Thermodynamic and Kinetic Calculation of High Strength Aluminum-Lithium Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
2.1. Thermodynamic Method of Calphad
2.2. Kinetic Method
2.3. Experimental Procedure
3. Results
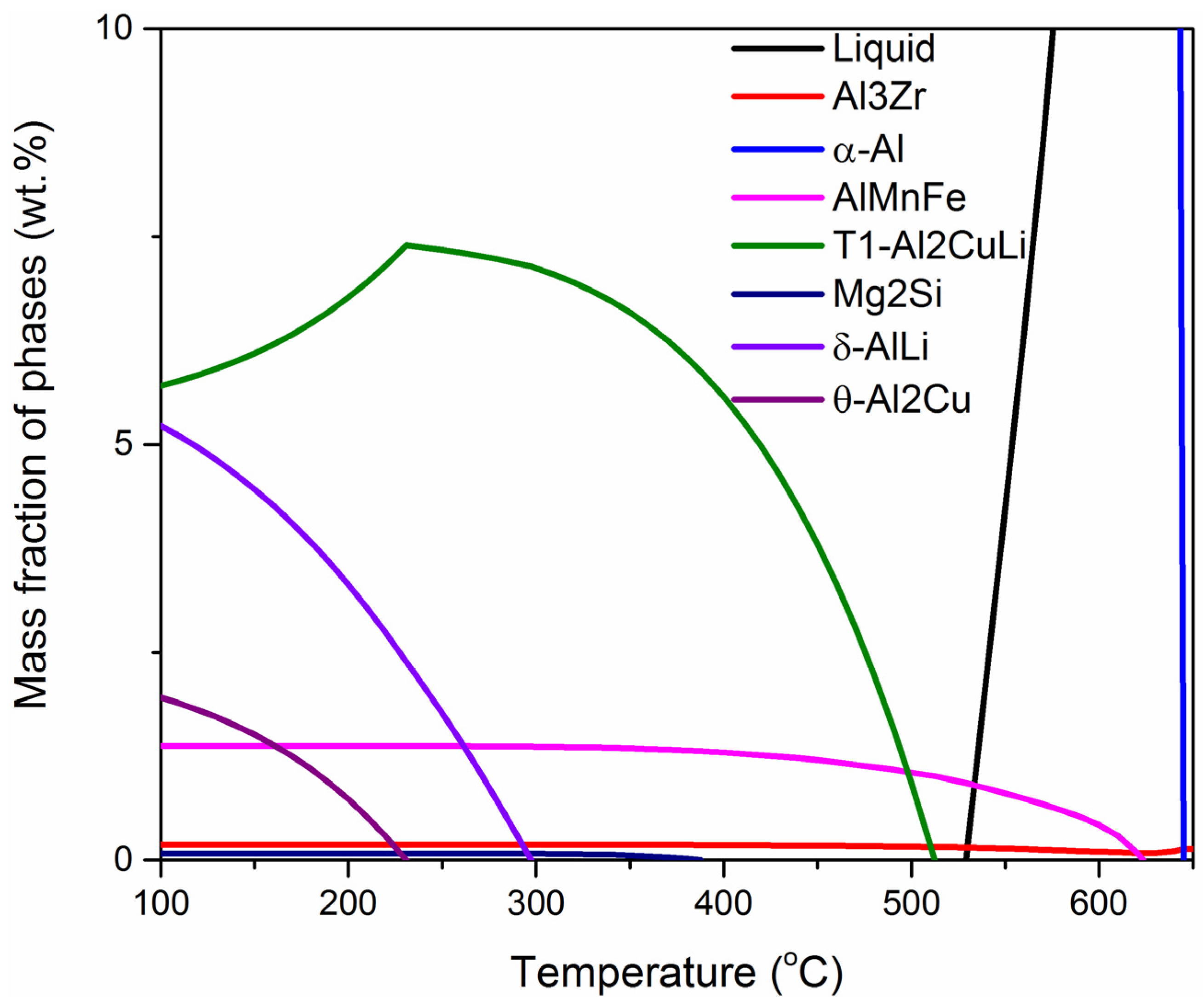
3.1. The Equilibrium and Solidification Phase Diagrams
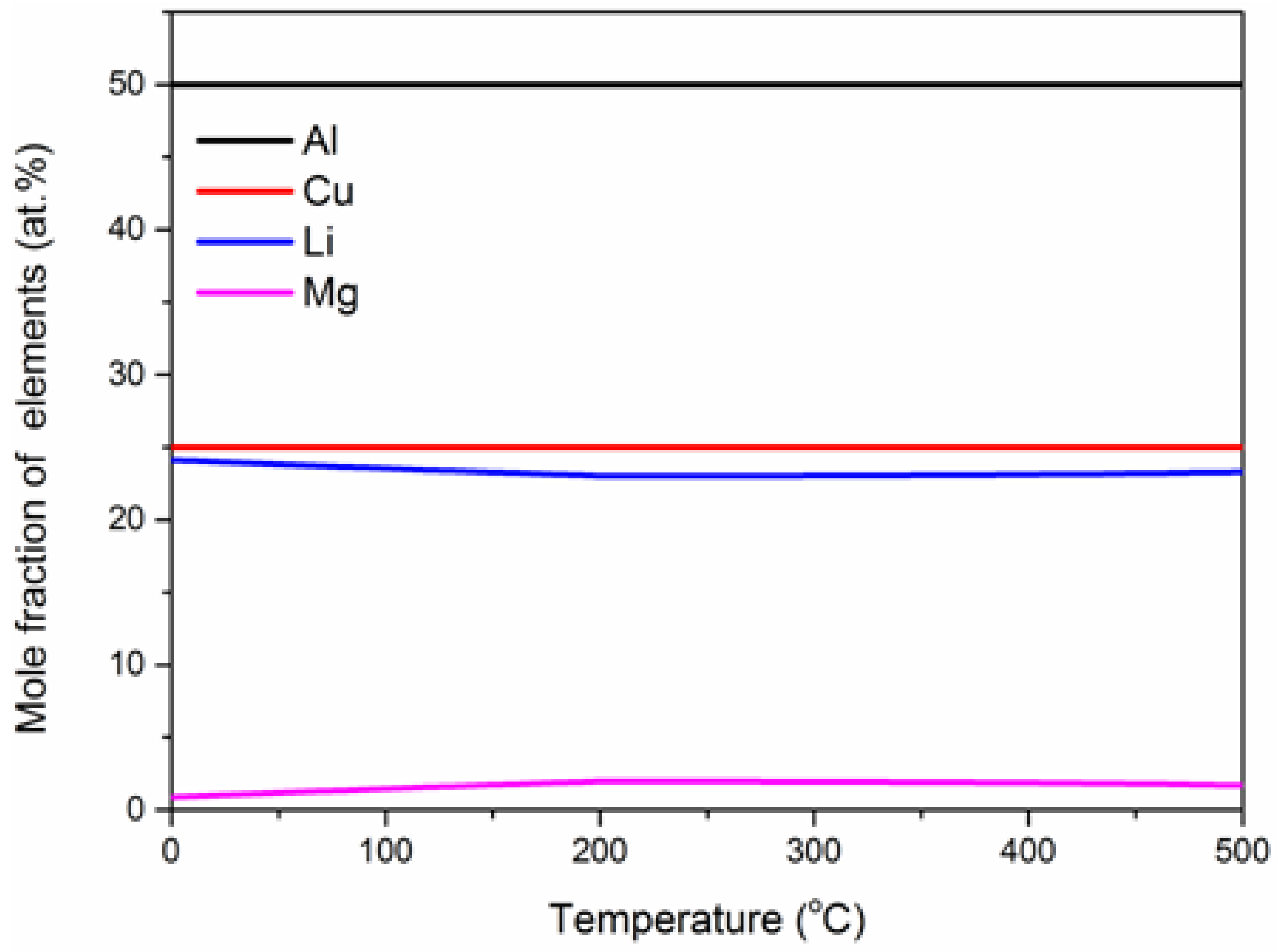
