Effect of Precursors Concentrations on the Photocatalysis Performance Stability of Electrodeposited ZnO Nanorods and Their Robustness in Aqueous Environments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
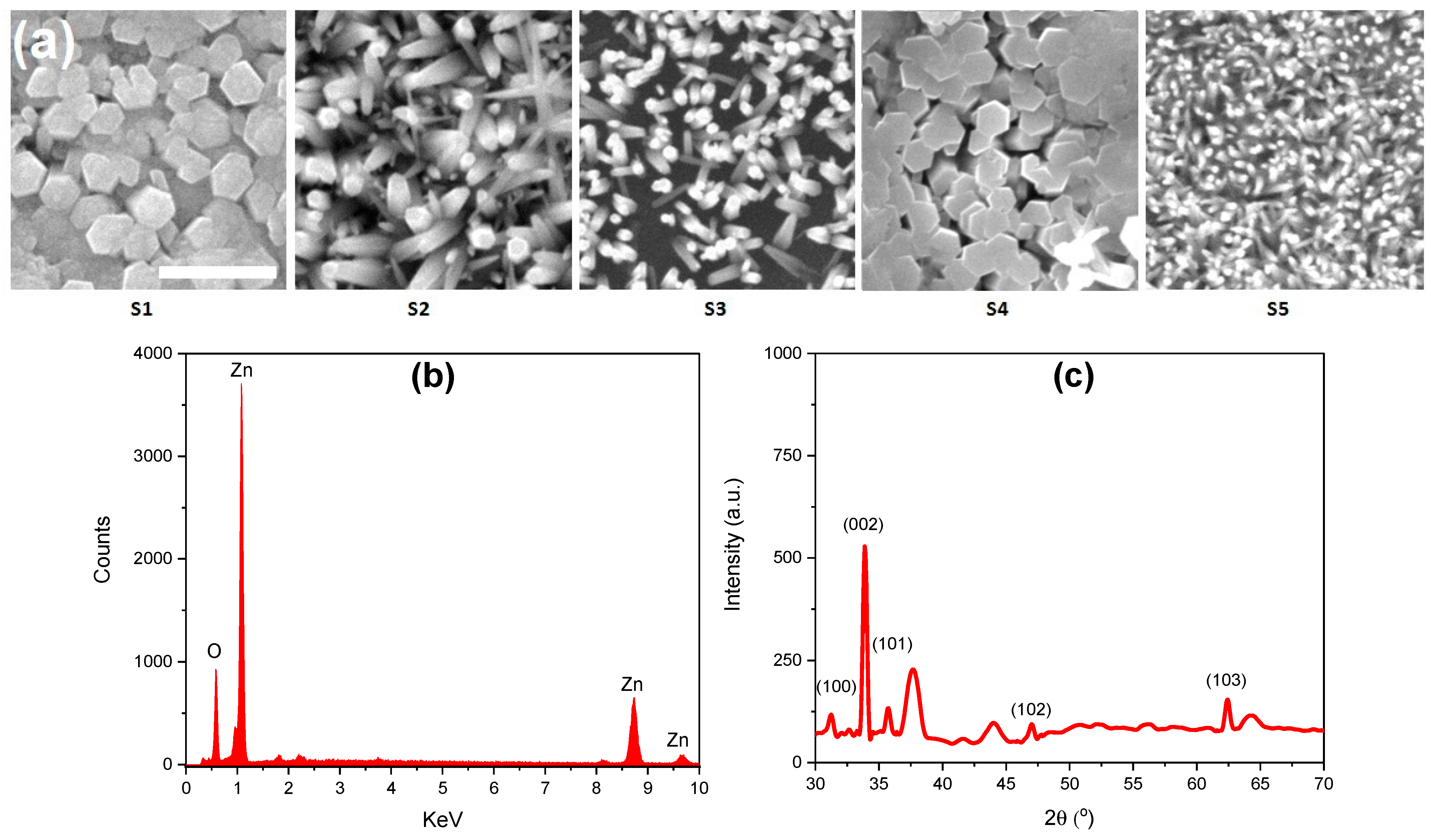
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khin, M.M.; Nair, A.; Babu, V.; Murugan, R.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on nanomaterials for environmental remediation. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 8075–8109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perreault, F.; De Faria, A.F.; Elimelech, M. Environmental applications of graphene-based nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5861–5896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemzadeh, G.; Momenpour, M.; Omidi, F.; Hosseini, M.; Ahani, M.; Barzegari, A. Applications of nanomaterials in water treatment and environmental remediation. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2014, 8, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshammari, A.S.; Alenezi, M.R.; Lai, K.T.; Silva, S.R.P. Inkjet printing of polymer functionalized CNT gas sensor with enhanced sensing properties. Mater. Lett. 2017, 189, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, G.; Surampalli, R.Y.; Tyagi, R.D.; Zhang, T.C. Nanomaterials for environmental burden reduction, waste treatment, and nonpoint source pollution control: A review. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 2009, 3, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yang, L.; Ding, L.; Deng, F.; Luo, X.; Luo, S. Principles for the application of nanomaterials in environmental pollution control and resource reutilization. In Nanomaterials for the Removal of Pollutants and Resource Reutilization; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Muruganandham, M.; Zhang, Y.; Suri, R.; Lee, G.; Chen, P.; Hsieh, S.; Sillanpyää, M.; Wu, J.J. Environmental applications of ZnO materials. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 6900–6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Tao, T. ZnO quantum dots for fluorescent detection of environmental contaminants. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Huang, G.; Hu, W.; Xiong, D.; Huang, W. Tunable synthesis of various ZnO architectural structures with enhanced photocatalytic activities. Mater. Lett. 2016, 175, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Shen, Y.; Sun, L.; Zeng, H.; Lu, Y. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of hierarchical ZnO nanoplate-nanowire architecture as environmentally safe and facilely recyclable photocatalyst. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 5020–5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udom, I.; Ram, M.K.; Stefanakos, E.K.; Hepp, A.F.; Goswami, D.Y. One dimensional-ZnO nanostructures: Synthesis, properties and environmental applications. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2013, 16, 2070–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.; Alshammari, A.S.; Almokhtar, M. Structure, morphology and photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanorods fabricated by electrochemical deposition. Appl. Phys. A 2020, 126, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, T.-J.; Lin, C.; Kuo, C.; Huang, M.H. Growth of ultralong ZnO nanowires on silicon substrates by vapor transport and their use as recyclable photocatalysts. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 5143–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, J.; Khushalani, D. Nonhydrolytic route for synthesis of ZnO and its use as a recyclable photocatalyst. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 2544–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limón-Rocha, I.; Guzmán-González, C.A.; Anaya-Esparza, L.M.; Romero-Toledo, R.; Rico, J.L.; González-Vargas, O.A.; Pérez-Larios, A. Effect of the Precursor on the Synthesis of ZnO and Its Photocatalytic Activity. Inorganics 2022, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Flores, T.; Haro-Pérez, C.; Gerardo-Morales, E.E.; Huerta-Hernández, G.E.; González-Reyes, L.; Hernández-Pérez, I. Influence of Precursor Concentration in the Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles on their Morphological, Structural, and Photocatalytic Properties. Top. Catal. 2022, 65, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qin, L.; Xue, Y.; Yu, P.; Zhang, B.; Wang, L.; Liu, R. Effect of aspect ratio and surface defects on the photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanorods. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Kang, Z.H.; Chen, Z.H.; Shafiq, I.; Zapien, J.A.; Bello, I.; Zhang, W.J.; Lee, S.T. Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic application of different ZnO nanostructures in array configurations. Cryst. Growth Des. 2009, 9, 3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.B.; Ng, L.Y.; Mohammad, A. A review of ZnO nanoparticles as solar photocatalysts: Synthesis, mechanisms and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, B.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, C.; Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, W.; Cheng, H.; Zhao, F. A facile strategy for confining ZnPd nanoparticles into a ZnO@ Al2O3 support: A stable catalyst for glycerol hydrogenolysis. J. Catal. 2016, 337, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İkizler, B.; Peker, S. Stability of ZnO nanorods coated on the channel wall under continuous flow conditions. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2014, 5, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manthina, V.; Agrios, A.G. Single-pot ZnO nanostructure synthesis by chemical bath deposition and their applications. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2016, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Chen, X.; Deng, Z.X.; Li, Y.D. A CTAB-assisted hydrothermal orientation growth of ZnO nanorods. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2003, 78, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Gao, L. A new route toward ZnO hollow spheres by a base-erosion mechanism. Cryst. Growth Des. 2008, 8, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jin, Z.; Liu, Z.; Yu, K.; Bu, S. Nanostructured ZnO films obtained by a basic erosion method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 8668–8672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Wang, Z.; Du, Y.; Qi, X.; Huang, Y.; Xue, C.; Zhang, H. Full solution-processed synthesis of all metal oxide-based tree-like heterostructures on fluorine-doped tin oxide for water splitting. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 5374–5378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, Q.; Jiang, J.; Mao, Y. Morphology-tunable synthesis of ZnO nanoforest and its photoelectrochemical performance. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 8769–8780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skompska, M.; Zarebska, K. Electrodeposition of ZnO Nanorod Arrays on Transparent Conducting Substrates—A Review. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 127, 467–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parize, R.; Garnier, J.; Chaix-Pluchery, O.; Verrier, C.; Appert, E.; Consonni, V. Effects of hexamethylenetetramine on the nucleation and radial growth of ZnO nanowires by chemical bath deposition. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 5242–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPeak, K.M.; Le, T.P.; Britton, N.G.; Nickolov, Z.S.; Elabd, Y.A.; Baxter, J.B. Chemical bath deposition of ZnO nanowires at near-neutral pH conditions without hexamethylenetetramine (HMTA): Understanding the role of HMTA in ZnO nanowire growth. Langmuir 2011, 27, 3672–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.F.; Tseng, T.Y.; Wang, Y.R.; Wang, C.Y.; Lu, H.C.; Shih, W.L. Effects of preparation conditions on the growth of ZnO nanorod arrays using aqueous solution method. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2008, 5, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Leem, J.-Y. Effect of the pH of an aqueous solution on the structural, optical, and photoresponse properties of hydrothermally grown ZnO nanorods and the fabrication of a high performance ultraviolet sensor. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2018, 72, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.-H.; Hu, J.; Li, S.S.; Zhang, F.; Liu, J.; Shi, J.; Li, X.; Tian, Z.Q.; Chen, Y. Improved seedless hydrothermal synthesis of dense and ultralong ZnO nanowires. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 245601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, R.; Saha, N.R.; Karmakar, A.; Dalapati, G.K.; Chattopadhyay, S. Generation of oxygen interstitials with excess in situ Ga doping in chemical bath deposition process for the growth of p-type ZnO nanowires. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 8796–8804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Jeong, H.; Jeong, M.S.; Jung, J.Y. Polymer-templated hydrothermal growth of vertically aligned single-crystal ZnO nanorods and morphological transformations using structural polarity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 3055–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.; Alfatah, A.A.; Alshammari, A.S. Structure, linear and nonlinear optical and photocatalytic properties investigation of ZnO nanorods: Influence of growth time. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2023, 34, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galenda, A.; Natile, M.M.; El Habra, N. Large-Scale MOCVD Deposition of Nanostructured TiO2 on Stainless Steel Woven: A Systematic Investigation of Photoactivity as a Function of Film Thickness. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltani, N.; Saion, E.; Yunus, W.M.M.; Navasery, M.; Bahmanrokh, G.; Erfani, M.; Zare, M.R.; Gharibshahi, E. Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue under visible light using PVP-capped ZnS and CdS nanoparticles. Solar Energy 2013, 97, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L. Magnetically separable CdFe2O4/graphene catalyst and its enhanced photocatalytic properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 3576–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, S.; Dutta, J. pH-dependent growth of zinc oxide nanorods. J. Cryst. Growth 2009, 311, 2549–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, C.; Heo, J.H.; Jeong, Y.I.; Oh, H.B.; Ryu, H.; Lee, W.J.; Chang, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, H. Structural and optical properties of hydrothermally grown zinc oxide nanorods on polyethersulfone substrates as a function of the growth temperature and duration. Thin Solid Film. 2012, 520, 2449–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirzad-Siboni, M.; Jonidi-Jafari, A.; Farzadkia, M.; Esrafili, A.; Gholami, M. Enhancement of photocatalytic activity of Cu-doped ZnO nanorods for the degradation of an insecticide: Kinetics and reaction pathways. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 186, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-H.; Cheng, S.Y.; Lin, R.J.; Wang, Y.H. Manipulation of ZnO nanowire by low-temperature solution approach. MRS Online Proc. Libr. 2005, 891, 0891-EE10-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafaie, H.; Samat, N.; Nor, R.M. Effect of pH on the growth of zinc oxide nanorods using Citrus aurantifolia extracts. Mater. Lett. 2014, 137, 297–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.; Huang, C.C.; Lee, Y.C.; Yang, C.S.; Yu, H.C.; Lee, J.W.; Hu, S.Y.; Chen, C.H. A study on morphology control and optical properties of ZnO nanorods synthesized by microwave heating. J. Lumin. 