalyzed by Au/CeO2
4.2. CO Oxidation
4.3. WGS
4.4. Preferential CO Oxidation (CO–PROX)
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raub, J.A.; Mathieu-Nolf, M.; Hampson, N.B.; Thom, S.R. Carbon monoxide poisoning—A public health perspective. Toxicology 2000, 145, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royer, S.; Duprez, D. Catalytic oxidation of carbon monoxide over transition metal oxides. ChemCatChem 2011, 3, 24–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruta, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Sano, H.; Yamada, N. Novel gold catalysts for the oxidation of carbon-monoxide at a temperature far below 0. DEG. C. Chem. Lett. 1987, 16, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, G.C.; Thompson, D.T. Gold-catalysed oxidation of carbon monoxide. Gold Bull. 2000, 33, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruta, M. Catalysis of gold nanoparticles deposited on metal oxides. Cattech 2002, 6, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.S.; Goodman, D.W. Structure-activity relationships in supported Au catalysts. Catal. Today 2006, 111, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A.; García, H. Supported gold nanoparticles as oxidation catalysts. In Nanoparticles and Catalysis; Astruc, D., Ed.; Willey-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; pp. 389–429. [Google Scholar]
- Corti, C.W.; Holliday, R.J.; Thompson, D.T. Progress towards the commercial application of gold catalysts. Top. Catal. 2007, 44, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortie, M.; Laguna, A.; Thompson, D. Gold 2006 highlights of 4th international conference on the science, technology and industrial applications of gold. Gold Bull. 2006, 39, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimm, D.L. Minimisation of carbon monoxide in a hydrogen stream for fuel cell application. Appl. Catal. A 2005, 296, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguna, O.H.; Pérez, A.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A. Synergy between gold and oxygen vacancies in gold supported on Zr-doped ceria catalysts for the CO oxidation. Appl. Catal. B 2015, 177, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Sarria, F.; Plata, J.J.; Laguna, O.H.; Márquez, A.M.; Centeno, M.A.; Sanz, J.F.; Odriozola, J.A. Surface oxygen vacancies in gold based catalysts for CO oxidation. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 13145–13152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milt, V.G.; Ivanova, S.; Sanz, O.; Dominguez, M.I.; Corrales, A.; Odriozola, J.A.; Centeno, M.A. Au/TiO2 supported on ferritic stainless steel monoliths as CO oxidation catalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 270, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, T.R.; Moreno, A.A.; Ivanova, S.; Odriozola, J.A.; Centeno, M.A. Influence of vanadium or cobalt oxides on the CO oxidation behavior of Au/MOx/CeO2–Al2O3 systems. ChemCatChem 2012, 4, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, T.R.; Ivanova, S.; Domínguez, M.I.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A. Sub-ambient CO oxidation over Au/MOx/CeO2–Al2O3 (M = Zn or Fe). Appl. Catal. A 2012, 420, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Sarria, F.; Dominguez, M.I.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A. CO oxidation at low temperature on Au/CePO4: Mechanistic aspects. Appl. Catal. B 2011, 107, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguna, O.H.; Centeno, M.A.; Romero-Sarria, F.; Odriozola, J.A. Oxidation of CO over gold supported on Zn-modified ceria catalysts. Catal. Today 2011, 172, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plata, J.J.; Marquez, A.M.; Sanz, J.F.; Avellaneda, R.S.; Romero-Sarria, F.; Dominguez, M.I.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A. Gold nanoparticles on yttrium modified titania: Support properties and catalytic activity. Top. Catal. 2011, 54, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguna, O.H.; Centeno, M.A.; Arzamendi, G.; Gandía, L.M.; Romero-Sarria, F.; Odriozola, J.A. Iron-modified ceria and Au/ceria catalysts for total and preferential oxidation of CO (TOX and PROX). Catal. Today 2010, 157, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, W.Y.; Romero-Sarria, F.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A. In Situ Characterization of the dynamic gold-support interaction over ceria modified Eu3+. Influence of the oxygen vacancies on the CO oxidation reaction. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 10857–10865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, M.I.; Romero-Sarria, F.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A. Gold/hydroxyapatite catalysts: Synthesis, characterization and catalytic activity to CO oxidation. Appl. Catal. B 2009, 87, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penkova, A.; Chakarova, K.; Laguna, O.H.; Hadjiivanov, K.; Saria, F.R.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A. Redox chemistry of gold in a Au/FeOx/CeO2 CO oxidation catalyst. Catal. Commun. 2009, 10, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Sarria, F.; Penkova, A.; Martinez, T.L.M.; Centeno, M.A.; Hadjiivanov, K.; Odriozola, J.A. Role of water in the CO oxidation reaction on Au/CeO2: Modification of the surface properties. Appl. Catal. B 2008, 84, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centeno, M.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Dominguez, M.I.; Navio, J.A.; Odriozola, J.A. Titania-supported gold catalysts: Comparison between the photochemical phenol oxidation and gaseous CO oxidation performances. Catal. Lett. 2008, 123, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Sarria, F.; Martinez, L.M.