3.2. The Metastable Phase
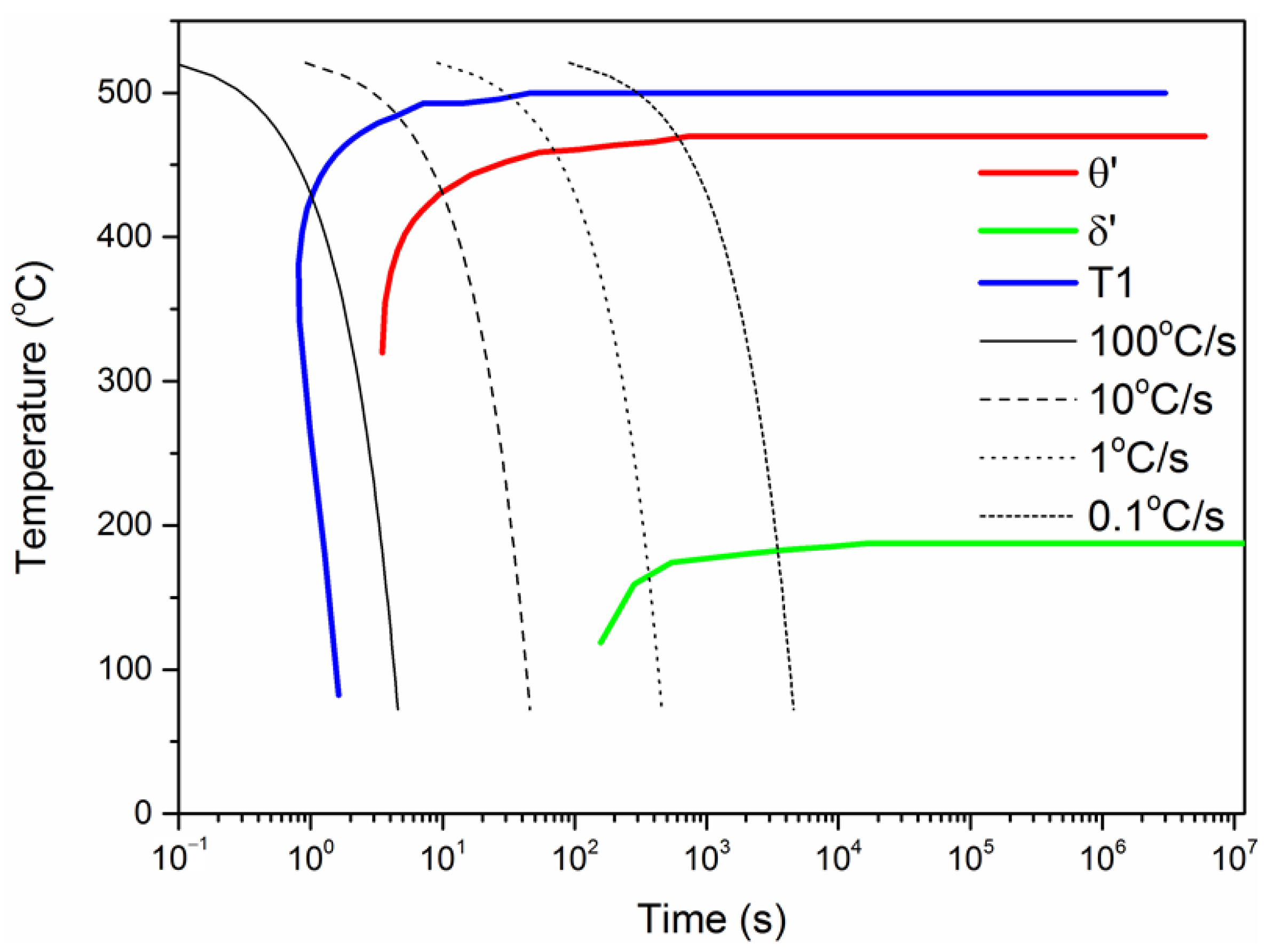
3.3. The CCT Curves
3.4. The Kinetic Curves of Aging
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- According to the experimental composition of 2A97 alloy, the equilibrium phase diagram and solidification phase diagram of 2A97 alloy were calculated by thermodynamic calculation and the SG model.
