Abstract
In spray studies related to selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems a common approach is to replace the urea–water solution (UWS) with pure water, even though there is very limited detailed information on the spray properties for these two liquids obtained under the same conditions using the same experimental equipment. Neither is it known how the possible differences in spray properties influence computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations. In this study, besides the flow characteristics, we compare both global and local spray parameters measured for UWS and pure water in the same conditions. To our knowledge, this is the first study which examines the influence on the injection process of replacing UWS with water over such a wide range. Moreover, the influence of different spray properties on CFD simulations is also examined. The experimental studies showed differences in almost all considered spray parameters. Moreover, different spray behaviour was noticed in terms of primary break-up. One important finding is that water and UWS sprays do have a similar Sauter mean diameter, but at the same time the droplet size distribution is considerably different. The simulation results indicated noticeable differences in terms of wall film formation; nevertheless, the overall mixing performance was not significantly affected.
Keywords:
urea–water solution; UWS; injection; spray; selective catalytic reduction; SCR; optical diagnostics; CFD; simulations 1. Introduction
The importance of spray properties in terms of efficient NOx reduction in urea–selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems is growing. This is caused by stricter emission limits directly, and indirectly, through the development of compact SCR units located close to the engine, so-called close-coupled SCRs. Close-coupled to the engine SCRs, due to higher exhaust gas temperatures, offer a huge potential of NOx reduction [1], especially in terms of catalyst warm-up time; but at the same time, decrease the available distance for mixing the urea–water solution (UWS) with the exhaust gases. When the space for mixing is limited, then the spray properties become the key factor in determining the quality of the SCR system. Therefore, besides investigating alternative solutions [2], the urea–water sprays are more often studied than in the past—when the inline underfloor SCR systems were a standard solution.
The experimental studies on UWS injection related to SCR systems’ development are usually aimed at spray characterization for proper injector selection, or determining the spray properties for further computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations, where full SCR system designs are optimized. These include both spray formation as well as spray-wall interaction. In many studies available in the literature, UWS is replaced with pure water [3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. For preliminary studies, such an approach seems to be justified since the physical properties influencing spray behaviour, specifically surface tension and viscosity, are similar for these two liquids. In certain cases, however, even small differences between the liquids can lead to different spray characteristics. Different spray characteristics in turn, may be crucial when highly accurate results are required. Moreover, some parameters differ more (e.g., specific heat). Different values of specific heat may lead to different droplet sizes at higher distances from the injector outlet, especially in hot flow conditions. Nevertheless, even in cold-flow studies on injector characterization, small differences in surface tension and viscosity together may have an influence on measured spray parameters. When spray characterization optical methods are applied a different refractive index may lead to different results as well, especially in the case of Mie scattering. A comparison of selected physical properties of water and UWS is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Physical properties of water and urea–water solution (UWS) (32.5% urea mass fraction).
If more precise studies are required, then before replacing UWS with water one needs to ensure that these two liquids produce similar sprays. However, detailed information on differences in spray parameters for the same conditions is very limited. Spiteri et al. [3], based on his earlier findings [20], stated that water and UWS sprays behave similarly. On the other hand, Birkhold et al. [21] noticed that the evaporation dynamics of UWS differ from pure water. They stated that the decrease in vapour pressure due to an increasing concentration of urea in the droplet results in a continuous increase of the droplet temperature and a slower evaporation, compared to pure water [21]. The model proposed by Ebrahiman et al. [17] confirmed that during vaporization urea concentration increases, which in turn leads to a decrease in vapour pressure. However, their calculations of droplet evaporation indicated the low influence of the presence of urea on water evaporation, even though it had a huge effect on the droplet temperature. If the evaporation is slower, as reported by Birkhold et al. [21], this may have an effect on droplet sizes at further distances.
The crucial element in the SCR system’s development is fine adjustment of the spray pattern and droplet size distribution to a specific SCR unit’s design. Thus, a fast and reliable method for spray characterization is very important for proper injector selection and spray pattern optimization.
Many of the studies available in the literature regarding sprays in SCR systems were based on a UWS injection. However, most of them were specifically aimed at the properties of the UWS, and no comparison with water was made. Grout et al. [22], based on the diameter change of individual droplets, calculated the evaporation rate of the UWS according to the D-square evaporation law. Postrioti et al. [23] observed urea–water sprays in order to determine the liquid mass distribution over the visualized area. They also used phase doppler anemometry (PDA) to determine droplet diameters. They determined the Sauter mean diameter at 16 locations at distances of 90 mm and 140 mm from the injector outlet. They made 5 additional measurements in order to compare the results with backlight imaging. Payri et al. [24] studied the atomization of UWS sprays in hot co-flow to simulate exhaust system conditions. They used a diffused back illumination technique at high imaging speed. They observed that droplet diameter and velocity are affected by injection pressure. Moreover, the differences were seen depending on the measurement position of the spray, which indicated the role of the evaporative conditions.
In this study, we combine global and local spray properties’ determination using optical techniques with flow characteristics’ measurements, in order to provide comprehensive data on the difference between UWS and water sprays. The parameters under consideration are: Droplet size distribution and statistical droplet parameters; spray angle (visualization angle, spray plume inclination angle); spray tip penetration; unbroken liquid length; initial jet velocity; static flow properties such as static flow rate (mass, volumetric and average velocity), Reynolds number, Weber number (referred to gas); and finally, Ohnesorge number.
To our knowledge, this is the first study which examines the influence on the injection process of replacing UWS with water over such a wide range. Both liquids were injected by the same commercial SCR system injector into ambient air under the same pressure and temperature. Long-distance microscopy with backlight illumination (shadowgraphy) was used to determine the droplet size distribution 20 mm from the injector’s outlet. It was also used to determine the unbroken liquid length and spray inclination angle. The spray visualization angle, spray tip penetration and initial jet velocity were determined by high-speed Mie scattering imaging. The static flow parameters were calculated based on the measurements of the injected mass over different injection durations.
Further, since CFD is extensively used for SCR systems’ development, the determined spray parameters were used in simulations of an exhaust system in order to examine the effect of using spray data obtained for water instead of UWS on the simulations’ results. Crucial parameters influencing the overall SCR system performance were compared, specifically wall film formation and ammonia homogenization. The simulations were performed for a light-duty close-coupled SCR system under various conditions relevant to an automotive diesel engine.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Experimental Study
The study was done in several steps, including: Determination of mass flow rate characteristics; measurements of global spray properties; as well as determination of droplet sizes, spray plume inclination angle and unbroken liquid length for both liquids, UWS and water. The results obtained in the separate steps are described in the following separate subsections. All tests were conducted for three different injection pressures 0.4, 0.45 and 0.5 MPa (gauge pressure).
2.1.1. Flow Characteristics
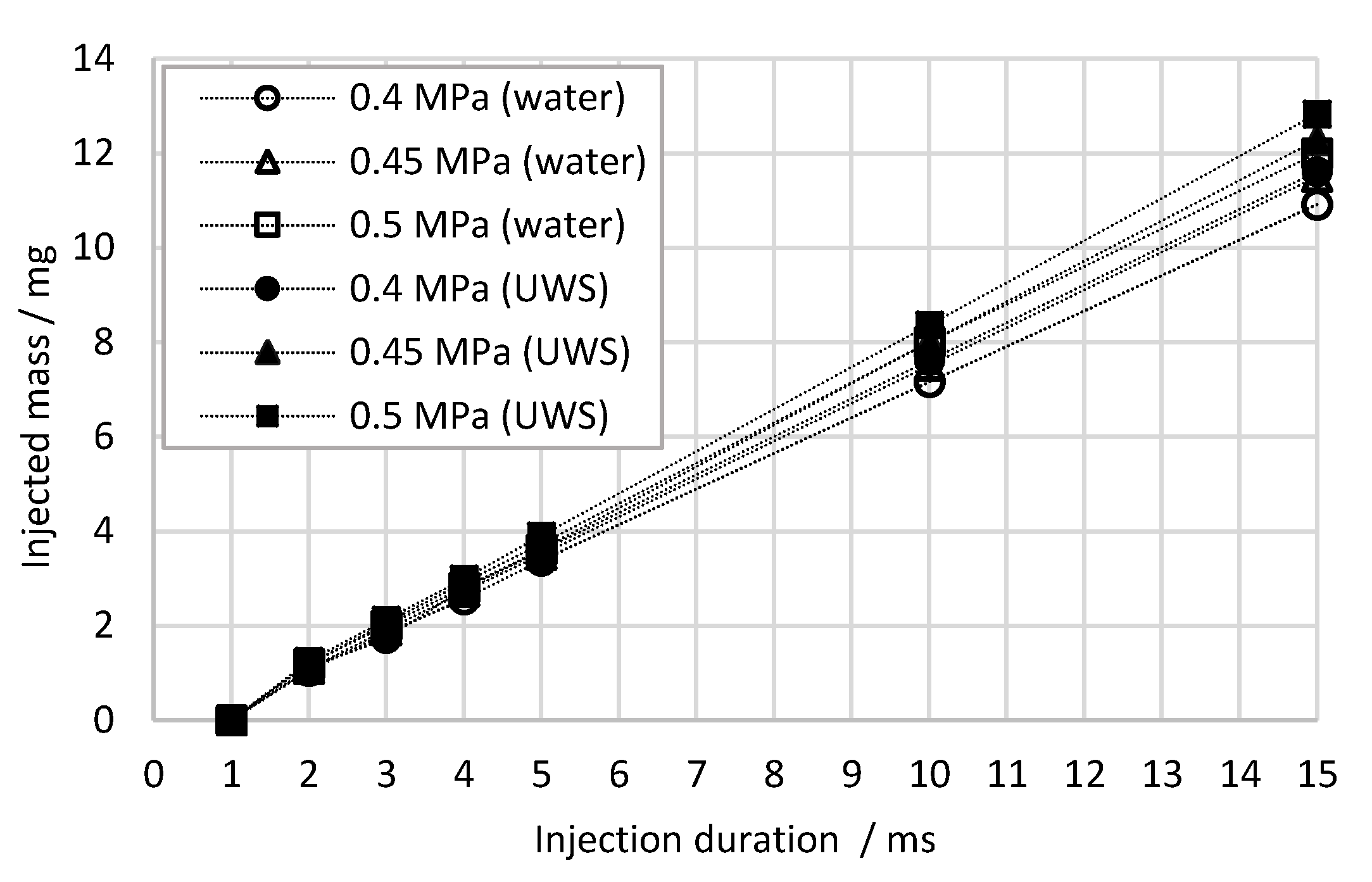
Flow characterization was based on measurement of the injected mass over 5000 injections. Seven different opening times of the injector were studied, specifically 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 15 ms. Each measurement series was repeated three times resulting in 15,000 injections in total per one operating point. The averaged results for three measurements series (15,000 injections per one point) are shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1.
Injected mass during single injection; average values for 3 measurements (each of 5000 injections) for water and UWS for different injector opening times for all considered injection pressures (gauge).
As seen in Figure 1, at 1 ms injector opening time no liquid was injected at all. In all other investigated opening times, the correlation was linear.
Based on measurements of injected mass for injection durations of 5 and 15 ms the static flow rate through the injector was determined. The static flow rate was then used to determine the average (in nozzle cross-section) flow velocity and further, the Reynolds number, Re, and Weber number, Weg (referred to the gas). The Reynolds number was calculated according to Equation (1):
where: —is the velocity of the liquid, d—is the nozzle diameter, —is the kinematic viscosity of the liquid.
The Weber number was calculated according to Equation (2):
where: —is the density of the gas, σ—is the surface tension.
The Ohnesorge number was calculated according to Equation (3):
where: —is the dynamic viscosity of the liquid, —is the density of the liquid.
The complete set of parameters including the Ohnesorge number, Oh, is shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
In-injector flow characteristics.
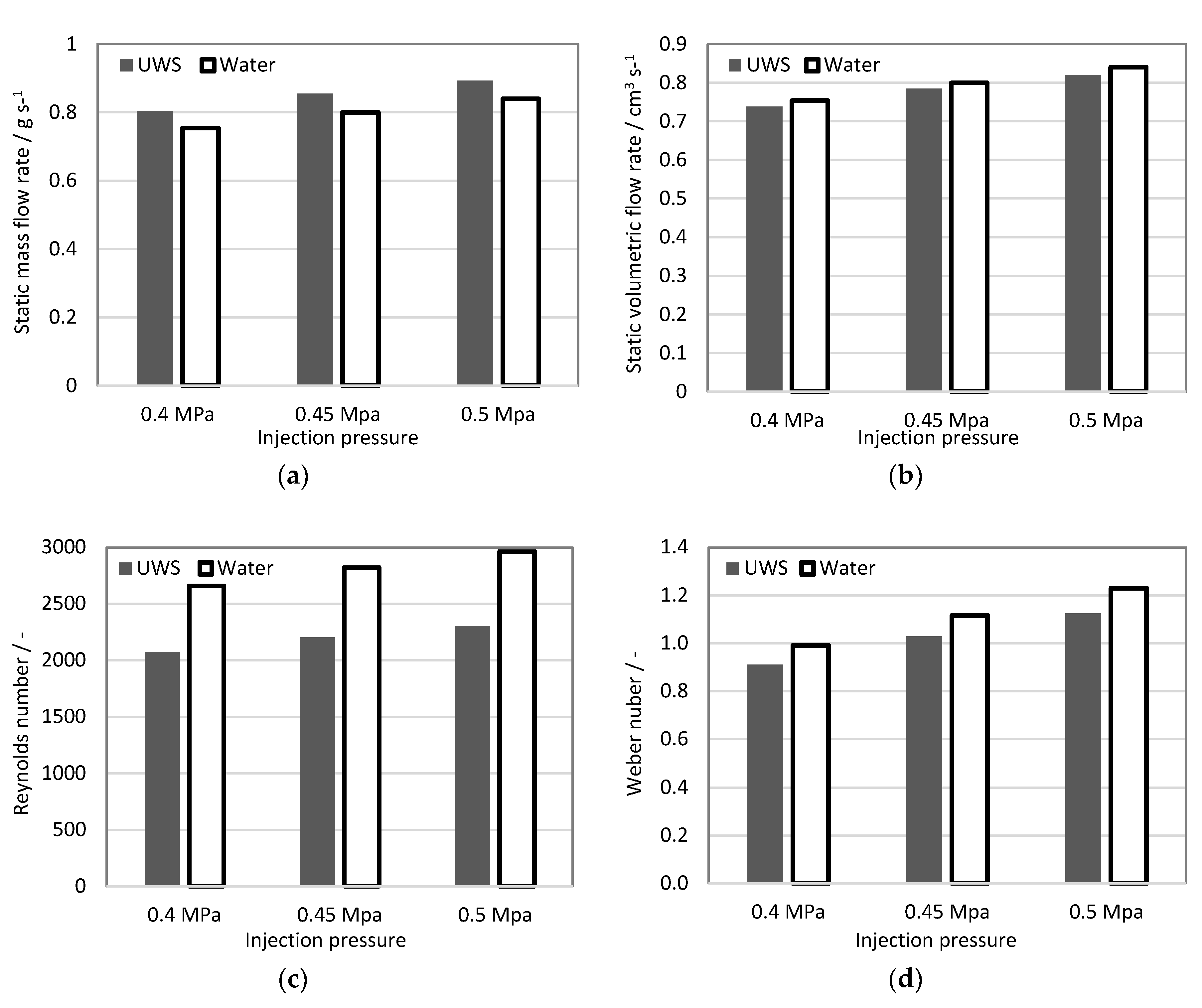
Selected parameters from Table 2 (mass flow rate, volumetric flow rate, Reynolds number and Weber number) are shown in graphs in Figure 2 to visualize the trends and differences between the two studied fluids.
