Abstract
This study highlights the advantages of employing acetylation to enhance the morphology and thermal properties of cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) derived from maize stalks. Utilizing a green synthesis approach for CNC extraction, this research presents a novel comparison between green extracted CNCs, and their acid hydrolysed, followed by their acetylated counterparts (ACCNCs). This comparison reveals significant improvements in the properties of acetylated CNCs over those produced through conventional acid hydrolysis. The study employs advanced characterization techniques, including Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, X-ray Diffraction (XRD), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), and Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA), to analyze untreated maize stalk extracted cellulose, green extracted CNCs, and acetylated CNCs. FTIR spectroscopy identifies changes in functional groups, underscoring the efficacy of the extraction and modification processes. XRD analysis demonstrates a beneficial transformation from cellulose I to cellulose II allomorphs post-acetylation, with increased crystallinity index values indicating effective removal of amorphous regions. SEM imaging reveals the preservation of rod-like structures in CNCs, while acetylated CNCs exhibit advantageous morphological changes, such as reduced nanocrystal length and increased branching. TGA results show superior thermal stability in green extracted CNCs and favorable thermal degradation behavior in acetylated CNCs. Overall, this study underscores the potential of acetylation to develop sustainable nanomaterials with tailored properties, offering significant advancements for various applications. Emphasizing the advantages of the prepared ACCNCs and the green synthesis method over traditional acid hydrolysis extraction, this research paves the way for innovative applications in diverse fields.
1. Introduction
Cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) have emerged as highly versatile and sustainable nanomaterials, captivating interest across diverse industries including food packaging, cosmetics, polymers, and biomedical applications [,,,,]. Their abundant availability, renewable nature, exceptional mechanical strength, low density, biodegradability, and potent reinforcing capabilities render them appealing for a broad spectrum of uses [,].
Crucially, the extraction process and the source of cellulose significantly influence the properties of CNCs, with acid hydrolysis standing out as the predominant extraction method []. Notably, sulphuric acid (H2SO4) has garnered acclaim for its efficacy in generating stable suspensions with high yields of CNC crystallization, owing to its interaction with cellulose hydroxyl groups [,,]. However, recent research endeavours have delved into the exploration of acid mixtures, seeking to amalgamate the desirable traits associated with H2SO4 and other acids []. These investigations have unveiled that acid mixtures yield CNCs with distinctive spherical morphologies and enhanced thermal properties attributed to the reduction in surface sulphate hydroxyl groups.
Additionally, the presence of hydroxyl groups on the CNC surface facilitates a myriad of chemical modifications, encompassing esterification, cationization, oxidation, polymer grafting, and nucleophilic substitution reactions [,,]. Among these modification methods, acetylation has emerged as particularly promising for altering CNC morphology while concurrently enhancing thermal properties and hydrophobicity [,]. For instance, Wu et al. (2018) studied the effect of acetylation of CNCs on the morphology properties, revealing that acetylated CNCs maintained the characteristics of the original crystal forms with rod-like structures intact, leading to improved thermal properties and hydrophobicity [].
Novo et al. [] proposed a method that employs subcritical water at 120 °C and 20.3 MPa for 60 min to partially hydrolyse cellulose, yielding 21.9 wt% CNCs with high crystallinity and enhanced thermal stability []. Recently, Potenza et al. (2022) suggested recycling Cynara scolymus L. wastes to create polymorph II CNCs through Soxhlet extraction and acid hydrolysis []. These CNCs exhibited excellent crystallinity, high hydrogen bonding intensity, and improved thermal stability. Similarly, Kang et al. (2018) introduced an eco-friendly method for producing CNCs by ball milling cellulose with water, yielding CNCs that enhanced the tensile strength of poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) composite films by 79% while maintaining good transparency and thermal stability [].
Acetylated CNCs have showcased augmented compatibility and mechanical properties when integrated into polymer matrices, such as polylactic acid (PLA), culminating in the development of biodegradable nanocomposites with superior performance []. This research project aims to compare the morphology and thermal properties of CNCs extracted from maize stalk using environmentally friendly methods versus those produced through acid hydrolysis followed by acetylation. By systematically elucidating the influence of extraction and modification processes on CNC characteristics, the study seeks to advance sustainable nanomaterials for applications in composite materials, biomedical devices, and renewable energy technologies. The novelty of this research lies in its focus on comparing the morphology and thermal properties of green-extracted and acetylated CNCs from maize stalk, an area with limited existing studies.
