Synthesis of Carbon Onion and Its Application as a Porous Carrier for Amorphous Drug Delivery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Carbon Onions from Thermal Annealing of Detonation Nanodiamonds
2.3. Physico-Chemical Characterisation
2.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.5. Preparation of Drug Loaded Carbon Onion and Determination of Drug Loading Efficiency
2.6. Characterisation of Drug Loaded Carbon Onion Complex
2.7. Drug Release Studies
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterisation of Annealed Nanodiamonds
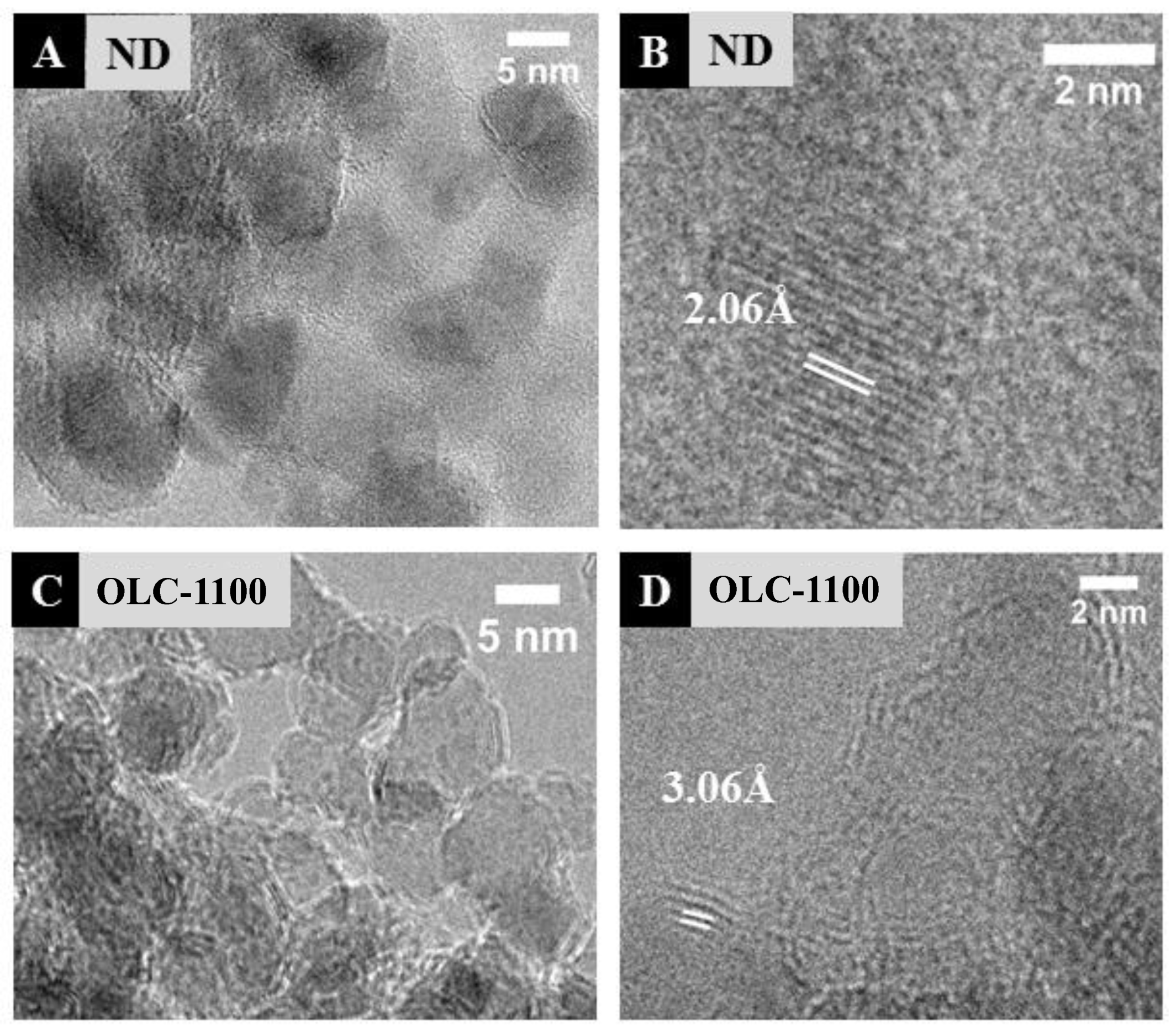
3.1.1. Surface Morphology
3.1.2. Surface Characterisation
3.1.3. Chemical Characterisation
3.2. Particle Size Analysis
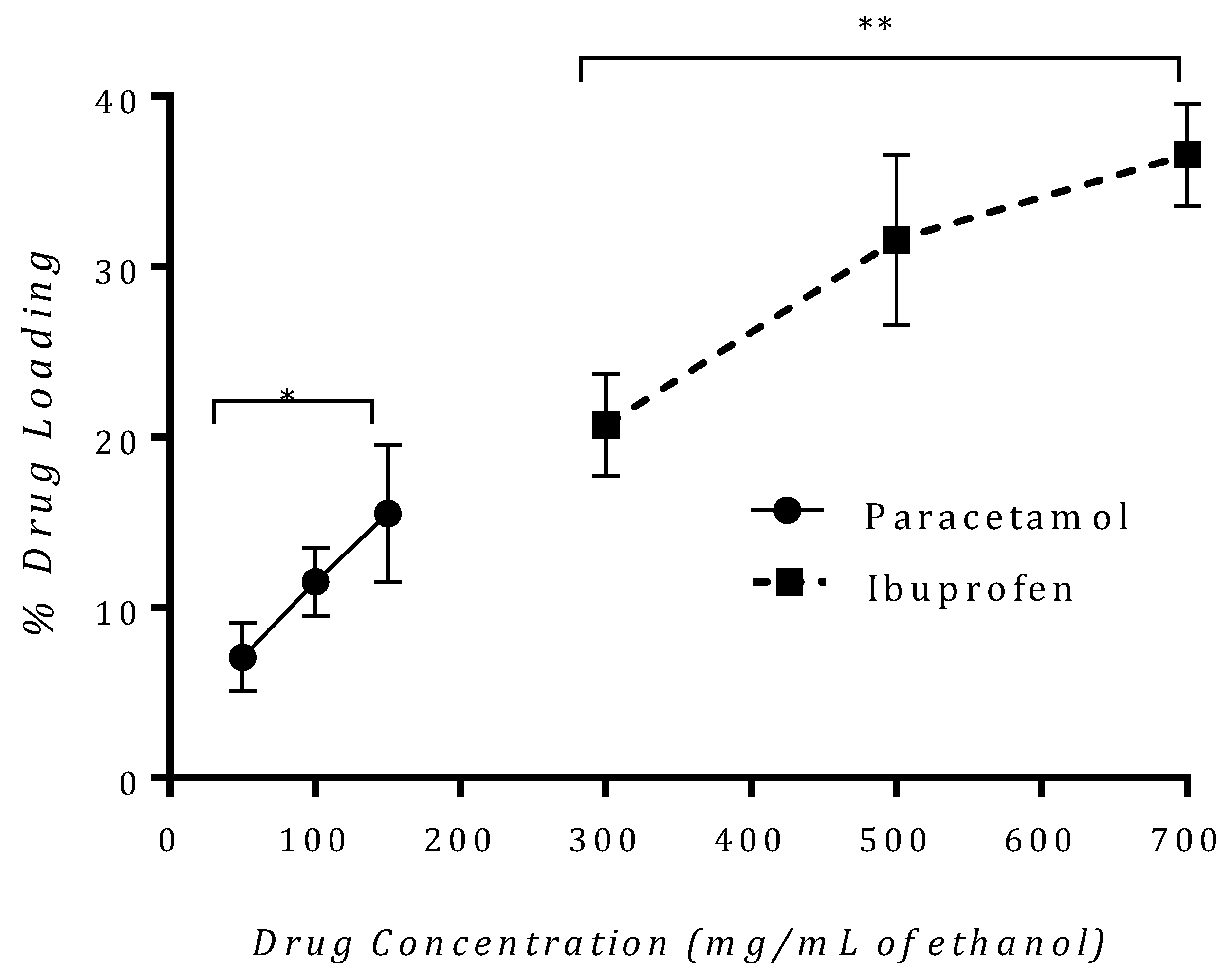
3.3. Drug Loading Efficiency
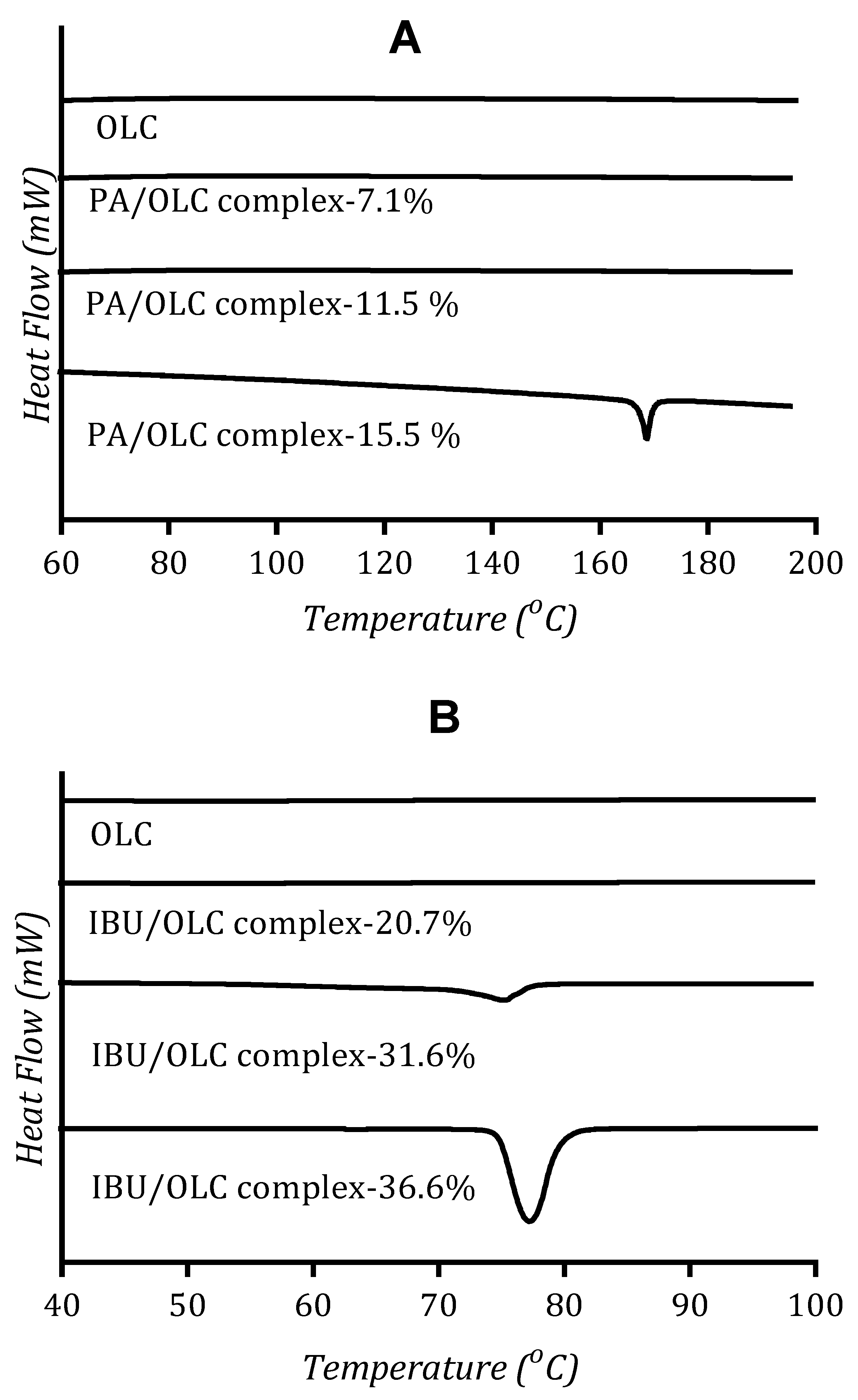
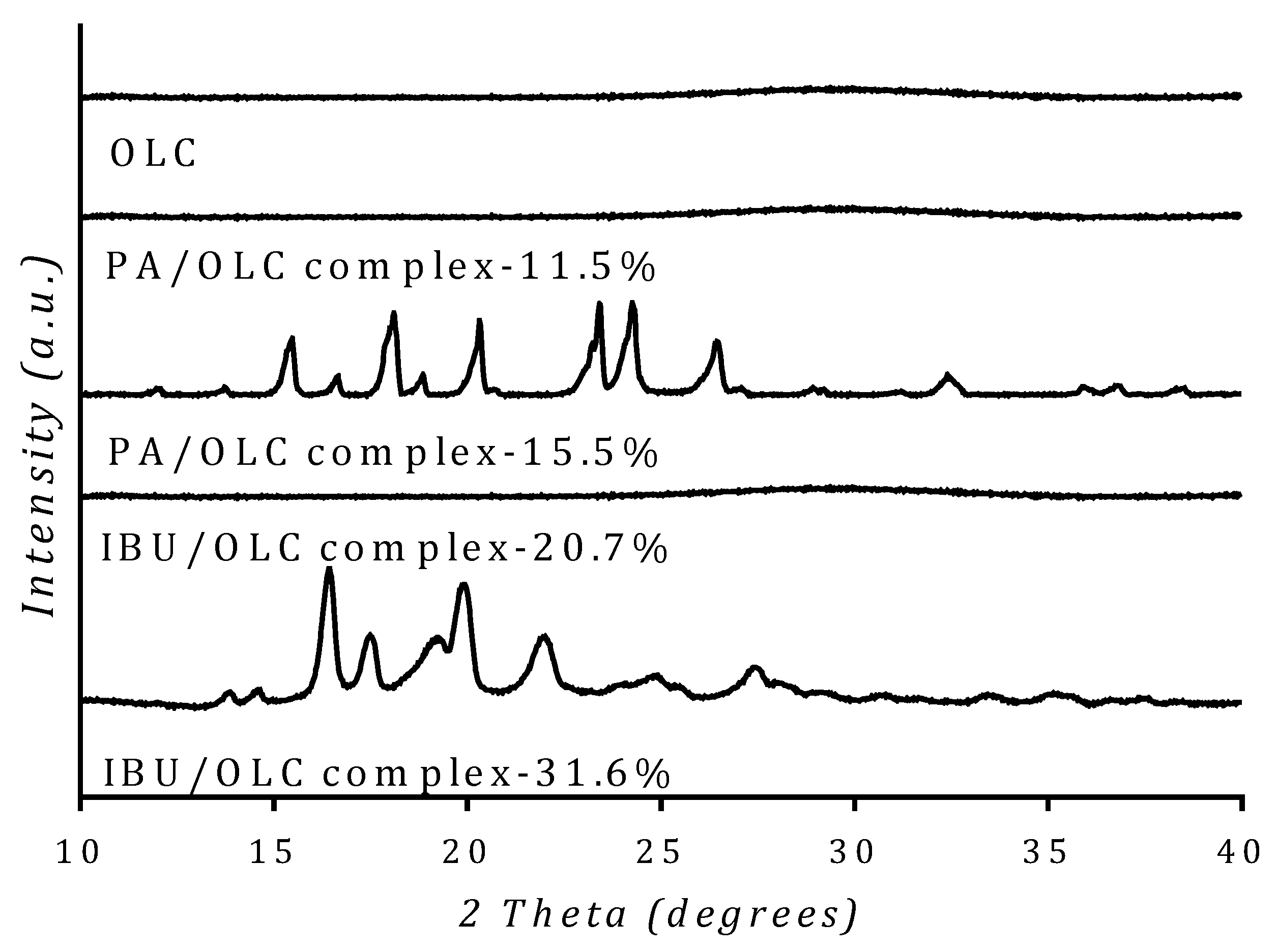
3.4. Solid State Analysis of Drug
3.5. Drug-Carrier Interactions
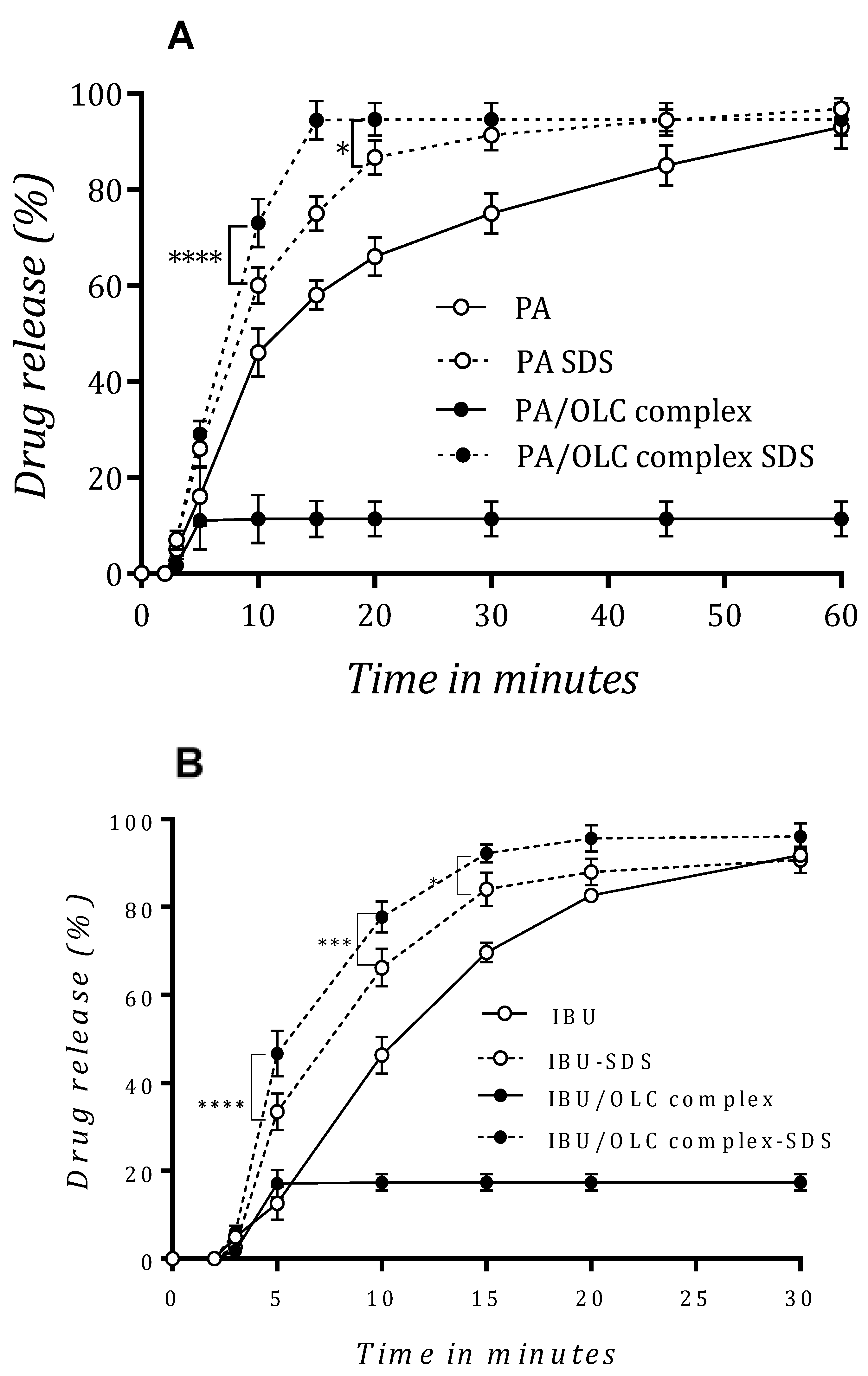
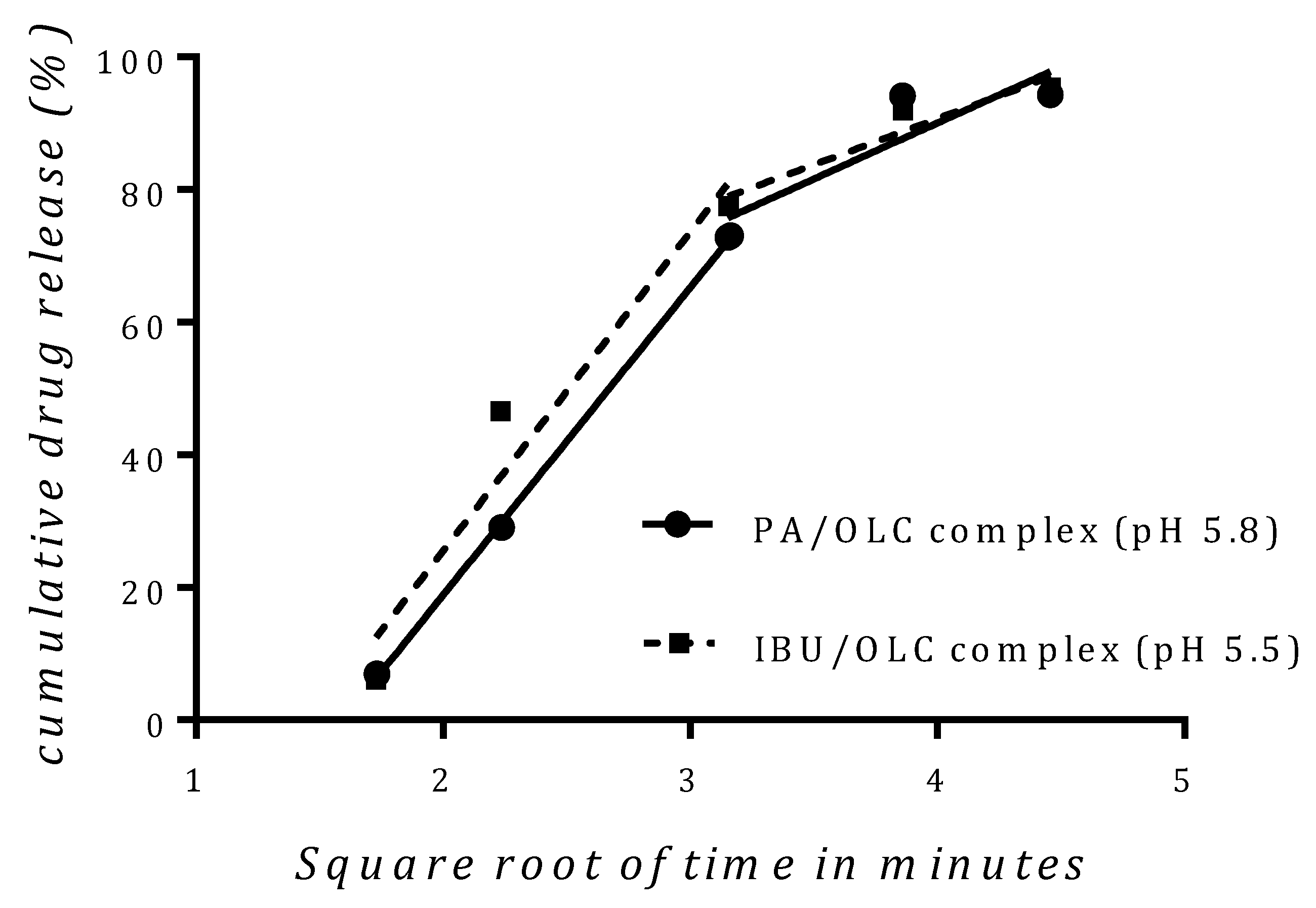
3.6. In Vitro Drug Release Studies
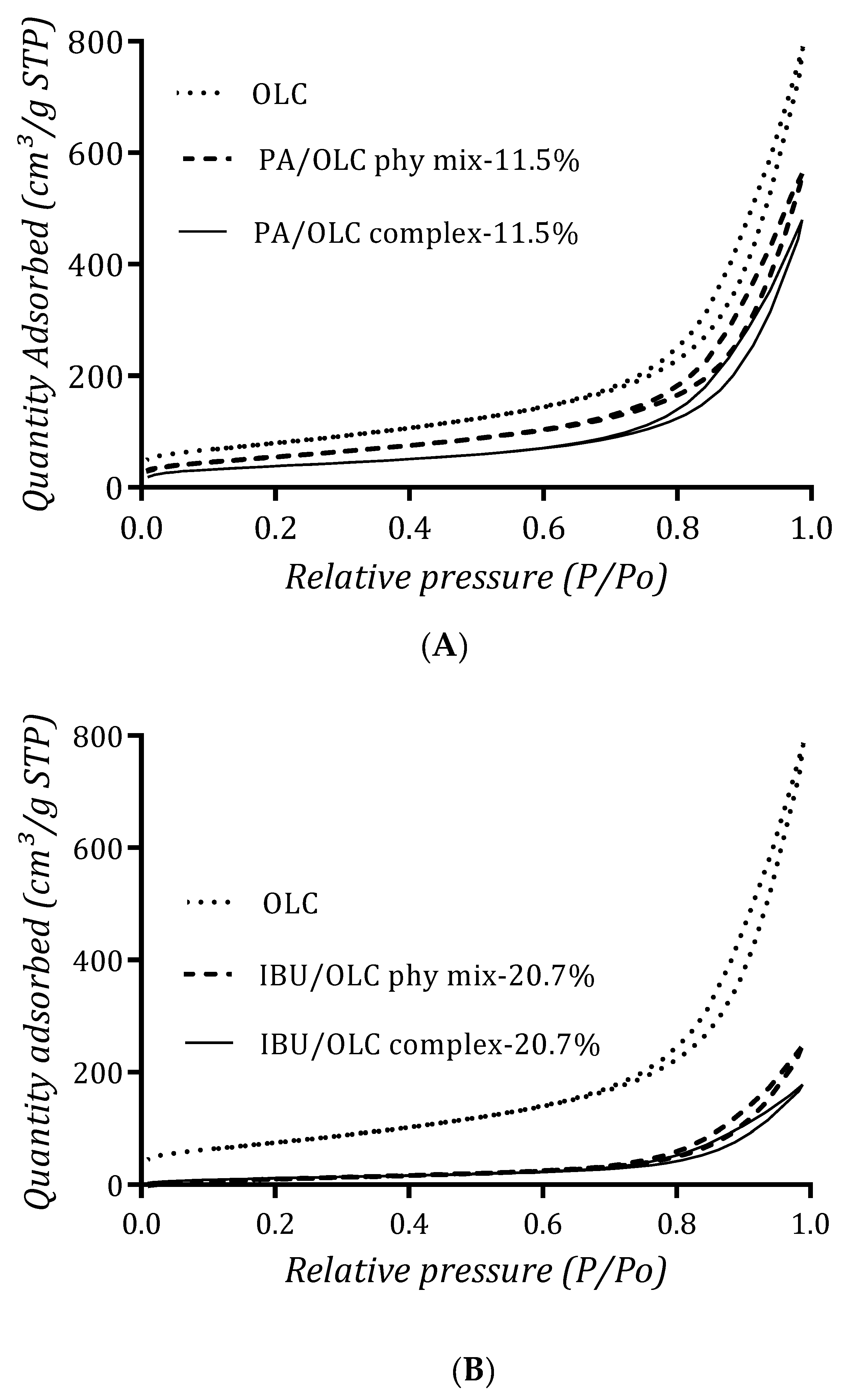
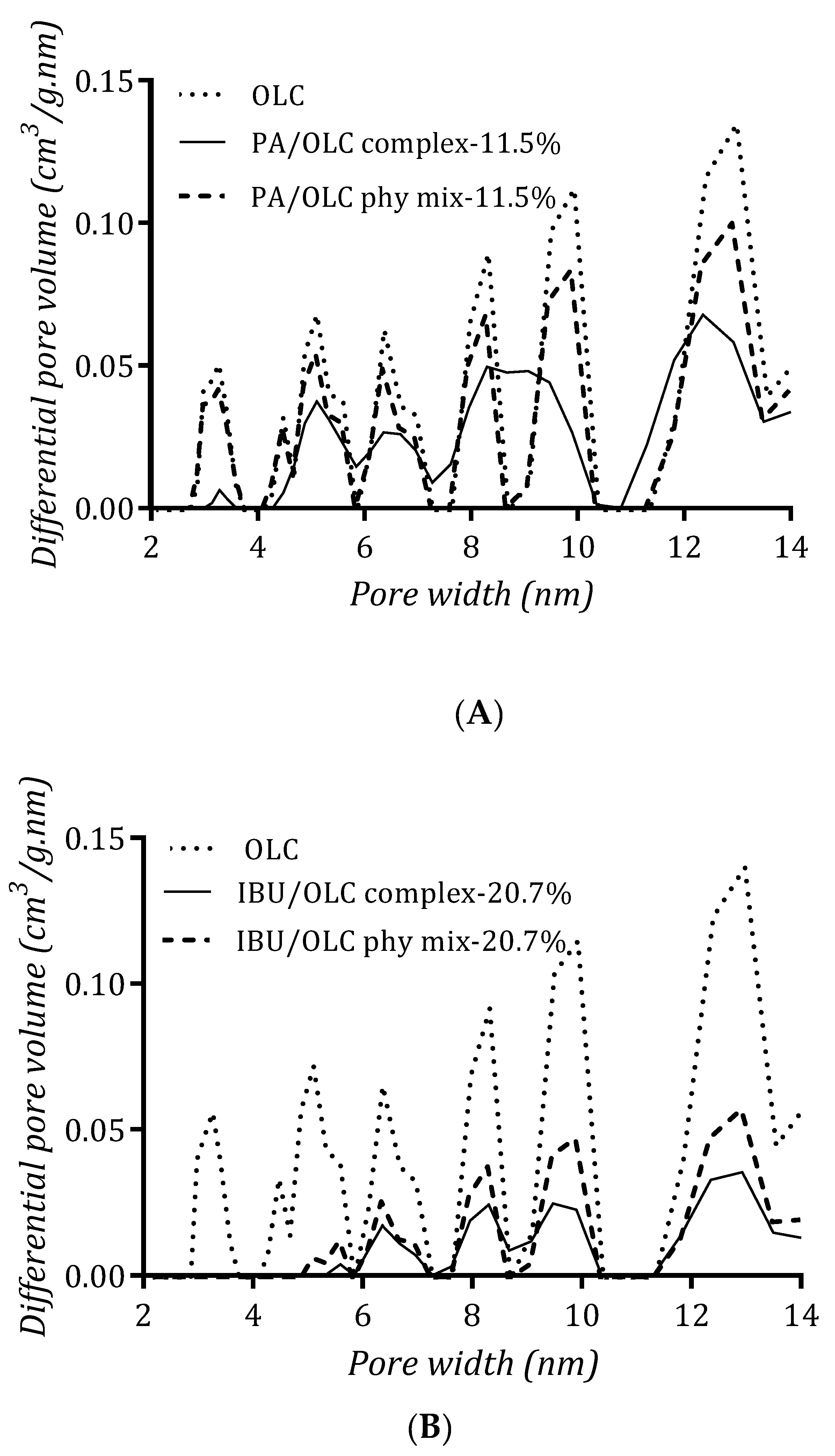
3.7. Porosity Analysis
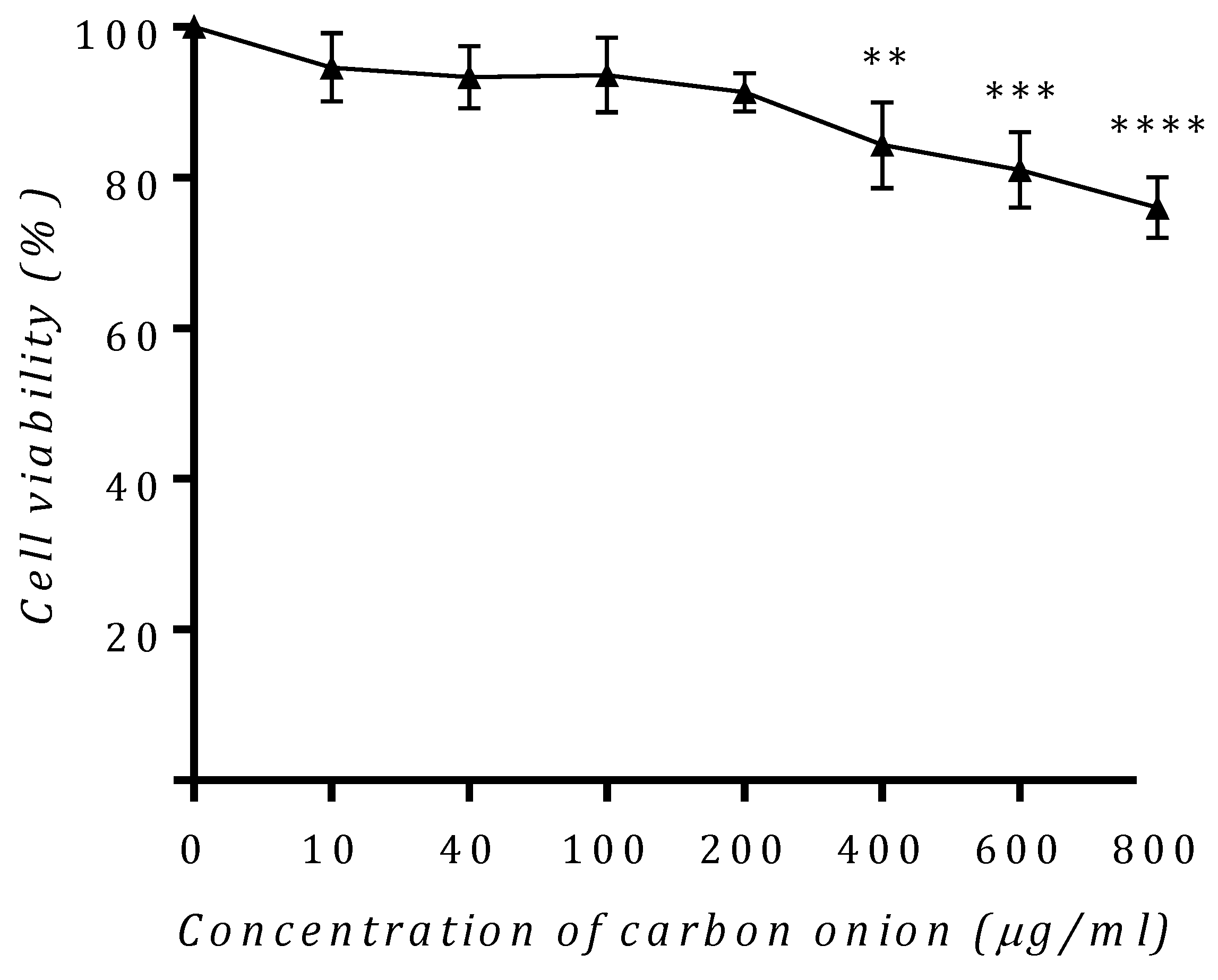
3.8. Toxicity Studies of Carbon Onion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dahan:, A.; Wolk, O.; Kim, Y.H.; Ramachandran, C.; Crippen, G.M.; Takagi, T.; Bermejo, M.; Amidon, G. Purely in Silico BCS Classification: Science Based Quality Standards for the World’s Drugs. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 4378–4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douroumis, D.; Fahr, A. Drug Delivery Strategies for Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Preisig, D.; Haid, D.; Varum, F.J.; Bravo, R.; Alles, R.; Huwyler, J.; Puchkov, M. Drug loading into porous calcium carbonate microparticles by solvent evaporation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 87, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salonen, J.; Laitinen, L.; Kaukonen, A.; Tuura, J.; Björkqvist, M.; Heikkilä, T.; Vähä-Heikkilä, K.; Hirvonen, J.T.; Lehto, V.