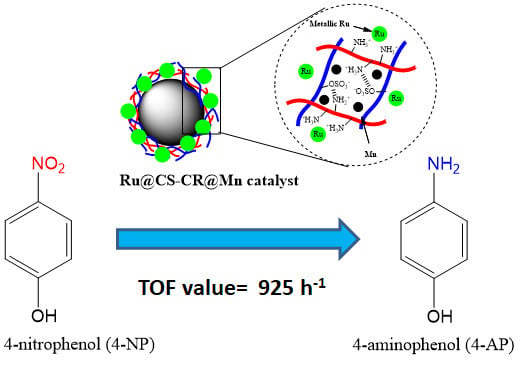
Ruthenium Supported on Ionically Cross-linked Chitosan-Carrageenan Hybrid MnFe2O4 Catalysts for 4-Nitrophenol Reduction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of Ru@CS-CR@Mn Catalyst
2.2. Catalytic Performance Test of Ru@CS-CR@Mn Catalyst
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of MnFe2O4 Nanoparticles
3.3. Preparation of Ru@CS-CR@Mn Catalyst
3.4. Characterization
3.5. Reduction of 4-NP to 4-AP
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gazi, S.; Ananthakrishnan, R. Metal-free-photocatalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol by resin-supported dye under the visible irradiation. Appl. Catal. B 2011, 105, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, X.D.; Dong, Z.P.; Liu, Y.S.; Jin, Z.C.; Huy, T.D.; Le, M.D.; Ma, J.T. Palladium nanoparticles immobilized on core–shell magnetic fibers as a highly efficient and recyclable heterogeneous catalyst for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol and Suzuki coupling reactions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 19696–19706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivancĕv-Tumbas, I.; Hobby, R.; Küchle, B.; Panglisch, S.; Gimbel, R. p-Nitrophenol removal by combination of powdered activated carbon adsorption and ultrafiltration-comparison of different operational modes. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4117–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osin, O.A.; Yu, T.; Cai, X.; Jiang, Y.; Peng, G.; Cheng, X.; Li, R.; Qin, Y.; Lin, S. Photocatalytic degradation of 4-nitrophenol by C, N-TiO2: Degradation efficiency vs. embryonic toxicity of the resulting compounds. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Li, F.; Wu, T.; Sun, D.; Li, Y. Adsorption of p-nitrophenol from aqueous solutions using nanographite oxide. Colloids Surf. A 2015, 464, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.C.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L. In situ synthesis of monodisperse silver nanoparticles on sulfhydryl-functionalized poly(glycidyl methacrylate) microspheres for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 6480–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, R.; Loganathan, B.; Dinesh, S.; Raghu, K. Strategic green synthesis, characterization and catalytic application to 4-nitrophenol reduction of palladium nanoparticles. J. Clust. Sci. 2017, 28, 2123–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.L.; Abu Bakar, N.H.H.; Abu Bakar, M. Catalytic reduction of p-nitrophenol using chitosan stabilized copper nanoparticles. Catal. Lett. 2015, 145, 1626–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Deka, S. Multiply twinned AgNi alloy nanoparticles as highly active catalyst for multiple reduction and degradation reactions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 16071–16081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aditya, T.; Pal, A.; Pal, T. Nitroarene reduction: A trusted model reaction to test nanoparticle catalysts. Chem. Comm. 2015, 51, 9410–9431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chairam, S.; Konkamdee, W.; Parakhun, R. Starch-supported gold nanoparticles and their use in 4-nitrophenol reduction. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2017, 21, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, P.; O’Connor, D.; Varma, R.S.; Yu, M.; Hou, D. One-pot green synthesis of bimetallic hollow palladium-platinum nanotubes for enhanced catalytic reduction of p-nitrophenol. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 539, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Kuwahara, Y.; Mori, K.; Che, M.; Yamashita, H. Plasmonic Ru/hydrogen molybdenum bronzes with tunable oxygen vacancies for light-driven reduction of p-nitrophenol. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 3783–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tan, F.; Wang, W.; Qiao, X.; Qiu, X.; Chen, J. Anchoring of silver nanoparticles on graphitic carbon nitride sheets for the synergistic catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Chemosphere 2017, 172, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anantharaj, S.; Jayachandran, M.; Kundu, S. Unprotected and interconnected Ru0 nano-chain networks: Advantages of unprotected surfaces in catalysis and electrocatalysis. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 3188–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ciganda, R.; Salmon, L.; Gregurec, D.; Irigoyen, J.; Moya, S.; Ruiz, J.; Astruc, D. Highly efficient transition metal nanoparticle catalysts in aqueous solutions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3091–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seth, J.; Dubey, P.; Chaudhari, V.R.; Prasad, B.L.V. Preparation of metal oxide supported catalysts and their utilization for understanding the effect of a support on the catalytic activity. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.V.; Namasivayam, D.; Lin, K.C.; Liu, S.B. Highly stable ruthenium nanoparticles on 3D mesoporous carbon: An excellent opportunity for the reduction reactions†. