Effect of Aluminum Addition on the Microstructure, Magnetic, and Mechanical Properties of FeCrCoNiMn High-Entropy Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
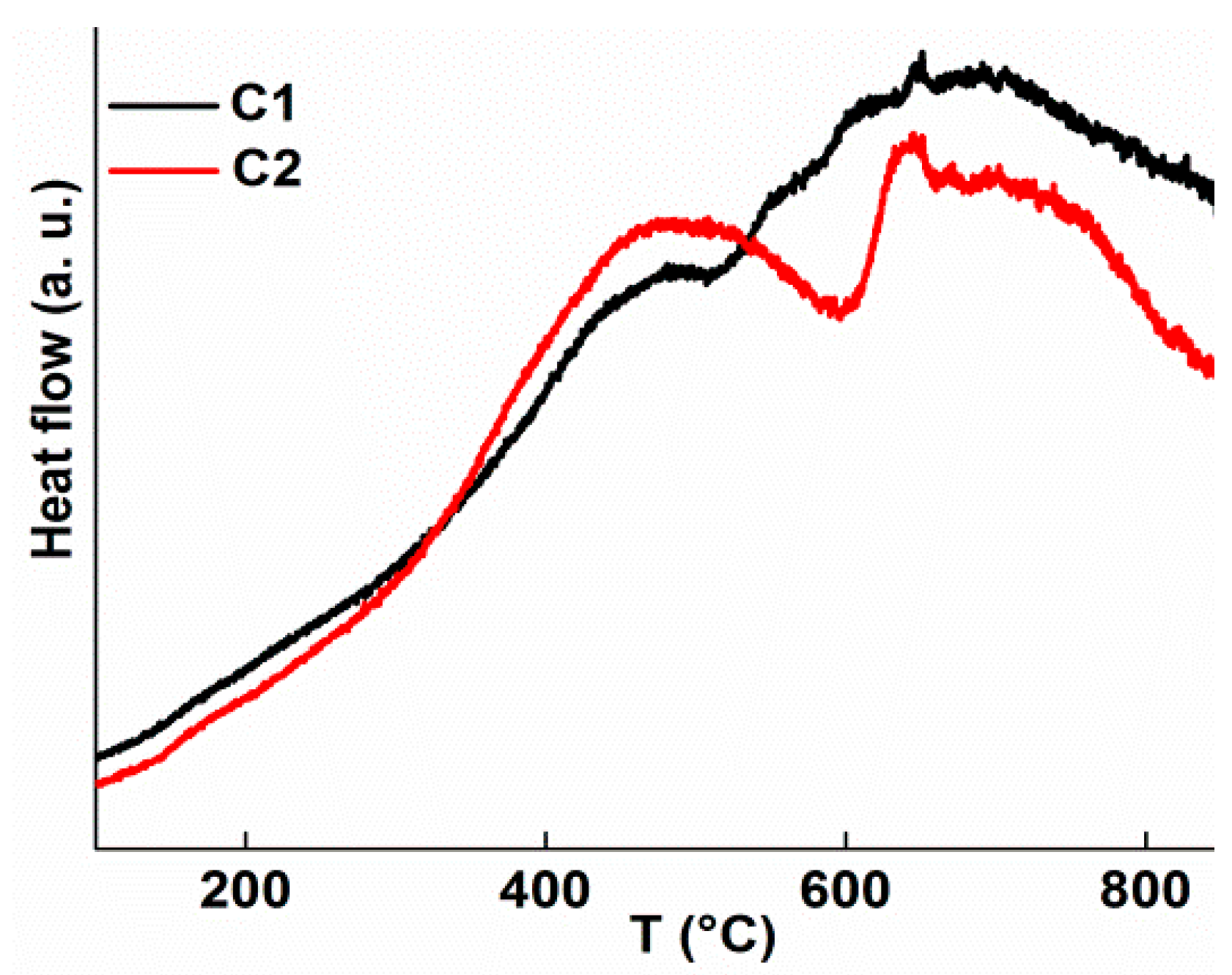
3. Results
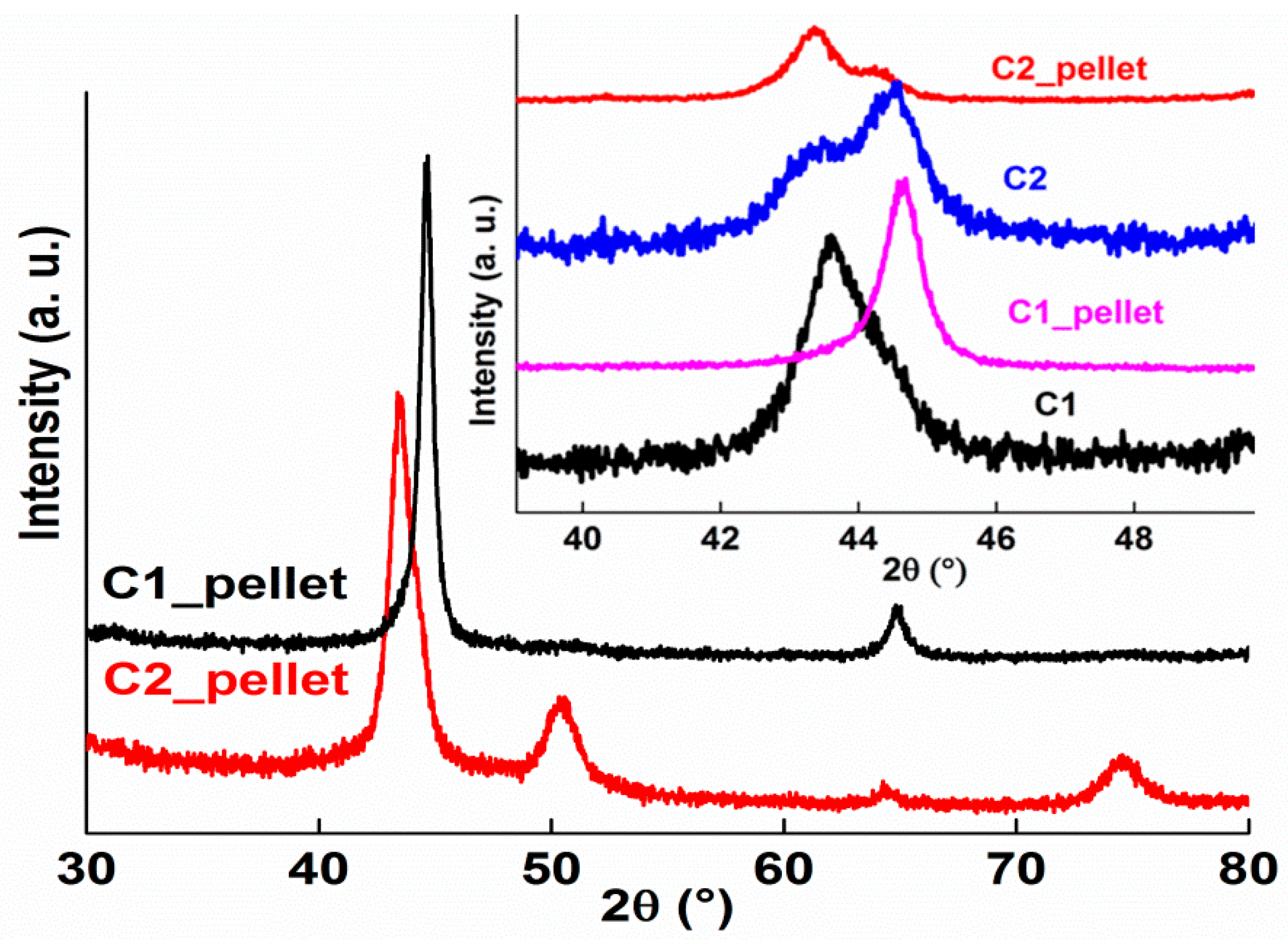
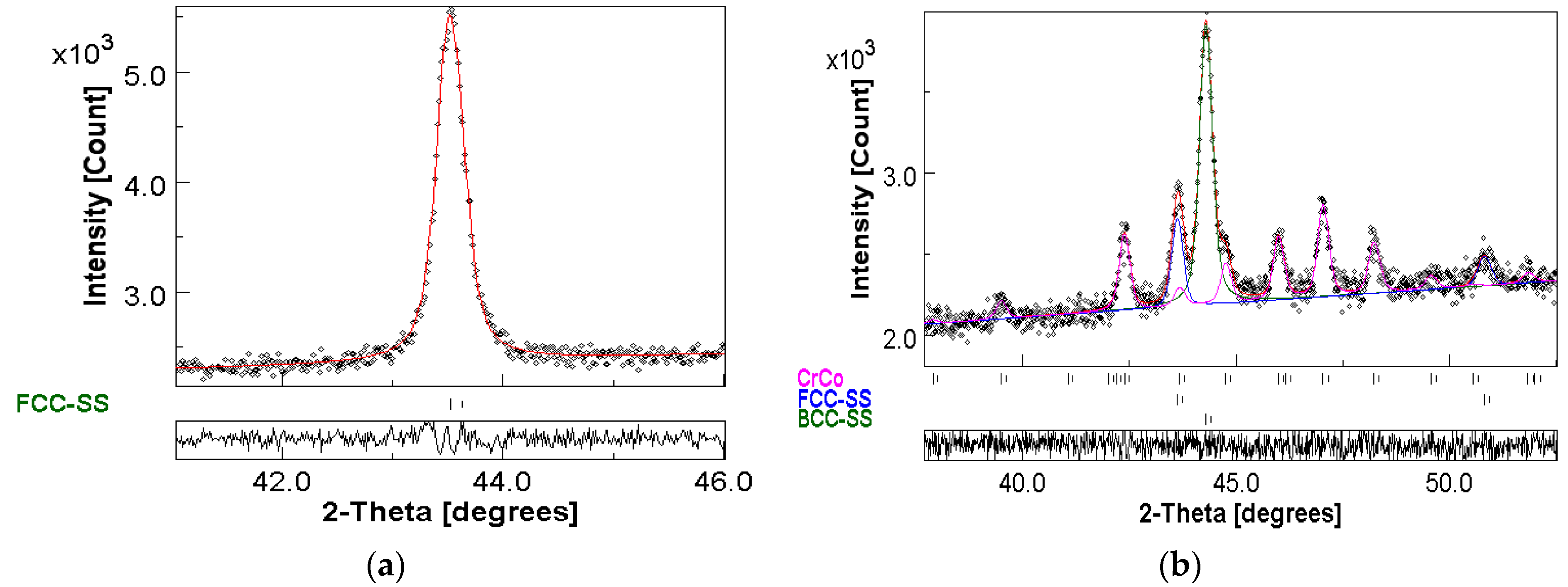
3.1. Phase Formation
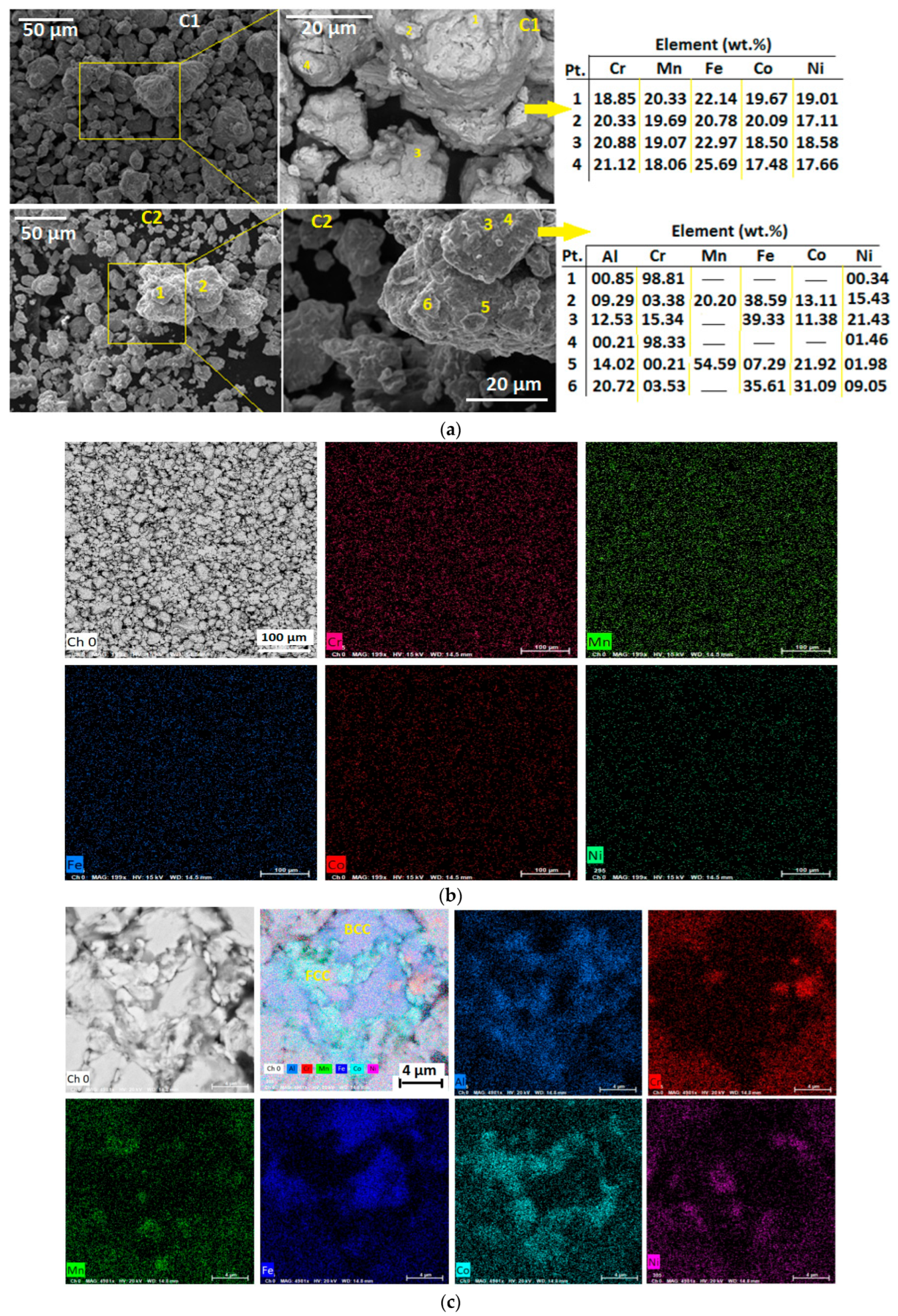
3.2. Morphology
3.3. Magnetic and Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
- The crystal structure of both the C1 and C2 powders consists of BCC + FCC phases;
- A mixture of BCC + FCC was observed for the C1_pellet and BCC + FCC + σ-CrCo phases for the C2_pellet;
- The heat-treated powders to 900 °C exhibit a single FCC phase for the C1_900 °C and a mixture of BCC + FCC + σ-CrCo for the C2_900 °C powders;
- The crystallite sizes of the C1, C2, C1_pellet, C1_900 °C, and C2_900 °C are in the range of 6-93 nm;
- The C1 and C2 powders exhibit a ferromagnetic behavior (Ms = 24.2 emu/g and Hc = 153.62 Oe) and C2 (Ms = 28.45 emu/g and Hc = 188.48 Oe) powders;
- The C1_900 °C powders show a paramagnetic behavior (Ms = 0.99 emu/g and Hc = 56.10 Oe);
- The C2_900 °C powders exhibit a ferromagnetic character with Ms = 32.28 emu/g and Hc = 56.18 Oe;
- Both C1_900 °C and C2_900 °C HEAs alloys show an exchange bias (EB) behavior at room temperature. The EB value is influenced by the Mn content;
- The Vickers microhardness values are 584.85 Hv for the C1_pellet and 522.65 Hv for the C2_pellet;