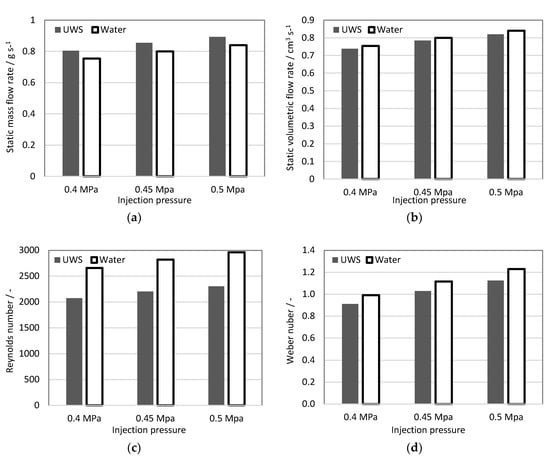
Figure 2.
In-injector flow characteristics: (a) static mass flow rate; (b) static volumetric flow rate; (c) Reynolds number; (d) Weber number (referred to gas).
The mass flow rate of UWS for all studied injection pressures was higher than for water. This can be directly linked to higher density. The volumetric flow rate in turn, was lower for UWS than for water, which can be related to a viscosity difference. Higher volumetric flow rate, and thus average flow velocity for water together with lower kinematic viscosity resulted in a much higher Reynolds number; Weg was also higher for water, due to a higher flow velocity, but also due to lower surface tension. It may be concluded that relatively small differences in viscosity and surface tension together led to considerably large differences in the Reynolds number (almost 29% increase) and the Weber number (almost 9% increase), when UWS was replaced with water.
2.1.2. Spray Tip Penetration
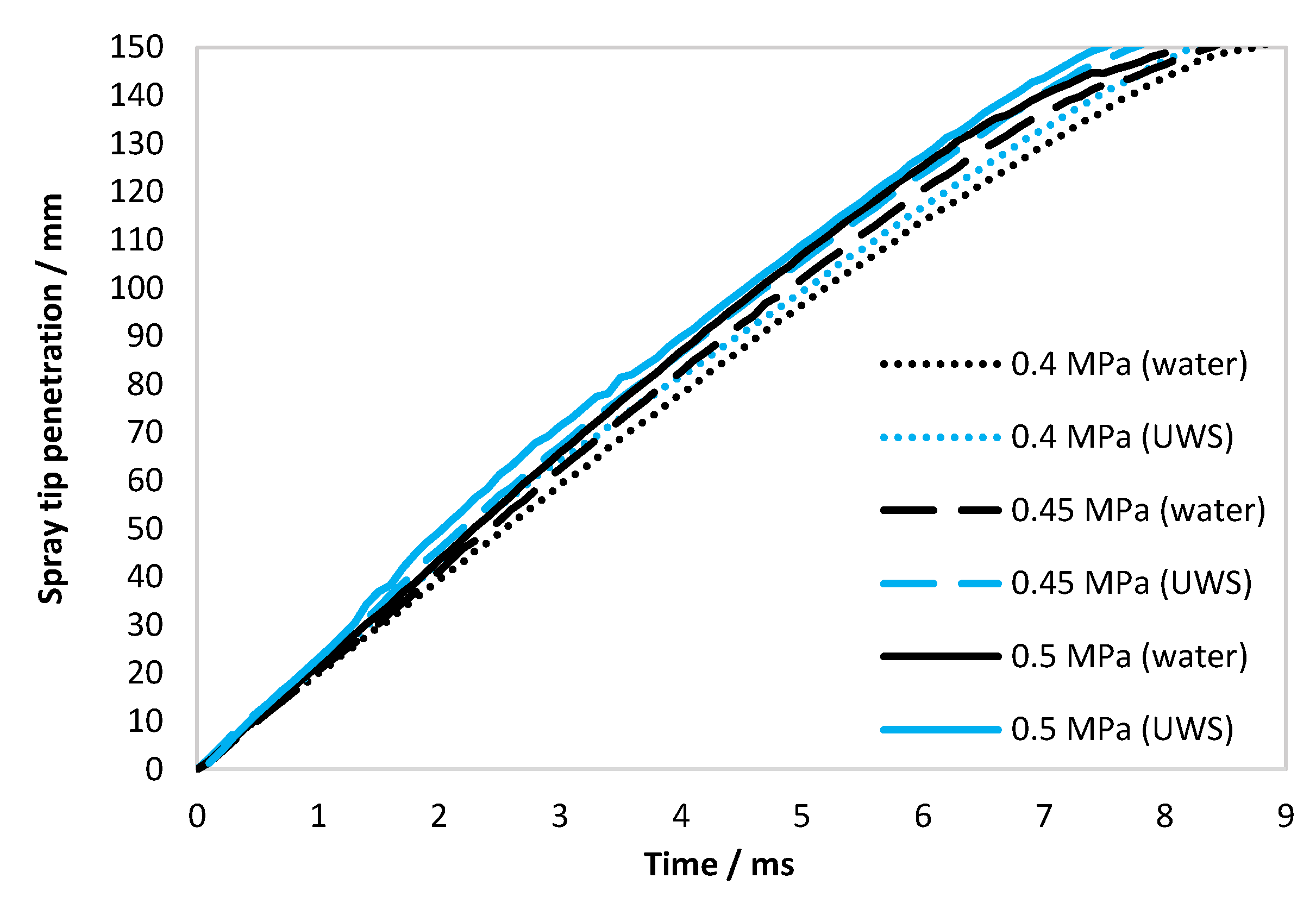
The spray penetration was determined based on high-speed Mie scattering images. The image processing methodology is provided in Section 3.1.2. The spray penetration evolution (average for five injections) for both liquids at all considered injection pressures is shown in Figure 3.
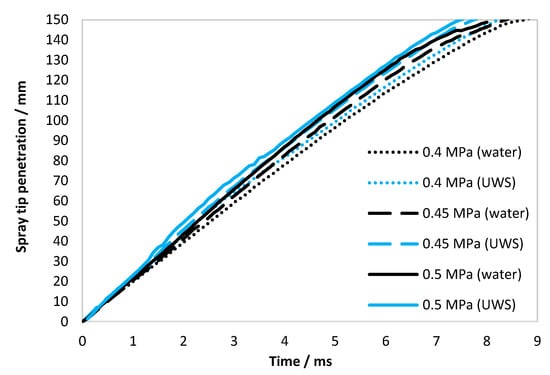
Figure 3.
Spray tip penetration for water and UWS for all considered injection pressures (gauge); each curve is an average for five injections.
As seen in Figure 3, the spray penetration for UWS is higher for all considered injection pressures. It might seem surprising since the static flow velocity is higher for water (Table 2), however, the penetration evolution of the spray considered here is the evolution of the spatial location of the initially released liquid. This is strongly dependent on the initial flow conditions (just after the injector opening), while the average flow velocity reported in Table 2 is a parameter of a steady flow. Thus, the spray tip penetration will be mainly dependent on the initial jet velocity as well as the liquid momentum and the aerodynamic drag force.
As the spray tip penetration was obtained by capturing the Mie signal, it should be noted that due to the different refractive index of UWS and water (see Table 1), the results could be different regardless of the spray’s behaviour. The simulations [25] suggest that the backscattering intensity (scattering angle: 150–180 degrees) of droplets within the size range observed here for a wavelength range 650–800 µm (range of highest quantum efficiency of CMOS (complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor) sensors, where the halogen light source signal is relatively high), can be more than doubled in the case of UWS when compared to water. In the case of spray penetration, this effect is assumed to be marginal, since the liquid ligaments exiting the nozzle (and the large droplets formed out of these ligaments) were generating a relatively strong signal of similar intensity in all cases. Moreover, the results of the initial jet velocity (reported in Section 2.1.3), which is not dependent on the intensity threshold (as it is based on the difference of spray tip positions at different time steps), showed higher values in the case of UWS. This also indicates that spray tip penetration was not affected by the difference in the refractive index between two studied liquids.
2.1.3. Initial Jet Velocity
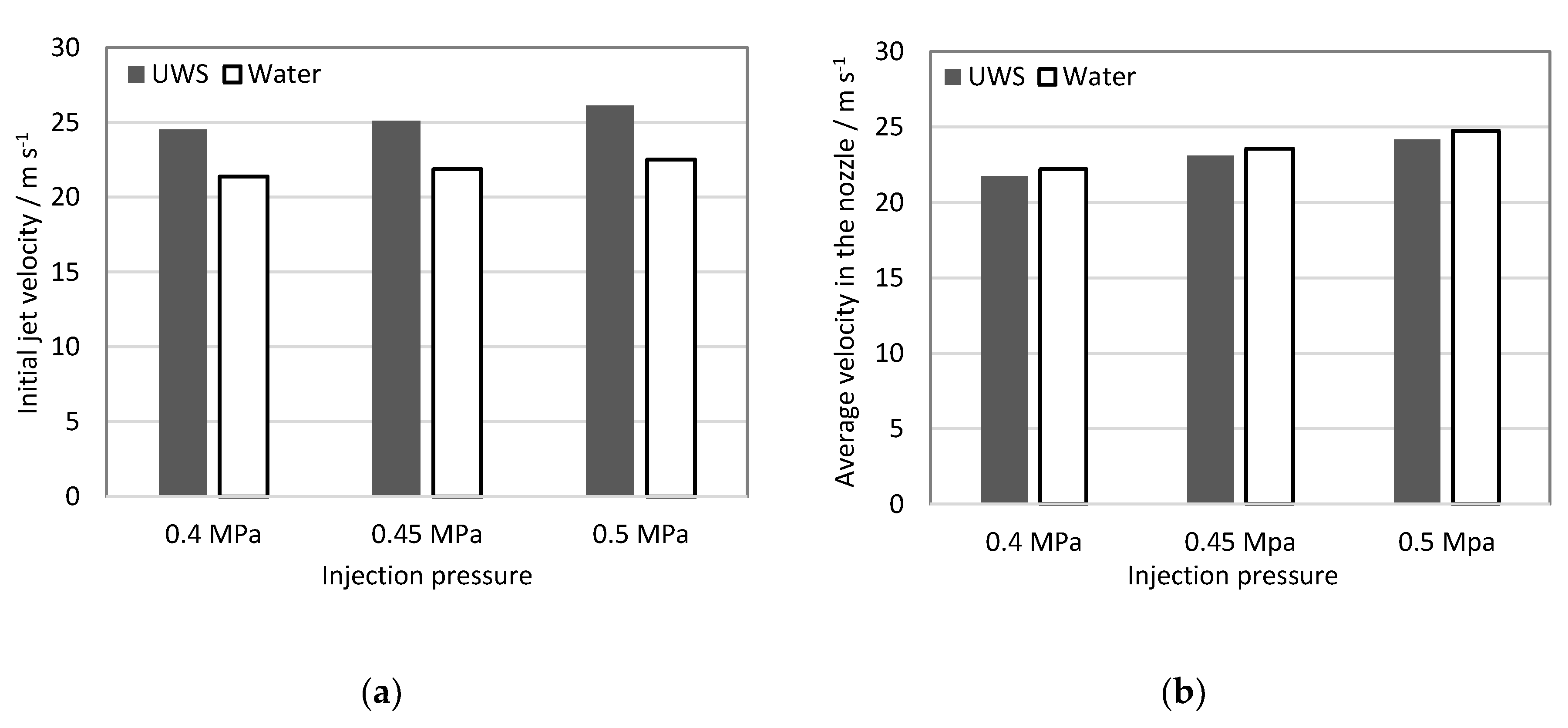
The initial jet velocity, defined as the velocity of the first liquid fragments emerging from the nozzle after the injector opening, was determined from the first three frames of the high-speed imaging sequence when liquid was observed using the same image processing procedures as for spray penetration determination (see Section 3.1.2). The results are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Initial jet velocity in m/s for water and UWS for all considered injection pressures (gauge).
In order to visualize the trends and differences between the two studied fluids, as well as the differences between the static flow velocity, the results were plotted on a graph (Figure 4a) and shown together with the static flow velocity (average velocity in the nozzle) reported earlier in Table 2 (Figure 4b).
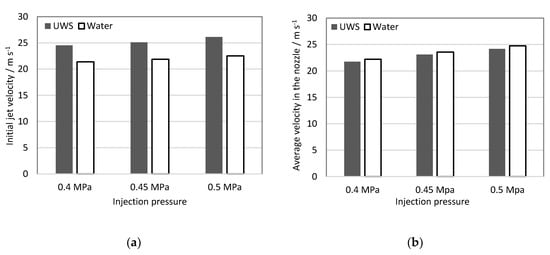
Figure 4.
(a) initial jet velocity; (b) static flow velocity (from Table 2).
The initial jet velocity in contrast to the static flow velocity is higher for UWS than for water. The reason for this difference could not be caused by the difference in the refractive index, since the initial jet velocity is calculated as the difference of the spray tip’s position after a certain time step, and the absolute spray tip penetration does not play a role.
It is assumed that two parameters together, higher density (and as a result inertia) and viscosity for UWS, lead to a longer delay and consequently, higher pressure build-up before the first liquid exits the nozzle after the injector opening signal. This in turn, results in higher initial jet velocity for UWS, even though the static volumetric flow rate for this liquid is lower. The longer delay was observed also in the images at the same trigger settings (camera and injector); in the case of UWS the first liquid exiting the nozzle was observed one frame later (0.1 ms later) than in the case of water.
The higher initial jet velocity together with higher density (and thus momentum) explain the higher spray tip penetration for all UWS cases.
