Microstructure, Hardness and EIS Evaluation of Ti-15Zr-5Nb Dental Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ti-15Zr-5Nb Alloy Preparation
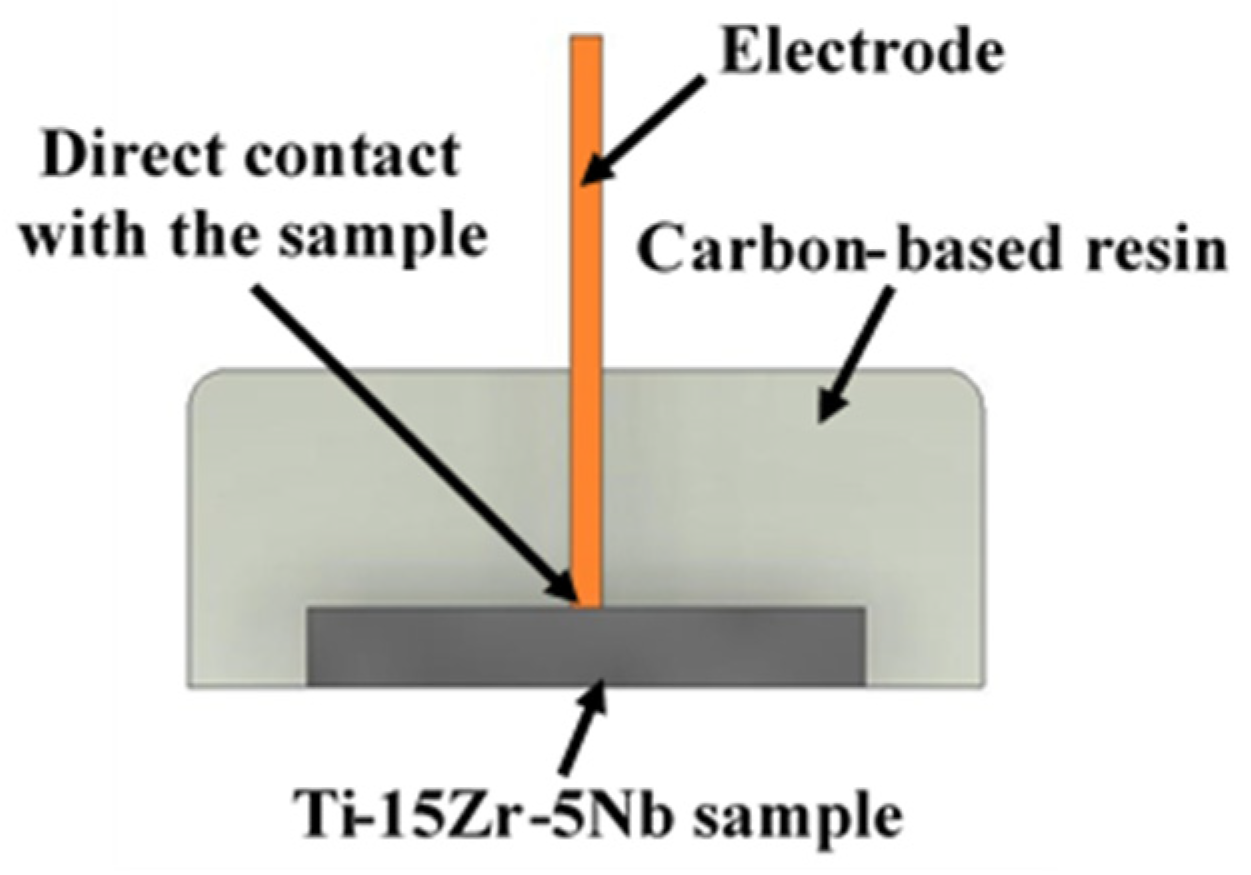
2.2. Characterization
3. Results and Discussions
