Study on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Martensitic Wear-Resistant Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
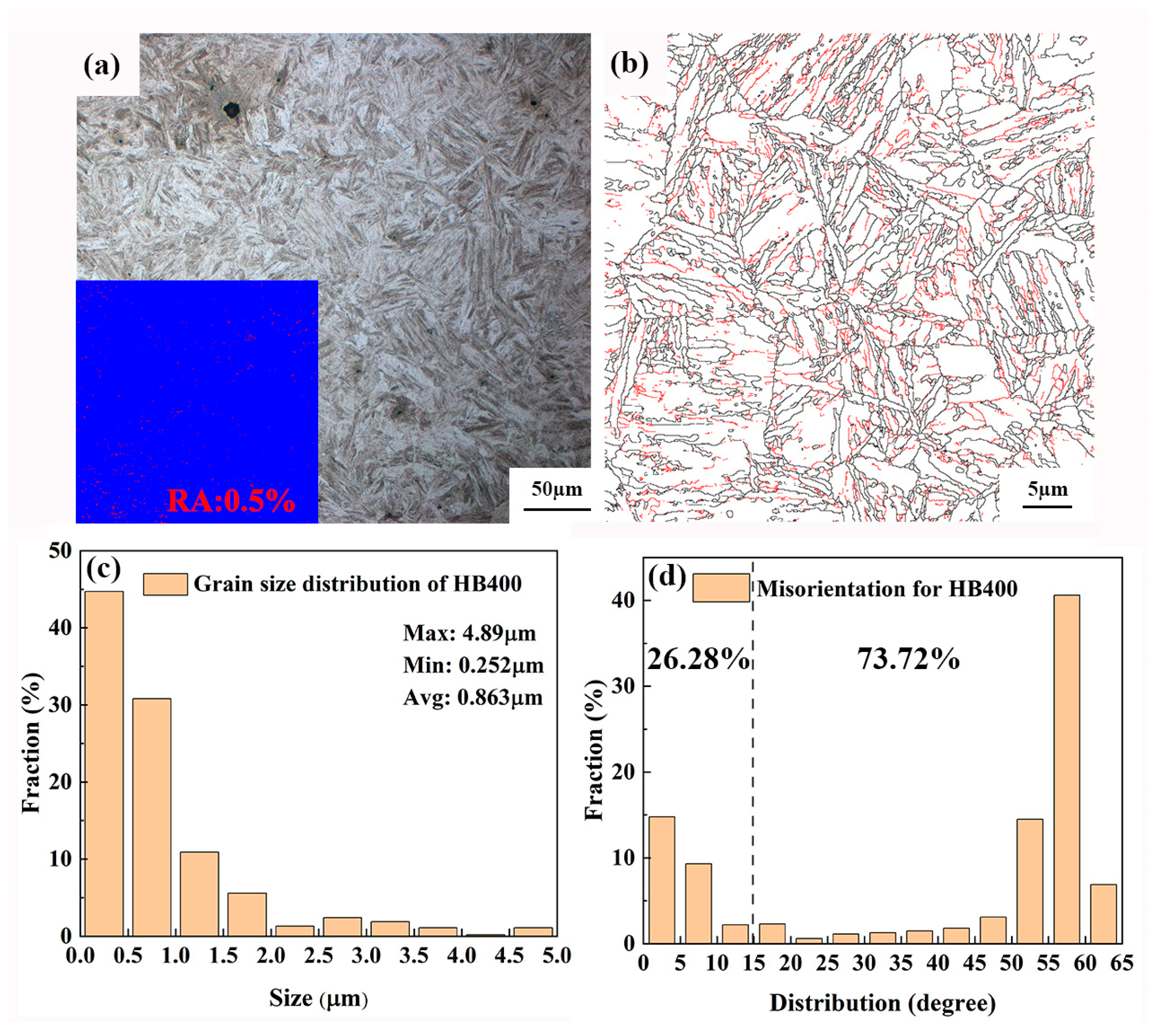
