Research Progress of Organic Corrosion Inhibitors in Metal Corrosion Protection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Classification of OCIs
2.1. Alkyl Chain CIs
| No. | Name | Molecular Structure | Metal/Corrosive Medium | Inhibitor Type/Adsorption Isotherm | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cetrimonium 4 hydroxy cinnamate (CTA-4OHcinn) |  | Aluminum/0.01 M NaCl solution with 6.5% ethanol | Mixed type/- | [14] |
| 2 | Cetrimonium 4 ethoxy cinnamate (CTA-4EtOcin) | 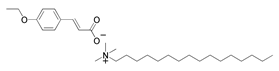 | |||
| 3 | Bis[2-hydroxy-3-(dodecyldimethylammonio) propyl]-isopropylamine dichloride |  | 2024 Al-Cu-Mg alloy/1 M HCl | Mixed type/Langmuir | [18] |
| 4 | Bis[2-amido-3-(dodecyldimethylammonium) propyl]-propylamine dichloride | 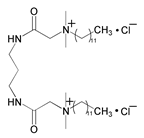 | 2024 Al-Cu-Mg alloy/1 M HCl | Mixed type/Langmuir | [19] |
| 5 | Hexanediyl-1,6-bis-(diethyl alkyl ammonium bromide) (CmC6Cm(Et)·2Br (m = 10, 12, 14, 16)) | 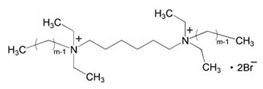 | Aluminum/1 M HCl | -/Langmuir | [20] |
| 6 | 1,3-butan-bis-(dimethyl dodecyl ammonium bromide) | 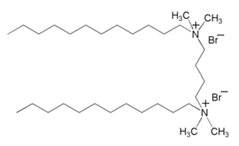 | Mild Steel/1 M HCl | -/- | [21] |
| 7 | Decyltriphenylphosphonium bromide | 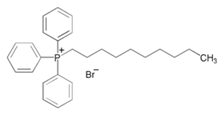 | Mild Steel/0.5 M H2SO4 | Mixed type/Langmuir | [22] |
| 8 | Methylamine-N,N-bis(methylenephosphonate) | 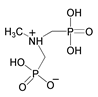 | C1010 carbon steel/3.5% NaCl solution (pH = 3) | Mixed type/Langmuir | [23] |
| 9 | Ehtylamine-N,N-bis(methylenephosphonate) | 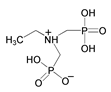 | |||
| 10 | Butylamine-N,N-bis(methylenephosphonate) | 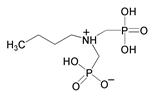 | |||
| 11 | Hexylamine-N,N-bis(methylenephosphonate) | 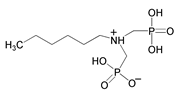 | |||
| 12 | Octylamine-N,N-bis(methylenephosphonate) | 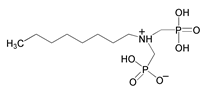 | |||
| 13 | Dodecylamine-N,N-bis(methylenephosphonate) | 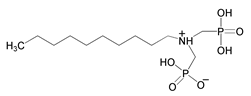 | |||
| 14 | 1,4-bis(dodecy dipropyl ammonium bromide)-butane | 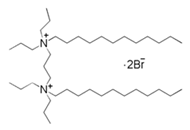 | Copper/3.5% NaCl | mixed type/Langmuir | [24] |
2.2. Imidazole and Its Derivatives
| No. | Name | Molecular Structure | Metal/Corrosive Medium | Inhibitor Type/Adsorption Isotherm | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Dissymmetric bis-quaternary ammonium salt (DBAS) |  | Q235 steel/2% NaCl solution saturated with CO2 | Mixed type/- | [30] |
| 2 | sodium 2-(1Himidazol-1-yl)-4-methylpentanoate (IZS-L) |  | Mild steel/Artificial seawater | Mixed type/Langmuir | [31] |
| 3 | sodium 2-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-3-phenyl propanoate (IZS-P) | 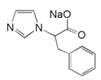 | |||
| 4 | sodium 2-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-4-(methylthio)butanoate (IZS-M) | 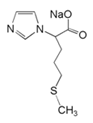 | |||
| 5 | Lauric acid/Myristic acid/Palmitic acid/Stearic acid based cationic Gemini imidazoline surfactants | 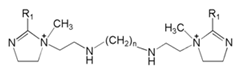 | X70 carbon steel/3.5% M NaCl solution | Mixed type/- | [32] |
| 6 | 1-hexyl-5-methyl-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazlol-1-ium bromide (HBT) | 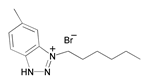 | Copper electrodes/seawater | Mixed type/Langmuir | [33] |
| 7 | 1-dodecyl-5-methyl-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazlol-1-ium bromide (DBT) |  | |||
| 8 | 1-octadecyl-5-methyl-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazlol-1-ium bromide (OBT) | 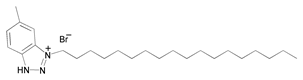 | |||
