In Situ EPR Characterization of a Cobalt Oxide Water Oxidation Catalyst at Neutral pH
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Performance of the Spectroelectrochemical Cell
2.2. Co(II) EPR Signature
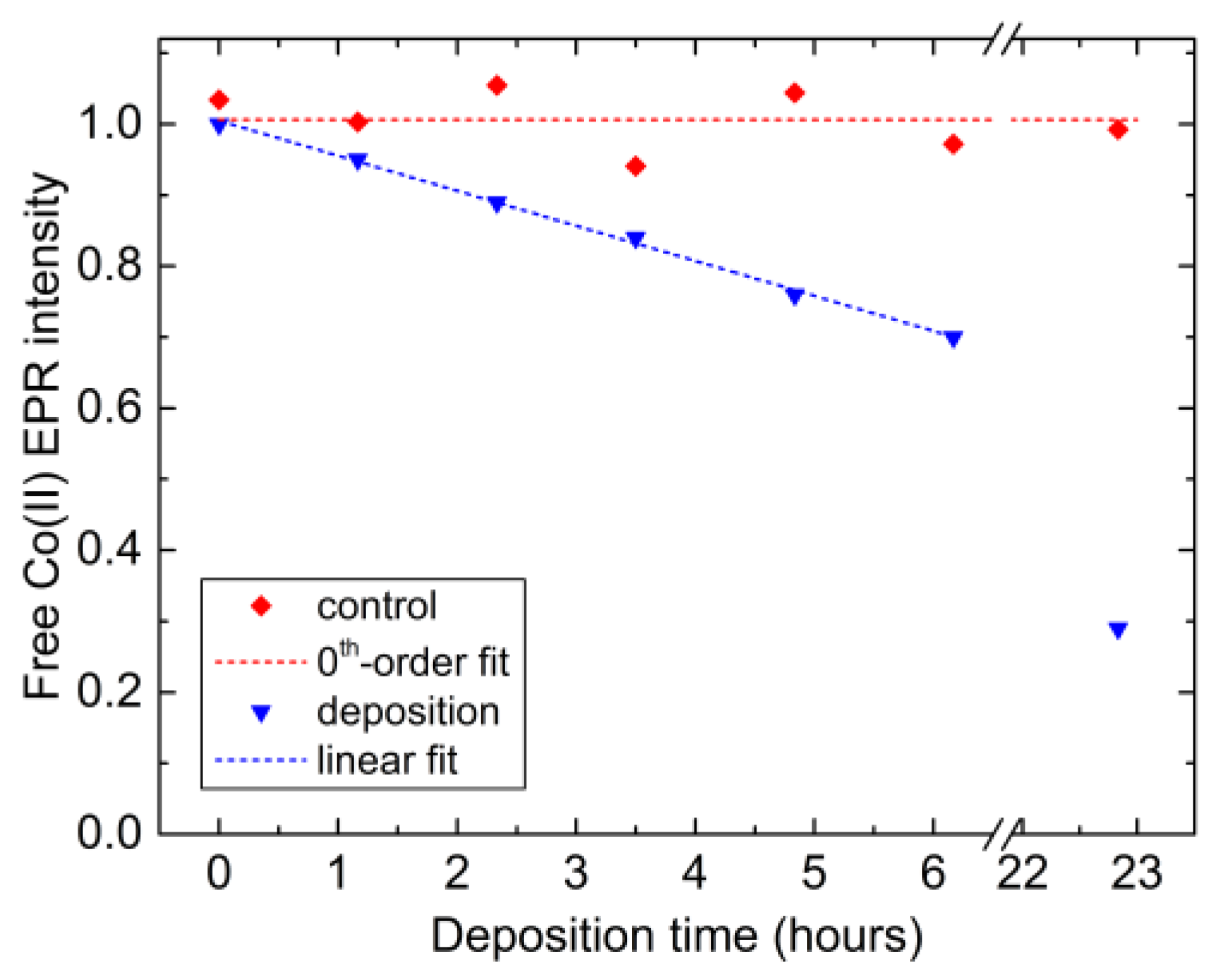
2.3. Co Uptake during the Electrodeposition
2.4. Potential Dependence of the Co-Pi EPR Spectrum
- (i)
- display larger crystal field splitting parameters, reducing the mixing via SOC within the d-orbital manifold; or
- (ii)
- the spin density migrates from the Co(IV) metal to its ligands, which again will reduce the overall SOC owing to the inclusion of lighter atoms.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Electrochemical Measurements
3.2. Synthesis of Catalyst Films
3.3. Potential Dependence
3.4. EPR Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kanan, M.W.; Nocera, D.G. In situ formation of an oxygen-evolving catalyst in neutral water containing phosphate and Co(2+). Science 2008, 321, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutterman, D.A.; Surendranath, Y.; Nocera, D.G. A Self-Healing Oxygen-Evolving Catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 3838–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubitz, W.; Reijerse, E.J.; Messinger, J. Solar water-splitting into H2 and O2: Design principles of photosystem II and hydrogenases. Energy Environ. Sci. 2008, 1, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanan, M.W.; Surendranath, Y.; Nocera, D.G. Cobalt-phosphate oxygen-evolving compound. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pijpers, J.J.H.; Winkler, M.T.; Surendranath, Y.; Buonassisi, T.; Nocera, D.G. Light-induced water oxidation at silicon electrodes functionalized with a cobalt oxygen-evolving catalyst. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 10056–10061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steinmiller, E.M.P.; Choi, K.-S. Photochemical deposition of cobalt-based oxygen evolving catalyst on a semiconductor photoanode for solar oxygen production. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20633–20636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esswein, A.J.; Surendranath, Y.; Reece, S.Y.; Nocera, D.G. Highly active cobalt phosphate and borate based oxygen evolving catalysts operating in neutral and natural waters. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reece, S.Y.; Hamel, J.A.; Sung, K.; Jarvi, T.D.; Esswein, A.J.; Pijpers, J.J.H.; Nocera, D.G. Wireless Solar Water Splitting Using Silicon-Based Semiconductors and Earth-Abundant Catalysts. Science 2011, 334, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Surendranath, Y.; Kanan, M.W.; Nocera, D.G. Mechanistic Studies of the Oxygen Evolution Reaction by a Cobalt-Phosphate Catalyst at Neutral pH. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 16501–16509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerken, J.B.; McAlpin, J.G.; Chen, J.Y.C.; Rigsby, M.L.; Casey, W.H.; Britt, R.D.; Stahl, S.S. Electrochemical Water Oxidation with Cobalt-Based Electrocatalysts from pH 0–14: The Thermodynamic Basis for Catalyst Structure, Stability, and Activity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 14431–14442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risch, M.; Khare, V.; Zaharieva, I.; Gerencser, L.; Chernev, P.; Dau, H. Cobalt-Oxo Core of a Water-Oxidizing Catalyst Film. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6936–6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanan, M.W.; Yano, J.; Surendranath, Y.; Dinca, M.; Yachandra, V.K.; Nocera, D.G. Structure and Valency of a Cobalt-Phosphate Water Oxidation Catalyst Determined by in Situ X-ray Spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 13692–13701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dau, H.; Limberg, C.; Reier, T.; Risch, M.; Roggan, S.; Strasser, P. The Mechanism of Water Oxidation: From Electrolysis via Homogeneous to Biological Catalysis. ChemCatChem 2010, 2, 724–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Nocera, D.G. Spectroscopic Studies of Nanoparticulate Thin Films of a Cobalt-Based Oxygen Evolution Catalyst. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 17060–17066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodsky, C.N.; Bediako, D.K.; Shi, C.; Keane, T.P.; Costentin, C.; Billinge, S.J.L.; Nocera, D.G. Proton–Electron Conductivity in Thin Films of a Cobalt–Oxygen Evolving Catalyst. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullman, A.M.; Brodsky, C.N.; Li, N.; Zheng, S.-L.; Nocera, D.G. Probing Edge Site Reactivity of Oxidic Cobalt Water Oxidation Catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 4229–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Siegbahn, P.E.M. Water Oxidation Mechanism for Synthetic Co–Oxides with Small Nuclearity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 13804–13813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodsky, C.N.; Hadt, R.G.; Hayes, D.; Reinhart, B.J.; Li, N.; Chen, L.X.; Nocera, D.G. In situ characterization of cofacial Co(IV) centers in Co4O4 cubane: Modeling the high-valent active site in oxygen-evolving catalysts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffat, B.; Demazeau, G.; Pouchard, M.; Dance, J.M.; Hagenmuller, P. Stabilization of tetravalent cobalt in an isolated six-coordinated site of an oxide lattice: A magnetic and ESR characterization. J. Solid State Chem. 1983, 50, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, M.G.; Hill, O.F. Tetravalent cobalt ion in alpha-Al2O3. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1965, 61, 2597–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zee, R.J.; Hamrick, Y.M.; Li, S.; Weltner, W. Cobalt, rhodium, and iridium dioxide molecules and Walsh-type rules. J. Phys. Chem. 1992, 96, 7247–7251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warda, S.A.; Massa, W.; Reinen, D.; Hu, Z.W.; Kaindl, G.; de Groot, F.M.F. The ordered K2NiF4-type structure of mixed crystals La2-xSrxLi1/2Co1/2O4 (x < 0.5) and the electronic properties of the constituting Co-III and Co-IV ions. J. Solid State Chem. 1999, 146, 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrou, K.; Brown, A.D.; Concolino, T.E.; Rheingold, A.L.; Christou, G. Mixed-valence, tetranuclear cobalt(III, IV) complexes: Preparation and properties of Co4O4(O2CR)(2)(bpy) (4) (3+) salts. Chem. Commun. 2001, 1284–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmer, J.; Van Doorslaer, S.; Gromov, I.; Broring, M.; Jeschke, G.; Schweiger, A. A pulse EPR and ENDOR investigation of the electronic structure of a sigma-carbon-bonded cobalt(IV) corrole. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 2801–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamian, V.A.; D’souza, F.; Licoccia, S.; Di Vona, M.L.; Tassoni, E.; Paolesse, R.; Boschi, T.; Kadish, K.M. Synthesis, Characterization, and Electrochemical Behavior of (5,10,15-Tri-X-phenyl-2,3,7,8,12,13,17,18-octamethylcorrolato)cobalt(III) Triphenylphosphine Complexes, Where X = p-OCH3, p-CH3, p-Cl, m-Cl, o-Cl, m-F, or o-F. Inorg. Chem. 1995, 34, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, R.D.; Heath, G.A.; Bond, A.M. Voltammetric, EPR and UV-VIS-NIR spectroscopic studies associated with the characterisation of electrochemically generated tris(dithiocarbamato)cobalt(IV) complexes in dichloromethane. J. Chem. Society-Dalton Trans. 