Abstract
With unique electrical and catalytic properties, CuO has been ubiquitously employed in many applications including electrochemical sensors. Enhanced electrocatalytic performance of CuO can be achieved through doping. This work explored the potential of 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) composite for nitrite detection. The undoped CuO and 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO powders, prepared using a solution combustion technique, had average particle sizes lower than 100 nanometres. Particle refinement and enhancement of the specific surface area were observed in 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO. CuO/MWCNT and 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT composites, prepared using the hydrothermal impregnation technique, were tested for their electrocatalytic activities in the presence of nitrite. Cyclic voltammetry results revealed reduction reaction at an applied voltage of approximately −0.4 V. Superior peak currents were evident in the 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT composite. With acceptable sensitivity, limit of detection, selectivity, reusability, and recovery percentage, the 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT composite demonstrated potential capability in the detection of nitrite.
1. Introduction
Nitrite salts, including sodium nitrite and potassium nitrite, have been recognized as food preservatives used for preventing the growth of bacteria such as Clostridium botulinum in meat products and for retarding the rancidity process [1]. Excessive residual nitrite in the human body has been reported to trigger the formation of carcinogenic substances, specifically nitrosamines and nitrosamides, which may cause gastric and oesophageal cancers [2,3]. It has also been reported that acute toxicity and methemoglobinemia can be triggered by excess nitrite concentrations in human blood. Methemoglobinemia, a condition where the concentration of methaemoglobin (metHb) exceeds 10% of normal haemoglobin (Hb) resulting in ineffective oxygen transportation to human organs, is caused by the oxidation of Hb by nitrite [4]. For these reasons, excessively high nitrite concentrations in the human body are considered detrimental to health.
According to European Commission Regulation No 1333/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council on Food Additives, the permitted levels for sodium nitrite in enzyme preparation and in final food products are 500 mg/kg and 0.01 mg/kg, respectively [5]. The World Health Organization (WHO) set the fatal dose of nitrite at 21.7 µM (1.0 mg/L). The WHO also reported that the level of nitrite in drinking water should generally be maintained below 14 µM (0.65 mg/L) [6].
Detection of nitrite is necessary to reduce the health risks associated with nitrite residue. Various nitrite-detection techniques have been reported, including spectrophotometric, chemiluminescent, high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and capillary electrophoresis [7,8,9,10]. With drawbacks such as the requirement of complex and expensive instruments as well as skilful operators, these techniques are not suitable for point-of-care-testing (POCT) techniques for nitrite detection [11,12].
Electrochemical techniques can be ideal for POCT as they are simple and cost-efficient with good sensitivity [13]. A simple electrochemical technique involves cyclic voltammetry (CV), which provides an electrical signal generated by redox reactions at a particular applied voltage. The electrodes used in electrochemical measurements consist of a reference electrode, an auxiliary or counter electrode, and a working electrode [14]. Detection performance is significantly influenced by the sensing materials in the working electrode. Some desirable characteristics of the sensing materials used in working electrodes include high electrocatalytic activity, high effective surface area, high transfer-charge rate, low interfacial interaction, and low charge-transfer resistance [15].
Copper oxide (CuO) is a p-type semiconductor with a narrow bandgap energy of 1.2 eV. With its unique properties, it has been commonly exploited in applications including photocatalysis, solar energy conversion, supercapacitors, electrodes for lithium-ion batteries, antimicrobials, and sensing applications [16]. Various synthesis techniques are capable of producing copper oxide. Some common methods include electrochemical techniques, sol-gel, precipitation, and microwave irradiation [17,18,19,20]. Solution combustion is a simple, efficient and robust method with low energy and time requirements for the synthesis of copper oxide with a fine particle size [21].
Enhanced catalytic and electrical properties of CuO can be achieved by doping with metals such as nickel, cobalt, iron, cadmium, zinc, and aluminium [22]. Through iron doping, improved charge-carrier mobility can be achieved [23]. According to Chafi et al., an increase in the concentration of Fe in Fe-doped CuO leads to enhanced electron mobility and conductivity. This is attributed to electron transfer between Cu2+/Fe2+ or Cu+/Fe3+ [24]. Nevertheless, at excessively high Fe-doping content (≥4 at%), the secondary phase of α-Fe2O3 is formed [25]. It has been reported that an Fe-doping concentration close to 3 at% demonstrates optimal charge transfer and high conductivity [23,26].
In addition to doping, improved electrode efficiency can be achieved through using supporting materials. With outstanding properties, including high specific surface area, high electron conductivity, and chemical stability, multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) are extensively used as supporting materials in modified electrodes [27]. Enhanced electrocatalytic activity of CuO/MWCNT composite has been reported by several researchers [28,29].
Despite numerous investigations on the properties of CuO and carbon-based materials, utilization of 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/carbon-based material composite in electrochemical sensor applications have not been extensively reported. This work, therefore, aimed at producing and characterizing 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT composite. The electrocatalytic activity and sensing performances of 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT electrode in the presence of nitrite were also evaluated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of CuO and 3 mol% Fe-Doped CuO Powders
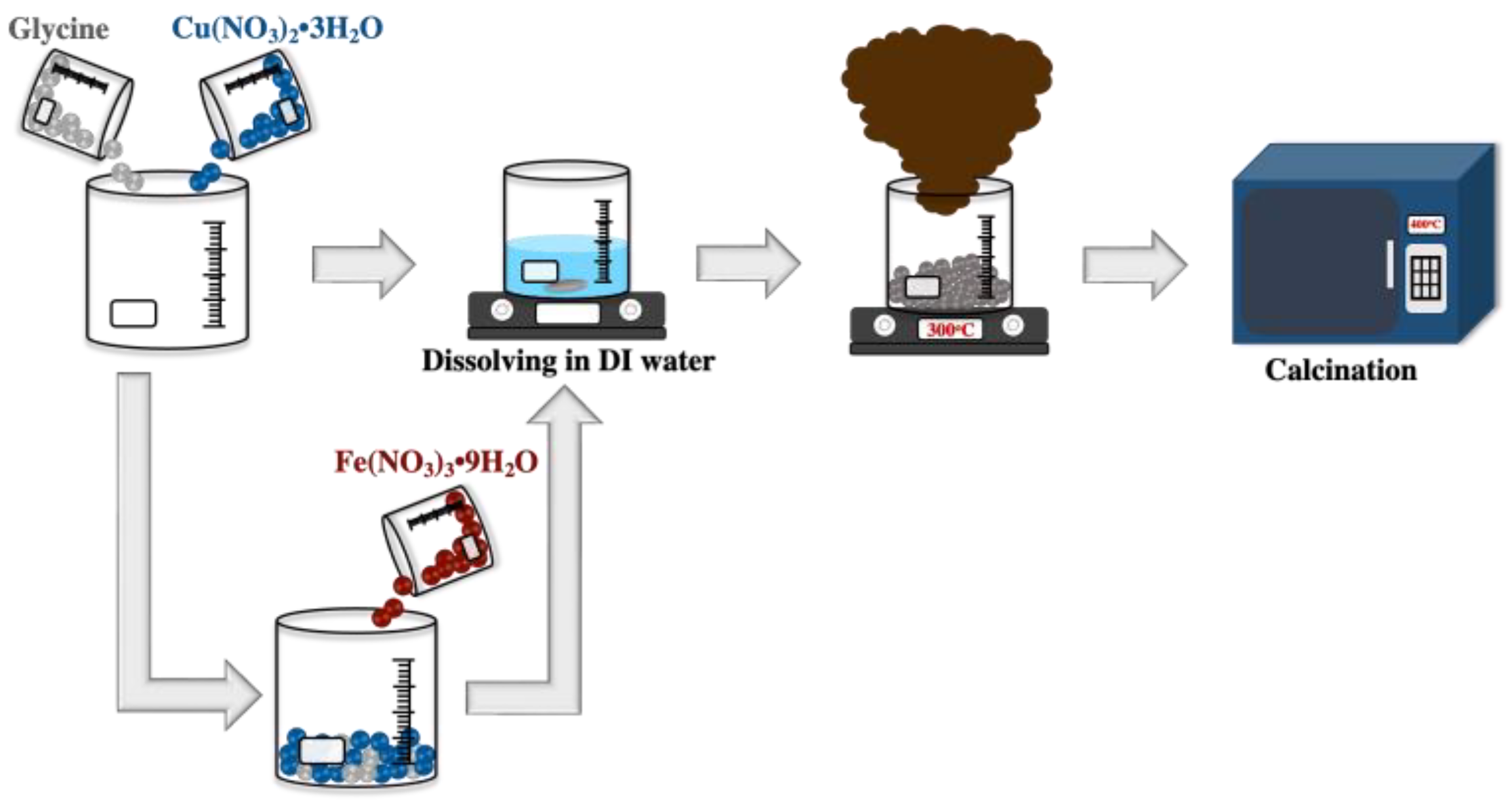
The solution combustion technique was used to synthesize the CuO and 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO powders. Copper (II) nitrate trihydrate (Cu(NO3)2 3H2O, Daejung) and iron (III) nitrate nonahydrate (Fe(NO3)3 9H2O, Daejung) were used as initial reagents and glycine (C2H5NO2, Daejung) was added as fuel to commence combustion. A homogeneous aqueous solution containing the initial reagents and fuel was prepared by adding the deionized water to the initial reagent and fuel. The prepared solution was heated at 300 °C until combustion was complete. Subsequently, the powder obtained from the combustion process was calcined at 400 °C for 3 h, as shown in Figure 1.
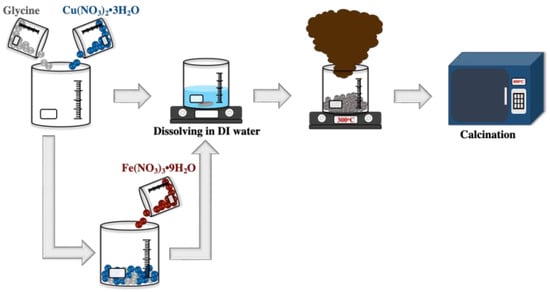
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the synthesis of undoped CuO and 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO powders.