-P. Mesoporous silicon microparticles for oral drug delivery: Loading and release of five model drugs. J. Control. Release 2005, 108, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laitinen, R.; Löbmann, K.; Strachan, C.J.; Grohganz, H.; Rades, T. Emerging trends in the stabilization of amorphous drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L. Amorphous pharmaceutical solids: Preparation, characterization and stabilization. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 48, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonen, J.; Kaukonen, A.M.; Hirvonen, J.T.; Lehto, V.-P. Mesoporous Silicon in Drug Delivery Applications. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 632–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regi, M.; Ramila, A.; Del Real, R.P.; Perez-Pariente, J. A New Property of MCM-41: Drug Delivery System. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Angelova, A.; Hu, F.; Garamus, V.; Peng, C.; Li, N.; Liu, J.; Liu, D.; Zou, A. pH Responsiveness of Hexosomes and Cubosomes for Combined Delivery of Brucea javanica Oil and Doxorubicin. Langmuir 2019, 35, 14532–14542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.G.; Prim, R.E.; Kim, K.H.; Kang, E.; Park, K.; Jeong, S.H. Combinatorial nanodiamond in pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 514, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, N.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, C.; Huang, Q. The Biocompatibility of Nanodiamonds and Their Application in Drug Delivery Systems. Theranostics 2012, 2, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Kong, H.; Tang, X.; Pan, L.; Xia, K.; Aldalbahi, A.; Li, A.; Tai, R.; et al. Sodium alginate-functionalized nanodiamonds as sustained chemotherapeutic drug-release vectors. Carbon 2016, 97, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Say, K.M. Nanodiamond as a drug delivery system: Applications and prospective. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 1, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Shenderova, O.A.; Zhirnov, V.V.; Brenner, D.W. Carbon Nanostructures. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2002, 27, 227–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojica, M.; Alonso, J.A.; Méndez, F. Synthesis of fullerenes. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2013, 26, 526–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyesmen, P.I.; Onoja, A.; Amah, A.N. Fullerenes synthesis by combined resistive heating and arc discharge techniques. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergin, I.L.; Witzmann, F.A. Nanoparticle toxicity by the gastrointestinal route: Evidence and knowledge gaps. Int. J. Biomed. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 3, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bielicka, A.; Wiśniewski, M.; Terzyk, A.P.; Gauden, P.; Furmaniak, S.; Roszek, K.; Kowalczyk, P.; Bieniek, A. Carbon materials as new nanovehicles in hot-melt drug deposition. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2013, 25, 355002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrones, H.; Terrones, M. Curved nanostructured materials. New J. Phys. 2003, 5, 126.1–126.37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, G.C.; McDonough, J.K.; Gogotsi, Y.; Navrotsky, A. Thermochemistry of onion-like carbons. Carbon 2014, 69, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiger, M.; Jäckel, N.; Aslan, M.; Weingarth, D.; Presser, V. Understanding structure and porosity of nanodiamond-derived carbon onions. Carbon 2015, 84, 584–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakhira, B.; Ghosh, M.; Allam, A.; Sarkar, S. Carbon nano onions cross the blood brain barrier. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 29779–29782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartelmess, J.; Giordani, S. Carbon nano-onions (multi-layer fullerenes): Chemistry and applications. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 1980–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamidi, N.; Castrejón, J.V.; González-Ortiz, A. Rational design and engineering of carbon nano-onions reinforced natural protein nanocomposite hydrogels for biomedical applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 104, 103696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamidi, N.; Gamero, M.R.M.; Castrejón, J.V.; Zúníga, A.E. Development of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene-functionalized carbon nano-onions composites for biomedical applications. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2019, 97, 107435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camisasca, A.; Giordani, S. Carbon nano-onions in biomedical applications: Promising theranostic agents. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2017, 468, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mykhailiv, O.; Zubyk, H.; Plonska-Brzezinska, M.E. Carbon nano-onions: Unique carbon nanostructures with fascinating properties and their potential applications. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2017, 468, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrowska, D.M.; Brzezinski, K.; Plonska-Brzezinska, M.E. PEGylated Carbon Nano-onions Composite as a Carrier of Polyphenolic Compounds: A Promising System for Medical Applications and Biological Sensors. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2017, 21, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V. Natural source derived carbon nano-onions as electrode material for sensing applications. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2018, 87, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amora, M.; Camisasca, A.; Boarino, A.; Arpicco, S.; Giordani, S. Supramolecular functionalization of carbon nano-onions with hyaluronic acid-phospholipid conjugates for selective targeting of cancer cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 188, 110779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.; Wang, M.; Li, Y. Onion-like carbon synthesis by annealing nanodiamond at lower temperature and vacuum. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2010, 5, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, V.; Butenko, Y.; Zaikovskii, V.; Chuvilin, A. Carbon redistribution processes in nanocarbons. Carbon 2004, 42, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonen, J.; Paski, J.; Heikkilä, T.; Björkqvist, M.; Vähä-Heikkilä, K.; Lehto, V.