- This study reveals that MA and sintering at 500 °C for 1 h can be used as an effective way to produce HEA alloys with higher microhardness values. The produced HEA alloys exhibit comparable characteristics in terms of structure, microstructure, mechanical, and magnetic properties.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raja, R.K.; Sinha, S.K. Synthesis and phase investigation of equiatomic AlCrFeMnNi alloys dispersed with partially stabilized zirconia for nuclear applications. Mater. Sci. Forum 2020, 978, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xie, D.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liaw, P.K. Mechanical behavior of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 118, 100777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, S.; Ritchie, R.O.; Meyers, M.A. Mechanical properties of high-entropy alloys with emphasis on face-centered cubic alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 102, 296–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yuan, X.; Huang, H.; Wen, X.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Z. Short-range ordering and its effects on mechanical properties of high-entropy alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 62, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onawale, O.T.; Cobbinah, P.V.; Nzeukou, R.A.; Matizamhuka, W.R. Synthesis route, microstructural evolution, and mechanical property relationship of high-entropy alloys (HEAs): A review. Materials 2021, 14, 3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konakoglou, K.; Mathiou, C.; Georgatis, E.; Georgarakis, K.; Karantzalis, A.E. (FeMnNi)84(AlTi)16 High-Entropy Alloy: Correlation of Microstructure, Strengthening Mechanisms and Hardness at Various Conditions (As-Cast, Solution Treated, Aged). Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 2022, 11, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Gao, Z.; Hu, S.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Wang, J. Effect of cooling rate on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al0.3CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 056540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogal, Ł. Semi-solid processing of the CoCrCuFeNi high entropy alloy. Mater. Des. 2017, 119, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendrachari, S. An overview of high-entropy alloys prepared by mechanical alloying followed by the characterization of their microstructure and various properties. Alloys 2022, 1, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila-Rubio, M.A.; Baldenebro-Lopez, J.A.; Soto-Rojo, R.; Ceballos-Mendivil, L.G.; Garza-Montes-de-Oca, N.F.; Baldenebro-Lopez, F.J. Effect of Mo and Ti on the microstructure and microhardness in AlCoFeNiMoTi high entropy alloys prepared by mechanical alloying and conventional sintering. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 1693–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Yao, C.; Feng, K.; Li, Z.; Chu, P.K. Cryogenic deformation mechanism of CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy fabricated by laser additive manufacturing process. Int. J. Lightweight Mater. Manuf. 2018, 1, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Hou, J.; Wang, X.; Qiao, J.; Wu, Y. Excellent room-temperature tensile ductility in as-cast Ti37V15Nb22Hf23W3 refractory high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2022, 151, 107735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jien-Wei, Y.E.H. Recent progress in high entropy alloys. Ann. Chim. Sci. Mat 2006, 31, 633–648. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.; Tiwary, C.S.; Biswas, K. Preparation of nanocrystalline high-entropy alloys via cryomilling of cast ingots. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 13411–13423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Nieh, T.G. Correlation between lattice distortion and friction stress in Ni-based equiatomic alloys. Intermetallics 2017, 86, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, F.; Cui, Y. Microstructural evolution, phase formation and mechanical properties of multi-component AlCoCrFeNix alloys. Appl. Phys. A 2019, 125, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Gao, X.; Jiang, L.; Chen, Z.; Wang, T.; Jie, J.; Kang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, S.; Ruan, H.; et al. Directly cast bulk eutectic and near-eutectic high entropy alloys with balanced strength and ductility in a wide temperature range. Acta Mater. 2017, 124, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Kumar, N.; Das, S.; Gurao, N.P.; Biswas, K. Effect of Al addition on the microstructural evolution of equiatomic CoCrFeMnNi alloy. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2018, 71, 2749–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.; Maity, T.N.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Sarkar, S.; Gurao, N.P.; Bhowmick, S.; Biswas, K. Powder metallurgical processing of equiatomic AlCoCrFeNi high entropy alloy: Microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 679, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Stanford, N.; Hodgson, P.; Fabijanic, D.M. Understanding the mechanical behaviour and the large strength/ductility differences between FCC and BCC AlxCoCrFeNi high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 726, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Wei, S.; Lau, K.B.; Teh, W.H.; Lee, J.J.; Seng, H.L.; Ramamurty, U. Compositionally graded AlxCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy manufactured by laser powder bed fusion. Materialia 2022, 21, 101308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.W.; Zhang, G.J.; Yin, K.X.; Cheng, W.L.; Wang, Y.N.; Huang, J.C. Effect of Ni content on the phase formation, tensile properties and deformation mechanisms of the Ni-rich AlCoCrFeNix (x = 2, 3, 4) high entropy alloys. Mater. Charact. 2021, 176, 111148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Li, B.S.; Ren, M.X.; Yang, C.; Fu, H.Z. Microstructure and compressive properties of AlCoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 491, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoni, A.; Daoud, H.; Volkl, R.; Glatzel, G.; Wanderka, N. Phase separation in equiatomic AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy. Ultramicroscopy 2013, 132, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.R.; Wan, W.L.; Wang, S.C.; Tsai, Y.C.; Lai, C.H.; Yeh, J.W. Effects of Al addition on the microstructure and mechanical property of AlxCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2012, 26, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutterotti, L. MAUD Program Version 2.992. Available online: https://maud.radiographema.com/ (accessed on 28 November 2021).