2.2. Preparation of CuO/MWCNT and 3 mol% Fe-Doped CuO/MWCNT Working Electrodes
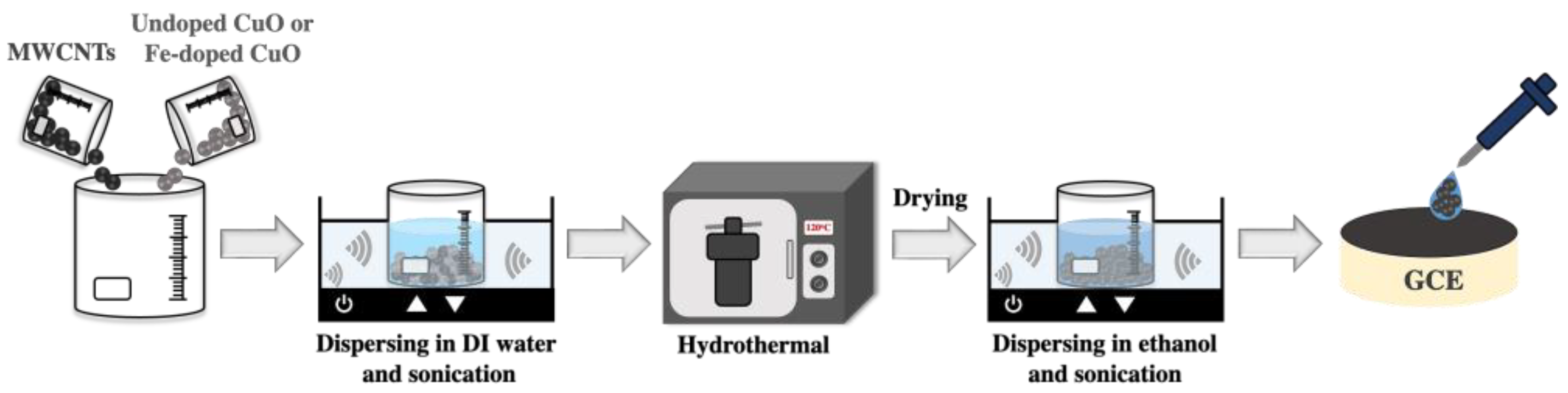
To obtain the undoped CuO (3 mol% Fe-doped CuO)/MWCNT composites used in the working electrode, the undoped CuO or 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO powders were mixed with multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) at a ratio of 1:1 by weight, dispersed in deionized water and sonicated for 30 min. The mixtures were autoclaved at 120 °C for 5 h, dried at 60 °C for 24 h, and subsequently dispersed in 99% ethanol (QRëc). A 5 μL volume of the prepared suspension was dropped onto a glassy carbon electrode (GCE, diameter = 3.0 mm) and dried overnight at room temperature, as schematically shown in Figure 2.
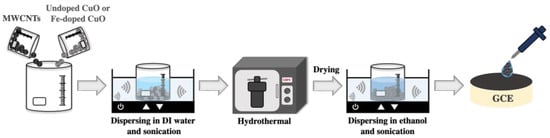
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the preparation of undoped CuO/MWCNT composite and 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT-composite-modified working electrodes.
2.3. Characterization
Phase identification of the undoped CuO and 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO powders was conducted using an X-ray diffractometer (XRD; Phillips, X’Pert diffractometer) over 2θ angles ranging from 20° to 80°, at a step size of 0.02. Rietveld refinement, using the X’Pert HighScore Plus Program, was conducted to determine lattice parameters of the undoped CuO and 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO powders. In addition, the XRD pattern was employed in determining the crystallite size of powders, following Scherrer’s equation shown in Equation (1).
where D is crystallite size of powder, λ is wavelength of X-ray beam (0.154 nm for CuKα radiation), FWHM is the full width at half maximum (radians), and θ is the Bragg-angle of the prominent diffracted peak.
The microstructure of the synthesized powders was examined via scanning electron microscopy (SEM; FEI, Quanta 450), and field emission transmission electron microscopy (FE-TEM; HR, JEM-3100). The Image J software was used in the analysis of the particle size of the powders.
The specific surface areas of the undoped CuO and 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO powders were determined using a surface area analyser (Micrometrics, 3Flex). The powders were degassed at 200 °C for 3 h prior to measurement. Adsorption-desorption of nitrogen (N2) was conducted at 77 K.
The electrocatalytic activities of the powders were evaluated using the CV technique. For the measurement, a potentiostatic machine (Zensor simulator, Dual Function Electrochemistry: ECAS100), with a Ag/AgCl reference electrode, a Pt auxiliary electrode, and undoped CuO (3 mol% Fe-doped CuO)/MWCNT working electrodes, was used in the presence of nitrite solution. Voltages ranging from −1.4 V to 1.4 V were applied during the measurement. Chronoamperometry and CV techniques were employed in the selectivity evaluation of the 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT-composite-modified electrode in the presence of glutamate (Glu), borax, nitrite, nitrate, and citric acid (CA).
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Composition and Structural Identification
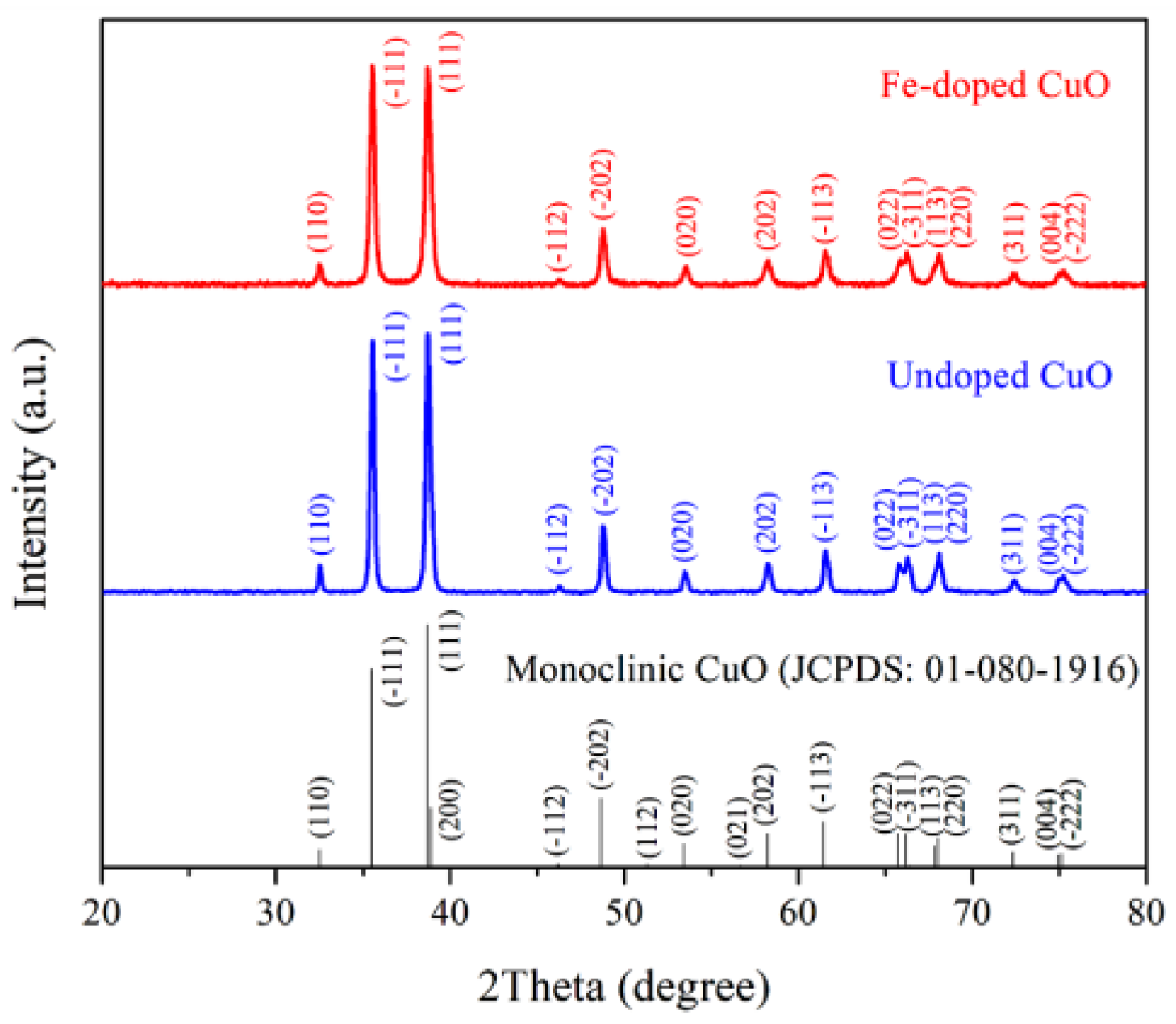
The XRD patterns of undoped CuO and 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO powders revealed prominent peaks at the 2θ angles close to 35.49°, 38.69°, 48.65°, and 61.45° which corresponded to (-111), (111), (-202), and (-113), as shown in Figure 3. The diffracted planes confirmed the formation of monoclinic CuO (JCPDS #01-080-1916). No evidence of diffracted peaks corresponding to a secondary phase was detected, indicating the potential of single-phase undoped CuO or Fe-doped CuO formation.
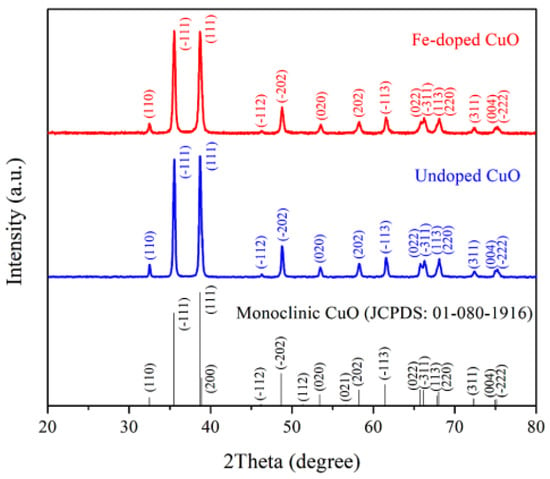
Figure 3.
