Synthesis and Characterization of Mechanically Alloyed Nanostructured (Ti,Cr)C Carbide for Cutting Tools Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
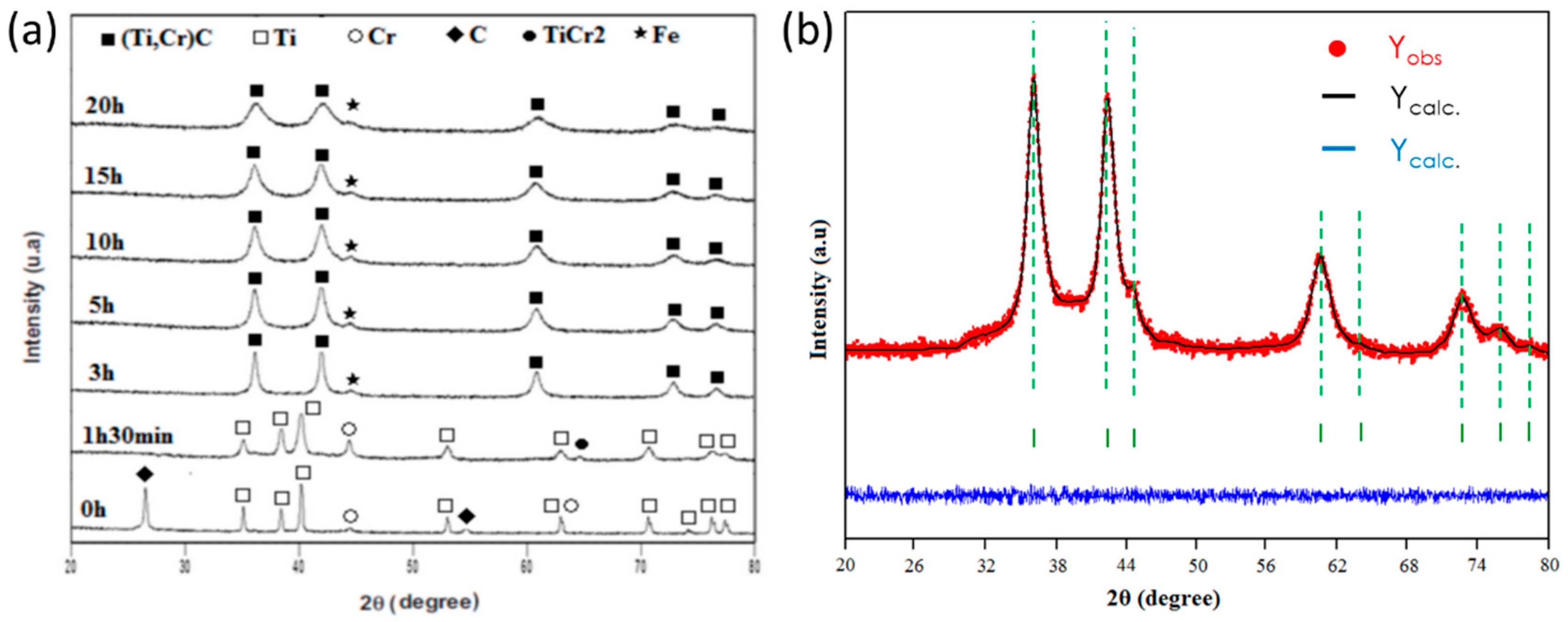
3.1. XRD Characterization
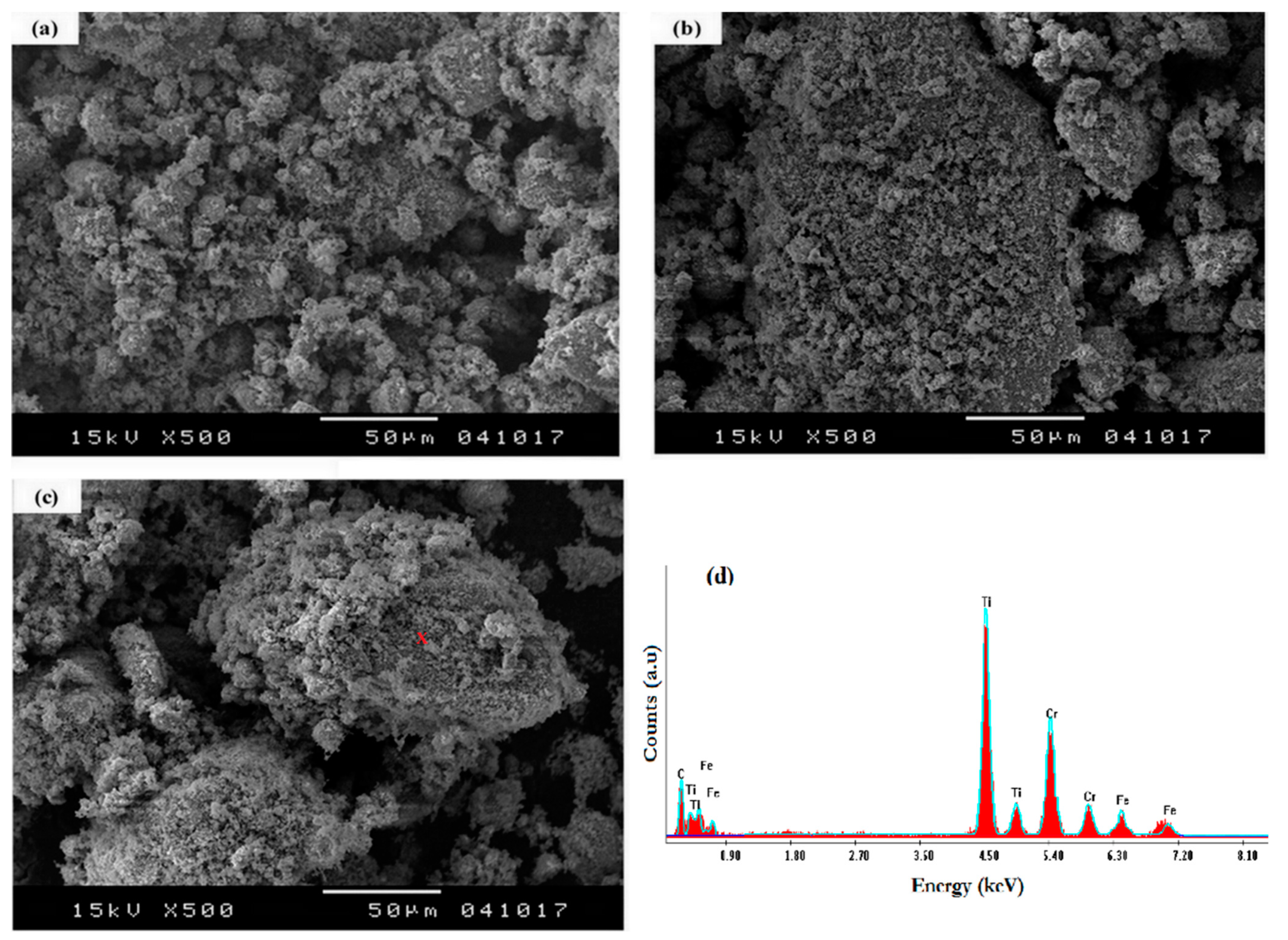
3.2. SEM Characterization
3.3. TEM Characterization
4. Conclusions
- Nanocrystalline solid solution (Ti,Cr)C with nano-sized crystallites was fabricated by mechanical alloying of Ti, Cr, and graphite elemental powders. The average grain size of the (Ti,Cr)C was 10 nm, and the average micro-strain was 1.34% for sample MA during 20 h.
- The (Ti,Cr)C solid solution having a NaCl type structure and a space group of Fm-3m, was formed after 3 h of the MA process.
- The crystallite size and the lattice parameter decrease by increasing milling time down to 10 nm and 0.43036 nm after 20 h of MA, respectively. This decrease can be attributed to the formation of crystal defects induced by high-energy ball milling. The microstrain increases with increasing milling time, which can be related to the strain-enhanced solubility of Cr in TiC matrix.