- Rietveld, H.M. The Rietveld method. Phys. Scr. 2014, 89, 098002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, M.; Pradeep, K.G.; Murty, B.S.; Wilde, G.; Divinski, S.V. Bulk tracer diffusion in CoCrFeNi and CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2018, 146, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, A.; Inoue, A. Classification of bulk metallic glasses by atomic size difference, heat of mixing and period of constituent elements and its application to characterization of the main alloying element. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 2817–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Li, C.J.; Mu, Y.K.; Jia, Y.D.; Song, K.K.; Tan, J.; Eckert, J. Strengthening and deformation mechanism of high-strength CrMnFeCoNi high entropy alloy prepared by powder metallurgy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 132, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, F.; Dlouhý, A.; Pradeep, K.G.; Kuběnová, M.; Raabe, D.; Eggeler, G.; George, E.P. Decomposition of the single-phase high-entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi after prolonged anneals at intermediate temperatures. Acta Mater. 2016, 112, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Y.; Liu, W.H.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.J.; Nieh, T.G.; Lu, Z.P. Effects of Al addition on structural evolution and tensile properties of the FeCoNiCrMn high-entropy alloy system. Acta Mater. 2014, 62, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, T.T.; Tang, Z.; Gao, M.C.; Dahmen, K.A.; Liaw, P.K.; Lu, Z.P. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater Sci 2014, 61, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, U. Hume-Rothery Rules for Structurally Complex Alloy Phases; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.F.; Ye, Y.F.; Yang, Y. Formation of Random Solid Solution in Multicomponent Alloys: From Hume-Rothery Rules to Entropic Stabilization. J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 2017, 38, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Bei, H.; Otto, F.; Pharr, G.M.; George, E.P. Recovery, Recrystallization, Grain Growth and Phase Stability of a Family of FCC-Structured Multi-component Equiatomic Solid Solution Alloys. Intermetallics 2014, 46, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.J.; Lin, J.P.; Chen, G.L.; Liaw, P.K. Solid-Solution Phase Formation Rules for Multi-component Alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2008, 10, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.F.; Wang, Q.; Lu, J.; Liu, C.T.; Yang, Y. High-Entropy Alloy: Challenges and Prospects. Mater. Today 2016, 19, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Li, J.; Qi, M.; Xu, Y.; Ezatpour, H.R. Effects of heat treatment on the microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of AlCoCrFeNiTi0.5 high-entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 884, 161026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christofidou, K.; Pickering, E.; Orsatii, P.; Mignanelli, P.; Slater, T.; Stone, H.; Jones, N. On the influence of Mn on the phase stability of the CrMnxFeCoNi high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2018, 92, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Xu, M.; Liu, N.; Liu, L.X. The formation of sigma phase in the CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys. Mater. Res. Express 2021, 8, 076514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Zeng, C.; Yang, W.; Chen, W.; Ai, Y. Impact of different Cr contents on microstructural evolution and mechanical behaviour of CoCrxCuFeMnNiV high-entropy alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 21, 4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.H.; Liu, X.D.; Yang, Y. Fracture of sigma phase containing Co–Cr–Ni–Mo medium entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 846, 156189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, S.; Wu, M.; Yang, S.; Xiang, D. Effects of Al or Mo Addition on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fe-Rich Nonequiatomic FeCrCoMnNi High-Entropy Alloy. Metals 2022, 12, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukawa, N.; Hida, M.; Imura, T.; Kawamura, M.; Mizuno, Y. Structure of chromium-rich Cr-Ni, Cr-Fe, Cr-Co, and Cr-Ni-Fe alloy particles made by evaporation in argon. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1972, 3, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alleg, S.; Hamza, L.; Ibrir, M.; Souilah, S.; Tebib, W.; Fenineche, N.E.; Greneche, J.M. Microstructural, hyperfine, and magnetic properties of FeSiBCuNb deposits. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2015, 28, 2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.F.; Zhang, L.J.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, H.; Ma, M.Z.; Li, Y.C.; Li, G.; Liaw, P.K.; Liu, R.P. The high-entropy alloys with high hardness and soft magnetic property prepared by mechanical alloying and high-pressure sintering. Intermetallics 2016, 70, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Han, B.; Song, L.; Li, J.; Yang, J. Investigation on microstructure and properties of AlxCoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloys by ultrasonic impact treatment. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 816, 152626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Element | Al | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atomic radii (nm) | 0.143 | 0.128 | 0.135 | 0.124 | 0.125 | 0.125 |
| VEC | 3 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Melting temperature (K) | 933 | 2180 | 1358 | 1811 | 1768 | 1728 |
| Crystal structure | FCC | BCC | Complex cubic | BCC | HCP | FCC |
| Activation energy (kJ/mol) | 210.4 | 313 | 272 | 309 | 270 | 304 |
| ΔHmix Al (kJ/mol) | ----- | −10 | −19 | −11 | −19 | −22 |
| ΔHmix Cr (kJ/mol) | −10 | ----- | −9 | −1 | −4 | −7 |
| ΔHmix Mn (kJ/mol) | −19 | −9 | ----- | 0 | −5 | −8 |
| ΔHmix Fe (kJ/mol) | −11 | −1 | 0 | ----- | −1 | −2 |
| ΔHmix Co (kJ/mol) | −19 | −4 | −5 | −1 | ----- | 0 |
| ΔHmix Ni (kJ/mol) | −22 | −7 | −8 | −2 | 0 | ----- |
| Sample | Structure | a ± 10−4 (Å) | Δa (%) | <L> ± 1 (nm) | r.m.s (%) | Weight Fraction ± 1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | BCC-SS | 2.8878 | 0.13 | 9.0 | 0.18 | 11.0 |
| FCC-SS | 3.5948 | 1.89 | 13.0 | 0.39 | 89.0 | |
| C2 | BCC-SS | 2.8822 | −0.06 | 9.9 | 0.01 | 68.0 |
| FCC-SS | 3.6221 | 2.66 | 9.2 | 0.46 | 32.0 |
| Sample | Structure | a ± 10−4 (Å) | c ± 10−4 (Å) | <L> ± 1 (nm) | r.m.s (%) | Weight Fraction ± 1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | BCC-SS | 2.8778 | ---- | 50.0 | 0.46 | 17.8 |
| FCC-SS | 3.5984 | ---- | 14.8 | 0.39 | 82.2 | |
| C2 | BCC-SS | 2.8853 | ---- | 77.6 | 0.42 | 16.13 |
| FCC-SS | 3.6099 | ---- | 16.7 | 0.39 | 78.54 | |
| σ-CrCo | 8.8955 | 4.6011 | 5.8 | 0.35 | 5.33 |
| Sample | Structure | a ± 10−4 (Å) | c ± 10−4 (Å) | <L> ± 1 (nm) | r.m.s (%) | Weight Fraction±1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1_900 °C | FCC-SS | 3.5987 | ---- | 72.0 | 0.09 | 100 |
| C2_900 °C | BCC-SS | 2.8896 | ---- | 63.5 | 0.14 | 33.9 |
| FCC-SS | 3.5909 | ---- | 81.0 | 0.13 | 13.5 | |
| σ-CoCr | 8.7953 | 4.5588 | 93.0 | 0.11 | 52.6 |
| Sample | Ms (emu/g) | Hc (Oe) | Mr (emu/g) | Mr/Ms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 24.20 | 153.62 | 3.995 | 0.165 |
| C1_900 °C | 0.99 | 56.10 | 0.039 | 0.039 |
| C2 | 28.45 | 188.48 | 4.897 | 0.172 |
| C2_900 °C | 32.28 | 56.18 | 3.471 | 0.107 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alleg, S.; Bekhouche, A.; Hachache, H.; Sunol, J.J. Effect of Aluminum Addition on the Microstructure, Magnetic, and Mechanical Properties of FeCrCoNiMn High-Entropy Alloy. Crystals 2023, 13, 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13101483
Alleg S, Bekhouche A, Hachache H, Sunol JJ. Effect of Aluminum Addition on the Microstructure, Magnetic, and Mechanical Properties of FeCrCoNiMn High-Entropy Alloy. Crystals. 2023; 13(10):1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13101483
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlleg, Safia, Ahlem Bekhouche, Hacene Hachache, and Joan Jose Sunol. 2023. "Effect of Aluminum Addition on the Microstructure, Magnetic, and Mechanical Properties of FeCrCoNiMn High-Entropy Alloy" Crystals 13, no. 10: 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13101483
APA StyleAlleg, S., Bekhouche, A., Hachache, H., & Sunol, J. J. (2023). Effect of Aluminum Addition on the Microstructure, Magnetic, and Mechanical Properties of FeCrCoNiMn High-Entropy Alloy. Crystals, 13(10), 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13101483