| 9 | 1-(2-aminobutyl)-2-ethyl]-1,3-diazacyclopenta-2,4-diene ionic liquid | 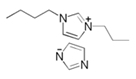 | API 5L-X52 steel/3% of NaCl saturated with CO2 | Mixed type/Langmuir | [34] |
| 10 | (E)-2-styryl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole (STBim) | 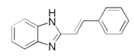 | carbon steel/15% HCl | Mixed type/Langmuir | [35] |
2.3. Pyridine and Its Derivatives CIs
| No. | Name | Molecular Structure | Metal/Corrosive Medium | Inhibitor Type/Adsorption Isotherm | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tetradecylpyridinium bromide |  | Aluminum/1.0 M HCl | Cathodic/Langmuir | [38] |
| 2 | Hexadecylpyridinium Bromide (HPyBr) |  | Mild steel/0.5 M H2SO4 | Mixed type/Langmuir | [39] |
| 3 | Hexadecylpyridinium Chloride (HPyCl) | 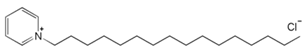 | |||
| 4 | 2-amino-6-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-4-phenylnicotinonitrile | 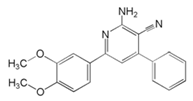 | Carbon steel/6 M H2SO4 | Mixed type/Langmuir | [40] |
| 5 | 2-amino-4-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-6-phenylnicotinonitrile | 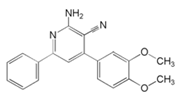 | |||
| 6 | N-alkyl-4-(4-hydroxybut-2-ynyl) pyridinium bromides | 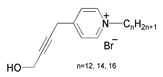 | X70 steel/5 M HCl | Mixed type/Langmuir | [41] |
| 7 | 4-(4-Methoyphenyl) 3,5-dimethyl-1,4,7,8-tetrahydrodipyrazolopyridine) |  | Mild steel/1 M HCl | Mixed type/Langmuir | |
| 8 | 3,5dimethyl-4-phenyl-1,4,7,8-tetrahydrodipyrazolopyridine | 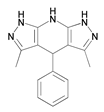 | [42] | ||
| 9 | 3,5-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4,7,8-tetrahyddrodipyrazolopyridine) | 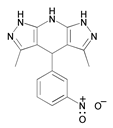 | |||
| 10 | 2-phenyl-5-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole (POX) | 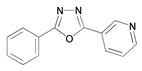 | Mild steel/1 M HCl | Mixed type/Langmuir | [43] |
| 11 | 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole (4-PMOX) | 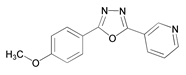 | |||
| 12 | 2-Amino-4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-6-phenylnicotinonitrile (AMP) | 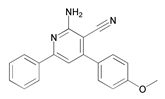 | N80 steel/15% HCl | Mixed type/Langmuir | [44] |
| 13 | 2-Amino-6-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-4-(4-methoxyphenyl)nicotinonitrile (ADP) | 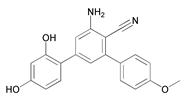 |
2.4. Quinoline and Its Derivatives
| No. | Name | Molecular Structure | Metal/Corrosive Medium | Inhibitor Type/Adsorption Isotherm | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8-hydroxyquinoline | 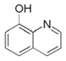 | X60 steel/15% HCl | Mixed type/- | [45] |
| 2 | 2-1-methyl-quinoline-nonyl |  | X80 pipeline steel/NACE solution (CO2 environment) | Cathodic/- | [46] |
| 3 | 2-chloro-3-formyl quinoline |  | Mild steel/1 M HCl | Mixed type/Freundlich | [47] |
| 4 | 8-hydroxyquinoline grafted triazole derivatives | 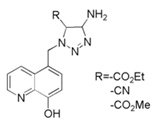 | Carbon steel/0.5 M H2SO4 | Mixed type/Langmuir | [48] |
| 5 | 4-chloro,8-(trifluoromethyl)quinoline (CTQ) | 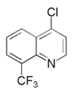 | Mild steel/1 M HCl | Mixed type/Langmuir | [49] |
| 6 | 2-(quinolin-2-yl)quinazolin-4(3H)-one |  | Q235 steel/1 M HCl | Mixed type/Langmuir | [50] |
| 7 | 3-((8-hydroxyquinolin-5-yl)-methyl)-2-phenylquinazolin-4(3H)-one (HQ-ZH) | 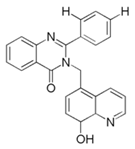 | Mild steel/1 M HCl | Mixed type/Langmuir | [51] |
| 8 | 2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-((8-hydroxyquinolin-5-yl)-methyl)-quinazolin-4(3H)-one (HQZOH) | 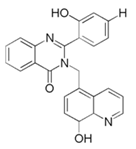 | |||