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A. Surface dynamics of Au/CeO2 catalysts during CO oxidation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 14469–14475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centeno, M.A.; Hadjiivanov, K.; Venkov, T.; Klimev, H.; Odriozola, J.A. Comparative study of Au/Al2O3 and Au/CeO2–Al2O3 catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A 2006, 252, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centeno, M.A.; Carrizosa, I.; Odriozola, J.A. Deposition-precipitation method to obtain supported gold catalysts: Dependence of the acid-base properties of the support exemplified in the system TiO2–TiOxNy–TiN. Appl. Catal. A 2003, 246, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centeno, M.A.; Portales, C.; Carrizosa, I.; Odriozola, J.A. Gold supported CeO2/Al2O3 catalysts for CO oxidation: Influence of the ceria phase. Catal. Lett. 2005, 102, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, A.S.K.; Hutchings, G.J. Gold catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 7896–7936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, S.; Laguna, O.H.; Centeno, M.A.; Eleta, A.; Montes, M.; Odriozola, J.A. Microprocess technology for hydrogen purification. In Renewable Hydrogen Technologies; Diéguez, P.M., Gandía, L.M., Arzamendi, G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 225–243. [Google Scholar]
- Arzamendi, G.; Diéguez, P.M.; Montes, M.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A.; Gandía, L.M. Integration of methanol steam reforming and combustion in a microchannel reactor for H2 production: A CFD simulation study. Catal. Today 2009, 143, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burch, R. Gold catalysts for pure hydrogen production in the water-gas shift reaction: Activity, structure and reaction mechanism. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 5483–5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnasamy, C.; Wagner, J.P. Water gas shift catalysis. Catal. Rev. Sci. Eng. 2009, 51, 325–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Saltsburg, H.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Active nonmetallic Au and Pt species on ceria-based water-gas shift catalysts. Science 2003, 301, 935–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, S.-I.; Takezawa, N. Difference in the selectivity of CO and CO2 methanation reactions. Chem. Eng. J. 1997, 68, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golunski, S. HotSpot™ fuel processor. Platin. Met. Rev. 1998, 42, 2–7. [Google Scholar]
- Avgouropoulos, G.; Ioannides, T. Selective CO oxidation over CuO–CeO2 catalysts prepared via the urea–nitrate combustion method. Appl. Catal. A 2003, 244, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, T.V.; Goodman, D.W. CO-free fuel processing for fuel cell applications. Catal. Today 2002, 77, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shodiya, T.; Schmidt, O.; Peng, W.; Hotz, N. Novel nano-scale Au/α-Fe2O3 catalyst for the preferential oxidation of CO in biofuel reformate gas. J. Catal. 2013, 300, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisel, R.; Weststrate, K.J.; Gluhoi, A.; Nieuwenhuys, B.E. Catalysis by gold nanoparticles. Gold Bull. 2002, 35, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisel, R.J.H.; Nieuwenhuys, B.E. Selective oxidation of CO, over supported Au catalysts. J. Catal. 2001, 199, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruta, M.; Tsubota, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Kageyama, H.; Genet, M.J.; Delmon, B. Low-temperature oxidation of CO over gold supported on TiO2, α-Fe2O3, and Co3O4. J. Catal. 1993, 144, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, R.M.T.; Ueda, A.; Tanaka, K.; Haruta, M. Selective oxidation of CO in hydrogen over gold supported on manganese oxides. J. Catal. 1997, 168, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, W.Y.; Centeno, M.A.; Romero-Sarria, F.; Ivanova, S.; Montes, M.; Odriozola, J.A. Modified cryptomelane-type manganese dioxide nanomaterials for preferential oxidation of CO in the presence of hydrogen. Catal. Today 2010, 157, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreeva, D.; Idakiev, V.; Tabakova, T.; Andreev, A.; Giovanoli, R. Low-temperature water-gas shift reaction on Auα-Fe2O3 catalyst. Appl. Catal. A 1996, 134, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, H.; Qin, Z.; Liang, F.; Wang, G.; Wang, J. Deactivation of a Au/CeO2–Co3O4 catalyst during CO preferential oxidation in H2-rich stream. J. Catal. 2009, 264, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovarelli, A. Catalytic properties of ceria and CeO2-containing materials. Catal. Rev. Sci. Eng. 1996, 38, 439–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovarelli, A. Structural properties and nonstoichiometric behavior of CeO2. In Catalysis by Ceria and Related Materials; Trovarelli, A., Ed.; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2002; pp. 15–50. [Google Scholar]
- Aneggi, E.; Boaro, M.; Leitenburg, C.D.; Dolcetti, G.; Trovarelli, A. Insights into the dynamics of oxygen storage/release phenomena in model ceria–zirconia catalysts as inferred from transient studies using H2, CO and soot as reductants. Catal. Today 2006, 112, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, A.A.; Fisher, J.M.; Ozkaya, D.; Shannon, M.D.; Thompsett, D. Ceria-zirconia supported Au as highly active low temperature water-gas shift catalysts. Top. Catal. 2007, 44, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguna, O.H.; Sarria, F.R.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A. Gold supported on metal-doped ceria catalysts (M = Zr, Zn and Fe) for the preferential oxidation of CO (PROX). J. Catal. 