- (2)
- Referring to the calculated phase diagram, the homogenization temperature was set to 450 °C/510 °C and the solid-solution treatment temperature was set to 520 °C. These results were used in the experiment.
- (3)
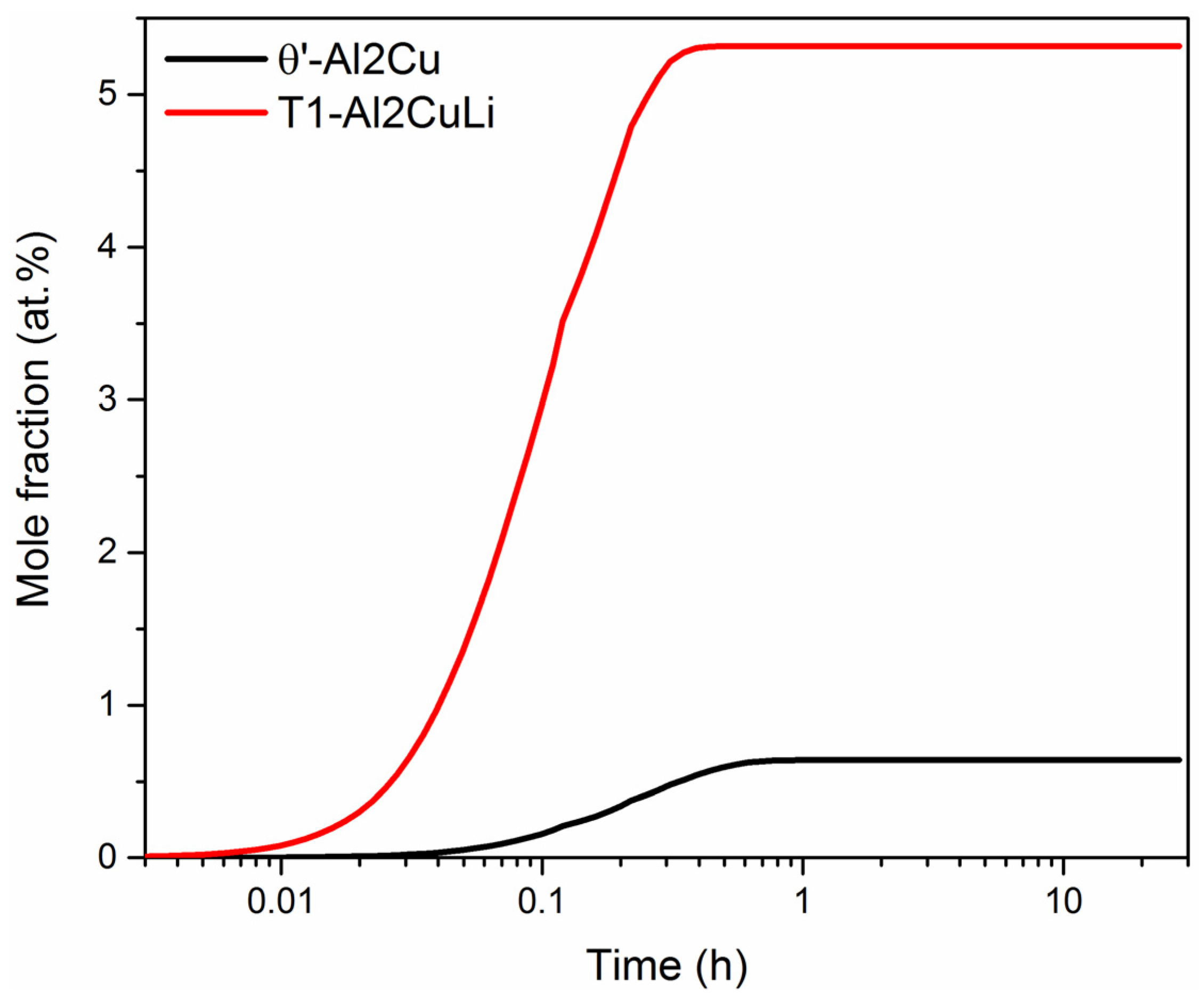
- The order of stability of aging precipitation phase is as follows: T1-Al2CuLi phase > θ’-Al2Cu phase > δ’-Al3Li. These three phases can precipitate simultaneously in the aging temperature range of 100 to 200 °C.
