Interface Behavior of Brazing between Zr-Cu Filler Metal and SiC Ceramic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
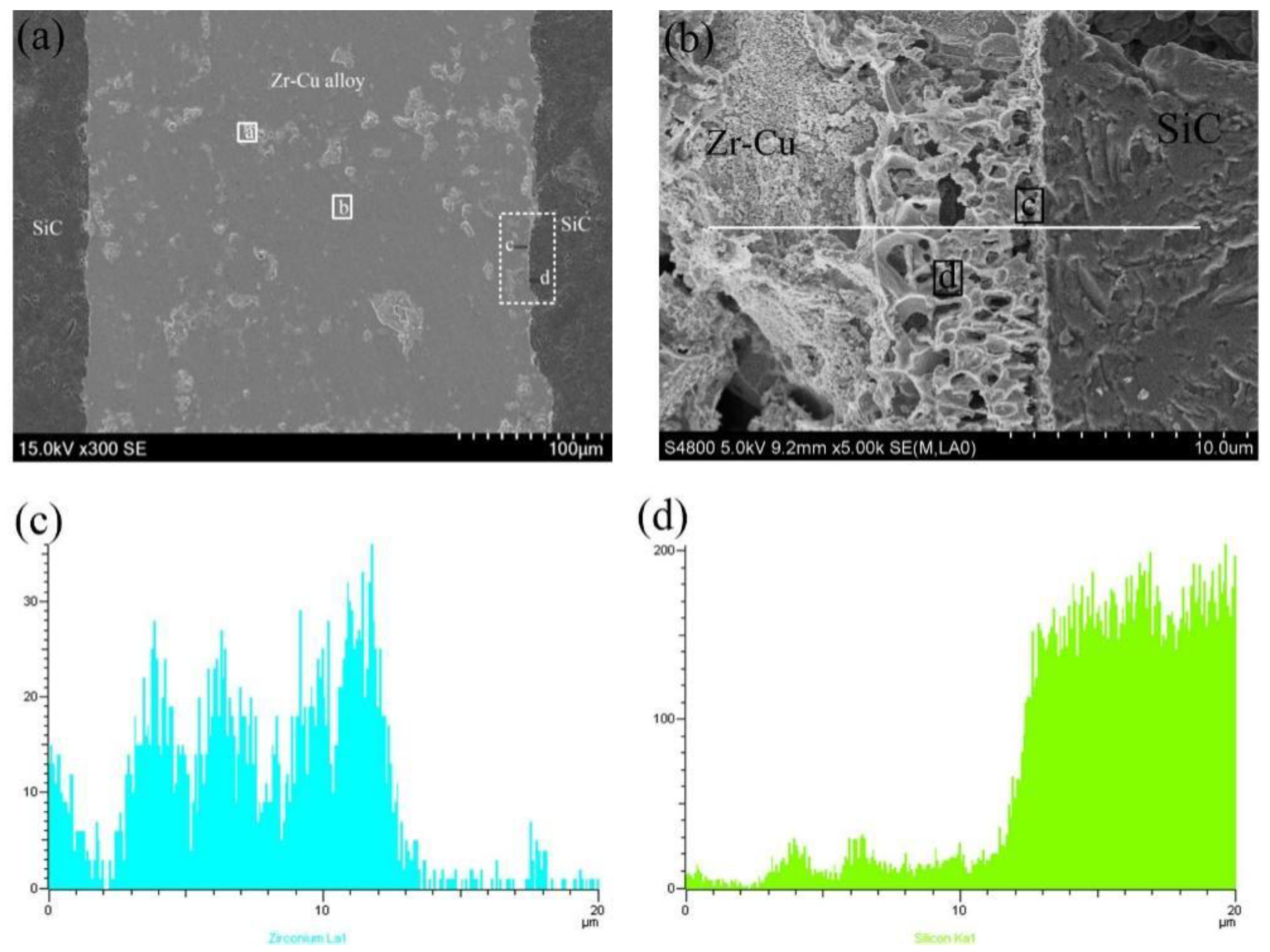
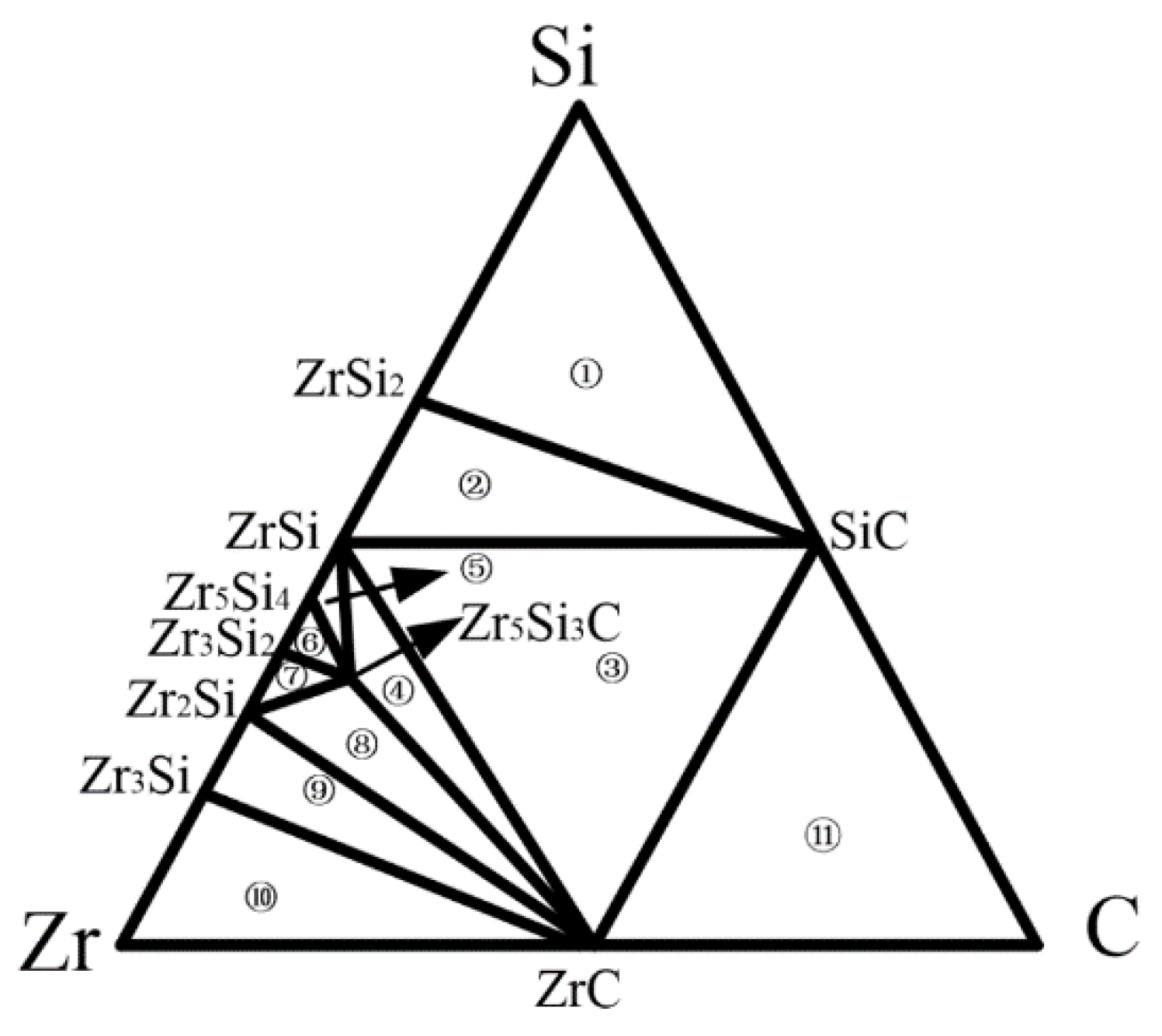
3.1. Formation of Interface Products and the Way of Element Diffusion
- (1)
- Zr—Zr3Si—Zr2Si—ZrC,
- (2)
- Zr—Zr3Si—Zr2Si—T—ZrC.
- (1)
- Si—ZrSi2—ZrSi—Zr5Si4—Zr3Si2—Zr2Si—T—ZrC,
- (2)
- Si—ZrSi2—ZrSi—Zr5Si4—Zr3Si2—Zr2Si—ZrC.
- (1)
- C—ZrC—T—Zr2Si,
- (2)
- C—ZrC—Zr2Si.
3.2. Growth Behavior of Interface Reaction Layer
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- In the brazing process of Zr-Cu filler metal and SiC ceramic, the main reaction is the interface reaction of the active element Zr and the SiC ceramic and the interface products are mainly ZrC and Zr2Si, which is consistent with the thermodynamic calculation. The potential stability phase diagram of the Zr-Si-C ternary system was used to explain the possible diffusion path of elements in the process of product formation.