Green extraction of CNCs offers numerous advantages over traditional acid hydrolysis, including environmental benefits, sustainability, safety, preservation of functional groups, improved thermal properties, cost efficiency, versatility, and compatibility with other green processes. These advantages position green-extracted CNCs as a promising alternative for various industrial applications, driving forward the development of sustainable and high-performance nanomaterials.
This research aims to optimize extraction and modification techniques for more efficient and eco-friendly processes. By characterizing and understanding the morphological and thermal properties of CNCs, the study provides crucial insights for designing materials suited to specific applications, including composite materials and biomedical devices. Evaluating the impact of acetylation on CNC properties holds promise for enhancing the performance of CNC-based materials, improving their compatibility with other materials, and enhancing their suitability for various applications.
Moreover, this research contributes to the broader development of CNC-based materials, spanning applications in composite materials, biomedical devices, and renewable energy technologies. By addressing sustainability concerns through the comparison of green-extracted and acetylated CNCs, the study underscores the importance of environmentally friendly extraction methods in nanomaterial production and processing.
Ultimately, this research advances knowledge in nanomaterial science, optimizes manufacturing processes, and fosters the development of sustainable materials for diverse applications. This aligns with the overarching goal of driving forward the field of nanotechnology for societal benefit, including the potential applications of acetylated CNCs and highlighting unique green extraction methods compared to other CNCs extracted from plants.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Maize stalk (MS) was collected from the homes of residences at Empangeni (KwaDlangezwa) in KwaZulu natal., South Africa. Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) 99.9%, sodium hypochlorite (NaClO2) 80%, ethanoic acid/glacial acetic acid (CH3COOH), sulphuric acid (H2SO4) 95–99%, perchloric acid (HClO4) 60%, and toluene ( were used. These chemicals were purchased at Merck chemicals and used without being purified.
2.2. Extraction of Cellulose
MS was mechanically ground using a Fritsch cutting mill pulveriser 15. The MS was then boiled in distilled water for 2 h before being dried in the oven overnight at 55 °C. The dried MS was treated chemically with 4 wt% NaOH at 80 °C for 1 h, then rinsed several times with distilled water. The alkali-treated MS was dried in a 55 °C oven overnight. After that, the alkali-treated MS was bleached in a buffer solution (54 g of NaOH and 150 mL of CH3COOH mixed with 2 L of 1.7 wt% NaClO2 solution) for an hour at 80 °C; this process was repeated two times. The bleached cellulose was then filtered and rinsed with water until it achieved a neutral pH, then dried in a 55 °C oven overnight.
2.2.1. Extraction of Cellulose Nanocrystals (Green Method)
The dried cellulose was finely grounded using a Fritsch cutting mill Pulveriser 15. A dried mass of 10 g of cellulose was weighed and transferred to a 600 mL beaker. A volume of 1 L deionised water was added to the same beaker. The solution was then stirred using a mechanical stirrer for 24 h. The cellulose suspension was sonicated for 3 h in an ultrasonication machine using an ice bath to control the temperature to room temperature. The suspension was then centrifuged for 15 min and dried in an oven at 100 °C for 24 h.
2.2.2. Extraction of Cellulose Nanocrystals
The dry cellulose sample was finely crushed in a Fritsch cutting mill Pulveriser 15. A mass of 15 g of finely dried cellulose was weighed and transferred into a 600 mL beaker. H2SO4 at a concentration of 65% was prepared. A volume of 250 mL of 65% H2SO4 was transferred to a beaker in an ice bath at 10 °C and stirred for 30 min with a mechanical stirrer. After stirring, the reaction was quenched with distilled water and allowed to rest overnight. Subsequently, the mixture was centrifuged for 15 min. Following that, dialysis with distilled water was performed for 5 days until the pH was neutral. The resultant CNCs were dried in an oven for 5 days at 30 °C.
2.2.3. Acetylation of Cellulose Nanocrystals
A mass of 1 g of dried CNCs was weighed and added into a 250 mL beaker. Volumes of 25 mL toluene, 20 mL acetic acid and 0.1 mL perchloric acid were added into the CNCs in a slow sequencing manner while continuously stirring with a PMDC Lab stirrer. Following this, the solution was further stirred continuously for 1 h at room temperature. After an hour, the acetylated CNCs (ACNCs) were washed three times with a 1:1 ratio solution of ethanol and distilled water using a centrifuge. The ACNCs were then dried.