2.1.4. Spray Visualization Angle
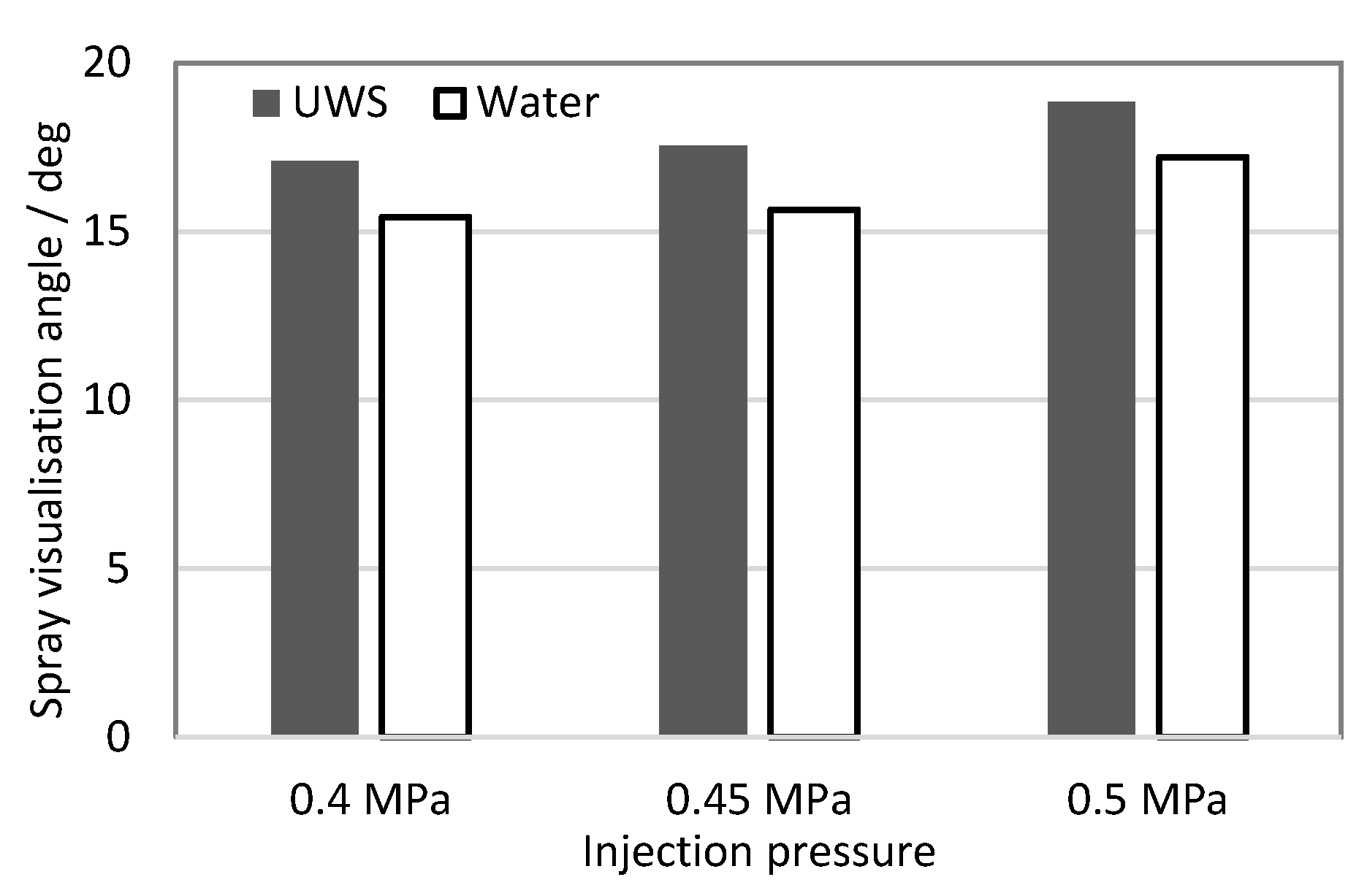
The spray visualization angle is a practical parameter describing a whole spray cloud formed by several spray plumes used for rapid injector comparison, and for selection for fitting the geometrical arrangement of the exhaust system. The visualization angle was measured also from high-speed images, using the same image intensity threshold to separate the spray from the background as that for the spray penetration determination. The graph presented in Figure 5 shows the average (for frames between 10 and 12 ms after start of injection, and for five injections) spray visualisation angle measured for both UWS and water at all considered injection pressures.
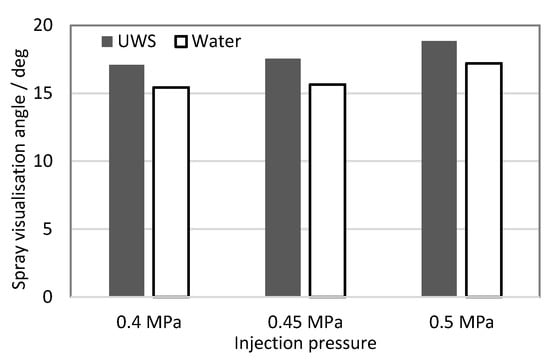
Figure 5.
Spray visualisation angle.
It may be observed that for both liquids the spray angle increases with injection pressure, which is consistent with results shown by other researchers for similar injection parameters [24,26]. When considering differences between the studied fluids it can be seen that the visualization angle determined for UWS was higher than for water for all considered injection pressures. If the droplet number and droplet size distribution are taken into account (see Table 4), the results may seem surprising. Water sprays in most cases produced a higher number of droplets and the volume of injected liquid over the same period was higher (Figure 1). In this case, the effect of different refractive indexes was supposed to have a major impact on the results. In a spray cloud the smallest droplets at the lowest concentration and thus generating the weakest signal are usually in the side peripheral region of the spray. As explained earlier, the Mie scattering signal for droplets within the size range observed here can be more than twice lower for water than for UWS. Different optical properties could be compensated (e.g., by using stronger light to illuminate the spray or by using a different intensity threshold value to separate the spray cloud from the background), but as stated earlier, the idea behind this work was to compare the sprays using the same set-up and the same conditions, which includes the data processing as well. Especially as setting the intensity threshold value for spray cloud separation from the background just above small random intensity fluctuations present in the background regardless of the fluid type seems to be the right choice.

Table 4.
Droplet cumulated statistics (for 99 injections).
2.1.5. Jet Inclination Angle
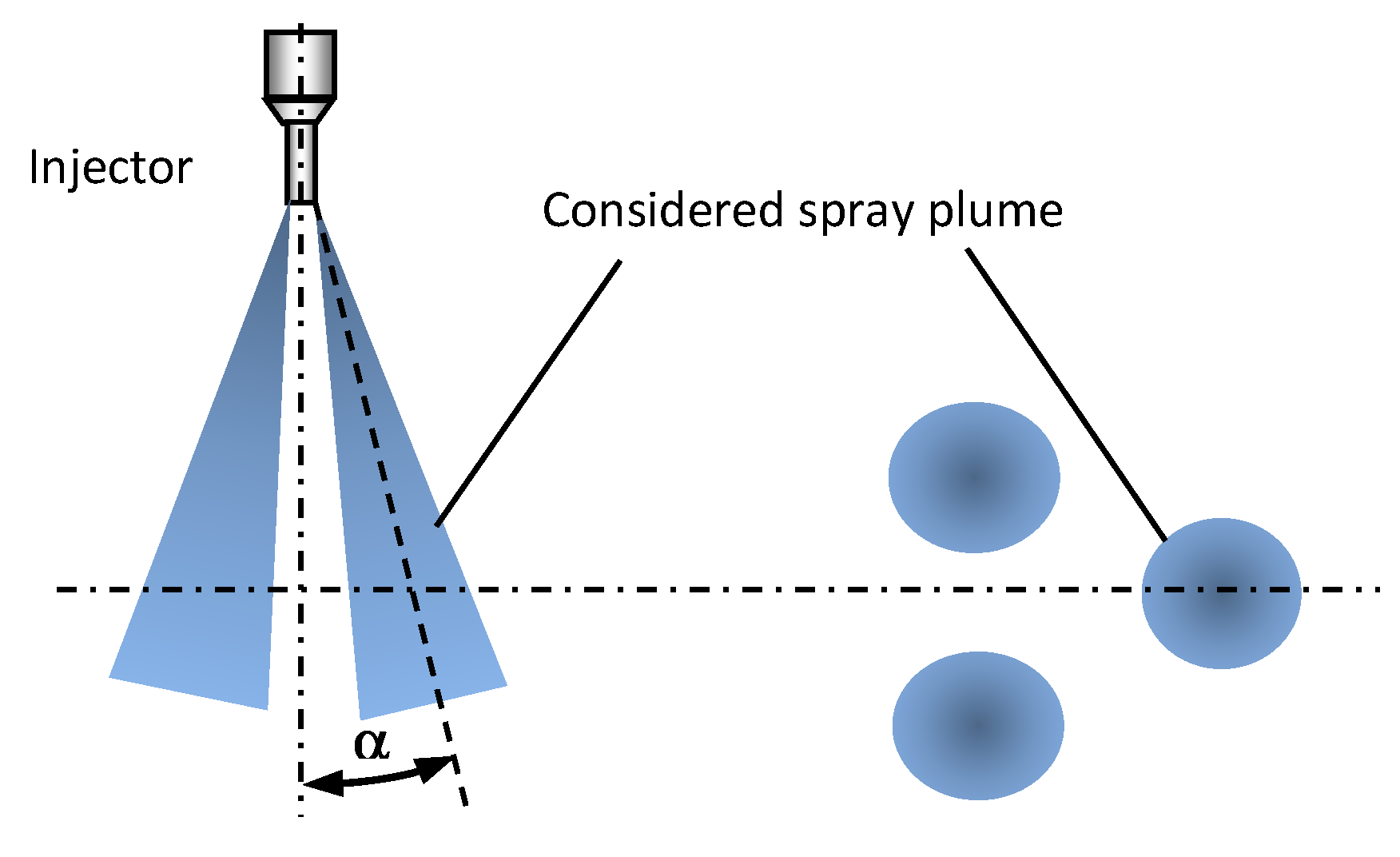
The jet inclination angle was expected to be insensitive to liquid change, however it was measured for the purpose of the numerical work. The measurement was done only for one selected nozzle where the axis was in the visualisation plane. The measurement was done based on averaged shadowgraphy images captured at the nozzle exit. The definition of the jet inclination angle is shown in Figure 6. The measured jet inclination angle was insensitive to both liquid type and injection pressure, and was 6 degrees for all cases.
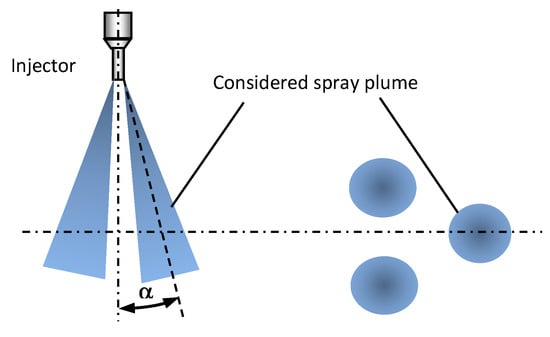
Figure 6.
Jet inclination angle, α definition.
2.1.6. Unbroken Liquid Length
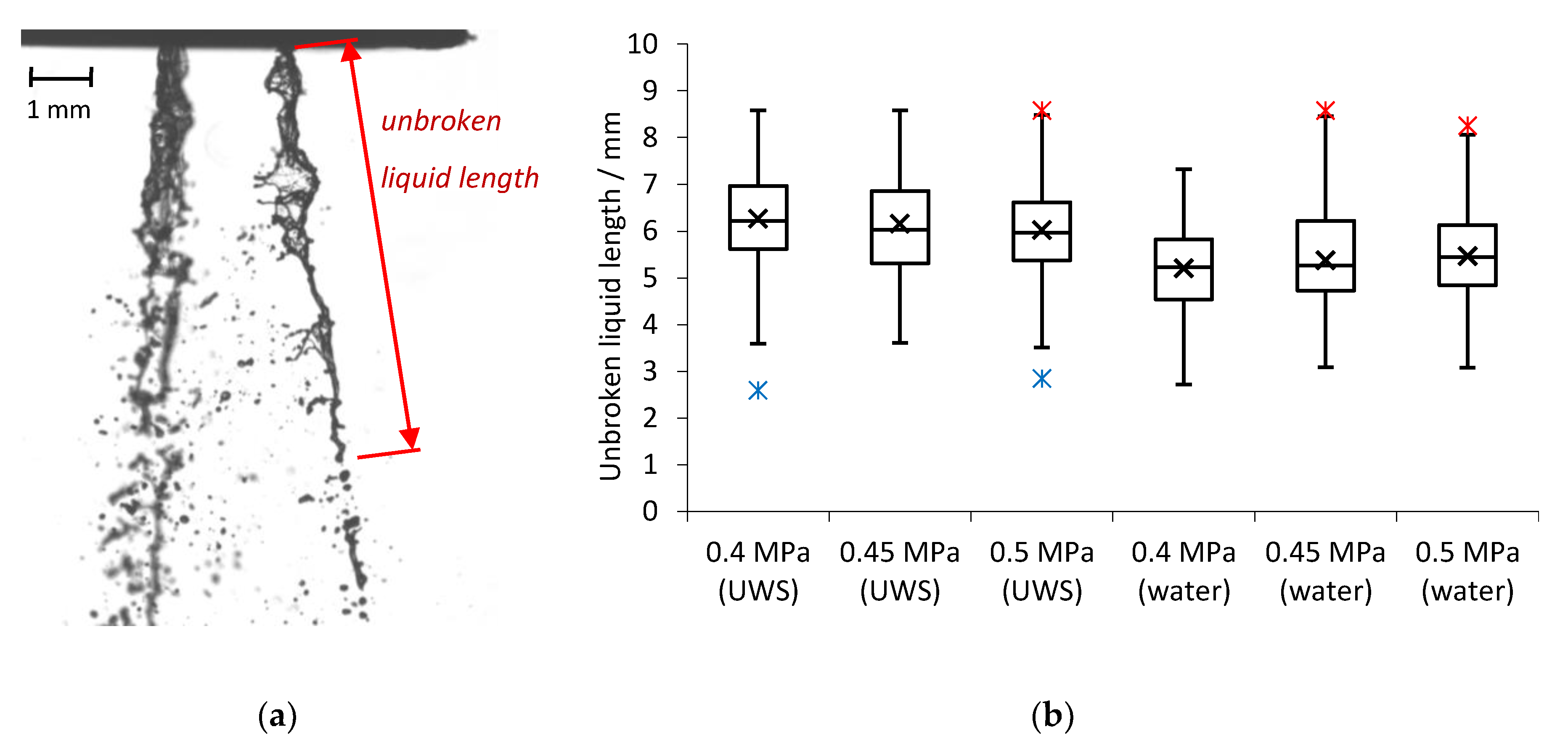
The unbroken liquid length was measured based on shadowgraphy imaging at the nozzle exit. In order to examine the developed sprays and exclude the effects of the injector opening, the images were captured 10 ms after the start of injection. At this time the flow is stable (as seen in Figure 1) and the first droplets released after the injector opening are already further than 150 mm from the injector’s outlet (Figure 3); while the unbroken liquid length is analysed close to the nozzle (up to 10 mm from the nozzle outlet). The single image of the visualised jets (water case, 0.5 MPa) together with the unbroken liquid length definition is shown in Figure 7a. The measured values of the unbroken liquid length are shown in Figure 7b.
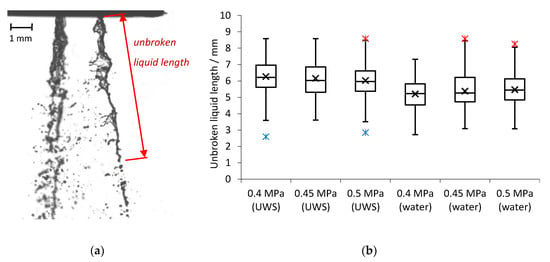
Figure 7.
(a) Visualised jets for water and unbroken liquid length definition; (b) measured unbroken liquid length (for 99 injections for each injection pressure).