- (2)
- Based on the Fick diffusion theory, the physical model of the brazing SiC ceramic experiment and the diffusion behavior of Zr in the interface reaction layer, the kinetics equation of the interface reaction layer growth is established and the diffusion constant = 2.1479 μm·s1/2 and activation energy Q = 42.65 KJ·mol−1 are calculated. The growth kinetics equation of the interfacial reaction layer thickness with holding time under different brazing temperature is obtained as follows:brazing temperature at 1200 °C:brazing temperature at 1300 °C: .
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Passerini, S.; Kazimi, M.S.; Shwageraus, E. A systematic approach to nuclear fuel cycle analysis and optimization. Nucl. Sci. Eng. 2014, 178, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorton, J.P.; Collins, B.S.; Wysocki, A.J.; Brown, N.R. Assessment of CASL VERA for BWR analysis and application to accident tolerant SiC/SiC channel box. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2020, 365, 110732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Hou, G.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, G.; Wu, Y. Microstructure and mechanical strength of SiC joints brazed with Cr3C2 particulate reinforced Ag-Cu-Ti brazing alloy. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 11862–11868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.P.; Chen, B.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, H.S.; Ye, L. Joining of Cf/SiC composite with a Cu-Au-Pd-V brazing filler and interfacial reactions. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 34, 1481–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Q.H.; Sun, D.L.; Han, X.; Tian, Q. Microstructure and mechanical properties of SiC/Ti diffusion bonding joints under electric field. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2016, 45, 1749–1754. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.-H.; Kim, D.S.; Lim, S.T.; Kim, D.K. Interfacial microstructure of diffusion-bonded SiC and Re with Ti interlayer. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 701, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Li, S.; Teng, Y.; Ma, W. Joining of SiC ceramic-based material with ternary carbide Ti3SiC2. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2011, 176, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Chien, H. Residual thermal stress analysis of SiC joint by polysiloxane silicon resin YR3187. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2013, 27, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Lu, C.; He, Y.; Zheng, W.; Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; Gao, Z. Characterization of SiC ceramic joints brazed using Au-Ni-Pd-Ti high-temperature filler alloy. Materials 2019, 12, 931. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Q.; Zhang, J.; Lu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Xuan, Y.; Liu, M. Microstructure and mechanical properties of the SiC/Zr4 joints brazed with TiZrNiCu filler for nuclear application. Mater. Int. 2018, 28, 378–385. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, W.B.; Sun, Z.M.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y.M.; Shi, J. Brazing of silicon carbide ceramics with Ni-Si-Ti powder mixtures. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 53, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhong, Z.; Wen, Q.; Song, K.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Y. Micro-alloying effects of yttrium on the microstructure and strength of silicon carbide joint brazed with chromium-silicon eutectic alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 738, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsukawa, Y.; Okuma, I.; Muta, H.; Shinohara, Y.; Suzue, R.; Yang, H.; Maruyama, T.; Toyama, T.; Shen, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Crystallographic analysis on atomic-plane parallelisms between bcc precipitates and hcp matrix in recrystallized Zr-2.5Nb alloys. Acta Mater. 2017, 126, 86–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zeng, Z.; Cai, Y.; Feng, K. FEM simulation and verification of brazing SiC ceramic with novel Zr-Cu filler metal. Materials 2019, 12, 3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, B.; Wang, J.; Feng, K.; Cai, Y.; Chen, S. Effect of brazing parameters on the microstructure and properties of SiC ceramic joint with Zr-Cu filler metal. Crystals 2020, 10, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, B.; Feng, K. Zr-Cu alloy filler metal for brazing SiC ceramic. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 26251–26254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, L.; Huang, C.; Liu, H.; Zou, B.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, G.; Wang, J. Study on the synthesis and growth mechanisms of the refractory ZrC whiskers. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2014, 42, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, H.; Lockhart, C.; Mariani, R.; Xu, P.; Corradini, M.; Sridharan, K. Evaluation of steam corrosion and water quenching behavior of zirconium-silicide coated LWR fuel claddings. J. Nucl. Mater. 2018, 499, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeske, T.; Schmitz, G. Nanoscale analysis of the early interreaction stages in Al/Ni. Scr. Mater. 2001, 45, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Carim, A.H. Ternary phase equilibria in the Zr-Si-C system. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1995, 78, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D. Thermodynamic Data Handbook of Inorganic Substances; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, J.O. Thermodynamic properties of Mo-C. Calphad 1988, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boettinger, W.J.; Perepezko, J.H.; Frankwicz, P.S. Application of ternary phase diagrams to the development of MoSi2-based materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1992, 155, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Properties | Maximum Temperature of Application | Density | Open Porosity | Bending Strength | Modulus of Elasticity | Thermal Conductivity | Coefficient of Thermal Expansion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBSiC | 1380 °C | >3.02 g/cm3 | <0.1% | 280 MPa | 300 GPa | 74 W/mK | 4.5 × 10−6 K−1 |
| Properties | Solidus Temperature | Liquidus Temperature | Thermal Neutron Absorption cross Section | Coefficient of Thermal Expansion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80Zr-20Cu (wt.%) | 1023 °C | 1056 °C | 1.074 × 10−28 m2 | 7.4 × 10−6 K−1 |
| Phase Region | Zr | Cu | Si | C | Possible Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 75.59 | 24.08 | 0.13 | 0.20 | CuZr2 + Zr |
| b | 70.48 | 27.94 | 0.50 | 1.08 | eutectic alloy |
| c | 63.58 | 9.80 | 19.39 | 7.23 | Zr2Si |
| d | 58.90 | 1.45 | 23.24 | 16.41 | ZrC + Zr2Si |
| Materials | Zr | Si | C | SiC | ZrC | ZrSi |
| G/kJ·mol−1 | −92.13 | −55.44 | −26.43 | −143.63 | −301.48 | −312.40 |
| Materials | ZrSi2 * | Zr2Si | Zr3Si * | Zr3Si2 * | Zr5Si4 * | Zr5Si3C * |
| G/kJ·mol−1 | −388.49 | −446.07 | −540.26 | −760.09 | −1386.32 | −1385.81 |
| No. | Three Phase Equilibrium Area | μZr/kJ·mol−1 | μSi/kJ mol−1 | μc/kJ mol−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ① | Si—SiC—ZrSi2 | −237.61 | −55.44 | −88.19 |
| ② | ZrSi—SiC—ZrSi2 | −236.31 | −76.09 | −67.54 |
| ③ | ZrSi—SiC—ZrC | −235.12 | −77.28 | −66.36 |
| ④ | ZrSi—ZrC—Zr5Si3C | −147.13 | −165.27 | −154.35 |
| ⑤ | ZrSi—Zr5Si4—Zr5Si3C | −136.72 | −175.68 | −175.17 |
| ⑥ | Zr3Si2—Zr5Si4—Zr5Si3C | −133.86 | −179.26 | −178.73 |
| ⑦ | Zr3Si2—Zr2Si—Zr5Si3C | −132.05 | −181.97 | −179.65 |
| ⑧ | Zr2Si—ZrC—Zr5Si3C | −108.94 | −228.19 | −192.54 |
| ⑨ | Zr2Si—ZrC—Zr3Si | −94.19 | −257.69 | −207.29 |
| ⑩ | Zr—ZrC—Zr3Si | −92.13 | −231.87 | −209.35 |
| ⑪ | C—SiC—ZrC | −275.05 | −117.20 | −26.43 |
| Temperature/°C | 5 min | 20 min | 60 min |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1200 | 1.1 | 2.9 | 7.1 |
| 1300 | 1.5 | 3.8 | 9.4 |
| Temperature/°C | d0 (μm) | KT (μm·s1/2) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1200 | 0.30352 | 0.066 | 0.99392 |
| 1300 | 0.42649 | 0.08236 | 0.99695 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, B.; Li, T.; Zhang, H.; Hou, J. Interface Behavior of Brazing between Zr-Cu Filler Metal and SiC Ceramic. Crystals 2021, 11, 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11070727
Zhou B, Li T, Zhang H, Hou J. Interface Behavior of Brazing between Zr-Cu Filler Metal and SiC Ceramic. Crystals. 2021; 11(7):727. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11070727
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Bofang, Taohua Li, Hongxia Zhang, and Junliang Hou. 2021. "Interface Behavior of Brazing between Zr-Cu Filler Metal and SiC Ceramic" Crystals 11, no. 7: 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11070727
APA StyleZhou, B., Li, T., Zhang, H., & Hou, J. (2021). Interface Behavior of Brazing between Zr-Cu Filler Metal and SiC Ceramic. Crystals, 11(7), 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11070727