2010, 276, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.Z.; Chen, X.; Fang, J.; Jiang, Z.Q.; Huang, W.X. Structure-activity relation of Fe2O3–CeO2 composite catalysts in CO oxidation. Catal. Lett. 2008, 125, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguna, O.H.; Centeno, M.A.; Boutonnet, M.; Odriozola, J.A. Fe-doped ceria solids synthesized by the microemulsion method for CO oxidation reactions. Appl. Catal. B 2011, 106, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Zied, B.M.; Soliman, S.A. Thermal decomposition of praseodymium acetate as a precursor of praseodymium oxide catalyst. Thermochim. Acta 2008, 470, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno-López, A.; Krishna, K.; Makkee, M.; Moulijn, J.A. Enhanced soot oxidation by lattice oxygen via La3+-doped CeO2. J. Catal. 2005, 230, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, W.Y.; Laguna, O.H.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A. Structural and catalytic properties of lanthanide (La, Eu, Gd) doped ceria. J. Solid State Chem. 2011, 184, 3014–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, W.Y.; Centeno, M.A.; Romero-Sarria, F.; Odriozola, J.A. Synthesis and Characterization of Ce1−xEuxO2−x/2 Mixed Oxides and Their Catalytic Activities for CO Oxidation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 5629–5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Lu, G. High performance rare earth oxides LnOx (Ln = La, Ce, Nd, Sm and Dy)-modified Pt/SiO2 catalysts for CO oxidation in the presence of H2. J. Power Sources 2008, 181, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellings, P.J.; Bouwmeester, H.J.M. Ion and mixed conducting oxides as catalysts. Catal. Today 1992, 12, 1–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, G.C.; Louis, C.; Thompson, D.T. Catalysis by gold. In Catalytic Science Series; Hutchings, G.J., Ed.; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2006; pp. 180–182. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Dai, S. Heterogeneous Gold Catalysts and Catalysis; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Corma, A.; Garcia, H. Supported gold nanoparticles as catalysts for organic reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 2096–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corma, A. Attempts to fill the gap between enzymatic, homogeneous, and heterogeneous catalysis. Catal. Rev. Sci. Eng. 2004, 46, 369–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, G.C.; Thompson, D.T. Catalysis by gold. Catal. Rev. Sci. Eng. 1999, 41, 319–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, T.; Rooke, J.C.; Genty, E.; Cousin, R.; Siffert, S.; Su, B.-L. Gold catalysts in environmental remediation and water-gas shift technologies. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 371–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruta, M. Gold as a novel catalyst in the 21st century: Preparation, working mechanism and applications. Gold Bull. 2004, 37, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyman, R. Gold nanoparticles a renaissance in gold chemistry. Gold Bull. 1996, 29, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Ma, Z. Water-gas shift on gold catalysts: Catalyst systems and fundamental studies. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 15260–15270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchings, G.J. Catalysis: A golden future. Gold Bull. 1996, 29, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruta, M. Size- and support-dependency in the catalysis of gold. Catal. Today 1997, 36, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruta, M.; Date, M. Advances in the catalysis of Au nanoparticles. Appl. Catal. A 2001, 222, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, G.J. Gold catalysis in chemical processing. Catal. Today 2002, 72, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.T. Perspective on industrial and scientific aspects of gold catalysis. Appl. Catal. A 2003, 243, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, D.; Holliday, R.; Thompson, D. Gold’s future role in fuel cell systems. J. Power Sources 2003, 118, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corti, C.W.; Holliday, R.J.; Thompson, D.T. Commercial aspects of gold catalysis. Appl. Catal. A 2005, 291, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, G.J. Catalysis by gold. Catal. Today 2005, 100, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, G.C.; Thompson, D.T. Status of catalysis by gold following an AURICAT Workshop. Appl. Catal. A 2006, 302, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scirè, S.; Liotta, L.F. Supported gold catalysts for the total oxidation of volatile organic compounds. Appl. Catal. B 2012, 125, 222–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Goodman, D.W. Catalytically active gold: From nanoparticles to ultrathin films. Acc. Chem. Res. 2006, 39, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorin, D.J.; Toste, F.D. Relativistic effects in homogeneous gold catalysis. Nature 2007, 446, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, G.L.; Kang, E.J.; Mba, M.; Toste, F.D. A powerful chiral counterion strategy for asymmetric transition metal catalysis. Science 2007, 317, 496–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haruta, A. When gold is not noble: Catalysis by nanoparticles. Chem. Rec. 2003, 3, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashmi, A.S.K. Homogeneous catalysis by gold. Gold Bull. 2004, 37, 51–65. [Google Scholar]
