Hydroconversion of Waste Cooking Oil into Bio-Jet Fuel over NiMo/SBUY-MCM-41
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Textural Structures of Zeolites
2.2. Acidity Distributions of Al-MCM-41 and SBUY-MCM-41
2.3. Reduction Behavior
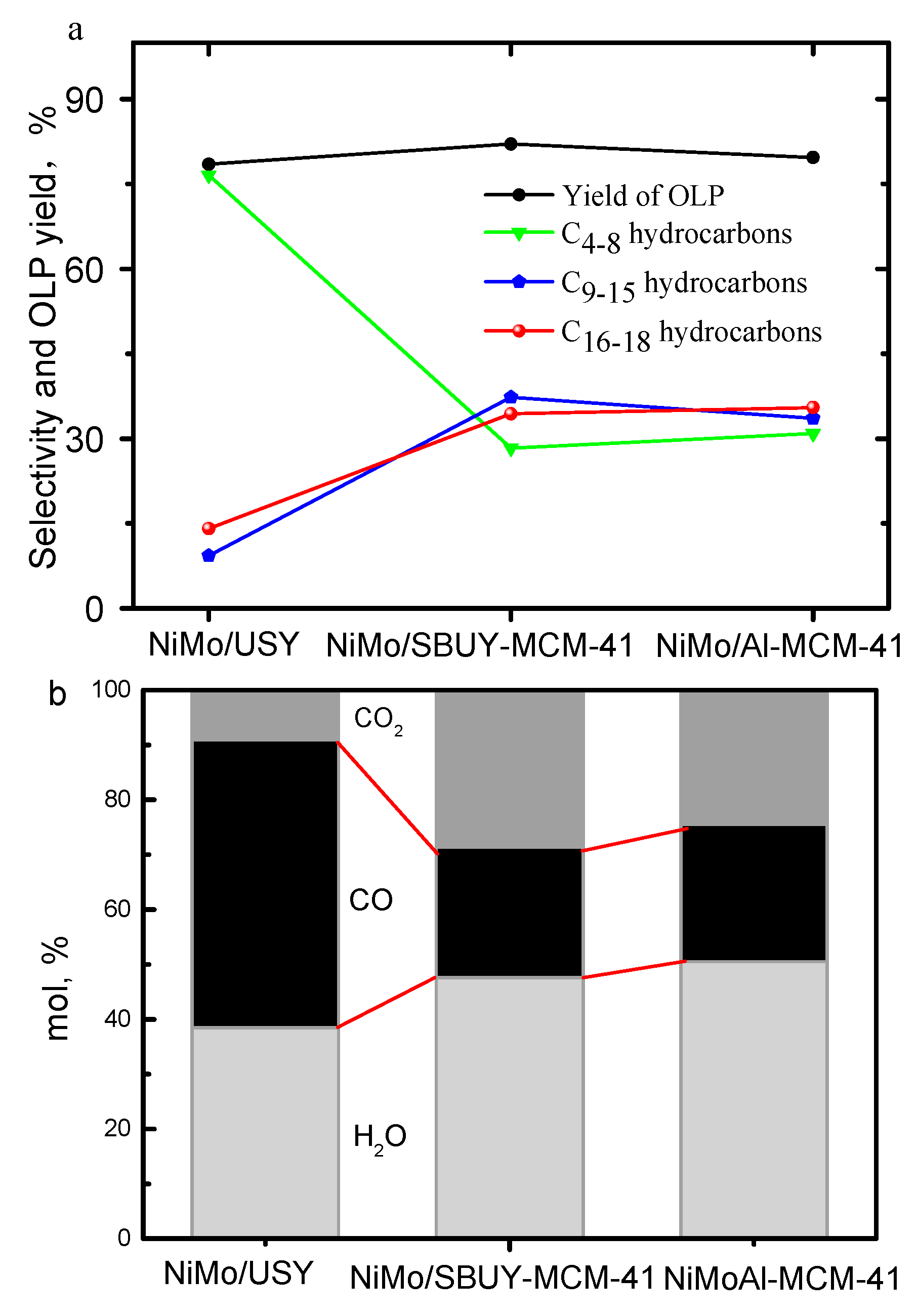
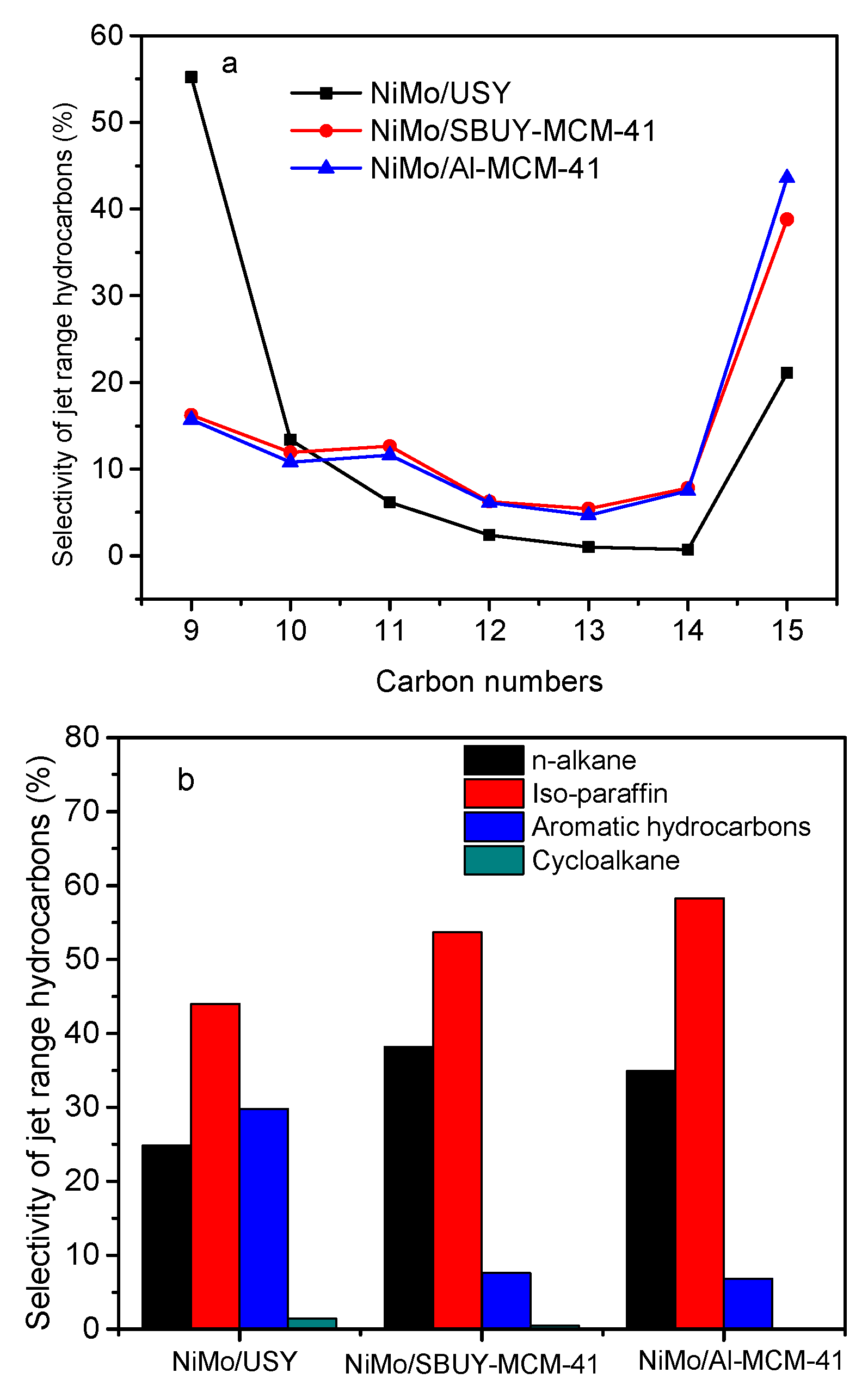
2.4. Hydrotreatment of WCO
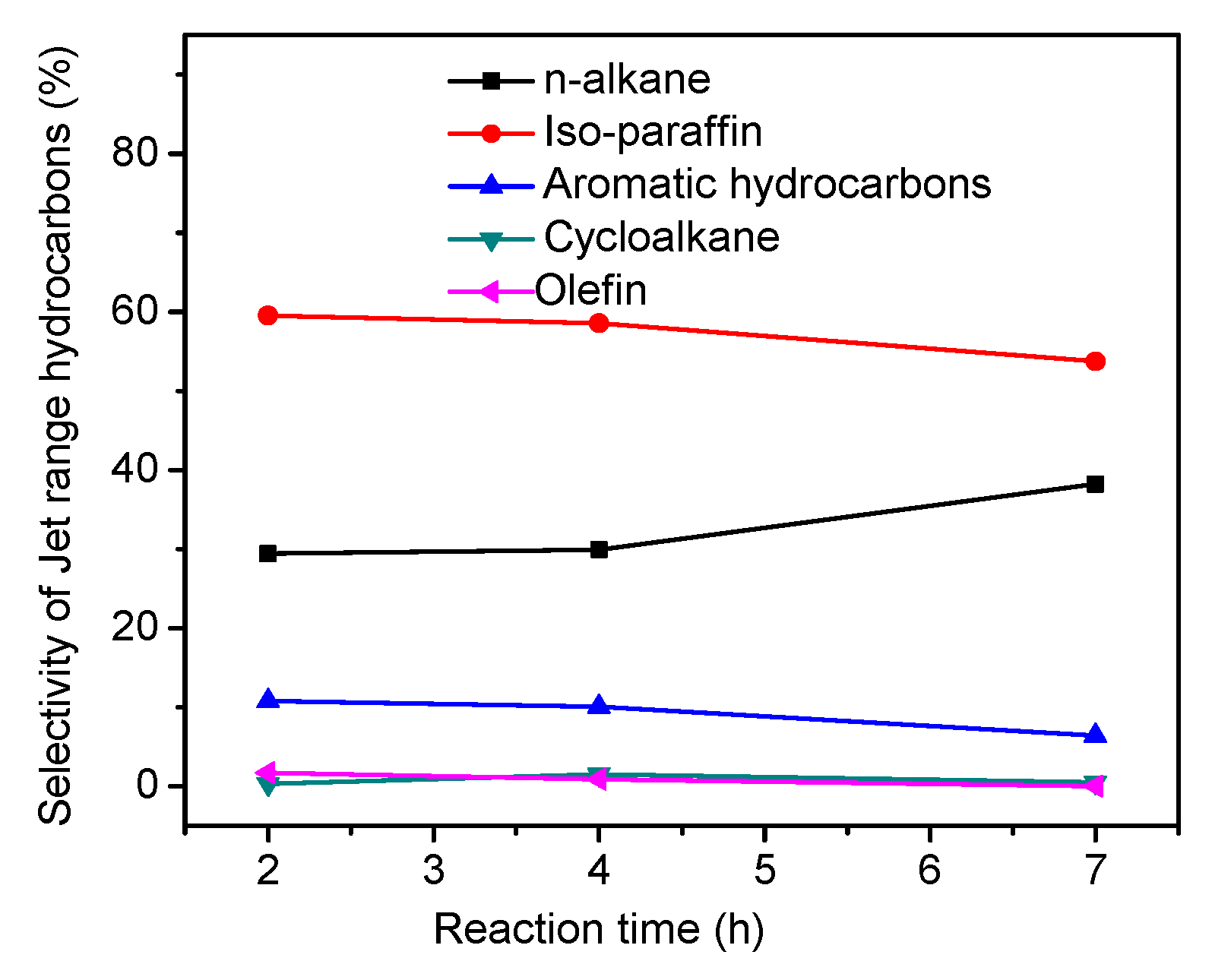
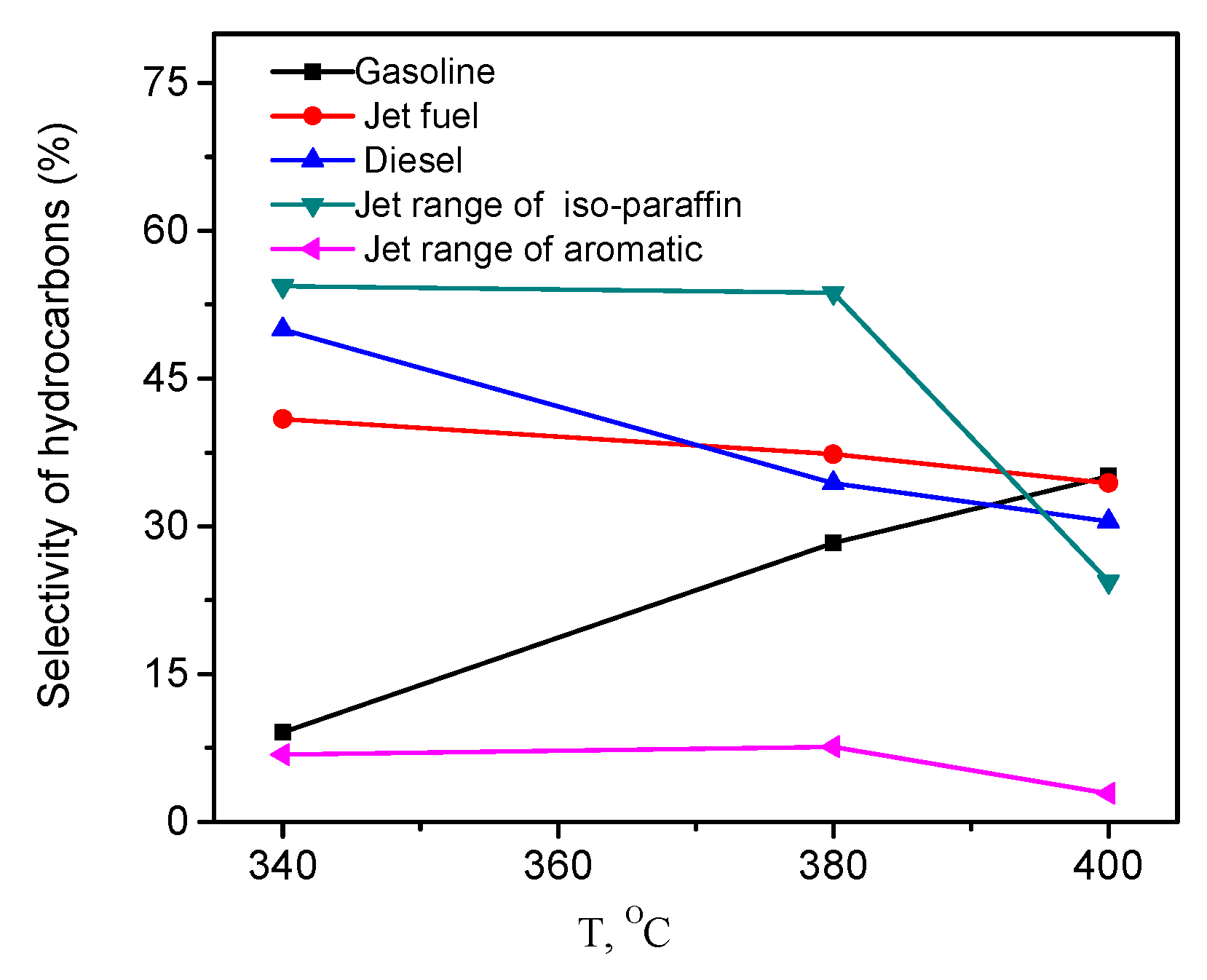
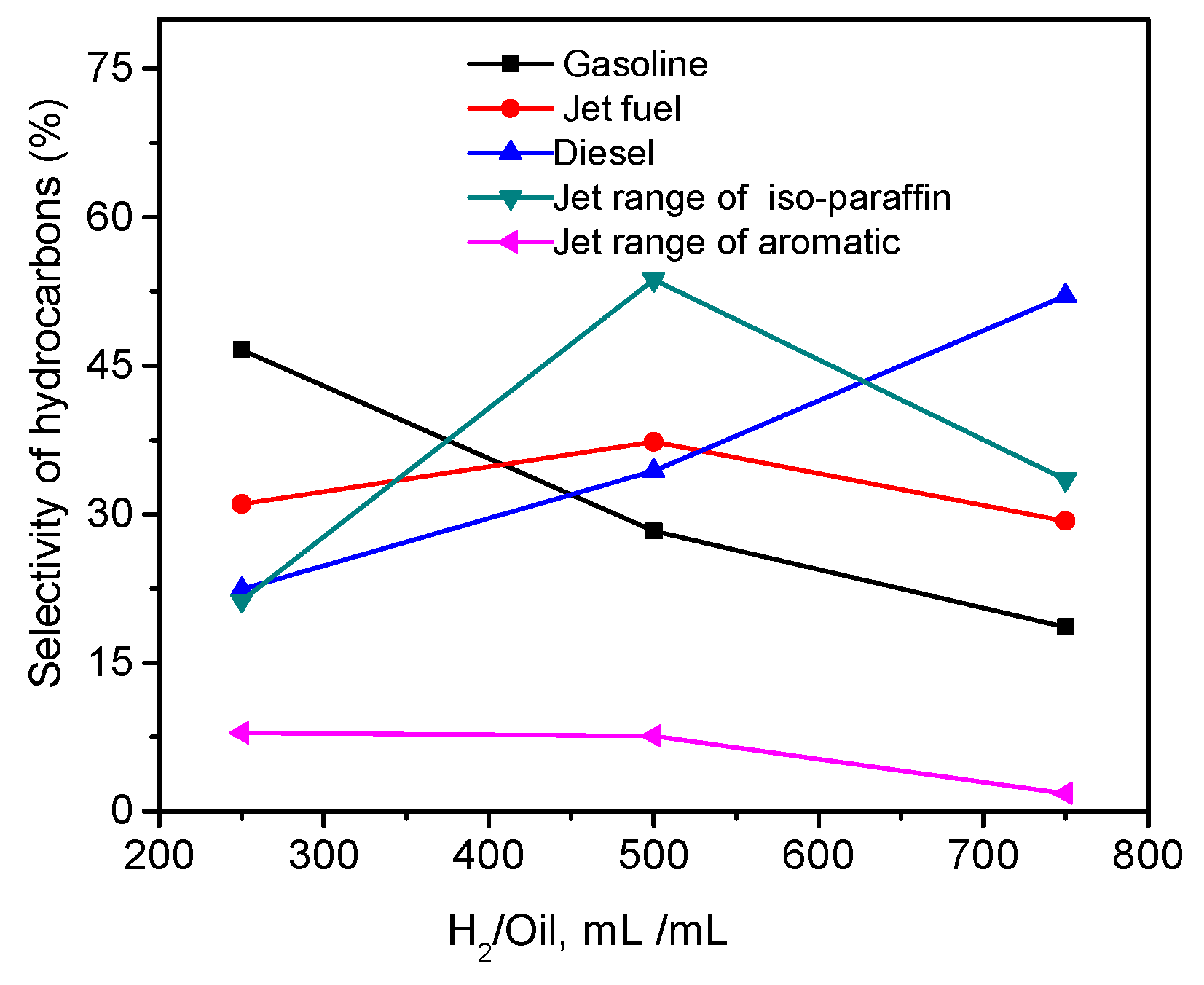
2.5. Effects of Temperature, Pressure, and Hydrogen-to-Oil Ratio on the Hydrotreatment of WCO
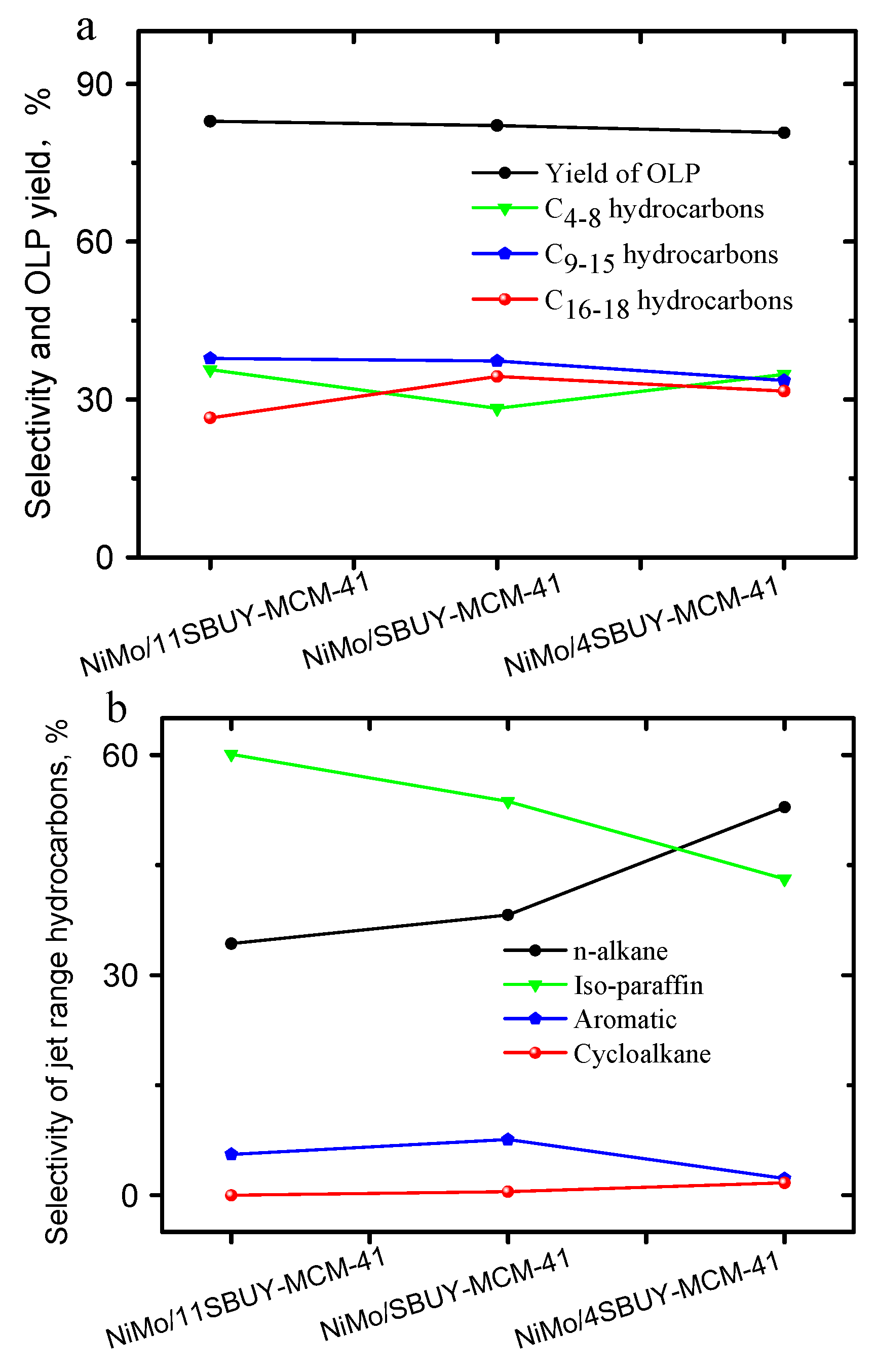
2.6. The Effects of USY Content on the Hydrotreatment of WCO
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
3.2. Catalyst Preparation
3.3. Characterizations
3.4. Hydrotreating of Waste Cooking Oil
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gutiérrez-Antonio, C.; Gómez-Castro, F.I.; de Lira-Flores, J.A.; Hernández, S. A review on the production processes of renewable jet fuel. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 709–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, M.; Fang, Y.; Tan, T.W. Highly efficient conversion of plant oil to bio-aviation fuel and valuable chemicals by combination of enzymatic transesterification, olefin cross-metathesis, and hydrotreating. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2018, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Xin, Z.H.; He, Q.; Corscadden, K.; Niu, H. An overview on performance characteristics of bio-jet fuels. Fuel 2019, 237, 916–936. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.P.; Chen, L.G.; Zhang, Q.H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, T.J.; Qiu, S.B.; Tan, J.; Li, K.; Ma, L.L. Process and techno-economic analysis of bio-jet fuel-range hydrocarbon production from lignocellulosic biomass via aqueous phase deconstruction and catalytic conversion. Energy Procedia 2017, 105, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, C.; Wang, M.; Huang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Tan, T.W. High-quality jet fuel blend production by oxygen-containing terpenoids hydroprocessing. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4871–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.J.; Xin, H.; Yang, H.R.; Du, X.Z.; Yang, R.; Li, D.; Hu, C.W. The Deoxygenation Pathways of Palmitic Acid into Hydrocarbons on Silica-Supported Ni12P5 and Ni2P Catalysts. Catalysts 2018, 8, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.F.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X.W.; Wang, Q.F. TPABr-grafted MWCNT as bifunctional template to synthesize hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolite. Mater. Lett. 2017, 197, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Q.F.; Zhang, X.W.; Wang, L. Quantitative conversion of triglycerides to hydrocarbons over hierarchical ZSM-5 catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 166–167, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Cheng, J.; Huang, R.; Zhou, J.; Cen, K. Conversion of waste cooking oil to jet biofuel with nickel-based mesoporous zeolite Y catalys. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 197, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezergianni, S.; Voutetakls, S.; Kalogianni, A. Catalytic hydrocracking of fresh and used cooking oil. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 8402–8406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebian-Kiakalaieha, A.; Amina, N.A.S.; Mazaheria, H. A review on novel processes of biodiesel production from waste cooking oil. Appl. Energy 2013, 104, 683–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, S.; Mata, T.M.; Martins, A.A.; Pinto, G.A.; Costa, C.A.V. Simulation and life cycle assessment of process design alternatives for biodiesel production from waste vegetable oils. J. Clean. Prod. 2010, 18, 1251–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verma, D.; Rana, B.S.; Kumar, R.; Sibi, M.G.; Sinha, A.K. Diesel and aviation kerosene with desired aromatics from hydroprocessing of jatropha oil over hydrogenation catalysts supported on hierarchical mesoporous SAPO-11. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2015, 490, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Z.; Wang, Q.F.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X.W. Hydroconversion of waste cooking oil into biojet fuel over hierarchical NiMo/USY@Al-SBA-15 zeolite. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2018, 41, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Z.; Wang, Q.F.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X.W. Hydroconversion of waste cooking oil into green biofuel over hierarchical USY supported NiMo catalyst a comparative study of desilication and dealumination. Catalysts 2017, 7, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Liu, L.P.; Xiong, G. Effect of zeolite precursor on the formation of MCM-41 molecular sieve containing zeolite Y building units. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 11248–11253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xiong, G.; Liu, L.P.; Wang, L.L. Investigation on the effect of zeolite precursor on the formation process of MCM-41 containing zeolite Y building units. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 107, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Tan, Q.F.; Liu, H.Y.; Bao, X.J. Templated Assembly of Nano-Crystals of Zeolite Y under Basic Conditions. Chem. React. Eng. Technol. 2013, 29, 470–480. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Wu, S.; Sun, Y.Y.; Li, D.S.; Xiao, F.S. Hydrothermally stable ordered hexagonal mesoporous aluminosilicates assembled from a triblock copolymer and preformed aluminosilicate precursors in strongly acidic media. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 1144–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, R.L.; Agudo, A.L. Effect of water extraction on the surface properties of Mo/Al2O3 and NiMo/Al2O3 hydrotreating catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2000, 202, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís, D.A.; Agudo, L.; Ramírez, J.; Klimova, T. Hydrodesulfurization of hindered dibenzothiophenes on bifunctional NiMo catalysts supported on zeolite–alumina composites. Catal. Today 2006, 116, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubička, D.; Horáček, J.; Setnička, M.; Bulánek, R.; Zukal, A.; Kubičková, I. Effect of support-active phase interactions on the catalyst activity and selectivity in deoxygenation of triglycerides. Appl. Catal. B 2014, 145, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Q.F.; Zhang, X.W.; Wang, L. Hydroconversion of Jatropha Oil to Alternative Fuel over Hierarchical ZSM-5. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 19916–19924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojet, B.L.; Miller, J.T.; Ramaker, D.E.; Koningsberger, D.C. A new model describing the metal-support interaction in noble metal catalysts. J. Catal. 1999, 186, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, S.; Marini, H.J.; Marzari, J.A.; Miranda, R. Silica-Alumina-Supported Acidic Molybdenum Catalysts-TPR and XRD Characterization. J. Catal. 1994, 147, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.H.; Wang, Q.F.; Zhang, X.W.; Wang, L.; Li, G.Z. Hydrotreating of C18 fatty acids to hydrocarbons on sulphided NiW/SiO2―Al2O3. Fuel Process Technol. 2013, 116, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Shinozaki, A.; Qian, E.W. Role of Support in Hydrotreatment of Jatropha Oil over Sulfided NiMo Catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 13953–13960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, W.; Zhao, Y.; Pan, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Kong, L. Synthesis, characterization, and catalytic performance of high-silica Y zeolites with different crystallite size. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 167, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjaye, J.D.; Katikaneni, S.P.R.; Bakhshi, N.N. Catalytic conversion of a biofuel to hydrocarbons: Effect of mixtures of HZSM-5 and silica-alumina catalysts on product distribution. Fuel Process. Technol. 1996, 48, 115–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliopoulou, E.F.; Heracleous, E.; Delimitis, A.; Lappas, A.A. Producing high quality biofuels: Pt-based hydroisomerization catalysts evaluated using BtL-naphtha surrogates. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 145, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cui, D.M.; Li, Q.Z. Synthesis, characterization and influence parameters on the overgrowth of micro/mesoporous Y-zeolite-MCM-41 composite material under acidic conditions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 142, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
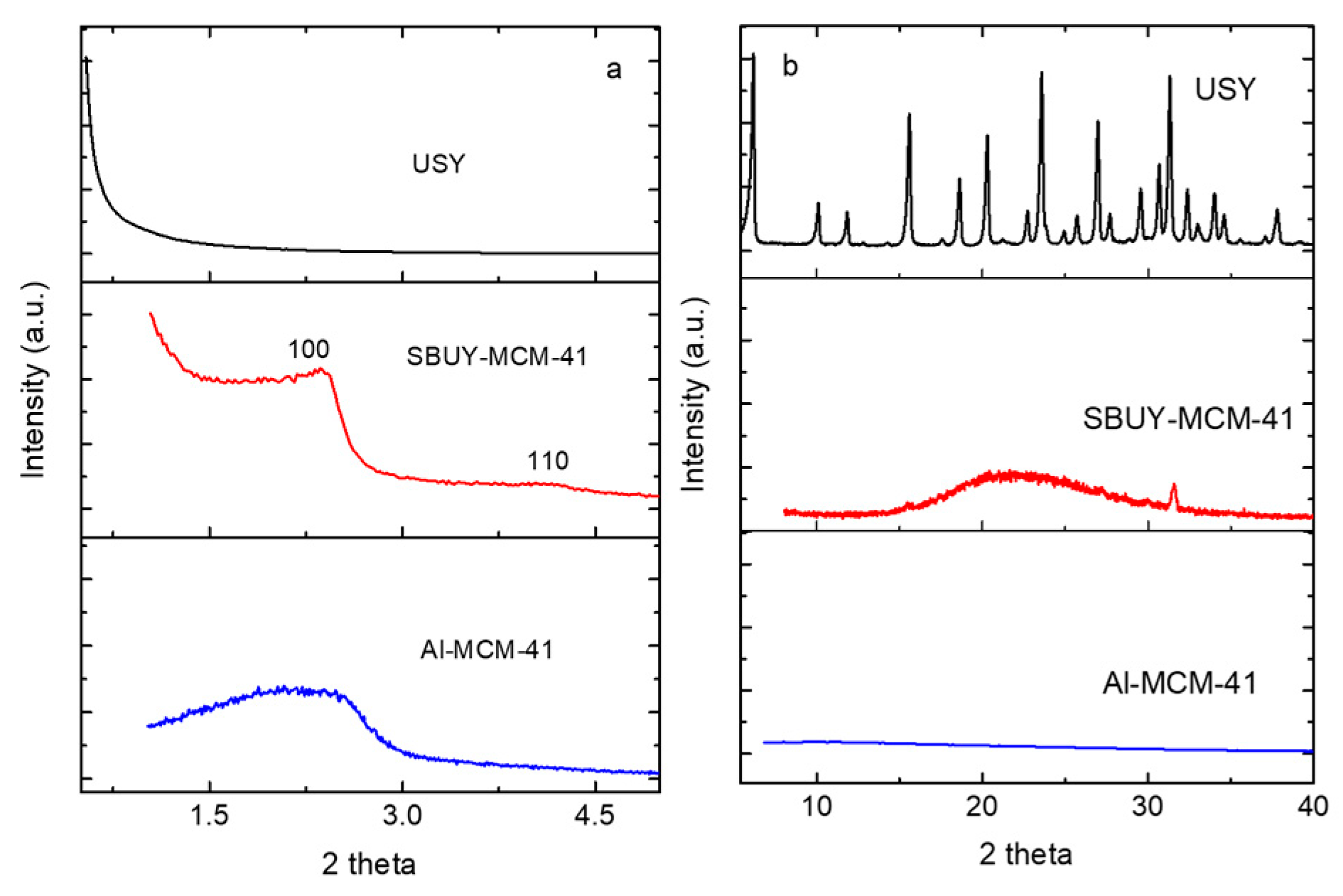


| Samples | SBET (m2 g−1) | Vtotal (cm3 g−1) | Unit Cell (nm) | Mesopore Size (nm) | Tpore wall (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USY | 658 | 0.35 | - | - | - |
| Al-MCM-41 | 885 | 0.83 | 4.09 | 2.8 | 1.29 |
| SBUY-MCM-41 | 820 | 0.64 | 4.55 | 2.6 | 1.95 |
| Sample | B | L | B/L | Weak | Medium | Strong |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acidity | Acidity | Acidity | ||||
| USY | 1851 | 634 | 2.9 | 158 | 530 | 598 |