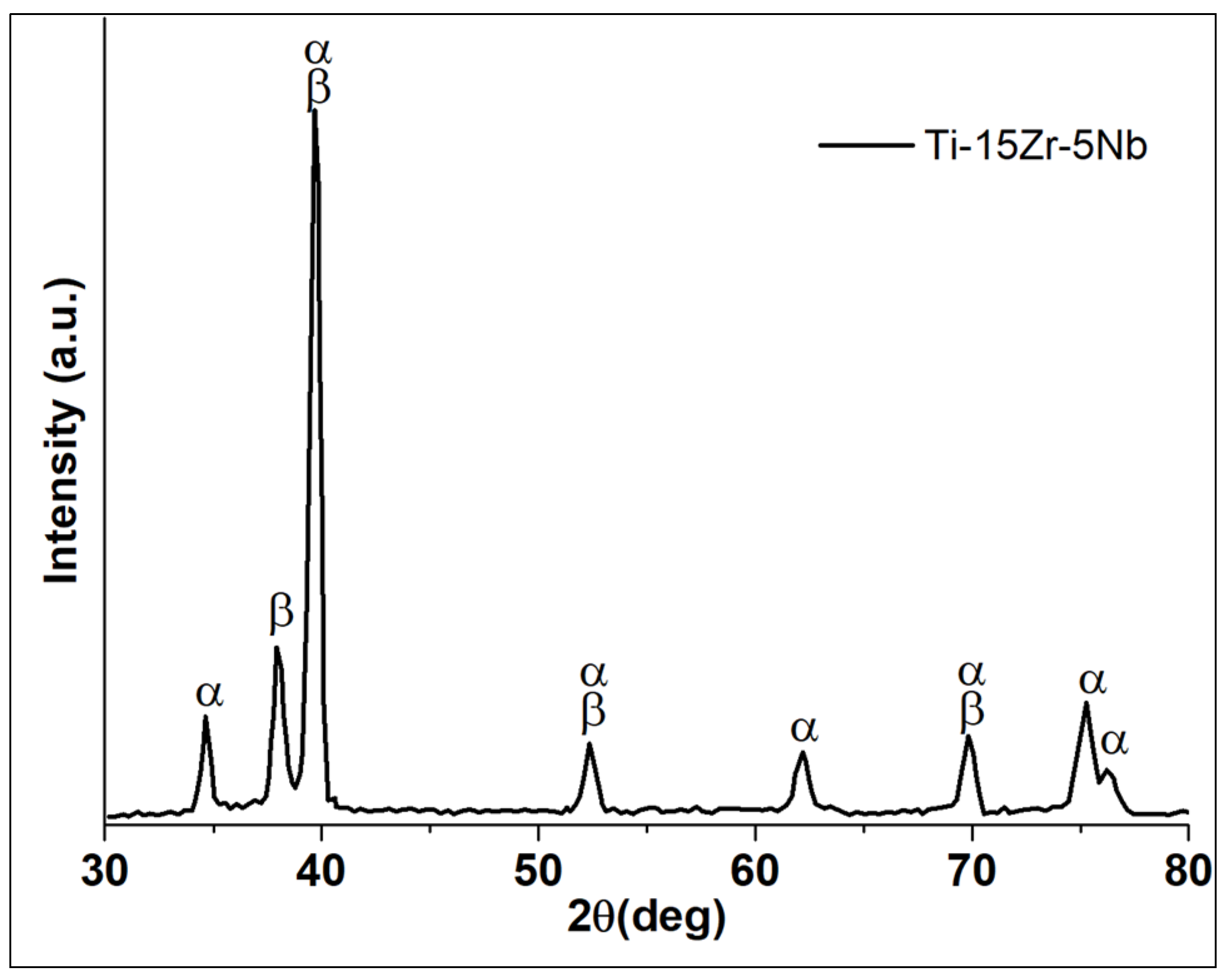
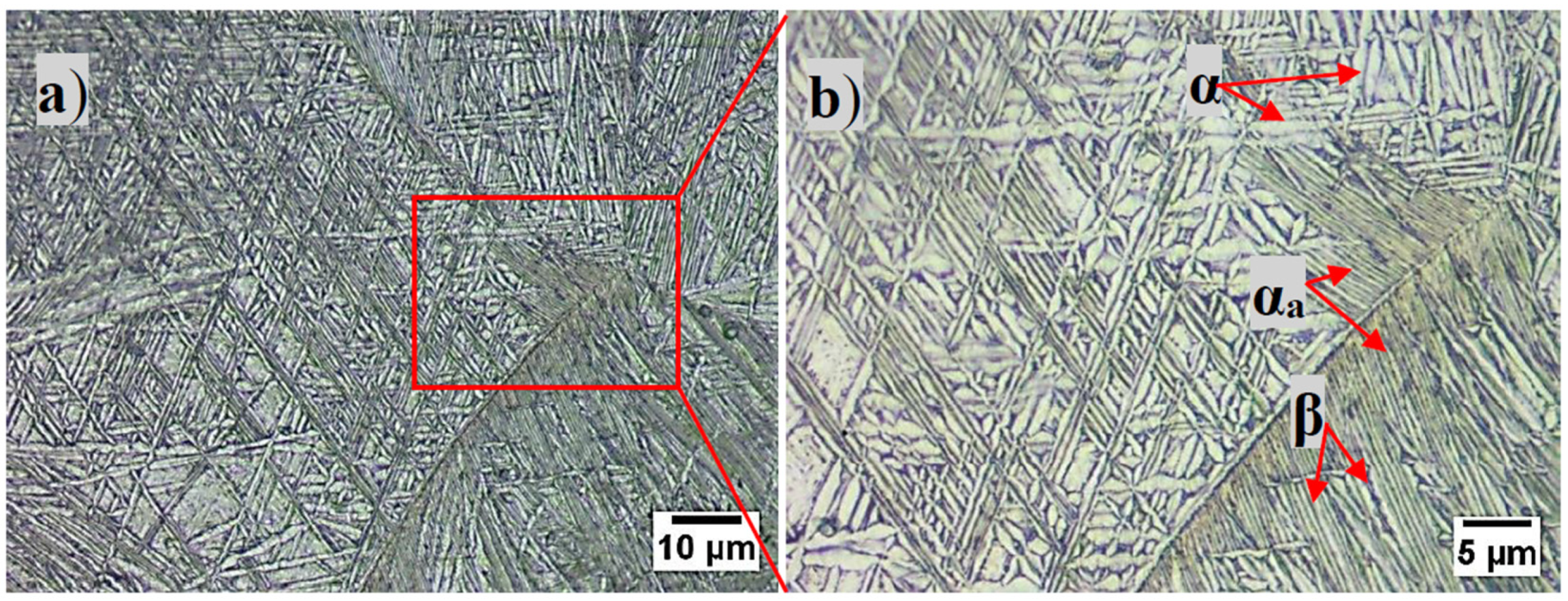
3.1. Microstructure
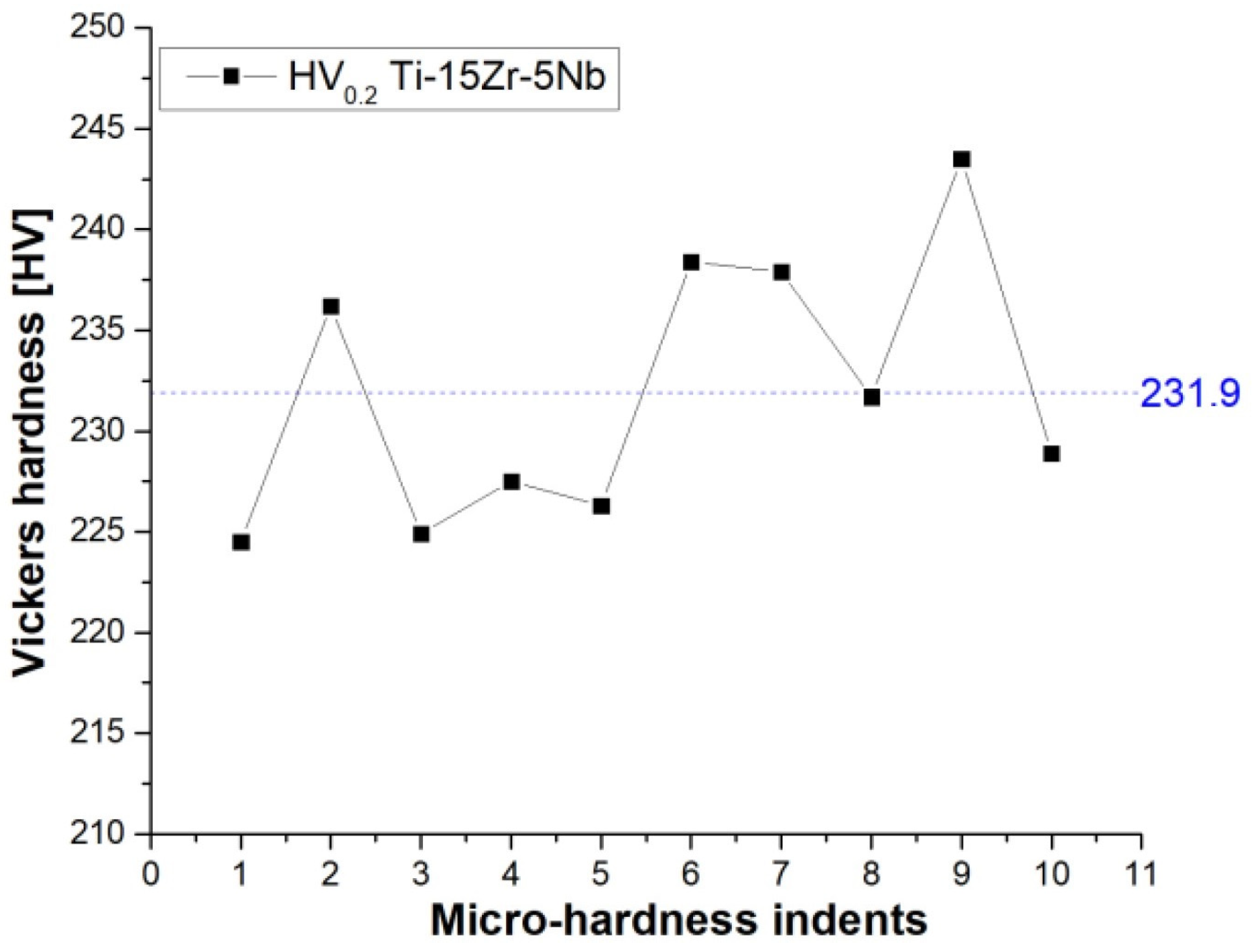
3.2. Microhardness
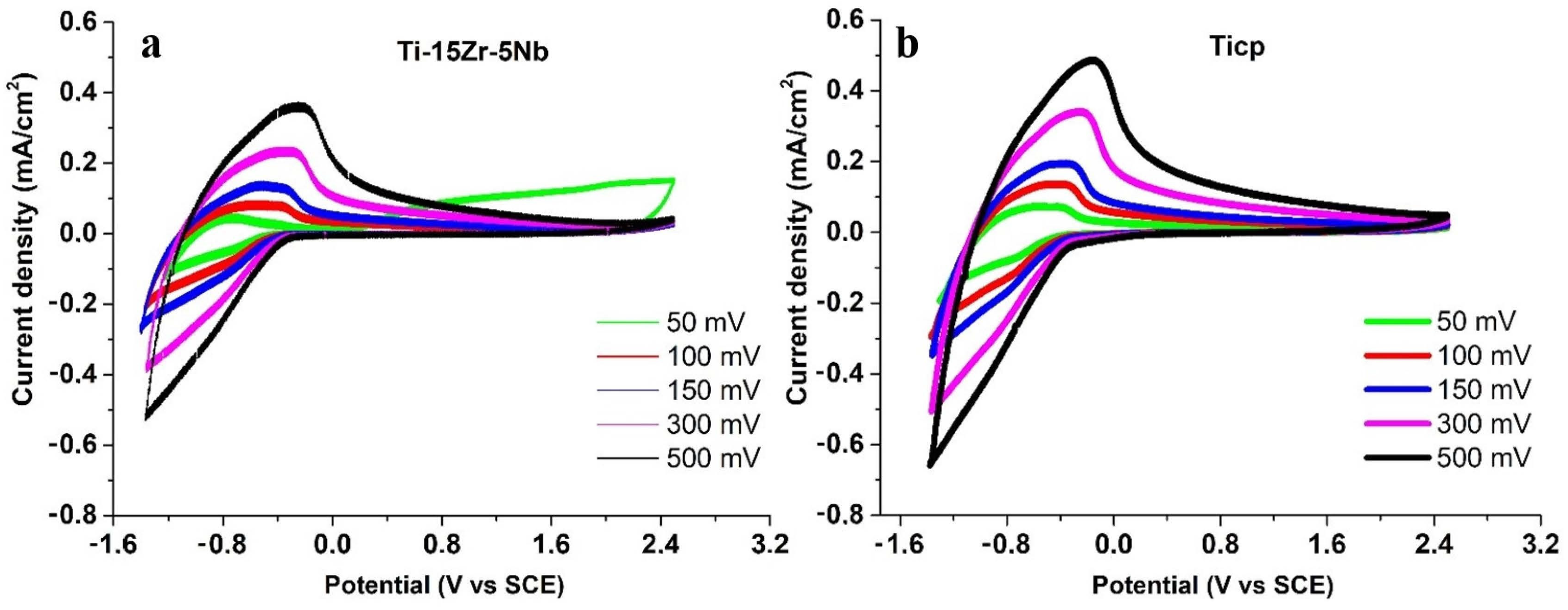
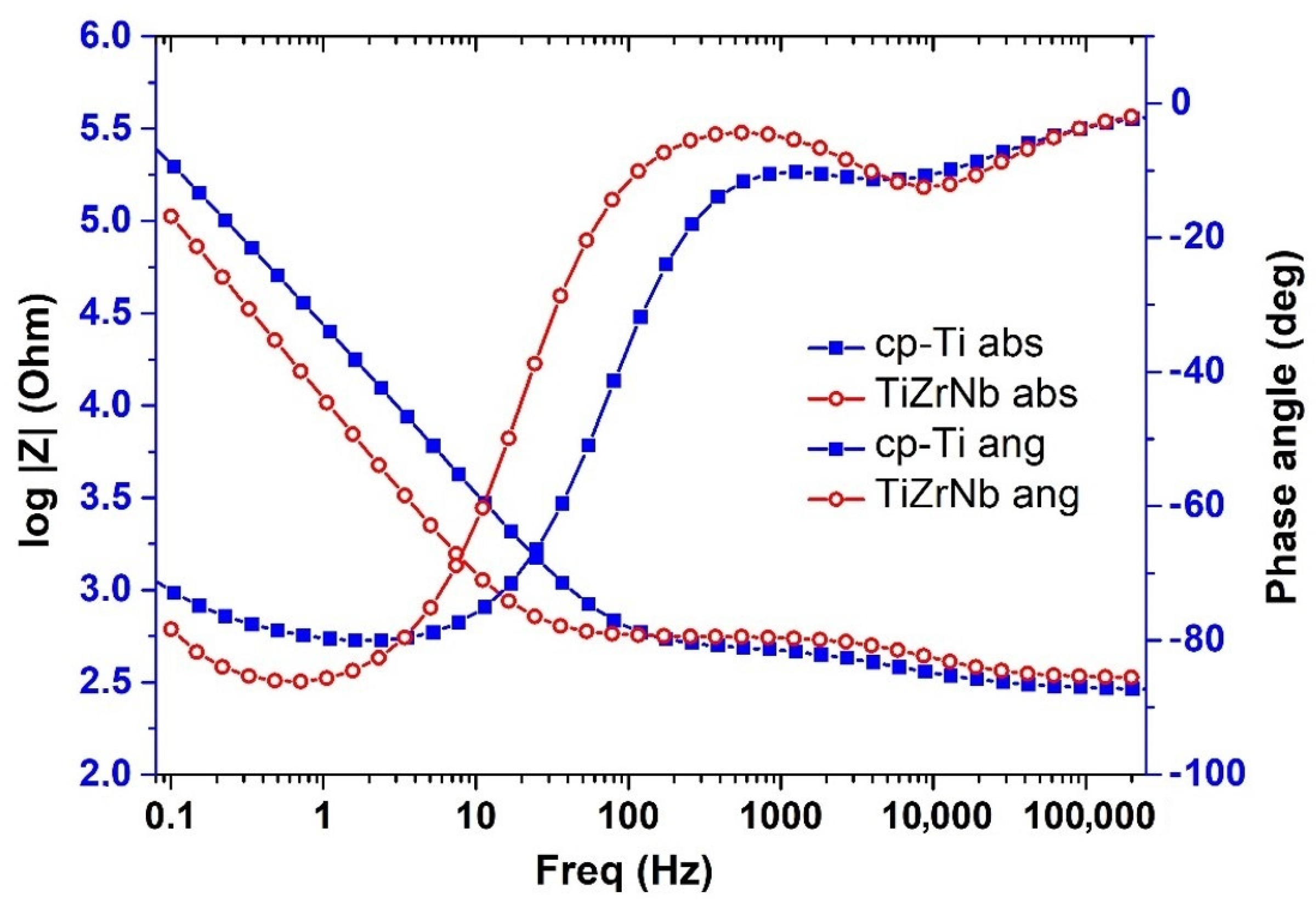