- Hashmi, A.S.K. The catalysis gold rush: New claims. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 6990–6993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchings, G.J.; Carrettin, S.; Landon, P.; Edwards, J.K.; Enache, D.; Knight, D.W.; Xu, Y.-J.; Carley, A.F. New approaches to designing selective oxidation catalysts: Au/C a versatile catalyst. Top. Catal. 2006, 38, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, M.C.; Davis, R.J.; Kung, H.H. Understanding Au-catalyzed low-temperature CO oxidation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 11767–11775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liotta, L.F. New frontiers in gold catalyzed reactions. Catalysts 2012, 2, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaylov, M.; Knoezinger, H.; Hadjiivanov, K.; Gates, B.C. Characterization of the oxidation states of supported gold species by IR spectroscopy of adsorbed CO. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2007, 79, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattrick, G.; van der Lingen, E.; Corti, C.W.; Holliday, R.J.; Thompson, D.T. The potential for use of gold in automotive pollution control technologies: A short review. Top. Catal. 2004, 1, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D. New advances in gold catalysis part I. Gold Bull. 1998, 31, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.T. Catalysis by gold/platinum group metals. Mixed metal systems displaying increased activity. Platin. Met. Rev. 2004, 48, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.T. An overview of gold-catalysed oxidation processes. Top. Catal. 2006, 38, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.T. Using gold nanoparticles for catalysis. Nano Today 2007, 2, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Kudriavtseva, S.; Saltsburg, H.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Gold–ceria catalysts for low-temperature water-gas shift reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 2003, 93, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabakova, T.; Boccuzzi, F.; Manzoli, M.; Sobczak, J.W.; Idakiev, V.; Andreeva, D. Effect of synthesis procedure on the low-temperature WGS activity of Au/ceria catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 2004, 49, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanella, R.; Giorgio, S.; Henry, C.R.; Louis, C. Alternative methods for the preparation of gold nanoparticles supported on TiO2. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 7634–7642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, S.; Pitchon, V.; Petit, C. Application of the direct exchange method in the preparation of gold catalysts supported on different oxide materials. J. Mol. Catal. A 2006, 256, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, S.; Petit, C.; Pitchon, V. A new preparation method for the formation of gold nanoparticles on an oxide support. Appl. Catal. A 2004, 267, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, S.; Pitchon, V.; Zimmermann, Y.; Petit, C. Preparation of alumina supported gold catalysts: Influence of washing procedures, mechanism of particles size growth. Appl. Catal. A 2006, 298, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredig, G.; Reinders, W. Anorganic enzymes. III. The gold catalysis of hydrogen peroxide. Z. Phys. Chem. Stochiometrie Verwandtschaftslehre 1901, 37, 323–341. [Google Scholar]
- Prati, L.; Rossi, M. Gold on carbon as a new catalyst for selective liquid phase oxidation of diols. J. Catal. 1998, 176, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prati, L.; Martra, G. New gold catalysts for liquid phase oxidation. Gold Bull. 1999, 32, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prati, L.; Villa, A.; Lupini, A.R.; Veith, G.M. Gold on carbon: One billion catalysts under a single label. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 2969–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshmanan, P.; Upare, P.P.; Le, N.-T.; Hwang, Y.K.; Hwang, D.W.; Lee, U.H.; Kim, H.R.; Chang, J.-S. Facile synthesis of CeO2-supported gold nanoparticle catalysts for selective oxidation of glycerol into lactic acid. Appl. Catal. A 2013, 468, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, G.J. Catalyst synthesis using supercritical carbon dioxide: A green route to high activity materials. Top. Catal. 2009, 52, 982–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miedziak, P.J.; Tang, Z.; Davies, T.E.; Enache, D.I.; Bartley, J.K.; Carley, A.F.; Herzing, A.A.; Kiely, C.J.; Taylor, S.H.; Hutchings, G.J. Ceria prepared using supercritical antisolvent precipitation: A green support for gold-palladium nanoparticles for the selective catalytic oxidation of alcohols. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 8619–8627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.H.; Liu, F.; Wei, Y.; Gu, C.L.; Zhang, L.H.; Liu, Y. Forming ceria shell on Au-core by LSPR photothermal induced interface reaction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 343, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsudome, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Maeno, Z.; Mizugaki, T.; Jitsukawa, K.; Kaneda, K. One-step synthesis of core-gold/shell-ceria nanomaterial and its catalysis for highly selective semihydrogenation of alkynes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 13452–13455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bera, P.; Hegde, M.S. Characterization and catalytic properties of combustion synthesized Au/CeO2 catalyst. Catal. Lett. 2002, 79, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Saoud, K.M.; Abdelsayed, V.; Glaspell, G.; Deevi, S.; El-Shall, M.S. Vapor phase synthesis of supported Pd, Au, and unsupported bimetallic nanoparticle catalysts for CO oxidation. Catal. Commun. 2006, 7, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potemkin, D.I.; Semitut, E.Y.; Shubin, Y.V.; Plyusnin, P.E.; Snytnikov, P.V.; Makotchenko, E.V.; Osadchii, D.Y.; Svintsitskiy, D.A.; Venyaminov, S.A.; Korenev, S.V.; et al. Silica, alumina and ceria supported Au–Cu nanoparticles prepared via the decomposition of [Au(en)2]2[Cu(C2O4)2]3·8H2O single-source precursor: Synthesis, characterization and catalytic performance in CO PROX. Catal. Today 2014, 235, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ge, Q. Oxide-supported Aun(SR)m nanoclusters for CO oxidation. Chin. J. Catal. 2015, 36, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, T.R.; Ivanova, S.