-P. Determination of drug load in porous silicon microparticles by calorimetry. Phys. Status Solidi 2005, 202, 1629–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miriyala, N.; Ouyang, D.; Perrie, Y.; Lowry, D.; Kirby, D.J. Activated carbon as a carrier for amorphous drug delivery: Effect of drug characteristics and carrier wettability. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 115, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiao, Z.; Li, J.; Zhao, N.; Shi, C.; Nash, P. Structural evolution and Raman study of nanocarbons from diamond nanoparticles. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2006, 429, 479–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.Y.; Xie, W.; Gong, L.; Zhang, W.H.; Chen, S.H.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Chen, J. Surface characterization on graphitization of nanodiamond powder annealed in nitrogen ambient. Surf. Interface Anal. 2010, 42, 1514–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.K.; Li, L. Characterization of amorphous and nanocrystalline carbon films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2006, 96, 253–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Chhowalla, M.; Wang, H.; Sano, N.; Alexandrou, I.; Clyne, T.; Amaratunga, G. Characterisation of carbon nano-onions using Raman spectroscopy. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2003, 373, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, B.; Liu, X.; Jia, H.; Hideki, I. The Raman spectrum of nano-structured onion-like fullerenes. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2005, 357, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochalin, V.N.; Pentecost, A.; Li, X.-M.; Neitzel, I.; Nelson, M.; Wei, C.; He, T.; Guo, F.; Gogotsi, Y. Adsorption of Drugs on Nanodiamond: Toward Development of a Drug Delivery Platform. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 3728–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Ouyang, G.; Liu, P.; Wang, C.X.; Yang, G.W. Reversible Nanodiamond-Carbon Onion Phase Transformations. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 3645–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, E.; He, X.; Nesterenko, E.; Brabazon, D.; Dey, A.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Nesterenko, P.N.; Paull, B. Thermally controlled growth of carbon onions within porous graphitic carbon-detonation nanodiamond monolithic composites. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 22906–22915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.H.; Pendleton, P. Adsorption of Anionic Surfactant by Activated Carbon: Effect of Surface Chemistry, Ionic Strength, and Hydrophobicity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 243, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titantah, J.; Lamoen, D. sp3/sp2 characterization of carbon materials from first-principles calculations: X-ray photoelectron versus high energy electron energy-loss spectroscopy techniques. Carbon 2005, 43, 1311–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.J.; Ojeda, J. Substrate and material transfer effects on the surface chemistry and texture of diamond-like carbon deposited by plasma-enhanced chemical vapour deposition. Surf. Interface Anal. 2012, 44, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaciulis, S. Spectroscopy of carbon: From diamond to nitride films. Surf. Interface Anal. 2012, 44, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moseenkov, S.I.; Kuznetsov, V.L.; Ishchenko, A.V. Change in sizes of carbon aggregates and primary particles of the onion-like carbon synthesized by high-temperature annealing of nanodiamond. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2014, 63, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Avalle, P.; Saklatvala, R.; Craig, D.Q.M. An investigation into the effects of thermal history on the crystallisation behaviour of amorphous paracetamol. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Sun, L.X.; Tan, Z.-C.; Liang, J.-G.; Li, R.