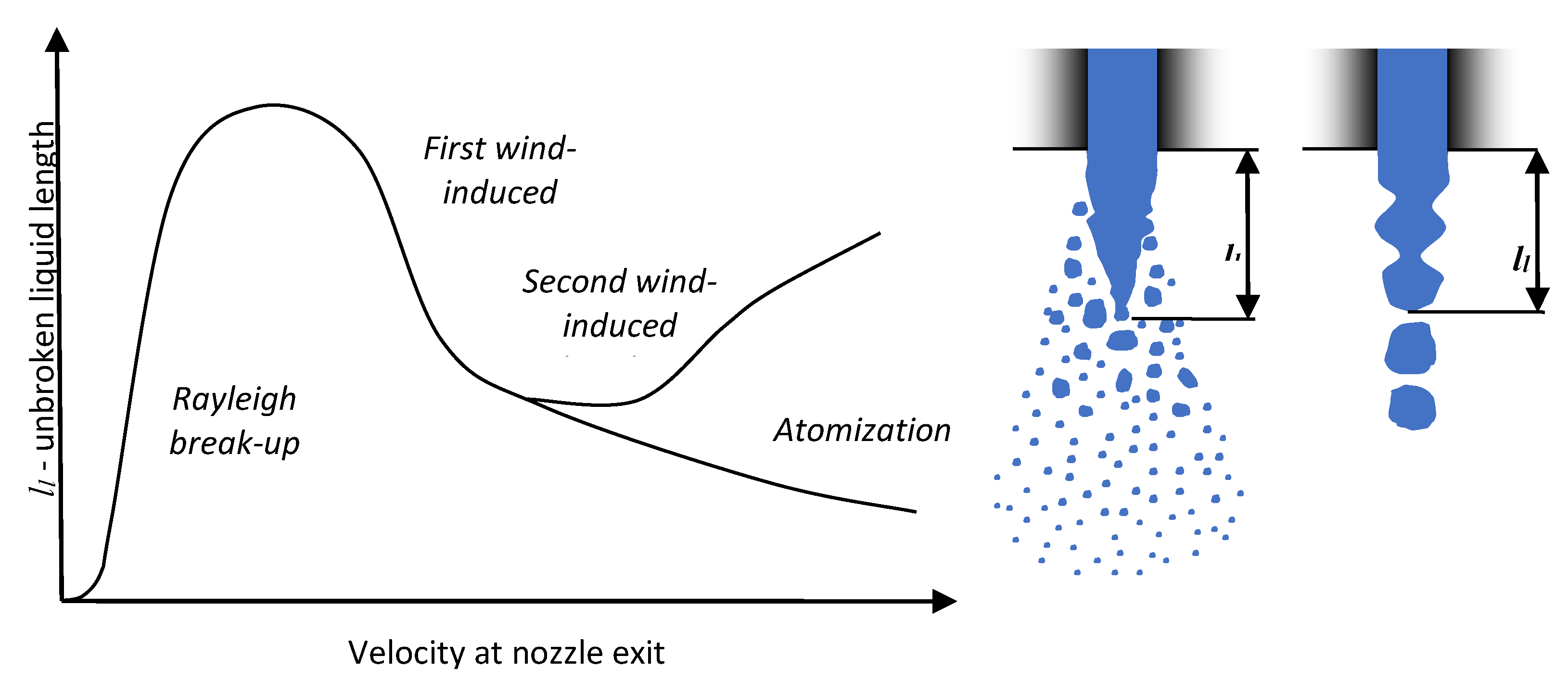
It may be observed that an increase in injection pressure for UWS caused a decrease of the unbroken liquid length (both average and median); while for water the effect was the opposite. When considering the average inner nozzle velocity, which is higher for water than for UWS and increases when injection pressure is increased (Figure 4b), and a relation proposed by Leroux [27] which links the unbroken liquid length of the jet with the velocity at the nozzle exit, one can conclude that replacing UWS with water moved the jet from the first wind-induced break-up regime to the second wind-induced regime (Figure 8). This is the only regime (besides the Rayleigh regime) where the unbroken liquid length was noticed to be increasing with increased jet velocity.
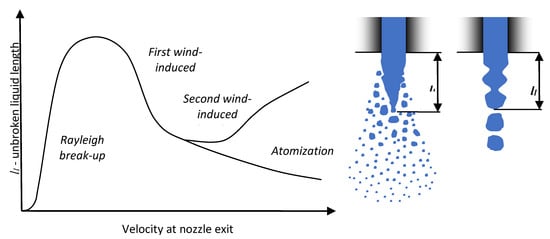
Figure 8.
Unbroken liquid length of the jet versus velocity at the nozzle exit and the definition of the unbroken liquid length for different types of break-up (based on [27,28,29]).
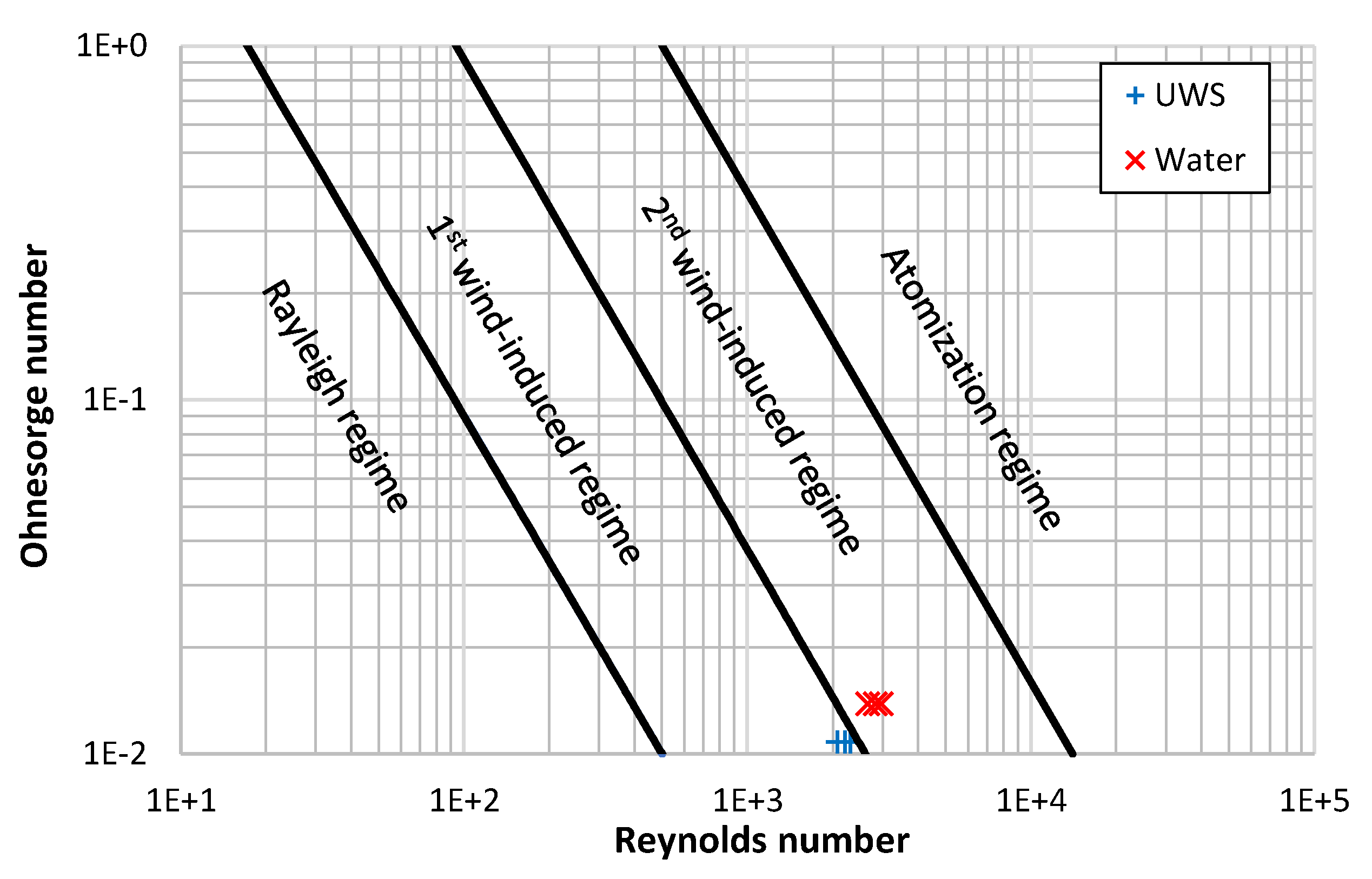
When the Weber number for gas, Weg, is considered, then according to Ranz [30] both jets should be in the first wind-induced regime (0.4 < Weg < 13). However, when a criterion of the Ohnesorge number, and the Reynolds number is considered (the reference then is to liquid density), the assumption of switching jet break-up regimes from first wind-induced break-up regime into the second wind-induced break-up regime by changing a fluid type from UWS to water is confirmed (Figure 9).
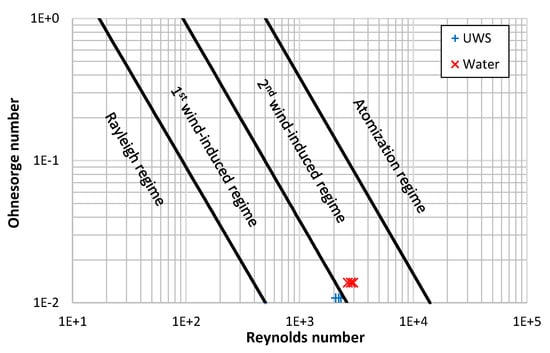
Figure 9.
Jet break-up regimes and the considered injection cases (based on [31,32]).
It needs to be emphasized that the change of break-up regime does not take place suddenly after certain parameters are reached or exceeded. The process is not instantaneous and considered criterions are invented. Both criterions (shown in Figure 8 and Figure 9) suggest that in the case of UWS the break-up regime was the first wind-induced regime and in the case of water the second wind-induced regime. However, it does not need to be similar for different set-ups (different injector nozzle diameter and injection pressure), the break-up regime can remain the same. Nevertheless, it can be concluded that replacing UWS with water (by the increased Ohnesorge number and Reynolds number) moves the jet droplet break-up process towards the next break-up regime.
2.1.7. Droplet Size Distribution
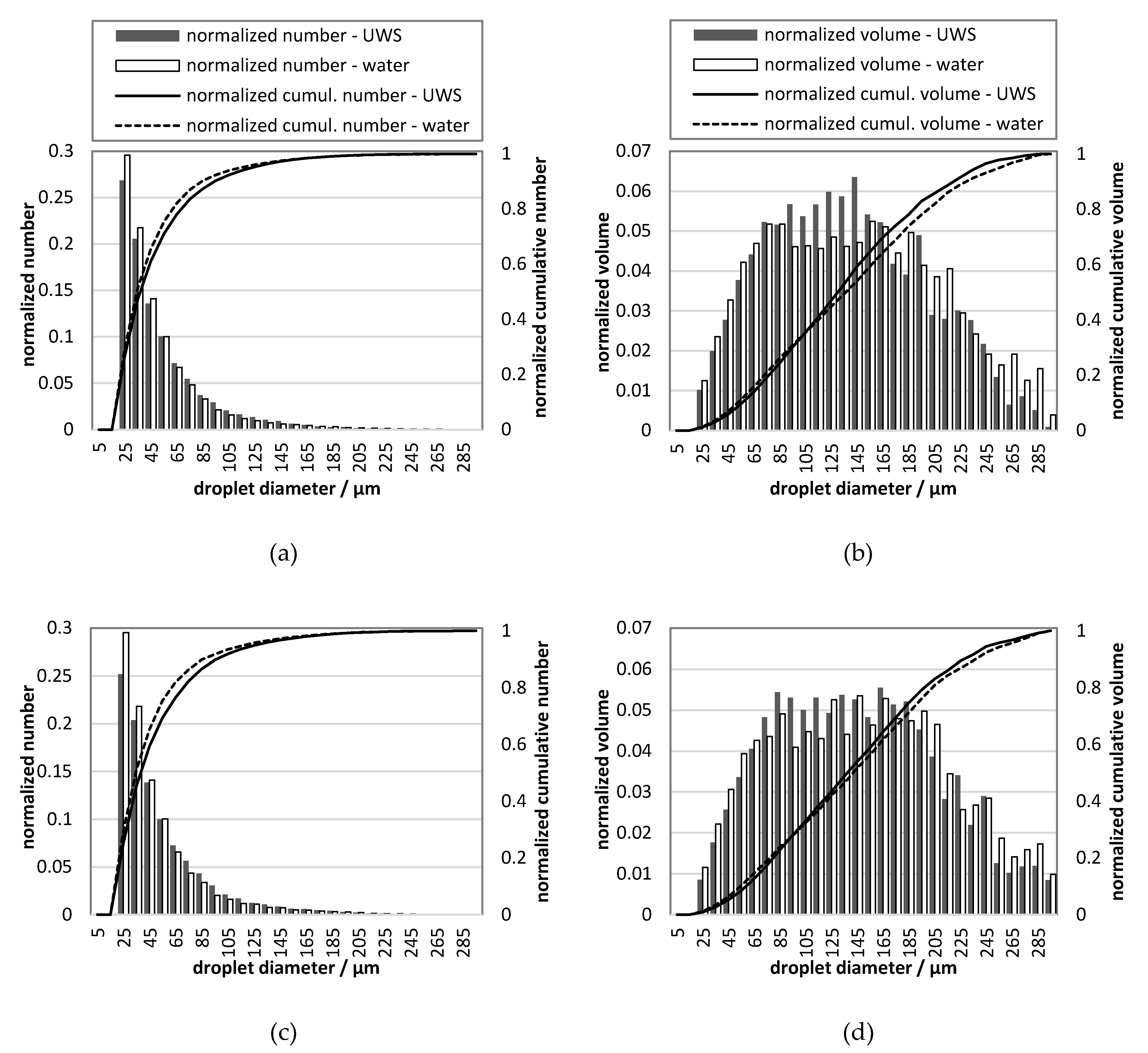
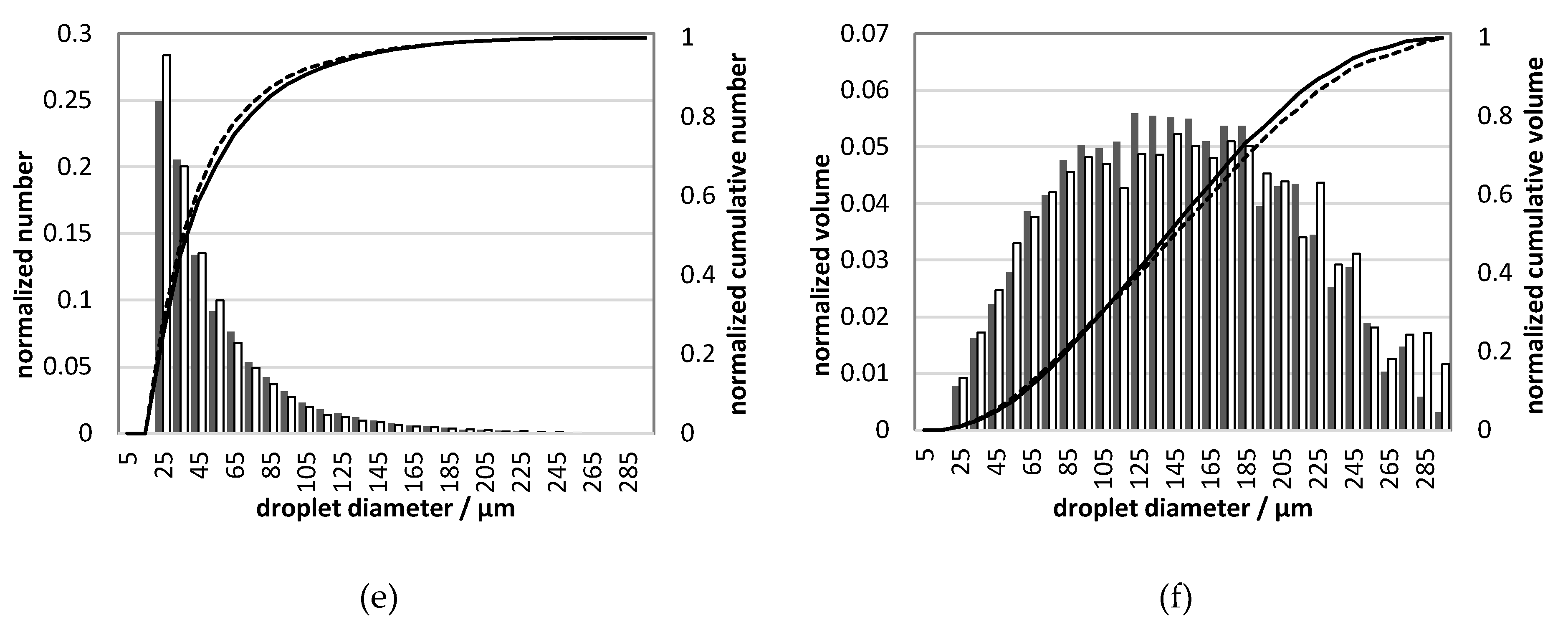
The droplet size distribution and statistical parameters of the sprays were determined for 99 injections, where one frame from each injection event was collected. The diameters of detected droplets were in the range between 20 µm and 300 µm. The droplet size distributions for UWS and water for different injection pressures are shown in Figure 10.