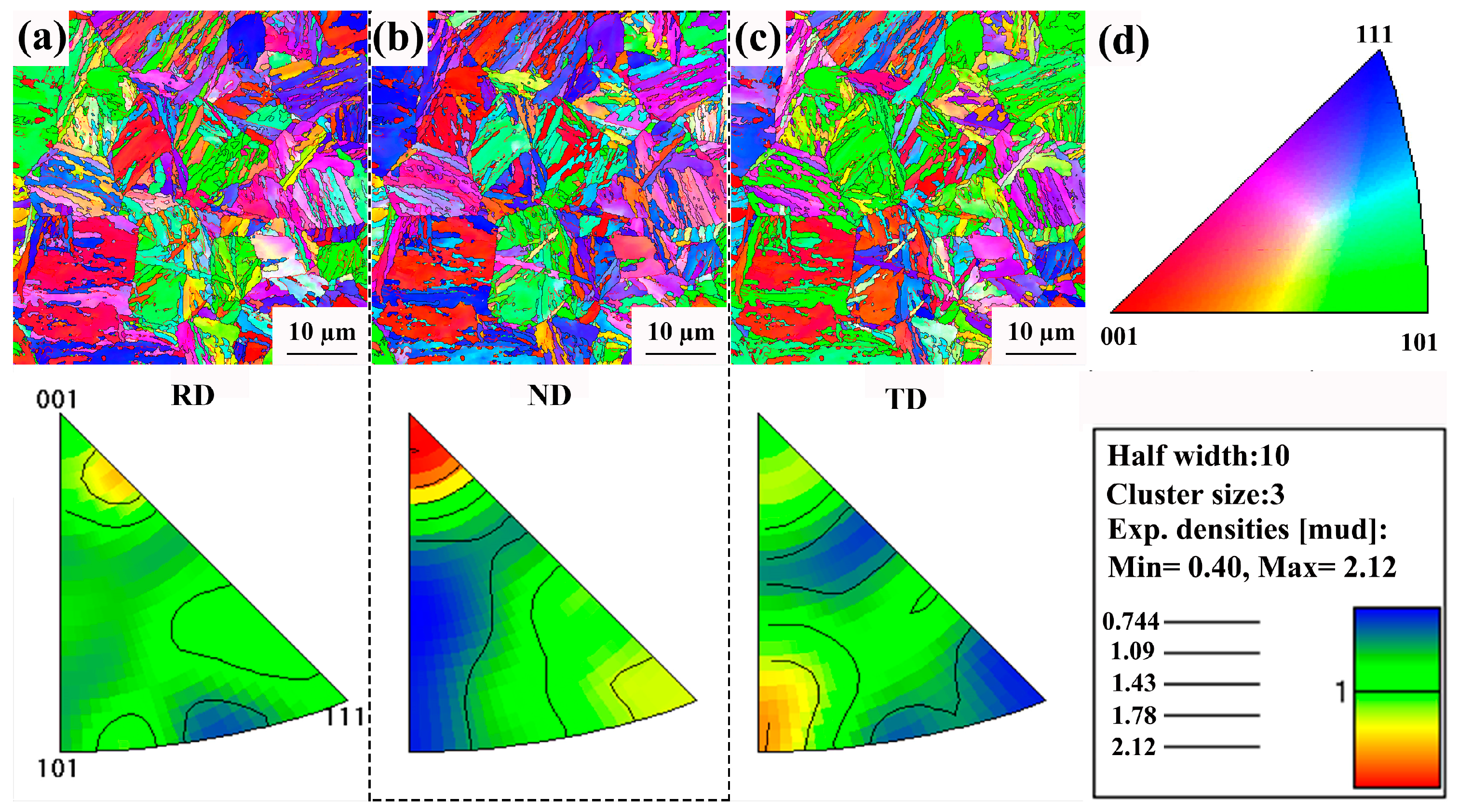
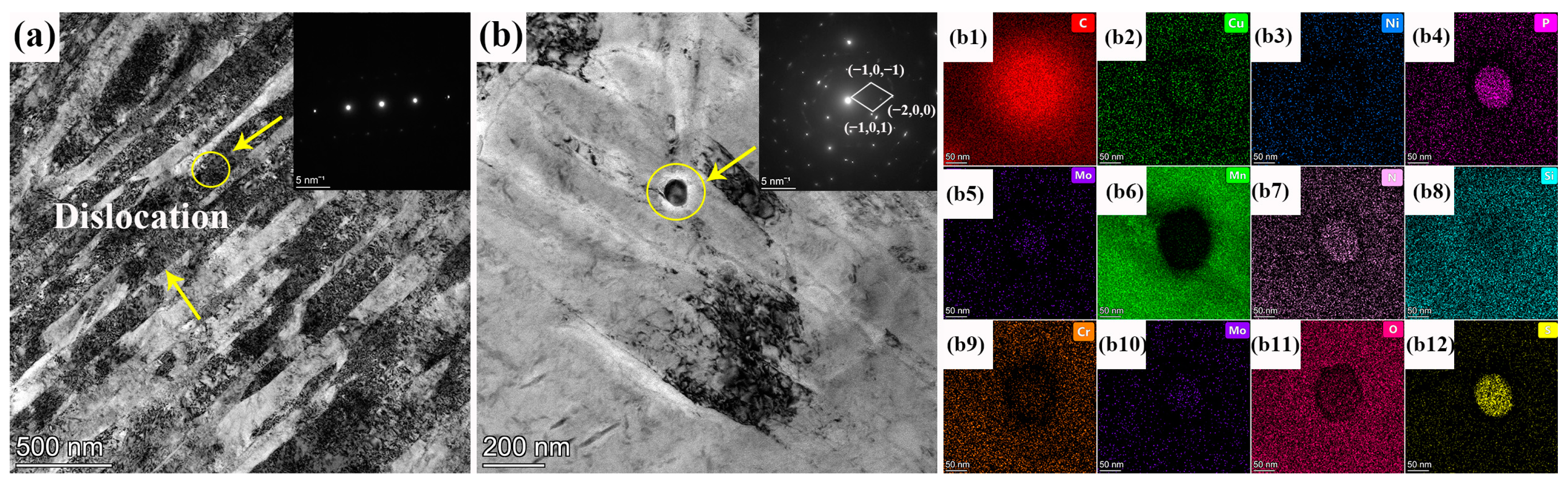
3.1. Microstructure
3.2. Mechanical Performance Test
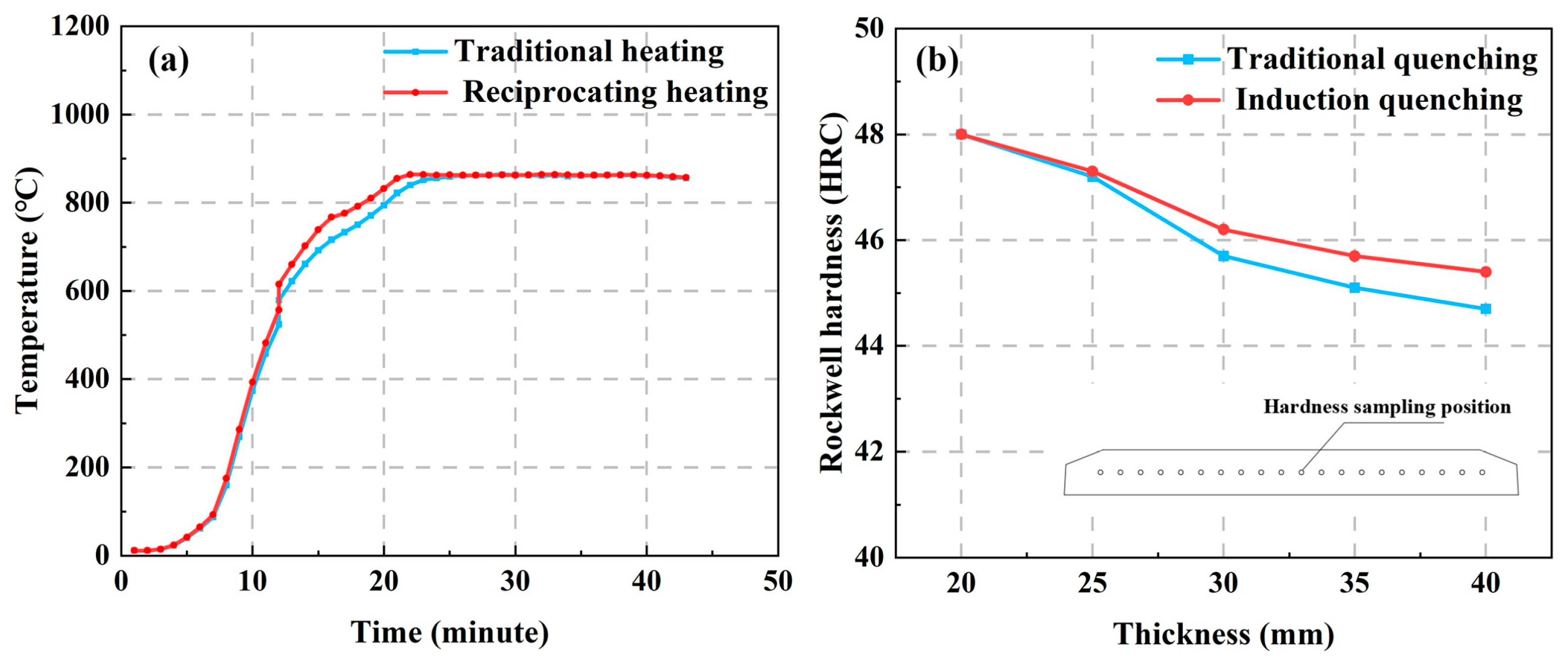