3.3. Electrochemical Behavior
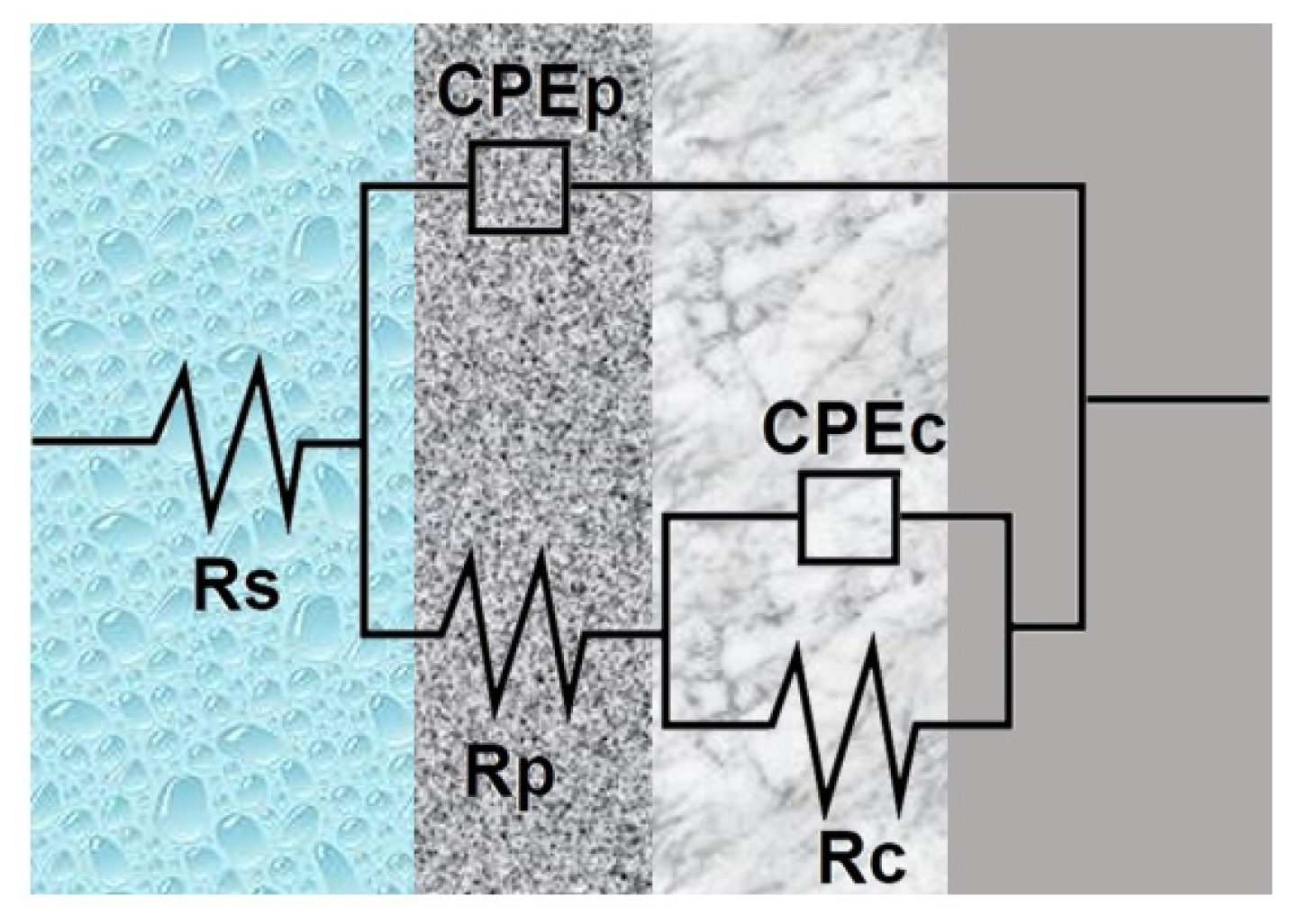
- -
- Solution resistance (Rs)—caused by the electrolyte through which the current flows;
- -
- CPEp—corresponds to the external passive film;
- -
- Rp—resistance attributed to the external film;
- -
- CPEc—corresponds a compact inner passive film;
- -
- Rc—represents the alloy’s polarization resistance.
4. Conclusions
- The structural analysis combined with the microscopic observations indicated that Ti-15Zr-5Nb is a biphasic alloy with the α phase having a hexagonal closed-package structure and the β phase having a body-centered cubic structure with lamellar and acicular structures and α grain boundaries. The microstructure is attributed to the solidification process which is responsible for the shape and size of the lamellas as well as for the formation of α rich grain boundaries.
- The β is enriched in alloying elements such as Nb and Zr which are β phase stabilizing elements.