-L. Thermodynamic study of ibuprofen by adiabatic calorimetry and thermal analysis. Thermochim. Acta 2004, 412, 33–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, H.; Gabas, N.; Canselier, J. Experimental study on the ibuprofen crystal growth morphology in solution. J. Cryst. Growth 2001, 224, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, P.; Tian, Y. Ordered mesoporous carbons for ibuprofen drug loading and release behavior. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 142, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, K.; Jiang, G.; Xiong, Y.; Du, Y.; Shi, X. Electrical Signal Guided Ibuprofen Release from Electrodeposited Chitosan Hydrogel. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2014, 2014, 736898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martín, Á.; Scholle, K.; Mattea, F.; Meterc, D.; Cocero, M.J. Production of Polymorphs of Ibuprofen Sodium by Supercritical Antisolvent (SAS) Precipitation. Cryst. Growth Des. 2009, 9, 2504–2511. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, J.; Lin, W.; Scholes, P.; Li, M. Investigating the Effects of Loading Factors on the In Vitro Pharmaceutical Performance of Mesoporous Materials as Drug Carriers for Ibuprofen. Materials 2017, 10, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Costa, P.; Lobo, J.M.S. Modeling and comparison of dissolution profiles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 13, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Martinez, Á.; Doadrio, J.C.; Perez-Pariente, J.; Vallet-Regi, M. Release evaluation of drugs from ordered three-dimensional silica structures. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 26, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertel, K.D.; Heasley, R.A.; Koegel, C.; Chakrabarti, A.; Carstensen, J.T. Determination of Ibuprofen Vapor Pressure at Temperatures of Pharmaceutical Interest. J. Pharm. Sci. 1990, 79, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.P.; Labhasetwar, V.; Amidon, G.; Levy, R.J. Gastrointestinal Uptake of Biodegradable Microparticles: Effect of Particle Size. Pharm. Res. 1996, 13, 1838–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Material | X10a (µm) | X50b (µm) | X90c (µm) | Volume Mean Diameter (µm) | Span |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon onion | 0.88 ± 0.0 | 2.2 ± 0.0 | 7.45 ± 0.02 | 3.37 ± 0.01 | 2.99 ± 0.01 |