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A. Low-temperature CO oxidation on multicomponent gold based catalysts. Front. Chem. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escamilla-Perea, L.; Nava, R.; Pawelec, B.; Rosmaninho, M.G.; Peza-Ledesma, C.L.; Fierro, J.L.G. SBA-15-supported gold nanoparticles decorated by CeO2: Structural characteristics and CO oxidation activity. Appl. Catal. A 2010, 381, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, J.A.; Gómez, S.; Pawelec, B.; Zepeda, T.A. CO oxidation on Au nanoparticles supported on wormhole HMS material: Effect of support modification with CeO2. Appl. Catal. B 2009, 89, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Bastos, S.S.T.; Órfão, J.J.M.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Delgado, J.J.; Figueiredo, J.L. Exotemplated ceria catalysts with gold for CO oxidation. Appl. Catal. A 2010, 381, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Silva, A.M.T.; Dražić, G.; Tavares, P.B.; Figueiredo, J.L. Gold nanoparticles on ceria supports for the oxidation of carbon monoxide. Catal. Today 2010, 154, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Silva, A.M.T.; Dražić, G.; Tavares, P.B.; Figueiredo, J.L. Effect of chloride on the sinterization of Au/CeO2 catalysts. Catal. Today 2010, 154, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, Q.; Li, C.; Hu, W.; Liu, Y.; Jing, P.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, J. Three-dimensionally ordered macroporous Au/CeO2–Co3O4 catalysts with mesoporous walls for enhanced CO preferential oxidation in H2-rich gases. J. Catal. 2012, 296, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, N.; Liu, J.; Shen, W. Tuning the shape of ceria nanomaterials for catalytic applications. Chin. J. Catal. 2013, 34, 838–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Duan, H.-H.; Li, L.-L.; Sun, L.-D.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Yan, C.-H. Controlled synthesis and assembly of ceria-based nanomaterials. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 335, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.-S.; Sun, H.; Wang, L.-C.; Liu, Y.-M.; Fan, K.-N.; Cao, Y. Morphology effects of nanoscale ceria on the activity of Au/CeO2 catalysts for low-temperature CO oxidation. Appl. Catal. B 2009, 90, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Zhang, H.; Li, W. Effect of the morphology of the ceria support on the activity of Au/CeO2 catalysts for CO oxidation. Chin. J. Catal. 2008, 29, 1089–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Deng, T.; Feng, L.; Xie, A.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Guo, J. Designed synthesis and formation mechanism of CeO2 hollow nanospheres and their facile functionalization with Au nanoparticles. Crystengcomm 2015, 17, 4850–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Chen, G.; Sun, S.; Sun, X. In situ growth of Au@CeO2 core-shell nanoparticles and CeO2 nanotubes from Ce(OH)CO3 nanorods. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xiang, S.; Sheng, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, C. Hierarchical structures based on gold nanoparticles embedded into hollow ceria spheres and mesoporous silica layers with high catalytic activity and stability. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 9372–9379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguna, O.H.; Dominguez, M.I.; Romero-Sarria, F.; Odriozola, J.A.; Centeno, M.A. Role of oxygen vacancies in gold oxidation catalysis. In Heterogeneous Gold Catalysts and Catalysis; Ma, Z., Dai, S., Eds.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2014; pp. 489–511. [Google Scholar]
- Guzman, J.; Carrettin, S.; Corma, A. Spectroscopic evidence for the supply of reactive oxygen during CO oxidation catalyzed by gold supported on nanocrystalline CeO2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 3286–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reina, T.R.; Papadopoulou, E.; Palma, S.; Ivanova, S.; Centeno, M.A.; Ioannides, T.; Odriozola, J.A. Could an efficient WGS catalyst be useful in the CO–PrOx reaction? Appl. Catal. B 2014, 150–151, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, T.R.; Ivanova, S.; Idakiev, V.; Tabakova, T.; Centeno, M.A.; Deng, Q.-F.; Yuan, Z.-Y.; Odriozola, J.A. Nanogold mesoporous iron promoted ceria catalysts for total and preferential CO oxidation reactions. J. Mol. Catal. A 2016, 414, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapovalov, V.; Metiu, H. Catalysis by doped oxides: CO oxidation by AuxCe1−xO2. J. Catal. 2007, 245, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreeva, D.; Petrova, P.; Ilieva, L.; Sobczak, J.W.; Abrashev, M.V. Design of new gold catalysts supported on mechanochemically activated ceria-alumina, promoted by molybdena for complete benzene oxidation. Appl. Catal. B 2008, 77, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreeva, D.; Petrova, P.; Sobczak, J.W.; Ilieva, L.; Abrashev, M. Gold supported on ceria and ceria–alumina promoted by molybdena for complete benzene oxidation. Appl. Catal. B 2006, 67, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avgouropoulos, G.; Manzoli, M.; Boccuzzi, F.; Tabakova, T.; Papavasiliou, J.; Ioannides, T.; Idakiev, V. Catalytic performance and characterization of Au/doped-ceria catalysts for the preferential CO oxidation reaction. J. Catal. 2008, 256, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Camellone, M.F.; Fabris, S. Fluxionality of Au clusters at ceria surfaces during CO oxidation: Relationships among reactivity, size, cohesion, and surface defects from DFT simulations. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 2256–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreeva, D.; Idakiev, V.; Tabakova, T.; Ilieva, L.; Falaras, P.; Bourlinos, A.; Travlos, A. Low-temperature water-gas shift reaction over Au/CeO2 catalysts. Catal. Today 2002, 72, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vindigni, F.; Manzoli, M.; Tabakova, T.; Idakiev, V.; Boccuzzi, F.; Chiorino, A. Gold catalysts for low temperature water-gas shift reaction: Effect of ZrO2 addition to CeO2 support. Appl. Catal. B 2012, 125, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, R.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Shape and crystal-plane effects of nanoscale ceria on the activity of Au-CeO2 catalysts for the water-gas shift reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 2884–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Ma, S.; Hrbek, J.; Rodriguez, J.A. Reaction of water with Ce–Au(111) and CeOx/Au(111) surfaces: Photoemission and STM studies. Surf. Sci. 2007, 601, 2445–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, T.R.; Ivanova, S.; Delgado, J.J.; Ivanov, I.; Idakiev, V.; Tabakova, T.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A. Viability of Au/CeO2–ZnO/Al2O3 catalysts for pure hydrogen production by the water-gas shift reaction. ChemCatChem 2014, 6, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar]
- Reina, T.R.; Castaño, M.G.; Palma, S.; Ivanova, S.; Odriozola, J.A. Twenty years of golden future in the water gas shift reaction. In Heterogeneous Gold Catalysts and Catalysis; Ma, Z., Dai, S., Eds.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2014; pp. 111–139. [Google Scholar]
- Reina, T.R.; Ivanova, S.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A. Boosting the activity of a Au/CeO2/Al2O3 catalyst for the WGS reaction. Catal. Today 2015, 253, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, T.R.; Ivanova, S.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A. Catalytic screening of Au/CeO2-MOx/Al2O3 catalysts (M = La, Ni, Cu, Fe, Cr, Y) in the CO–PrOx reaction. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 1782–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, T.R.; Ivanova, S.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A. The role of Au, Cu & CeO2 and their interactions for an enhanced WGS performance. Appl. Catal. B 2016, 187, 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.L.; Gao, H.J.; Shaikhutdinov, S.; Freund, H.J. Gold supported on well-ordered ceria films: Nucleation, growth and morphology in CO oxidation reaction. Catal. Lett. 2007, 114, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.A. Gold-based catalysts for the water–gas shift reaction: Active sites and reaction mechanism. Catal. Today 2011, 160, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Jesus, J.D.; Saltsburg, H.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Low-content gold–ceria catalysts for the water–gas shift and preferential CO oxidation reactions. Appl. Catal. A 2005, 291, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casaletto, M.P.; Longo, A.; Martorana, A.; Prestianni, A.; Venezia, A.M. XPS study of supported gold catalysts: The role of Au° and Au+d species as active sites. Surf. Interface Anal. 2006, 38, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.A.; Pérez, M.; Evans, J.; Liu, G.; Hrbek, J. Reaction of SO2 with Au/CeO2(111): Importance of O vacancies in the activation of gold. J. Chem. Phys. 2005, 122, 241101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez, M.I.; Sanchez, M.; Centeno, M.A.; Montes, M.; Odriozola, J.A. 2-Propanol oxidation over gold supported catalysts coated ceramic foams prepared from stainless steel wastes. J. Mol. Catal. A 2007, 277, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konya, Z.; Puntes, V.F.; Kiricsi, I.; Zhu, J.; Ager, J.W.; Ko, M.K.; Frei, H.; Alivisatos, P.; Somorjai, G.A. Synthetic insertion of gold nanoparticles into mesoporous silica. Chem. Mat. 2003, 15, 1242–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.-Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, S. Effects of the structure of ceria on the activity of gold/ceria catalysts for the oxidation of carbon monoxide and benzene. J. Catal. 2006, 237, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtois, X.; Bion, N.; Marécot, P.; Duprez, D. The role of cerium-based oxides used as oxygen storage materials in DeNOx catalysis. In Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis; Granger, P., Pârvulescu, V.I., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 235–259. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, H.C.; Yao, Y.F.Y. Ceria in automotive exhaust catalysts: I. Oxygen storage. J. Catal. 1984, 86, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, J.D.S.L.; Ferreira, H.S.; Bion, N.; Pirault-Roy, L.; Rangel, M.D.C.; Duprez, D.; Epron, F. Cooperative effect between copper and gold on ceria for CO–PROX reaction. Catal. Today 2012, 180, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, B.; Norskov, J.K. Why gold is the noblest of all the metals. Nature 1995, 376, 238–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, G.J. Vapor phase hydrochlorination of acetylene: Correlation of catalytic activity of supported metal chloride catalysts. J. Catal. 1985, 96, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, M.M.; Hackenberg, S.; van Veen, A.C.; Muhler, M.; Plzak, V.; Behm, R.J. CO oxidation over supported gold catalysts—“Inert” and “active” support materials and their role for the oxygen supply during reaction. J. Catal. 2001, 197, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguna, O.H.; Domínguez, M.I.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A. Forced deactivation and postmortem characterization of a metallic microchannel reactor employed for the preferential oxidation of CO (PROX). Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 302, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguna, O.H.; Ngassa, E.M.; Oraá, S.; Álvarez, A.; Domínguez, M.I.; Romero-Sarria, F.; Arzamendi, G.; Gandía, L.M.