- (4)
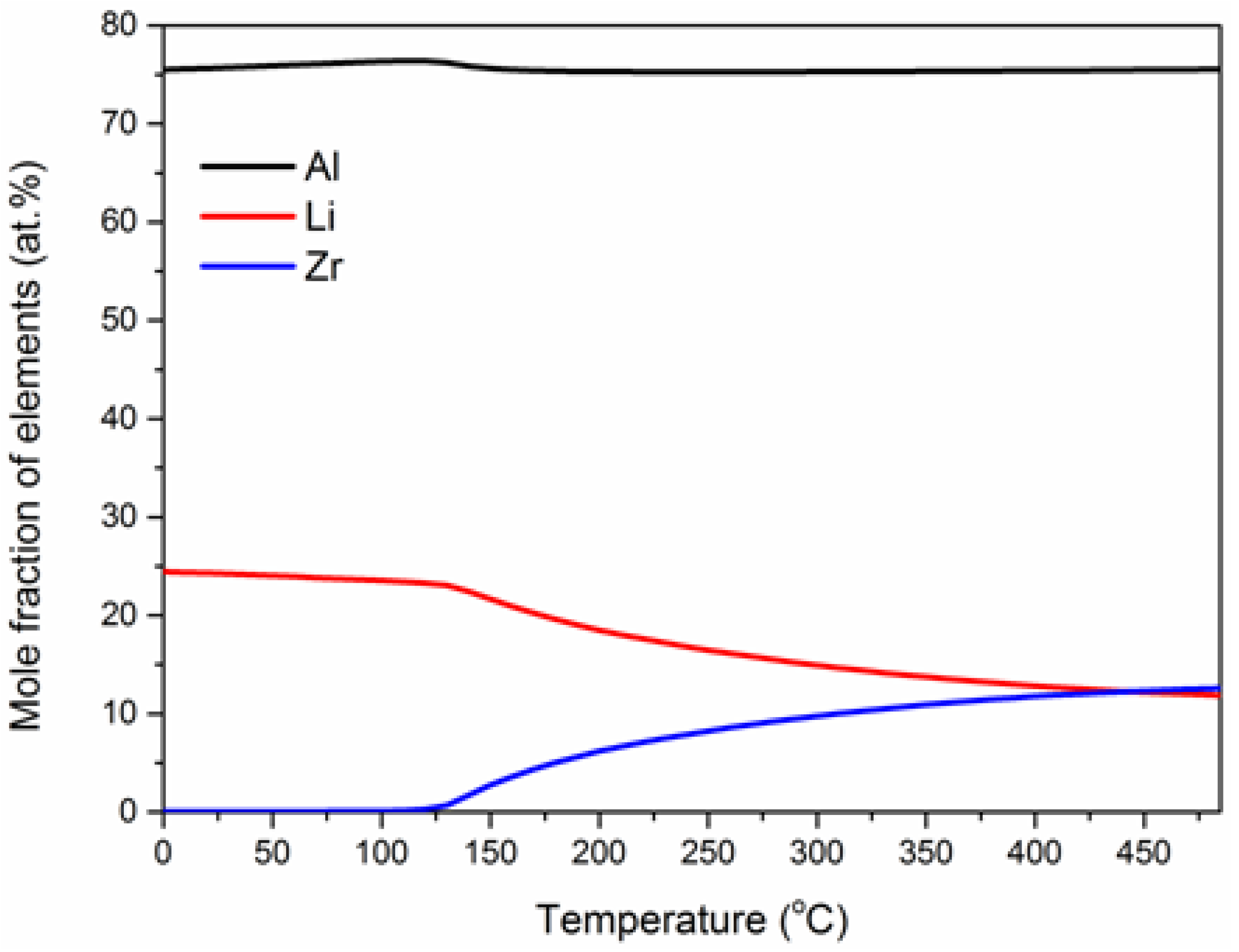
- δ’-Al3Li phase consists of Al, Zr and Li, and the effect of Li on δ’-Al3Li is greater than that of Zr when aging below 200 °C.
- (5)
- Aging and strengthening phases T1-Al2CuLi, δ’-Al3Li and θ’-Al2Cu will be formed during solid-solution treatment, thus inevitably resulting in the loss of aging mechanical properties.