XRD patterns of undoped CuO and 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO.
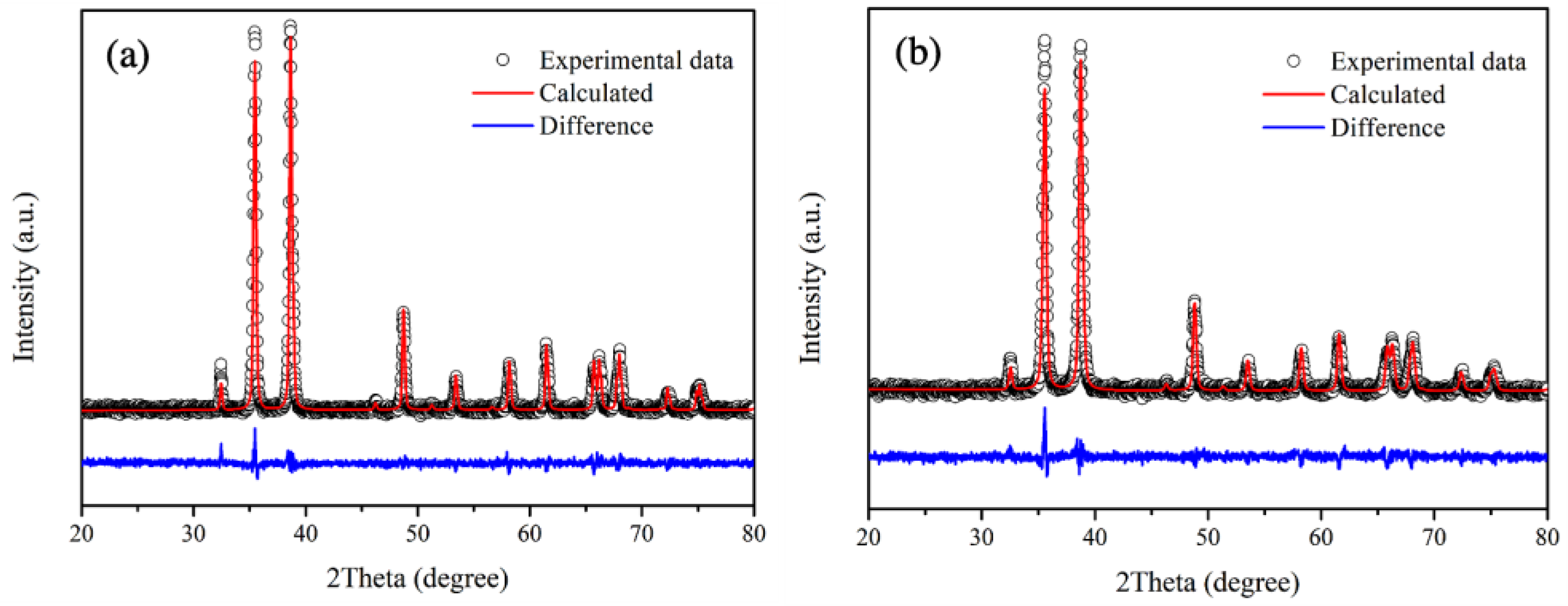
Rietveld refinement is employed in the structural analysis of undoped CuO and 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO samples, as shown in Figure 4a,b. It has been generally accepted that good refinements should exhibit a profile factor (Rp) and weighted profile factor (Rwp) lower than 10%, and goodness of fit (χ2) close to 1.0 [30,31]. In this study, as shown in Table 1, the refinement parameters of all samples (Rp, Rwp) are in the range below 8% with χ2 close to 1.1. The results, therefore, demonstrated good fit with CuO in Crystallography Open Database ID 9016326 (space group: C1c1). According to the refinement results, lattice parameters of 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO and undoped CuO did not differ noticeably. The results agree with those in studies by Chafi et al. and Layek et al., who reported that insignificant distortion of CuO structure was evident when doped with Fe. This might be attributed to comparable ionic radii sizes between copper and iron ions ( = 0.73 Å, = 0.64 Å, and = 0.74 Å) [32,33].
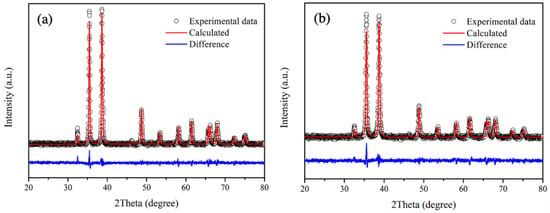
Figure 4.
Rietveld refinement patterns of (a) undoped CuO and (b) 3 mol% Fe-doped.

Table 1.
Rietveld refinement parameters of undoped CuO and 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO.
With the single-phase XRD pattern and Rietveld refinement analysis, the results revealed successful incorporation of Fe dopants into the CuO lattice. Enhancement of electrical and electrocatalytic properties is achievable via successful doping of CuO with Fe. It has been reported that the conductivity of Fe-doped CuO thin films increased with the dopant concentration. This was attributed to superior mobility of the charge carriers [24].
3.2. Microstructural Examination
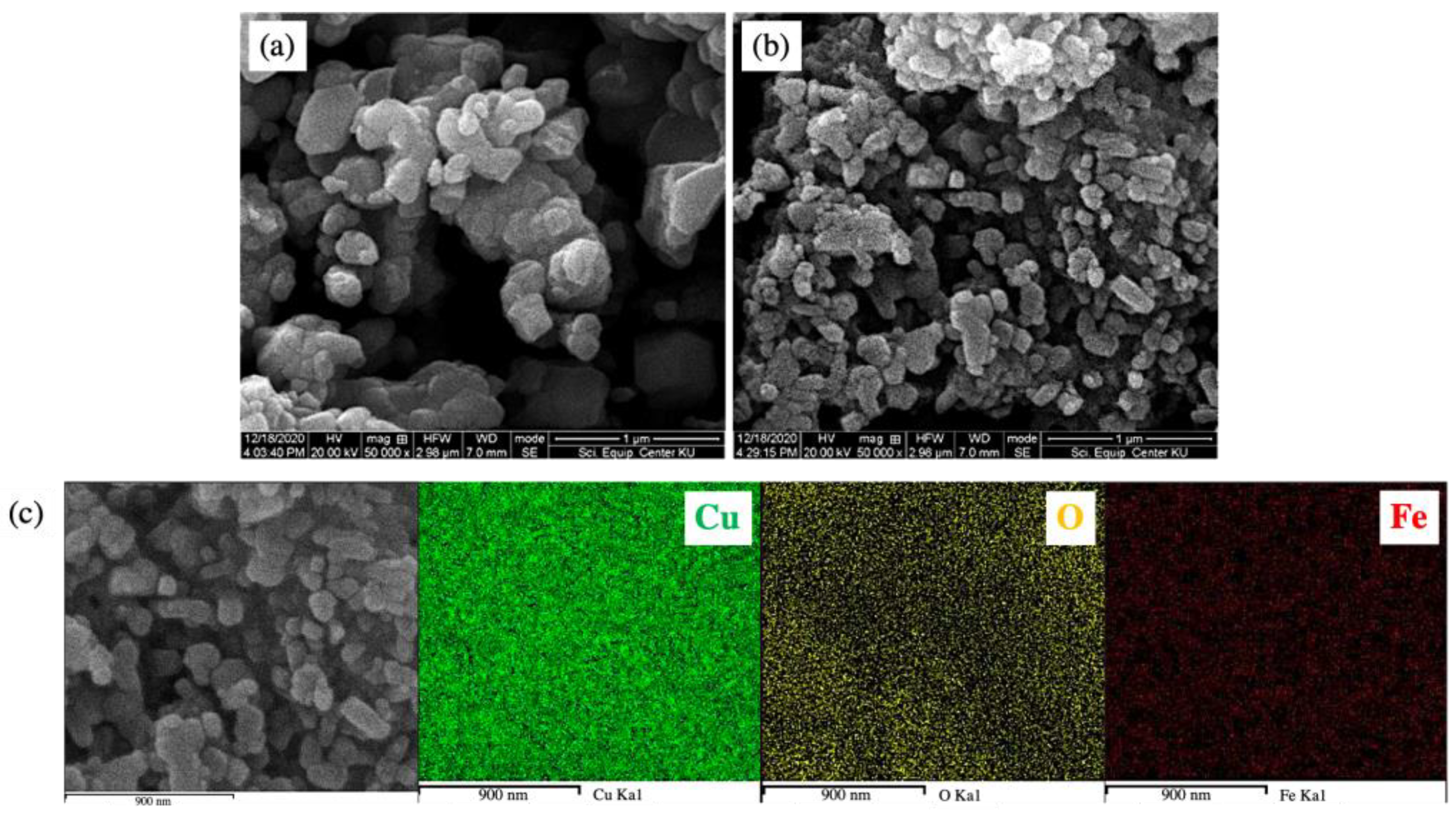
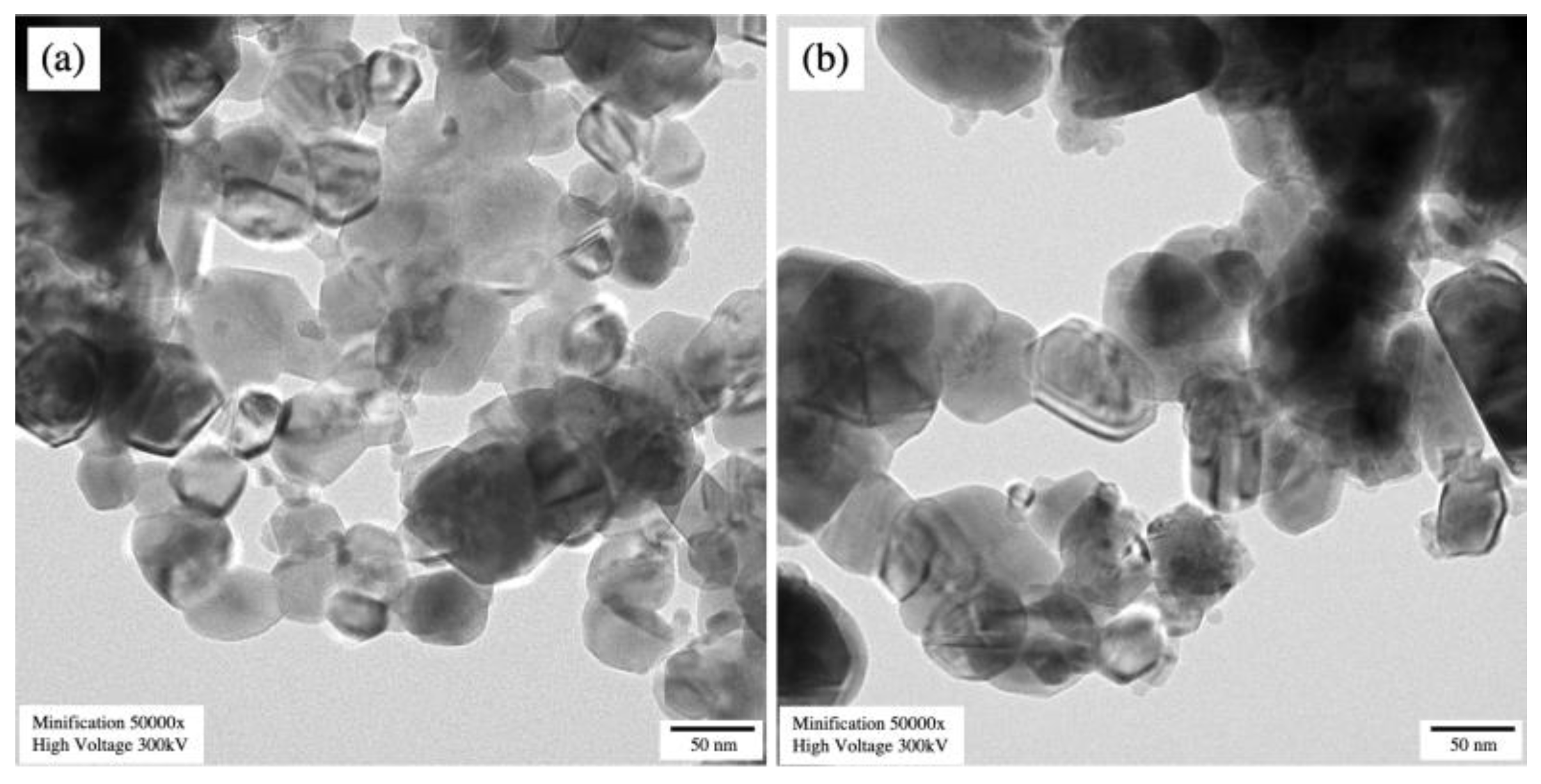
Scanning electron micrographs, as displayed in Figure 5a,b, showed that the undoped CuO and 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO particles had a spherical shape. For 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO, slightly elongated particles were also observed. Results of the particle size analysis using Image J software showed that the average (±standard deviation) sizes were 112.61 ± 58.74 nm and 70.09 ± 29.95 nm in undoped CuO and 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO, respectively. The TEM results, as shown in Figure 6, also reveal a slight refinement of the particles as a result of Fe doping. The results obtained from the transmission electron micrographs agreed with those from SEM. Refinement of the particles was also observed, from 82.07 ± 30.94 nm in undoped CuO to 52.58 ± 28.68 nm in 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO, as shown in Table 2. In addition, EDS was employed for elemental analysis of the samples. The elemental mapping from EDS of 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO powder clearly demonstrated a uniform distribution of copper (Cu), oxygen (O), and iron (Fe) in the sample, as shown in Figure 5c.
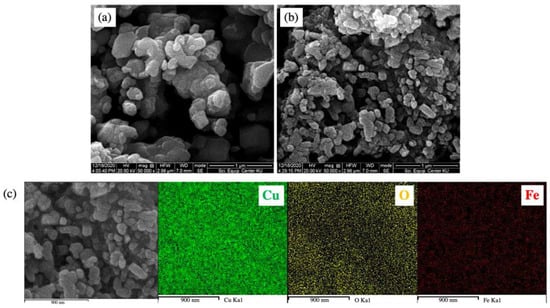
Figure 5.
Scanning electron micrographs of (a) undoped CuO, (b) 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO, and (c) EDS mapping of 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO.
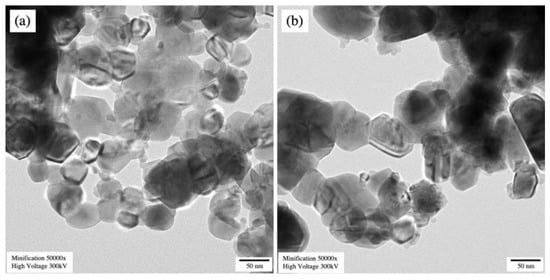