| 9 | 3-((8-hydroxyquinliene-5-yl)-2-(4-nitrophenyl)-quinazolin-4(3H)-one (HQ-ZNO2) | 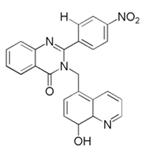 |
2.5. Natural Products
| Name | Molecular Structure | Metal/Corrosive Medium | Inhibitor Type/Adsorption Isotherm | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rhamnolipid-1 | 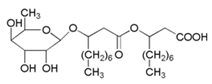 | X70 carbon steel/Simulated seawater | Mixed type/- | [3] |
| Rhamnolipid-2 |  | |||
| Caffeic acid (Caf) | 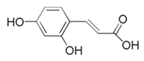 | Mg alloy AZ91D/3.5 wt% NaCl | Mixed type/- | [52] |
| Chichoric acid (Chi) | 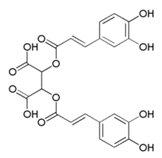 | |||
| 2-(3,4-Dihydroxy-phenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-chromen-4-one (DPT) | 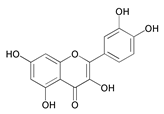 | Q235 steel/1M HCl | Mixed type/Langmuir | [53] |
| 6,7-Dimethoxy-2-(4-methoxy-phenyl)-chromen-4-one (DMP) | 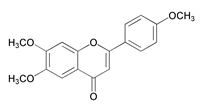 | |||
| 3-(3-Hydroxy-4-methoxy-phenyl)-6,8-dimethoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-naphthalen-2-ol (HMP) |  | |||
| 5,7-Dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-3-methyl-chroman-4-one (DHP) | 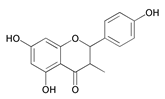 | |||
| Phenyl alanine |  | Mg-Al-Zn alloy/chloride-free neutral aqueous buffer solution | Anodic/Langmuir | [55] |
| A representation of Elaeis guineensis oil | 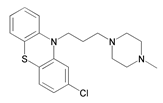 | AA6063 Al-Mg-Si alloy/3.5% NaCl | Mixed type/Langmuir | [56] |
| Chlorogenic acid |  | A36 mild steel/1M HCl | Mixed type/Langmuir | [58] |
| Vanillic acid |  | |||
| Scopoletin |  | |||
| Trans-1,4-polyisoprene (TPI) | 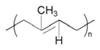 | Q235 steel/3.5 wt% NaCl | -/- | [59] |
| Poly(citric acid-curcumin) (Cur-PCA) |  | 3105 aluminum alloy/1 mol/L HCl prepared using 3.5% NaCl solution | Mixed type/El-Awady | [60] |
| Bisabolol | 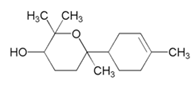 | Aluminum/3.5 wt% NaCl | Mixed type/Freundlich | [61] |
| Camphene |  | |||
| Cineole | 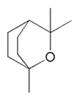 |
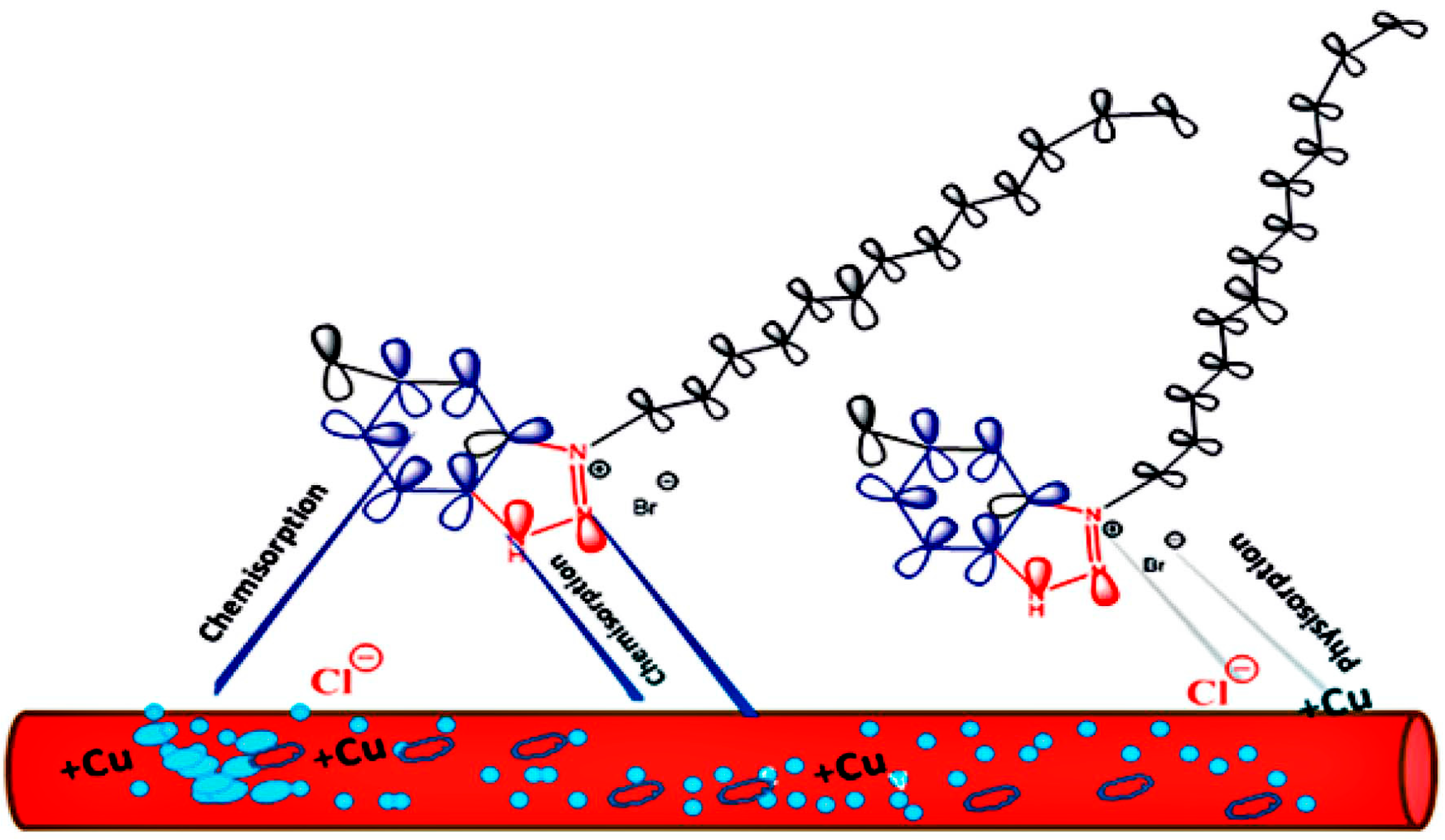
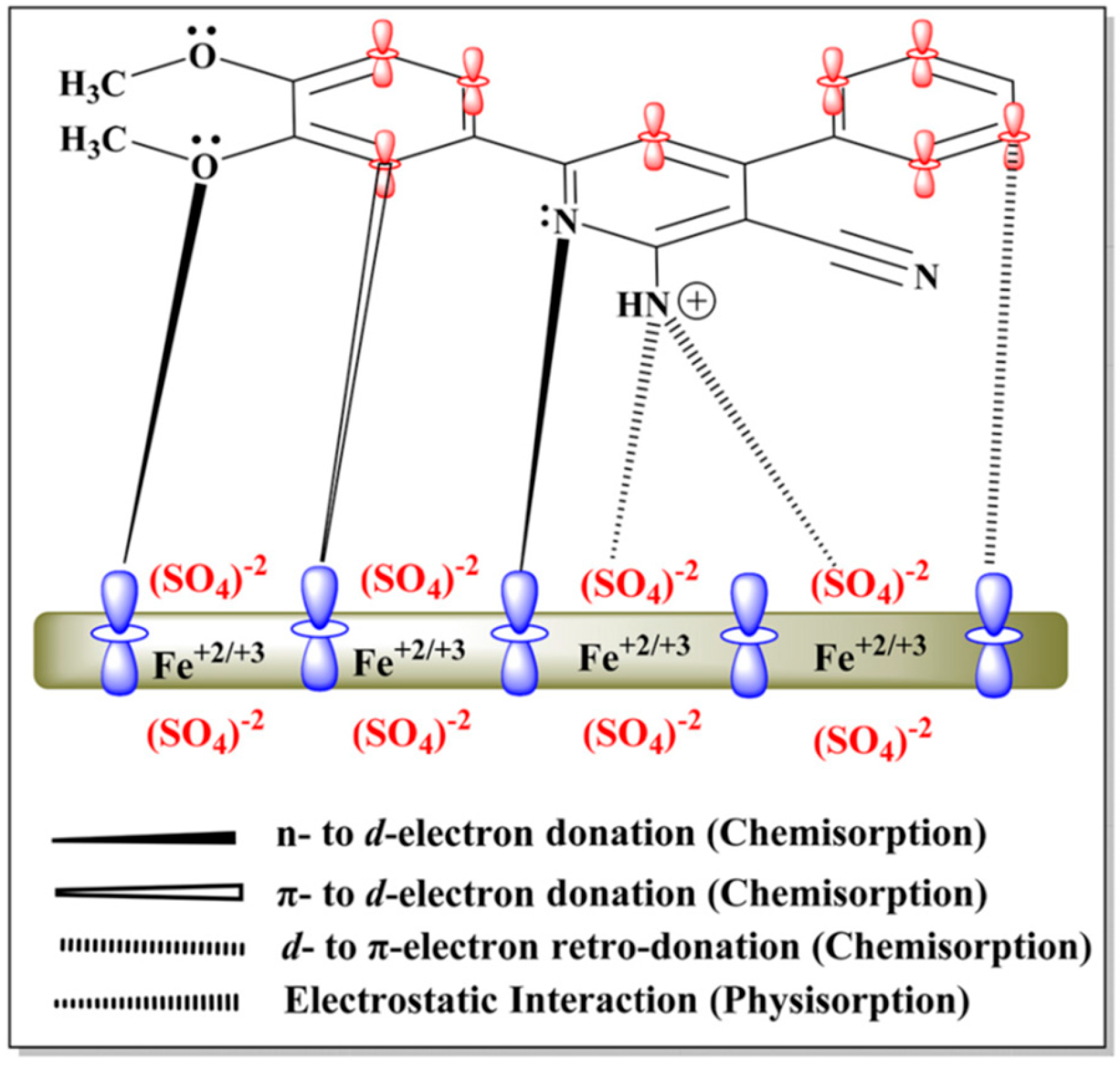
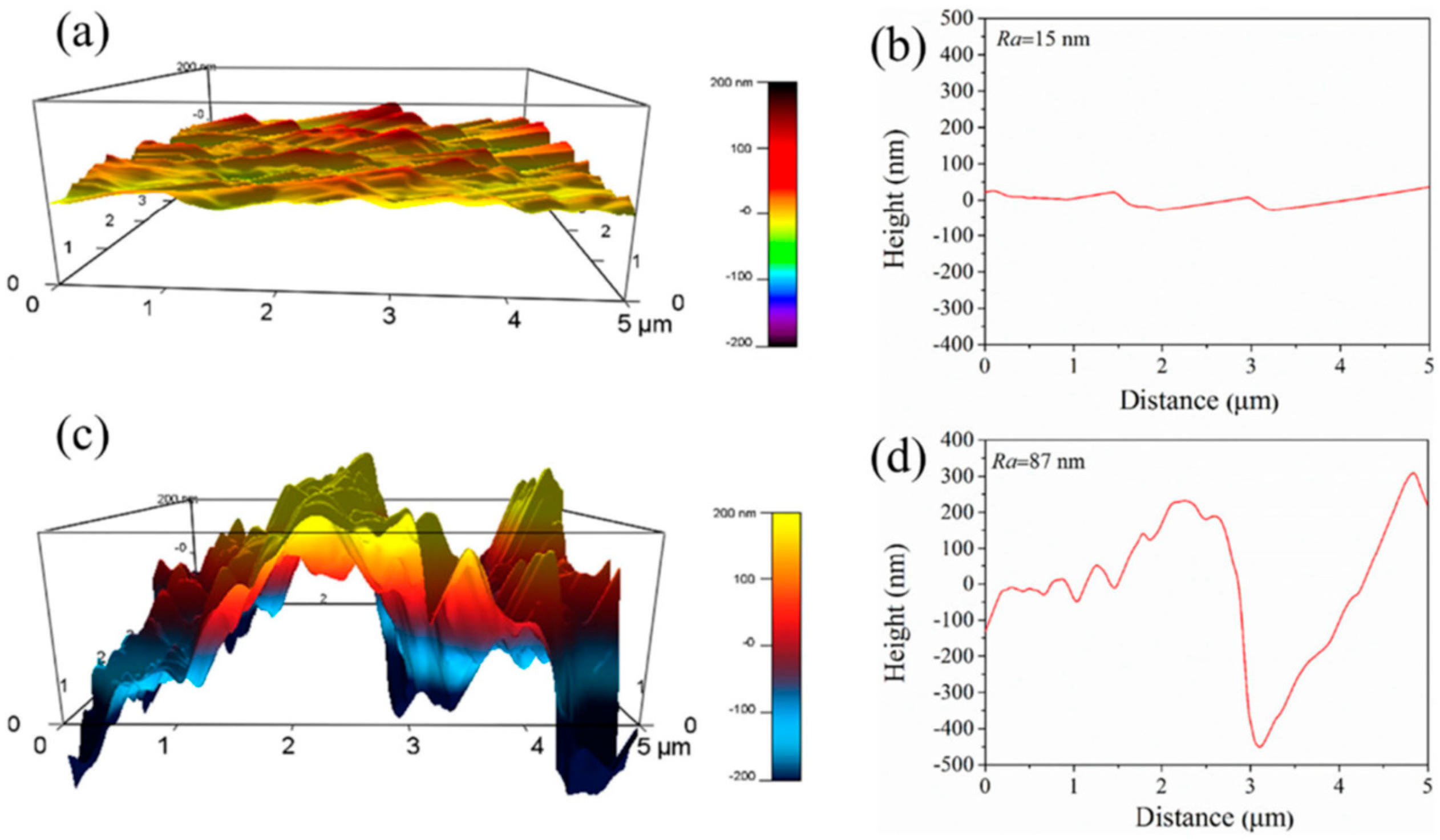
3. Mechanism of OCIs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, C. Introduction to metal corrosion priciple and protection. Total Corros. Control 2019, 33, 18–20. [Google Scholar]
- Sabel, C.F.; Victor, D.G. Governing global problems under uncertainty: Making bottom-up climate policy work. Clim. Chang. 2015, 144, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yuan, X.; Sun, M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, D.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, M.; Fan, Y.; Xu, D.; Wang, F. Rhamnolipid as an eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor for microbiologically influenced corrosion. Corros. Sci. 2022, 204, 110390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A. A review of green corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in seawater. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2016, 11, 8710–8714. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, M.; Zhang, X. Research progress on corrosion inhibitor for hydrochloric acis pickling of carbon steel. Guangzhou Chem. Ind. 2020, 48, 20–21+57. [Google Scholar]