| Higuchi Diffusion Two Step | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Duration | Rate Constant | Linear Regression Coefficient |
| PA/OLC complex at pH 5.8 | 3–10 min | 46.34 | 0.999 |
| 10–20 min | 16.91 | 0.797 | |
| IBU/OLC complex at pH 7.2 | 3–10 min | 48.07 | 0.94 |
| 10–20 min | 13.87 | 0.916 | |
| Sample | Specific Surface Area1 (m2/g) | Total Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Micro Pore Volume2 (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| OLC | 293.3 | 1.2 | 0.03 |
| PA/OLC complex-11.5% | 138.4 | 0.73 | 0.002 |
| PA/OLC phy mix-11.5% | 210.1 | 0.86 | 0.015 |
| IBU/OLC complex-20.7% | 46.1 | 0.27 | 0 |
| IBU/OLC phy mix-20.7% | 65.4 | 0.38 | 0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miriyala, N.; Kirby, D.J.; Cumont, A.; Zhang, R.; Shi, B.; Ouyang, D.; Ye, H. Synthesis of Carbon Onion and Its Application as a Porous Carrier for Amorphous Drug Delivery. Crystals 2020, 10, 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10040281
Miriyala N, Kirby DJ, Cumont A, Zhang R, Shi B, Ouyang D, Ye H. Synthesis of Carbon Onion and Its Application as a Porous Carrier for Amorphous Drug Delivery. Crystals. 2020; 10(4):281. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10040281
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiriyala, Nikhila, Daniel J. Kirby, Aude Cumont, Ruoying Zhang, Baogui Shi, Defang Ouyang, and Haitao Ye. 2020. "Synthesis of Carbon Onion and Its Application as a Porous Carrier for Amorphous Drug Delivery" Crystals 10, no. 4: 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10040281
APA StyleMiriyala, N., Kirby, D. J., Cumont, A., Zhang, R., Shi, B., Ouyang, D., & Ye, H. (2020). Synthesis of Carbon Onion and Its Application as a Porous Carrier for Amorphous Drug Delivery. Crystals, 10(4), 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10040281