Figure 6.
Transmission electron micrographs of (a) undoped CuO and (b) 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO.

Table 2.
Average crystallite sizes and particle sizes of undoped CuO and 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO.
Along with particle size examination, the average crystallite sizes of the powders were examined from XRD pattern using Scherrer’s equation. Moreover, the results revealed that the doping of CuO with Fe led to refinement of crystallites. It was found that the undoped CuO and 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO exhibit average crystallite sizes of 30.73 ± 2.83 and 24.57 ± 2.64 nm, respectively, as shown in Table 2.
The effects of doping on particle refinement were commonly observed in metal oxides. According to Jongprateep et al., doping of ZnO with Ag contributed to the formation of defects, which inhibited the growth of crystallites [34]. It has been reported that fine precipitates resulting from doping also behave as pinning centres at the grain boundary. Therefore, the growth of crystallites is obstructed by the pinning effect [35]. It has been well-established that particle refinement leads to specific surface area enhancement, consequently resulting in an increased number of active reaction sites.
3.3. Specific Surface Area
The specific surface area was determined using the Brunauer, Emmett and Teller (BET) technique. As shown in Table 3, the specific surface areas of undoped CuO and 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO were 2.46 and 4.67 m2/g, respectively. The low specific surface of samples resulted from the agglomeration of particles which corresponds to SEM and TEM results. As mentioned in the previous section, the refinement of the particles occurred as a result of Fe-doping, leading to slight enhancement of the particles’ surface area.

Table 3.
Specific surface area of undoped CuO, 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO, undoped CuO/MWCNT composite, and 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT composite.
Significant improvement of the specific surface area could be achieved in the composite. The undoped CuO/MWCNT composite and 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT composite exhibited a specific surface area 20-fold higher than the particles. This is attributed to the high specific surface area of MWCNTs. According to Bernard et al., the specific surface area influences the reaction rate in heterogeneous catalysis. The increased surface area generally contributes to improved catalytic effects [36].
3.4. Electrocatalytic Activities
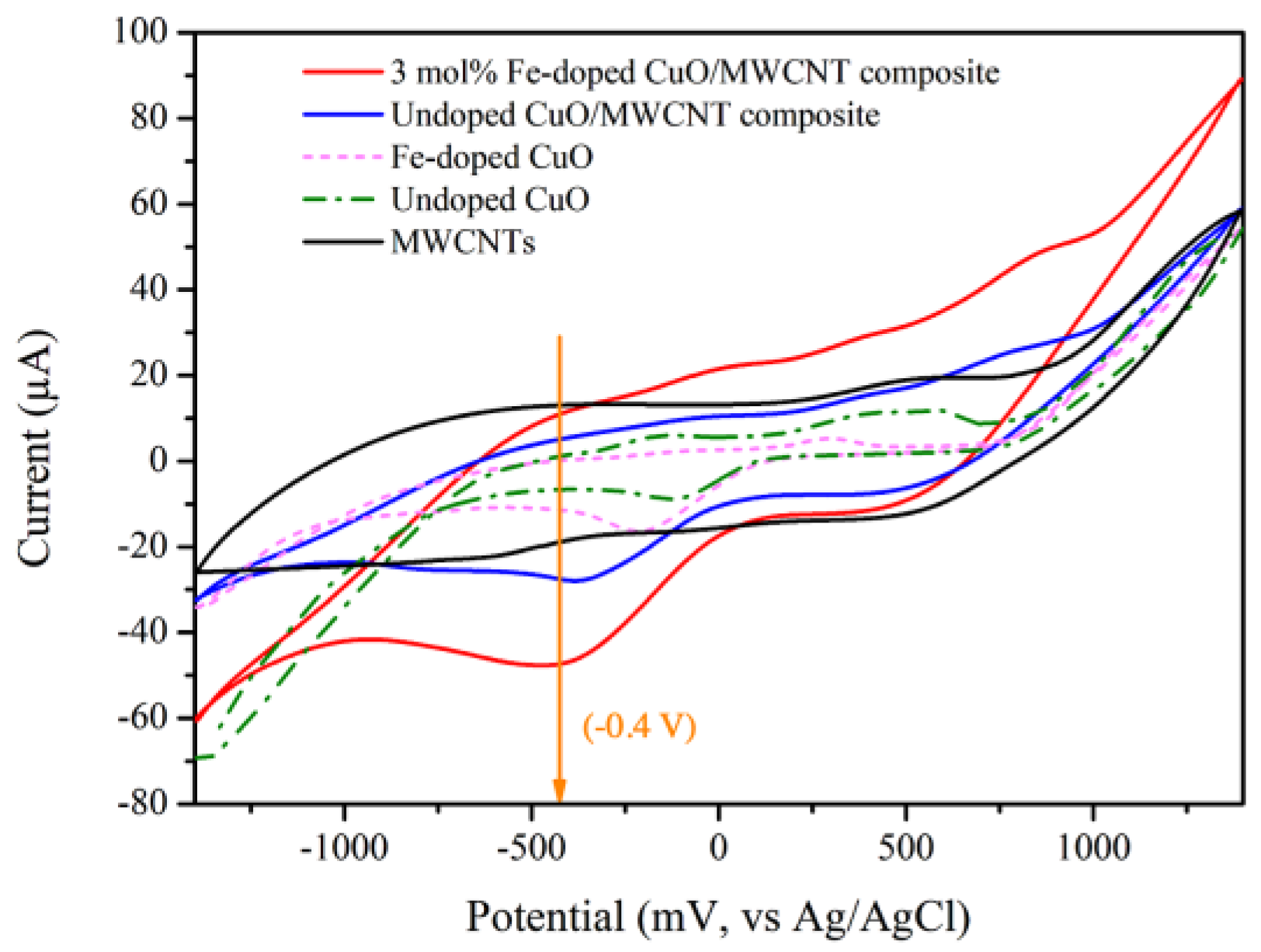
The electrocatalytic performance of the modified electrodes containing MWCNTs, undoped CuO, 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO, undoped CuO/MWCNT composite, and 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT composite were evaluated. As shown in Figure 7, the CV of modified electrodes with undoped CuO, 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO, undoped CuO/MWCNT composite, and 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT composite exhibited a prominent reduction reaction at an applied voltage close to −0.4 V when tested in nitrite solution. It has been reported that at an applied voltage of −0.4 V, nitrite () is reduced to ammonia (). Electrochemical reduction of nitrite could be explained through the following reactions [37].