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A. Preferential oxidation of CO (CO–PROX) over CuOx/CeO2 coated microchannel reactor. Catal. Today 2012, 180, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, T.R.; Megías-Sayago, C.; Florez, A.P.; Ivanova, S.; Centeno, M.Á.; Odriozola, J.A. H2 oxidation as criterion for PrOx catalyst selection: Examples based on Au–CoOx-supported systems. J. Catal. 2015, 326, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avgouropoulos, G.; Ioannides, T. TPD and TPSR study of CO interaction with CuO–CeO2 catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A 2008, 296, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabakova, T.; Manzoli, M.; Paneva, D.; Boccuzzi, F.; Idakiev, V.; Mitov, I. CO-free hydrogen production over Au/CeO2–Fe2O3 catalysts: Part 2. Impact of the support composition on the performance in the water-gas shift reaction. Appl. Catal. B 2011, 101, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Chen, L. Synthesis of doped ceria with mesoporous flowerlike morphology and its catalytic performance for CO oxidation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 120, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.A.; Ma, S.; Liu, P.; Hrbek, J.; Evans, J.; Perez, M. Activity of CeOx and TiOx nanoparticles grown on Au(111) in the water-gas shift reaction. Science 2007, 318, 1757–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Hwang, G.S. Adsorption of Au atoms on stoichiometric and reduced TiO2(110) rutile surfaces: A first principles study. Surf. Sci. 2003, 542, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Michaelides, A.; King, D.A.; Jenkins, S.J. Anchoring sites for initial Au nucleation on CeO2{111}: O vacancy versus Ce vacancy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 6411–6417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabakova, T.; Boccuzzi, F.; Manzoli, M.; Andreeva, D. FTIR study of low-temperature water-gas shift reaction on gold/ceria catalyst. Appl. Catal. A 2003, 252, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlström, E.; Lopez, N.; Schaub, R.; Thostrup, P.; Ronnau, A.; Africh, C.; Laegsgaard, E.; Norskov, J.K.; Besenbacher, F. Bonding of gold nanoclusters to oxygen vacancies on rutile TiO2(110). Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman, J.; Carrettin, S.; Fierro-Gonzalez, J.C.; Hao, Y.L.; Gates, B.C.; Corma, A. CO oxidation catalyzed by supported gold: Cooperation between gold and nanocrystalline rare-earth supports forms reactive surface superoxide and peroxide species. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 4778–4781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, R.Q.; Huang, Y.P.; Wan, H.L. Surface oxygen species over cerium oxide and their reactivities with methane and ethane by means of in situ confocal microprobe Raman spectroscopy. J. Raman Spectrosc. 1997, 28, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penkova, A.; Laguna, O.H.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A. CO-induced morphology changes in Zn-modified ceria: A FTIR spectroscopic study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 5747–5756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuilloud, E.; Delley, B.; Schneider, W.D.; Baer, Y. Spectroscopic evidence for localized and extended F-symmetry states in CeO2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1984, 53, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panhans, M.A.; Blumenthal, R.N. A thermodynamic and electrical conductivity study of nonstoichiometric cerium dioxide. Solid State Ion. 1993, 60, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binet, C.; Badri, A.; Lavalley, J.C. A spectroscopic characterization of the reduction of ceria from electronic-transitions of intrinsic point-defects. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 6392–6398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamarra, D.; Martínez-Arias, A. Preferential oxidation of CO in rich H2 over CuO/CeO2: Operando-DRIFTS analysis of deactivating effect of CO2 and H2O. J. Catal. 2009, 263, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, T.R.; Ivanova, S.; Idakiev, V.; Delgado, J.J.; Ivanov, I.; Tabakova, T.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A. Impact of Ce–Fe synergism on the catalytic behaviour of Au/CeO2–FeOx/Al2O3 for pure H2 production. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 779–787. [Google Scholar]
- Sudarsanam, P.; Mallesham, B.; Reddy, P.S.; Großmann, D.; Grünert, W.; Reddy, B.M. Nano-Au/CeO2 catalysts for CO oxidation: Influence of dopants (Fe, La and Zr) on the physicochemical properties and catalytic activity. Appl. Catal. B 2014, 144, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamarra, D.; Hornés, A.; Koppány, Z.; Schay, Z.; Munuera, G.; Soria, J.; Martínez-Arias, A. Catalytic processes during preferential oxidation of CO in H2-rich streams over catalysts based on copper–ceria. J. Power Sources 2007, 169, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Yang, C.K.; Haile, S.M. Ceria-zirconia solid solutions (Ce1−xZrxO2-delta, x ≤ 0.2) for solar thermochemical water splitting: A thermodynamic study. Chem. Mat. 2014, 26, 6073–6082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, B.; Li, G.; Zhou, R. Application of rare earth modified Zr-based ceria-zirconia solid solution in three-way catalyst for automotive emission control. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3870–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Li, G.; Zhao, B.; Zhou, R. The effect of rare earth modification on ceria–zirconia solid solution and its application in Pd-only three-way catalyst. J. Mol. Catal. A 2011, 339, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Veser, G. Mixed lanthana/ceria nanorod-supported gold catalysts for water-gas-shift. Catal. Lett. 2012, 142, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Deng, W.; Saltsburg, H.