| Al-MCM-41 | 158 | 212 | 0.7 | 78 | 184 | 52 |
| SBUY-MCM-41 | 442 | 558 | 0.8 | 71 | 224 | 198 |
| Sample | Adsorbed CO (μmol g−1) |
|---|---|
| NiMo/USY | 1.33 |
| NiMo/Al-MCM-41 | 3.03 |
| NiMo/SBUY-MCM-41 | 3.25 |
| Property | Waste Cooking Oil |
|---|---|
| Acid value (mg KOH−1) | 65.47 |
| Palmitic acid (C16:0, wt %) | 25.02 |
| Linoleic acid (C18:2, wt %) | 28.85 |
| Oleic acid (C18:1, wt %) | 39.69 |
| Stearic acid (C18:0, wt %) | 6.27 |
| Other acid (wt %) | 0.17 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X. Hydroconversion of Waste Cooking Oil into Bio-Jet Fuel over NiMo/SBUY-MCM-41. Catalysts 2019, 9, 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9050466
Zhang Z, Wang Q, Zhang X. Hydroconversion of Waste Cooking Oil into Bio-Jet Fuel over NiMo/SBUY-MCM-41. Catalysts. 2019; 9(5):466. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9050466
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zongwei, Qingfa Wang, and Xiangwen Zhang. 2019. "Hydroconversion of Waste Cooking Oil into Bio-Jet Fuel over NiMo/SBUY-MCM-41" Catalysts 9, no. 5: 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9050466
APA StyleZhang, Z., Wang, Q., & Zhang, X. (2019). Hydroconversion of Waste Cooking Oil into Bio-Jet Fuel over NiMo/SBUY-MCM-41. Catalysts, 9(5), 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9050466