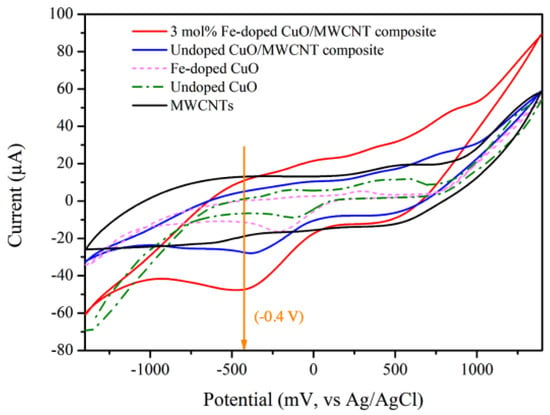
Figure 7.
CV of MWCNTs, undoped CuO, 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO, undoped CuO/MWCNT composite, and 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT-composite-modified electrodes in presence of 1 mM nitrite, measured at scan rate 100.0 mV/s.
As shown in Table 4, the voltammetry results also reveal that the greatest peak current is achieved in the modified electrode with 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT composite. This is attributed to high surface area available for reaction between the sensing material and analyte as well as enhanced electron transfer. A similar observation was reported by Fayemi et al., who examined detection of dopamine using bare glassy carbon electrode (GCE), GCE-metal oxide, GCE-MWCNT, and GCE-MWCNT-metal oxide (NiO, ZnO, and Fe3O4). The results revealed that bare GCE and GCE-metal oxide electrode demonstrated slow electron transfer, whereas the GCE-MWCNT-metal oxide electrode exhibited the highest electrochemical response [38].

Table 4.
Peak current of MWCNTs, undoped CuO, 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO, undoped CuO/MWCNT composite, and 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT-composite-modified electrodes in presence of 1 mM nitrite.
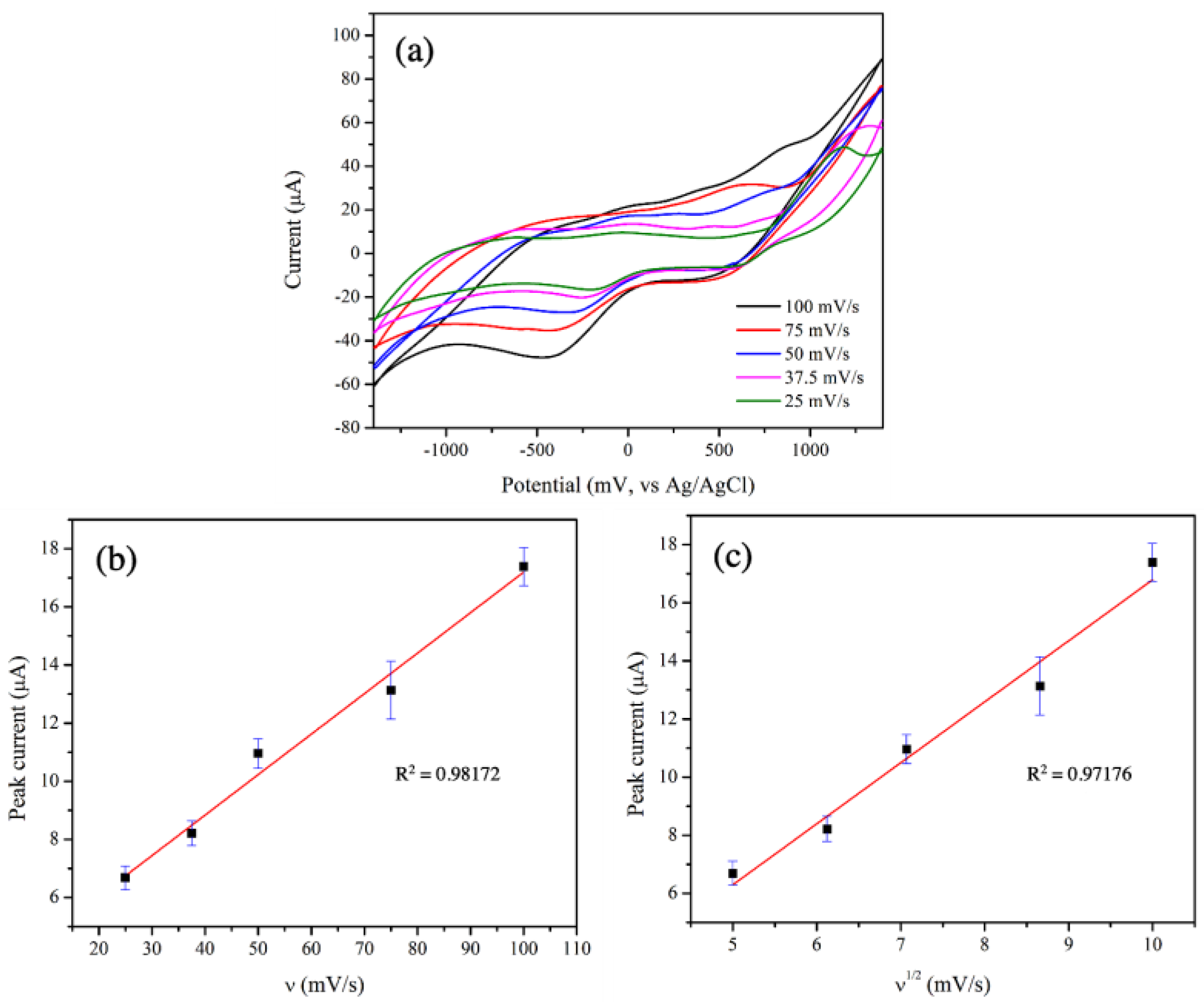
With the greatest electrocatalytic performance, the 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT-modified-electrode was further tested at scan rates ranging from 25.0 to 100.0 mV/s, as shown in Figure 8a. The peaks corresponding to reduction reactions were evident at applied voltages in the range from −0.16 V to −0.4 V.
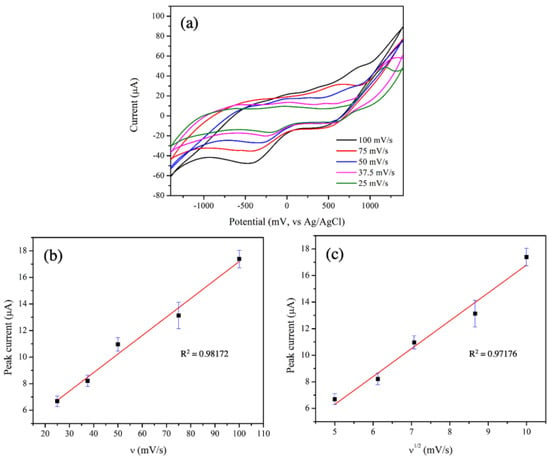
Figure 8.
(a) CV of 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT-modified electrode at scan rates ranging from 25.0 to 100.0 mV/s, (b) relationship between peak current of reduction reaction and scan rate at −0.4 V, and (c) relationship between peak current and square root of scan rate at −0.4 V, measured in 1 mM nitrite solution.
To determine controlled mechanism in electrocatalytic activity between sensing material and analyte, the relationships between scan rate and peak current were examined. Key mechanisms controlling electrocatalytic activities include adsorption and diffusion. The adsorption-controlled reaction is generally demonstrated by a linear relationship between the scan rate and the peak current, whereas the diffusion-controlled reaction exhibits a linear relationship between the square root of scan rate and the peak current. Figure 8b,c clearly show the good linear relationships between the scan rate and the peak current (R2 = 0.98) as well as between the square root of the scan rate and the peak current (R2 = 0.97). These results reveal that both adsorption and diffusion governed the electrocatalytic reactions in this study. A similar observation was reported by Wu et al. who reported that electrocatalytic activities of a glassy carbon electrode in the presence of micro-emulsion containing TanshinoneⅡA were determined using the CV technique. Their results indicated a good linear relationship between the scan rate and the peak current, as well as between the square root of the scan rate and the peak current [39].
In addition to scan rate, the effect of pH on electrocatalytic performance was also examined. The 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT-modified electrode was tested in nitrite solution with pH ranging between 4 and 10. As shown in Table 5, the greatest peak current is achieved at pH 8. Li et al. also reported that an electrochemical sensor consisting of CuO/H-C3N4/rGO nanocomposite exhibited optimal electrocatalytic activity in a nitrite solution with an approximate pH value of 8. Attributable to the instability of nitrite in acid solution, the peak current increased when the nitrite solution pH increased from 4 to 8. Nevertheless, at pH levels higher than 8, the peak current decreased due to proton depletion, which suppressed reduction reaction of nitrite [40].