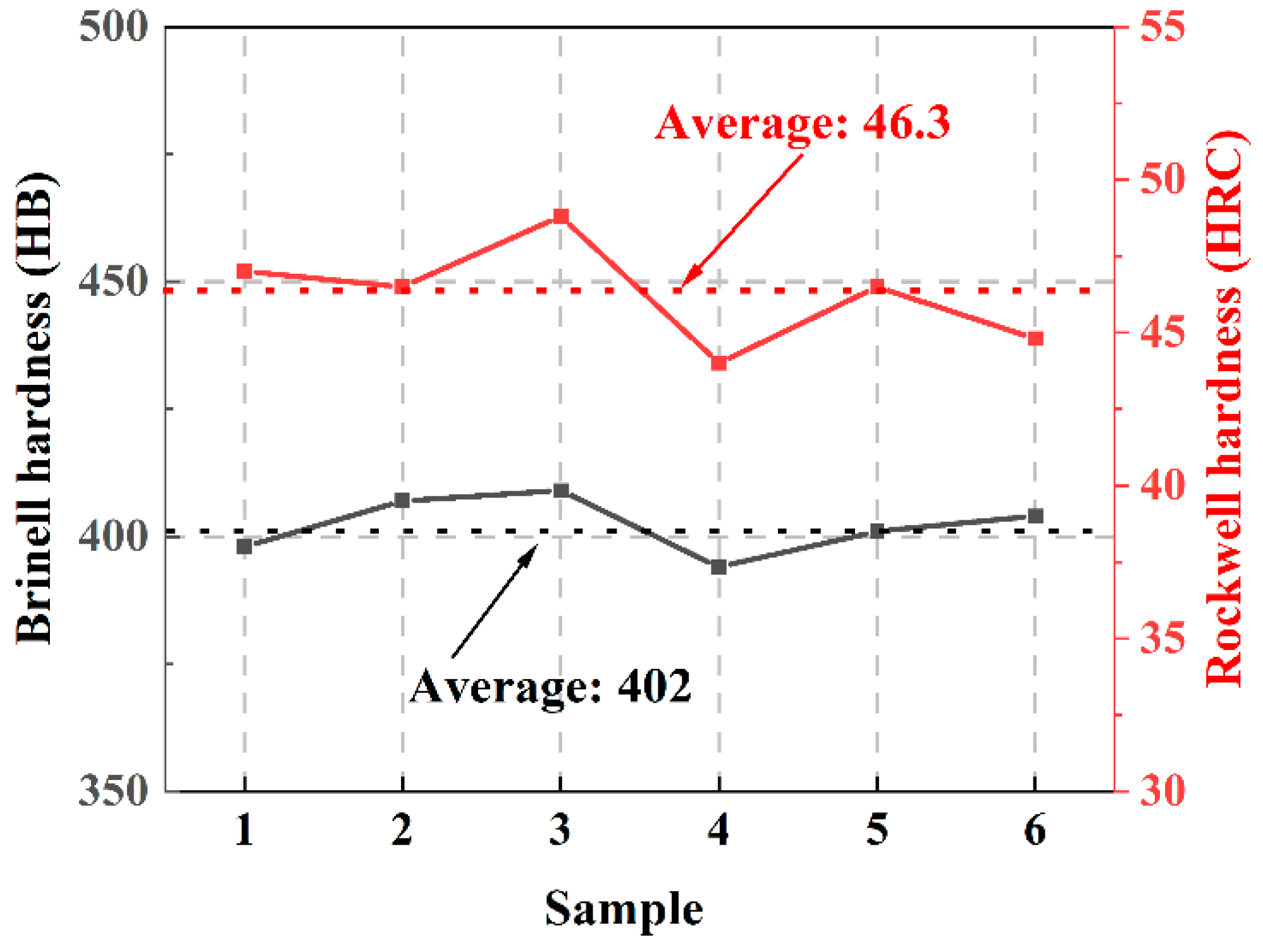
3.2.1. Hardness Test
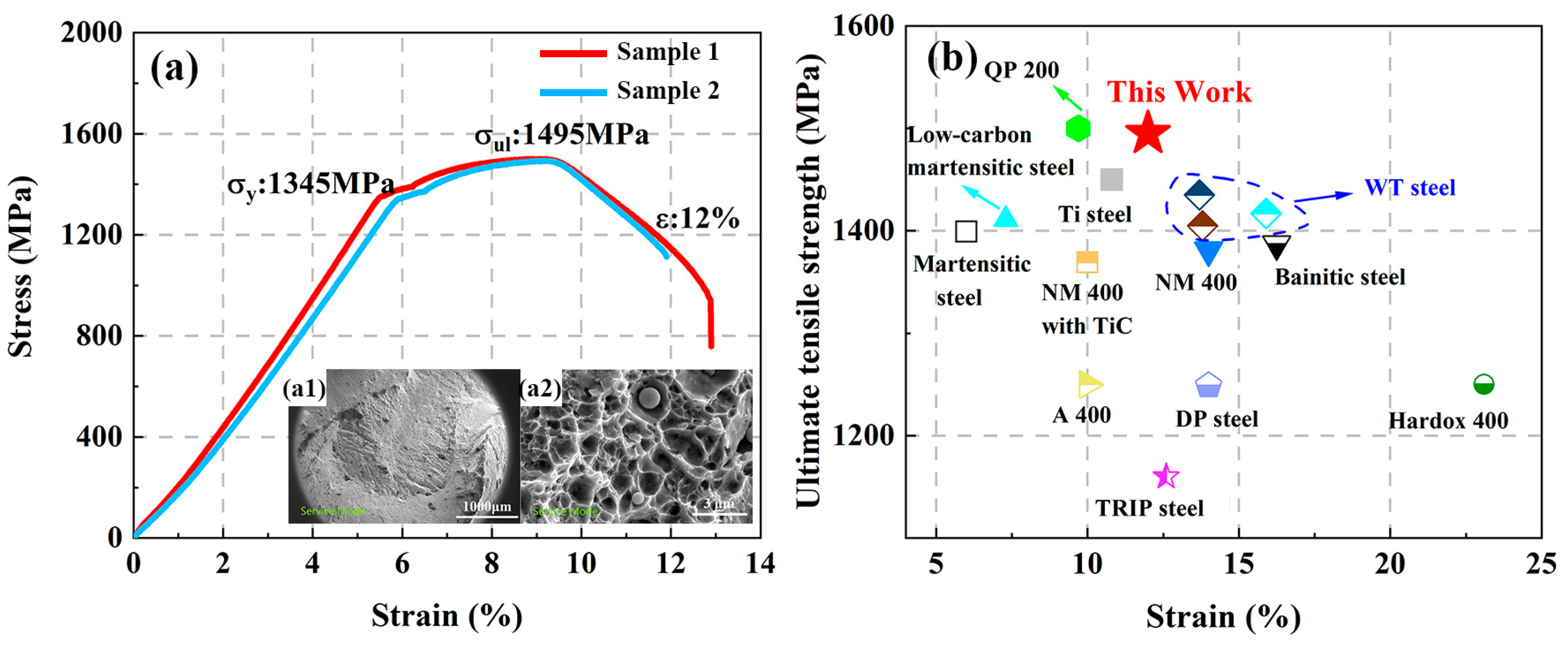
3.2.2. Tensile Properties
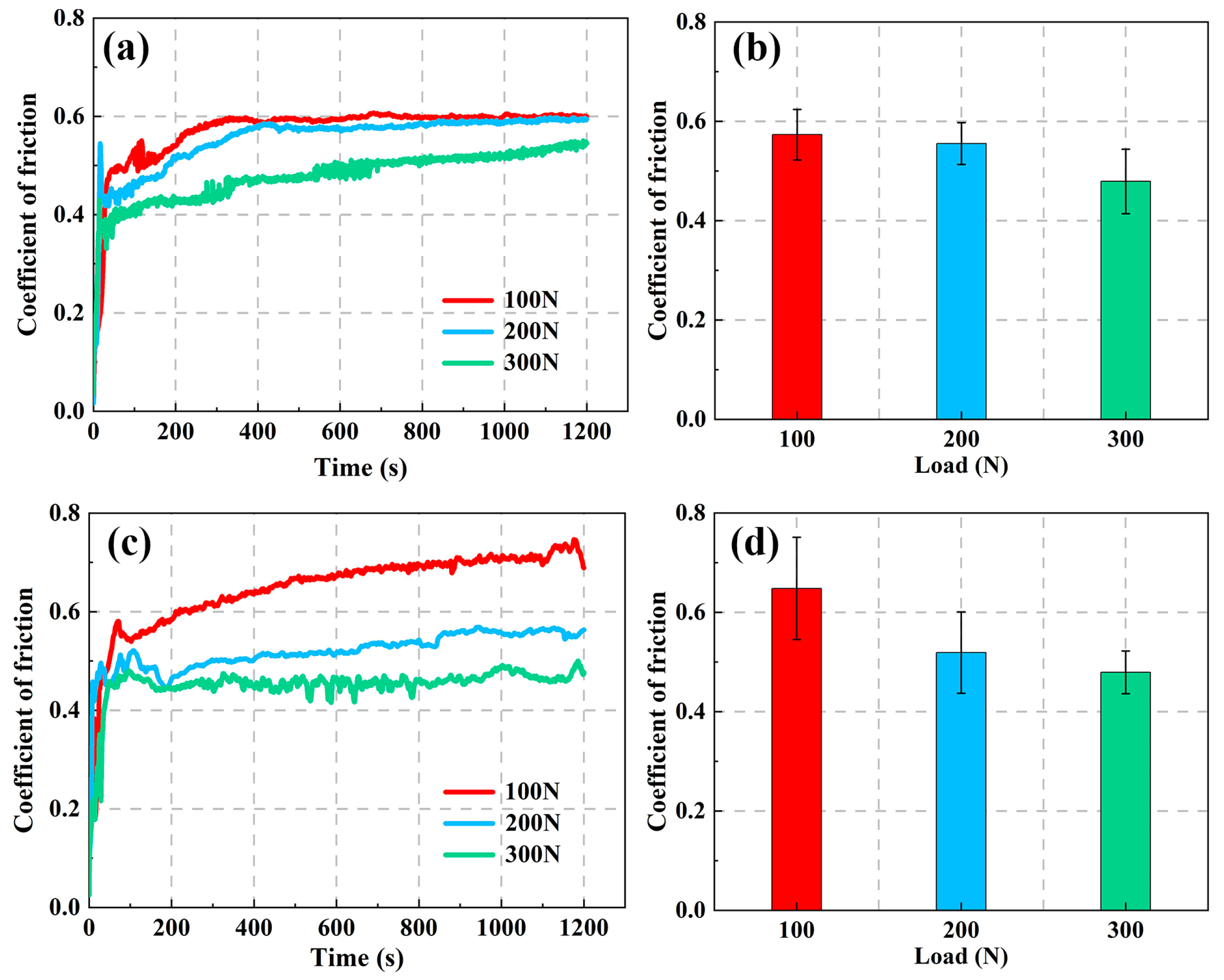
