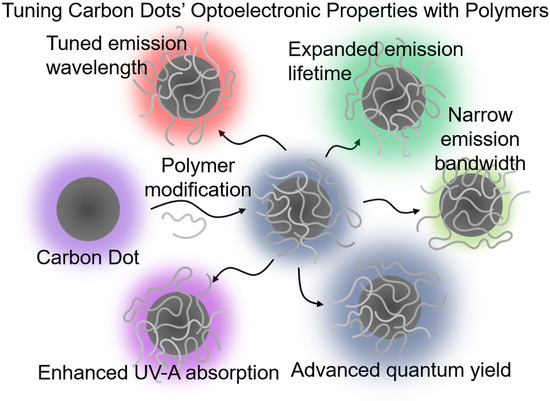
Tuning Carbon Dots’ Optoelectronic Properties with Polymers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Enhancing Carbon Dots’ Features Via Passivation
3. Tuning Optical Properties with Polymers
3.1. Expanding Emission Lifetimes
3.2. Advancing Quantum Yields
3.3. Tuning Absorption/Emission Wavelengths
3.3.1. Visible Spectrum
3.3.2. Near Infrared
3.4. Enhancing UV-A Absorption
3.5. Narrowing Emission Bandwidths
4. Perspectives for Polymers in Carbon Dots
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lim, S.Y.; Shen, W.; Gao, Z. Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimos, K. Carbon Quantum Dots: Surface Passivation and Functionalization. Curr. Org. Chem. 2016, 20, 682–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.C.; Yu, K.S.; Han, S.Y.; Kim, J.-J.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, N.S.; Jeong, Y.G.; Kim, D.K. Highly photoluminescent N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAAM) passivated carbon dots for multicolor bioimaging applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 98, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Sun, Y.; Geng, X.; Hu, Y.; Meng, H.; Ge, J.; Qu, L. Synthesis of Luminescent Carbon Dots with Ultrahigh Quantum Yield and Inherent Folate Receptor-Positive Cancer Cell Targetability. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, D.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, H.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X.; Haddad, R.E.; Fan, H.; Sun, Z. Formation mechanism and optimization of highly luminescent N-doped graphene quantum dots. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, S.; Choudhary, R.; Roy, E.; Madhuri, R.; Sharma, P.K. Triple signalling mode carbon dots-based biodegradable molecularly imprinted polymer as a multi-tasking visual sensor for rapid and “on-site” monitoring of silver ions. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 11965–11976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, C. Graphene quantum dots: Emergent nanolights for bioimaging, sensors, catalysis and photovoltaic devices. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 3686–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Zhu, A.; Tian, Y. Functional Surface Engineering of C-Dots for Fluorescent Biosensing and in Vivo Bioimaging. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, A.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, C.; Gao, N.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Recent advances in bioapplications of C-dots. Carbon 2015, 85, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Xia, Y. Synthesis-Modification Integration: One-Step Fabrication of Boronic Acid Functionalized Carbon Dots for Fluorescent Blood Sugar Sensing. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 5323–5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Sun, Y.; Yang, J.; Hu, Y.; Yang, R.; Li, Z.; Qu, L.; Lin, Y. High performance fluorescence biosensing of cysteine in human serum with superior specificity based on carbon dots and cobalt-derived recognition. Sens. Actuators B 2019, 280, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.-Y.; Li, J.; Ge, J.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.-L.; Li, Z.-H.; Qu, L.-B. A rapid fluorescence “switch-on” assay for glutathione detection by using carbon dots–MnO2 nanocomposites. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 72, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Yan, X.; Li, Z.; Qu, L.; Zhu, C.; Ye, R.; Li, S.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Highly photoluminescent carbon dots derived from linseed and their applications in cellular imaging and sensing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 3181–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ray, R.; Gu, Y.; Ploehn, H.J.; Gearheart, L.; Raker, K.; Scrivens, W.A. Electrophoretic Analysis and Purification of Fluorescent Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Fragments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12736–12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.-P.; Zhou, B.; Lin, Y.; Wang, W.; Fernando, K.A.S.; Pathak, P.; Meziani, M.J.; Harruff, B.A.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Quantum-Sized Carbon Dots for Bright and Colorful Photoluminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7756–7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Sharma, S.K.; Peng, Z.; Leblanc, R.M. Polymers in Carbon Dots: A Review. Polymers 2017, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, V.; Margraf, J.T.; Dolle, C.; Butz, B.; Nacken, T.J.; Walter, J.; Bauer, W.; Peukert, W.; Spiecker, E.; Clark, T.; et al. Carbon Nanodots: Toward a Comprehensive Understanding of Their Photoluminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 17308–17316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimos, K.; Arcudi, F.; Kouloumpis, A.; Koutselas, I.B.; Rudolf, P.; Gournis, D.; Prato, M. Top-down and bottom-up approaches to transparent, flexible and luminescent nitrogen-doped carbon nanodot-clay hybrid films. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 10256–10262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, K.; Wang, Y.; Cai, C.; Lin, H. Activating Room Temperature Long Afterglow of Carbon Dots via Covalent Fixation. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 4866–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Zhang, L.; Lu, J.; Xu, C.; Cai, C.; Lin, H. Triple-Mode Emission of Carbon Dots: Applications for Advanced Anti-Counterfeiting. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 7231–7235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Zou, R.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, L.; Yue, D. Large-scale synthesis of N-doped carbon quantum dots and their phosphorescence properties in a polyurethane matrix. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 4742–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardekani, S.M.; Dehghani, A.; Hassan, M.; Kianinia, M.; Aharonovich, I.; Gomes, V.G. Two-photon excitation triggers combined chemo-photothermal therapy via doped carbon nanohybrid dots for effective breast cancer treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Souza, D.R.; Caminhas, L.D.; de Mesquita, J.P.; Pereira, F.V. Luminescent carbon dots obtained from cellulose. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 203, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Jiang, W.; Qiu, L.; Jiang, X.; Zuo, D.; Wang, D.; Yang, L. One pot synthesis of highly luminescent polyethylene glycol anchored carbon dots functionalized with a nuclear localization signal peptide for cell nucleus imaging. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 6104–6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, W.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X. One-Pot to Synthesize Multifunctional Carbon Dots for Near Infrared Fluorescence Imaging and Photothermal Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 23533–23541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Di, J.; Sun, Y.; Fu, J.; Wei, Z.; Matsui, H.; del C. Alonso, A.; Zhou, S. Biocompatible PEG-Chitosan@Carbon Dots Hybrid Nanogels for Two-Photon Fluorescence Imaging, Near-Infrared Light/pH Dual-Responsive Drug Carrier, and Synergistic Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 5537–5547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momper, R.; Steinbrecher, J.; Dorn, M.; Rörich, I.; Bretschneider, S.; Tonigold, M.; Ramanan, C.; Ritz, S.; Mailänder, V.; Landfester, K.; et al. Enhanced photoluminescence properties of a carbon dot system through surface interaction with polymeric nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 518, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Hu, Y.; Wang, P.; Yang, L.; Al Awak, M.M.; Tang, Y.; Twara, F.K.; Qian, H.; Sun, Y.-P. Modified facile synthesis for quantitatively fluorescent carbon dots. Carbon 2017, 122, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Duan, J.; Xiao, Y.; Tang, G.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xue, W. Microenvironment-Driven Cascaded Responsive Hybrid Carbon Dots as a Multifunctional Theranostic Nanoplatform for Imaging-Traceable Gene Precise Delivery. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 3438–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, C. Polyethyleneimine-Functionalized Fluorescent Carbon Dots: Water Stability, pH Sensing, and Cellular Imaging. ChemNanoMat 2015, 1, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Trinchi, A.; Atkin, P.; Cole, I. Tunable Photoluminescence Across the Entire Visible Spectrum from Carbon Dots Excited by White Light. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 2970–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, A.; Lee, J.; Park, B.; Ray, C.; Sankar, K.V.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, S.H.; Cho, I.-J.; Jun, S.C. Facile approach to synthesize highly fluorescent multicolor emissive carbon dots via surface functionalization for cellular imaging. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 513, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, M.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, L.; Guo, L.; Niu, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, P.; et al. Two-photon-excited near-infrared emissive carbon dots as multifunctional agents for fluorescence imaging and photothermal therapy. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 3113–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Ge, J.; Liu, W.; Niu, G.; Jia, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, P. Tunable multicolor carbon dots prepared from well-defined polythiophene derivatives and their emission mechanism. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Jia, Q.; Liu, W.; Lan, M.; Zhou, B.; Guo, L.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Gu, Y.; et al. Carbon Dots with Intrinsic Theranostic Properties for Bioimaging, Red-Light-Triggered Photodynamic/Photothermal Simultaneous Therapy In Vitro and In Vivo. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Jia, Q.; Liu, W.; Guo, L.; Liu, Q.; Lan, M.; Zhang, H.; Meng, X.; Wang, P. Red-Emissive Carbon Dots for Fluorescent, Photoacoustic, and Thermal Theranostics in Living Mice. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4169–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virca, C.N.; Winter, H.M.; Goforth, A.M.; Mackiewicz, M.R.; McCormick, T.M. Photocatalytic water reduction using a polymer coated carbon quantum dot sensitizer and a nickel nanoparticle catalyst. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 195402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Jing, P.; Sun, L.; An, Y.; Shan, X.; Lu, X.; Zhou, D.; Han, D.; Shen, D.; Zhai, Y.; et al. Near-Infrared Excitation/Emission and Multiphoton-Induced Fluorescence of Carbon Dots. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, X.; Hu, R.; Chen, H.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Lv, F.; Liang, X.-J.; et al. Near-Infrared (NIR)-Absorbing Conjugated Polymer Dots as Highly Effective Photothermal Materials for In Vivo Cancer Therapy. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 8669–8675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, S.C.; Permatasari, F.A.; Fukazawa, H.; Schneider, E.M.; Balgis, R.; Ogi, T.; Okuyama, K.; Stark, W.J. Direct synthesis of carbon quantum dots in aqueous polymer solution: One-pot reaction and preparation of transparent UV-blocking films. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 5187–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, C.-S.; Fang, C.-C.; Yan, J.-Y.; Tseng, P.-J.; Pyle, J.R.; Chen, C.-P.; Lin, S.-Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Chan, Y.-H. Molecular Engineering and Design of Semiconducting Polymer Dots with Narrow-Band, Near-Infrared Emission for in Vivo Biological Imaging. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 3166–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Sun, S.; Wang, Y.; Deng, S.; Qian, G.; Wang, M.; Hu, A. Preparation of carbon nanodots from single chain polymeric nanoparticles and theoretical investigation of the photoluminescence mechanism. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, L.; Li, B.; Song, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, S.; Lu, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; et al. Investigation of photoluminescence mechanism of graphene quantum dots and evaluation of their assembly into polymer dots. Carbon 2014, 77, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Yu, S.-B.; Wei, J.-S.; Xiong, H.-M. Full-Color Light-Emitting Carbon Dots with a Surface-State-Controlled Luminescence Mechanism. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Yang, S.; Wang, Z.; Shen, H.; Xu, T.; Sun, L.; Li, H.; Chen, W.; Jiang, X.; Ding, G.; et al. Ultra-High Quantum Yield of Graphene Quantum Dots: Aromatic-Nitrogen Doping and Photoluminescence Mechanism. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2015, 32, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eda, G.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Mattevi, C.; Yamaguchi, H.; Chen, H.-A.; Chen, I.S.; Chen, C.-W.; Chhowalla, M. Blue Photoluminescence from Chemically Derived Graphene Oxide. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, L.; Zhou, N.; Zhao, X.; Song, Y.; Maharjan, S.; Zhang, J.; Lu, L.; Wang, H.; Yang, B. The crosslink enhanced emission (CEE) in non-conjugated polymer dots: From the photoluminescence mechanism to the cellular uptake mechanism and internalization. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 13845–13848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Pang, D.-W. Photoluminescence-Tunable Carbon Nanodots: Surface-State Energy-Gap Tuning. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, K.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Y.; Wu, A.; Cai, C.; Lin, H. Red, Green, and Blue Luminescence by Carbon Dots: Full-Color Emission Tuning and Multicolor Cellular Imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 5360–5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Song, Y.; Zhao, X.; Shao, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B. The photoluminescence mechanism in carbon dots (graphene quantum dots, carbon nanodots, and polymer dots): Current state and future perspective. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 355–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhou, M.; Yang, Q.; Wu, Q.; Shi, J.; Gong, A.; Yang, M. Efficient Room-Temperature Phosphorescence from Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots in Composite Matrices. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 8221–8227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; An, X.; Gong, J. Novel pH sensitive N-doped carbon dots with both long fluorescence lifetime and high quantum yield. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 32319–32322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Wei, L.; Su, Y.; Li, Z.; Geng, H.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Y. Efficient long lifetime room temperature phosphorescence of carbon dots in a potash alum matrix. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 2798–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhao, D.; Chen, X.; Wang, F.; Song, H.; Shen, D. Long lifetime pure organic phosphorescence based on water soluble carbon dots. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 5751–5753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golden, J.H.; Deng, H.; DiSalvoa, F.J.; Fréchet, J.M.J.; Thompson, P.M. Monodisperse Metal Clusters 10 Angstroms in Diameter in a Polymeric Host: The “Monomer as Solvent” Approach. Science 1995, 268, 1463–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.M.; Mancini, M.C.; Nie, S. Second window for in vivo imaging. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 710–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wei, J.-S.; Zhang, P.; Niu, X.-Q.; Zhao, W.; Zhu, Z.-Y.; Ding, H.; Xiong, H.-M. Red-Emissive Carbon Dots for Fingerprints Detection by Spray Method: Coffee Ring Effect and Unquenched Fluorescence in Drying Process. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 18429–18433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, X.; Qu, D.; Yang, D.; Nie, B.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, H.; Sun, Z. Synthesis of Carbon Dots with Multiple Color Emission by Controlled Graphitization and Surface Functionalization. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, K.; Lin, H. Near-infrared emissive carbon dots for two-photon fluorescence bioimaging. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 17350–17356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghamsari, M.S.; Bidzard, A.M.; Han, W.; Park, H.-H. Wavelength-tunable visible to near-infrared photoluminescence of carbon dots: The role of quantum confinement and surface states. J. Nanophotonics 2016, 10, 026028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, K.; Wu, A.; Lin, H. Toward High-Efficient Red Emissive Carbon Dots: Facile Preparation, Unique Properties, and Applications as Multifunctional Theranostic Agents. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 8659–8668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.-P.; Zhou, B.; Shen, X.-C.; Yu, Y.-X.; Ji, S.-C.; Wen, C.-C.; Liang, H. Selective Probing of Gaseous Ammonia Using Red-Emitting Carbon Dots Based on an Interfacial Response Mechanism. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 18993–18999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, K.; Reckmeier, C.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, J.; Wu, C.; Yu, W.W.; Rogach, A.L. Combination of carbon dot and polymer dot phosphors for white light-emitting diodes. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 12045–12050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yuan, F.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Zhong, H.; Fan, L.; Yang, S. 53% Efficient Red Emissive Carbon Quantum Dots for High Color Rendering and Stable Warm White-Light-Emitting Diodes. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1702910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Sui, L.; Liu, J.; Zhu, S.; Chen, A.; Jin, M.; Yang, B. Near-Infrared Photoluminescent Polymer-Carbon Nanodots with Two-Photon Fluorescence. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, F.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Tan, Z.A.; Fan, L.; Yang, S. Bright Multicolor Bandgap Fluorescent Carbon Quantum Dots for Electroluminescent Light-Emitting Diodes. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.-Y.; Gong, X.-J.; Liu, Y.; Lu, W.-J.; Gao, Y.-F.; Xian, M.; Shuang, S.-M.; Dong, C. Facile preparation of bright orange fluorescent carbon dots and the constructed biosensing platform for the detection of pH in living cells. Talanta 2018, 189, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Sun, S.; Zhang, A.; Jiang, K.; Zhang, L.; Dong, C.; Huang, Q.; Wu, A.; Lin, H. Truly Fluorescent Excitation-Dependent Carbon Dots and Their Applications in Multicolor Cellular Imaging and Multidimensional Sensing. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 7782–7787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, S.; Zhou, D.; Li, D.; Ji, W.; Jing, P.; Han, D.; Liu, L.; Zeng, H.; Shen, D. Toward Efficient Orange Emissive Carbon Nanodots through Conjugated sp2-Domain Controlling and Surface Charges Engineering. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3516–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, T.-F.; Huang, W.-L.; Chung, C.-J.; Chiang, I.T.; Chen, L.-C.; Chang, H.-Y.; Su, W.-C.; Cheng, C.; Chen, S.-J.; Teng, H. Elucidating Quantum Confinement in Graphene Oxide Dots Based on Excitation-Wavelength-Independent Photoluminescence. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 2087–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konwar, A.; Gogoi, N.; Majumdar, G.; Chowdhury, D. Green chitosan–carbon dots nanocomposite hydrogel film with superior properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutsioukis, A.; Akouros, A.; Zboril, R.; Georgakilas, V. Solid phase extraction for the purification of violet, blue, green and yellow emitting carbon dots. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 11293–11296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alas, M.O.; Genc, R. An investigation into the role of macromolecules of different polarity as passivating agent on the physical, chemical and structural properties of fluorescent carbon nanodots. J. Nanopart. Res. 2017, 19, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhu, S.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, C.; Sun, L.; Tang, W.; Liu, R.; Sun, Y.; Yu, M. Nitrogen-doped carbon dots with excitation-independent long-wavelength emission produced by a room-temperature reaction. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 11912–11914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourlinos, A.B.; Trivizas, G.; Karakassides, M.A.; Baikousi, M.; Kouloumpis, A.; Gournis, D.; Bakandritsos, A.; Hola, K.; Kozak, O.; Zboril, R.; et al. Green and simple route toward boron doped carbon dots with significantly enhanced non-linear optical properties. Carbon 2015, 83, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Xiang, W.; Gao, H.; Wang, J.; Ni, Y.; Liang, X. Facile synthesis of tunable fluorescent carbon dots and their third-order nonlinear optical properties. Dyes Pigments 2016, 128, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannouli, I.; Bourlinos, A.B.; Bakandritsos, A.; Couris, S. Nonlinear optical properties of colloidal carbon nanoparticles: Nanodiamonds and carbon dots. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 40152–40160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Feng, M.; Li, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhan, H. Enhanced nonlinear optical properties of nonzero-bandgap graphene materials in glass matrices. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 4121–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloukos, P.; Papagiannouli, I.; Bourlinos, A.B.; Zboril, R.; Couris, S. Third-order nonlinear optical response and optical limiting of colloidal carbon dots. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 12013–12027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.; Yamada, Y.; Zhou, S.; Shimotsuma, Y.; Miura, K.; Qiu, J. Carbon nanodots with strong nonlinear optical response. Carbon 2014, 69, 638–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamijala, S.S.R.K.C.; Mukhopadhyay, M.; Pati, S.K. Linear and Nonlinear Optical Properties of Graphene Quantum Dots: A Computational Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 12079–12087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Polymers | Notes/Specific Applications | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| PEG and PVA | Expanded emission lifetime-Phosphorescence-Data encryption [19] | [19,20] |
| PU 1 | PU suppresses nonradiative transitions-Phosphorescence | [21] |
| PEG | Advancing quantum yield (QY) [22,23,24], Tuning emission [25,26] | [22,23,24,25,26] |
| Chitosan and PS 2 | Advancing QY by attaching carbon dots on PS | [27] |
| PEI | Advancing QY [28,29,30], Tune emission across visible [31,32] | [28,29,30,31,32] |
| PT 3 | Tune emission to visible and/or near-IR | [33,34,35,36] |
| PVP 4 | Advancing QY [37], Tune emission to near-IR [38] | [37,38] |
| PSMA 5 | Tune absorption to near-IR-Photothermal therapy | [39] |
| b-PEI and PVA | Enhancing UV-A absorption | [40] |
| Various | Narrowing emission bandwidth | [41] |
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dimos, K. Tuning Carbon Dots’ Optoelectronic Properties with Polymers. Polymers 2018, 10, 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121312
Dimos K. Tuning Carbon Dots’ Optoelectronic Properties with Polymers. Polymers. 2018; 10(12):1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121312
Chicago/Turabian StyleDimos, Konstantinos. 2018. "Tuning Carbon Dots’ Optoelectronic Properties with Polymers" Polymers 10, no. 12: 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121312
APA StyleDimos, K. (2018). Tuning Carbon Dots’ Optoelectronic Properties with Polymers. Polymers, 10(12), 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121312