Table 5.
Peak current of 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT-modified electrode in presence of 1 mM nitrite at pH range of 4–10.
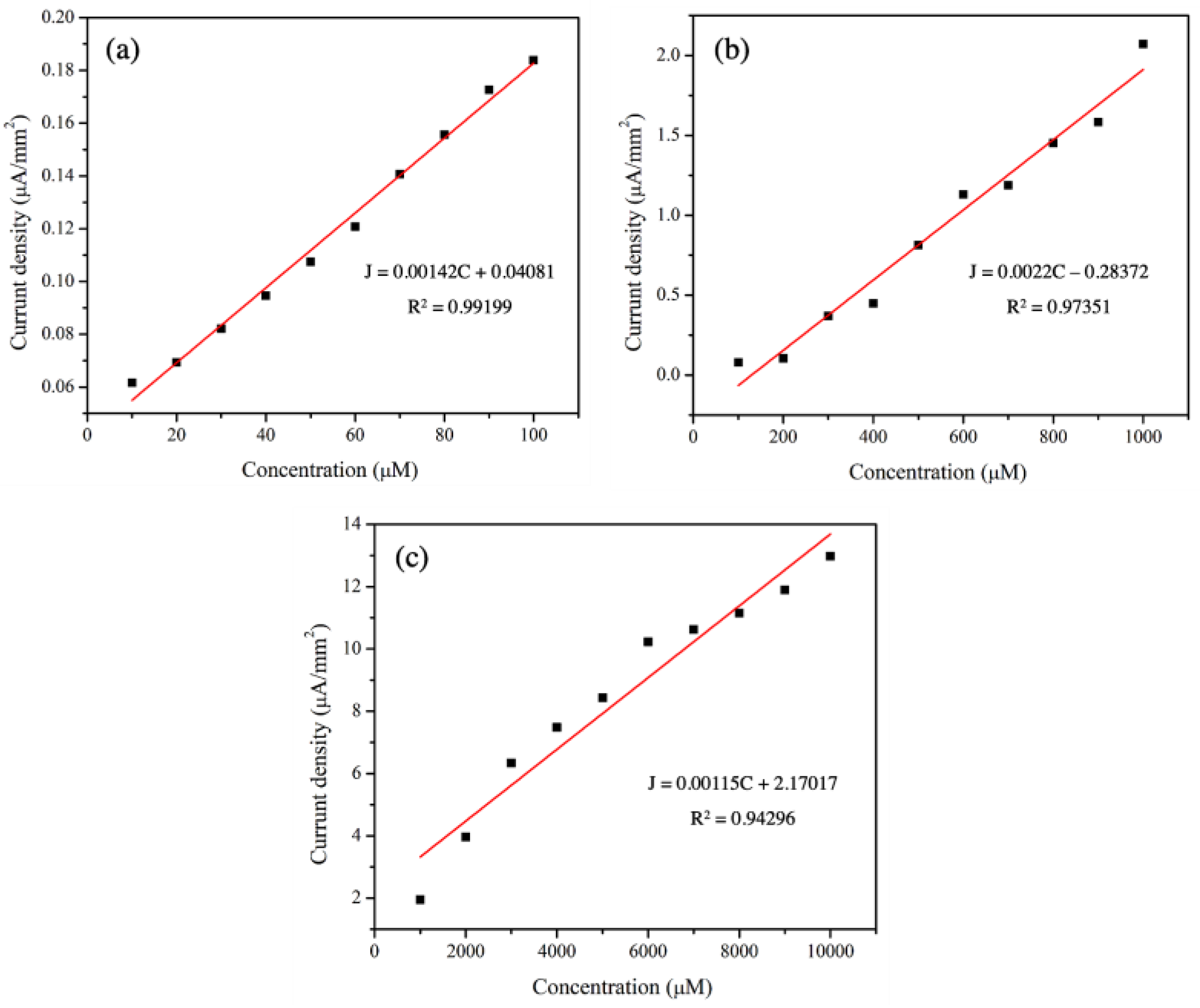
The sensitivity values of 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT-modified electrodes were determined based on the slopes of the calibration curves (concentration of analytes versus current density). As shown in Figure 9 and Table 6, there were good linear relationships between the current density and concentration with R2 values higher than 0.94. The sensitivity values were 1.42 × 10−3, 2.2 × 10−3, and 1.15 × 10−3 µA µMࢤ1 mmࢤ2 from measurements taken in the presence of nitrite with concentration ranges of 10–100 µM, 100–1000 µM, and 1000–10,000 µM, respectively.
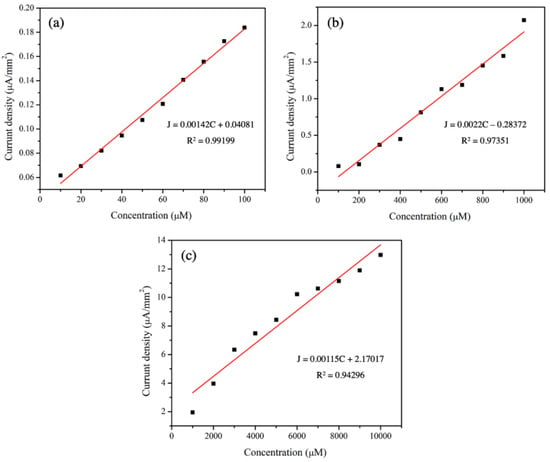
Figure 9.
Calibration curves of 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT-modified electrode in nitrite with concentration ranges: (a) 10–100 µM, (b) 100–1000 µM, and (c) 1000–10,000 µM at scan rate 50.0 mV/s.

Table 6.
Sensitivity of 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT-modified electrode, measured in nitrite solution with concentration range 10–10,000 µM.
As shown in Table 7, the sensitivity values obtained in this study were in comparable ranges with reported research results [41,42,43]. Ranges in the measuring concentration of 10–10,000 µM also covered the limitation for nitrite concentration set by the WHO and by European Commission Regulation No 1333/2008 [5,6].

Table 7.
Linear range, sensitivity, and limit of detection (LOD) of various electrodes for nitrite detection.
The limit of detection (LOD) was also determined using Equation (3);
where σ is the standard deviation of the blank (n = 5) and S is the slope of the calibration curve.
LOD = 3.3σ/S
It was found that the limit of detection for the 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT-modified electrode in the presence of nitrite was 10.54 µM. This value was in a comparable range with other studies, as shown in Table 7.
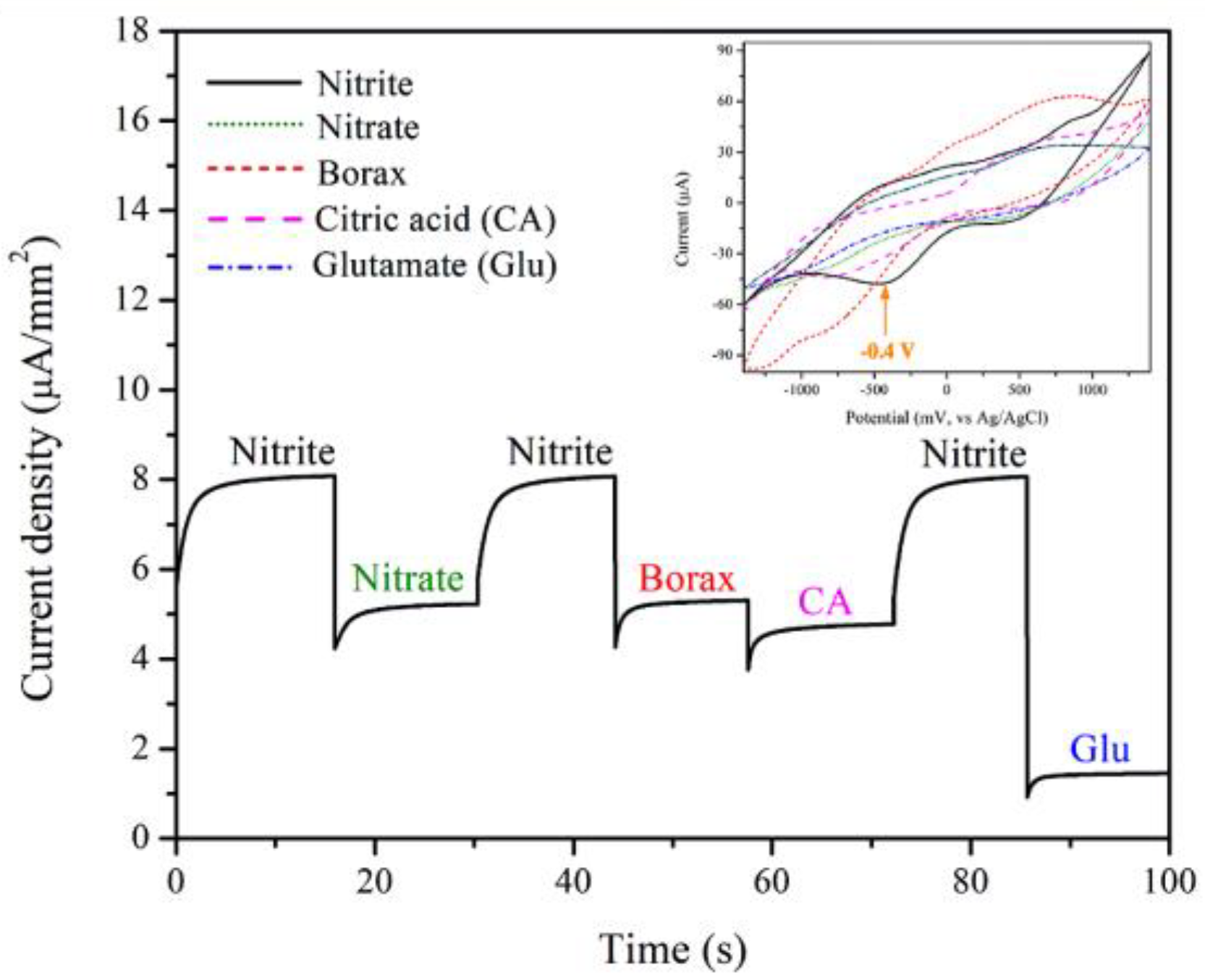
The selectivity for detection of the 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT-modified electrode in nitrite solution was tested using chronoamperometry and CV techniques. The measurement was conducted at an applied voltage of −0.4 V in the presence of nitrite, nitrate, borax, citric acid (CA), and glutamate (Glu), as shown in Figure 10. The results presented the distinguishing peaks of nitrite, revealing fair selectivity of the electrode.