- (6)
- The main precipitation phases are T1-Al2CuLi phase and θ’-Al2Cu phase at 200 °C. At 165 and 135 °C, δ’-Al3Li phase appears during aging and increases with the decrease in temperature.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Starke, E.A.; Staley, J.T. Application of Modern Aluminum Alloys to Aircraft. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 1996, 32, 131–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elagin, V.I.; Zakharov, V.V. Modern Al-Li alloys and prospects of their development. Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 2013, 55, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lequeu, P.; Smith, K.P.; Daniélou, A. Aluminum-copper-lithium Alloy 2050 Developed for Medium to Thick Plate. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2010, 19, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deschamps, A.; Decreus, B.; Geuser, F.D. The influence of precipitation on plastic deformation of Al-Cu-Li alloys. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 4010–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Arabi, H.; Shokuhfar, A. Formation Mechanisms of Precipitates in an Al–Cu–Li–Zr Alloy and their Effects on Strength and Electrical Resistance of the Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 484, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.L.; Yan, H.; Feng, Z.H.; Lu, Z. Effect of aging treatment on microstructure andmechanical properties of 2A97 Al-Li alloy. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2014, 24, 1206–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.S.; Wu, X.L.; Lu, Z.; Xie, Y.H.; Dai, S.L.; Liu, C.S. The Aging Behavior of Aluminum-Lithium Alloy 2A97. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2008, 37, 1898–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.S.; Lu, Z.; Xie, Y.H.; Dai, S.L.; Liu, C.S. Effects of aging treatment on microstructure andproperties of 2A97 aluminum-lithium alloy. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2006, 16, 2027–2033. [Google Scholar]