3. Characterization Methods
3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
The diffuse reflectance mode of a Perkin Elmer attenuated total reflection FTIR spectrometer (Perkin Elmer UATR Two) was used to analyse the structural functional groups of polymer materials. During sample analysis, the spectral range between 4000 and 500 cm−1 was employed.
3.2. X-ray Diffraction
The crystallinity of all the materials analysed was investigated using a Bruker AXS Advance D8 diffractometer from Karsruhe, Germany, equipped with a monochromatic Cu K (=1.5406) X-ray source operating at 40 KV and 40 mA at ambient temperature. According to Park, S. et al. [], the crystallinity index (CI) was calculated using both the Segal empirical approach and the deconvolution method.
3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
The morphological features of the polymer materials tested were investigated using FEI Quanta 200 electron microscopy with a 20 KV accelerating voltage. Edward’s E306A coating system was used to carbon-coat the samples prior to examination.
3.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis
The thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was carried out utilizing a TGA analyser (Perkin Elmer Pyris 6, Perkin Elmar, Johannesburg, South Africa). Samples ranging from 10 to 15 mg were heated in a nitrogen environment at a flow rate of 20 mL/min−1 at temperatures ranging from 35 to 800 °C at a heating rate of 5 °C per minute.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. FTIR Spectroscopy Analysis
Figure 1 depicts the FTIR spectra of untreated maize stalk, cellulose, cellulose nanocrystals, and acetylated cellulose nanocrystals. The untreated maize stalk seemed to have accumulated a level of moisture that gave rise to (—OH stretching) at 3339 cm−1. The stalk also showed peaks at 2849 cm−1 (C—H vibrations), 1640 cm−1 (C=C aromatic vibration), 1368 cm−1 (CH2 bending), 1034 cm−1 (C—O stretching), and 893 cm−1 [,,,,,]. There was also a doublet peak at 2922 cm−1 (C—H stretching of methyl group) and 2849 cm−1 (C—H stretching of methylene group), which was absent in the extracted cellulose as well as in CNCs and also known for the removal of the methyl group and alkalization process []. In addition, CNCs and extracted cellulose spectra showed a clear additional peak at roughly 1310 cm−1. The peak could be related to the C—H wagging that normally occurs when the hydrogen bond is broken []. However, removal of the amorphous areas of cellulosic materials resulted in the increase in peak intensity at 892 cm−1 []. The green-extracted CNCs showed a similar peak pattern to the extracted cellulose but less pronounced. The acetylation CNCs showed a new absorption peak at around 1255 cm−1 assigned to the stretching acetyl C—O groups during the acetylation process []. The observation is backed up with weak intensities of the peaks at 3339 cm−1 (—OH stretching) and 1643 cm−1 (intramolecular hydrogen bonding) after acetylation []. The FTIR spectrum of acetylated CNCs revealed key changes compared to non-acetylated CNCs, primarily due to the introduction of acetyl groups. These changes include the appearance of a strong C=O stretching peak around 1255 cm−1, a reduction in the broad O-H stretching peak around 3339 cm−1 and shifts in the C-O stretching region. These spectral features confirm the successful acetylation of CNCs.
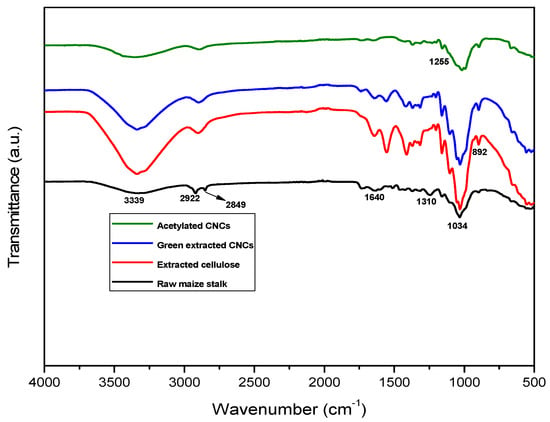
Figure 1.
FTIR spectra of the untreated maize stalk, extracted cellulose, green-extracted CNCs, and acetylated CNCs.