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 23448–23457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashani, S.H.; Moghadam, M.; Tangestaninejad, S.; Mirkhani, V.; Baltork, I.M. Ruthenium nanoparticles immobilized on nano-silica functionalized with thiol-based dendrimer: A nanocomposite material for oxidation of alcohols and epoxidation of alkenes. Catal. Lett. 2018, 148, 1110–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Shen, C.; Qiao, J.; Tong, J.; Jin, J.; Zhang, P. Novel magnetically-recyclable, nitrogen-doped Fe3O4@Pd NPs for Suzuki–Miyaura coupling and their application in the synthesis of crizotinib. Catalysts 2018, 8, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subha, V.; Divya, K.; Gayathri, S. Applications of iron oxide nano composite in waste water treatment–dye decolourisation and anti‒microbial activity. MOJ Drug Des. Develop. Ther. 2018, 2, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Miao, C.; Liu, H.; Feng, L.; Yang, X.; Guo, H. A hydrothermal synthesis of Fe3O4@C hybrid nanoparticle and magnetic adsorptive performance to remove heavy metal ions in aqueous solution. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Zhang, W.; Xu, J.; Cao, J.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y. Facile fabrication of highly active magnetic aminoclay supported palladium nanoparticles for the room temperature catalytic reduction of nitrophenol and nitroanilines. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazarika, M.; Chinnamuthu, P.; Borah, J.P. MWCNT decorated MnFe2O4 nanoparticles as an efficient photo-catalyst for phenol degradation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 12231–12240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.H.; Salabas, E.L.; Schüth, F. Magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1222–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahia, M.; Zeinalia, S.; Nasirimoghaddama, S.; Sabbaghi, S. Effective removal of As(III) from drinking water samples by chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticles. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 56, 2092–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guibal, E. Heterogeneous catalysis on chitosan-based materials: A review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2005, 30, 71–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.W.; Jeon, B.H.; Chon, C.M.; Schwartz, F.W.; Jeong, Y.J.; Song, H.C. Magnetic chitosan composite for adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes in aqueous solution. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 28, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsupikhe, R.F.; Shameli, K.; Ahmad, M.B.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Zainudin, N. Green sonochemical synthesis of silver nanoparticles at varying concentrations of κ-carrageenan. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, C.; Pereira, A.M.; Fernandes, C.; Rocha, M.; Mendes, R.; Fernández-García, M.P.; Guedes, A.; Tavares, P.B.; Grenèche, J.M.; Araújo, J.P.; et al. Superparamagnetic MFe2O4 (M = Fe, Co, Mn) nanoparticles: Tuning the particle size and magnetic properties through a novel one-step coprecipitation route. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 1496–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, K.H.; Rocha, M.; Pereira, C.; Pires, A.L.; Pereira, A.M.; Yarmo, M.A.; Juan, J.C.; Yusop, R.M.; Peixoto, A.F.; Freire, C. Highly active ruthenium supported on magnetically recyclable chitosan-based nanocatalyst for nitroarenes reduction. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 3930–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenha, A.; Gomes, M.E.; Rodrigues, M.; Santo, V.E.; Mano, J.F.; Neves, N.M.; Reis, R.L. Development of new chitosan/carrageenan nanoparticles for drug delivery applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 92, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Hein, S.; Wang, K. Chitosan-carrageenan polyelectrolyte complex for the 512 delivery of protein drugs. Biomaterials 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janik, L.J.J.; Skjemstad, O.; Shepherd, K.D.; Spouncer, L.R. The prediction of soil carbon fractions using mid-infrared-partial least square analysis. Aust. J. Soil. Res. 2007, 45, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, R.B.N.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Varma, R.S. Ruthenium on chitosan: A recyclable heterogeneous catalyst for aqueous hydration of nitriles to amides. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 2122–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Hernández, A.; Gracida, J.; García-Almendárez, B.E.; Regalado, C.; Núñez, R.; Amaro-Reyes, A. Characterization of magnetic nanoparticles coated with chitosan: A potential approach for enzyme immobilization. J. Nanomater. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, M.Y.; Pan, L.Q.; Javed, Q.U.A.; Iqbal, M.Z.; Qiu, H.M.; Farooq, M.H.; Guo, Z.G.; Tanveer, M. Growth of monodisperse nanospheres of MnFe2O4 with enhanced magnetic and optical properties. Chin. Phys. B 2013, 22, 107101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, M.; Fernandes, C.; Pereira, C.; Rebelo, S.L.H.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Freire, C. Gold-supported magnetically recyclable nanocatalysts: A sustainable solution for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol in water. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 5131–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.C.; Vongehr, S.; Meng, X.K. Controllable incorporation of Ag and Ag–Au nanoparticles in carbon spheres for tunable optical and catalytic properties. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 5436–5445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, F.; Yang, W.; Ren, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y. PdO nanoparticles enhancing the catalytic activity of Pd/carbon nanotubes for 4-nitrophenol reduction. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 27526–27532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Guo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Gong, X.; Lu, G. Polymer-templated synthesis of hollow Pd-CeO2 nanocomposite spheres and their catalytic activity and thermal stability. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 23230–23239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Pal, A.; Kundu, S.; Basu, S.; Pal, T. Photochemical green synthesis of calcium-alginate-stabilized Ag and Au nanoparticles and their catalytic application to 4-nitrophenol reduction. Langmuir 2010, 26, 2885–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Qi, W.; Xu, X.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, W.; Pan, X.; Su, D. Covalently functionalized carbon nanotube supported Pd nanoparticles for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 6609–6616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Q.; Du, J. Reduction of 4-nitrophenol catalyzed by silver nanoparticles supported on polymer micelles and vesicles. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 16425–16428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.T.; Liu, X.G.; Xing, X.J.; Li, B.; Wang, K.; Chen, S.T.; Wu, Z.; Qiu, D.F. Ordered mesoporous silica cubic decorated with silver nanoparticles: A highly active and recyclable heterogeneous catalyst for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 2692–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansar, S.M.; Kitchens, C.L. The Impact of Gold Nanoparticle Stabilizing Ligand on Colloidal Catalytic Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 5553–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, P.; Remunan-Lopez, C.; Vila-Jato, J.L.; Alonso, M.J. Novel hydrophilic chitosan-polyethylene oxide nanoparticles as protein carriers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 63, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Materials | MS300 K | Mr300 K | Hc | Mr/MS Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (emu/g) | (emu/g) | (Oe) | ||
| MnFe2O4 | 63.3 | 1.7 | 15.0 | 0.027 |
| Ru@CS-CR@Mn | 38.5 | 1.7 | 15.9 | 0.047 |
| Catalyst | Metal Loading | Completion Time (s) | Rate Constant (s−1) | TOF (h−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ru colloidal solution | - | 840 | 16.8 | 4800 | [15] |
| Pd/PdO | 9.5 wt. % | 240 | 0.01 | 750 | [41] |
| Pd-CeO2 | 2.15 wt. % | 120 | - | 335 | [42] |
| Pd NP/CNT-220 | 1.69 wt. % | 300 | 0.01 | 18 | [43] |
| Ag@micelle-2 | 5.0 mg mL−1 | 80 | 0.02 | 48.7 | [44] |
| Ag-OMS-C | 3.86 wt. % | 150 | 0.03 | 91.2 | [45] |
| AuNPs-SPEG | - | - | 0.035 | 1.14 | [46] |
| Ru@CS-CR@Mn | 0.46 wt. % | 60 | 0.078 | 925 | This work |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liew, K.H.; Lee, T.K.; Yarmo, M.A.; Loh, K.S.; Peixoto, A.F.; Freire, C.; Yusop, R.M. Ruthenium Supported on Ionically Cross-linked Chitosan-Carrageenan Hybrid MnFe2O4 Catalysts for 4-Nitrophenol Reduction. Catalysts 2019, 9, 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9030254
Liew KH, Lee TK, Yarmo MA, Loh KS, Peixoto AF, Freire C, Yusop RM. Ruthenium Supported on Ionically Cross-linked Chitosan-Carrageenan Hybrid MnFe2O4 Catalysts for 4-Nitrophenol Reduction. Catalysts. 2019; 9(3):254. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9030254
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiew, Kin Hong, Tian Khoon Lee, Mohd Ambar Yarmo, Kee Shyuan Loh, Andreia F. Peixoto, Cristina Freire, and Rahimi M. Yusop. 2019. "Ruthenium Supported on Ionically Cross-linked Chitosan-Carrageenan Hybrid MnFe2O4 Catalysts for 4-Nitrophenol Reduction" Catalysts 9, no. 3: 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9030254
APA StyleLiew, K. H., Lee, T. K., Yarmo, M. A., Loh, K. S., Peixoto, A. F., Freire, C., & Yusop, R. M. (2019). Ruthenium Supported on Ionically Cross-linked Chitosan-Carrageenan Hybrid MnFe2O4 Catalysts for 4-Nitrophenol Reduction. Catalysts, 9(3), 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9030254