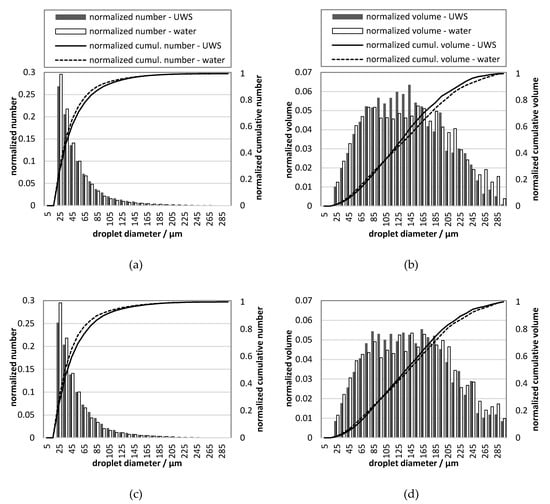
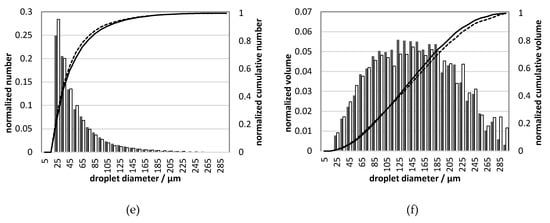
Figure 10.
Droplet size distribution for UWS and water for different injection pressures (gauge): (a) number, 0.5 MPa; (b) volumetric, 0.5 MPa; (c) number, 0.45 MPa; (d) volumetric, 0.45 MPa; (e) number, 0.4 MPa; (f) volumetric, 0.4 MPa; legend shown in (a) is valid also in (c,e); legend shown in (b) is valid also in (d,f).
The statistical parameters related to droplet size such as volume median diameter (DV50), ninetieth percentile of volume distribution (DV90), tenth percentile of volume distribution (DV10), and Sauter mean diameter (D32) are shown in Table 4.
The differences in D32 can be considered as small, which initially could lead to the conclusion that there is a minor influence from replacing UWS with water on the generated droplets. However, if DV10 and DV90 are considered, it may be observed that the sprays differ considerably; DV10 for water is for all considered pressures, smaller. On the other hand, DV90 is always smaller for UWS. These two observations together mean that in the case of water more volume (normalized) is stored in very large and very small droplets than in the case of UWS. It is clearly visible in the droplet size distributions presented in Figure 10.
As seen in Figure 10, the normalized number of droplets of the size range from 20–30 µm is in all cases higher for water than for UWS. This is in accordance with the volumetric droplet size distributions which show that for water more volume (normalized) is stored in the droplets of that size. The volumetric droplet size distributions reveal also that much more volume for water is stored in the biggest droplets (200–300 µm). These observations together explain why D32 is similar, even though the droplet size distributions are considerably different.
2.2. Numerical Simulations
The numerical study was performed to evaluate how the results of exhaust system simulations change when the spray input parameters are based on experiments made for water instead of UWS. Therefore, the simulations were performed for two set-ups where the set-up #1 was based on UWS experimental data; while the set-up #2 was based on spray data obtained for water. The simulations were compared in terms of wall film formation and ammonia distribution. The results are shown in the following subsections.
2.2.1. Wall Film Formation
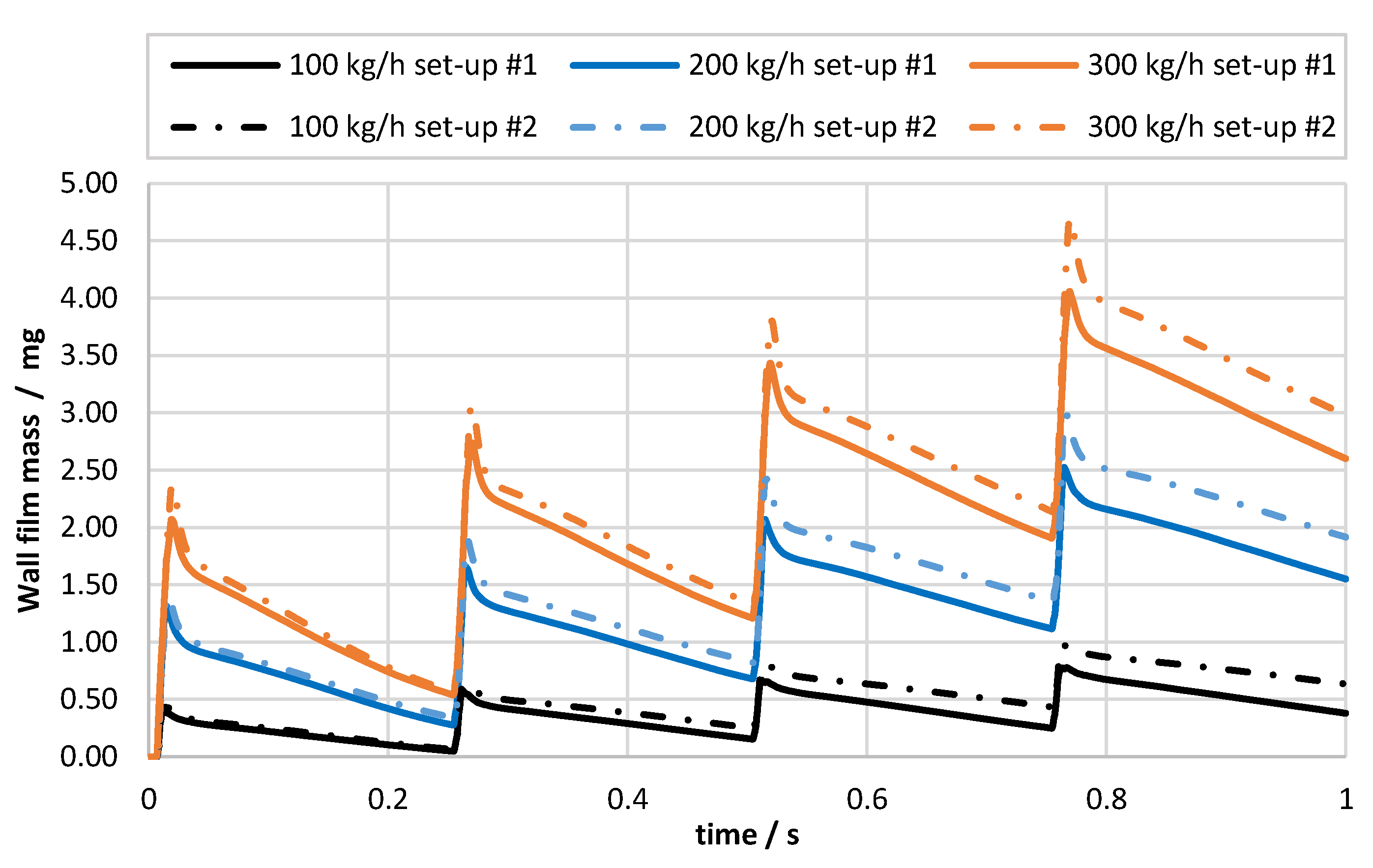
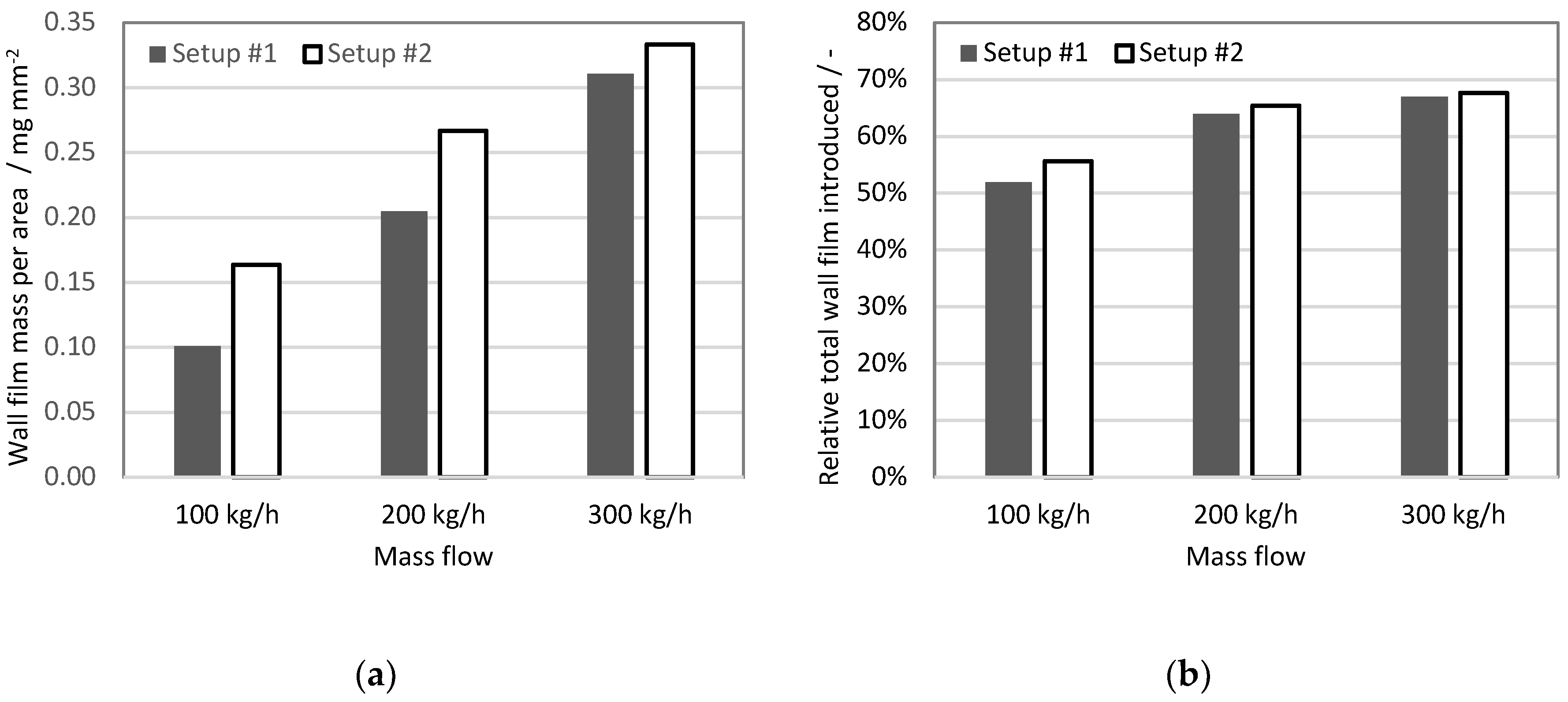
Figure 11 shows the mass of the wall film deposited in the exhaust system for different exhaust gas mass flows and for two set-ups: #1 was based on UWS experimental data; while #2 was based on the data obtained for water. The simulation time covered four injection events (at 4 Hz frequency); therefore, four cycles of wall film accumulation (peaks after 0, 0.25, 0.5 and 0.75 s) and the following phases of evaporation can be observed. It can be noticed that the simulation set-up based on water spray data led to higher wall film formation for each operating point. It is presumed that the smaller spray cone angle together with lower injection velocity and different droplet size distribution promoted stronger wall film accumulation.
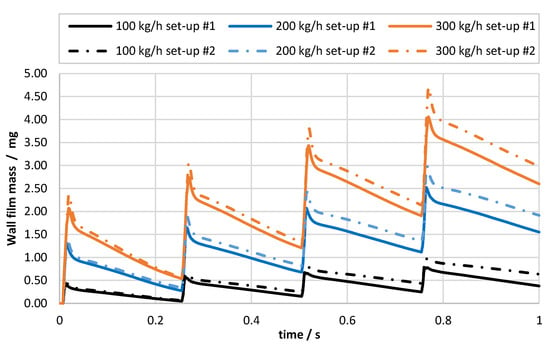
Figure 11.
Wall film mass evolution for different exhaust gas mass flow and different simulation set-ups; set-up #1 was based on UWS experimental data, set-up #2 was based on water experimental data.
Figure 12a shows the total wall film mass at the end of the fourth injection cycle divided by the wetted area, (mean wall film thickness expressed in unit of mass per unit of area). The simulations based on the UWS experiment (set-up #1) show lower values for each exhaust gas mass flow condition. However, the difference between the set-ups is not constant, and it decreases for higher exhaust gas mass flows. Figure 12b shows the relative total wall film introduced, which is an integral of mass that is stacked to the walls over the simulation time, normalized by the total liquid mass injected. It may be observed that the deposited mass fraction of injected liquid increases along with the exhaust gas flow. Moreover, the solver based on the water data (set-up #2) under all exhaust gas conditions led to a higher relative total wall film being introduced. The difference between solvers decreased with increased mass flow, and amounts to 3.8, 1.5 and 0.7 percentage points for 100, 200, 300 kg/h exhaust gas mass flows, respectively. This trend is similar to the trend observed for wall film thickness, which suggests that for a longer injector opening time the amount of injected liquid starts to be a dominant factor for the wall film formation. Whereas for a lower UWS dosage, the injection velocity, spray angle and particle size distribution may play major roles; for instance, by shifting droplets from deposition to a splash regime in the Kuhnke model, and thus also affecting film accumulation.
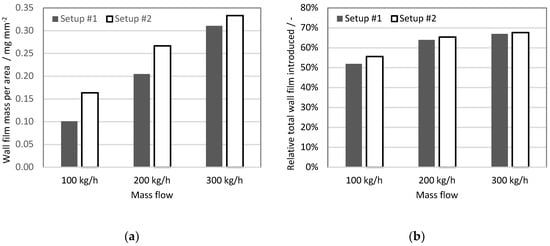
Figure 12.
Wall film analysis: (a) wall film mass to wall film area ratio at the end of 4th injection cycle; (b) relative total wall film mass introduced (normalized by the total mass injected).
Regardless of the reason for the observed small differences, the most important aspect is that using experimental data for water instead of data for UWS did not lead to underestimation of the wall film formation.