4.2. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
The XRD spectra of untreated maize stalk, extracted cellulose, green-extracted CNCs and acetylated CNCs are depicted in Figure 2. Untreated maize stalk extracted cellulose and green-extracted cellulose displayed the main peaks at 2θ = 16.5, 22.5 and 35.5°, conforming to the (110), (200), and (040) planes, respectively, typical of cellulose I allomorph []. It can be noted that after the acetylation of CNCs, the main peaks at 2θ = 15.0, 16.4, 22.5 and 35.5° were converted to 2θ = 12.0, 20.1, 21.6 and 35.5° for (1–10), (110), (020), and (0.40) planes of cellulose II [,]. This clearly proves that the obtained ACNCs were the allomorph of cellulose II.
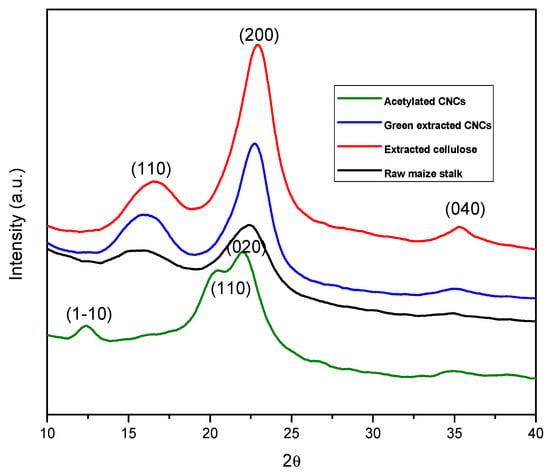
Figure 2.
XRD spectra of the untreated maize stalk, extracted cellulose, green-extracted CNCs, and acetylated CNCs.
Table 1 shows the crystallinity index values calculated using both the Segal empirical method and the deconvolution method. It can be noted that the CI values of untreated maize stalk notably increased when compared to all other samples. This feature put further emphasis on the removal of amorphous noncellulosic material as discussed in FTIR. In addition, the green-extracted CNCs displayed a gradual increase in CI compared to the extracted cellulose. This is due to the further removal of amorphous regions. Furthermore, the acetylated CNCs showed the greatest CI values, and this is due to both the acid hydrolysis and the acetylation process, which further removed the amorphous regions. The order of crystallinity was observed to be untreated maize stalk < extracted cellulose < green-extracted CNCs < acetylated CNCs.

Table 1.
Crystalline Index values of materials studied using Segal and deconvolution methods.
4.3. Scanning Electron Microscope
Figure 3 shows the SEM images of Figure 3a untreated maize stalk, Figure 3b shows extracted cellulose, Figure 3c shows green-extracted CNCs and Figure 3d shows acetylated cellulose. It is obvious that there are particles on the surface of the image in Figure 3a. These particles most likely originate from pectin, hemicellulose, and waxes [,]. Nonetheless, bleaching and alkalization seemed to have removed those particles as confirmed by Figure 3b. This observation seems to confirm the amplified crystallinity index as shown from XRD analysis. Additionally, the image revealed a rod-like structure of CNC fibers with no apparent breakage or only minor fiber breakage. Figure 3c showed rod-like fibers with a deformed shape, no fiber breakage and pull-out observed (see arrows). In fact, the crystal-like structure shown in Figure 3d is completely different compared to other materials following acetylation. In summary, the environmentally friendly extraction methods employed yield CNCs characterized by high aspect ratio nanocrystals with uniform sizes, as indicated by SEM analysis, which highlights the preservation of cellulose structure integrity. Conversely, acetylation introduces changes in surface chemistry, leading to alterations in morphology, including reduced nanocrystal length and increased branching, as evident from comparative SEM images.
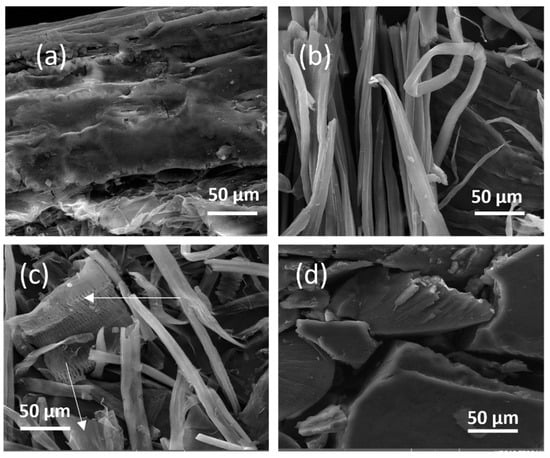
Figure 3.