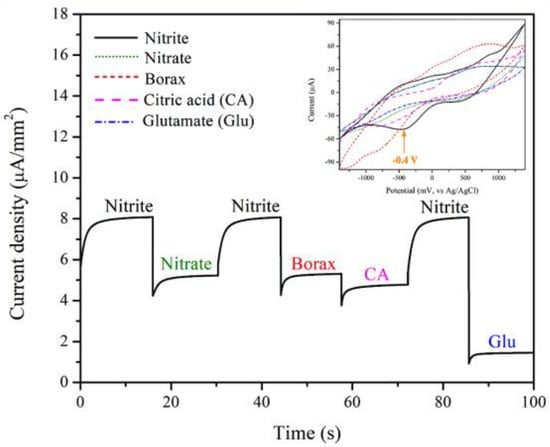
Figure 10.
Selectivity of 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT-modified electrode in presence of 1 mM nitrite, 1 mM nitrate, 1 mM borax, 1 mM citric acid (CA), and 1 mM glutamate (Glu). The inset shows cyclic voltammograms of 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT-modified electrode in the presence of nitrite, nitrate, borax, citric acid (CA), and glutamate (Glu).
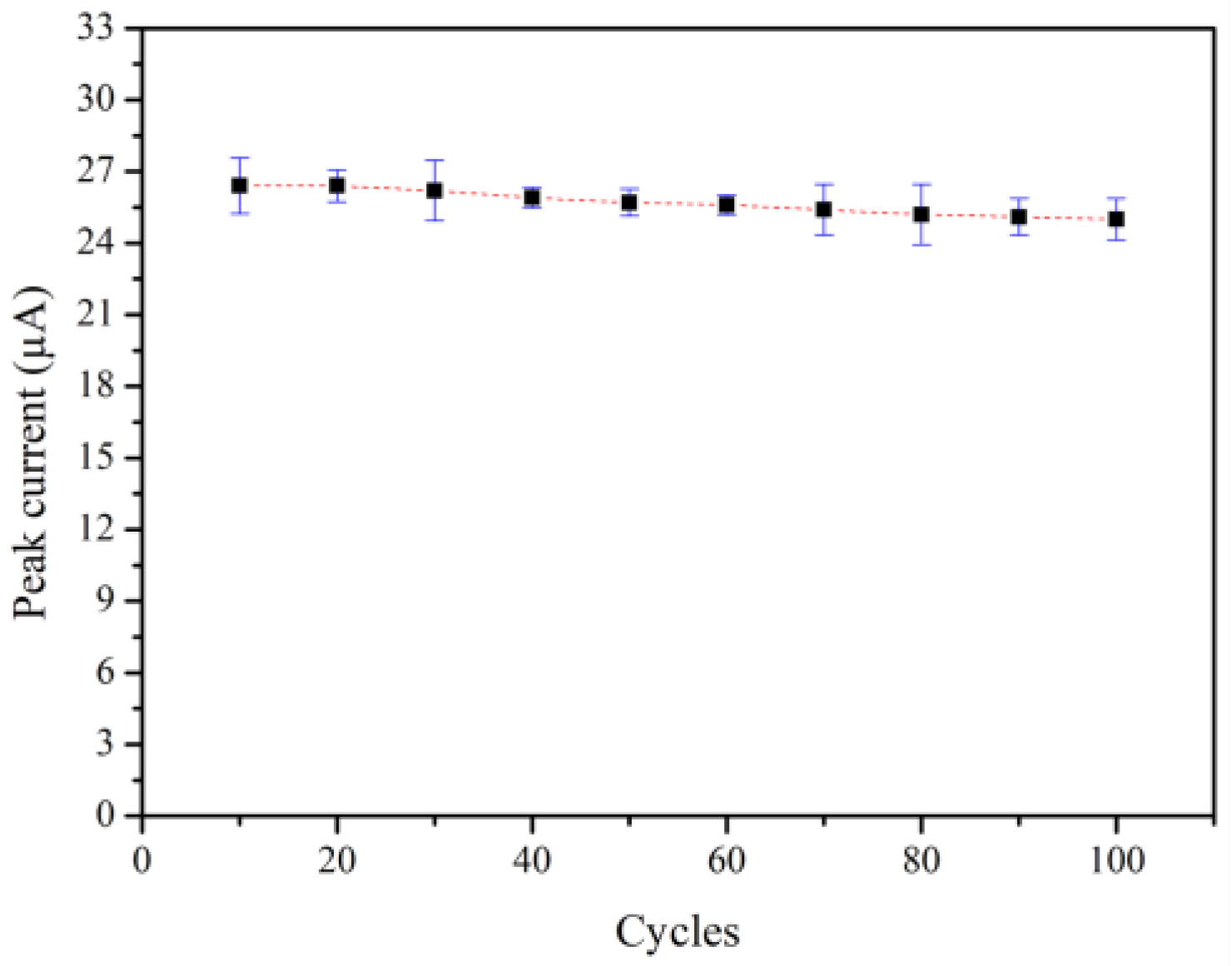
The reusability of the 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT-modified electrode in nitrite solution was evaluated though repeated measurements of the peak current at an applied voltage of −0.4 V. The results revealed decent reusability. As shown in Figure 11, the peak current of the 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT electrode is only degraded by 5.30% after 100 measurement cycles.
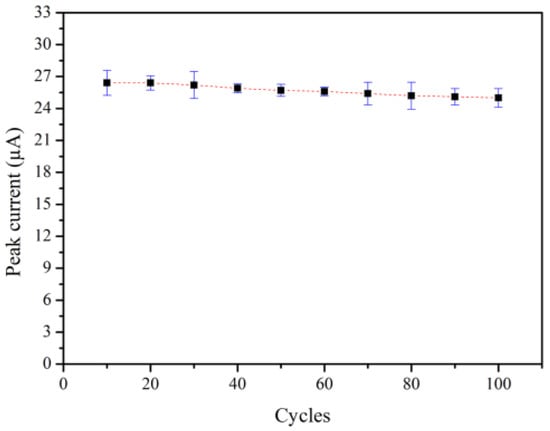
Figure 11.
Reusability of 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT-modified electrode in 1 mM nitrite at scan rate 100.0 mV/s.
To determine the feasibility of nitrite detection in real samples, the 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT-modified electrode was tested in drinking water, tap water, and rainwater in the presence of nitrite, nitrate, borax, citric acid (CA), and glutamate (Glu), and at concentrations of 10 µM and 1000 µM. The recovery percentages are found to be 92.10–101.10% and 98.42–106.42% in the detection of 10 µM and 1000 µM nitrite, respectively, as shown in Table 8. The recovery percentage of the present work is in a comparable range with that reported by other researchers [44,45,46].

Table 8.
The recovery percentages of nitrite detection in drinking water, tap water and rainwater.