2.2.2. Ammonia Distribution
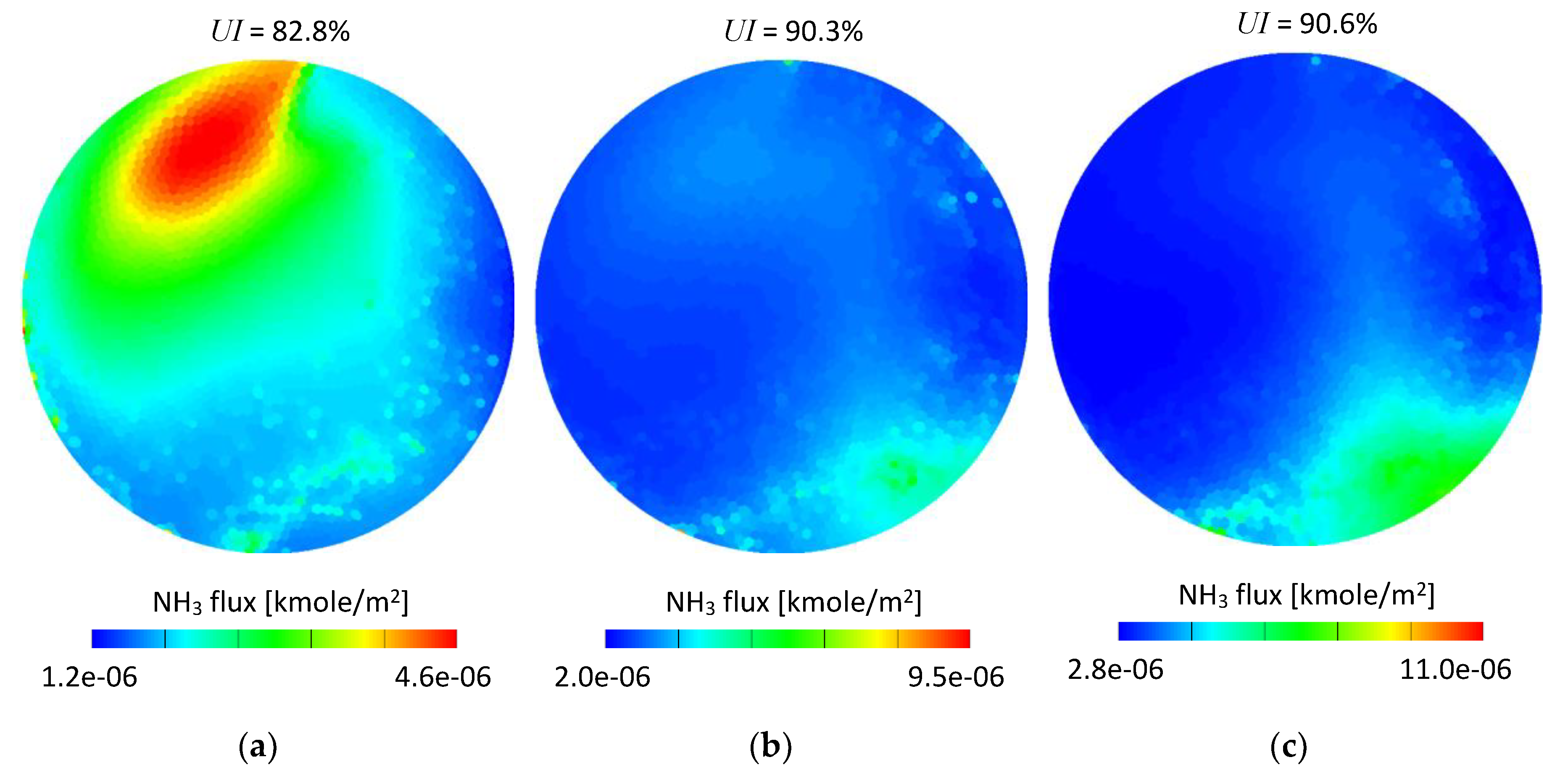
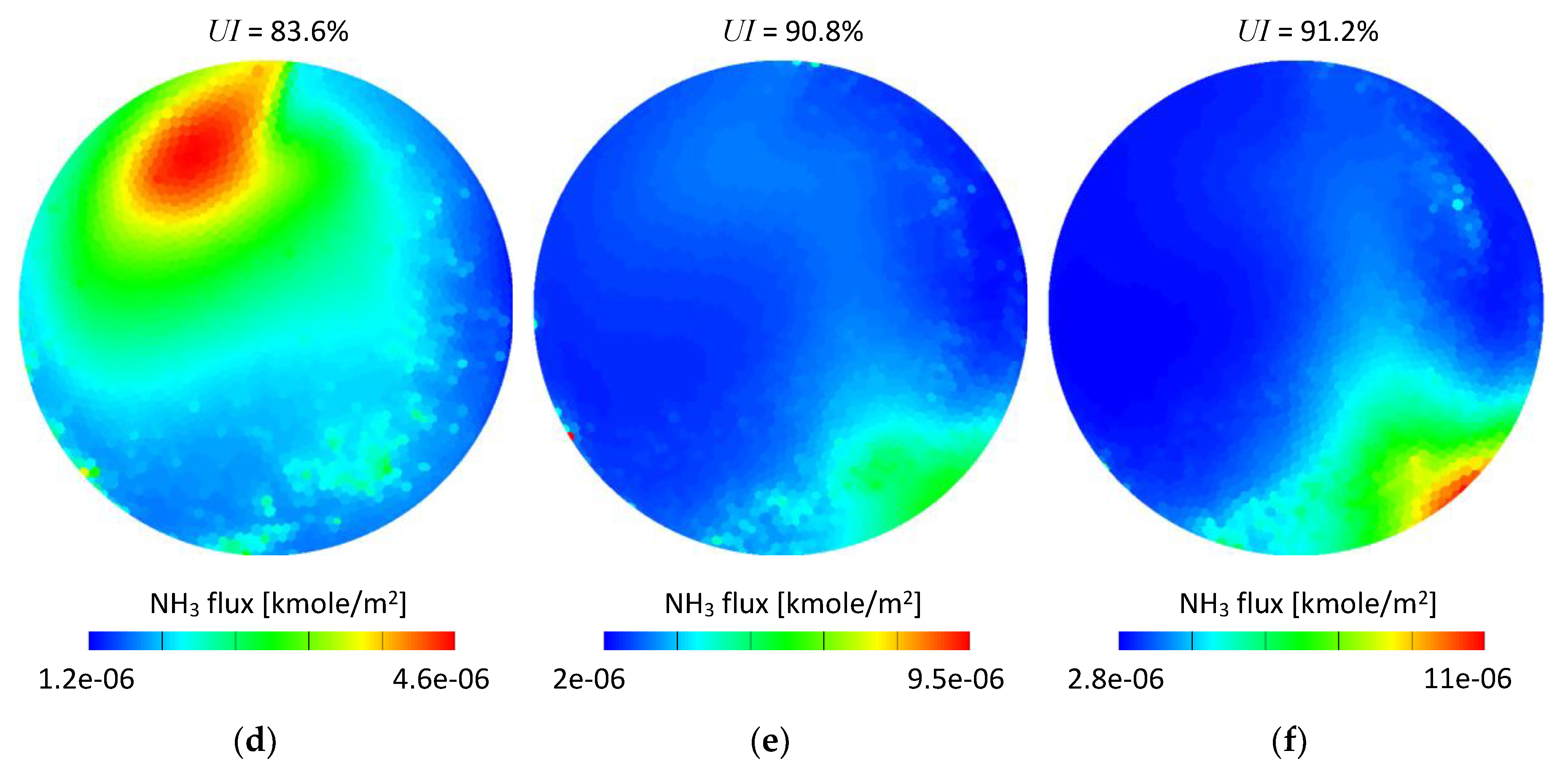
Figure 13 shows time integrated ammonia flux referred to the cell face area. The measurement plane was created 12 mm downstream from the SCRF (selective catalytic reduction on filter) inlet. It can be seen that for both set-ups the ammonia flux maps are in general in good agreement for the given exhaust gas mass flow conditions. A few details can be observed if set-up #1 and set-up #2 are compared, specifically: Higher ammonia concentration in the bottom right area (Figure 13f) and a slightly smaller area in the medium range of the scale (green area) in Figure 13b,c. The low mass flow conditions (Figure 13a,d) led to similar results and only small differences could be noticed.
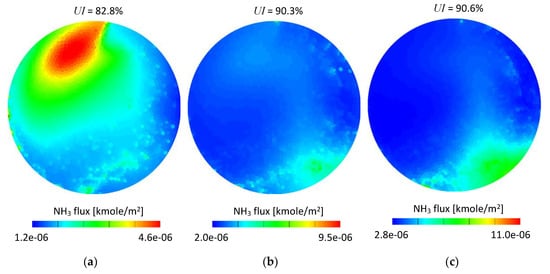
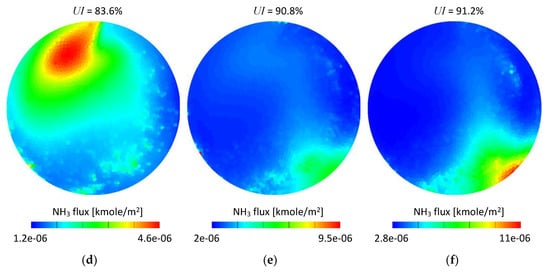
Figure 13.
Time integrated NH3 molar flux scaled to the cell face area-12 mm from the SCRF inlet: (a) 100 kg/h set-up #1; (b) 200 kg/h set-up #1; (c) 300 kg/h set-up #1; (d) 100 kg/h set-up #2; (e) 200 kg/h set-up #2; (f) 300 kg/h set-up #2.
In order to quantitatively assess the difference between the set-ups, the time-averaged ammonia mass uniformity index (UI), which is a well-established and convenient parameter used for mixing performance evaluation in both the numerical [33,34,35] and experimental [36] studies was used. The uniformity index was calculated for each case according to Equation (4) for the same cross section planes as shown in Figure 13. The UI values were shown in Figure 13 as well.
where, XNH3,i is the time-averaged NH3 mass fraction over the i-th face; is the time-averaged mean NH3 mass fraction; Ai is the cell face area.
As seen in Figure 13, the UI is very similar for both set-ups. The differences are 0.8, 0.5 and 0.6 percentage points for 100, 200 and 300 kg/h exhaust gas mass flows, respectively. Although the differences can be considered as very low, it needs to be noticed that for all considered mass flow conditions the obtained values were higher for the water-based set-up (set-up #2); which suggests that using experimental data obtained for water may lead to overestimation of mixing performance.
It cannot be claimed that the same trends would be obtained for a different geometrical set-up. Nevertheless, it needs to be taken into account that the results may be too optimistic when using water spray-based data for SCR system simulations.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Experimental Set-Up
In the study, several measurement methods and techniques were used, which are described in the following separate subsections. The injector, injector controller and whole water/UWS supply system were the same in all experiments. The injector used in the study was a commercial 3-hole injector for SCR systems (Bosch 0 280 158 720, Gerlinger, Germany).
3.1.1. Flow Rate Measurement Set-Up
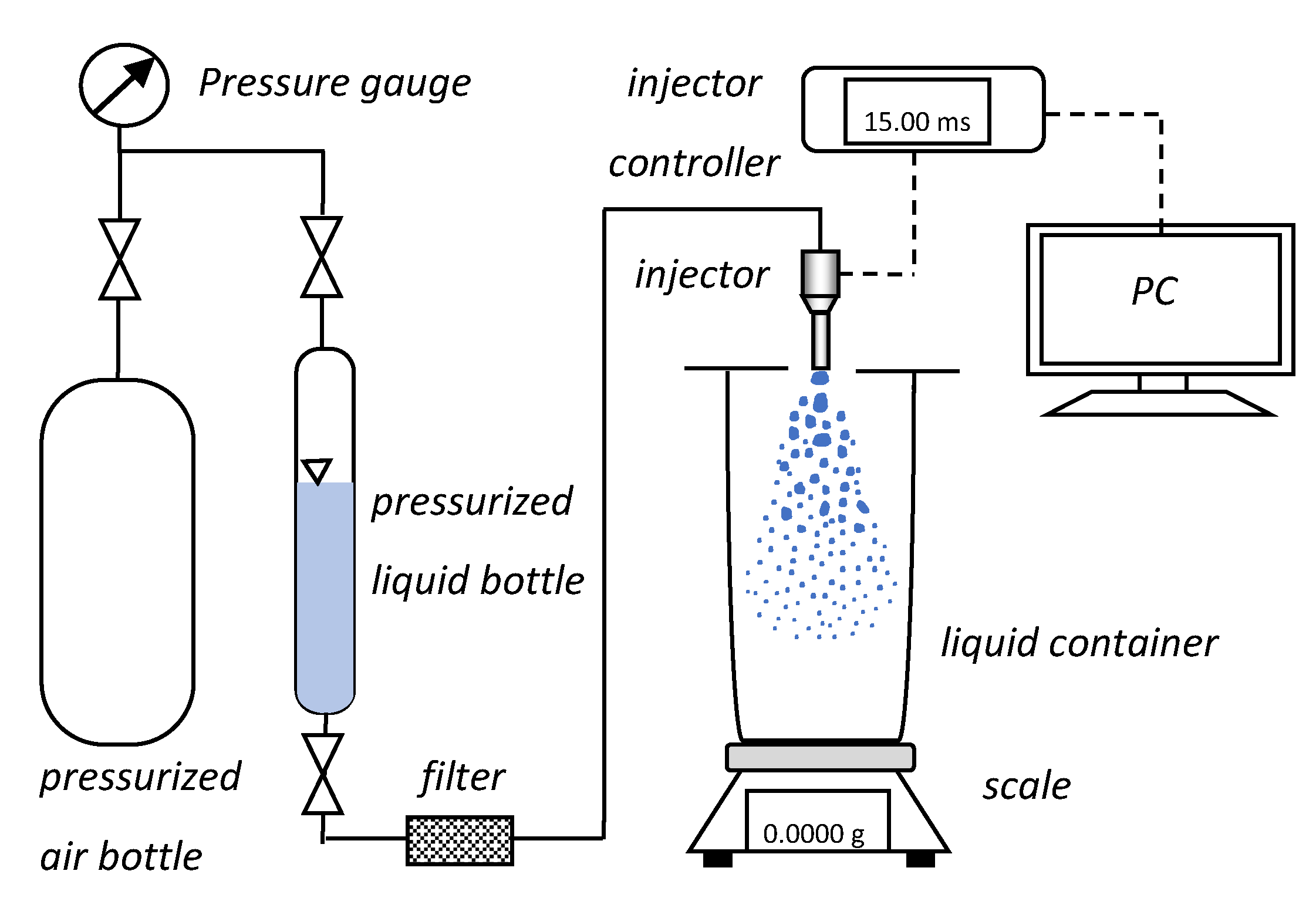
The experimental set-up for the flow rate characteristics (Figure 14) consisted of a pressurized air bottle with pressure regulator connected to another bottle with water/UWS by high-pressure tubing, including several valves and a precise pressure gauge (WIKA CPG1500, measuring range 0–1 MPa gauge, accuracy 0.1% FS, Frankfurt, Germanry) in order to monitor the pressure. The pressurized bottle containing the liquid was connected to a filter and to the injector. The injector was located above the container for collecting the sprayed liquid. The container was covered to prevent liquid from splashing outside. The injector was connected to the controller integrated with the computer. The injection process was triggered through the computer, where also the current in the injector circuit was monitored.