SEM images of (a) untreated maize stalk, (b) extracted cellulose, (c) green-extracted CNCs, and (d) acetylated CNCs.
4.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis
Thermogravimetric analysis was used to investigate the thermal properties of the studied materials. TGA and DTG curves of untreated maize stalk, extracted cellulose, green-extracted CNCs and acetylated CNCs are shown in Figure 4, respectively. The first instance of weight loss following moisture evaporation was observed just below 100 °C []. The untreated maize stalk displayed two degradation steps at 219 °C and 344 °C. The first degradation step is attributed to the loss of hemicellulose, pectin and waxes, while the second degradation step is due to lignin degradation [,,,]. With regard to extracted cellulose, there was a notable increase in thermal stability compared to the untreated maize stalk. The increase in thermal stability may be attributed to the removal of amorphous regions during the alkalization and the bleaching steps because lignin is known for accelerating thermal degradation of cellulose []. The first degradation step was observed at 306 °C, while the second was observed at 426 °C due to the removal of lignin.
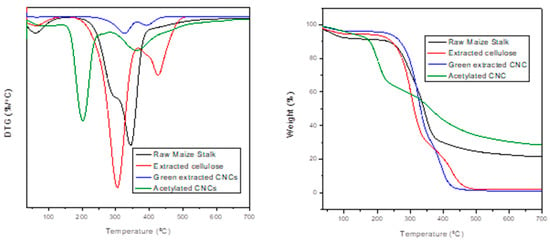
Figure 4.
TGA and DTG spectra of the untreated maize stalk, extracted cellulose, green-extracted CNCs, and acetylated CNCs.
In addition, a further increase in thermal stability was observed for green-extracted CNCs. The first degradation step was observed at 324 °C, while the second was observed at 392 °C. Furthermore, the acetylated CNCs displayed two degradation steps at 201 °C and at 361 °C. The thermal stability of ACNCs was observed to be the lowest amongst all the studied material. This may be due to the diversities that are caused by different surface groups, which may result in the externally attached polymer and long chain alkane coating. This also may result in a new cross-linked material produced from the thermal crosslinking reaction []. A relatively high char content (30%) was observed for ACNCs. This may be due to the sulphate groups acting as a flame retardant during acid hydrolysis with sulfuric acid [].
In summary, green-extracted CNCs typically revealed gradual weight loss with increasing temperature, implying commendable thermal stability, with the onset of decomposition occurring at relatively high temperatures, indicating the capability of CNCs to withstand thermal processing conditions. Concerning acetylated CNCs, it was observed that the acetylation process significantly influenced their thermal properties. TGA curves of acetylated CNCs displayed modified thermal degradation behaviour compared to green-extracted CNCs, potentially attributed to chemical structural changes induced by acetylation.
5. Conclusions
The investigation into the effect of acetylation on the morphology and thermal properties of maize stalk cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) has provided valuable insights into the potential applications and processing techniques of these nanomaterials. This study titled “Effect of Acetylation on the Morphology and Thermal Properties of Maize Stalk Cellulose Nanocrystals: A Comparative Study of Green-Extracted CNC vs. Acid Hydrolysed Followed by Acetylation” aimed to elucidate the influence of chemical treatments on CNC characteristics and behaviour through a series of extraction and modification steps.
FTIR analysis revealed significant changes in functional groups after each processing step. The removal of impurities and amorphous regions was evident from the disappearance of specific peaks in the spectra, while the introduction of acetyl groups during acetylation was confirmed by the emergence of new absorption bands. These findings underscore the effectiveness of the extraction and modification processes in altering the chemical composition of CNCs.
XRD analysis provided valuable insights into the crystalline structure of CNCs. The transformation from cellulose I to cellulose II allomorphs following acetylation highlighted the structural modifications induced by chemical treatments. Moreover, the increase in crystallinity index values throughout the processing steps demonstrated the progressive removal of amorphous regions, ultimately leading to enhanced crystallinity in acetylated CNCs.