4. Conclusions
Fe-doped CuO nanoparticles were successfully synthesized using a solution combustion technique, whereas the 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT composite was prepared using a hydrothermal method. The electrocatalytic activities of the 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT-modified electrodes in the presence of nitrite were also evaluated based on cyclic voltammetry. The voltammogram revealed prominent reduction reaction peaks at an applied voltage of approximately −0.4 V. Sensitivity values of 1.42 × 10−3, 2.2 × 10−3, and 1.15 × 10−3 µA µM−1 mm−2 were observed for nitrite concentrations in the ranges 10–100 µM, 100–1000 µM, and 1000–10,000 µM, respectively. The limit of detection was 10.54 µM. The good selectivity of nitrite was clearly demonstrated in the presence of nitrate, borax, citric acid, and glutamate. With good performance regarding sensitivity, limit of detection, selectivity, reusability and recovery percentage, the 3 mol% Fe-doped CuO/MWCNT composites demonstrate potential for utilization as electrode materials for nitrite detection.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.P., K.A. and O.J.; methodology, S.P., K.A., N.S. and K.J.; software, S.P., K.A., N.S. and K.J.; validation, O.J.; formal analysis, S.P., K.A. and O.J.; investigation, R.T., G.P., J.O. and O.J.; resources, R.T., G.P. and O.J.; data curation, S.P., K.A. and O.J.; visualization, S.P., K.A. and O.J.; writing—original draft preparation, S.P., K.A. and O.J.; writing—review and editing, R.T., G.P. and O.J.; supervision, O.J.; project administration, R.T., G.P., J.O. and O.J.; funding acquisition, R.T., G.P., J.O. and O.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Office of the Ministry of Higher Education, ICE-Matter consortium of AUN/SEED-Net, and Kasetsart University Research and Development Institute (KURDI), grant no. FF(KU) 25.64. The APC was funded by Office of the Ministry of Higher Education.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
The Kasetsart University Research and Development Institute (KURDI) and the ASEAN University Network/Southeast Asia Engineering Education Development Network (AUN/SEED-Net) provided financial support. This work was also financially supported by the Office of the Ministry of Higher Education, Science, Research and Innovation; and the Thailand Science Research and Innovation through the Kasetsart University Reinventing University Program 2021. The Department of Materials Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Kasetsart University provided equipment support. Chatchawal Wongchoosuk and Maythee Saisriyoot provided valuable suggestions and fruitful discussion.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mortensen, A.; Aguilar, F.; Crebelli, R.; Di Domenico, A.; Dusemund, B.; Frutos, M.J.; Galtier, P.; Gott, D.; Gundert-Remy, U.; Lambre, C.; et al. Re-evaluation of potassium nitrite (E 249) and sodium nitrite (E 250) as food additives. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griesenbeck, J.S.; Steck, M.D.; Huber, J.C.; Sharkey, J.R.; Rene, A.A.; Brender, J.D. Development of estimates of dietary nitrates, nitrites, and nitrosamines for use with the short willet food frequency questionnaire. Nutr. Metab. 2009, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakszyn, P.; Gonzalez, C.A. Nitrosamine and related food intake and gastric and oesophageal cancer risk: A systematic review of the epidemiological evidence. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 4296–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, C.H.; Seo, D.W.; Ryoo, S.M.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, W.Y.; Lim, K.S.; Oh, B.J. Life-threatening methemoglobinemia after unintentional ingestion of antifreeze admixtures containing sodium nitrite in the construction sites. Clin. Toxicol. 2014, 52, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrenk, D.; Bignami, M.; Bodin, L.; Chipman, J.K.; Mazo, J.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; Hoogenboom, L.R.; Leblanc, J.; Nebbia, C.S.; Nielsen, E.; et al. Risk assessment of nitrate and nitrite in feed. EFSA J. 2020, 18, e06290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; WHO Publications: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ensafi, A.A.; Rezaei, B.; Nouroozi, S. Simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of nitrite and nitrate by flow injection analysis. Anal. Sci. 2004, 20, 1749–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagababu, E.; Rifkind, J.M. Measurement of plasma nitrite by chemiluminescence without interference of S-, N-nitroso and nitrated species. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 42, 1146–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, I.M.; Silva, S. Quantification of residual nitrite and nitrate in ham by reverse-phase high performance liquid chromatography/diode array detector. Talanta 2008, 74, 1598–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merusi, C.; Corradini, C.; Cavazza, A.; Borromei, C.; Salvadeo, P. Determination of nitrates, nitrites and oxalates in food products by capillary electrophoresis with pH-dependent electroosmotic flow reversal. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorcroft, M.J.; Davis, J.; Compton, R.G. Detection and determination of nitrate and nitrite: A review. Talanta 2001, 54, 785–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.-H.; Yu, L.-J.; Liu, Y.; Lin, L.; Lu, R.-g.; Zhu, J.-p.; He, L.; Lu, Z.-L. Methods for the detection and determination of nitrite and nitrate: A review. Talanta 2017, 165, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, R.; Chen, T.-W.; Chen, S.-M.; Baskar, T.; Kannan, R.; Elumalai, P.; Raja, P.; Jeyapragasam, T.; Dinakaran, K.; Gnana Kumar, G.G. A review of the advanced developments of electrochemical sensors for the detection of toxic and bioactive molecules. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2019, 6, 3418–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, F.R.; Xavier, M.G. 6-Electrochemical Sensors. In Nanoscience and Its Applications, 1st ed.; de Oliveira, O.N., Jr., Ferreira, L., Marystela, G., de Lima Leite, F., Da Róz, A.L., Eds.; William Andrew Publishing: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 155–178. [Google Scholar]
- Fethi, A. Novel materials for electrochemical sensing platforms. Sens. Int. 2020, 1, 100035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.H.; Nguyen, V.T. Copper oxide nanomaterials prepared by solution methods, some properties, and potential applications: A brief review. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2014, 2014, 856592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgohain, K.; Singh, J.B.; Rama Rao, M.V.; Shripathi, T.; Mahamuni, S. Quantum size effects in CuO nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 61, 11093–11096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnes, C.L.; Stipp, J.; Klabunde, K.J.; Bonevich, J. Synthesis, characterization, and adsorption studies of nanocrystalline copper oxide and nickel oxide. Langmuir 2002, 18, 1352–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahooli, M.; Sabbaghi, S.; Saboori, R. Synthesis and characterization of mono sized CuO nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 2012, 81, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, J.-Z.; Zhu, J.-J.; Chen, H.-Y. Preparation of CuO nanoparticles by microwave irradiation. J. Cryst. Growth 2002, 244, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Kecsenovity, E.; Varga, A.; Molnár, M.; Janáky, C.; Rajeshwar, K. Solution combustion synthesis of complex oxide semiconductors. Int. J. Self-Propagating High-Temp. Synth. 2018, 27, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhim, R.G.; Kzar, B.R.S. Effect of Cd doping on structural and some optical studies of nano CuO films prepared by sol-gel technique. World Sci. News 2017, 64, 69–83. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, J.; Ryu, H.; Lee, W.-J. Effects of Fe doping on the photoelectrochemical properties of CuO photoelectrodes. Compos. B Eng. 2019, 163, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chafi, F.Z.; Bahmad, L.; Hassanain, N.; Fares, B.; Laanab, L.; Mzerd, A. Characterization techniques of Fe-doped CuO thin films deposited by the Spray Pyrolysis method. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.09697. [Google Scholar]
- Sakthivel, B.; Gopalakrishnan, N. Effect of Fe doping on the NH3 sensing properties of CuO nanostructures. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 6920–6928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.K.; Dobhal, R.; Rini, E.G.; Kumar, M.; Sen, S. Rapid organic dye degradation and wavelength dependent sensing study in Cu1-xFexO. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 5995–6006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagan-Murphy, A.; Kataria, S.; Patel, B.A. Electrochemical performance of multi-walled carbon nanotube composite electrodes is enhanced with larger diameters and reduced specific surface area. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2016, 20, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Devasenathipathy, R.; Rani, K.K.; Wang, S. Synthesis of multi walled carbon nanotubes covered copper oxide nanoberries for the sensitive and selective electrochemical determination of hydrogen peroxide. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2017, 12, 5910–5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.M.; Asiri, A.M.; Rahman, M.M. A non-enzymatic electrochemical approach for l-lactic acid sensor development based on CuO·MWCNT nanocomposites modified with a nafion matrix. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 9775–9787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, Z.F.; Sun, Y.P.; Zhu, X.B.; Yang, Z.R.; Dai, J.M.; Song, W.H. Synthesis of magnetoresistive La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 nanoparticles by an improved chemical coprecipitation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 2378–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Sharma, S.; Soni, S.; Sharma, S.; Kohli, N. Influence of different milling media on structural, morphological and optical properties of the ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by ball milling process. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2019, 98, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chafi, F.Z.; Fares, B.; Hadri, A.; Nassiri, C.; Laaneb, L.; Hassanain, N.; Mzerd, A. Fe-doped CuO deposited by spray pyrolysis technique. In Proceedings of the 2015 3rd International Renewable and Sustainable Energy Conference (IRSEC), Marrakech, Morocco, 10–13 December 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layek, S.; Verma, H.C. Room temperature ferromagnetism in Fe-doped CuO nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 13, 1848–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongprateep, O.; Meesombad, K.; Techapiesancharoenkij, R.; Surawathanawises, K.; Siwayaprahm, P.; Watthanarat, P. Influences of chemical composition, microstructure and bandgap energy on photocatalytic and antimicrobial activities of ZnO and Ag-doped ZnO by solution combustion technique. J. Met. Mater. Miner. 2019, 29, 78–85. [Google Scholar]
- Ravichandran, K.; Sathish, P.; Snega, S.; Karthika, K.; Rajkumar, P.V.; Subha, K.; Sakthivel, B. Improving the antibacterial efficiency of ZnO nanopowders through simultaneous anionic (F) and cationic (Ag) doping. Powder Technol. 2015, 274, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, P.; Stelmachowski, P.; Broś, P.; Makowski, W.; Kotarba, A. Demonstration of the influence of specific surface area on reaction rate in heterogeneous catalysis. J. Chem. Educ. 2021, 98, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreyse, P.; Isaacs, M.; Calfumán, K.; Cáceres, C.; Aliaga, A.; Aguirre, M.J.; Villagra, D. Electrochemical reduction of nitrite at poly-[Ru(5-NO2-phen)2Cl] tetrapyridylporphyrin glassy carbon modified electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 5230–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayemi, O.; Adekunle, A. Metal oxide nanoparticles/multi-walled carbon nanotube nanocomposite modified electrode for the detection of dopamine: Comparative electrochemical study. J. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 6, 10–4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-J.; Wang, W.-T.; Wang, M.; Liu, H.; Pan, H.-C. Electrochemical behavior and direct quantitative determination of Tanshinone IIA in micro-emulsion. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2016, 11, 5165–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cheng, C.; Yang, Y.; Dun, X.; Gao, J.; Jin, X.-J. A novel electrochemical sensor based on CuO/H-C3N4/rGO nanocomposite for efficient electrochemical sensing nitrite. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 798, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, U.P.; Ganesan, V. Efficient sensing of nitrite by Fe(bpy)32+ immobilized nafion modified electrodes. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 6156–6158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, K.; Sun, Y.; Sun, C. Hemoglobin/colloidal silver nanoparticles immobilized in titania sol–gel film on glassy carbon electrode: Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis. Bioelectrochemistry 2006, 69, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salagare, S.; Shivappa Adarakatti, P.; Venkataramanappa, Y. Designing and construction of carboxyl functionalised MWCNTs/Co-MOFs-based electrochemical sensor for the sensitive detection of nitrite. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 2, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guo, B.; Guo, X.M.; Wang, F. The electrochemical sensor based on electrochemical oxidation of nitrite on metalloporphyrin–graphene modified glassy carbon electrode. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 90480–90488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zou, N.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Li, H.; Gao, C.; Wang, T.; Wang, X. An electrochemical sensor for determination of nitrite based on Au nanoparticles decorated MoS2 nanosheets. Chem. Pap. 2020, 74, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, S.; Krishnamoorthy, K.; Sekar, C.; Wilson, J.; Kim, S.J. A highly sensitive electrochemical sensor for nitrite detection based on Fe2O3 nanoparticles decorated reduced graphene oxide nanosheets. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 148–149, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).