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Activity and stability of low-content gold–cerium oxide catalysts for the water–gas shift reaction. Appl. Catal. B 2005, 56, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilaire, S.; Wang, X.; Luo, T.; Gorte, R.J.; Wagner, J. A comparative study of water-gas-shift reaction over ceria supported metallic catalysts. Appl. Catal. A 2001, 215, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, C.E.; Permana, H.; Ng, K.Y.S.; Brenner, A.; More, K.; Rahmoeller, K.M.; Belton, D. Thermal stability of oxygen storage properties in a mixed CeO2–ZrO2 system. Appl. Catal. B 1998, 16, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, G.; Waghmare, U.V.; Baidya, T.; Hegde, M.S.; Priolkar, K.R.; Sarode, P.R. Reducibility of Ce1−xZrxO2: Origin of enhanced oxygen storage capacity. Catal. Lett. 2006, 108, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamboa-Rosales, N.K.; Ayastuy, J.L.; González-Marcos, M.P.; Gutiérrez-Ortiz, M.A. Oxygen-enhanced water gas shift over ceria-supported Au–Cu bimetallic catalysts prepared by wet impregnation and deposition–precipitation. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 7005–7016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamboa-Rosales, N.K.; Ayastuy, J.L.; Iglesias-González, A.; González-Marcos, M.P.; Gutiérrez-Ortiz, M.A. Oxygen-enhanced WGS over ceria-supported Au–Co3O4 bimetallic catalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 207–208, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado-Juan, M.-A.; Yeung, C.M.Y.; Tsang, S.C. A study of co-precipitated bimetallic gold catalysts for water–gas shift reaction. Catal. Commun. 2008, 9, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.L.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. On the issue of the deactivation of Au/ceria and Pt-ceria water-gas shift catalysts in practical fuel-cell applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 2285–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Castaño, M.; Reina, T.R.; Ivanova, S.; Tejada, L.M.M.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A. O2-assisted water gas shift reaction over structured Au and Pt catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 2016, 185, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbeláez, O.; Reina, T.R.; Ivanova, S.; Bustamante, F.; Villa, A.L.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A. Mono and bimetallic Cu–Ni structured catalysts for the water gas shift reaction. Appl. Catal. A 2015, 497, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giroux, T.; Hwang, S.; Liu, Y.; Ruettinger, W.; Shore, L. Monolithic structures as alternatives to particulate catalysts for the reforming of hydrocarbons for hydrogen generation. Appl. Catal. B 2005, 56, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colussi, S.; Katta, L.; Amoroso, F.; Farrauto, R.J.; Trovarelli, A. Ceria-based palladium zinc catalysts as promising materials for water gas shift reaction. Catal. Commun. 2014, 47, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luengnaruemitchai, A.; Osuwan, S.; Gulari, E. Selective catalytic oxidation of CO in the presence of H2 over gold catalyst. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2004, 29, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlich, M.J.; Gasteiger, H.A.; Behm, R.J. Kinetics of the selective low-temperature oxidation of CO in H2-rich gas over Au/α-Fe2O3. J. Catal. 1999, 182, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.D.; Bollinger, M.; Vannice, M.A. Low-temperature CO oxidation over Au/TiO2 and Au/SiO2 catalysts. Catal. Lett. 1993, 17, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Chu, W.; Dai, X.; Pitchon, V. Bimetallic Au–Cu supported on ceria for PROX reaction: Effects of Cu/Au atomic ratios and thermal pretreatments. Appl. Catal. B 2013, 142–143, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriazo, J.G.; Martínez, L.M.; Odriozola, J.A.; Moreno, S.; Molina, R.; Centeno, M.A. Gold supported on Fe, Ce, and Al pillared bentonites for CO oxidation reaction. Appl. Catal. B 2007, 72, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, C.K.; Yang, J.H.; Law, H.Y.; Wang, Y.; Lin, J.N.; Marks, L.D.; Kung, M.C.; Kung, H.H. On the potential role of hydroxyl groups in CO oxidation over Au/Al2O3. Appl. Catal. A 2003, 243, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujitani, T.; Nakamura, I.; Haruta, M. Role of water in CO oxidation on gold catalysts. Catal. Lett. 2014, 144, 1475–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avgouropoulos, G.; Ioannides, T.; Papadopoulou, C.; Batista, J.; Hocevar, S.; Matralis, H.K. A comparative study of Pt/gamma-Al2O3, Au/alpha-Fe2O3 and CuO–CeO2 catalysts for the selective oxidation of carbon monoxide in excess hydrogen. Catal. Today 2002, 75, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Centeno, M.A.; Ramírez Reina, T.; Ivanova, S.; Laguna, O.H.; Odriozola, J.A. Au/CeO2 Catalysts: Structure and CO Oxidation Activity. Catalysts 2016, 6, 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6100158
Centeno MA, Ramírez Reina T, Ivanova S, Laguna OH, Odriozola JA. Au/CeO2 Catalysts: Structure and CO Oxidation Activity. Catalysts. 2016; 6(10):158. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6100158
Chicago/Turabian StyleCenteno, Miguel Angel, Tomás Ramírez Reina, Svetlana Ivanova, Oscar Hernando Laguna, and José Antonio Odriozola. 2016. "Au/CeO2 Catalysts: Structure and CO Oxidation Activity" Catalysts 6, no. 10: 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6100158
APA StyleCenteno, M. A., Ramírez Reina, T., Ivanova, S., Laguna, O. H., & Odriozola, J. A. (2016). Au/CeO2 Catalysts: Structure and CO Oxidation Activity. Catalysts, 6(10), 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6100158