SEM imaging unveiled the morphological evolution of CNCs during processing. From the irregular surface features of untreated maize stalk to the well-defined rod-like structures of extracted cellulose and green-extracted CNCs, the preservation of cellulose nanocrystal integrity was evident. However, acetylated CNCs exhibited distinct changes in morphology, including reduced nanocrystal length and increased branching, attributed to the acetylation process.
TGA provided valuable insights into the thermal stability of CNCs. The progressive increase in thermal stability from untreated maize stalk to green-extracted CNCs underscored the removal of thermally labile components during processing. However, acetylated CNCs displayed modified thermal degradation behaviour, potentially due to chemical structural changes induced by acetylation.
It is well known that CNC I has superior mechanical properties, while CNC II is more efficient in terms of functionality and exhibits better thermal stability, which is crucial for its use as an additive or filler in composite materials. This is due to CNC II’s stronger hydrogen bond network. CNC II can be utilized directly or chemically functionalized for applications such as membranes for water pollution control, particularly for the adsorption of cationic metals, charged particles, and organic dyes. Additionally, cellulose nanocrystals of polymorph II have diverse applications including packaging, nanocomposite synthesis, drug carriers, food thickeners, and biomedical products.
The study also included a comparative analysis of green-extracted CNCs versus acid-hydrolysed CNCs followed by acetylation. This comparison highlighted the differences in environmental impact, efficiency, and material properties between the two extraction methods. The green extraction process proved to be a more sustainable and eco-friendly approach, while acid hydrolysis followed by acetylation yielded CNCs with modified properties suitable for specific high-performance applications.
In conclusion, the systematic investigation into the effect of acetylation on the morphology and thermal properties of maize stalk CNCs has shed light on the intricate interplay between extraction techniques, chemical modifications, and resulting material characteristics. These findings hold significant implications for the development of sustainable nanomaterials with tailored properties for diverse applications, including composite materials, biomedical devices, and renewable energy technologies. By advancing our understanding of CNC processing techniques, including a comparative study of green-extracted versus acid hydrolysed and acetylated CNCs, this research paves the way for the future design and optimization of nanomaterials with enhanced performance and sustainability.
Author Contributions
Methodology, N.L.K.; Investigation, N.L.K.; Writing—original draft, N.L.K.; Supervision, S.M.M. and T.E.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
There authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ahmad, E.; Luyt, A.S.; Djoković, V. Thermal and dynamic mechanical properties of bio-based poly (furfuryl alcohol)/sisal whiskers nanocomposites. Polym. Bull. 2013, 70, 1265–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, J.; Wada, M.; Kuga, S. Steric stabilization of a cellulose microcrystal suspension by poly (ethylene glycol) grafting. Langmuir 2001, 17, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arserim-Uçar, D.K.; Korel, F.; Liu, L.; Yam, K.L. Characterization of bacterial cellulose nanocrystals: Effect of acid treatments and neutralization. Food Chem. 2021, 336, 127597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, M.; Saraswatula, S.; Williams, A.; Brettmann, B. Effect of purification methods on commercially available cellulose nanocrystal properties and TEMPO Oxidation. Processes 2020, 8, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazeau, L.; Cavaille, J.; Canova, G.; Dendievel, R.; Boutherin, B. Viscoelastic properties of plasticized PVC reinforced with cellulose whiskers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 71, 1797–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidi, N.; Hequet, E.; Cabrales, L. Applications of Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy to study cotton fibers. In Fourier Transform—New Analytical Approaches and FTIR Strategies; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 89–114. [Google Scholar]
- Achoundong, C.S.; Bhuwania, N.; Burgess, S.K.; Karvan, O.; Johnson, J.R.; Koros, W.J. Silane modification of cellulose acetate dense films as materials for acid gas removal. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 5584–5594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, A.C.; de Morais Teixeira, E.; Pessan, L.A.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Cellulose nanofibers from curaua fibers. Cellulose 2010, 17, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, Y.; Lucia, L.A.; Rojas, O.J. Cellulose nanocrystals: Chemistry, self-assembly, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 3479–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Lin, N.; Chang, P.R.; Huang, J. Reinforcement and nucleation of acetylated cellulose nanocrystals in foamed polyester composites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 129, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xu, J.; Gong, J.; Li, J.; Mo, L. Preparation, characterization and acetylation of cellulose nanocrystal allomorphs. Cellulose 2018, 25, 4905–4918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wu, Z.; Wu, Q.; Kuang, Y. Acetylated cellulose nanocrystals with high-crystallinity obtained by one-step reaction from the traditional acetylation of cellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novo, L.P.; Bras, J.; García, A.; Belgacem, N.; Curvelo, A.A. Subcritical water: A method for green production of cellulose nanocrystals. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2839–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potenza, M.; Bergamonti, L.; Lottici, P.P.; Righi, L.; Lazzarini, L.; Graiff, C. Green extraction of cellulose nanocrystals of polymorph II from Cynara scolymus L.: Challenge for a “zero waste” economy. Crystals 2022, 12, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Kuga, S.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, M.; Huang, Y. Green preparation of cellulose nanocrystal and its application. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2954–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Huang, J.; Chang, P.R.; Feng, J.; Yu, J. Surface acetylation of cellulose nanocrystal and its reinforcing function in poly (lactic acid). Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1834–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Baker, J.O.; Himmel, M.E.; Parilla, P.A.; Johnson, D.K. Cellulose crystallinity index: Measurement techniques and their impact on interpreting cellulase performance. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2010, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, S.; Thakur, K.; Celli, A.; Kiechel, M.A.; Schauer, C.L. Surface modification of plant fibers using environment friendly methods for their application in polymer composites, textile industry and antimicrobial activities: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Kumar, R.; Zhang, L. Investigation into hemp fiber-and whisker-reinforced soy protein composites. Front. Chem. China 2009, 4, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Han, F.; Xu, C.; Jiang, S.; Huang, L.; Liu, L.; Xia, Z. Effects of preparation methods on the morphology and properties of nanocellulose (NC) extracted from corn husk. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 109, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunaver, M.; Anžlovar, A.; Zagar, E. The fast and effective isolation of nanocellulose from selected cellulosic feedstocks. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 148, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lani, N.; Ngadi, N.; Johari, A.; Jusoh, M. Isolation, characterization, and application of nanocellulose from oil palm empty fruit bunch fiber as nanocomposites. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 702538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassab, Z.; Kassem, I.; Hannache, H.; Bouhfid, R.; Qaiss, A.E.K.; El Achaby, M. Tomato plant residue as new renewable source for cellulose production: Extraction of cellulose nanocrystals with different surface functionalities. Cellulose 2020, 27, 4287–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranger, L.A.; Nunnery, G.A.; Tannenbaum, R. Mechanism of the nanoparticle-catalyzed polymerization of furfuryl alcohol and the thermal and mechanical properties of the resulting nanocomposites. Compos. Part B: Eng. 2012, 43, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Cao, J.; He, E.; Wu, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, L. Facile preparation PCL/modified nano ZnO organic-inorganic composite and its application in antibacterial materials. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, E.; Guo, J.; Yang, F.; Zhu, Y.; Song, J.; Jin, Y.; Rojas, O.J. On the polymorphic and morphological changes of cellulose nanocrystals (CNC-I) upon mercerization and conversion to CNC-II. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 143, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, J.; Gong, J.; Kuang, Y.; Mo, L.; Song, T. Cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) with different crystalline allomorph for oil in water Pickering emulsions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 183, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ianchis, R.; Rosca, I.; Ghiurea, M.; Spataru, C.; Nicolae, C.; Gabor, R.; Raditoiu, V.; Preda, S.; Fierascu, R.; Donescu, D. Synthesis and properties of new epoxy-organolayered silicate nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 103, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Xu, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, S.; Gao, Y.; Shi, C. The effect of surface modification on chemical and crystalline structure of the cellulose III nanocrystals. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 235, 115962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Nascimento, D.M.; Almeida, J.S.; Vale, M.d.S.; Leitão, R.C.; Muniz, C.R.; de Figueirêdo, M.C.B.; Morais, J.P.S.; Rosa, M.d.F. A comprehensive approach for obtaining cellulose nanocrystal from coconut fiber. Part I: Proposition of technological pathways. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 93, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, R.; Zhang, X.; Tian, D.; Zhou, Z.; Lu, C. Comparing microcrystalline with spherical nanocrystalline cellulose from waste cotton fabrics. Cellulose 2012, 19, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).