- Decreus, B.; Deschamps, A.; De Geuser, F. The Influence of Cu/Li Ratio on Precipitation in Al-Cu-Li-x Alloys. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rioja, R.J.; Liu, J. The Evolution of Al-Li Base Products for Aerospace and Space Applications. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2012, 43, 3325–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polmear, I.J. Aluminium Alloys—A Century of Age Hardening. Mater. Forum 2004, 28, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Dursun, T.; Soutis, C. Recent Developments in Advanced Aircraft Aluminium Alloys. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zeng, W.; Yang, W. Ageing Response of Al–Cu–Li 2198 Alloy. Mater. Des. 2014, 63, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, H. Effect of Heat Treatment Process on Tensile Properties of 2A97 Al-Li Alloy: Experiment and BP neural Network simulation. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2013, 23, 1728–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, G.; Yang, L.; Yu, J. Effect of Thermo-mechanical Treatment Process on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 2A97 Al-Li Alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 2196–2202. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.Y.; Kang, W.; Lu, X.C. Effect of Age-forming on Microstructure, Mechanical and Corrosion Properties of a Novel Al–Li Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 640, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y.G.; Chen, C.Q.; Shen, J.Y. Thermodynamic calculation and TEM observation of microstructure of Al-Li-Mg-Si alloys. Chin. J. Mater. Res. 2000, 14, 271–276. [Google Scholar]
- Deschampsa, A.; Siglib, C.; Moureyab, T. Experimental and modelling assessment of precipitation kinetics in an Al–Li–Mg alloy. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 1917–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, R.; Konno, T.J.; Abe, E. Transmission Electron Microscopy Study of the Early Stage of Precipitates in Aged Al–Li–Cu alloys. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 2891–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.C.; Ardell, A.J. Strengthening Mechanisms Associated with T1 Particles in Al-Li-Cu Alloys. J. Phys. 1987, 48, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Saunders, N.; Miodownik, A.P. The coarsening kinetics of γ′ particles in nickel-based alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2002, 33, 3367–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkaldy, J.S. Diffusion-controlled phase transformations in steels. Theory and applications. Scand. J. Metall. 1991, 20, 50–61. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.H.; Lee, H.K.; Yeona, S.M. Selective compositional range exclusion via directed energy deposition to produce a defect-free Inconel 718/SS 316L functionally graded material. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 47, 102288–102299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Yeona, S.M.; Lee, J.H. Additive manufacturing of a shift block via laser powder bed fusion: The simultaneousutilisation of optimised topology and a lattice structure. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2020, 15, 460–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Zheng, Z.Q.; Liao, Z.Q.; Cai, B. Effects of aging treatment on strength and fracture toughness of 2A97 aluminum-lithium alloy. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2011, 21, 546–553. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.S.; Lu, Z.; Xie, Y.H.; Wu, X.L.; Dai, S.L.; Liu, C.S. Study on Double-Aging of 2A97 Aluminum-Lithium Alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2011, 40, 443–446. [Google Scholar]
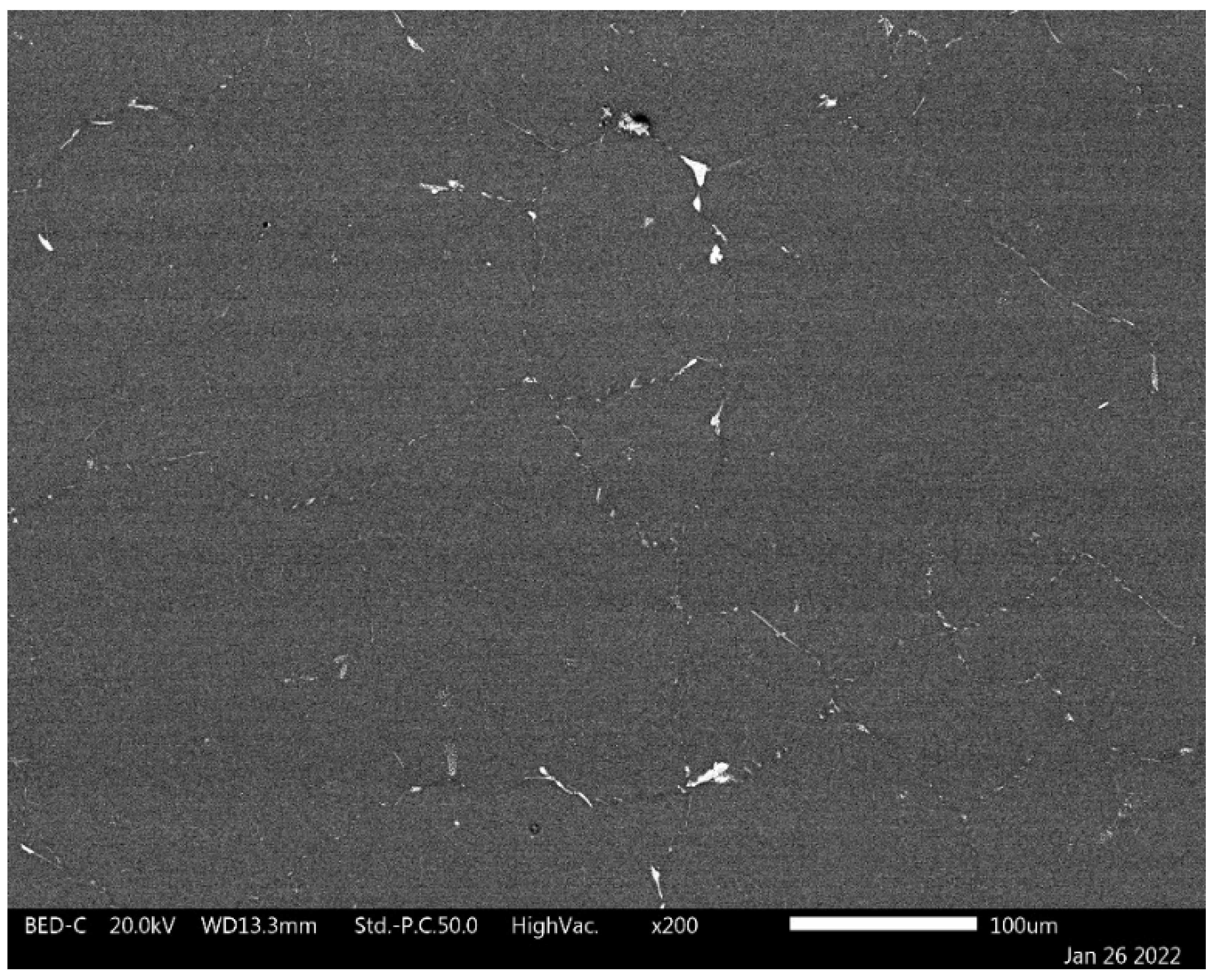
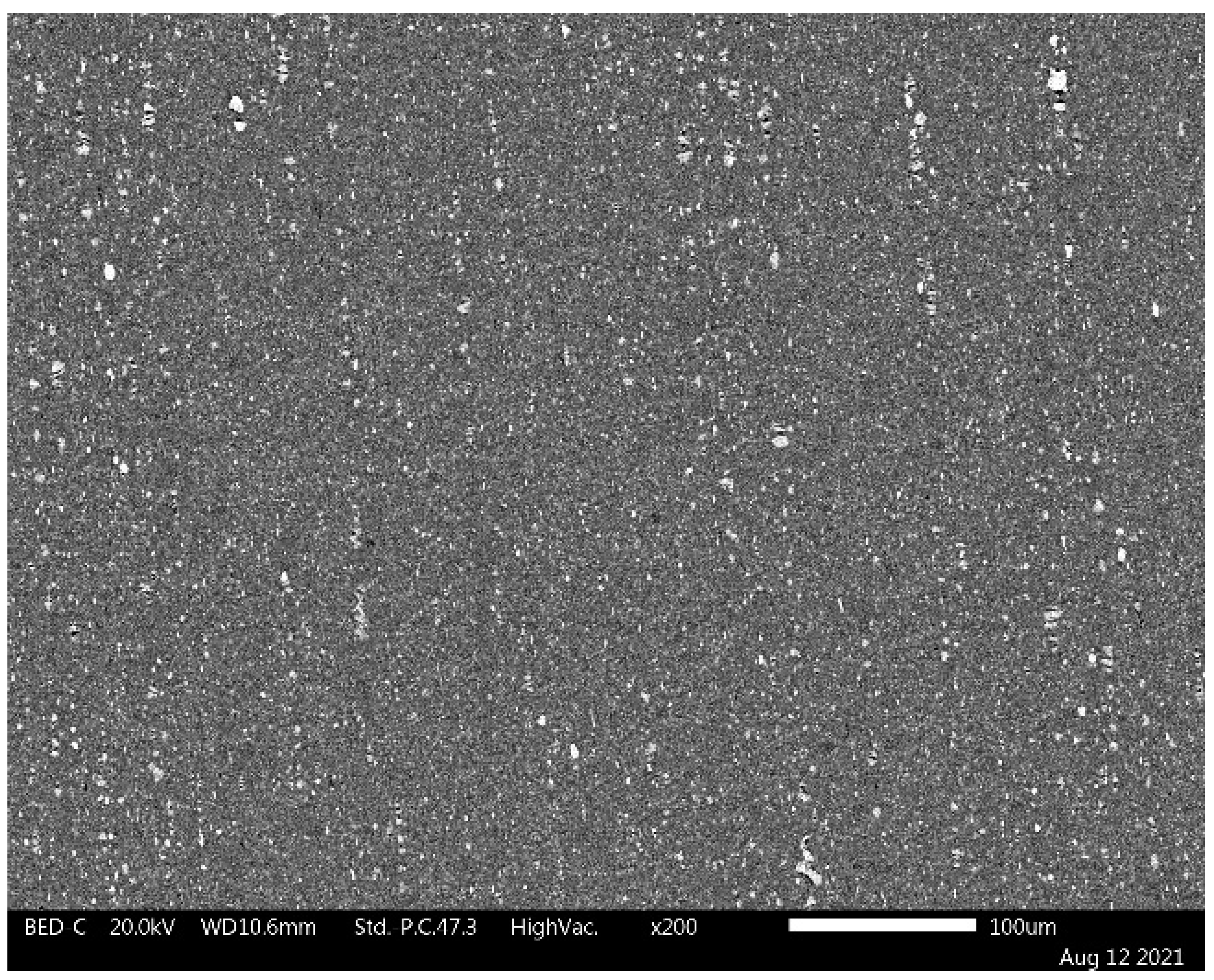


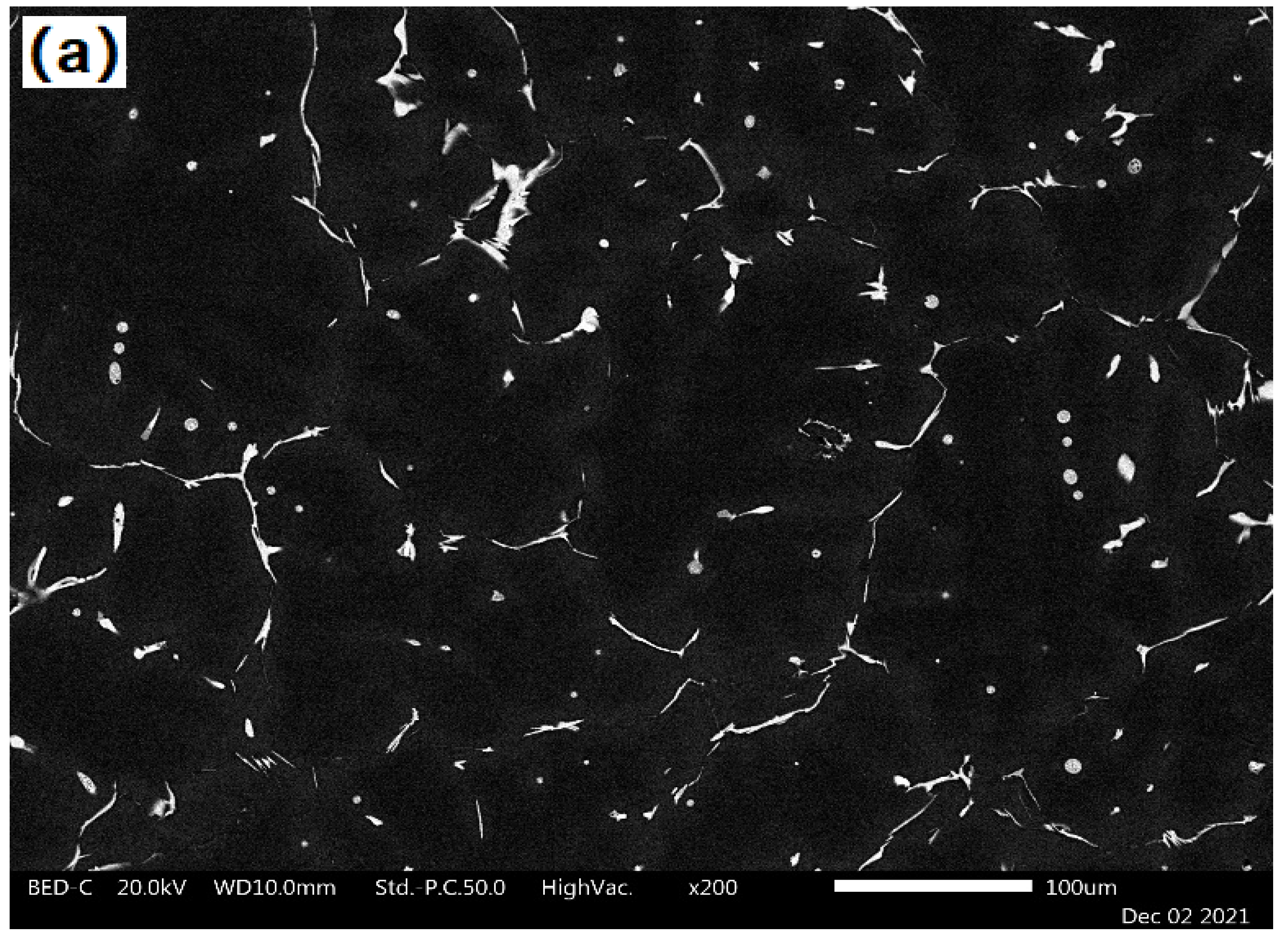
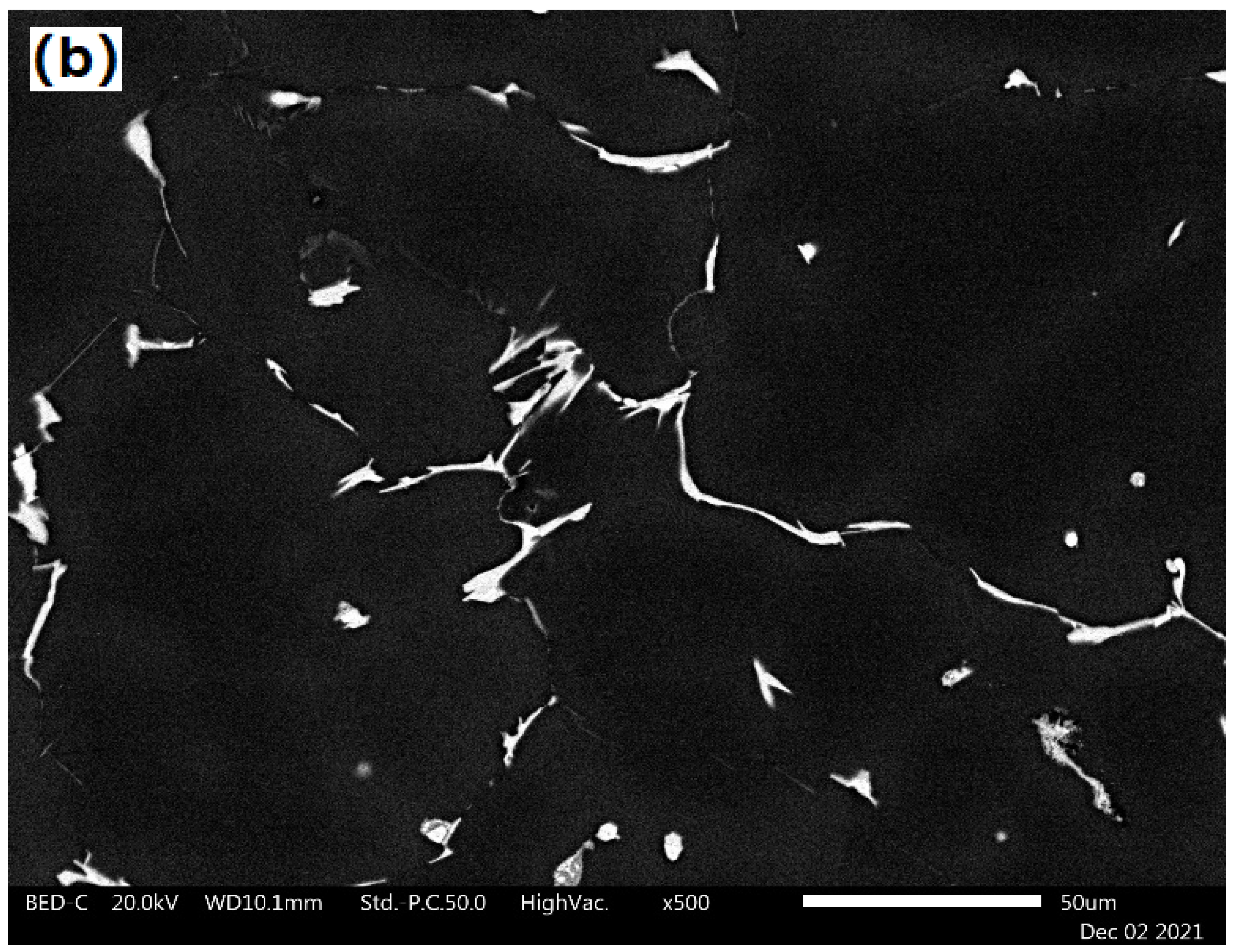









| Alloy | Main Elements | Microalloying Elements | Impurities | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li | Cu | Zn | Mg | Mn | Zr | Fe | Si | Al | |
| 2A97 | 1.5 | 3.8 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0.03 | Bal. |
| Mg | Al | Si | Ti | Mn | Fe | Cu | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5.55 | 39.54 | 1.39 | 30.06 | ||||
| 2 | 2.50 | 34.37 | 38.03 | |||||
| 3 | 1.51 | 40.00 | 29.03 | |||||
| 4 | 4.10 | 44.84 | 26.22 | |||||