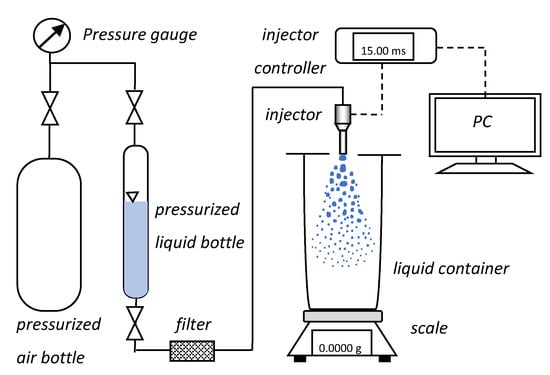
Figure 14.
Schematic diagram of the experimental set-up for flow measurements.
The measurement procedure was based on collecting liquid for 5000 injections. After 5000 injections the mass of the liquid collected in the container was measured. For this purpose, a precision balance (Radwag PS1000.R1, Radom, Poland) with readability of 1 mg and repeatability of 1.5 mg was used. The measurement procedure was repeated three times in order to avoid random errors. The measurements were done for seven different opening times of the injector, specifically 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10 and 15 ms.
3.1.2. High-Speed Imaging
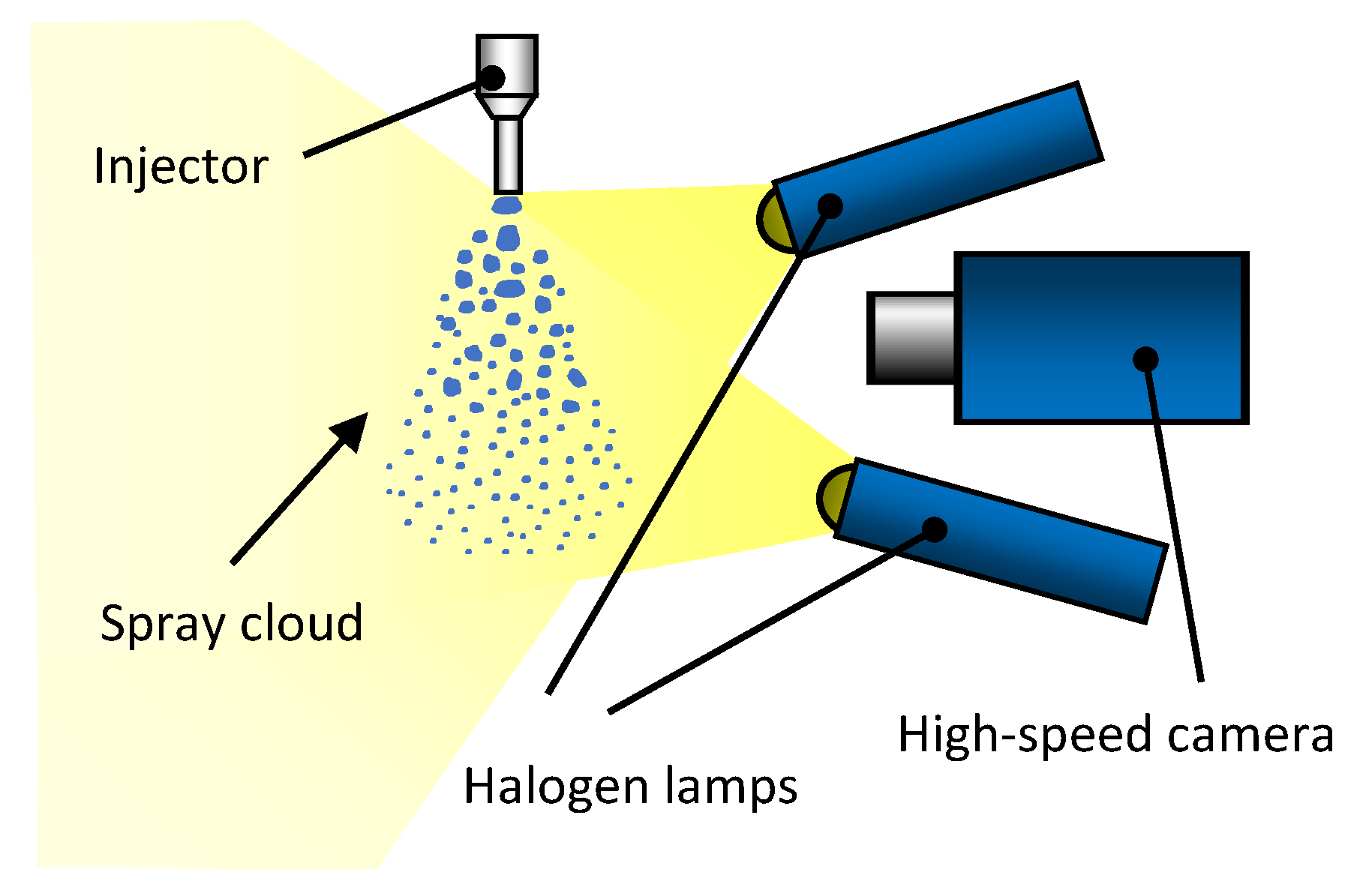
For global spray parameters (i.e., spray tip penetration and spray visualization angle) and initial jet velocity measurements, high-speed Mie scattering imaging was used. The set-up was based on global illumination provided by two halogen lights (500 W each) and a high-speed camera (Photron SA1.1, Tokyo, Japan) equipped with a Nikon f 2.8 50-mm lens (Tokyo, Japan). The recording was done at a frame rate of 10,000 fps. The image resolution was of 1024 × 450 pixels. The schematic set-up is shown in Figure 15.

Figure 15.
Experimental set-up for global spray parameters’ determination.
The image processing was done using LaVision DaVis version 8.4 software (Gottingen, Germany) and included the following steps: Background subtraction, spray separation from the surroundings, and angle or tip penetration determination. The first frame of each image sequence was used (image without spray) as the background image. The spray cloud separation from the surroundings was based on an intensity threshold of 10 counts (after background subtraction); this was the minimum value to exclude camera noise (similar in all cases), which became visible after background subtraction. Spray tip penetration was determined as a distance of 97% of pixels above 10 counts. The spray angle was determined so the 97% of pixels above 10 counts were between the two sides of the angle.
3.1.3. Shadowgraphy with a Long-Distance Microscope
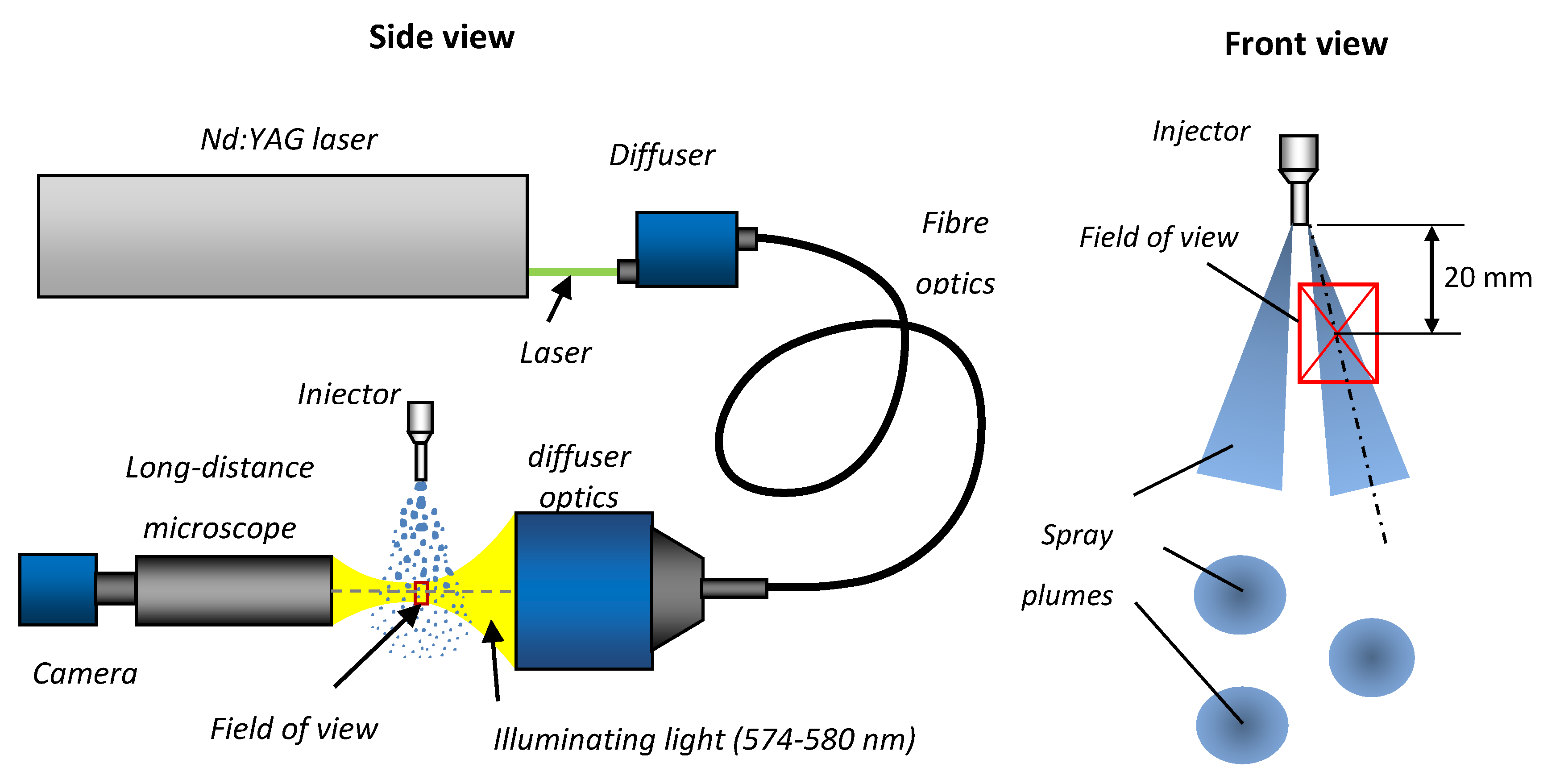
The set-up, based on shadowgraphy with a long-distance microscope, was used to determine droplet size distribution, unbroken liquid length and jet inclination angle at the nozzle exit. The set-up used here was set to visualize an area of 4.5 × 10 mm of the spray in a single frame. The measurement area for the droplet size determination was located 20 mm below the nozzle exit in the axis of a single plume (the location referred to the centre of the image). It is schematically shown in Figure 16. The measurement area for the unbroken liquid length determination covered a distance from the injector outlet up to 10 mm downstream.
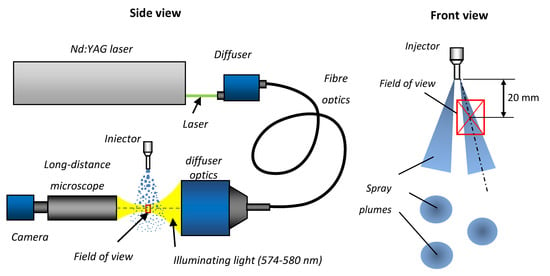
Figure 16.
Experimental set-up for shadowgraphy with long-distance microscope.
The shadowgraphy set-up was based on an Nd:YAG laser (Spectra Physics Quanta-Ray Pro-230, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The 532 nm wavelength was used to excite the dye in the diffuser, and the light from the diffuser (574-580 nm) was used to illuminate the spray. The camera (LaVision SCMOS) was equipped with a long-distance microscope. The schematic diagram of the set-up is shown in Figure 16.
3.2. Numerical Simulations
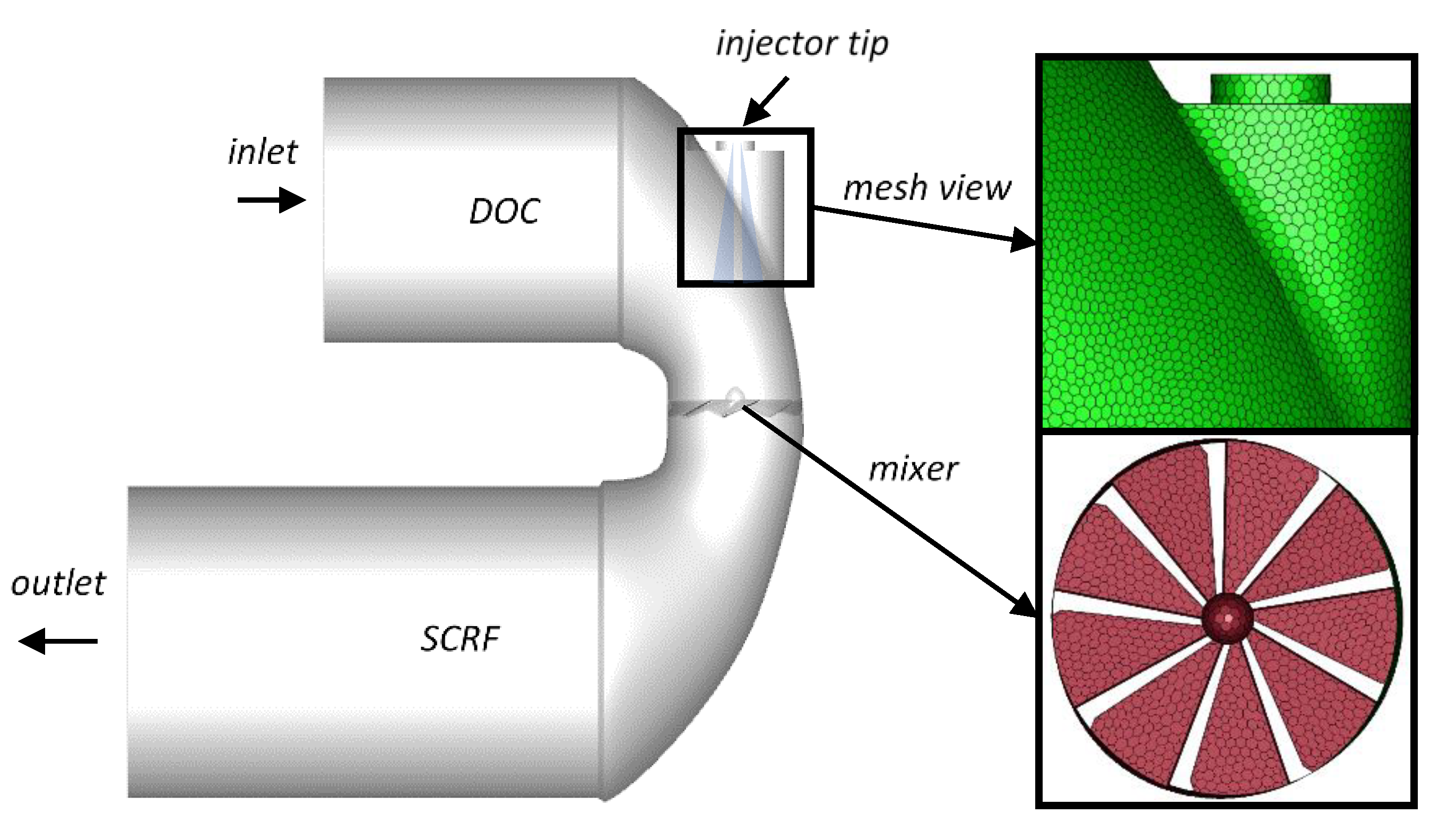
The simulations were performed using AVL FIRE™ v. 2014.2 (Graz, Austria). The geometrical model used in the simulations (shown in Figure 17) was based on the most recent close-coupled SCR aftertreatment configuration, with the selective catalytic reduction on filter (SCRF) placed downstream of the diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC). To enhance mixing before the inlet to the SCRF catalyst a single-spin static mixer was used. The injector was located between the DOC and the SCRF, so the UWS was injected into the hot gas stream towards the static mixing device.