- Raja, P.B.; Sethuraman, M.G. Inhibitive effect of black pepper extract on the sulphuric acid corrosion of mild steel. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 2977–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gu, W.; Guo, R.; Fu, W. Inhibition effect of environmental protection inorganic corrosion inhibitor on AZ91D magnesium alloy. Plat. Finish. 2020, 42, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W. Synthesis of Acridines Inhibitors and Study on Its Corrosion Inhibition Performance of Carbon Steel. Ph.D. Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Quraishi, M.A.; Chauhan, D.S.; Ansari, F.A. Development of environmentally benign corrosion inhibitors for organic acid environments for oil-gas industry. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 329, 115514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Seyeux, A.; Zanna, S.; Pailleret, A.; Nesic, S.; Marcus, P. Adsorption mechanism of quaternary ammonium corrosion inhibitor on carbon steel surface using ToF-SIMS and XPS. Corros. Sci. 2023, 213, 110952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Lin, Y.; Guo, T.; Wen, R.; Yu, Q.; Wang, C.; Tu, Y.; Sas, G.; Elfgren, L. The adsorption of two organic inhibitors on stainless steel passive film: A reactive force field study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 607, 154965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, W.; Gong, M.; Yin, L. Experimental and theoretical studies of two imidazolium-based ionic liquids as inhibitors for mild steel in sulfuric acid solution. Corros. Sci. 2015, 95, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negm, N.A.; El Hashash, M.A.; Abd-Elaal, A.; Tawfik, S.M.; Gharieb, A. Amide type nonionic surfactants: Synthesis and corrosion inhibition evaluation against carbon steel corrosion in acidic medium. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 256, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, M.; Puelles, J.S.; Forsyth, M.; Zhu, H.; Crawford, S.; Chen, F.; Cáceres-Vélez, P.R.; Jusuf, P.R.; Somers, A. Engineering advanced environmentally friendly corrosion inhibitors, their mechanisms, and biological effects in live Zebrafish embryos. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 2960–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, Y.I. Triazoles as a class of multifunctional corrosion inhibitors. A review. Part I. 1,2,3-Benzotriazole and its derivatives. Copper, zinc and their alloys. Int. J. Corros. Scale Inhib. 2018, 7, 271–307. [Google Scholar]
- Labena, A.; Hegazy, M.A.; Sami, R.M.; Hozzein, W.N. Multiple applications of a novel cationic Gemini surfactant: Anti-microbial, anti-biofilm, biocide, salinity corrosion inhibitor, and biofilm dispersion (Part II). Molecules 2020, 25, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.-H.; Wu, S.-B.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.-Q.; Sun, Y.-H.; Zhu, R.-K.; Luo, J.-L. Hydrogen-enhanced surface reactivity of X80 pipeline steel observed by scanning electrochemical microscopy. Electrochemistry 2016, 84, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Q.; Hu, X. Synthesis of a novel Gemini cationic surfactant and its inhibition behaviour and mechanism study on 2024 Al-Cu-Mg alloy in acid solution. Int. J. Corros. 2018, 2018, 9890504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, D.; Shuai, J.; Fan, Y.; Ziming, W.; Haipeng, S.; Xudong, Y.; Fusheng, W. The preparation of a novel corrosion inhibitor and its corrosion inhibition behavior on 2024 Al-Cu-Mg alloy in acid solution. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2019, 22, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Gao, Z.; Xu, F.; Zou, X. Adsorption and corrosion inhibitive properties of gemini surfactants in the series of hexanediyl-1,6-bis-(diethyl alkyl ammonium bromide) on aluminium in hydrochloric acid solution. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 380, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asefi, D.; Arami, M.; Mahmoodi, N.M. Electrochemical effect of cationic gemini surfactant and halide salts on corrosion inhibition of low carbon steel in acid medium. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, M.; Vashisht, H.; Hamed Alrefaee, S.; Jain, R.; Kumar, S.; Kaya, S.; Guo, L.; Verma, C. Decyltriphenylphosphonium bromide containing hydrophobic alkyl-chain as a potential corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in sulfuric acid: Theoretical and experimental studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 336, 116166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschona, A.; Plesu, N.; Colodrero, R.M.P.; Cabeza, A.; Thomas, A.G.; Demadis, K.D. Homologous alkyl side-chain diphosphonate inhibitors for the corrosion protection of carbon steels. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 405, 126864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Sun, H.; Zhao, X.; Hou, B. Investigation of novel gemini surfactant with long chain alkyl ammonium headgroups as corrosion inhibitor for copper in 3.5% NaCl. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2014, 9, 8106–8119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odewunmi, N.A.; Solomon, M.M.; Umoren, S.A.; Ali, S.A. Comparative studies of the corrosion inhibition efficacy of a dicationic monomer and its polymer against API X60 steel corrosion in simulated acidizing fluid under static and hydrodynamic conditions. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 27057–27071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Jia, H.; Wang, Q.; Yan, H.; Wei, Z.; Wen, X.; Wang, Q.; Fan, F.; Wen, S.; Huang, P.; et al. Experimental and theoretical studies of the corrosion inhibition performance of fatty acid-based Iionic liquids for mild steel in 1 M HCl: Effects of the varied alkyl chain length in the anionic group. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 17151–17166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Jia, H.; Song, L.; Qin, X.; Fan, F.; Li, Z.; Huang, P. Investigation of anionic group effects on the shale inhibition performance of fatty acid-based ionic liquids and their inhibition mechanism. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 636, 128135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, J.; Aslam, R.; Verma, C. Imidazole and its derivatives as corrosion inhibitors. In Organic Corrosion Inhibitors: Synthesis, Characterization, Mechanism, and Applications; Wiely: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 95–122. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.P.; Wu, Q.; Li, C.M.; Gu, N. Copper corrosion inhibition by polyaspartic acid and imidazole. Mater. Corros. 2013, 64, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shi, D.; Gong, X.; Zhu, F.; Du, M. Inhibition performance of novel dissymmetric bisquaternary ammonium salt with an imidazoline ring and an ester group. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2013, 16, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, J.; Zulkifli, M.F.R.; Ismail, N.; Quraishi, M.A.; Mohd Ghazali, M.S.; Berdimurodov, E.; Wan Nik, W.M.N.B. Environmentally benign water-soluble sodium L-2-(1-imidazolyl) alkanoic acids as new corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in artificial seawater. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 24797–24812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, W.; Wang, X.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, D.; Zhang, R.; Wu, C. Imidazoline Gemini surfactants as corrosion inhibitors for carbon ateel X70 in NaCl aolution. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 5653–5660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migahed, M.A.; Nasser, A.; Elfeky, H.; El-Rabiei, M.M. The synthesis and characterization of benzotriazole-based cationic surfactants and the evaluation of their corrosion inhibition efficiency on copper in seawater. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 27069–27082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ontiveros-Rosales, M.; Espinoza-Vázquez, A.; Gómez, F.J.R.; Valdez-Rodríguez, S.; Miralrio, A.; Acosta-Garcia, B.A.; Castro, M. Imidazolate of 1-butyl-3-ethyl imidazole as corrosion inhibitor on API 5L X52 steel in NaCl saturated with CO2. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 363, 119826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, V.; Salman, M.; Chauhan, D.S.; Abdel-Azeim, S.; Quraishi, M.A. (E)-2-styryl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole as novel green corrosion inhibitor for carbon steel: Experimental and computational approach. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 324, 115010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguzzi, G.; Luvidi, L. Evaluation of the anticorrosive properties of benzotriazole alkyl derivatives on 6% Sn bronze alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 2442–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrebh, A.; Rammal, M.B.; Omanovic, S. A pyridine derivative 2-(2-Methylaminoethyl)pyridine (MAEP) as a ‘green’ corrosion inhibitor for low-carbon steel in hydrochloric acid media. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1238, 130333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Deng, S.; Fu, H. Inhibition by tetradecylpyridinium bromide of the corrosion of aluminium in hydrochloric acid solution. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 1529–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.M.; Mahmoud, M.G.; El-Lateef, H.M.A. Comparative study of synergistic inhibition of mild steel and pure iron by 1-hexadecylpyridinium chloride and bromide ions. Corros. Sci. 2019, 154, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, A.A.; Mohamed, E.A.; Sayed, G.H.; Anwer, K.E. Experimental/computational assessments of API steel in 6 M H2SO4 medium containing novel pyridine derivatives as corrosion inhibitors. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 330, 115705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, S.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, L.; Duan, M.; Wang, H.; Jiang, X. Synthesis of N-alkyl-4-(4-hydroxybut-2-ynyl) pyridinium bromides and their corrosion inhibition activities on X70 steel in 5 M HCl. Corros. Sci. 2012, 65, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohare, P.; Quraishi, M.A.; Verma, C.; Lgaz, H.; Salghi, R.; Ebenso, E.E. Ultrasound induced green synthesis of pyrazolo-pyridines as novel corrosion inhibitors useful for industrial pickling process: Experimental and theoretical approach. Results Phys. 2019, 13, 102344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Thakur, A.; Sharma, M.K.; Sharma, R.; Kumar, S.; Sihmar, A.; Dahiya, H.; Jhaa, G.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, A.K.; et al. Effective corrosion inhibition of mild steel using novel 1,3,4-oxadiazole-pyridine hybrids: Synthesis, electrochemical, morphological, and computational insights. Environ. Res. 2023, 234, 116555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, K.R.; Quraishi, M.A.; Singh, A. Pyridine derivatives as corrosion inhibitors for N80 steel in 15% HCl: Electrochemical, surface and quantum chemical studies. Measurement 2015, 76, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obot, I.B.; Ankah, N.K.; Sorour, A.A.; Gasem, Z.M.; Haruna, K. 8-Hydroxyquinoline as an alternative green and sustainable acidizing oilfield corrosion inhibitor. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2017, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.R.; Zhang, D.L.; Wang, J.J.; Jin, Y.H. Effect of a new quinoline inhibitor on corrosion of X80 pipeline steel. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 644–650, 5273–5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, B.M.; Praveen, B.M.; Hebbar, N.; Venkatesha, T.V.; Tandon, H.C. Inhibition study of mild steel corrosion in 1 M hydrochloric acid solution by 2-chloro 3-formyl quinoline. Int. J. Ind. Chem. 2015, 7, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouifi, Z.; Benhiba, F.; El Faydy, M.; Laabaissi, T.; Oudda, H.; Lakhrissi, B.; Guenbour, A.; Warad, I.; Zarrouk, A. 8-hydroxyquinoline grafted triazole derivatives as corrosion inhibitors for carbon steel in H2SO4 solution: Electrochemical and theoretical studies. Ionics 2021, 27, 2267–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebbar, N.; Praveen, B.M.; Prasanna, B.M.; Vishwanath, P. Electrochemical and adsorption studies of 4-Chloro,8-(trifluoromethyl)quinoline (CTQ) for mild steel in acidic medium. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 2020, 20, 1516–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ma, R.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Niu, L. Electrochemical and surface analysis studies of 2-(quinolin-2-yl)quinazolin-4(3H)-one as corrosion inhibitor for Q235 steel in hydrochloric acid. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 222, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rbaa, M.; Galai, M.; Benhiba, F.; Obot, I.B.; Oudda, H.; Touhami, M.E.; Lakhrissi, B.; Zarrouk, A. Synthesis and investigation of quinazoline derivatives based on 8-hydroxyquinoline as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in acidic environment: Experimental and theoretical studies. Ionics 2018, 25, 3473–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
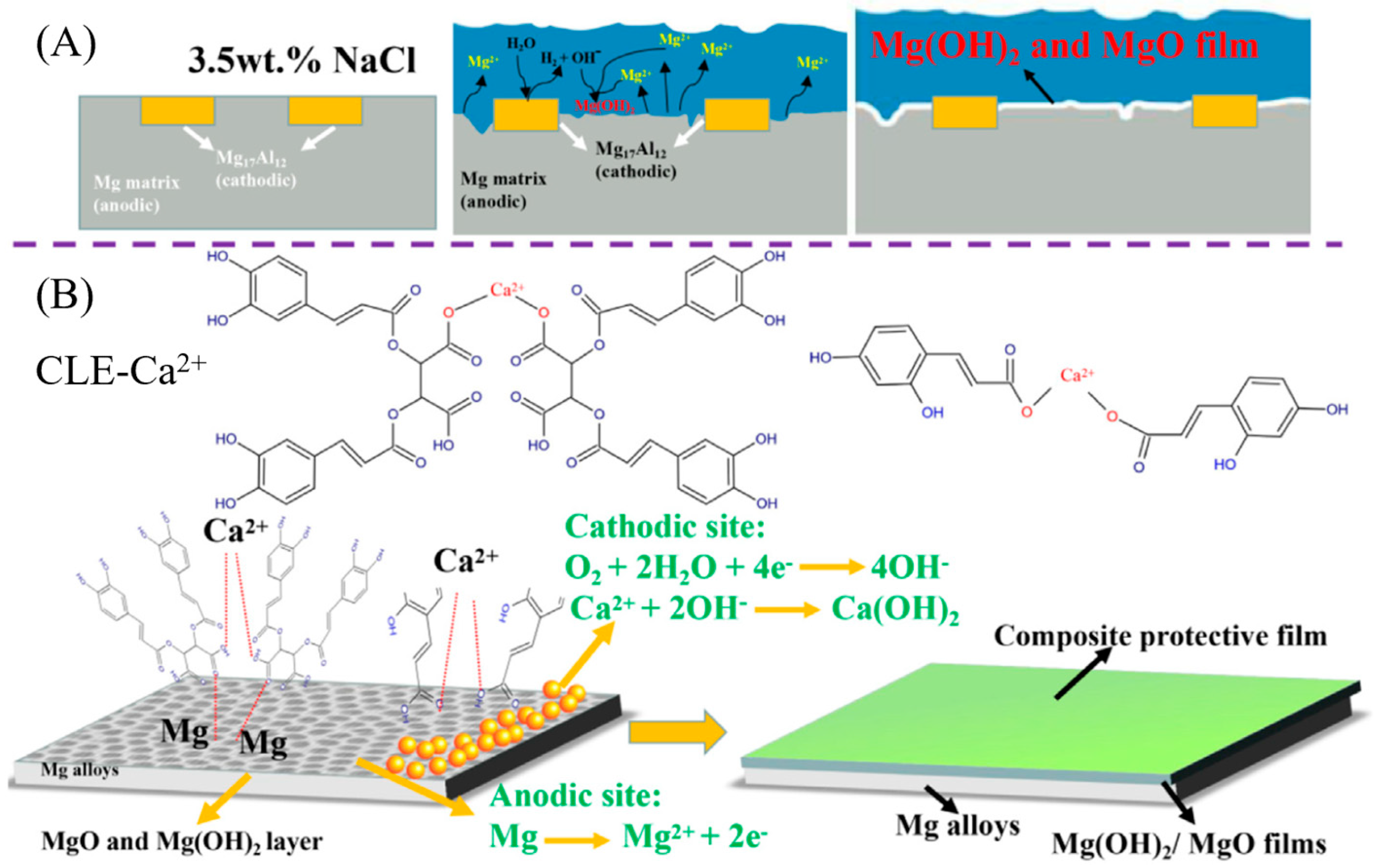
- Li, P.; Shao, Z.; Fu, W.; Ma, W.; Yang, K.; Zhou, H.; Gao, M. Enhancing corrosion resistance of magnesium alloys via combining green chicory extracts and metal cations as organic-inorganic composite inhibitor. Corros. Commun. 2023, 9, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhao, H.; Chen, S.; Wen, P.; Wang, H.; Li, W. Camphor leaves extract as a neoteric and environment friendly inhibitor for Q235 steel in HCl medium: Combining experimental and theoretical researches. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 312, 113433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, M.E.H.N.; Ramezanzadeh, M.; Ramezanzadeh, B. Highly-effective/durable method of mild-steel corrosion mitigation in the chloride-based solution via fabrication of hybrid metal-organic film (MOF) generated between the active Trachyspermum ammi bio-molecules-divalent zinc cations. Corros. Sci. 2021, 184, 109383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helal, N.H.; Badawy, W.A. Environmentally safe corrosion inhibition of Mg–Al–Zn alloy in chloride free neutral solutions by amino acids. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 6581–6587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayomi, O.S.I.; Popoola, A.P.I. The inhibitory effect and adsorption mechanism of roasted Elaeis guineensis as green inhibitor on the corrosion processof extruded AA6063 Al-Mg-Si Alloy in Simulated Solution. Silicon 2014, 6, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, A.; Bahlakeh, G.; Ramezanzadeh, B. Green Eucalyptus leaf extract: A potent source of bio-active corrosion inhibitors for mild steel. Bioelectrochemistry 2019, 130, 107339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Hernandez, A.; Campechano-Lira, C.; Espinoza-Vázquez, A.; Ramírez-Cano, J.A.; Orozco-Cruz, R.; Galván-Martínez, R. Electrochemical and DFT theoretical evaluation of the Randia monantha Benth extract as an eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in 1 M HCl solution. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2023, 147, 104913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C. Trans-1,4-polyisoprene (TPI) Extracted from Eucommia bark as natural corrosion inhibitor for carbon steel in the simulated concrete pore solution. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2022, 17, 220615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Shao, H.; He, S.; Chen, Z.; Yang, W. Natural polycitric acid-curcumin for highly efficient corrosion inhibition of aluminum alloys. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 36, 106659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, H.A.; Anaee, R.A.; Khadom, A.A.; Ali, A.T.A.; Malik, A.H.; Kadhim, M.M. Experimental and theoretical assessments of the chamomile flower extract as a green corrosion inhibitor for aluminum in artificial seawater. Results Chem. 2023, 6, 101035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.; Olasunkanmi, L.O.; Ebenso, E.E.; Quraishi, M.A.; Obot, I.B. Adsorption behavior of glucosamine-based, pyrimidine-fused heterocycles as green corrosion inhibitors for mild steel: Experimental and theoretical studies. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 11598–11611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaei, Z.; Bahlakeh, G.; Ramezanzadeh, B.; Ramezanzadeh, M. Application of green molecules from Chicory aqueous extract for steel corrosion mitigation against chloride ions attack; the experimental examinations and electronic/atomic level computational studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 290, 111176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Gao, Y.; Miao, W. The inhibition mechanism of organic inhibitor on metal surface. Total Corros. Control 2005, 19, 25–28. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, W.; Li, F.; Lv, X.; Chang, J.; Shen, S.; Dai, P.; Xia, Y.; Cao, Z. Research Progress of Organic Corrosion Inhibitors in Metal Corrosion Protection. Crystals 2023, 13, 1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13091329
Zhao W, Li F, Lv X, Chang J, Shen S, Dai P, Xia Y, Cao Z. Research Progress of Organic Corrosion Inhibitors in Metal Corrosion Protection. Crystals. 2023; 13(9):1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13091329
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Wenwen, Feixiang Li, Xianghong Lv, Jianxiu Chang, Sicong Shen, Pan Dai, Yuan Xia, and Zhongyue Cao. 2023. "Research Progress of Organic Corrosion Inhibitors in Metal Corrosion Protection" Crystals 13, no. 9: 1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13091329
APA StyleZhao, W., Li, F., Lv, X., Chang, J., Shen, S., Dai, P., Xia, Y., & Cao, Z. (2023). Research Progress of Organic Corrosion Inhibitors in Metal Corrosion Protection. Crystals, 13(9), 1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13091329