2001, 3189–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, T.J.; Powell, R.D.; Slebodnick, C.; Uffelman, E.S. Stable highly oxidizing cobalt complexes of macrocyclic ligands. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 8419–8425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, J.; Topich, J.; Zamaraev, K.I. Electron paramagnetic resonance spectra and electronic structures of organobis(dimethylglyoximato)cobalt(IV) complexes. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1976, 20, L21–L24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topich, J.; Halpern, J. Organobis(dioximato)cobalt(IV) complexes: Electron paramagnetic resonance spectra and electronic structures. Inorg. Chem. 1979, 18, 1339–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitaeva, G.A.; Nikitaev, A.T.; Zamaraev, K.I.; Sigan, A.L.; Levitin, I.Y.; Volpin, M.E. ESR spectra and electronic structure of the oxidized forms of alkyl-bis (salicylidenato) ethylenediaminecobalt. J. Struct. Chem. 1978, 19, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAlpin, J.G.; Surendranath, Y.; Dinca, M.; Stich, T.A.; Stoian, S.A.; Casey, W.H.; Nocera, D.G.; Britt, R.D. EPR Evidence for Co(IV) Species Produced During Water Oxidation at Neutral pH. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 6882–6883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabarty, R.; Bora, S.J.; Das, B.K. Synthesis, structure, spectral and electrochemical properties, and catalytic use of cobalt(III)-Oxo cubane clusters. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 9450–9462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAlpin, J.G.; Stich, T.A.; Ohlin, C.A.; Surendranath, Y.; Nocera, D.G.; Casey, W.H.; Britt, R.D. Electronic Structure Description of a Co(III)(3)Co(IV)O(4) Cluster: A Model for the Paramagnetic Intermediate in Cobalt-Catalyzed Water Oxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 15444–15452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegbahn, P.E.M. Theoretical Studies of O–O Bond Formation in Photosystem II. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 1779–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Potential (V) | Peak-to-Peak Line Width (mT) | Effective g-Factor |
|---|---|---|
| 1.2 | 53.9(5) | 2.316(6) |
| 1.3 | 52.7(4) | 2.270(3) |
| 1.4 | 49.6(4) | 2.257(3) |
| 1.5 | 47.3(4) | 2.227(3) |
| 1.6 | 47.6(4) | 2.217(3) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kutin, Y.; Cox, N.; Lubitz, W.; Schnegg, A.; Rüdiger, O. In Situ EPR Characterization of a Cobalt Oxide Water Oxidation Catalyst at Neutral pH. Catalysts 2019, 9, 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9110926
Kutin Y, Cox N, Lubitz W, Schnegg A, Rüdiger O. In Situ EPR Characterization of a Cobalt Oxide Water Oxidation Catalyst at Neutral pH. Catalysts. 2019; 9(11):926. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9110926
Chicago/Turabian StyleKutin, Yury, Nicholas Cox, Wolfgang Lubitz, Alexander Schnegg, and Olaf Rüdiger. 2019. "In Situ EPR Characterization of a Cobalt Oxide Water Oxidation Catalyst at Neutral pH" Catalysts 9, no. 11: 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9110926
APA StyleKutin, Y., Cox, N., Lubitz, W., Schnegg, A., & Rüdiger, O. (2019). In Situ EPR Characterization of a Cobalt Oxide Water Oxidation Catalyst at Neutral pH. Catalysts, 9(11), 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9110926