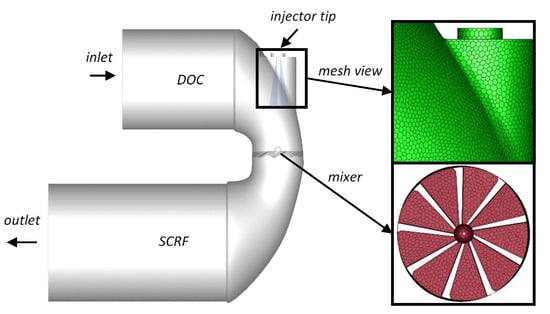
Figure 17.
Urea–selective catalytic reduction (SCR) model with zoom in on the mesh and the mixer.
The polyhedral mesh was built in the catalysts’ connector (Figure 17—mesh view) using AVL Fire M™ v.2018. The base cell size was 4 mm, while the size of the face element was 3 mm. The elements on the mixer surface were refined to 2 mm. Both the DOC and SCRF bricks were made as structural meshes by extruding the middle-cone inlet/outlet surfaces by 4 mm steps up to 90 mm and 180 mm respectively; and thus, were composed mainly of hexagonal prism elements. The final mesh was composed of 429,341 elements; among which 1423 elements were tetrahedral and 3219 hexahedral.
The flow inside the system was considered as turbulent and it was modelled by the Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) method. To model the turbulences the k-ζ-f model [37] was used. In order to obtain realistic conditions inside the spray-cone, the DOC and SCRF were modelled as one-directional porous medium zones with the pressure drop described by the Forchheimer formula, which takes into account linear viscous losses corrected by quadratic inertial losses [38].
For modelling the spray, the well-established Lagrangian method was used; in which droplet parcels are introduced into the computational domain and treated as a discrete source for a continuous phase. The parameters, like the initial jet velocity and the spray plume angle, were treated as boundary conditions for the spray calculations, and were taken from the experiments. Moreover, as the UWS injector is typically a low pressure injector, a common practice is to set the particle size distribution at the nozzle outlet [39]. This approach was used in this study as well.
A Birkhold approach [21] was used for modelling the UWS decomposition. In his approach, after UWS is injected into the hot exhaust gas it undergoes the 2-step process; where first, water evaporates from the droplets until only urea remains, and then urea decomposes into NH3 and HNCO through a thermolysis process.
As shown in Figure 17, UWS injection is performed directly towards the mixer, hence, the wall film formation at the mixer’s surface is expected. According to the Kuhnke model [40], which was used in this study, four different scenarios may occur. The droplet can be deposited on the wall, splashed, rebounded or thermally broken up. The most appropriate scenario is chosen depending on a droplet’s dimensionless velocity and temperature.
The simulations were performed for two different spray set-ups, where set-up #1 was based on UWS experimental data; while set-up #2 was based on spray data obtained for water. The spray model parameters for both set-ups are shown in Table 5. Note that for both simulation set-ups data for the numerical simulations were taken from the experiments for 0.5 MPa injection pressure.

Table 5.
Spray parameters used for simulations.
In order to evaluate the effect of using water spray data instead of UWS spray data in different engine operating conditions, the simulations were performed for three different exhaust gas mass flows (Table 6).

Table 6.
Boundary conditions for computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations.
The UWS dosage calculations were done assuming the same number of moles of NO2 and NO and the stochiometric fast-SCR reaction (i.e., 1 mole of NH3 is needed for 1 mole of NOx). Thus, the dosage of UWS was calculated with regards to the NOx concentration and the exhaust gas mass flow. Since the volumetric flow rates obtained for UWS and for water were different, the injection time at each exhaust gas condition differed between the set-ups as well. The injector opening times for set-ups #1 and #2 were calculated based on the urea dosage and volumetric flow rates obtained for UWS and water respectively, assuming a constant injection frequency of 4 Hz in all cases. The exhaust gas was composed of NOx, H2O, O2, CO2 and N2.
Moreover, for each set-up a different droplet size distribution was set according to Figure 10a: UWS for set-up #1 and water for set-up #2.
4. Conclusions
In this study, UWS and pure water were compared in terms of spray properties generated from the same set-up under the same conditions. The parameters under consideration were: Droplet size distribution and statistical droplet parameters; spray angle (visualization angle, spray plume inclination angle); spray tip penetration; unbroken liquid length; initial jet velocity; static flow properties such as static flow rate (mass, volumetric and average velocity), Reynolds number, Weber number (referred to gas); and finally, Ohnesorge number. Moreover, the influence of different spray properties on CFD simulations was also studied.
The experimental studies showed differences in almost all considered spray parameters. The jet inclination angle was the only parameter unaffected by replacing UWS with water. The Reynolds number, Weber number (referred to gas) and Ohnesorge number in all considered cases were higher for water. The static volumetric flow rate and, thus, average velocity in the nozzle was higher for water; while the initial jet velocity and the spray tip penetration were higher for UWS. It is supposed that the higher initial jet velocity in the case of UWS was caused by higher UWS density (and as a result inertia), and viscosity leading to a longer delay and consequently, higher pressure build-up before the exit of the first liquid from the nozzle. In turn, higher initial jet velocity together with higher density and thus momentum, explain the higher spray tip penetration for all UWS cases. The spray angle was also dependent on the fluid type—the visualization angle for UWS was higher than for water for all considered injection pressures—even though the number of observed droplets and the injected volume was higher for water. It is presumed that the decreased spray angle for water resulted mainly from the different refractive index, making the water sprays less visible and more difficult to separate from the background. This feature also needs to be taken into account when UWS is replaced with water.
Moreover, different spray behaviour was noticed in terms of primary break-up. The unbroken liquid length for UWS tended to decrease with the increased injection pressure (and flow velocity); while for water, the effect was opposite. This suggests that the replacement of UWS with water caused the change in the break-up regime from the first wind-induced regime into the second wind-induced regime. It needs to be emphasized that in the case of different injection set-ups (injection pressure, nozzle diameter) the same jet break-up regime can be maintained. Nevertheless, it can be generally concluded that replacing UWS with water (by increased Ohnesorge number and Reynolds number) moves the jet droplet break-up process towards the next break-up regime.
An important finding was shown in that water and UWS sprays do have a similar Sauter mean diameter, but at the same time the droplet size distributions are considerably different. The normalized number and normalized volume of the smallest and the biggest droplets for water were higher than for UWS.
The differences between the measured spray parameters for UWS and water affected the simulations’ results. The simulation set-up based on spray data obtained for water resulted in higher wall film accumulation at the end of each injection event, and at the end of the simulations. This leads to an important conclusion that using experimental data obtained for water instead of UWS did not cause an underestimation of the wall film formation. As far as the ammonia uniformity index is concerned, the differences between the simulations based on the UWS spray data and the water spray data were very low. However, unlike the case of the wall film, the effect was opposite as the simulations based on the water spray data led to more optimistic results for all considered exhaust gas mass flows. This shall be taken into consideration when developing an SCR system using CFD simulations.
Author Contributions
Ł.J.K. designed and performed the experiments; R.R. designed and performed the numerical simulations; M.S., R.R. and M.Z. supported the experiments; Ł.J.K. and A.T. supervised the study; Ł.J.K., M.S. and R.R. wrote the paper; Ł.J.K. and A.T. acquired funding.
Funding
Current work was supported by the European Smart Growth Operational Programme 2014-2020 through the project “Development of mixing and urea–water solution conversion unit in SCR systems in order to start production of exhaust system for compression ignition engine that meets the Euro 7 emission standards”, grant number: POIR.04.01.04-00-0060/15-02.
Acknowledgments
The AVL FIRE™ calculation code was used as per the AVL AST University Partnership Programme.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kojima, H.; Fischer, M.; Haga, H.; Ohya, N.; Nishi, K.; Mito, T.; Fukushi, N. Next Generation All in One Close-Coupled Urea-SCR System; SAE Technical Paper 2015-01-0994; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sala, R.; Bielaczyc, P.; Brzezanski, M. Concept of vaporized urea dosing in selective catalytic reduction. Catalysts 2017, 7, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiteri, A.; Eggenschwiler, P.D. Experimental fluid dynamic investigation of urea—Water sprays for diesel selective catalytic reduction—DeNOx applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 3047–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baleta, J.; Vujanović, M.; Pachler, K.; Duić, N. Numerical modeling of urea water based selective catalytic reduction for mitigation of NOx from transport sector. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 88, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varna, A.; Spiteri, A.C.; Wright, Y.M.; Dimopoulos, P. Experimental and numerical assessment of impingement and mixing of urea—Water sprays for nitric oxide reduction in diesel exhaust Q. Appl. Energy 2015, 157, 824–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocivelli, L.; Montenegro, G.; Liao, Y.; Dimopoulos, P. Modeling of aqueous urea solution injection with characterization of spray-wall cooling effect and risk of onset of wall wetting. Energy Procedia 2015, 82, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapusta, Ł.J. LIF/Mie droplet sizing of water sprays from SCR system injector using structured illumination. In Proceedings of the ILASS2017–28th European Conference on Liquid Atomization and Spray Systems, Valencia, Spain, 6–8 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kapusta, Ł.J.; Teodorczyk, A. Laser diagnostics for urea-water solution spray characterization. MATEC Web Conf. 2017, 118, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Furrer, R.; Dimopoulos, P.; Boulouchos, K. Experimental investigation of the heat transfer characteristics of spray/wall interaction in diesel selective catalytic reduction systems. Fuel 2017, 190, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics: A Ready-Reference Book of Chemical and Physical Data, 93rd ed.; Haynes, W.M. (Ed.) CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization. Technical Report No. 22241-1:2019 Standard; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Halonen, S.; Kangas, T.; Haataja, M.; Lassi, U. Urea-water-solution properties: Density, viscosity, and surface tension in an under-saturated solution. Emiss. Control Sci. Technol. 2017, 3, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkhold, F.; Meingast, U.; Wassermann, P.; Deutschmann, O. Analysis of the Injection of Urea-Water-Solution for Automotive SCR DeNOx-Systems: Modeling of Two-Phase Flow and Spray/Wall-Interaction; SAE Technical Paper 2006-01-0643; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Der Wiesche, S. Numerical heat transfer and thermal engineering of AdBlue (SCR) tanks for combustion engine emission reduction. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2007, 27, 1790–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramires, M.L.V.; Nieto de Castro, C.A.; Nagasaka, Y.; Nagashima, A.; Assael, M.J.; Wakeham, W.A. Standard reference data for the thermal conductivity of water. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1995, 24, 1377–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgeman, O.C.; Aldrich, E.W. Vapor pressure tables for water. J. Heat Transfer 1964, 86, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimian, V.; Nicolle, A.; Habchi, C. Detailed modeling of the evaporation and thermal decomposition of urea-water solution in SCR systems. AIChE J. 2012, 58, 1998–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, G.M.; Querry, M.R. Optical constants of water in the 200-Nm to 200-μm wavelength region. Appl. Opt. 1973, 12, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polcar, A.; Čupera, J.; Kumbár, V.; Dostál, P.; Votava, I. Influence of urea concentration on refractive index of ad blue fluid evaluated by regression analysis. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendelianae Brun. 2016, 64, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiteri, A.; Srna, A.; Eggenschwiler, P.D. Characterization of sprays of water and urea-water solution from a commercial injector for SCR DeNOx applications. In Proceedings of the 13 Internationales Stuttgarter Symposium 2013 Automobil-und Motorentechnik, Stuttgart, Germany, 26–27 February 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Birkhold, F.; Meingast, U.; Wassermann, P.; Deutschmann, O. Modeling and simulation of the injection of urea-water-solution for automotive SCR DeNOx-systems. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2007, 70, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grout, S.; Blaisot, J.-B.; Pajot, K.; Osbat, G. Experimental investigation on the injection of an urea–Water solution in hot air stream for the SCR application: Evaporation and spray/wall interaction. Fuel 2013, 106, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postrioti, L.; Brizi, G.; Ungaro, C.; Mosser, M.; Bianconi, F. A Methodology to investigate the behaviour of urea-water sprays in high temperature air flow for SCR de-NOx applications. Fuel 2015, 150, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payri, R.; Bracho, G.; Gimeno, J.; Moreno, A. Investigation of the urea-water solution atomization process in engine exhaust-like conditions. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2019, 108, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mie Simulator GUI; Virtual Photonics Technology Initiative: Irvine, CA, USA, 2019.
- Payri, R.; Bracho, G.; Gimeno, J.; Moreno, A. Spray characterization of the urea-water solution (UWS) injected in a hot air stream analogous to SCR system operating conditions. In WCX SAE World Congress Experience; SAE International: Detroit, MI, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Leroux, S.; Dumouchel, C.; Ledoux, M. The stability curve of newtonian liquid jets. Atom. Sprays 1996, 6, 623–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumouchel, C. On the experimental investigation on primary atomization of liquid streams. Exp. Fluids 2008, 45, 371–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.P.; Reitz, R.D. Drop and spray formation from a liquid jet. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1998, 30, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranz, W.E. On Sprays and Spraying; Department of Engineering Research, Pennsylvania State University: State College, PA, USA, 1956; Volume 65. [Google Scholar]
- Reitz, R.D.; Bracco, F.V. Mechanisms of breakup of round liquid jets. In Encyclopedia of Fluid Mechanics; Cheremisinoff, N.P., Ed.; Gulf Publishing Company: Houston, TX, USA, 1986; pp. 233–249. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgarten, C. Mixture Formation in Internal Combustion Engines, 1st ed.; Mewes, D., Mayinger, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jaworski, P.; Kapusta, Ł.J.; Jarosiński, S.; Ziółkowski, A.; Capetillo, A.C.; Grzywnowicz, R. SCR systems FOR NOx reduction in heavy duty vehicles. J. KONES 2015, 22, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworski, P.; Jarosiński, S.; Kapusta, Ł.J.; Ziółkowski, A. SCR systems for NOx reduction in heavy and light duty vehicles. Combust. Engines 2016, 164, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Capetillo, A.; Ibarra, F. Multiphase injector modelling for automotive SCR systems: A full factorial design of experiment and optimization. Comput. Math. Appl. 2017, 74, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, R.; Dzida, J.; Krasowski, J. Ammonia concentration distribution measurements on selective catalytic reduction catalysts. Catalysts 2018, 8, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanjalić, K.; Popovac, M.; Hadžiabdić, M. A robust near-wall elliptic-relaxation eddy-viscosity turbulence model for CFD. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2004, 25, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AVL FIRETM User Manual, Version 2014.2; AVL List GmbH: Graz, Austria, 2014.
- Gapin, A.; Demoulin, F.-X.; Dumouchel, C.; Pajot, K.; Patte-Rouland, B.; Reveillon, J. Development of an initial drop-size distribution model and introduction in a CFD code to predict spray evolution. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conferrence Multiph, Flow ICMF, Tampa, FL, USA, 30 May–4 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhnke, D. Spray/Wall-Interaction Modelling by Dimensionless Data Analysis; Shaker Verlag: Herzogenrath, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).