- The crystallite size obtained from XRD is well correlated with the results of TEM analyses.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, X.M.; Zhi, W.; Li, H.D. Investigation of TiC Films Synthesized by Low Energy Ion Bombardment. J. Mater. Res. 1994, 9, 2355–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.J.; Li, X.K.; Yuan, G.M.; Cui, Z.W.; Cong, Y.; Westwood, A. Tensile Strength, Oxidation Resistance and Wettability of Carbon Fibers Coated with a TiC Layer Using a Molten Salt Method. Mater. Des. 2013, 50, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonruang, C.; Thongtem, S. Fast Processing Technique for TiC Coatings on Titanium. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2010, 37, 206–212. [Google Scholar]
- Brama, M.; Rhodes, N.; Hunt, J.; Ricci, A.; Teghil, R.; Migliaccio, S.; Rocca, C.D.; Leccisotti, S.; Lioi, A.; Scandurra, M.; et al. Effect of Titanium Carbide Coating on the Osseointegration Response in Vitro and in Vivo. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, F.; Raygan, S.; Abdizadeh, H.; Dolatmoradi, A. Preparing TiC Coating on AISI D2 Steel Using Mechanical Milling Technique. Powder Technol. 2013, 246, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarova, R.; Petrov, R.H.; Gaydarova, V.; Alexeev, A.; Manchev, M.; Manolov, V. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of P265GH Cast Steel after Modification with TiCN Particles. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 2734–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Shi, J.; Xu, L.; Cao, W.Q.; Dong, H. TiC Precipitation Induced Effect on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties in Low Carbon Medium Manganese Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 530, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Kang, S. Sintered (Ti,W)C Carbides. Scr. Mater. 2007, 56, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhadhbi, M. Structural and Morphological Studies of Nanostructured TiC Powders Prepared by Mechanical Alloying. Mod. App. Mater. Sci. 2021, 3, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hu, W.; Xiang, J.; Wen, F.; Xu, B.; Yu, D.; He, J.; Tian, Y.; Liu, Z. Mechanical Properties of Nanocrystalline TiC-ZrC Solid Solutions Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 10517–10522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M.; Mamyouda, T.; Habuka, H.; Ishiguro, A.; Ishii, S.; Daigo, Y.; Ito, H.; Mizushima, I.; Takahashi, Y. Design of a Silicon Carbide Chemical Vapor Deposition Reactor Cleaning Process Using Chlorine Trifluoride Gas Accounting for Exothermic Reaction Heat. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 104008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana, C. Mechanical Alloying and Milling. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2001, 46, 1–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kang, S. Toughened Ultra-fine (Ti,W)(CN)-Ni Cermets. Scr. Mater. 2005, 52, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.K.; Shim, J.H.; Yang, H.S.; Park, J.K. Mechanochemical Synthesis of Nanocomposite Powder for Ultrafine (Ti, Mo)C-Ni Cermet Without Core-rim Structure. Int. Ref. Met. Hard. Mater. 2004, 22, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.; Jung, S.A.; Suh, C.Y.; Roh, K.M.; Kim, W. Mechanical Properties of (Ti,V)C-Ni Composite Prepared Using Ultrafine Solid-Solution (Ti,V)C Phase. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 12579–12583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Dutta, H.; Pradhan, S.K. XRD and HRTEM Characterization of Mechanosynthesized Ti0.9W0.1C Cermet. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 581, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Guo, Z.; Xiong, J.; Liu, F.; Qi, K. Microstructural Changes of (Ti,W)C Solid Solution Induced by Ball Milling. Int. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2017, 66, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, H.; Sen, A.; Pradhan, S.K. Microstructure Characterization of Ball-mill Prepared Ternary Ti0.9Al0.1C by X-ray Diffraction and Electron Microscopy. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 501, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Qu, S. Development and Characterization of (Ti, Mo)C Carbides Reinforced Fe-based Surface Composite Coating Produced by Laser Cladding. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2010, 48, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, A.B.; Yixuan, H.; Babu, R.P.; Hansen, T.C.; Eriksson, M.; Reddy, K.M.; Hedström, P. Design, Synthesis, Structure, and Stability of Novel Multi-Principal Element (Ti,Zr,Hf,W)C Ceramic with a Miscibility Gap. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 42, 4429–4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorotilo, S.; Kiryukhantsev-Korneev, P.V.; Seplyarskii, B.S.; Kochetkov, R.A.; Abzalov, N.I.; Kovalev, I.D.; Lisina, T.G.; Zaitsev, A.A. (Ti,Cr)C-Based Cermets with Varied Nicr Binder Content via Elemental SHS for Perspective Cutting Tools. Crystals 2020, 10, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisov, Y.S.; Borisova, A.L.; Kolomytsev, M.V.; Masyuchok, O.P.; Timofeeva, I.I.; Vasilkovskaya, M.A. High-Velocity Air Plasma Spraying of (Ti, Cr)C–32 wt.% Ni Clad Powder. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 2005, 56, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal, R. Recent Advances in Magnetic Structure Determination by Neutron Powder Diffraction. J. Phys. B 1993, 192, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietveld, H.M. A Profile Refinement Method for Nuclear and Magnetic Structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1969, 2, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loshe, B.H.; Calka, A.; Wexler, D. Synthesis of TiC by Controlled Ball Milling of Titanium and Carbon. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arao, Y.; Tanks, J.D.; Aida, K.; Kubouchi, M. Exfoliation Behavior of Large Anionic Graphite Flakes in Liquid Produced by Salt-Assisted Ball Milling. Processes 2020, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübler, D.; Gradt, T. Effect of Different Binders and Secondary Carbides on NbC Cermets. Forsch. Ingenieurwes. 2022, 86, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.N.; Nie, W.Y.; Guan, R.; Jia, W.K.; Yan, F.G. Study on Damage Behavior of Carbide Tool for Milling Difficult-to-Machine Material Show Less. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2018, 233, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, I.J.; Oh, H.S.; Lim, J.W.; Kwon, H. Mechanical Properties and Consolidation of Binderless Nanostructured (Ti,Cr)C from Mechanochemically-Synthesized Powder by High-Frequency Induction Heating Sintering. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 9721–9726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.M.A.K.; Chen, D.L. Carbon Nanotube-Reinforced Aluminum Matrix Composites. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2020, 22, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.T.; Huang, J.Y.; Gubicza, J.; Ungar, T.; Wang, Y.M.; Ma, E.; Valiev, R.Z. Nanostructures in Ti Processed by Severe Plastic Deformation. J. Mater. Res. 2003, 18, 1908–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mhadhbi, M.; Khitouni, M.; Escoda, L.; Suñol, J.J.; Dammak, M. Characterization of Mechanically Alloyed Nanocrystalline Fe(Al): Crystallite Size and Dislocation Density. J. Nanometer. 2010, 2010, 712407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, J.C. Atomic Radii in Crystals. J. Chem. Phys. 1964, 41, 3199–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrinfar, N.; Shipway, P.H.; Kennedy, A.R.; Saidi, A. Carbide Stoichiometry in TiCx and Cu-TiCx Produced by Self-Propagating High-Temperature Synthesis. Scr. Mater. 2002, 46, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groß, H.; Ekici, Y.; Poschmann, M.; Croeneveld, D.; Dankwort, T.; Koenig, J.D.; Bensch, W.; Kienle, L. Does a Low Amount of Substituents Improve the Thermoelectric Properties of Cr2−xMxS3 (M = Ti, V, Sn)? J. Electron. Mater. 2022, 51, 3510–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana, C. Mechanical Alloying: A Novel Technique to Synthesize Advanced Materials. Research 2019, 2019, 4219812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.; Jung, S.A.; Kim, W. (Ti,Cr)C Synthesized In Situ by Spark Plasma Sintering of TiC/Cr3C2 Powder Mixtures. Mater. Trans. 2015, 56, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, B.; Ghosh, S.; Roy, D.; Samanta, L.K. Preparation of Nanocrystalline CuAlFeS2-Mixed Chalcopyrite by High-energy Ball Milling. Physica 2006, 33, 66–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| MA Time (h) | Phase | Space Group | Lattice Parameter (nm) | Crystallite Size (nm) | Microstrain (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 | Ti | Fm-3m | a = 0.43281(4) | 55 | 0.25 ± 0.01 |
| Cr | Im-3m | a = 0.29236(1) | 40 | 0.94 ± 0.01 | |
| TiCr2 | P6₃/mmc | a = 0.69011(3) | 31 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | |
| 3 | (Ti,Cr)C | Fm-3m | a = 0.44169(5) | 18 | 0.12 ± 0.02 |
| Fe | Im-3m | a = 0.2873(5) | 17 | 0.21± 0.01 | |
| 5 | (Ti,Cr)C | Fm-3m | a = 0.44033(4) | 15 | 0.25 ± 0.03 |
| Fe | Im-3m | a = 0.2874(3) | 15 | 0.22 ± 0.01 | |
| 10 | (Ti,Cr)C | Fm-3m | a = 0.44949(4) | 13 | 1.28 ± 0.04 |
| Fe | Im-3m | a = 0.2876(2) | 13 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | |
| 15 | (Ti,Cr)C | Fm-3m | a = 0.43033(2) | 11 | 1.33 ± 0.04 |
| Fe | Im-3m | a = 0.2877(5) | 11 | 0.25 ± 0.01 | |
| 20 | (Ti,Cr)C | Fm-3m | a = 0.43036(3) | 10 | 1.34 ± 0.04 |
| Fe | Im-3m | a = 0.2879(4) | 11 | 0.26 ± 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mhadhbi, M.; Polkowski, W. Synthesis and Characterization of Mechanically Alloyed Nanostructured (Ti,Cr)C Carbide for Cutting Tools Application. Crystals 2022, 12, 1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12091280
Mhadhbi M, Polkowski W. Synthesis and Characterization of Mechanically Alloyed Nanostructured (Ti,Cr)C Carbide for Cutting Tools Application. Crystals. 2022; 12(9):1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12091280
Chicago/Turabian StyleMhadhbi, Mohsen, and Wojciech Polkowski. 2022. "Synthesis and Characterization of Mechanically Alloyed Nanostructured (Ti,Cr)C Carbide for Cutting Tools Application" Crystals 12, no. 9: 1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12091280
APA StyleMhadhbi, M., & Polkowski, W. (2022). Synthesis and Characterization of Mechanically Alloyed Nanostructured (Ti,Cr)C Carbide for Cutting Tools Application. Crystals, 12(9), 1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12091280







