Review of Progress in Shape Memory Epoxies and Their Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
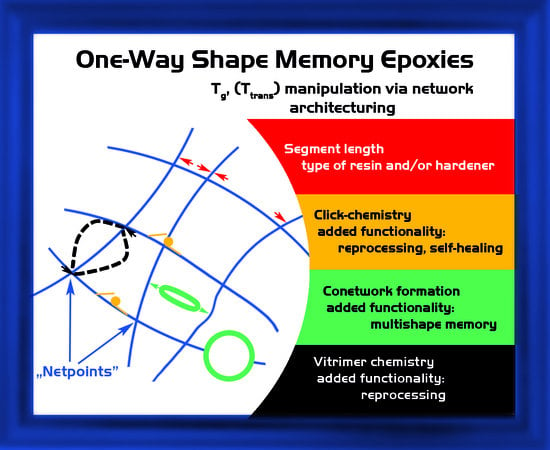
2. One-Way, Dual-Shape Memory Epoxy (EP) Formulations
2.1. (Co)network Structure
2.2. Phase Separated Morphology
3. Multi-Shape Memory Epoxies
4. Multi-Functional EP Formulations
5. Shape Memory EP Composites
5.1. Particulate-Filled
5.2. Fibre- and Fabric-Reinforced
6. Shape Memory EP Foams
7. Shape Memory EP/Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) Combinations
8. Two-Way Shape Memory EP Systems
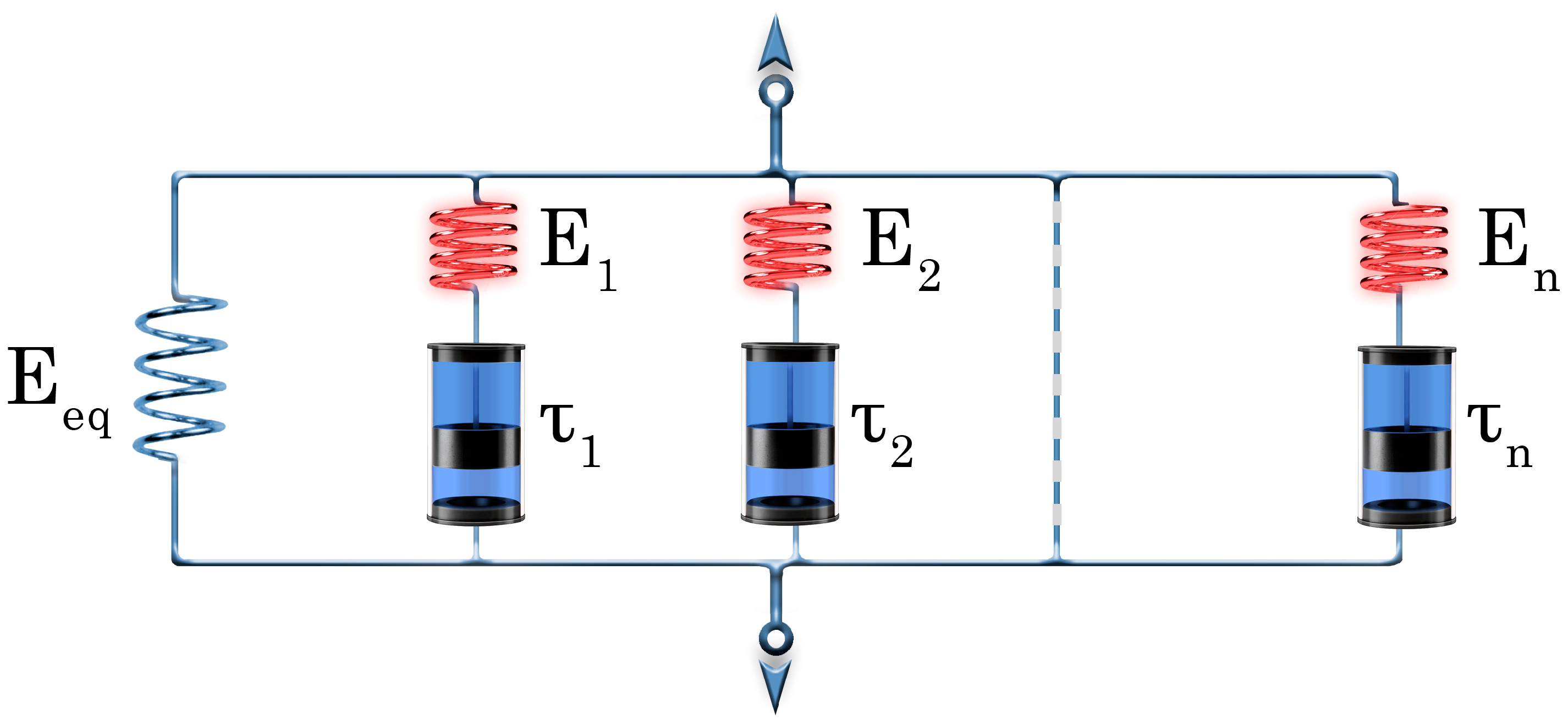
9. Modelling of SM Behaviour
9.1. Macroscale Modelling Approaches
9.2. Mesoscale Modelling Approaches
9.3. Microscale Modelling Approaches
10. Outlook and Future Trends
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lendlein, A. Shape-Memory Polymers; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J. Shape memory polymers with novel functions: Electro-active, magnetically-active, light-adaptive and phase change materials. In Advances in Shape Memory Polymers; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tandon, G.; Baur, J.; McClung, A. Shape Memory Polymers for Aerospace Applications: Novel Synthesis, Modelling, Characterization and Design; DEStech Publications, Incorporated: Lancaster, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Leng, J.; Lan, X.; Liu, Y.; Du, S. Shape-memory polymers and their composites: Stimulus methods and applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2011, 56, 1077–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Huang, W.; Ding, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Purnawali, H.; Tang, C. Stimulus-responsive shape memory materials: A review. Mater. Des. 2012, 33, 577–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Huang, W. Shape memory effect in polymeric materials: Mechanisms and optimization. Proc. IUTAM 2015, 12, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, H.; Lu, J. Recent advances in shape–memory polymers: Structure, mechanism, functionality, modeling and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1720–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, B.A.; King, W.P.; Gall, K. Shape recovery of nanoscale imprints in a thermoset “shape memory” polymer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 103108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montarnal, D.; Capelot, M.; Tournilhac, F.; Leibler, L. Silica-like malleable materials from permanent organic networks. Science 2011, 334, 965–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Zou, W.; Luo, Y.; Xie, T. Shape memory polymer network with thermally distinct elasticity and plasticity. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauter, T.; Heuchel, M.; Kratz, K.; Lendlein, A. Quantifying the shape-memory effect of polymers by cyclic thermomechanical tests. Polym. Rev. 2013, 53, 6–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souri, M.; Lu, Y.C.; Erol, A.; Pulla, S.S.; Karaca, H.E. Characterization of unconstraint and constraint shape recoveries of an epoxy based shape memory polymer. Polym. Test. 2015, 41, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Li, G. A review of stimuli-responsive shape memory polymer composites. Polymer 2013, 54, 2199–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, M.; Razzaq, M.Y.; Lendlein, A. Multifunctional shape-memory polymers. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 3388–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mather, P.T.; Luo, X.; Rousseau, I.A. Shape memory polymer research. ACS Macro Lett. 2009, 39, 445–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Mohamadian, H.; Stubblefield, M.; Jerro, D.; Ibekwe, S.; Pang, S.-S.; Li, G. Various shape memory effects of stimuli-responsive shape memory polymers. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 093001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Huang, L.; Leng, J.; Liu, Y. Thermoset shape memory polymers and their composites. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2016, 27, 2433–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhosh Kumar, K.S.; Biju, R.; Reghunadhan Nair, C.P. Progress in shape memory epoxy resins. React. Funct. Polym. 2013, 73, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, I.A.; Xie, T. Shape memory epoxy: Composition, structure, properties and shape memory performances. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 3431–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidil, T.; Tournilhac, F.; Musso, S.; Robisson, A.; Leibler, L. Control of reactions and network structures of epoxy thermosets. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 62, 126–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandini, S.; Bignotti, F.; Baldi, F.; Passera, S. Network architecture and shape memory behavior of cold-worked epoxies. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2013, 24, 1583–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Han, C.; Tan, H.; Du, X. Thermal, mechanical and shape memory properties of shape memory epoxy resin. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2010, 527, 2510–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldkamp, D.M.; Rousseau, I.A. Effect of chemical composition on the deformability of shape-memory epoxies. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2011, 296, 1128–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Rousseau, I.A. Facile tailoring of thermal transition temperatures of epoxy shape memory polymers. Polymer 2009, 50, 1852–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Wang, L.Y.; Wang, Z. Synthesis and thermomechanical research of shape memory epoxy systems. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2011, 529, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, A.B.; Fasce, L.A.; Zucchi, I.A.; Hoppe, C.E.; Soulé, E.R.; Pérez, C.J.; Williams, R.J.J. Shape memory epoxies based on networks with chemical and physical crosslinks. Eur. Polym. J. 2011, 47, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Liu, Y.; Tan, H.; Du, X. A new method to improve the stability, tensile strength and heat resistant properties of shape-memory epoxy resins: Two-stages curing. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 39882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biju, R.; Nair, C.P.R. Synthesis and characterization of shape memory epoxy-anhydride system. J. Polym. Res. 2013, 20, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biju, R.; Nair, C.P.R.; Gouri, C.; Ninan, K.N. Rheokinetic cure characterization of epoxy-anhydride polymer system with shape memory characteristics. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2012, 107, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Kang, S.; Xu, X.; Xiao, F.; Ge, X. Effect of the crosslinking density and programming temperature on the shape fixity and shape recovery in epoxy-anhydride shape-memory polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denissen, W.; Winne, J.M.; Du Prez, F.E. Vitrimers: Permanent organic networks with glass-like fluidity. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloxin, C.J.; Bowman, C.N. Covalent adaptable networks: Smart, reconfigurable and responsive network systems. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7161–7173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altuna, F.I.; Hoppe, C.E.; Williams, R.J.J. Shape memory epoxy vitrimers based on dgeba crosslinked with dicarboxylic acids and their blends with citric acid. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 88647–88655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yu, J.; Hu, Z. Bio-based epoxy vitrimers: Reprocessibility, controllable shape memory and degradability. J. Polym. Sci. A 2017, 55, 1790–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Dam, M.A.; Ono, K.; Mal, A.; Shen, H.; Nutt, S.R.; Sheran, K.; Wudl, F. A thermally re-mendable cross-linked polymeric material. Science 2002, 295, 1698–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Zheng, X.; Sun, Y.; Yu, K.; He, M.; Guo, Y. A molecular dynamics study on the surface welding and shape memory behaviors of diels-alder network. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2017, 139, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, L.; Zou, W.; Xi, X.; Xie, T. Exploring dynamic equilibrium of diels-alder reaction for solid state plasticity in remoldable shape memory polymer network. ACS Macro Lett. 2016, 5, 805–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, C.L.; Dell, E.M. A review of shape memory polymers bearing reversible binding groups. J. Polym. Sci. B 2016, 54, 1340–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmonte, A.; Russo, C.; Ambrogi, V.; Fernández-Francos, X.; De la Flor, S. Epoxy-based shape-memory actuators obtained via dual-curing of off-stoichiometric “thiol-epoxy” mixtures. Polymers 2017, 9, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Zhu, G.; Tang, Y.; Liu, T.; Xie, J. The effects of crosslink density on thermo-mechanical properties of shape-memory hydro-epoxy resin. J. Mater. Res. 2013, 28, 2903–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Zhou, X.; Wei, K.; Bo, Y.; You, Z. Analysis of preparation and properties on shape memory hydrogenated epoxy resin used for asphalt mixtures. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Zhu, G.; Tang, Y.; Niu, L. Shape-memory effects of a hydro-epoxy resin system. J. Polym. Res. 2013, 20, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Tan, H. Toughening-modified epoxy-amine system: Cure kinetics, mechanical behavior and shape memory performances. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, J. Thermal, mechanical and shape memory properties of an intrinsically toughened epoxy/anhydride system. J. Polym. Res. 2014, 21, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, J. Curing kinetics and shape-memory behavior of an intrinsically toughened epoxy resin system. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2015, 119, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, W. A new shape memory epoxy resin with excellent comprehensive properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 3231–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, Y.; Zheng, J.; Gan, J.; Liang, L.; Wu, K.; Lu, M. Reinforcement in the mechanical properties of shape memory liquid crystalline epoxy composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, Y.; Zheng, J.; Gan, J.; Liang, L.; Wu, K.; Lu, M. High thermo-responsive shape memory epoxies based on substituted biphenyl mesogenic with good water resistance. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 67247–67257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merline, J.D.; Reghunadhan Nair, C.P.; Gouri, C.; Sadhana, R.; Ninan, K.N. Poly(urethane-oxazolidone): Synthesis, characterisation and shape memory properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 3629–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biju, R.; Gouri, C.; Reghunadhan Nair, C.P. Shape memory polymers based on cyanate ester-epoxy-poly (tetramethyleneoxide) co-reacted system. Eur. Polym. J. 2012, 48, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Yang, B.; Fu, Y. Polyurethane Shape Memory Polymers; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ursache, O.; Gaina, C.; Gaina, V. Polyurethanes based on thermoreversible networks designed by diels-alder reaction. Express Polym. Lett. 2017, 11, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Cui, B.; Wu, Q.; Yu, H. Bio-based polyurethanes with shape memory behavior at body temperature: Effect of different chain extenders. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 17888–17895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, J. Synthesis and properties of shape memory poly(γ-benzyl-l-glutamate)-b-poly(propylene glycol)-b-poly(γ-benzyl-l-glutamate). Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Wu, Q.; Gu, L.; Shen, L.; Yu, H. High performance bio-based polyurethane elastomers: Effect of different soft and hard segments. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2016, 34, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Gu, L.; Zhang, K.; Yu, H. Bio-based (co)polylactide-urethane networks with shape memory behavior at body temperature. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 79268–79274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariraman, M.; Sasikumar, R.; Alagar, M. Shape memory effect on the formation of oxazoline and triazine rings of bcc/dgeba copolymer. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 69720–69727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grishchuk, S.; Mbhele, Z.; Schmitt, S.; Karger-Kocsis, J. Structure, thermal and fracture mechanical properties of benzoxazine-modified amine-cured dgeba epoxy resins. Express Polym. Lett. 2011, 5, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grishchuk, S.; Schmitt, S.; Vorster, O.C.; Karger-Kocsis, J. Structure and properties of amine-hardened epoxy/benzoxazine hybrids: Effect of epoxy resin functionality. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 2824–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimdusit, S.; Lohwerathama, M.; Hemvichian, K.; Kasemsiri, P.; Dueramae, I. Shape memory polymers from benzoxazine-modified epoxy. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 075033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanpitaksit, T.; Jubsilp, C.; Rimdusit, S. Effects of benzoxazine resin on property enhancement of shape memory epoxy: A dual function of benzoxazine resin as a curing agent and a stable network segment. Express Polym. Lett. 2015, 9, 824–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunitha, K.; Santhosh Kumar, K.S.; Mathew, D.; Reghunadhan Nair, C.P. Shape memory polymers (SMPs) derived from phenolic cross-linked epoxy resin via click chemistry. Mater. Lett. 2013, 99, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acebo, C.; Alorda, M.; Ferrando, F.; Fernandez-Francos, X.; Serra, A.; Morancho, J.M.; Salla, J.M.; Ramis, X. Epoxy/anhydride thermosets modified with end-capped star polymers with poly(ethyleneimine) cores of different molecular weight and poly(epsilon-caprolactone) arms. Express Polym. Lett. 2015, 9, 809–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, D.; Fernández-Francos, X.; Ferrando, F.; De la Flor, S. Shape-memory effect in hyperbranched poly(ethyleneimine)-modified epoxy thermosets. J. Polym. Sci. B 2015, 53, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, D.; Fabregat-Sanjuan, A.; Ferrando, F.; De la Flor, S. Recovery stress and work output in hyperbranched poly(ethyleneimine)-modified shape-memory epoxy polymers. J. Polym. Sci. B 2016, 54, 1002–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, H.; Karak, N. Shape-memory property and characterization of epoxy resin-modified mesua ferrea l. Seed oil-based hyperbranched polyurethane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, I.A. Challenges of shape memory polymers: A review of the progress toward overcoming smp’s limitations. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2008, 48, 2075–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakacki, C.M.; Ortega, A.M.; Frick, C.P.; Lakhera, N.; Xiao, R.; Nguyen, T.D. Unique recovery behavior in amorphous shape-memory polymer networks. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2012, 297, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldkamp, D.M.; Rousseau, I.A. Effect of the deformation temperature on the shape-memory behavior of epoxy networks. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2010, 295, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gall, K.; Dunn, L.M.; McCluskey, P. Thermomechanical recovery couplings of shape memory polymers in flexure. Smart Mater. Struct. 2003, 12, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, G.P.; Goecke, K.; Cable, K.; Baur, J. Durability assessment of styrene- and epoxy-based shape-memory polymer resins. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2009, 20, 2127–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, J.; Xie, F.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y. Effect of the γ-radiation on the properties of epoxy-based shape memory polymers. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2014, 25, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretsch, T. Review on the functional determinants and durability of shape memory polymers. Polymers 2010, 2, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parameswaranpillai, J.; Hameed, N.; Pionteck, J.; Woo, E.M. Handbook of Epoxy Blends; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Karger-Kocsis, J.; Friedrich, K. Fatigue crack propagation and related failure in modified andhydride-cured epoxy resins. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1992, 270, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha; Revathi, A.; Rao, S.; Srihari, S.; Dayananda, G.N. Characterization of shape memory behaviour of ctbn-epoxy resin system. J. Polym. Res. 2012, 19, 9894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revathi, A.; Rao, S.; Rao, K.V.; Singh, M.M.; Murugan, M.S.; Srihari, S.; Dayananda, G.N. Effect of strain on the thermomechanical behavior of epoxy based shape memory polymers. J. Polym. Res. 2013, 20, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, H.; Tan, H.; Du, X. Modified shape memory epoxy resin composites by blending activity polyurethane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 3152–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.-Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, L.; Qiao, J.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. Thermal, mechanical and shape-memory properties of nanorubber-toughened, epoxy-based shape-memory nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grishchuk, S.; Gryshchuk, O.; Weber, M.; Karger-Kocsis, J. Structure and toughness of polyethersulfone (PESU)-modified anhydride-cured tetrafunctional epoxy resin: Effect of pesu molecular mass. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 123, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karger-Kocsis, J.; Kéki, S. Biodegradable polyester-based shape memory polymers: Concepts of (supra)molecular architecturing. Express Polym. Lett. 2014, 8, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lützen, H.; Gesing, T.M.; Kim, B.K.; Hartwig, A. Novel cationically polymerized epoxy/poly(ɛ-caprolactone) polymers showing a shape memory effect. Polymer 2012, 53, 6089–6095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lützen, H.; Gesing, T.M.; Hartwig, A. Nucleation as a new concept for morphology adjustment of crystalline thermosetting epoxy polymers. React. Funct. Polym. 2013, 73, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnebold, A.; Hartwig, A. Fast switchable, epoxy based shape-memory polymers with high strength and toughness. Polymer 2016, 83, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyengar, P.K.; Bhat, K.A.; Sangeetha, D.; Moorthy, T.V. Polymethyl methacrylate nanofiber-reinforced epoxy composite for shape-memory applications. High Perform. Polym. 2013, 25, 1000–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimoto, T.; Takayama, T.; Uyama, H. Biodegradable shape memory polymeric material from epoxidized soybean oil and polycaprolactone. Polymers 2015, 7, 2165–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryshchuk, O.; Karger-Kocsis, J. Influence of the type of epoxy hardener on the structure and properties of interpenetrated vinyl ester/epoxy resins. J. Polym. Sci. A 2004, 42, 5471–5481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grishchuk, S.; Sorochynska, L.; Vorster, O.C.; Karger-Kocsis, J. Structure, thermal and mechanical properties of ddm-hardened epoxy/benzoxazine hybrids: Effects of epoxy resin functionality and etbn toughening. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 5082–5093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Mather, P.T. Triple-shape polymeric composites (TSPCs). Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 2649–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Luo, X.; Iversen, C.B.; Mather, P.T.; Dunn, M.L.; Qi, H.J. Mechanisms of triple-shape polymeric composites due to dual thermal transitions. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 2212–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fejős, M.; Molnár, K.; Karger-Kocsis, J. Epoxy/polycaprolactone systems with triple-shape memory effect: Electrospun nanoweb with and without graphene versus co-continuous morphology. Materials 2013, 6, 4489–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Torbati, A.H.; Nejad, H.B.; Ponce, M.; Sutton, J.P.; Mather, P.T. Properties of triple shape memory composites prepared via polymerization-induced phase separation. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 3112–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Yin, T.; Rong, M.; Zhang, M. Self healing in polymers and polymer composites. Concepts, realization and outlook: A review. Express Polym. Lett. 2008, 2, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, T.; Xiao, X.; Cheng, Y.-T. Revealing triple-shape memory effect by polymer bilayers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2009, 30, 1823–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Liu, M.; Ni, Q.; Fu, Y. Epoxy resin composite bilayers with triple-shape memory effect. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 475316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, R.F. A review of recent research on mechanics of multifunctional composite materials and structures. Compos. Struct. 2010, 92, 2793–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xiao, X.; Xie, T. Viscoelastic behavior and force nature of thermo-reversible epoxy dry adhesives. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2010, 31, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, T.; Xiao, X. Self-peeling reversible dry adhesive system. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 2866–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkby, E.L.; Michaud, V.J.; Månson, J.A.E.; Sottos, N.R.; White, S.R. Performance of self-healing epoxy with microencapsulated healing agent and shape memory alloy wires. Polymer 2009, 50, 5533–5538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Zhu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Song, Y.; Yang, G.; Rong, M.; Zhang, M. Improvement of fatigue resistance of epoxy composite with microencapsulated epoxy-sbf5 self-healing system. Express Polym. Lett. 2017, 11, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, P.; AlMaadeed, M.A. “Containers” for self-healing epoxy composites and coating: Trends and advances. Express Polym. Lett. 2016, 10, 506–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, P. A self-healing particulate composite reinforced with strain hardened short shape memory polymer fibers. Polymer 2013, 54, 5075–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Ajisafe, O.; Meng, H. Effect of strain hardening of shape memory polymer fibers on healing efficiency of thermosetting polymer composites. Polymer 2013, 54, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Mather, P.T. Shape memory assisted self-healing coating. ACS Macro Lett. 2013, 2, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Yao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. A dual-functional polymeric system combining shape memory with self-healing properties. Compos. B 2015, 83, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karger-Kocsis, J. Self-healing properties of epoxy resins with poly(ε-caprolactone) healing agent. Polym. Bull. 2016, 73, 3081–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Deng, L.; Zhang, D.; Qian, H.; Du, C.; Li, X.; Mol, J.M.C.; Terryn, H.A. Shape memory composite (smc) self-healing coatings for corrosion protection. Prog. Org. Coat. 2016, 97, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigato, A.; Canclini, P.; Unterberger, S.H.; Pegoretti, A. Phase changing nanocomposites for low temperature thermal energy storage and release. Express Polym. Lett. 2017, 11, 738–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Fan, J.; Li, G. Intrinsic healable and recyclable thermoset epoxy based on shape memory effect and transesterification reaction. Polymer 2016, 105, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, W.; Huang, Y.; Leng, J. Thermosetting epoxy reinforced shape memory composite microfiber membranes: Fabrication, structure and properties. Compos. A 2015, 76, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Hu, J. A review of shape memory polymer composites and blends. Compos. A 2009, 40, 1661–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunes, I.S.; Jana, S.C. Shape memory polymers and their nanocomposites: A review of science and technology of new multifunctional materials. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2008, 8, 1616–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhou, T.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. Stimulus methods of multi-functional shape memory polymer nanocomposites: A review. Compos. A 2017, 100, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Liang, X. Investigation of stress relaxation behavior of carbon-containing shape memory epoxy composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 1322–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhaure, J.; Kim, S. An internally heated shape memory polymer dry adhesive. Polymers 2014, 6, 2274–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Singh, K. An experimental investigation of the effect of strain on the electrical conductivity of a shape memory polymer. Polym. Test. 2016, 49, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karger-Kocsis, J.; Kmetty, Á.; Lendvai, L.; Drakopoulos, S.; Bárány, T. Water-assisted production of thermoplastic nanocomposites: A review. Materials 2015, 8, 72–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, Y.; Ni, Q.; Fu, Y. Preparation and characterization of water-borne epoxy shape memory composites containing silica. Compos. A 2015, 72, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gall, K.; Dunn, M.L.; McCluskey, P. Thermomechanics of shape memory polymer nanocomposites. Mech. Mater. 2004, 36, 929–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, K.; Dunn, M.L.; Liu, Y.; Finch, D.; Lake, M.; Munshi, N.A. Shape memory polymer nanocomposites. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 5115–5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, K.; Dunn, M.L.; Liu, Y.; Stefanic, G.; Balzar, D. Internal stress storage in shape memory polymer nanocomposites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 290–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazelton, C.S.; Arzberger, S.C.; Lake, M.S.; Munshi, N.A. Rf actuation of a thermoset shape memory polymer with embedded magnetoelectroelastic particles. J. Adv. Mater. 2007, 39, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Iijima, M.; Kobayakawa, M.; Yamazaki, M.; Ohta, Y.; Kamiya, H. Anionic surfactant with hydrophobic and hydrophilic chains for nanoparticle dispersion and shape memory polymer nanocomposites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 16342–16343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Han, C.; Tan, H.; Du, X. Organic-montmorillonite modified shape memory epoxy composite. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2011, 22, 2017–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloshenko, V.A.; Varyukhin, V.N.; Voznyak, Y.V. Electrical properties of carbon-containing epoxy compositions under shape memory effect realization. Compos. A 2005, 36, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloshenko, V.A.; Beygelzimer, Y.E.; Borzenko, A.P.; Varyukhin, V.N. Shape memory effect in the epoxy polymer–thermoexpanded graphite system. Compos. A 2002, 33, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Feng, X.; Li, Y.; Mi, X. Shape memory effect and mechanical properties of graphene/epoxy composites. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2014, 56, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Feng, X.; Mi, X.; Li, Y.; Xie, H.; Yin, X. Mechanical reinforcement and shape memory effect of graphite nanoplatelet–reinforced epoxy composites. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2015, 26, 1491–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. Nanocomposites of epoxy-based shape memory polymer and thermally reduced graphite oxide: Mechanical, thermal and shape memory characterizations. Compos. B 2016, 91, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhong, J.; Meng, J.; Xian, G. The reinforcement efficiency of carbon nanotubes/shape memory polymer nanocomposites. Compos. B 2013, 44, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Yao, Y.; Huang, W.M.; Leng, J.; Hui, D. Significantly improving infrared light-induced shape recovery behavior of shape memory polymeric nanocomposite via a synergistic effect of carbon nanotube and boron nitride. Compos. B 2014, 62, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Arsalan, A.; Dong, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Qian, C.; Wang, R.; Cuilan, C.; Fu, Y.; Ni, Q.-Q.; Ali, K.N. Shape memory effect and recovery stress property of carbon nanotube/waterborne epoxy nanocomposites investigated via tma. Polym. Test. 2017, 59, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Xia, H.; Zhu, Y.; Ni, Q.; Fu, Y. Effect of epoxy-graft-polyoxyethylene octyl phenyl ether on preparation, mechanical properties and triple-shape memory effect of carbon nanotube/water-borne epoxy nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 120, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abishera, R.; Velmurugan, R.; Gopal, K.V.N. Reversible plasticity shape memory effect in carbon nanotubes reinforced epoxy nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 137, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abishera, R.; Velmurugan, R.; Gopal, K.V.N. Reversible plasticity shape memory effect in epoxy/cnt nanocomposites—A theoretical study. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 141, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Gou, J.; Leng, J.; Du, S. Synergistic effect of carbon nanofiber and sub-micro filamentary nickel nanostrand on the shape memory polymer nanocomposite. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 035017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, Y. Preparation and properties of silanized vapor-grown carbon nanofibers/epoxy shape memory nanocomposites. Polym. Compos. 2014, 35, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Ni, Q. Effect of vapor-grown carbon nanofibers and in situ hydrolyzed silica on the mechanical and shape memory properties of water-borne epoxy composites. Polym. Compos. 2015, 36, 1712–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Ni, Q.; Li, L.; Fu, Y. Novel vapor-grown carbon nanofiber/epoxy shape memory nanocomposites prepared via latex technology. Mater. Lett. 2014, 132, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Lei, M.; Leng, J. Significantly improving electro-activated shape recovery performance of shape memory nanocomposite by self-assembled carbon nanofiber and hexagonal boron nitride. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Huang, W.M.; Leng, J. Functionally graded and self-assembled carbon nanofiber and boron nitride in nanopaper for electrical actuation of shape memory nanocomposites. Compos. B 2014, 62, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. Carbon nanopaper enabled shape memory polymer composites for electrical actuation and multifunctionalization. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2012, 297, 1138–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, D.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J.; Bhattacharyya, D. Electrical actuation properties of reduced graphene oxide paper/epoxy-based shape memory composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 106, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Satarkar, N.; Xie, T.; Cheng, Y.-T.; Hilt, J.Z. Remote controlled multishape polymer nanocomposites with selective radiofrequency actuations. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 3192–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gall, K.; Mikulas, M.; Munshi, N.A.; Beavers, F.; Tupper, M. Carbon fiber reinforced shape memory polymer composites. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2000, 11, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Chang, R. Micromechanism of deformation in emc laminates. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2008, 496, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y. Microbuckling solution of elastic memory laminates under bending. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2009, 20, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basit, A.; L’Hostis, G.; Durand, B. High actuation properties of shape memory polymer composite actuator. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 025023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basit, A.; Hostis, G.; Pac, M.; Durand, B. Thermally activated composite with two-way and multi-shape memory effects. Materials 2013, 6, 4031–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basit, A.; L’Hostis, G.; Durand, B. Multi-shape memory effect in shape memory polymer composites. Mater. Lett. 2012, 74, 220–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, T.; Shindo, Y.; Narita, F. Flexural stiffness variations of woven carbon fiber composite/shape memory polymer hybrid layered beams. J. Compos. Mater. 2015, 49, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Du, H.; Liu, L.; Leng, J. Shape memory polymers and their composites in aerospace applications: A review. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 023001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santo, L.; Quadrini, F.; Accettura, A.; Villadei, W. Shape memory composites for self-deployable structures in aerospace applications. Procedia Eng. 2014, 88, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liu, L.; Lan, X.; Zhou, X.; Bian, W.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. Preliminary design and analysis of a cubic deployable support structure based on shape memory polymer composite. Int. J. Smart Nano Mater. 2016, 7, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fejős, M.; Romhány, G.; Karger-Kocsis, J. Shape memory characteristics of woven glass fibre fabric reinforced epoxy composite in flexure. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2012, 31, 1532–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fejos, M.; Karger-Kocsis, J. Shape memory performance of asymmetrically reinforced epoxy/carbon fibre fabric composites in flexure. Express Polym. Lett. 2013, 7, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abrahamson, E.R.; Lake, M.S.; Munshi, N.A.; Gall, K. Shape memory mechanics of an elastic memory composite resin. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2003, 14, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fejős, M.; Karger-Kocsis, J.; Grishchuk, S. Effects of fibre content and textile structure on dynamic-mechanical and shape-memory properties of elo/flax biocomposites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2013, 32, 1879–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, H.; Liang, F.; Gou, J.; Leng, J.; Du, S. Synergistic effect of ag nanoparticle-decorated graphene oxide and carbon fiber on electrical actuation of polymeric shape memory nanocomposites. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 085034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Yao, Y.; Huang, W.M.; Hui, D. Noncovalently functionalized carbon fiber by grafted self-assembled graphene oxide and the synergistic effect on polymeric shape memory nanocomposites. Compos. B 2014, 67, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Wang, X.; Yao, Y.; Gou, J.; Hui, D.; Xu, B.; Fu, Y. Synergistic effect of siloxane modified aluminum nanopowders and carbon fiber on electrothermal efficiency of polymeric shape memory nanocomposite. Compos. B 2015, 80, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Yao, Y.; Lin, L. Temperature sensing and actuating capabilities of polymeric shape memory composite containing thermochromic particles. Pigment Resin Technol. 2015, 44, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.-T.; Lau, K.-T.; Tam, W.-Y.; Leng, J.; Wang, W.; Li, W.; Wei, H. Degradation of nano-zno particles filled styrene-based and epoxy-based smps under uva exposure. Compos. Struct. 2015, 132, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, G.P.; Goecke, K.; Cable, K.; Baur, J. Environmental durability of fabric-reinforced shape-memory polymer composites. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2010, 21, 1365–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadrini, F.; Bellisario, D.; Ciampoli, L.; Costanza, G.; Santo, L. Auxetic epoxy foams produced by solid state foaming. J. Cell. Plast. 2015, 52, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadrini, F.; Santo, L.; Squeo, E.A. Shape memory epoxy foams for space applications. Mater. Lett. 2012, 69, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hearon, K.; Singhal, P.; Horn, J.; Small, W.; Olsovsky, C.; Maitland, K.C.; Wilson, T.S.; Maitland, D.J. Porous shape-memory polymers. Polym. Rev. 2013, 53, 41–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santo, L. Shape memory polymer foams. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2016, 81, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prima, M.A.D.; Lesniewski, M.; Gall, K.; McDowell, D.L.; Sanderson, T.; Campbell, D. Thermo-mechanical behavior of epoxy shape memory polymer foams. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, 2330–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Prima, M.A.; Gall, K.; McDowell, D.L.; Guldberg, R.; Lin, A.; Sanderson, T.; Campbell, D.; Arzberger, S.C. Cyclic compression behavior of epoxy shape memory polymer foam. Mech. Mater. 2010, 42, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vialle, G.; Di Prima, M.; Hocking, E.; Gall, K.; Garmestani, H.; Sanderson, T.; Arzberger, C.S. Remote activation of nanomagnetite reinforced shape memory polymer foam. Smart Mater. Struct. 2009, 18, 115014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squeo, E.A.; Quadrini, F. Shape memory epoxy foams by solid-state foaming. Smart Mater. Struct. 2010, 19, 105002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadrini, F.; Santo, L.; Squeo, E.A. Solid-state foaming of nano-clay-filled thermoset foams with shape memory properties. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2012, 51, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santo, L.; Quadrini, F.; Squeo, E.A.; Dolce, F.; Mascetti, G.; Bertolotto, D.; Villadei, W.; Ganga, P.L.; Zolesi, V. Behavior of shape memory epoxy foams in microgravity: Experimental results of sts-134 mission. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 2012, 24, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Ding, J.; Wang, J.; Fu, X.; Hu, H.; Li, S.; Yang, H.; Xu, C.; Du, M.; Fu, Y. Synthesis and properties of the vapour-grown carbon nanofiber/epoxy shape memory and conductive foams prepared via latex technology. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 76, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Fu, Y.; Ni, Q. In-situ grown silica/water-borne epoxy shape memory composite foams prepared without blowing agent addition. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Nettles, D. Thermomechanical characterization of a shape memory polymer based self-repairing syntactic foam. Polymer 2010, 51, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Rao, A.; Srinivasa, A.R. Design of multi-state and smart-bias components using shape memory alloy and shape memory polymer composites. Mater. Des. 2013, 44, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Jani, J.; Leary, M.; Subic, A.; Gibson, M.A. A review of shape memory alloy research, applications and opportunities. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 1078–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobushi, H.; Hayashi, S.; Hoshio, K.; Makino, Y.; Miwa, N. Bending actuation characteristics of shape memory composite with sma and smp. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2006, 17, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murkute, V.; Gupta, A.; Thakur, D.G.; Harshe, R.; Joshi, M. Improvisation of interfacial bond strength in shape memory alloy hybrid polymer matrix composites. Proc. Mater. Sci. 2014, 6, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.-T.; Chan, A.W.-L.; Shi, S.-Q.; Zhou, L.-M. Debond induced by strain recovery of an embedded niti wire at a niti/epoxy interface: Micro-scale observation. Mater. Des. 2002, 23, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.H.; Siochi, E.J.; Penner, R.K.; Turner, T.L. Enhanced adhesive strength between shape memory polymer nanocomposite and titanium alloy. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 96, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonnalagadda, K.D.; Sottos, N.R.; Qidwai, M.A.; Lagoudas, D.C. Transformation of embedded shape memory alloy ribbons. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 1998, 9, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoi, K.A.; Stalmans, R.; Schrooten, J.; Wevers, M.; Mai, Y.-W. Impact damage behaviour of shape memory alloy composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2003, 342, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Wang, Z.; Yang, B.; Sun, X. Experimental investigation of gf/epoxy laminates with different smas positions subjected to low-velocity impact. Compos. Struct. 