| 5 | 3.83 | 51.52 | 21.19 | |||||
| 6 | 2.84 | 38.54 | 0.78 | 2.13 | 2.65 | 22.61 | 1.99 | |
| 7 | 2.73 | 53.96 | 16.04 | |||||
| 8 | 58.33 | 13.66 | ||||||
| 9 | 3.40 | 45.42 | 21.03 | |||||
| 10 | 3.48 | 53.67 | 18.58 | |||||
| 11 | 41.02 | 2.41 | 7.55 | 24.45 | ||||
| 12 | 3.26 | 47.93 | 21.16 | |||||
| 13 | 46.22 | 2.12 | 5.48 | 19.14 | ||||
| 14 | 3.18 | 48.14 | 20.58 | |||||
| 15 | 69.52 | 4.36 | ||||||
| 16 | 72.51 | 2.60 | ||||||
| 17 | 67.05 | 11.69 | ||||||
| 18 | 59.41 | 0.89 | 2.89 | 14.30 | ||||
| 19 | 76.34 | 2.07 | ||||||
| 20 | 48.07 | 26.97 | ||||||
| 21 | 65.32 | 10.30 | ||||||
| 22 | 57.67 | 2.09 | 3.97 | 16.47 |
| Mg | Al | Ti | Mn | Fe | Cu | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.85 | 95.66 | 3.49 | |||
| 2 | 2.65 | 60.97 | 13.04 | 3.90 | 2.54 | 16.90 |
| 3 | 66.87 | 2.69 | 7.45 | 22.99 | ||
| 4 | 54.16 | 5.95 | 9.35 | 30.55 | ||
| 5 | 8.03 | 57.06 | 34.91 | |||
| 6 | 51.93 | 5.48 | 9.09 | 33.50 | ||
| 7 | 52.91 | 6.43 | 11.65 | 29.01 |
| Aging Temperature | Calculated Results | Experimental Data |
|---|---|---|
| 200 °C | T1-Al2CuLi and θ’-Al2Cu | T1-Al2CuLi and θ’-Al2Cu [6] |
| 165 °C | T1-Al2CuLi, θ’-Al2Cu and δ’-Al3Li | T1-Al2CuLi, θ’-Al2Cu and δ’-Al3Li [7] |
| 135 °C | T1-Al2CuLi, θ’-Al2Cu and δ’-Al3Li | T1-Al2CuLi, θ’-Al2Cu and δ’-Al3Li [8] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Xiao, X. Thermodynamic and Kinetic Calculation of High Strength Aluminum-Lithium Alloy. Crystals 2022, 12, 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12040472
Wang J, Xiao X. Thermodynamic and Kinetic Calculation of High Strength Aluminum-Lithium Alloy. Crystals. 2022; 12(4):472. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12040472
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jinsan, and Xiang Xiao. 2022. "Thermodynamic and Kinetic Calculation of High Strength Aluminum-Lithium Alloy" Crystals 12, no. 4: 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12040472
APA StyleWang, J., & Xiao, X. (2022). Thermodynamic and Kinetic Calculation of High Strength Aluminum-Lithium Alloy. Crystals, 12(4), 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12040472