- The hardness measurements revealed an increased hardness compared to Ti-CP with fluctuations caused due to the differences of hard and soft regions ascribed to the α and β phases identified within the microstructure.
- Despite the very good corrosion properties of Ti-15Zr-5Nb in simulated body fluids, compared to Ti-CP reported by other authors, the present study reveals that the Ti-15Zr-5Nb alloy has lower corrosion resistance in a strong acid environment compared to Ti-CP.
- From the results of the fitting, it was observed that the resistance against corrosion of the Ti-15Zr-5Nb in an aggressive environment such as HCl was a few times less compared with that of Ti-CP.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- John, K.R.S. Mechanical biocompatibility of dental materials. In Biocompatibility of Dental Biomaterials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niinomi, M. Mechanical biocompatibilities of titanium alloys for biomedical applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2008, 1, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliaz, N. Corrosion of metallic biomaterials: A review. Materials 2019, 12, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warlimont, H. Titanium and Titanium Alloys. In Handbook of Materials Data; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niinomi, M.; Nakai, M.; Hieda, J. Development of new metallic alloys for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 3888–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, C.M.; Ong, J.L.; Appleford, M.R.; Mani, G. Introduction to Biomaterials; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadija, G.; Saleem, A.; Akhtar, Z.; Naqvi, Z.; Gull, M.; Masood, M.; Mukhtar, S.; Batool, M.; Saleem, N.; Rasheed, T.; et al. Short term exposure to titanium, aluminum and vanadium (Ti 6Al 4V) alloy powder drastically affects behavior and antioxidant metabolites in vital organs of male albino mice. Toxicol. Reports 2018, 5, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemeyer, T.C.; Grandini, C.R.; Pinto, L.M.C.; Angelo, A.C.D.; Schneider, S.G. Corrosion behavior of Ti-13Nb-13Zr alloy used as a biomaterial. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 476, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvijović-Alagić, I.; Cvijović, Z.; Mitrović, S.; Panić, V.; Rakin, M. Wear and corrosion behaviour of Ti-13Nb-13Zr and Ti-6Al-4V alloys in simulated physiological solution. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.C.; Vasilescu, E.; Drob, P.; Osiceanu, P.; Vasilescu, C.; Drob, S.; Popa, M. Surface and electrochemical characterization of a new ternary titanium based alloy behaviour in electrolytes of varying pH. Corros. Sci. 2013, 77, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazek-Kesik, A.; Krok-Borkowicz, M.; Jakóbik-Kolon, A.; Pamuła, E.; Simka, W. Biofunctionalization of Ti-13Nb-13Zr alloy surface by plasma electrolytic oxidation. Part II. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2015, 276, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Mahobia, G.S.; Mandal, S.; Singh, V.; Chattopadhyay, K. Enhanced corrosion resistance of the surface modified Ti-13Nb-13Zr alloy by ultrasonic shot peening. Corros. Sci. 2021, 189, 109597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yuan, T.; Li, R.; Tang, J.; Wang, G.; Guo, K.; Yuan, J. Densification, microstructure evolution and fatigue behavior of Ti-13Nb-13Zr alloy processed by selective laser melting. Powder Technol. 2019, 342, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Mechanical properties of TiN ceramic coating on a heat treated Ti-13Zr-13Nb alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 724, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, V.; Pawlak, A.; Szymczyk-Ziółkowska, P.; Jaśkiewicz, T.; Rusińska, M.; Dybała, B. Investigation of Ti-13Nb-13Zr alloy powder properties and development of the L-PBF process. Mater. Des. 2022, 217, 110546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.; Lai, X.; An, X.; Feng, W.; Lu, C.; Wu, J.; Wu, C.; Wu, L.; Wang, Q. Characterization and corrosion behaviour of Ti-13Nb-13Zr alloy prepared by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 23, 101130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, A.; Cai, D.; Hu, J.; Zhao, X.; Qin, G.; Han, Y.; Zhang, E. Development of a low elastic modulus and antibacterial Ti-13Nb-13Zr-5Cu titanium alloy by microstructure controlling. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 126, 112116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, J.M.C.; Vasilescu, C.; Drob, S.I.; Neacsu, E.I.; Popa, M. Evaluation of the microstructural, mechanical and anti-corrosive properties of a new ternary Ti–15Zr–5Nb alloy in simulated oral environment. Mater. Corros. 