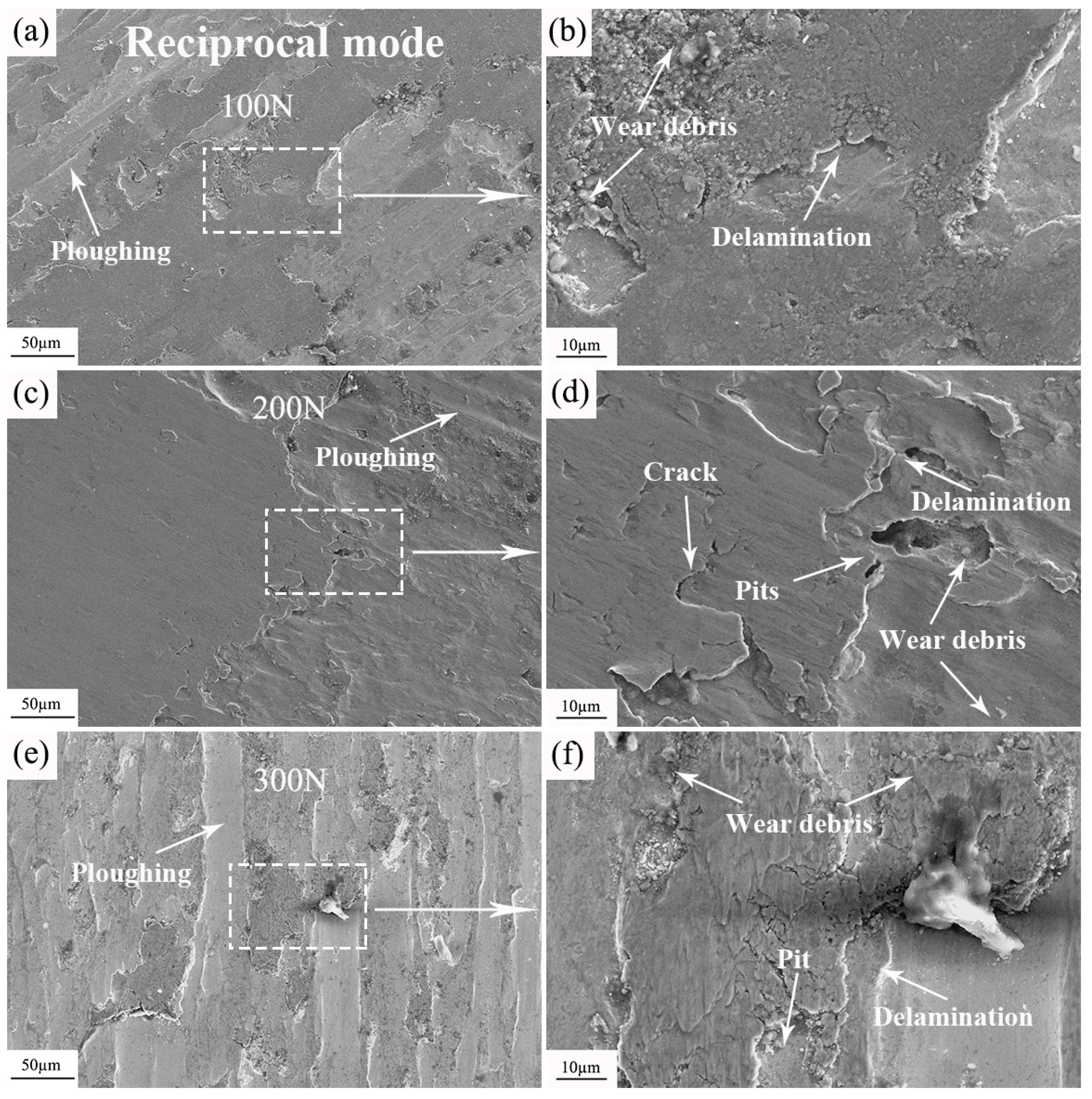
3.2.3. Wear Resistance Test
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The optimized HB400 exhibited finer grains, a uniform distribution of martensite laths, and a residual austenite content of only 0.5%. Additionally, higher-density dislocation loops were observed within the martensite laths.
- (2)
- In the mechanical property tests of HB400, the hardness met the standard requirements. The grain refinement and dislocation strengthening contributed to the improvement of tensile strength and yield strength.