2012, 132, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulati, A.; Usman Ali, S.M.; Riaz, M.; Amin, G.; Nur, O.; Willander, M. Miniaturized pH sensors based on zinc oxide nanotubes/nanorods. Sensors 2009, 9, 8911–8923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourfaa, F.; Boutelala, A.; Aida, M.S.; Attaf, N.; Ocak, Y.S. Influence of Seed Layer Surface Position on Morphology and Photocatalysis Efficiency of ZnO Nanorods and Nanoflowers. J. Nanomater. 2020, 2020, 4072351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, P.; Manna, A.; Mishra, N.C.; Varma, S. Synthesis and characterization of aligned ZnO nanorods for visible light photocatalysis. Phys. E 2019, 107, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, K.; Bidin, N. Morphological driven photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanostructures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 394, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Liu, C.; Wan, Y.; Li, W.; Ma, C.; Liu, S.; Heeres, H.J.; Zheng, W.; Seshan, K.; He, S. Self-assembly of single-crystal ZnO nanorod arrays on flexible activated carbon fibers substrates and the superior photocatalytic degradation activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 513, 145878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xian, F.; Pei, S.; Zhu, Y. Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes using ZnO nanorods supported by stainless steel wire mesh deposited by one-step method. Optik 2020, 203, 164036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample | Zinc Nitrate Concentration (M) | HMTA Concentration (M) | Molarity Ratio ZN/HMTA | Growth Temperature (°C) | Applied Potential (V) | Growth Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0.03 | 0.015 | 2.00 | 80 | −1.0 | 60 |
| S2 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 0.67 | 80 | −1.0 | 60 |
| S3 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 1.00 | 80 | −1.0 | 60 |
| S4 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 1.50 | 80 | −1.0 | 60 |
| S5 | 0.015 | 0.03 | 0.50 | 80 | −1.0 | 60 |
| Sample | Growth Method | Optimization Parameter | Achieved Enhancement in MB Degradation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnO NRs | Hydrothermal | Seed layer | 50% | [47] |
| ZnO NRs | Hydrothermal | Seed layer | 16.25% | [48] |
| ZnO NRs | Laser ablation/ Hydrothermal | pH | 13.26% | [49] |
| ZnO NRs | sol–gel/ Hydrothermal | ZnO dosage | 46% | [50] |
| ZnO NRs | sol–gel | Coated layers | 74.5% | [51] |
| ZnO NRs | Electrodeposition | Precursors concentration ratio | 122% | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alshammari, A.S.; Mohamed, M.; Khan, Z.R.; Bouzidi, M.; Gandouzi, M. Effect of Precursors Concentrations on the Photocatalysis Performance Stability of Electrodeposited ZnO Nanorods and Their Robustness in Aqueous Environments. Crystals 2024, 14, 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14050393
Alshammari AS, Mohamed M, Khan ZR, Bouzidi M, Gandouzi M. Effect of Precursors Concentrations on the Photocatalysis Performance Stability of Electrodeposited ZnO Nanorods and Their Robustness in Aqueous Environments. Crystals. 2024; 14(5):393. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14050393
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlshammari, Abdullah S., Mansour Mohamed, Ziaul Raza Khan, Mohamed Bouzidi, and Mohamed Gandouzi. 2024. "Effect of Precursors Concentrations on the Photocatalysis Performance Stability of Electrodeposited ZnO Nanorods and Their Robustness in Aqueous Environments" Crystals 14, no. 5: 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14050393
APA StyleAlshammari, A. S., Mohamed, M., Khan, Z. R., Bouzidi, M., & Gandouzi, M. (2024). Effect of Precursors Concentrations on the Photocatalysis Performance Stability of Electrodeposited ZnO Nanorods and Their Robustness in Aqueous Environments. Crystals, 14(5), 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14050393