2014, 65, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.M.C.; Vasilescu, C.; Drob, S.I.; Popa, M.; Drob, P.; Vasilescu, E. Electrodeposition, characterization, and corrosion stability of nanostructured anodic oxides on new Ti-15Zr-5Nb alloy surface. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Zheng, L. The passive properties of TA10 in Coca-Cola containing oral environment. Anti-Corrosion Methods Mater. 2021, 68, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, A.; Kumar, M.; Kumar, K.; Pranitha, K.; Kishore, K.; Rajavardhan, K. Erosive potential of cola and orange fruit juice on tooth colored restorative materials. Ann. Med. Health Sci. Res. 2014, 4, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radzikowska, J.; Stachailczyk, J. Application of Color Metallographic Techniques to Study the Microstructure of Titanium Alloys. Sci. Technol. 1999, 6, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Gheorghe, D.; Pop, D.; Ciocoiu, R.; Trante, O.; Milea, C.; Mohan, A.; Benea, H.; Saceleanu, V. Microstructure development in titanium and its alloys used for medical applications. UPB Sci. Bull. Ser. B Chem. Mater. Sci. 2019, 81, 244–258. [Google Scholar]
- Pesode, P.; Barve, S. A review—Metastable β titanium alloy for biomedical applications. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2023, 70, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Addison, O.; Davenport, A. Temperature-Dependence Corrosion Behavior of Ti6Al4V in the Presence of HCl. Front. Mater. 2022, 9, 880702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.H.; El-Hadad, S.; Ahmed, M.; Elshaer, R.N. Effects of Multistage Aging Treatment on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of α + β-Type Ti-6Al-7Nb Alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2023, 32, 11367–11380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, N.; Gülenç, B.; Findik, F. Joining of titanium/stainless steel by explosive welding and effect on interface. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2005, 169, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulka, I.; Uțu, I.-D.; Brito-Garcia, S.; Verdu-Vazquez, A.; Mirza-Rosca, J.C. Electrochemical Study and Mechanical Properties of Ti-Zr Alloy for Biomedical Applications. Crystals 2024, 14, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourbaix, M. Atlas of Electrochemical Equilibria in Aqueous Solutions, 2nd ed.; National Association of Corrosion: Houston, TX, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, D.; Bai, X.; Pan, F.; Sun, H.; Chen, B. Influence of titanium ions implantation on corrosion behavior of zirconium in 1 M H2SO4. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 2196–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauline, S.A.; Rajendran, N. Corrosion behaviour and biocompatibility of nanoporous niobium incorporated titanium oxide coating for orthopaedic applications. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 1731–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukamp, B.A. A Nonlinear Least Squares Fit procedure for analysis of immittance data of electrochemical systems. Solid State Ionics 1986, 20, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Rs [Ω·cm2] | Yo [Ω−1·cm−2·s−n] | n | Rp [Ω·cm2] | Yo [Ω−1·cm−2·s−n] | n | Rc [Ω·cm2] | χ2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti-CP | 285.4 | 2.98 × 10−6 | 0.72 | 246.9 | 4.31 × 10−6 | 0.97 | 2.21 × 106 | 2.5 × 10−3 |
| Ti-15Zr-5Nb | 334.1 | 3.42 × 10−7 | 0.88 | 232.1 | 1.43 × 10−5 | 1 | 5.48 × 105 | 3.2 × 10−2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hulka, I.; Mirza-Rosca, J.C.; Saceleanu, A.; Uțu, I.-D. Microstructure, Hardness and EIS Evaluation of Ti-15Zr-5Nb Dental Alloy. Crystals 2024, 14, 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14070602
Hulka I, Mirza-Rosca JC, Saceleanu A, Uțu I-D. Microstructure, Hardness and EIS Evaluation of Ti-15Zr-5Nb Dental Alloy. Crystals. 2024; 14(7):602. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14070602
Chicago/Turabian StyleHulka, Iosif, Julia C. Mirza-Rosca, Adriana Saceleanu, and Ion-Dragoș Uțu. 2024. "Microstructure, Hardness and EIS Evaluation of Ti-15Zr-5Nb Dental Alloy" Crystals 14, no. 7: 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14070602
APA StyleHulka, I., Mirza-Rosca, J. C., Saceleanu, A., & Uțu, I.-D. (2024). Microstructure, Hardness and EIS Evaluation of Ti-15Zr-5Nb Dental Alloy. Crystals, 14(7), 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst14070602