2017, 171, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogisu, T.; Shimanuki, M.; Kiyoshima, S.; Takeda, N. A basic study of cfrp laminates with embedded prestrained sma foils for aircraft structures. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2005, 16, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, S.M.R.; Shokuhfar, A.; Malekzadeh, K.; Ashenai Ghasemi, F. Low-velocity impact response of active thin-walled hybrid composite structures embedded with sma wires. Thin Wall Struct. 2007, 45, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkby, E.L.; Rule, J.D.; Michaud, V.J.; Sottos, N.R.; White, S.R.; Månson, J.-A.E. Embedded shape-memory alloy wires for improved performance of self-healing polymers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 2253–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umezaki, E. Temperature distributions of sma wires embedded in epoxy resin plates and heated by supplying electric current. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2006, 17, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Ni, Q.; Natsuki, T.; Iwamoto, M. Mechanical properties of composites filled with sma particles and short fibers. Compos. Struct. 2007, 79, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulla, S.S.; Karaca, H.E.; Lu, Y.C. Numerical design of shape memory polymer composites with temperature-responsive sma fillers. Compos. B 2016, 96, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Batra, R.C. Micromechanical modeling of a composite containing piezoelectric and shape memory alloy inclusions. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2001, 12, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glock, S.; Canal, L.P.; Grize, C.M.; Michaud, V. Magneto-mechanical actuation of ferromagnetic shape memory alloy/epoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 114, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todoroki, A.; Kumagai, K.; Matsuzaki, R. Self-deployable space structure using partially flexible cfrp with sma wires. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2009, 20, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Ni, Q.; Masuda, A.; Yamamura, T.; Iwamoto, M. Vibration characteristics of laminated composite plates with embedded shape memory alloys. Compos. Struct. 2006, 74, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Liu, L.; Lan, X.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. Dynamic responses of sma-epoxy composites and application for piezoelectric energy harvesting. Compos. Struct. 2016, 153, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meo, M. Chapter 23—Multifunctional sma-based composites for aerospace applications. In Multifunctionality of Polymer Composites; William Andrew Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 709–724. [Google Scholar]
- Romhány, G.; Czigány, T.; Karger-Kocsis, J. Failure assessment and evaluation of damage development and crack growth in polymer composites via localization of acoustic emission events: A review. Polym. Rev. 2017, 57, 397–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Qin, H.; Mather, P.T. Review of progress in shape-memory polymers. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 1543–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, M.; Kratz, K.; Zotzmann, J.; Nöchel, U.; Lendlein, A. Reversible bidirectional shape-memory polymers. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 4466–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Hu, J.; Han, J.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, H.; Li, J.; Tang, B. Two-way shape memory polymer with “switch-spring” composition by interpenetrating polymer network. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 18816–18822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, R.S.; Lendlein, A. Shape Memory Polymers. U.S. Patent 6,388,043, 14 May 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Belmonte, A.; Lama, G.C.; Gentile, G.; Cerruti, P.; Ambrogi, V.; Fernández-Francos, X.; De la Flor, S. Thermally-triggered free-standing shape-memory actuators. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 97, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Song, W.; Ke, L.; Wang, Y. Shape memory polymer composite structures with two-way shape memory effects. Mater. Lett. 2012, 89, 216–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baz, A.; Ro, J. Thermo-dynamic characteristics of nitinol-reinforced composite beams. Compos. Eng. 1992, 2, 527–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.M.; Ding, Z.; Wang, C.C.; Wei, J.; Zhao, Y.; Purnawali, H. Shape memory materials. Mater. Today 2010, 13, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, P.; Cantwell, W.J.; Kuang, K.S.C.; Quek, S.T. The morphing properties of a smart fiber metal laminate. Polym. Compos. 2008, 29, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Lloyd, P. Design, manufacture and evaluation of bending behaviour of composite beams embedded with sma wires. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 2034–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoru, T.; Yuanchang, L.; Onur, C.N.; Hirohisa, T.; Tucker, H. Design of two-way reversible bending actuator based on a shape memory alloy/shape memory polymer composite. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 105003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurka, M. Chapter 24—Active hybrid structures made of shape memory alloys and fiber-reinforced composites. In Multifunctionality of Polymer Composites; William Andrew Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 727–751. [Google Scholar]
- Hübler, M.; Gurka, M.; Schmeer, S.; Breuer, U.P. Performance range of sma actuator wires and sma–frp structure in terms of manufacturing, modeling and actuation. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 094002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashir, M.; Hahn, L.; Kluge, A.; Nocke, A.; Cherif, C. Development of innovative adaptive 3d fiber reinforced plastics based on shape memory alloys. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 126, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freed, Y.; Aboudi, J. Micromechanical prediction of the two-way shape memory effect in shape memory alloy composites. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2009, 46, 1634–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, B.-S.; Kong, J.-P.; Li, N.; Kim, Y.-M.; Kim, M.-S.; Ahn, S.-H.; Cho, M. Numerical simulation and verification of a curved morphing composite structure with embedded shape memory alloy wire actuators. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2013, 24, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratna, D.; Karger-Kocsis, J. Recent advances in shape memory polymers and composites: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 254–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Yu, K.; Dunn, L.M.; Qi, H.J. Shape memory polymers: Mechanisms and constitutive models. Int. J. Aerosp. Lightweight Struct. 2013, 3, 1–53. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. Thermoviscoelastic shape memory behavior for epoxy-shape memory polymer. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 055025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westbrook, K.K.; Kao, P.H.; Castro, F.; Ding, Y.; Jerry Qi, H. A 3d finite deformation constitutive model for amorphous shape memory polymers: A multi-branch modeling approach for nonequilibrium relaxation processes. Mech. Mater. 2011, 43, 853–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; McClung, A.J.W.; Tandon, G.P.; Baur, J.W.; Jerry Qi, H. A thermomechanical constitutive model for an epoxy based shape memory polymer and its parameter identifications. Mech. Time Depend. Mater. 2014, 18, 453–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Ge, Q.; Qi, H.J. Reduced time as a unified parameter determining fixity and free recovery of shape memory polymers. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, M.; Yu, K.; Lu, H.; Qi, H.J. Influence of structural relaxation on thermomechanical and shape memory performances of amorphous polymers. Polymer 2017, 109, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Sun, H.; Fang, C. A finite deformation constitutive model for thermally activated amorphous shape memory polymers. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2015, 26, 1530–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azra, C.; Plummer, J.G.C.; Månson, E.J.-A. Dynamic mechanical analysis for rapid assessment of the time-dependent recovery behavior of shape memory polymers. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 075037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuki, Á.; Czifrák, K.; Karger-Kocsis, J.; Zsuga, M.; Kéki, S. An approach to predict the shape-memory behavior of amorphous polymers from dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) data. Mech. Time Depend. Mater. 2015, 19, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Sun, H.; Gu, J. A fractional calculus approach to the prediction of free recovery behaviors of amorphous shape memory polymers. J. Mech. 2015, 32, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarali, C.S.; Raja, S.; Kiefer, B. Modeling the effective properties and thermomechanical behavior of sma-smp multifunctional composite laminates. Polym. Compos. 2011, 32, 910–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gall, K.; Dunn, M.L.; Greenberg, A.R.; Diani, J. Thermomechanics of shape memory polymers: Uniaxial experiments and constitutive modeling. Int. J. Plast. 2006, 22, 279–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lagoudas, D.C. A constitutive theory for shape memory polymers. Part I: Large deformations. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2008, 56, 1752–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lagoudas, D.C. A constitutive theory for shape memory polymers. Part II: A linearized model for small deformations. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2008, 56, 1766–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Prima, M.A.; Gall, K.; McDowell, D.L.; Guldberg, R.; Lin, A.; Sanderson, T.; Campbell, D.; Arzberger, S.C. Deformation of epoxy shape memory polymer foam: Part II. Mesoscale modeling and simulation. Mech. Mater. 2010, 42, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Chen, Q.; Naguib, H.E. Constitutive modeling and experimental validation of the thermo-mechanical response of a shape memory composite containing shape memory alloy fibers and shape memory polymer matrix. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2016, 27, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zou, K.; Liang, X. Investigation of thermomechanical behaviors of epoxy shape memory polymers by molecular dynamics simulation. In Applied Mechanics and Materials; Scitec Publications Ltd.: Zurich, Switzerland, 2013; Volume 273, pp. 463–467. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Shi, X. A molecular dynamics investigation of the deformation mechanism and shape memory effect of epoxy shape memory polymers. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2016, 59, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Koo, B.; Liu, Y.; Zou, J.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Dai, L. A novel statistical spring-bead based network model for self-sensing smart polymer materials. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 085022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karger-Kocsis, J.; Mahmood, H.; Pegoretti, A. Recent advances in fiber/matrix interphase engineering for polymer composites. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 73, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szebényi, G.; Czigány, T.; Magyar, B.; Karger-Kocsis, J. 3d printing-assisted interphase engineering of polymer composites: Concept and feasibility. Express Polym. Lett. 2017, 11, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.N.; Zhu, C.; Duoss, E.B.; Wilson, T.S.; Spadaccini, C.M.; Lewicki, J.P. Shape-morphing composites with designed micro-architectures. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, K.; Breuer, U. Multifunctionality of Polymer Composites: Challenges and New Solutions; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, D.; Barrett, R.; Lake, M.S.; Adams, L.; Abramson, E.; Scherbarthn, M.R.; Welsh, J.S.; Freebury, G.; Beidleman, N.; Abbot, J. Development of a novel, passively deployed roll-out solar array. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 4–11 March 2006; p. 9. [Google Scholar]
- Sofla, A.Y.N.; Meguid, S.A.; Tan, K.T.; Yeo, W.K. Shape morphing of aircraft wing: Status and challenges. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuder, I.K.; Arrieta, A.F.; Raither, W.E.; Ermanni, P. Variable stiffness material and structural concepts for morphing applications. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2013, 63, 33–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, M.S.; Campbell, D. The Fundamentals of Designing Deployable Structures with Elastic Memory Composites. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 6–13 March 2004; pp. 2745–2756. [Google Scholar]











© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karger-Kocsis, J.; Kéki, S. Review of Progress in Shape Memory Epoxies and Their Composites. Polymers 2018, 10, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010034
Karger-Kocsis J, Kéki S. Review of Progress in Shape Memory Epoxies and Their Composites. Polymers. 2018; 10(1):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010034
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarger-Kocsis, József, and Sándor Kéki. 2018. "Review of Progress in Shape Memory Epoxies and Their Composites" Polymers 10, no. 1: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010034
APA StyleKarger-Kocsis, J., & Kéki, S. (2018). Review of Progress in Shape Memory Epoxies and Their Composites. Polymers, 10(1), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010034