- (3)
- Under loads ranging from 100 to 300 N, the wear resistance of HB400 increased with the increasing load. When the load reached 300 N, the growth of wear volume in HB400 slowed down, and the lubricating effect of the peeled oxide layer reduced wear, thereby enhancing the wear resistance of HB400 under high loads.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, X.J.; Xu, W.; Ederveen, F.H.; Zwaag, S.V. Design of low hardness abrasion resistant steels. Wear 2013, 301, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendón, J.; Olsson, M. Abrasive wear resistance of some commercial abrasion resistant steels evaluated by laboratory test methods. Wear 2009, 267, 2055–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muley, A.V. Wear and friction (Tribological) characteristic of aluminum based metal matrix hybrid composite: An overview. Mat. Today Proc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiko, O.; Somani, M.; Porter, D.; Kantanen, P.; Kömi, J.; Ojala, N.; Heino, V. Comparison of impact-abrasive wear characteristics and performance of direct quenched (DQ) and direct quenched and partitioned (DQ&P) steels. Wear 2018, 400–401, 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Haiko, O.; Valtonen, K.; Kaijalainen, A.; Uusikallio, S.; Hannula, J.; Liimatainen, T.; Kömi, J. Effect of tempering on the impact-abrasive and abrasive wear resistance of ultra-high strength steels. Wear 2019, 440–441, 203098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valtonen, K.; Ojala, N.; Haiko, O.; Kuokkala, V. Comparison of various high-stress wear conditions and wear performance of martensitic steels. Wear 2019, 426–427, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcagnotto, M.; Ponge, D.; Raabe, D. On the Effect of Manganese on Grain Size Stability and Hardenability in Ultrafine-Grained Ferrite/Martensite Dual-Phase Steels. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2012, 43, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiko, O.; Pallaspuro, S.; Javaheri, V.; Kaikkonen, P.; Ghosh, S.; Valtonen, K.; Kaijalainen, A.; Kömi, J. High-stress abrasive wear performance of medium-carbon direct-quenched and partitioned, carbide-free bainitic, and martensitic steels. Wear 2023, 526–527, 204925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.H.; Sun, Y.H.; Lin, Y.T.; Tu, J.F.; Yen, H.W. Mechanism of twinning induced plasticity in austenitic lightweight steel driven by compositional complexity. Acta Mater. 2021, 210, 116814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derazkola, H.A.; García Gil, E.; Murillo-Marrodán, A.; Méresse, D. Review on Dynamic Recrystallization of Martensitic Stainless Steels during Hot Deformation: Part I—Experimental Study. Metals 2021, 11, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derazkola, H.A.; Garcia, E.; Murillo-Marrodán, A.; Hardell, J. The effect of temperature and strain rate on the mechanical properties and microstructure of super Cr13 martensitic stainless steel. JMRT 2023, 24, 3464–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.L.; Wang, Z.; Gan, J.; Wang, X.L.; Yang, Y.; He, J.X.; Wei, T.T.; Qin, X.P. Numerical simulation of martensitic transformation plasticity of 42CrMo steel based on spot continual induction hardening model. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 385, 125428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coupard, D.; Palin-luc, T.; Bristiel, P.; Ji, V.; Dumas, C. Residual stresses in surface induction hardening of steels: Comparison between experiment and simulation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 487, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areitioaurtena, M.; Segurajauregi, U.; Fisk, M.; Cabello, M.J.; Ukar, E. Numerical and experimental investigation of residual stresses during the induction hardening of 42CrMo4 steel. Eur. Mech. J. A/Solids 2022, 96, 104766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathinasuriyan, C.; Karthik, K.; Udhayaraj, S.; Bishwakarma, S. Investigation of induction hardening on heat-treated EN8 steel by alternately timed quenching process. Mat. Today Proc. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.T.; Fu, T.L.; Wang, Z.D. Epsilon carbide precipitation and wear behaviour of low alloy wear resistant steels. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, A.J.; Miller, M.K.; Field, R.D.; Coughlin, D.R.; Gibbs, P.J.; Clarke, K.D.; Alexander, D.J.; Powers, K.A.; Papin, P.A.; Krauss, G. Atomic and nanoscale chemical and structural changes in quenched and tempered 4340 steel. Acta Mater. 2014, 77, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qiu, H.; Zhang, X.F.; Yu, H.L.; Yang, J.J.; Tu, X.H.; Li, W. Effects of (Ti, Mo) C particles on the abrasive wear-corrosion of low alloy martensitic steel. Wear 2022, 496–497, 204288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, J.; Das, K.; Das, S. An investigation of mechanical property and sliding wear behaviour of 400Hv grade martensitic steels. Wear 2020, 458–459, 203436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostryzhev, A.G.; Killmore, C.R.; Yu, D.; Pereloma, E.V. Martensitic wear resistant steels alloyed with titanium. Wear 2020, 446–447, 203203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.T.; Huang, L.; Wang, Q.; Fu, T.L.; Wang, Z.D. Three-body abrasion wear resistance of TiC-reinforced low-alloy abrasion-resistant martensitic steel under dry and wet sand conditions. Wear 2020, 452–453, 203310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.R.; Wang, W.; Liu, M.; Tian, J.Y.; Xu, G. Comparison of wear performance of bainitic and martensitic structure with similar fracture toughness and hardness at different wear conditions. Wear 2023, 512–513, 204512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shen, F.H.; Liu, H.Q.; Könemann, M.; Münstermann, S. Temperature-dependent deformation and fracture properties of low-carbon martensitic steel in different stress states. Mater. J. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 1931–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalácska, Á.; Baets, P.D.; Hamouda, H.B.; Theuwissen, K.; Sukumaran, J. Tribological investigation of abrasion resistant steels with martensitic and retained austenitic microstructure in single- and multi–asperity contact. Wear 2021, 482–483, 203980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.C.; Hu, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W. Obtaining superior low-temperature wear resistance in Q&P-processed medium Mn steel with a low initial hardness. Tribol. Int. 2022, 175, 107803. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, Z.Z.; Song, R.B.; Ba, Q.N.; Feng, Y.F. Dimensionality wear analysis: Three-body impact abrasive wear behavior of a martensitic steel in comparison with Mn13Cr2. Wear 2018, 414–415, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pondicherry, K.; Fauconnier, D.; Baets, P.D. Synergism in multi-asperity abrasion-corrosion of martensitic and dual phase steels in three aqueous electrolytes. Wear 2020, 452–453, 203286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, G.; Ma, L. Friction and Wear Behavior of NM500 Wear-Resistant Steel in Different Environmental Media. Crystals 2023, 13, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeev, V.R.; Dwivedi, D.K.; Jain, S.C. Effect of load and reciprocating velocity on the transition from mild to severe wear behavior of Al–Si–SiCp composites in reciprocating conditions. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 4951–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.H.; Ji, P.F.; Li, B.; Zhang, G.F.; Ma, W.; Wang, F.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ma, M.Z.; Liu, R.P. Effect of loading on microstructure and friction and wear behavior of an austenite lightweight steel. Tribol. Int. 2023, 177, 108006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.A.; Chai, L.J.; Yang, T.; Wang, H.; Shen, J.; Guo, N.; Yin, X.; Xiao, J. Laser-clad FeCrAl/TiC composite coating on ferrite/martensitic steel: Significant grain refinement and wear resistance enhancement induced by adding TiSurf, C. Coat. Technol. 2023, 456, 129272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.H.; Li, J.C.; Zhang, R.F.; Li, H.Y.; Li, J.; Ma, L.F. Wear behavior of copper containing antibacterial stainless steel in different environmental media and EBSD analysis of its sub surface structure. Mater. Charact. 2023, 197, 112690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussa, A.; Krakhmalev, P.; Bergström, J. Wear mechanisms and wear resistance of austempered ductile iron in reciprocal sliding contact. Wear 2022, 498–499, 204305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Yuan, X.M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.L. Wear properties and application of hot-rolled medium manganese steel. JCCS 2019, 47, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.L.; Yang, X.F.; Song, F.; Wu, M.; Zhu, Y.Q.; Wang, Z.Y. Anti-friction and wear resistance analysis of cemented carbide coatings. IJAMT 2022, 122, 2795–2821. [Google Scholar]
- Kennett, S.C.; Krauss, G.; Findley, K.O. Prior austenite grain size and tempering effects on the dislocation density of low-C Nb-Ti microalloyed lath martensite. Scr. Mater. 2015, 107, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.H.; Yang, G.W.; Zhao, G.; Mao, X.P.; Gan, X.L.; Yin, Q.L.; Yi, H. Effect of Nb on the microstructure and properties of Ti-Mo microalloyed high-strength ferritic steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 736, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gündüz, S.; Kaçar, R.; Soykan, H.Ş. Wear behaviour of forging steels with different microstructure during dry sliding. Tribol. Int. 2008, 41, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, G.; Han, Z.; Lu, K. Grain size effect on wear resistance of a nanostructured AISI52100 steel. Scr. Mater. 2008, 58, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabarro, F.R.N.; Basinski, Z.S.; Holt, D.B. The plasticity of pure single crystals. Adv. Phys. 1964, 13, 193–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.Y.; Yang, G.W.; Fu, Z.X.; Xu, D.M.; Xu, Y.W.; Zhao, G. Effect of low-temperature hot rolling on the microstructure and mechanical properties of air-cooling medium manganese martensitic wear-resistant steel. Mater. Charact. 2023, 203, 113139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.S.; Chen, J.; Tu, X.Y.; Han, Y.H. Effect of finish rolling temperature on microstructures and mechanical properties of 1000 MPa grade tempered steel plate for hydropower station. Manuf. J. Process. 2021, 67, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, N.P. An overview of the delamination theory of WEAR. Wear 1977, 44, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Element | Fe | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | B | Cu | Mo | Ni | Ti | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardox400 | Bal. | 0.18 | 0.7 | 1.6 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 1.0 | 0.004 | 0.25 | 0.25 | |||
| HB400 | Bal. | 0.21 | 0.35 | 1.32 | 0.017 | 0.008 | 0.61 | 0.002 | 0.022 | 0.016 | 0.039 |
| Mode | Load (N) | Stroke/Diameter (mm) | Frequency (Hz)/ Rate (r/min) | Time/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reciprocal | 100/200/300 | 10 | 1 | 1200 |
| Rotation | 100/200/300 | 10 | 200 | 1200 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, S.; Zhang, S.; Lin, J.; Zhu, X.; Li, S.; Sun, Y.; Xia, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, C. Study on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Martensitic Wear-Resistant Steel. Crystals 2023, 13, 1210. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13081210
Jiang S, Zhang S, Lin J, Zhu X, Li S, Sun Y, Xia Y, Liu W, Wang C. Study on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Martensitic Wear-Resistant Steel. Crystals. 2023; 13(8):1210. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13081210
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Shaoning, Shoushuai Zhang, Jianghai Lin, Xiaoyu Zhu, Sensen Li, Yu Sun, Yuhai Xia, Wenjun Liu, and Chaofeng Wang. 2023. "Study on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Martensitic Wear-Resistant Steel" Crystals 13, no. 8: 1210. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13081210
APA StyleJiang, S., Zhang, S., Lin, J., Zhu, X., Li, S., Sun, Y., Xia, Y., Liu, W., & Wang, C. (2023). Study on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Martensitic Wear-Resistant Steel. Crystals, 13(8), 1210. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13081210





